Diagnostic Imaging- FInal Exam: Intro to CT and MRI
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
computed tomography
what does CT stand for?
x-ray based imaging modality
what is a CT?
there is an x-ray tube and set of detectors that rotate around the patient
how does a CT work?
true
T/F: the image a CT shows is cross sectional
-cross sectional
-greater tissue contrast
-can manipulate images to emphasize tissue contrast
-objective measurements of density
-highlight vasculature and pathology via contrast
what are the advantages of CT over radiography?
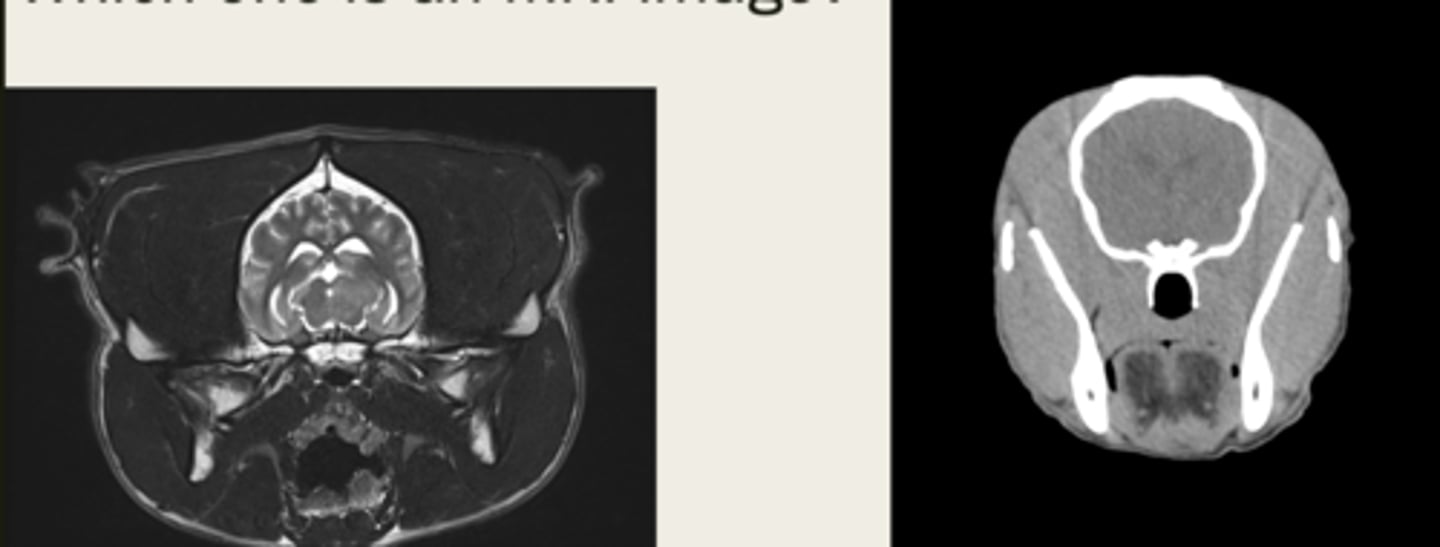
CT
is the left image a CT or MRI?
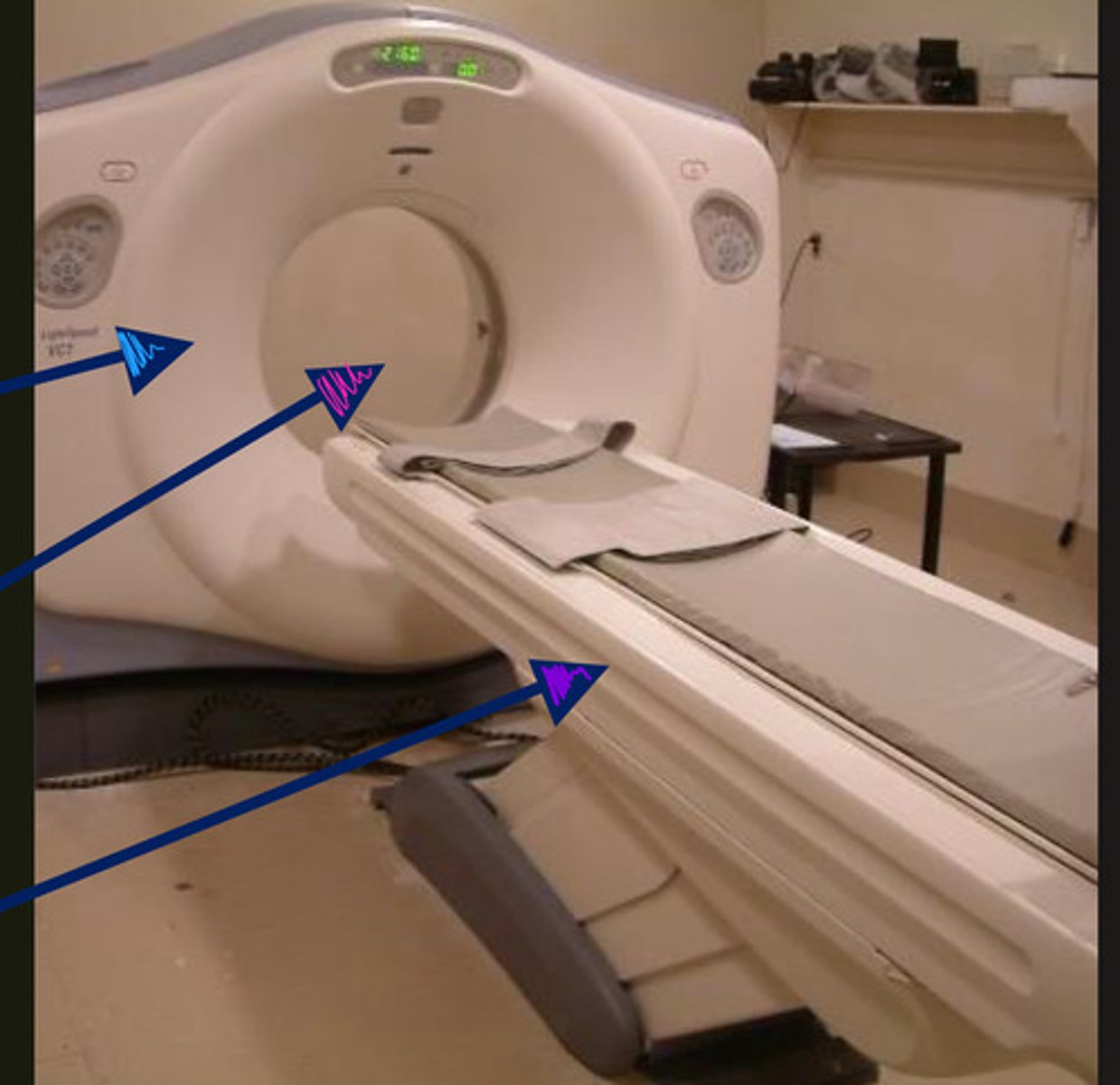
blue- gantry
pink- bore
purple- couch/table
ID parts of CT machine
x-ray tube and detectors
what two parts does the gantry of the CT machine include?
