connect exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
Prior to the arrival of a signal from a presynaptic input, the post-synaptic membrane is polar with a greater relative __________ charge in the ECF.
positive
2
New cards
In somatic neurons, an action potential arrives at the synapse causing synaptic vesicles to fuse with the _____________ membrane.
presynaptic
3
New cards
The presynaptic membrane releases (via exocytosis) acetylcholine (ACh) into the
ECF of the synaptic cleft.
4
New cards
The ACh diffuses across the cleft and binds to the ____________ channels.
ligand-regulated sodium
5
New cards
Activated (open) sodium channels allow a rapid diffusion of ____________ down its electrochemical gradient towards the ICF.
sodium
6
New cards
The movement of positive charges to the ___________ causes the relative charge across the membrane to become positive on the inner surface.
ICF
7
New cards
An action potential arriving at the presynaptic terminal causes what to occur?
Voltage-gated calcium ion channels open, and calcium ions diffuse into the cell.
8
New cards
What happens as a result of ion flow at a presynaptic terminal?
Synaptic vesicles migrate to the plasma membrane and release acetylcholine.
9
New cards
Acetylcholine has which effect on the postsynaptic neuron?
Ligand-gated sodium ion channels open, and sodium diffuses in.
10
New cards
True or false: If the postsynaptic membrane potential reaches threshold level, an action potential will be produced.
true
11
New cards
true or false: Acetylcholine is actively transported from the presynaptic membrane to the postsynaptic membrane.
false
12
New cards
- muscle spindles are the receptor
- initiated by an increase in muscle length
- is monosynaptic
- initiated by an increase in muscle length
- is monosynaptic
stretch reflex
13
New cards
- marked by removal of the body from injurious elements
flexor reflex
14
New cards
- utilizes an integrating center
all reflexes
15
New cards
- inhibits excessive muscle contraction
- tendon organs are the receptors
- tendon organs are the receptors
tendon reflex
16
New cards
- marked by actions to stabilize the limb opposite of injurious agents
