L14 The Brain (Imported from Quizlet)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
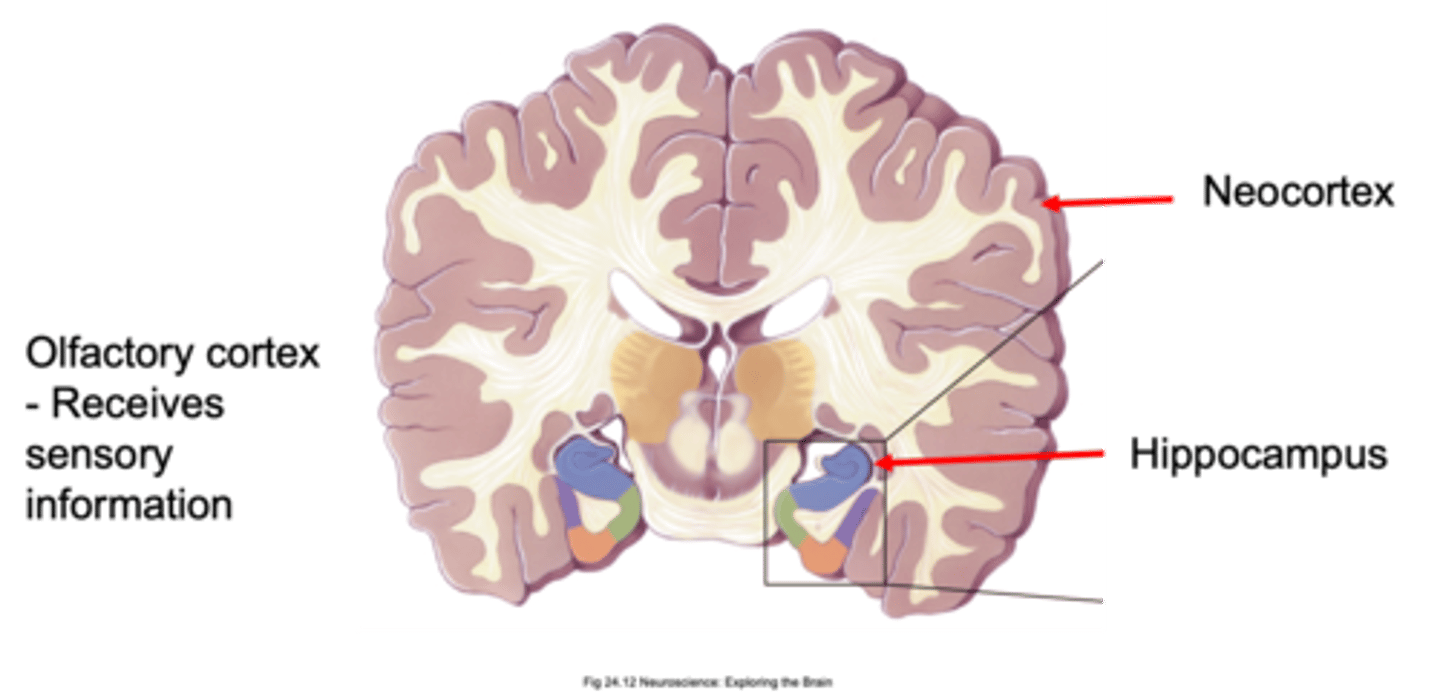
Neocortex, hippocampus, olfactory cortex
What are the 3 types of cerebral cortex? (you must be able to name all 3 of these)
Receives sensory information (receives direct sensory innervation from olfactory bulbs)
What does the olfactory cortex do?
Olfactory cortex
What is the oldest part of the cerebral cortex?
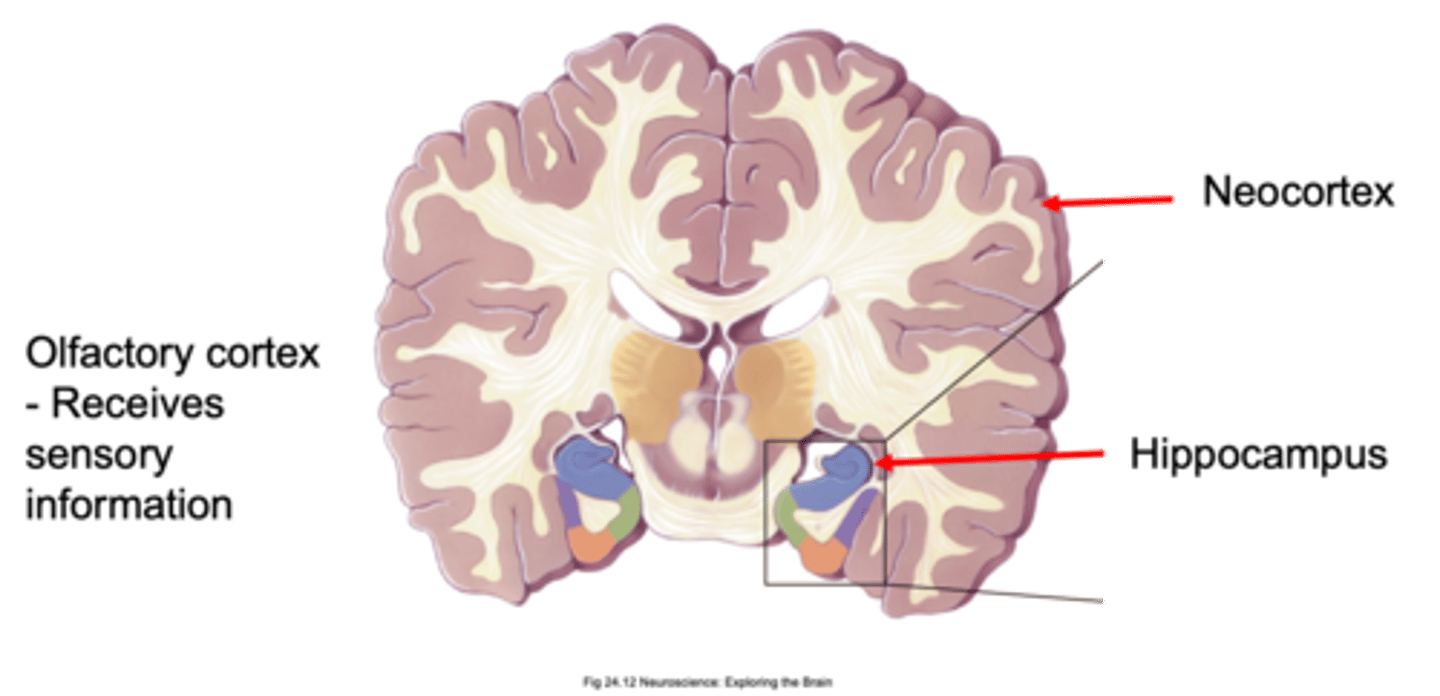
Neocortex
What is the youngest part of the cerebral cortex?
In each temporal lobe
Where is the hippocampus found?