FALSE, can be positioned in multiple ways depending on body part scanned
T/F: the patient has to be in one position no matter the body part being scanned
false!! can use both
T/F: you cannot use sedation for CTs
no, CT imaging is fairly fast so it is not necessary
do you have to use general anesthesia for CT scans?
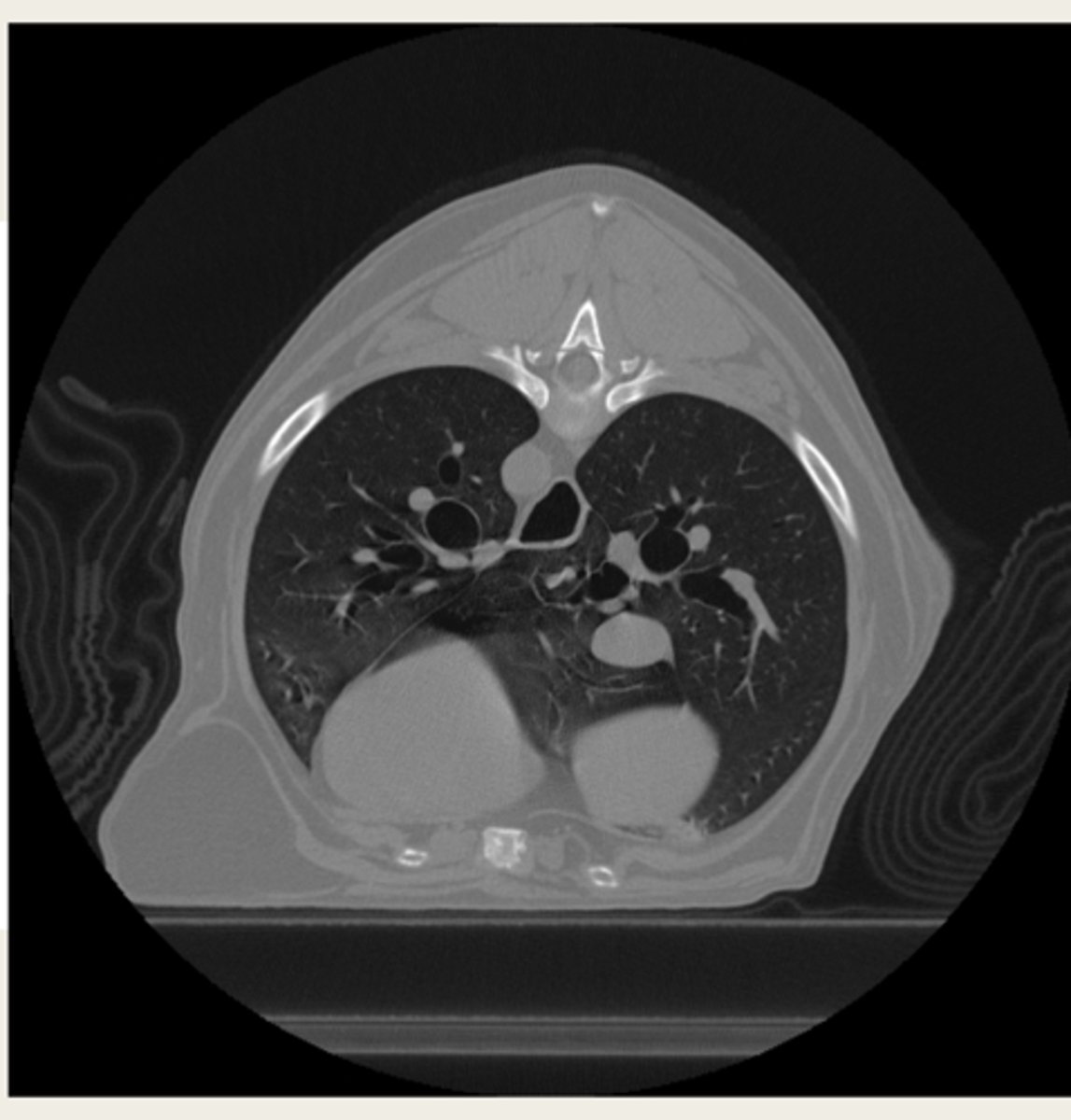
transverse
CT images are typically acquired in transverse/sagittal/dorsal?
left- bone window
right- tissue window
which CT window shows bone window or tissue window?
left- soft tissue window
right- bone window
ID the CT windows
iodine
which contrast medium do you use for CT?
IV
iodine is generally given IV or IM or orally?
pre contrast
make sure to get a __________ scan first for comparison before doing a contrast CT
vasculature
an iodine contrast CT highlights what?
in areas of abnormal or increased vascularity
for a contrast CT with iodine, the contrast accumulates where?
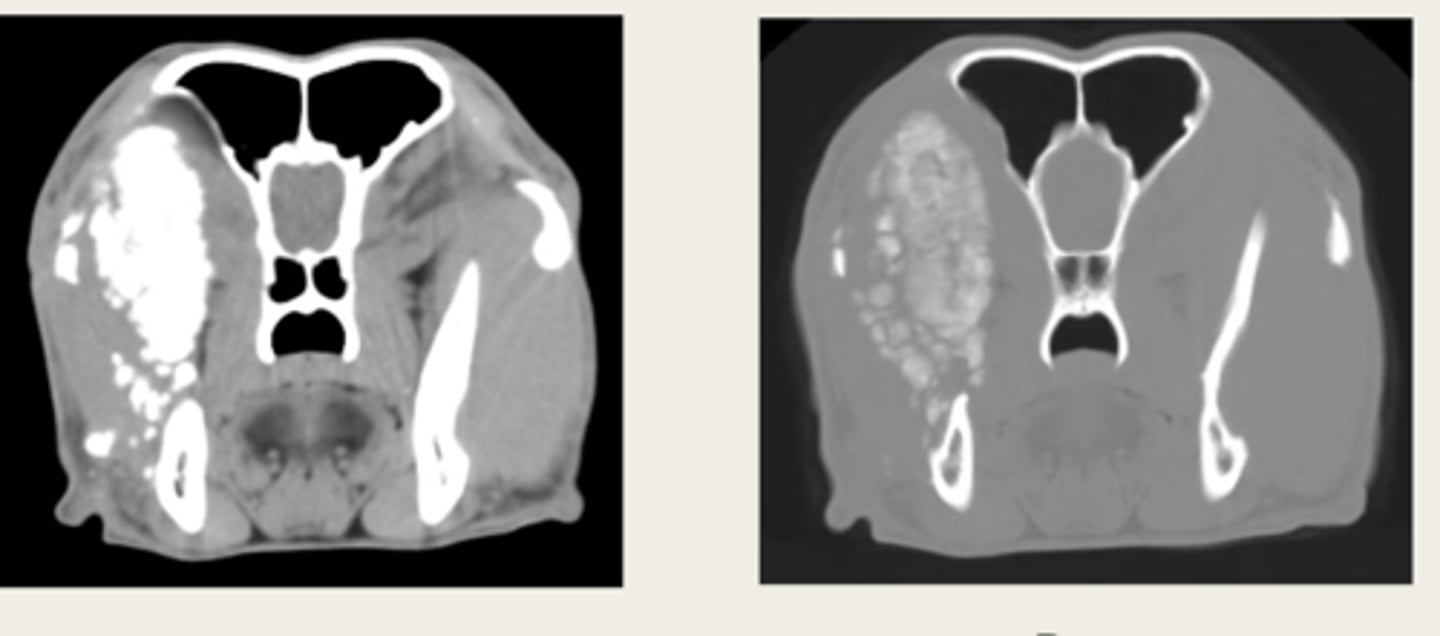
left- pre contrast
right- post contrast
window- soft tissue window
which CT images are pre and post contrast? what type of window is being shown in both?