- is contralateral
- marked by actions that stabilize the contralateral limb
- is contralateral
- marked by actions that stabilize the contralateral limb
crossed-extensor reflex
17
New cards
Which spinal nerve roots carry sensory nerve signals?
Posterior
18
New cards
In an adult, the spinal cord ends at which vertebra?
Between L1 and L2
19
New cards
cervical enlargement
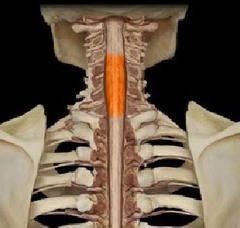
20
New cards
lumbosacral enlargement
21
New cards
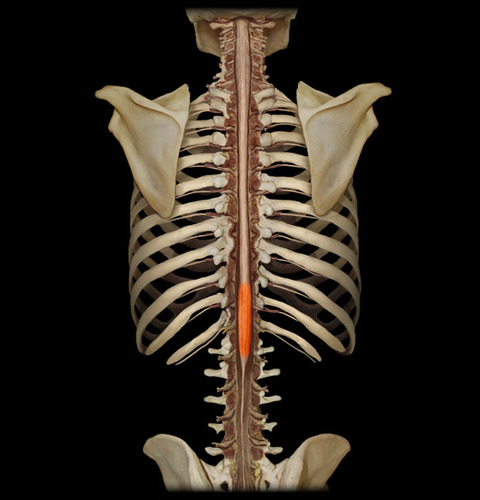
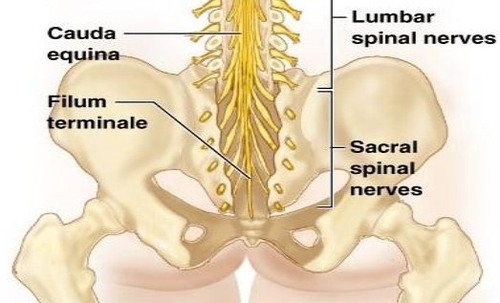
medullary cone
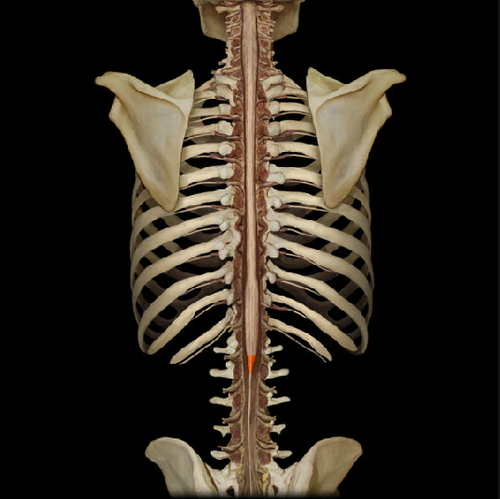
22
New cards
cuada equina
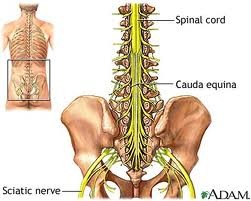
23
New cards
terminal filum
24
New cards
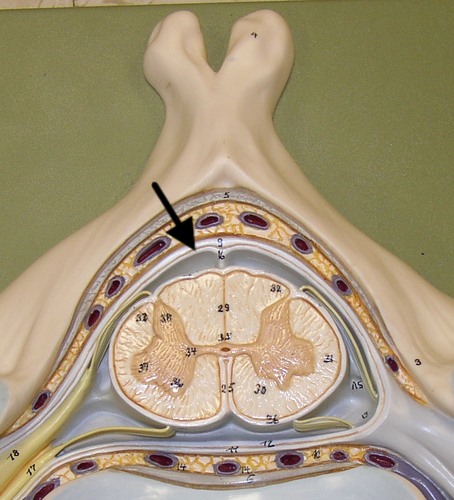
dural sheath
25
New cards
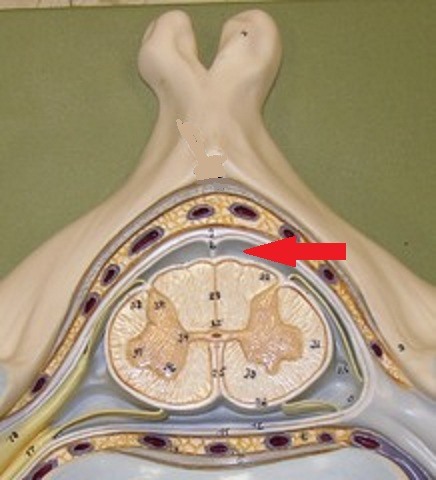
subarachnoid space
26
New cards
A damaged ________ nerve fiber may regenerate if its soma is intact and some neurilemma remains.
peripheral
27
New cards
When a nerve fiber is cut, the fiber distal to the injury _______ survive.
cannot
28
New cards
Near the site of injury, the basal lamina and the neurilemma form a ________ tube.
regeneration
29
New cards
The tube guides the growing sprout back to the original target cells, reestablishing ________ contact.
synaptic
30
New cards
When contact is established, the ________ shrinks, and reinnervated muscle fibers regrow.
soma
31
New cards
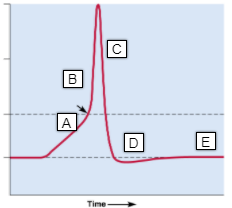
A
- Na+ arrive at the axon hillock and depolarize the membrane at that point
- potential across the membrane is becoming less negative
- potential across the membrane is becoming less negative
32
New cards
B
- -55 mV
- at threshold, voltage-gated Na+ channels open quickly
- at threshold, voltage-gated Na+ channels open quickly
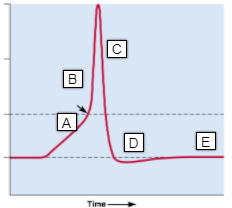
33
New cards
C
- voltage-regulated K+ channels open
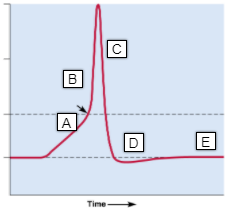
34
New cards
D
- hyperpolarization
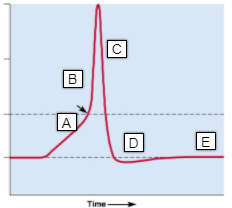
35
New cards
E
- resting membrane potential
- -70 mV
- -70 mV
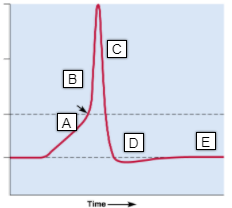
36
New cards
Which of the following are made of gray matter?