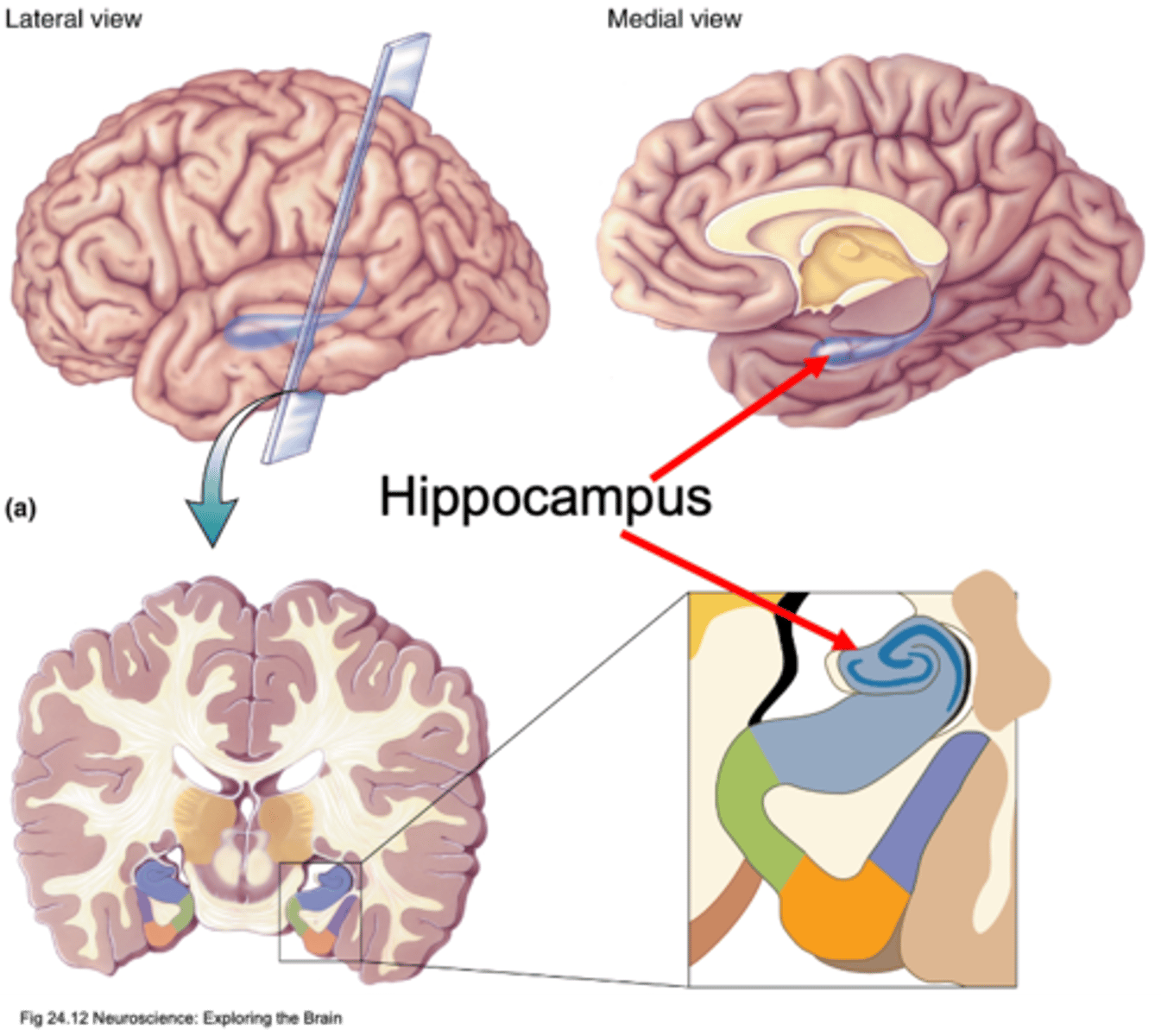
Memory
What is the hippocampus involved in?
3
How many layers does the hippocampus have?
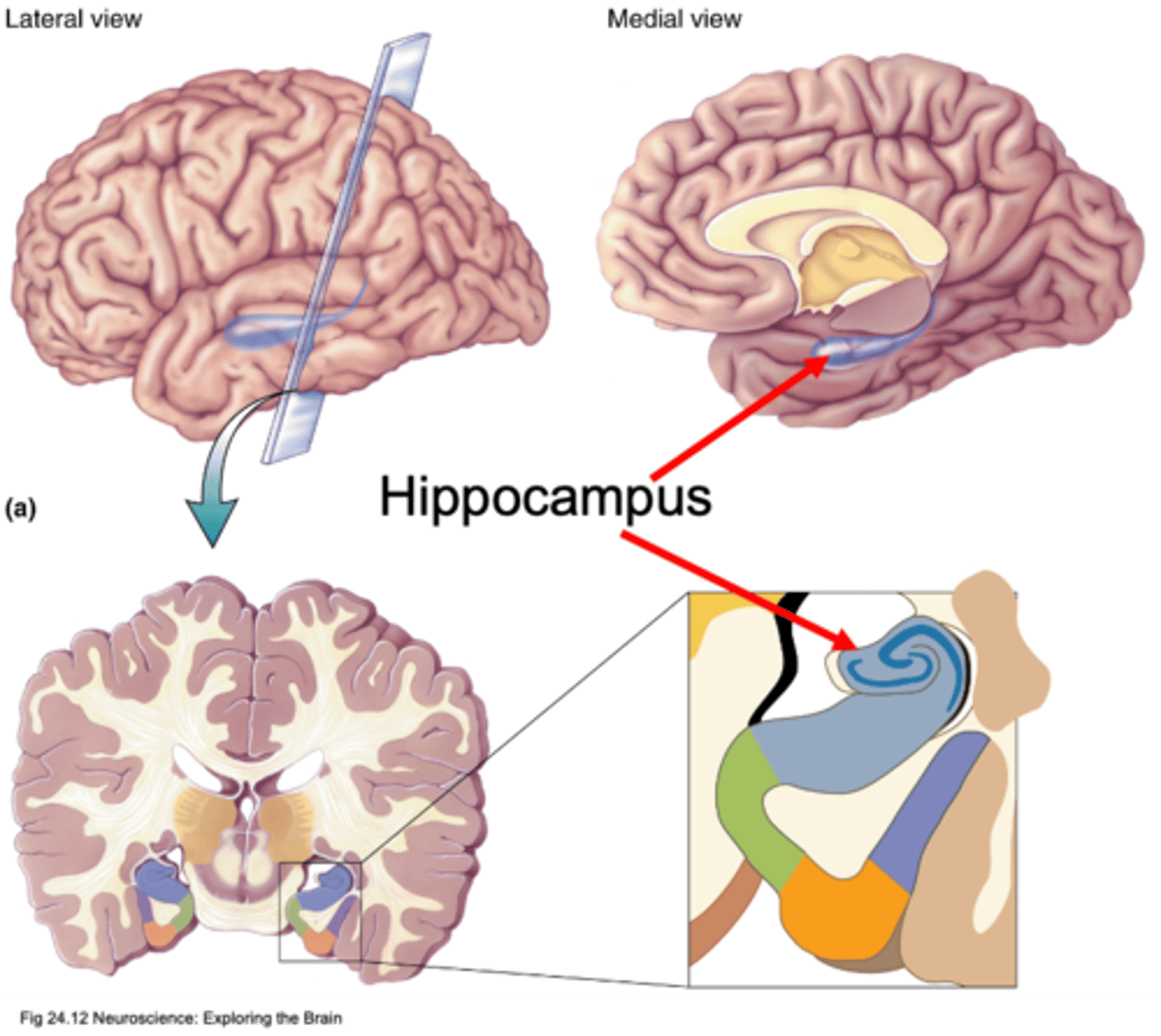
Birth of new neurons in adulthood
The hippocampus is one of the only areas where you can have what?
Gyri, sulci
To distinguish between lobes, you must look for key ______ and _______
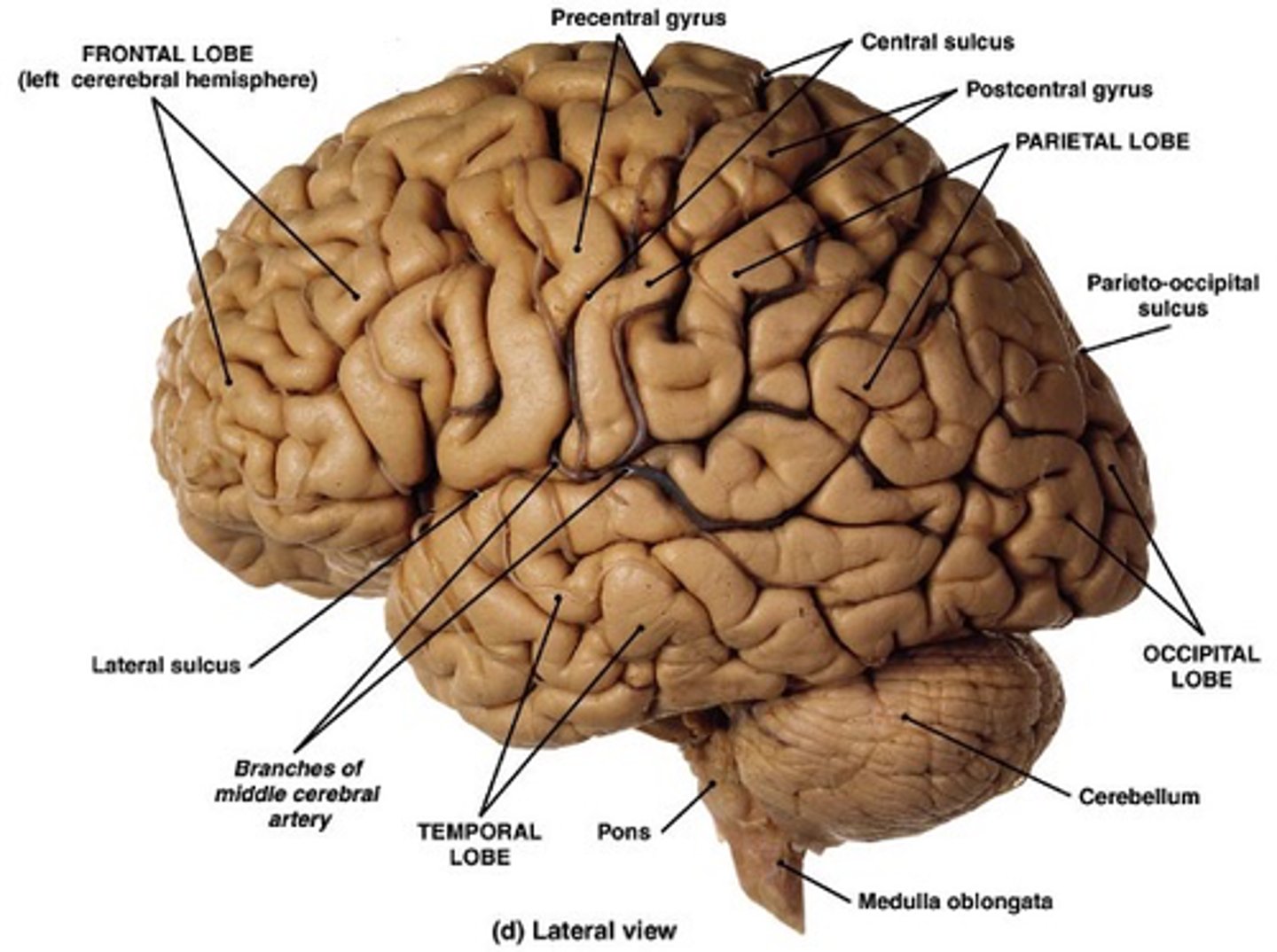
Central sulcus
What separates the frontal lobe from parietal lobe?