Hounsfield Unit (HU)
what unit is tissue density measured in CT?
water
Hounsfield Unit (HU) is based off of what material?
positive, negative
anything more dense than water will be _______ and anything less dense than water will be _______ in Hounsfield Units (HU)
tissue density
what is this CT measuring?
-size
-shape
-location
-number
-margination
-density
what are the roentgen signs for CT?
-gas
-fat
-fluid/soft tissue
-bone
-metal
what are the different densities that can be interpreted with CT?
-lumps/bumps
-trauma
-lung disease
-nasal disease
-orbital masses
-bone disease
-IVDD
-abdominal disease
what are some CT indications?
-surgical planning
-radiation therapy planning
-3D printing
CT is primarily used for diagnosing problems, but can also be used for what three other things?
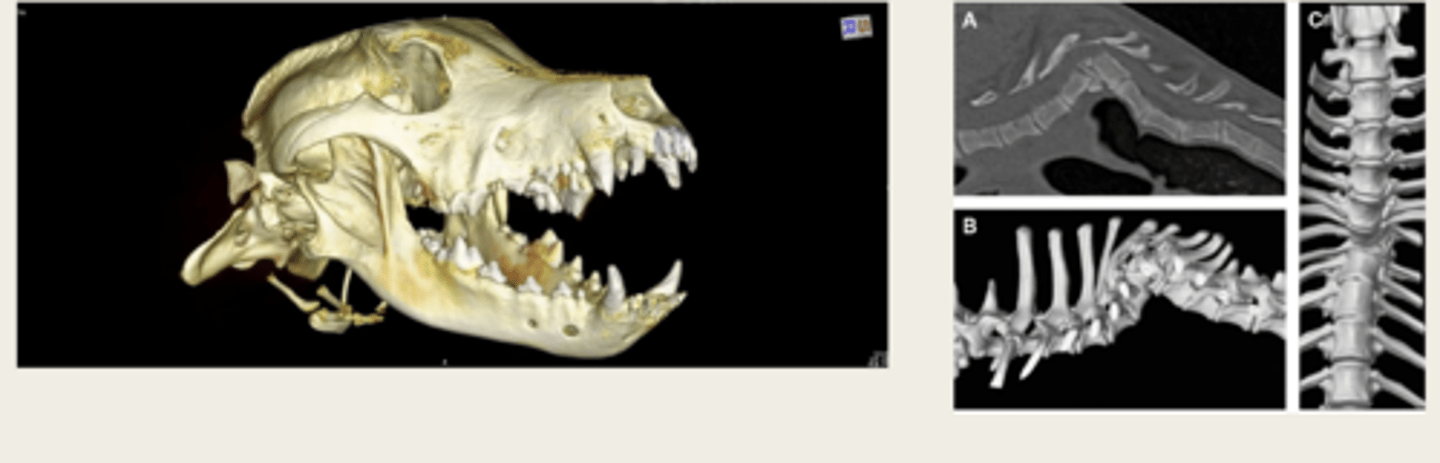
CT volume rendering/3D reconstruction
what is the image on the left showing?
magnetic resonance imaging
what does MRI stand for?
utilizes strong magnetic field and radio frequency waves
how does an MRI operate?
true
T/F: MRI images are cross sectional
no! non ionizing
is MRI ionizing?
no!
is MRI an x-ray based modality like CT is?
MRI
does CT or MRI have better soft tissue contrast?
MRI
can MRI or CT determine tissue/lesion composition by signal intensities in different sequences
MRI
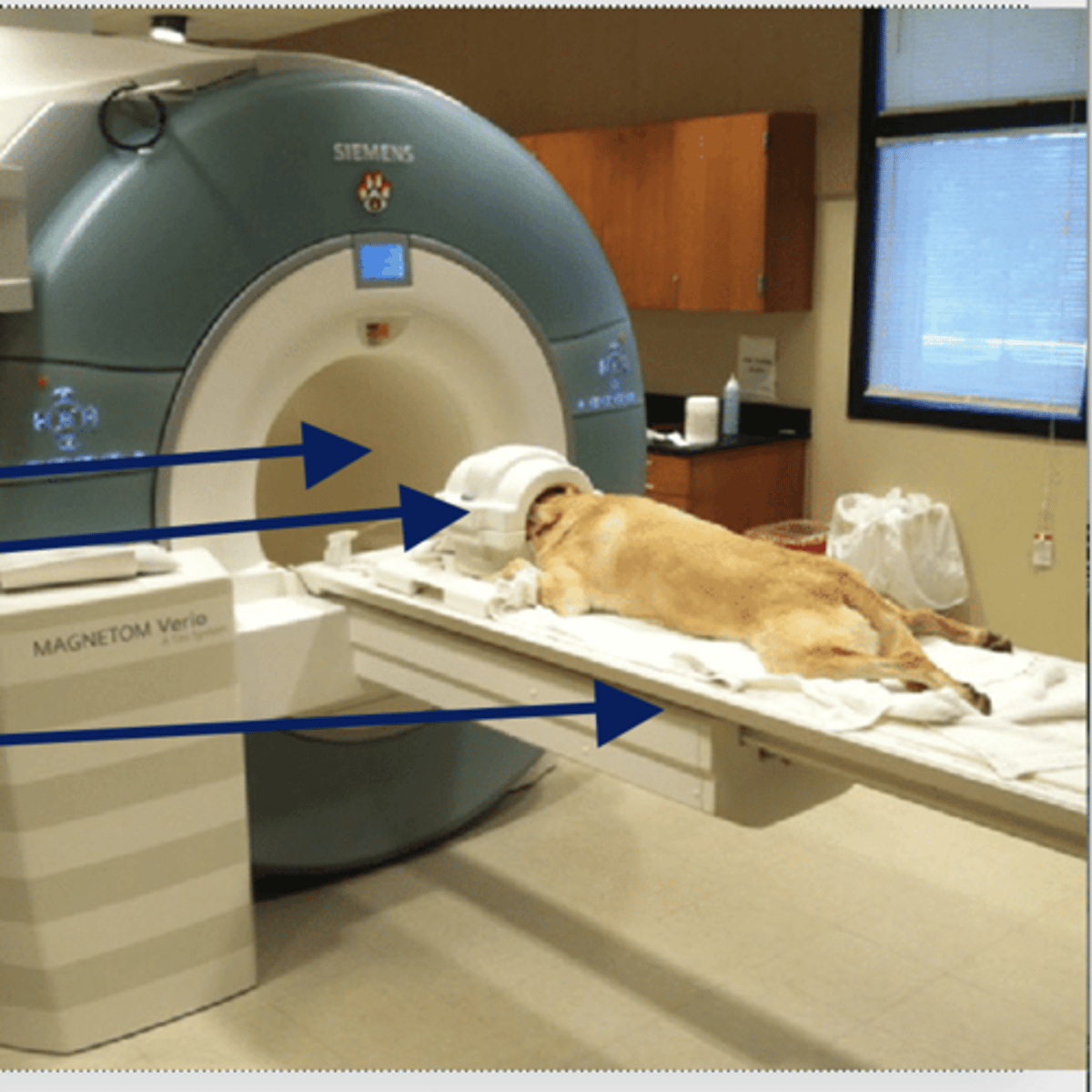
which takes longer, CT or MRI?