Anterior, posterior, and lateral horns
37
New cards
What is the loose connective tissue surrounding an individual nerve fiber called?
Endoneurium
38
New cards
what neurons: One axon; multiple dendrites
Multipolar neurons
39
New cards
what neurons: One axon; one dendrite
Bipolar neurons
40
New cards
what neurons: A single process
Unipolar neurons
41
New cards
what neurons: No axon; multiple dendrites
Anaxonic neurons
42
New cards
Why is myelin important?
- It speeds up signal conduction in the nerve fiber.
- It is formed to assist in the regeneration of damaged fibers.
- It insulates the nerve fiber.
- It is formed to assist in the regeneration of damaged fibers.
- It insulates the nerve fiber.
43
New cards
anatomical features of a neuron.
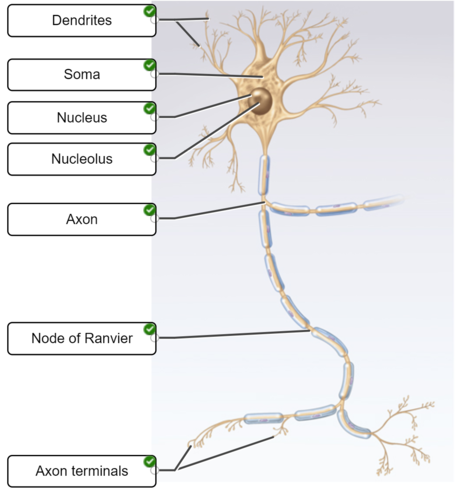
44
New cards
What are the three general classes of neurons that correspond to the three major aspects of nervous system function?
- Motor neurons that send signals predominantly to muscle and gland cells
- Interneurons that lie between, and interconnect the incoming sensory pathways and the outgoing motor pathways of the CNS
- Sensory neurons that are specialized to detect stimuli such as light, heat, pressure, and chemicals and transmit information about them to the CNS
- Interneurons that lie between, and interconnect the incoming sensory pathways and the outgoing motor pathways of the CNS
- Sensory neurons that are specialized to detect stimuli such as light, heat, pressure, and chemicals and transmit information about them to the CNS
45
New cards
he reflex that results in quick contraction of the same muscle stimulated is called the _________ reflex.
stretch
46
New cards
A reflex hammer striking the tendon is the ________ that triggers the __________.
stimulus; receptor
47
New cards
The afferent neuron synapses with the ___________ in the integrating center.
efferent neuron
48
New cards
This makes it a(n) ___________ reflex arc
monosynaptic
49
New cards
If we are using the patellar ligament as the example, the quadriceps muscles are the _________.
effectors
50
New cards
The antagonists will be inhibited. This is an example of __________.
reciprocal inhibition
51
New cards
Assume all of the presynaptic synapses identified produce EPSPs. If two of these synapses fired simultaneously, which synaptic combination brings the initial segment closest to threshold based on spatial summation?
3 and 4
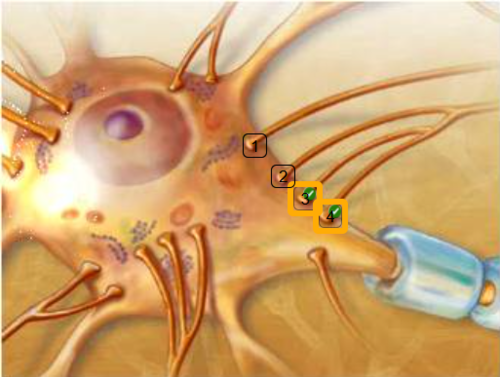
52
New cards
Graded potentials result from the opening of
ligand-gated channels
53
New cards
Indicate the summative effect that brings the initial segment closest to threshold.