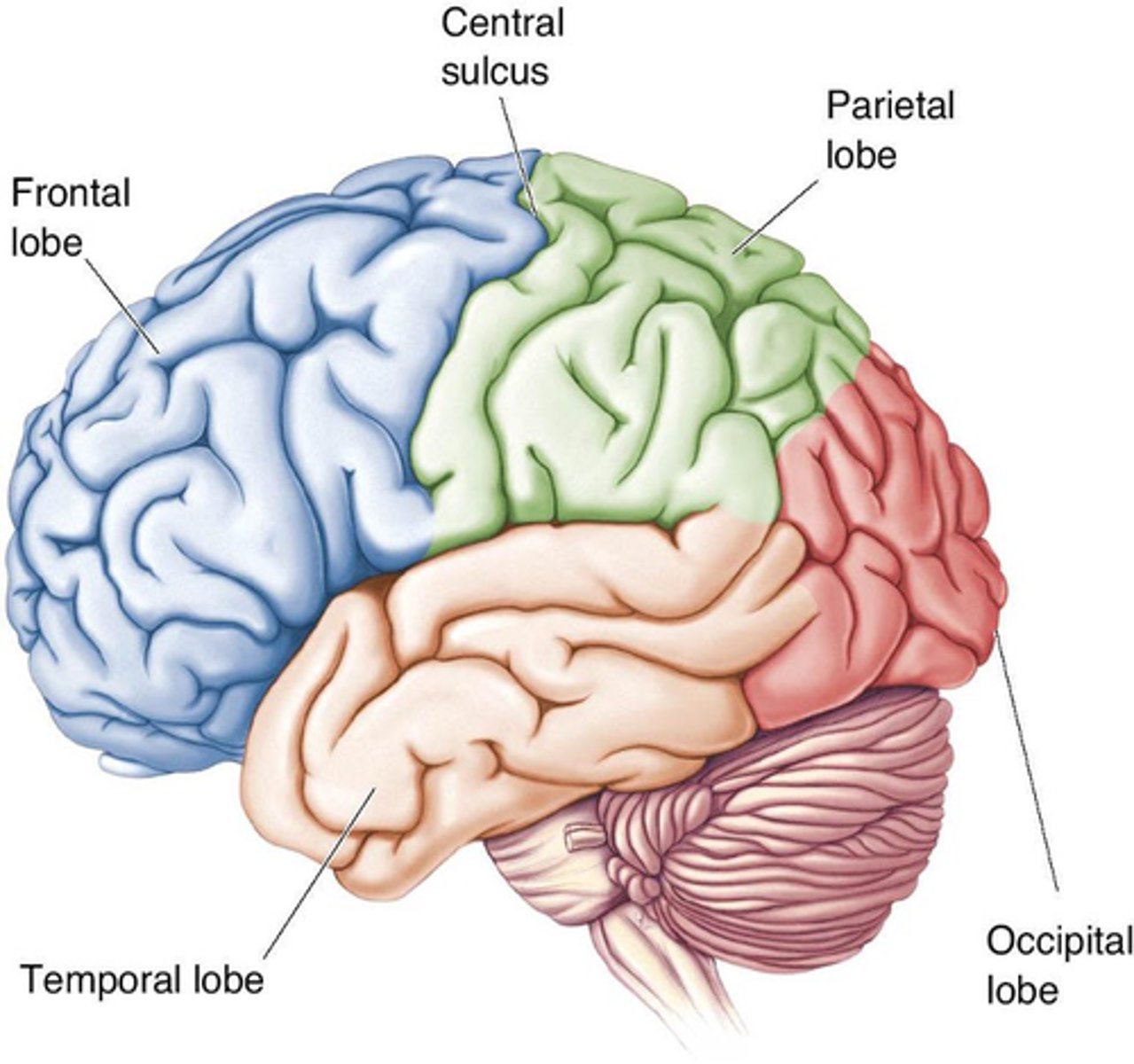
Lateral sulcus
What separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe?
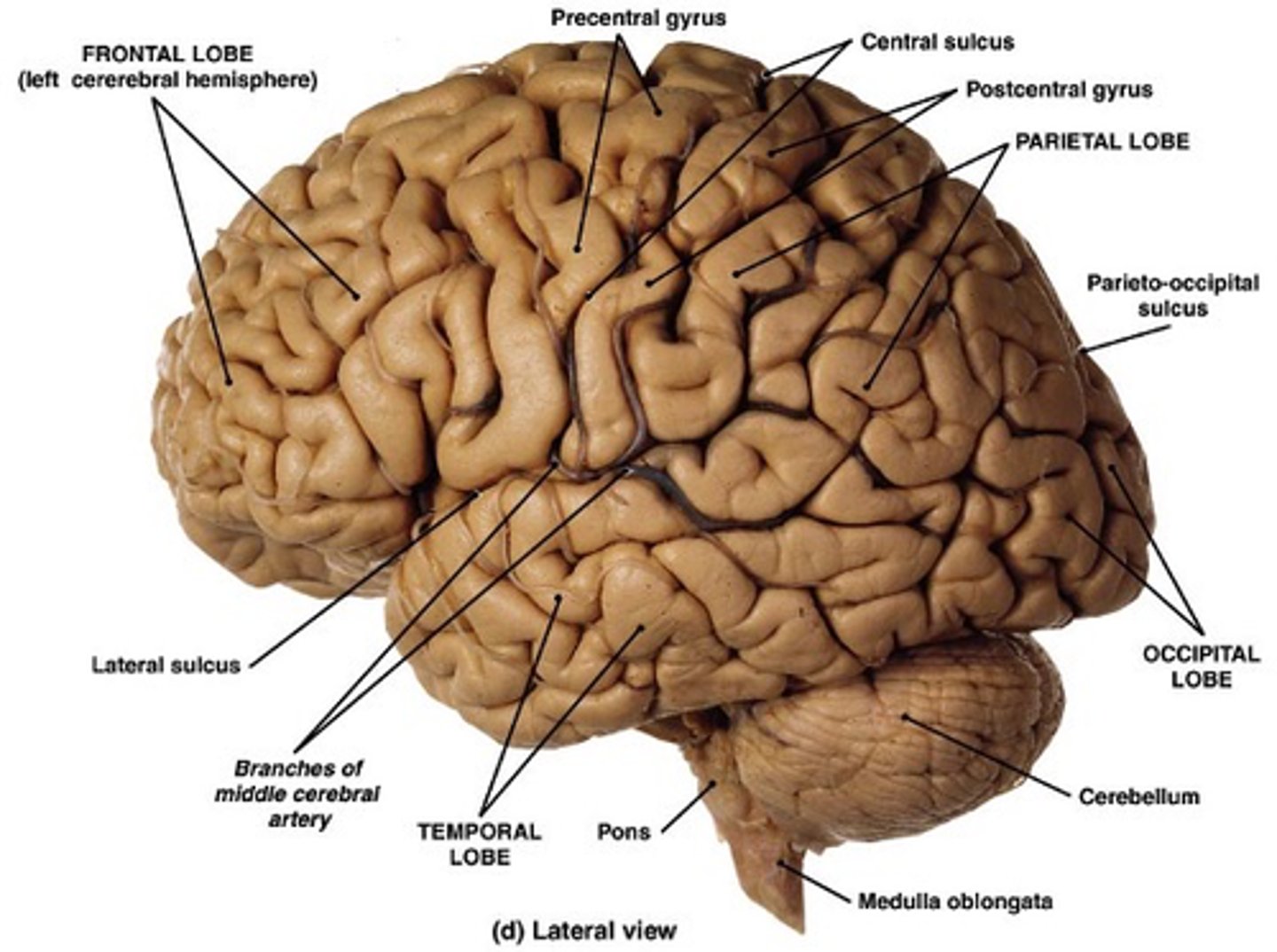
Parieto-occipital sulcus
What separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe?