MRI, takes a long time and LOUD
does CT or MRI REQUIRE general anesthesia? why?
MRI
is MRI or CT the gold standard for imaging of most neurologic conditions
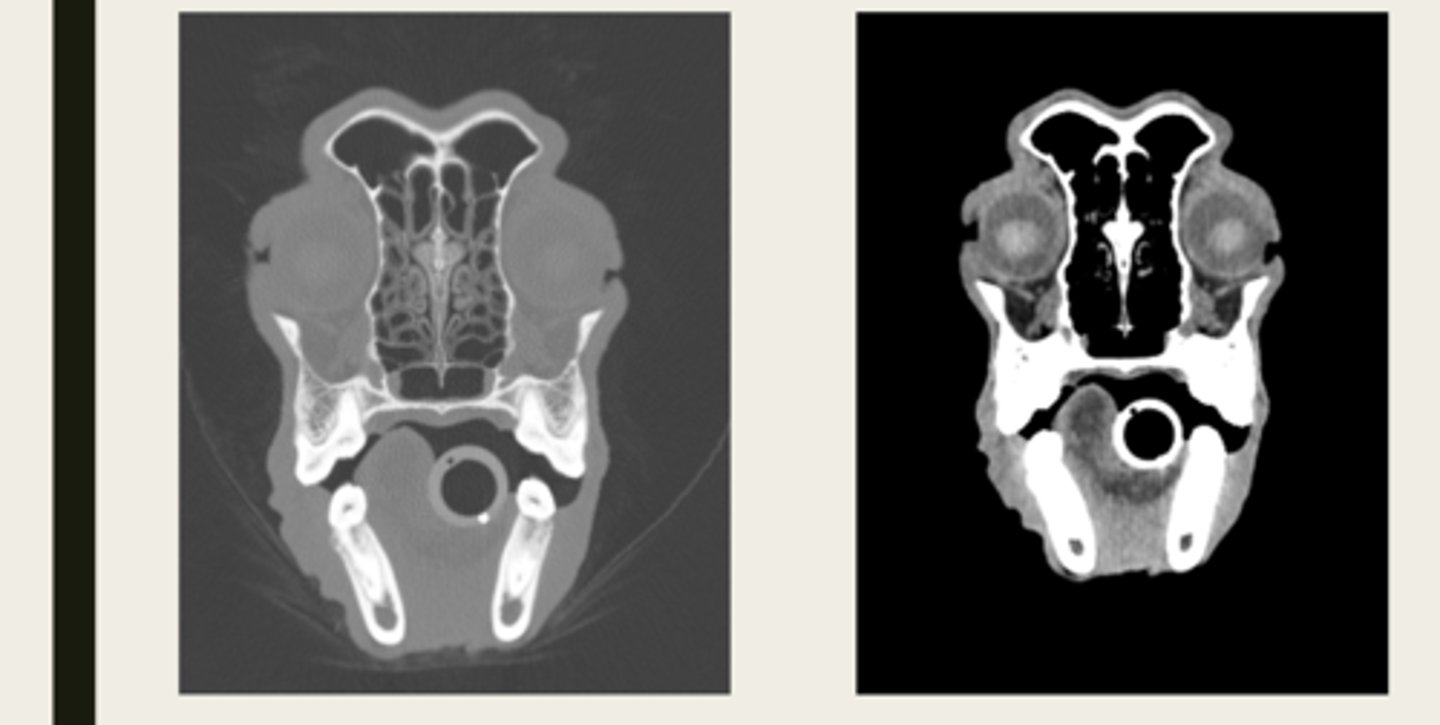
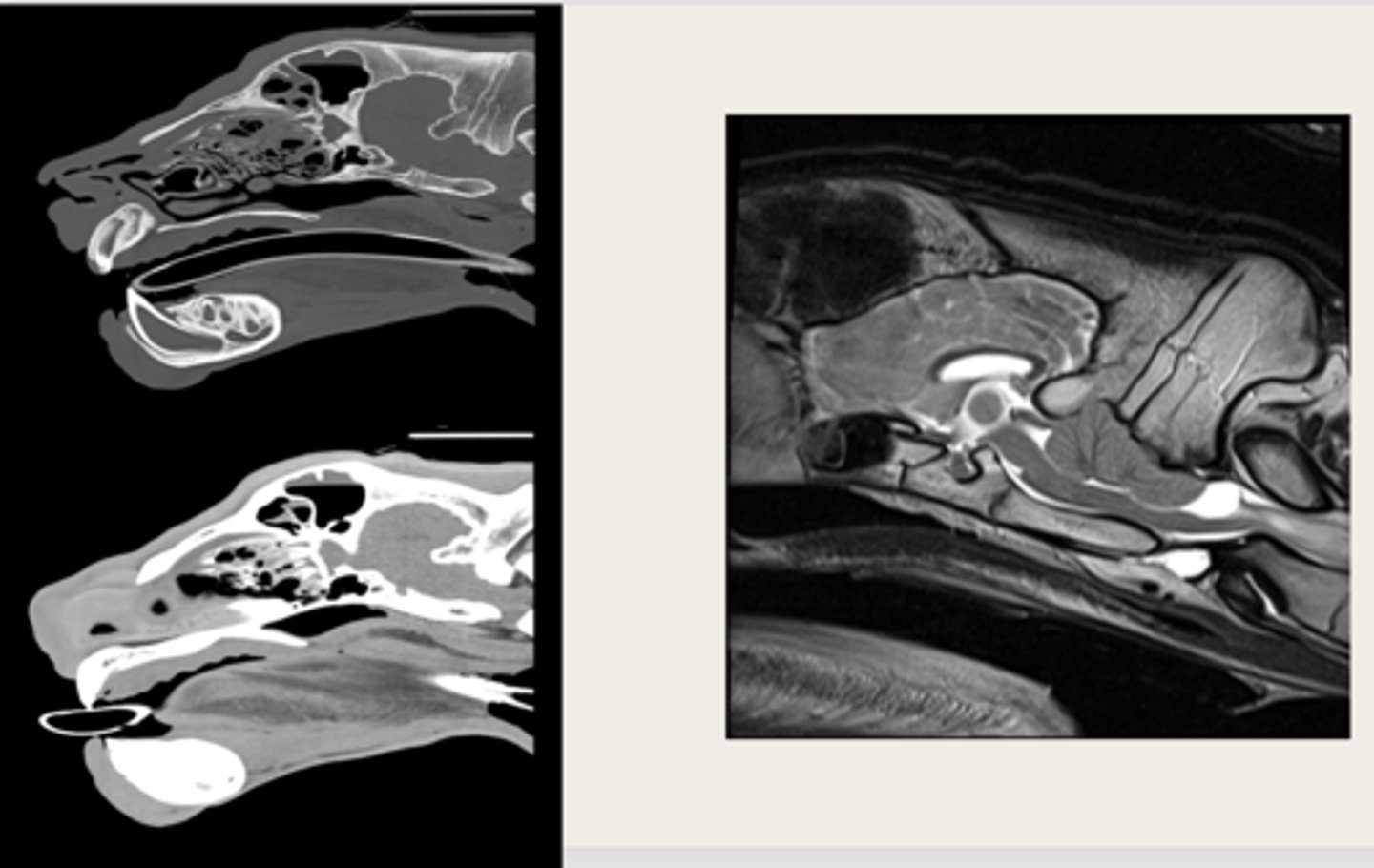
left- CT
right- MRI
which images are CT and which are MRI?
the hydrogen nucleus
in regards to MRI physics, the MRI manipulates what?
the magnetic fields line up from the spinning proton of the hydrogen nucleus
when the patient is put into an MRI machine, what occurs in regards to the magnetic fields?
they disturb the small magnetic fields that are lined up
the radio frequency waves do what in an MRI?
they release energy which is detected by the MRI machine
as the protons return to their original orientation in an MRI, what then occurs?
return to their original orientation
differences in rate at which protons in different tissues _____________ determines what we see