Two EPSPs in proximity to each other
54
New cards
_______________ the time between signals sent from the same presynaptic terminal increases the strength of the graded potential. This is an example of ________________ summation.
Reducing; temporal
55
New cards
Substances that cause facilitation of a neuron ____________________________
cause the neuron to fire that may not fire under the same circumstances in the absence of the facilitator
56
New cards
Assume in a laboratory you were able to isolate a neuron and remove the Acetylcholine receptors from the postsynaptic membrane. The substance _________________ would no longer cause facilitation of this neuron.
nicotine
57
New cards
lumbosacral enlargement
thoracic region
58
New cards
cervical enlargement
cervical region
59
New cards
- medullary cone
- cauda equina
- terminal filum
- cauda equina
- terminal filum
sacral and lumbar region
60
New cards
Which portion of a reflex arc is located entirely within the central nervous system?
Interneuron
61
New cards
true or false: Reflexes have four important properties: they require stimulation, they are quick, they are involuntary, and they are stereotyped.
true
62
New cards
Which of the following cause a postsynaptic transmission to stop?
- Diffusion of the neurotransmitter into the nearby extra-cellular fluid
- Reuptake of the neurotransmitter by endocytosis
- Degradation of the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
- Reuptake of the neurotransmitter by endocytosis
- Degradation of the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
63
New cards
regions of a neuron
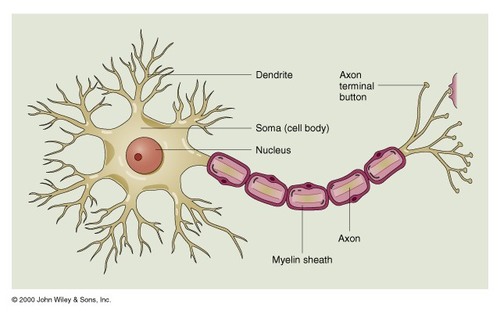
64
New cards
Normally, sodium and potassium leakage channels differ because ___________________.
sodium ions diffuse through leakage channels into the cell, but potassium ions diffuse through leakage channels out of the cell