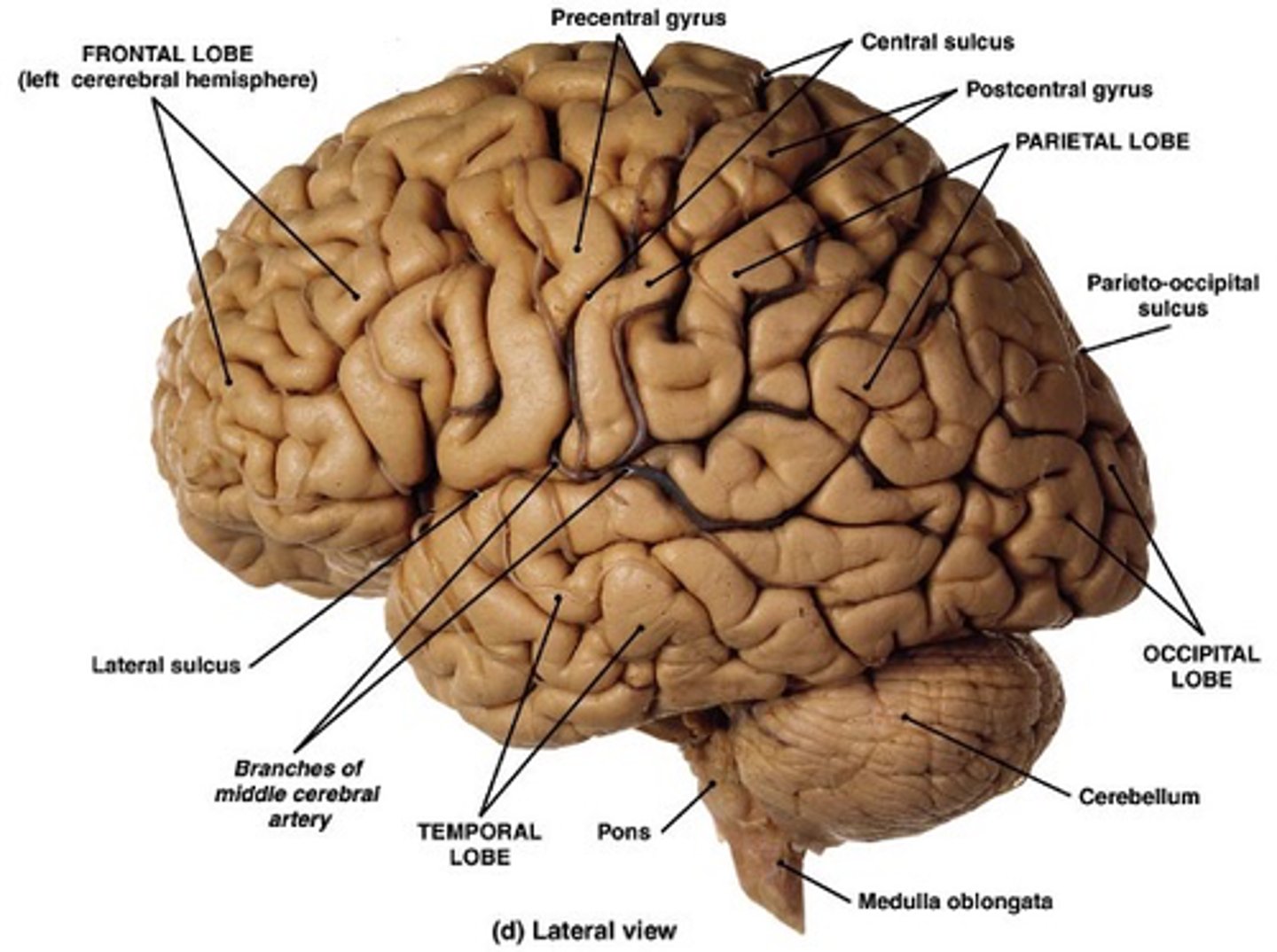
Frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe
What are the names of the 4 lobes?
6
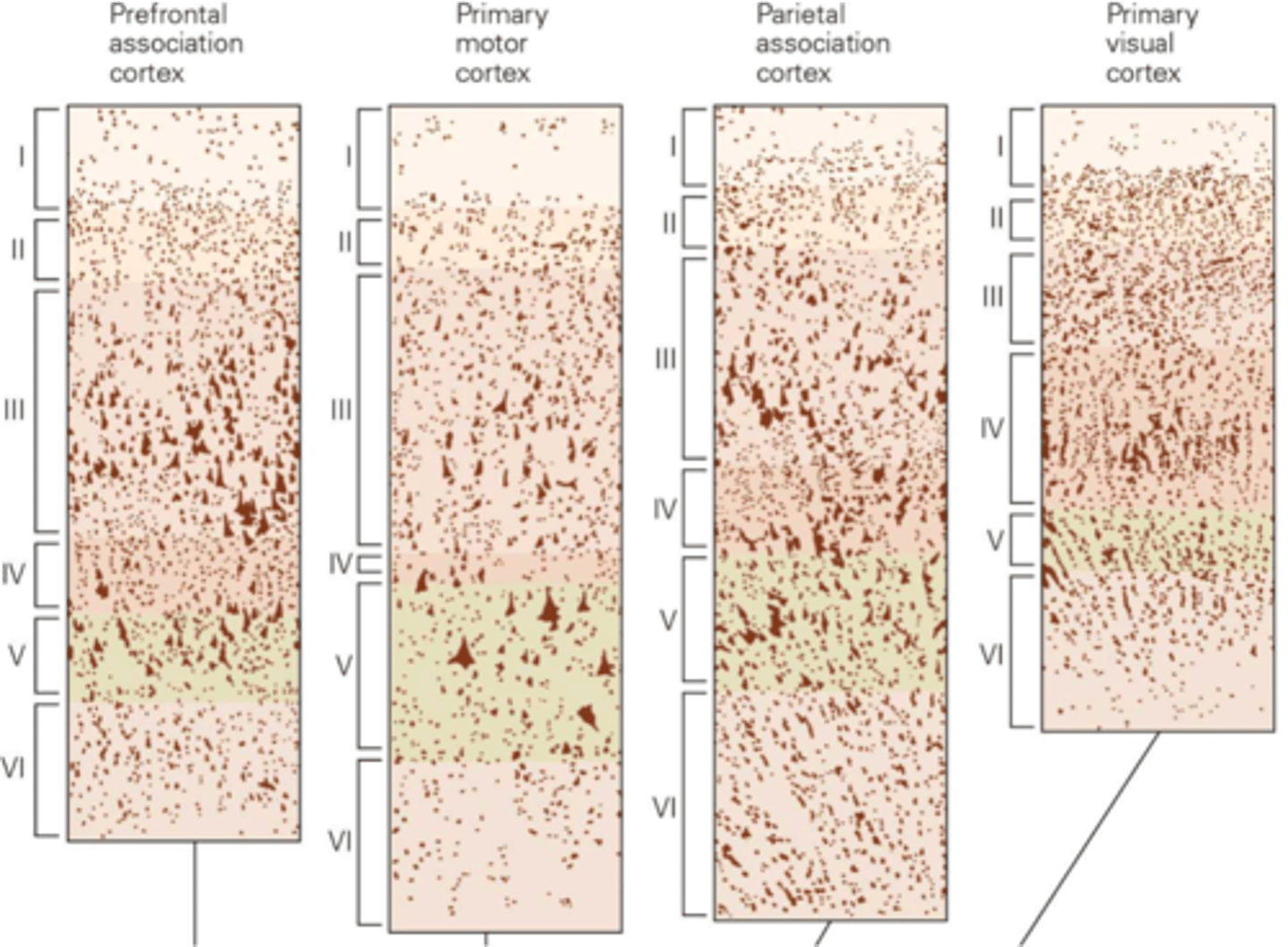
How many layers does the neocortex have?