top- bore
middle- RF coil
bottom- couch/table
what are the parts of the MRI machine from top to bottom?
yes!
does strength matter in MRI?
better
the higher the main magnet field strength usually the _______ the images
tesla (T)
what is the unit of magnetic field strength?
Same as CT but actually acquired in different planes, not post processing like in CT
what are the MRI planes compared to CT?
different tissue types
different sequences of MRI can be produced to highlight or suppress what?
by the timing of the radiofrequency pulses applied from the machine and received from the tissues
how are MRI sequences determined?
TR (time of repetition) and TE (time to echo)
what are the two parameters of MRI sequences?
-T1 weighted
-T2 weighted
what are the two main MRI sequences?
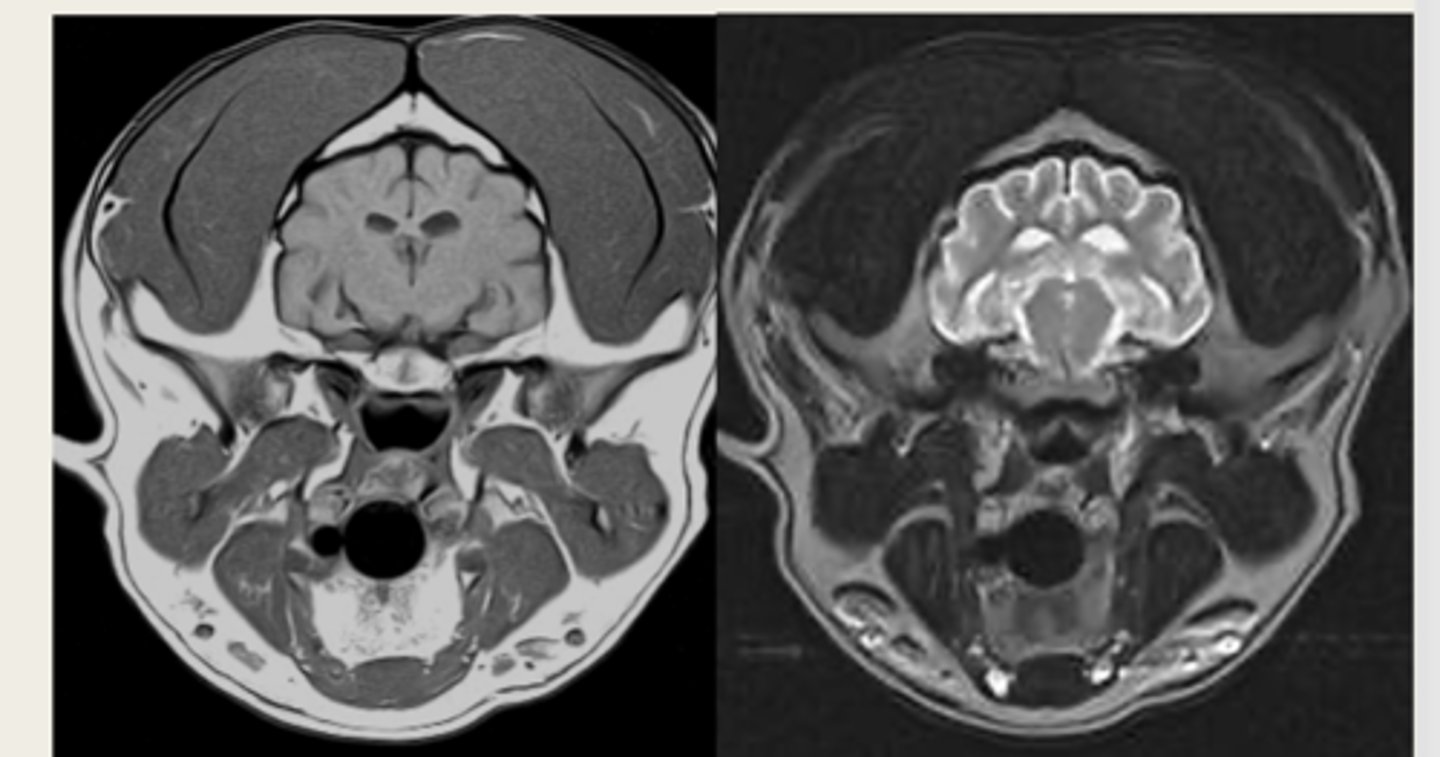
left- T1 weighted
right- T2 weighted
which image is T1 weighted and which is T2 weighted?