65
New cards
A resting membrane potential of -70 mV indicates that the ________________.
charges lining the inside of the plasma membrane are negative compared to the charges lining the outside
66
New cards
spinal nerves: Sacral plexus
L4, L5, and S1-S4
67
New cards
spinal nerves: Brachial plexus
C5 to T1
68
New cards
spinal nerves: Lumbar plexus
L1-L4
69
New cards
spinal nerves: Cervical plexus
C1-C5
70
New cards
diverging neural cicuits
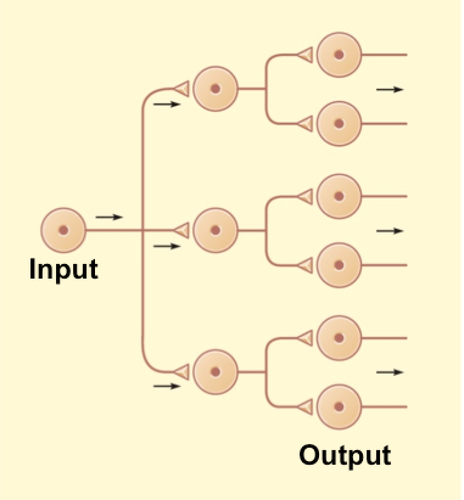
71
New cards
converging neural circuits
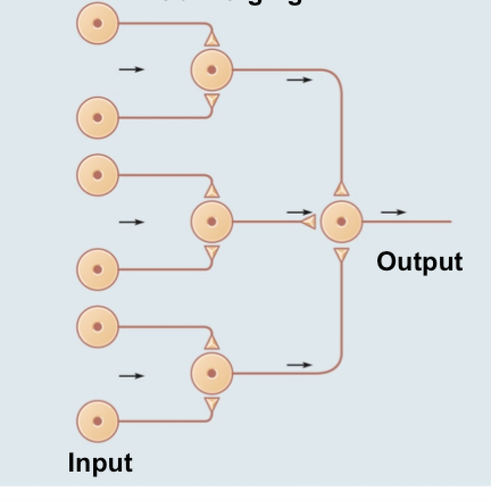
72
New cards
parallel after-discharge neural circuits
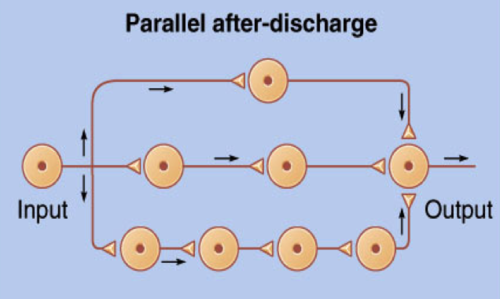
73
New cards
reverberating neural circuits
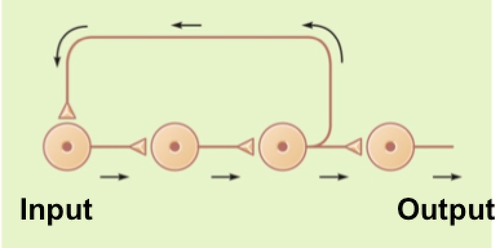
74
New cards
spinal nerves and their plexuses
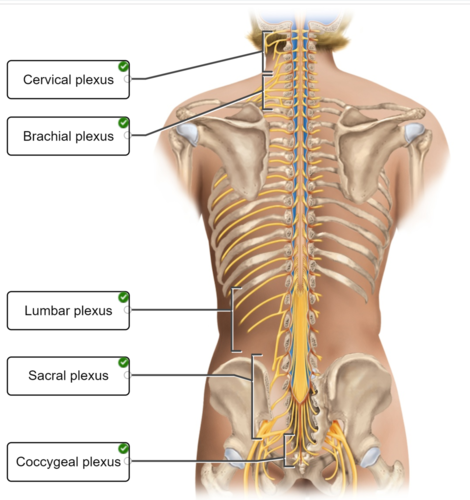
75
New cards
Which term describes all neurons that carry signals towards the CNS?
Afferent
76
New cards
anatomical features of the neuroglia
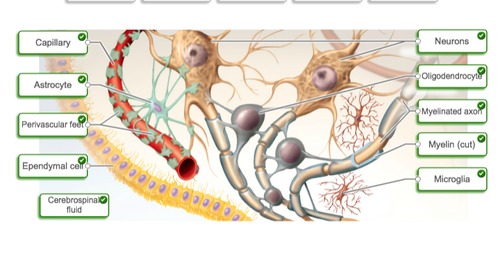
77
New cards
action potential order: 1
a neuron starts at its resting membrane potential
78
New cards
action potential order: 2
excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP's) are received
79
New cards
action potential order: 3
Na+ flows into the cell making the inside more positive
80
New cards
action potential order: 4
the cell reaches threshold
81
New cards
action potential order: 5
voltage-gated Na+ channels open
82
New cards
action potential order: 6
an action potential is generated
83
New cards
An unmyelinated fiber has voltage-gated ion gates along its entire _______
length
84
New cards
An action potential at the ________ zone causes sodium to diffuse into the cell.
trigger
85
New cards
This results in membrane ___________
depolarization
86
New cards
The depolarization causes a _________ that excites the entire membrane.