Differs, regions
The exact structure of the layers ______ between ________ of the neocortex
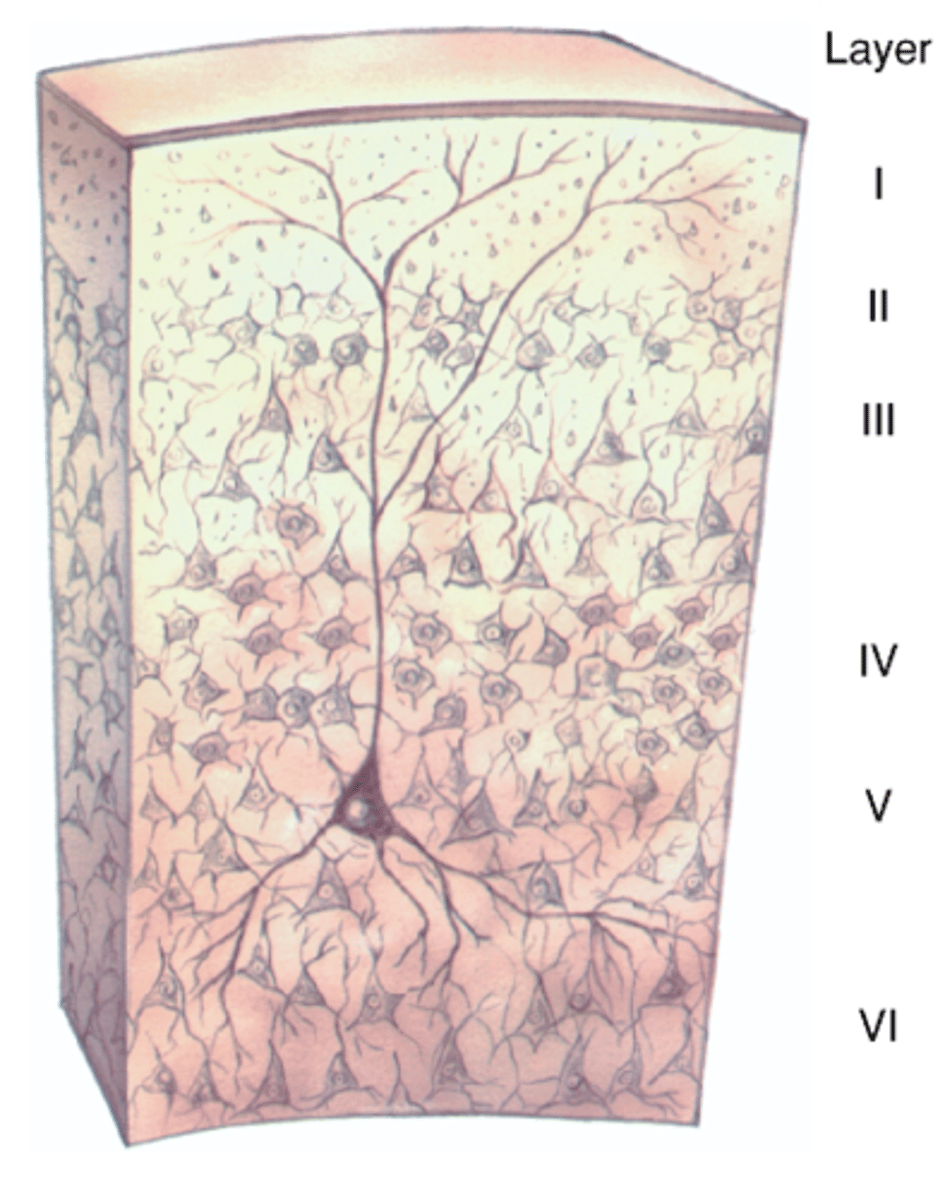
Outermost, cell bodies, dendrites, axons
Molecular layer is ___________ layer nearest Pia mater, it has no ____ ________ but lots of __________ and ________
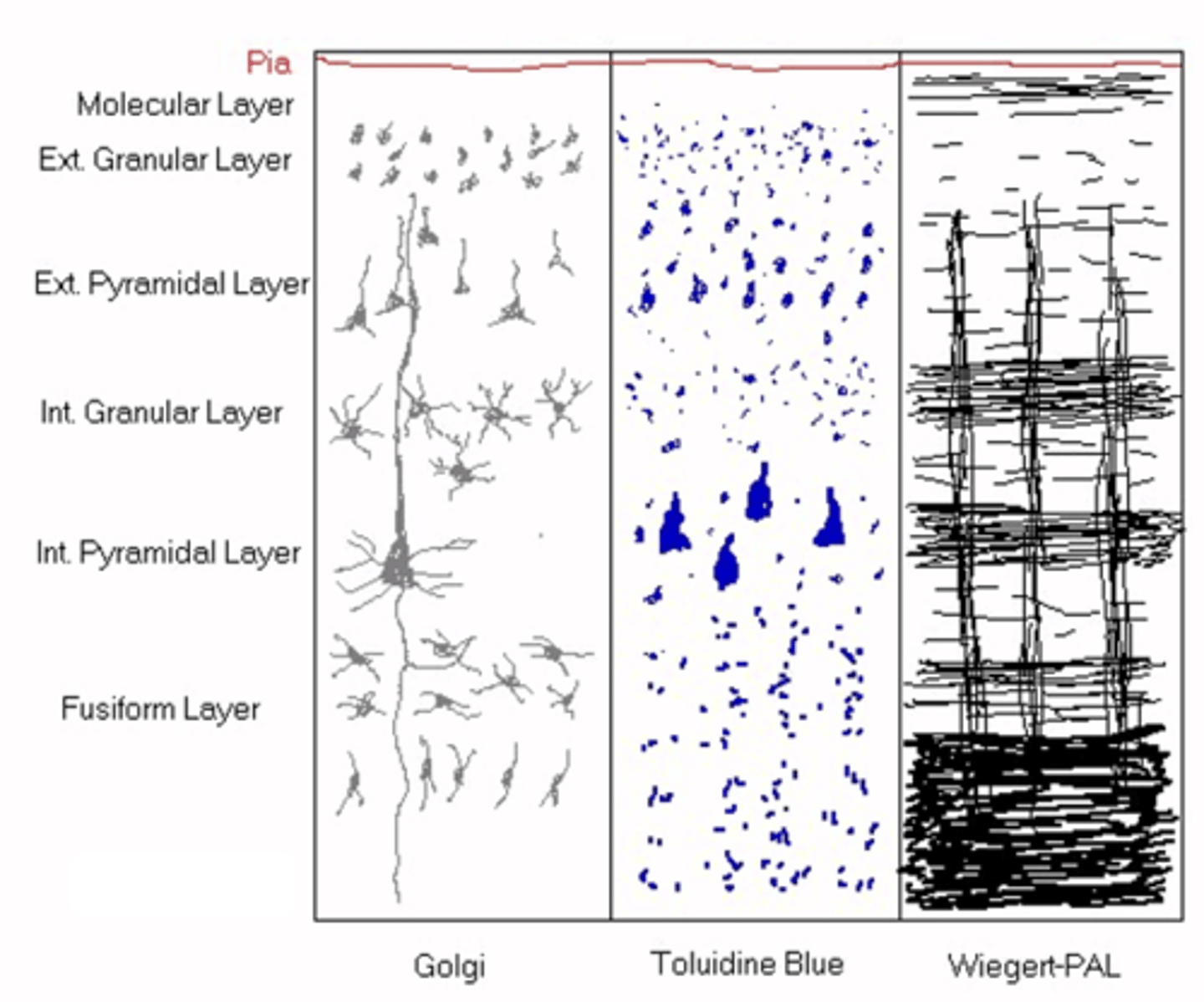
Smaller neurons and granular neurons
What do you get in the external granular layer?