Size
Shape
Location
Number
Margination
Intensity
what are the roentgen signs of MRI?
NO! based off of intensity
T/F: MRI is interpreted based off of opacity/echogenicity
-hyperintense
-hypointense
MRI signal intensity is described as bright or ___________ OR dark or _________
amount of protons in a tissue and sequence selection
MRI signal intensity depends on what?
anatomy
T1 weighted images are good for ________
pathology
T2 weighted images are good for identifying __________
hyperintense
Pathologic tissues such as tumors or areas of inflammation are "juicy" so they are what intensity?
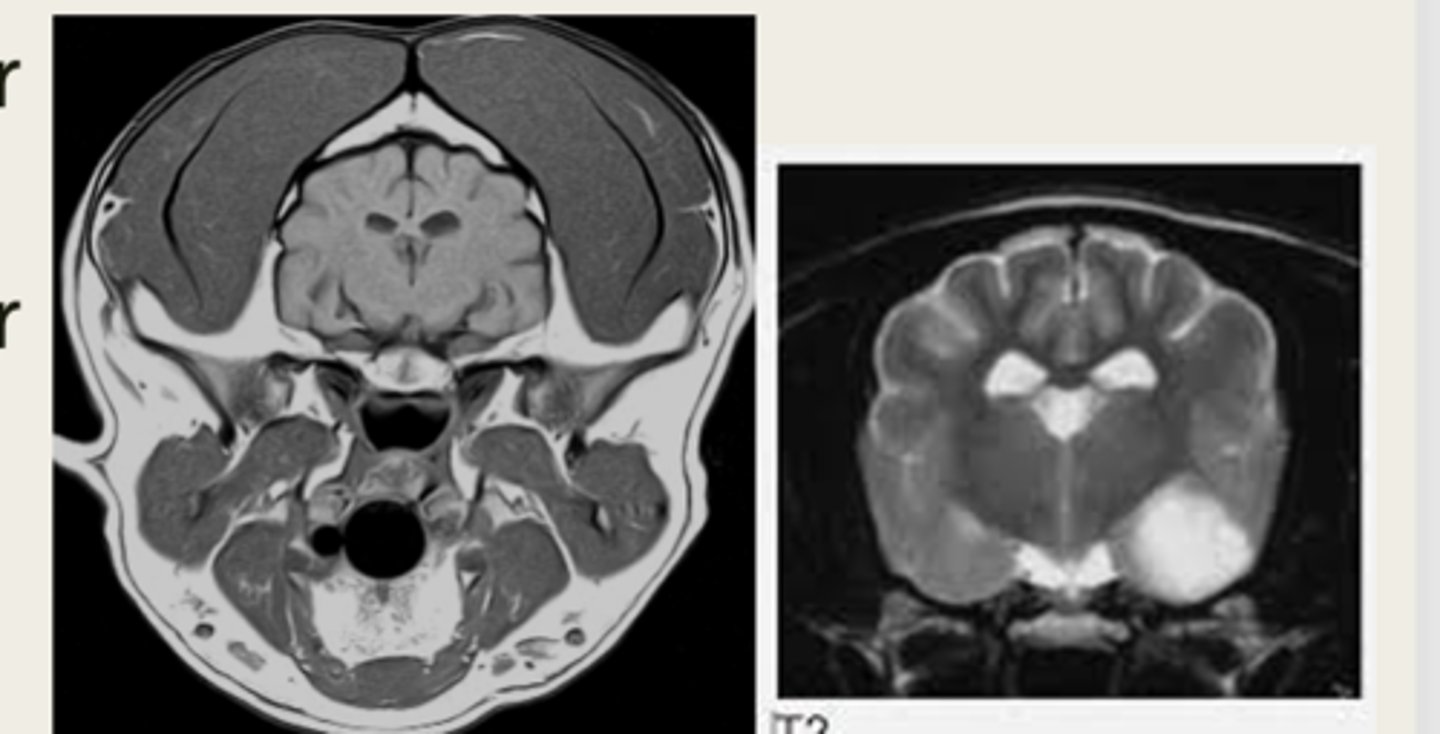
left- T1 weighted
right- T2 weighted
which MRI image is T1 or T2 weighted?
Gadolinum
what contrast can be given for MRI?
IV
Gadolinum is given SQ/IM/IV?
T1 weighted
are contrast MRIs done in T1 weighted or T2 weighted?
Differentiates abnormal tissue from surrounding tissue
what is the benefit of doing a contrast MRI?