repetition
87
New cards
This continues until the traveling signal reaches the end of the ___________
axon
88
New cards
anatomical features of a neuron
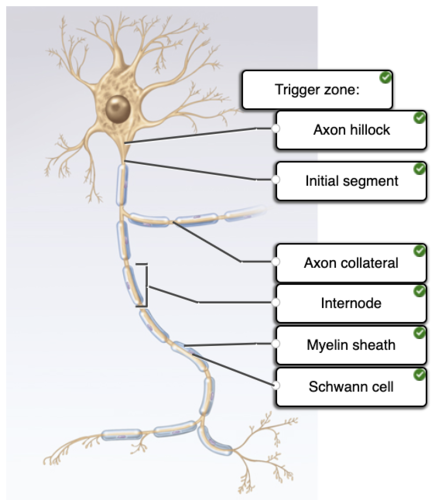
89
New cards
anatomical features of the spinal cord
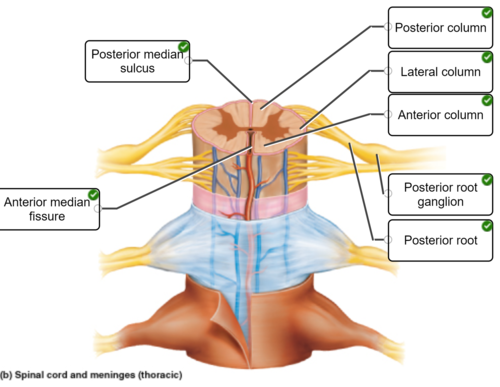
90
New cards
Which of the following describes a reverberating circuit?
There is a prolonged or repetitive effect that lasts until one or more neurons in the circuit fail to fire or until an inhibitory signal from another source stops one of them from firing. Neurons stimulate each other in a linear sequence such as A→B→C→D, but neuron C sends an axon collateral back to A.
91
New cards
anatomical features of a neuron
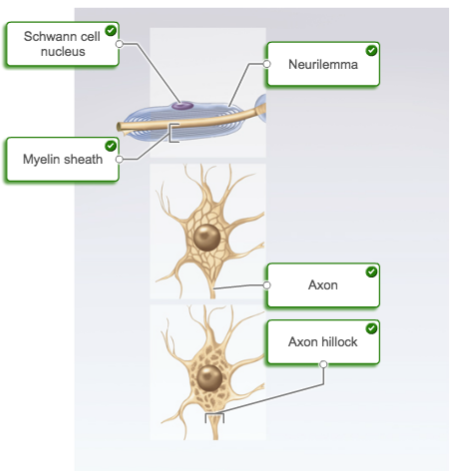
92
New cards
phases of action potential
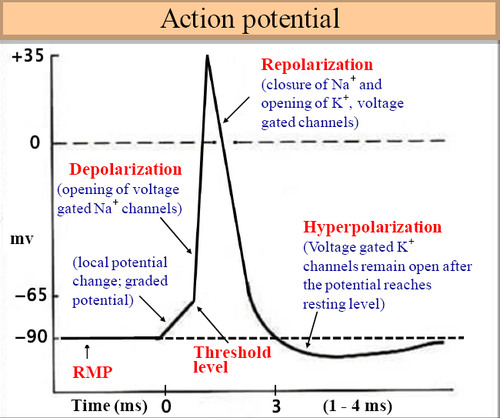
93
New cards
When voltage-gated sodium channels are open, sodium flows _____________ the neuron, making the inside of the cell more _______________.
into; positive
94
New cards
The following information best describes the _____________ phase of an action potential.
repolarization
95
New cards
Action potentials occur ____________________________.
in the unmyelinated regions of an axon
96
New cards
Demyelinating diseases cause a(n) ______________ in the conduction velocity of action potentials.
decrease
97
New cards
If demyelination occurs, why don't action potentials occur at regions of the axon that were previously myelinated?
These regions lack the appropriate concentration of voltage-gated sodium channels
98
New cards
postsynaptic potential
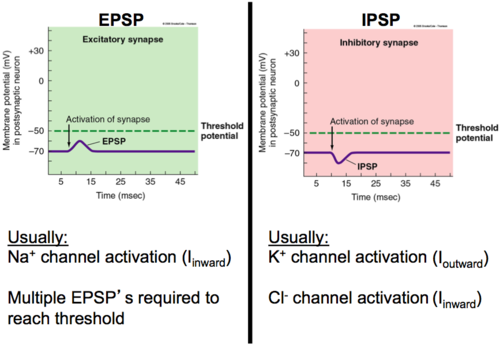
99
New cards
Graded potentials are produced within the _______________________ segment of a neuron
receptive
100
New cards
Graded potentials result from the opening of ________________.
ligand-gated channels