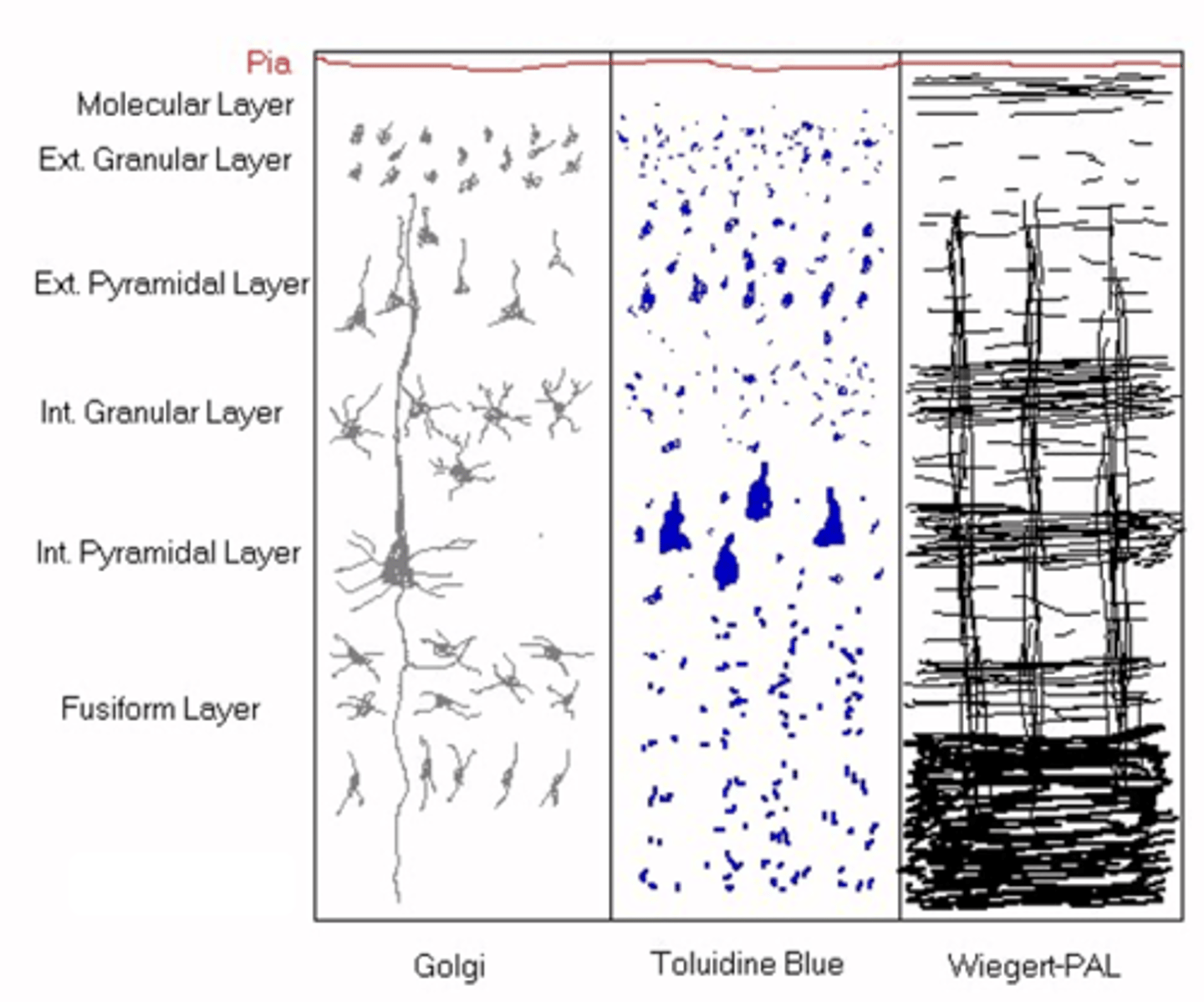
Pyramidal shape to small neurons
What is found in the external pyramidal layer?
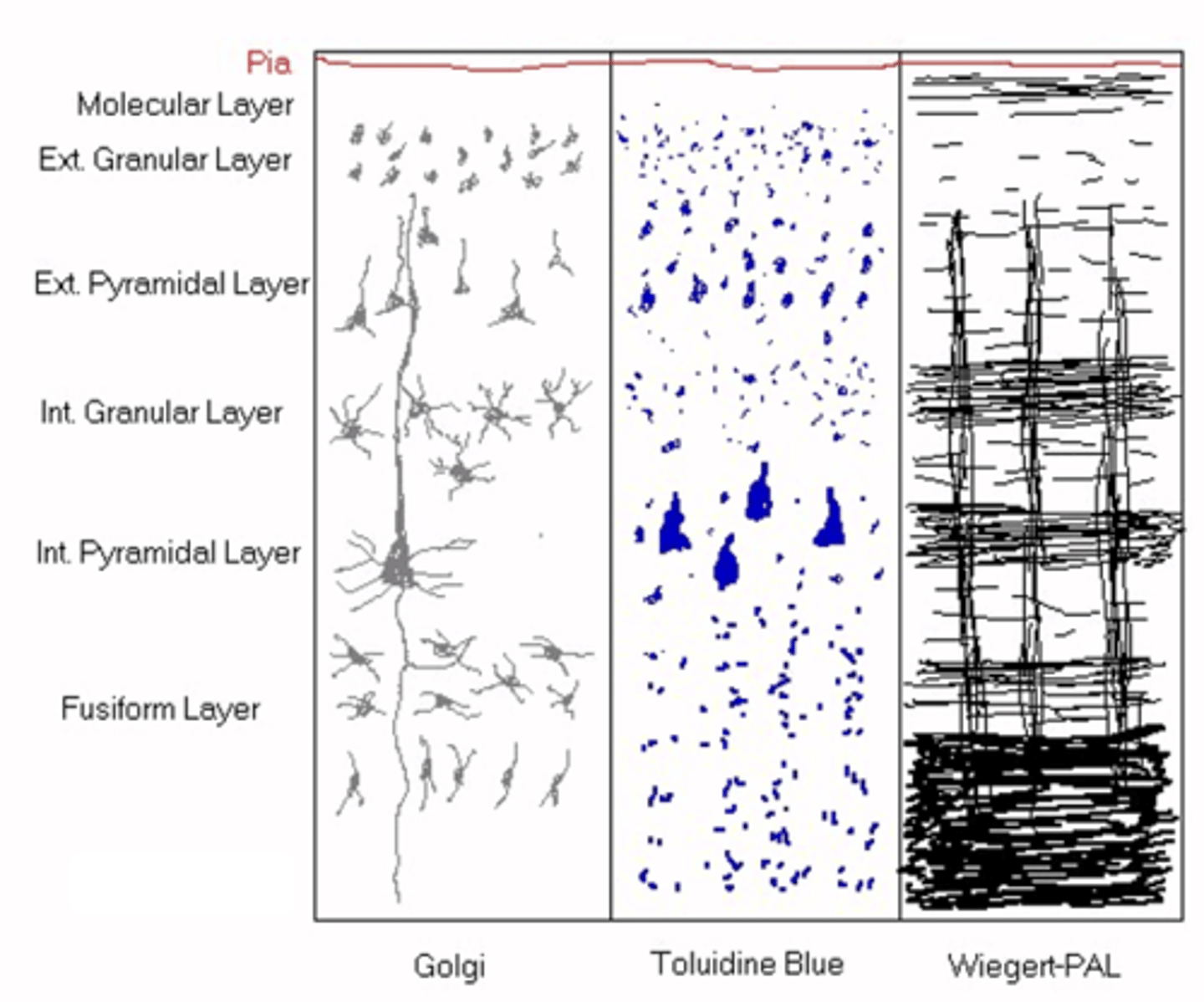
Larger neurons
What do you get in the internal granular layer?
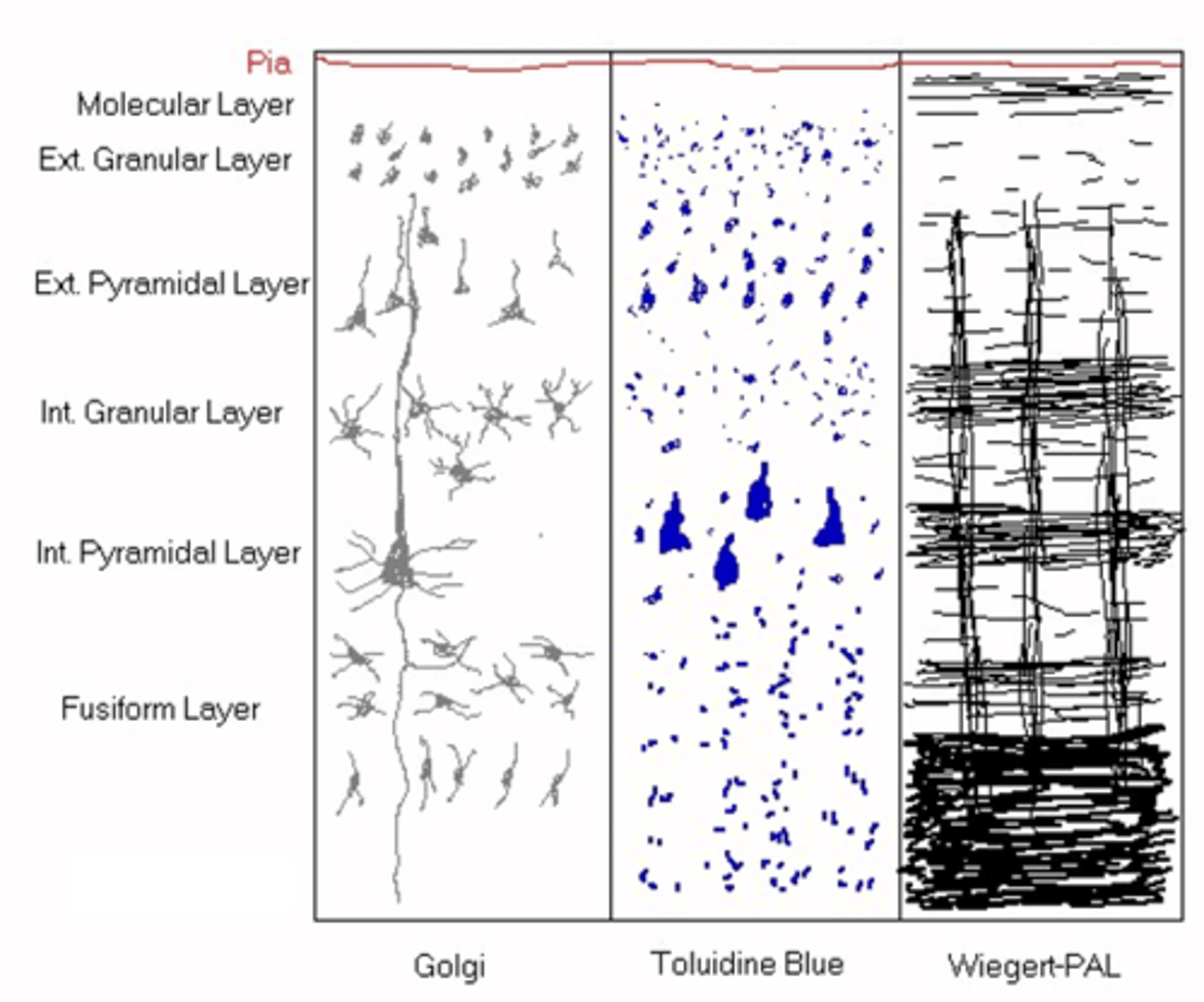
Massive pyramidal bodies
What do you get in the internal pyramidal layer?