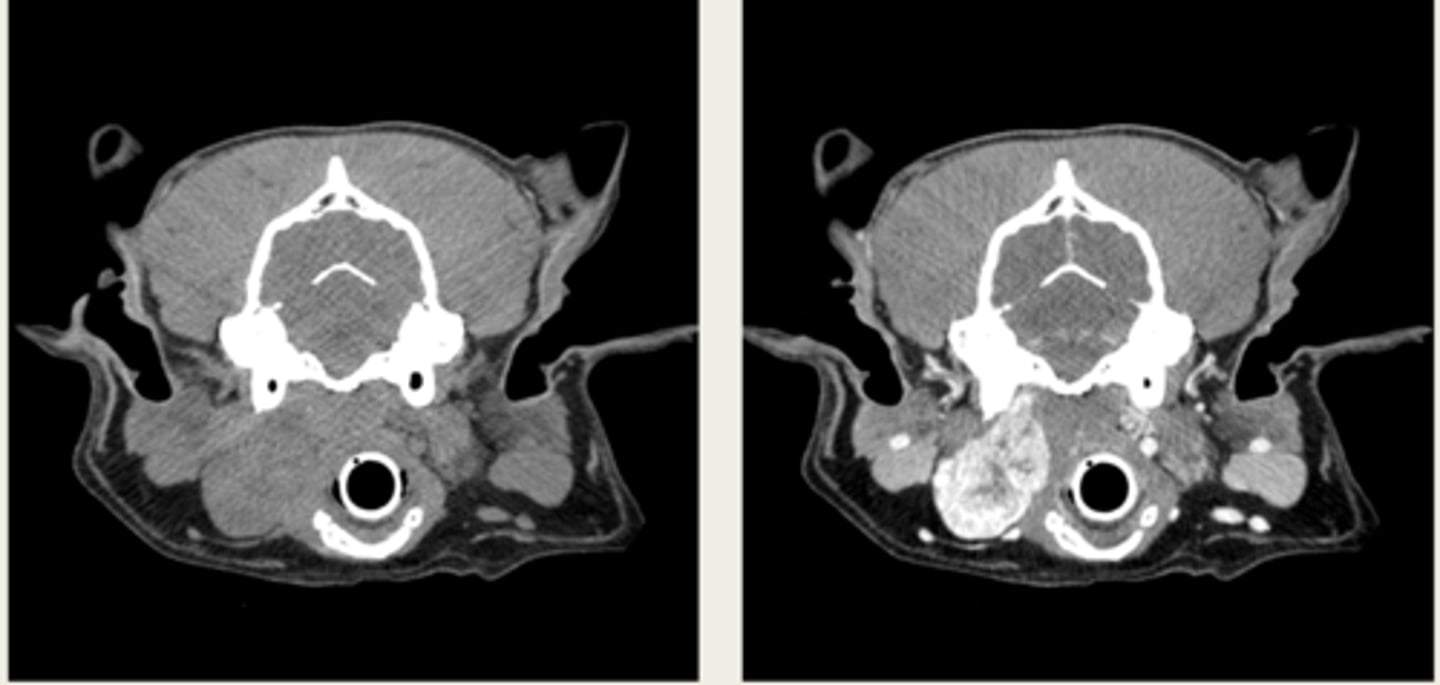
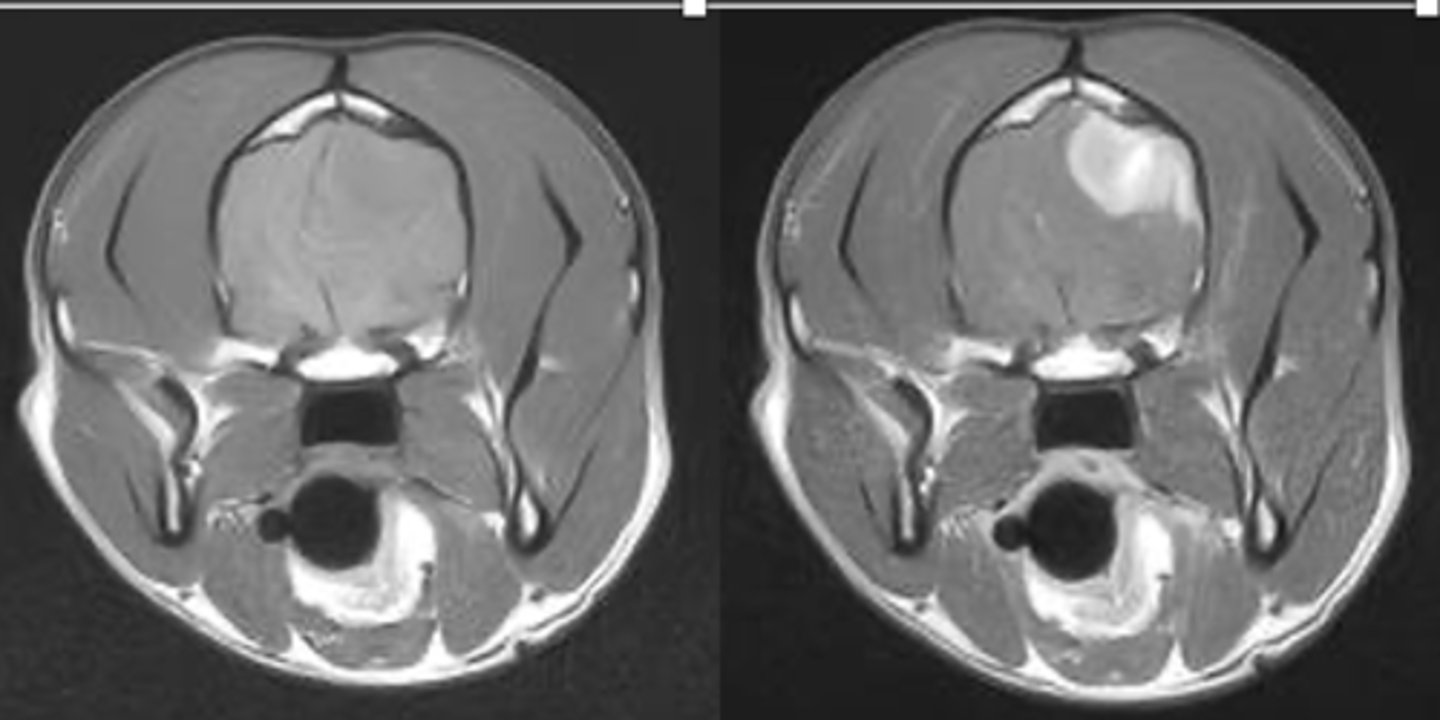
left- pre contrast
right- post contrast
which MRI is pre and post contrast?
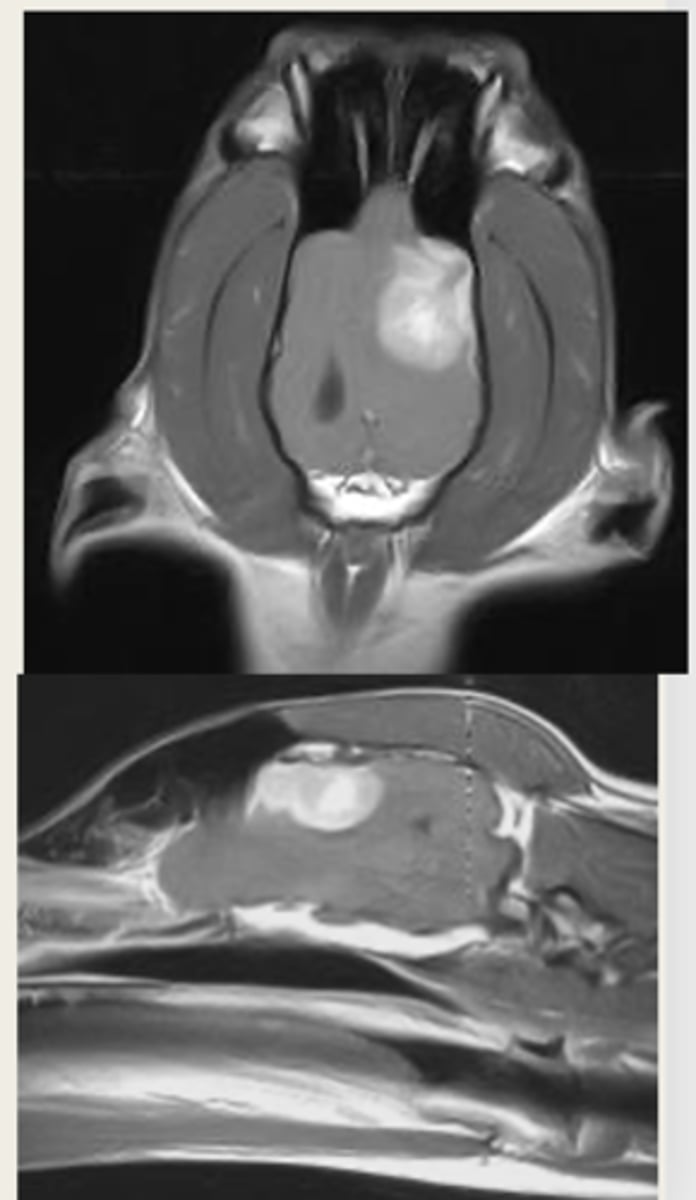
MRI
is this an MRI or CT?
magnet
the MRI is a big _________, so be careful!