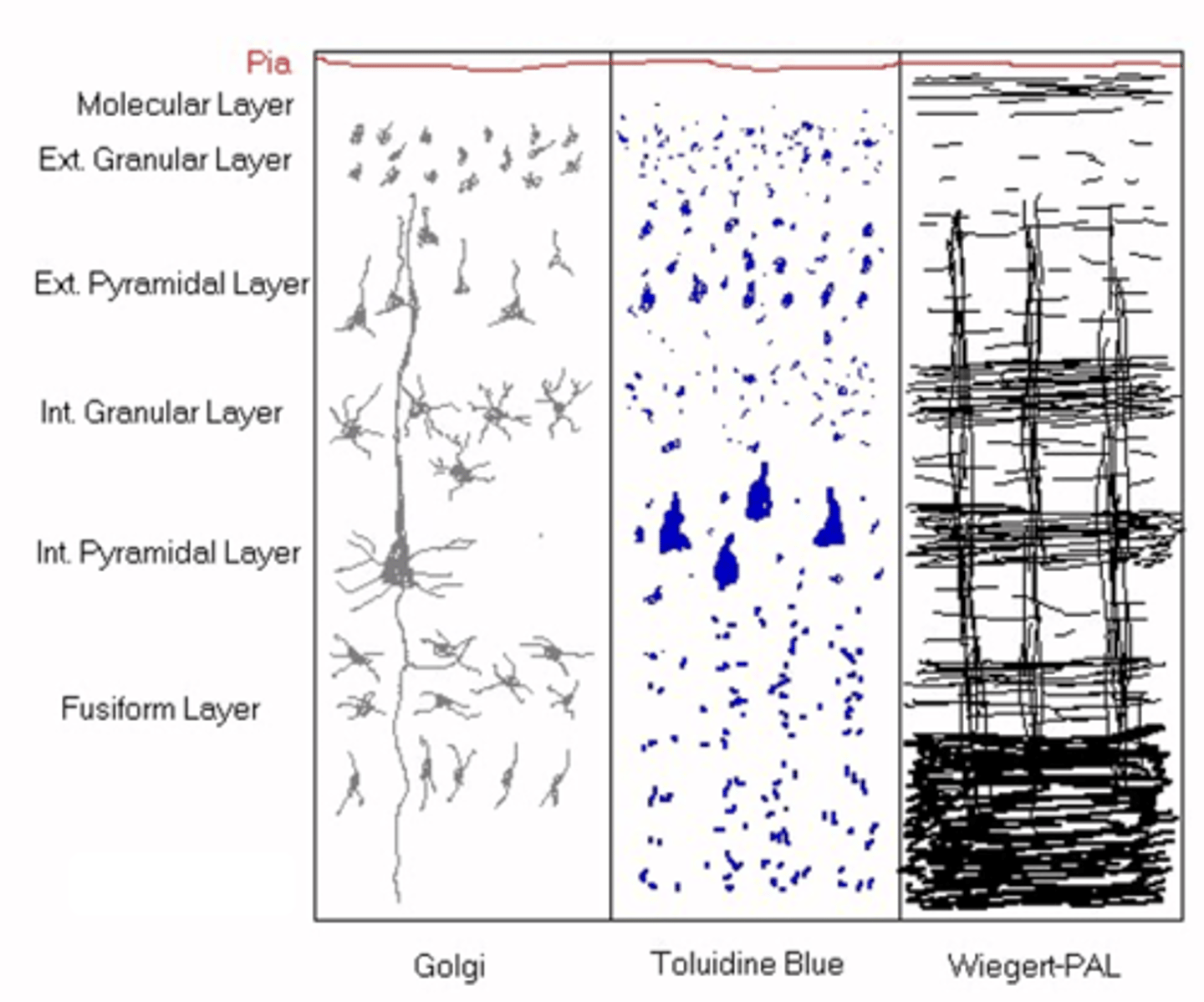
Smaller neurons (don't project their axons outside of the CNS)
What do you get in the fusiform layer?
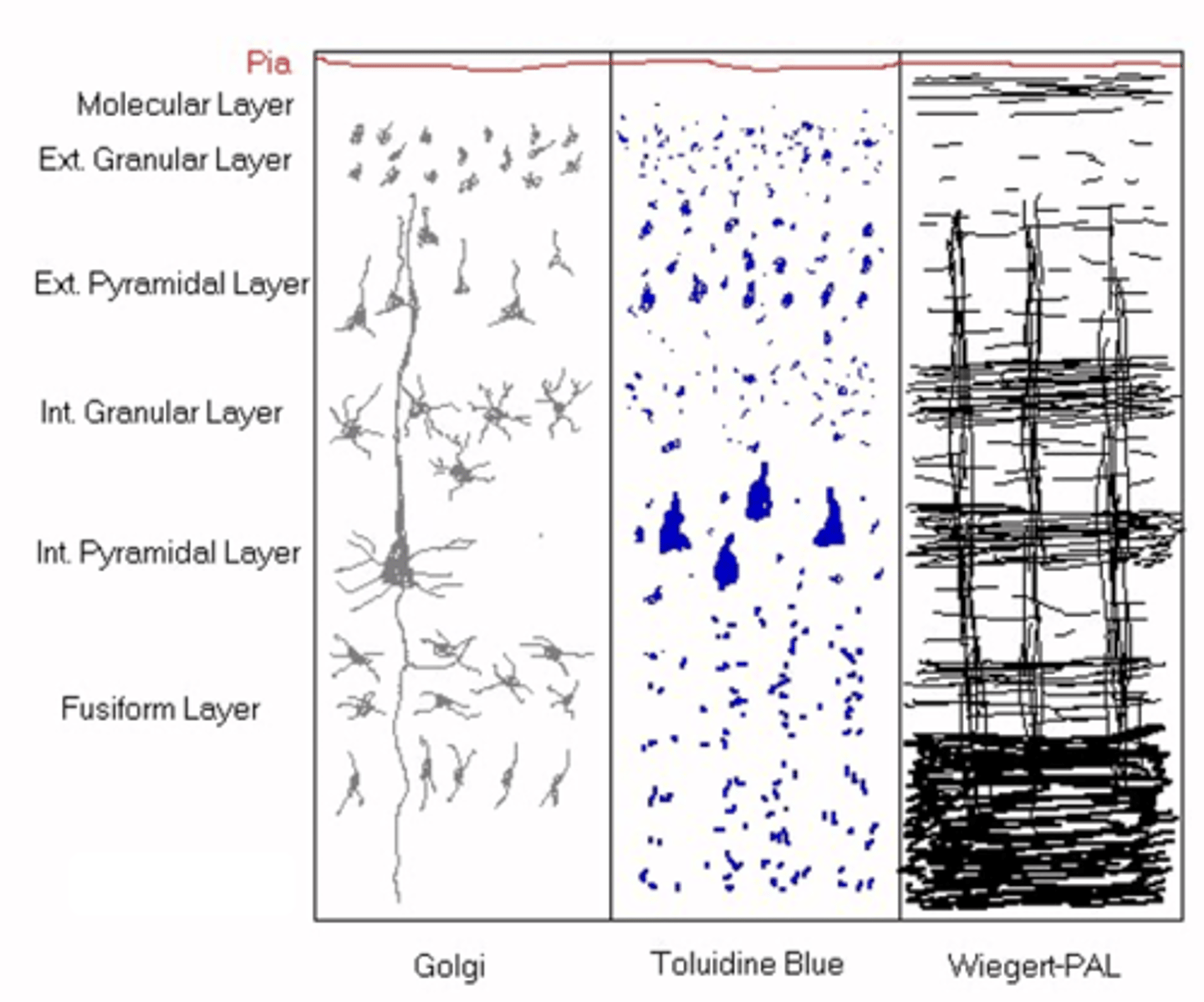
Myelin
What do you think Wiegert-PAL highlights out of the following: neurites, astrocytes, capillaries or myelin?