CT
should you do a CT or MRI for the thorax/metastasis?
MRI
should you do a CT or MRI for the brain/seizures?
CT
should you do a CT or MRI for the elbows/suspected elbow dysplasia ?
MRI
should you do a CT or MRI for the suspected intervertebral disc disease?
CT
should you do a CT or MRI for a cervical spine problem in a dog with a pacemaker?
-cross sectional
-same area
-TRANSVERSE PLANE
how are these images the same?
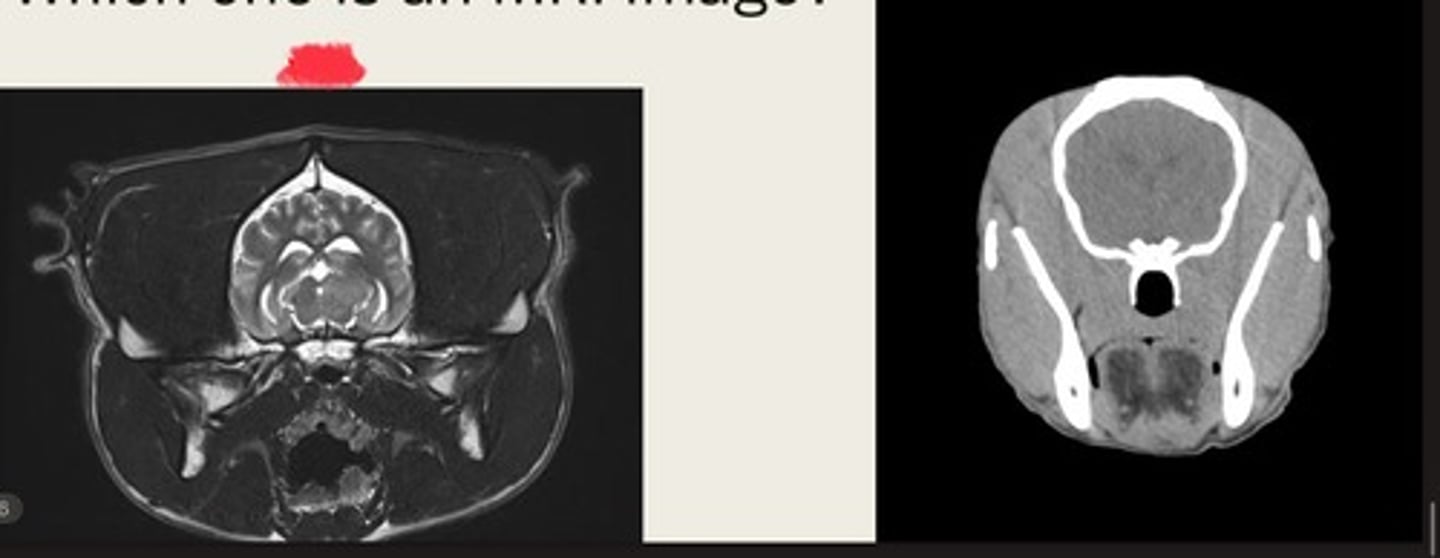
right- bright bone
left- less bright bone, more definition in tissue
how are these images different?
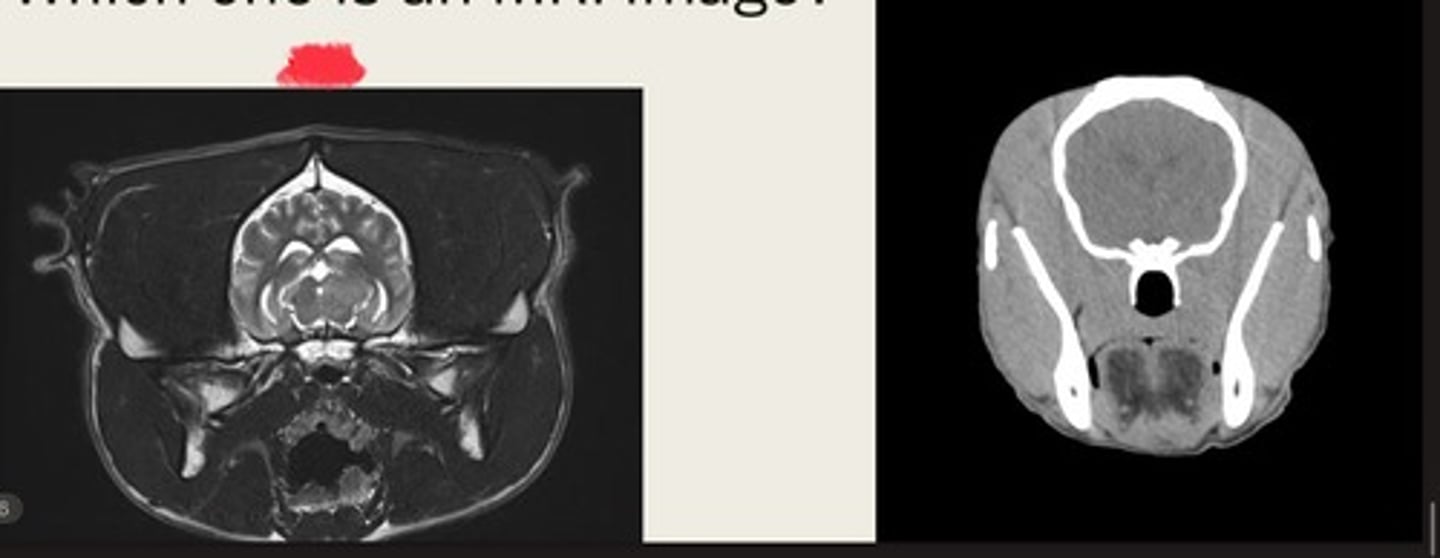
left- MRI
right- CT
which one is the CT and which is the MRI?