Cytoarchitecture of the neocortex
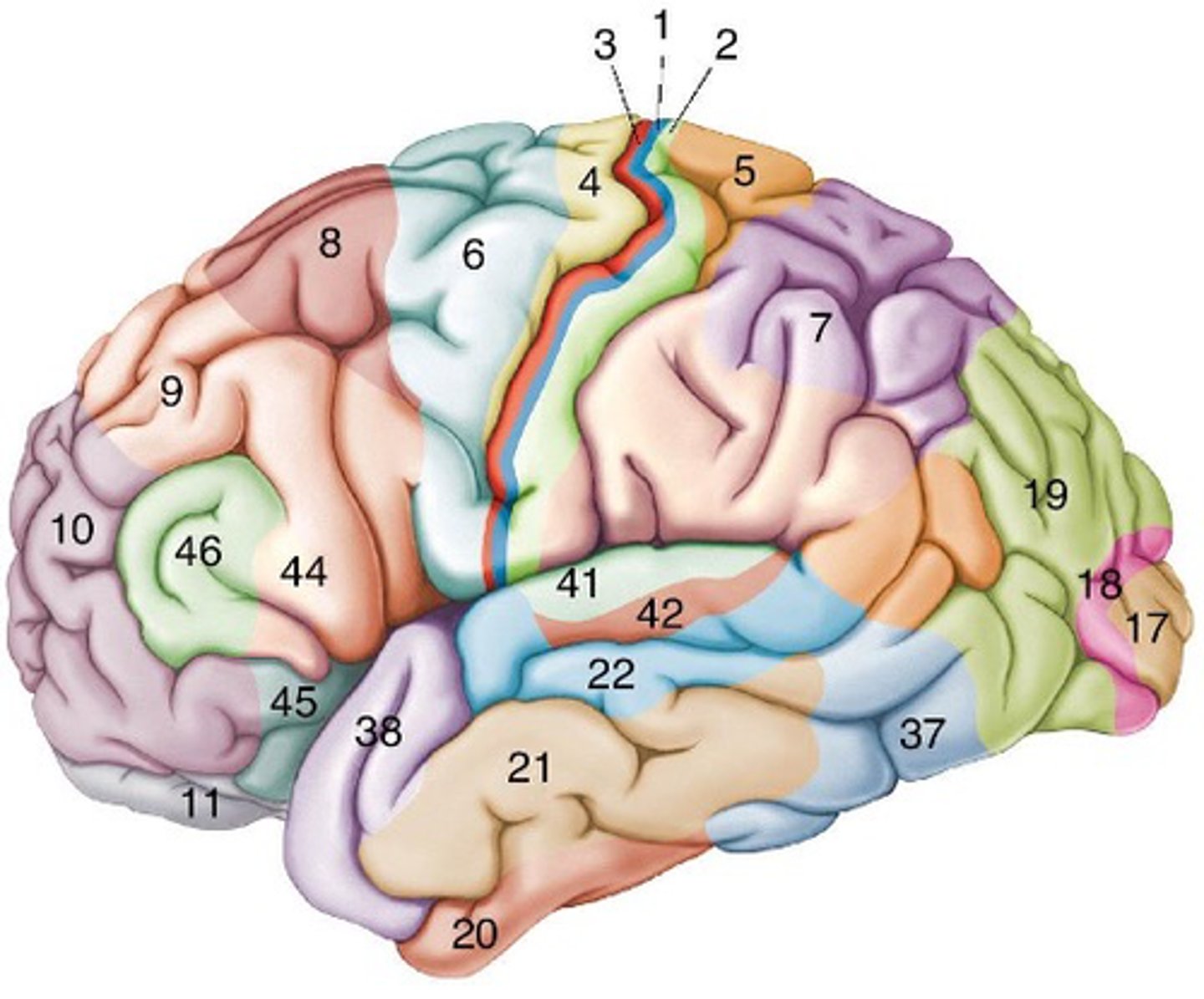
Brodmann's cytoarchitectural map, neocortical
This image shows ___________ _____________________ ___ and every different number has a different ____________ structure
Lesions, stimulation
You can map the neocortex using _______ or direct ______________
Positron Emission Tomography (PET), Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI), Electroencephalography (EEG)
What are the 3 kinds of non-invasive functional imaging you can use to map the cortex?
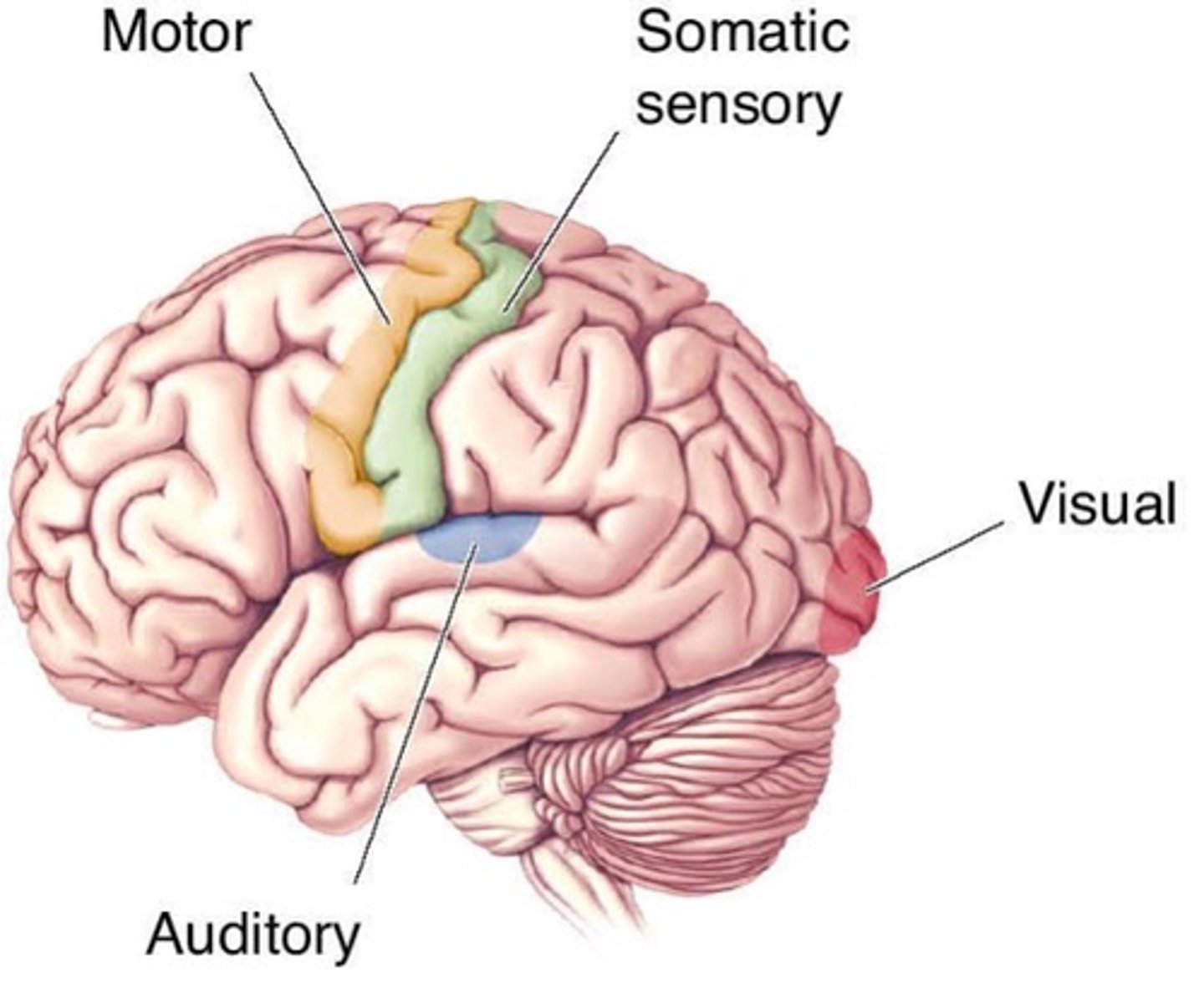
Primary sensory areas, secondary sensory areas, motor areas and association areas/cortex (rest of cortex)
There are 4 kinds of areas in the neocortex (lateral view), what are they?
Emotion, attention and motivation
What is the limbic lobe associated with?
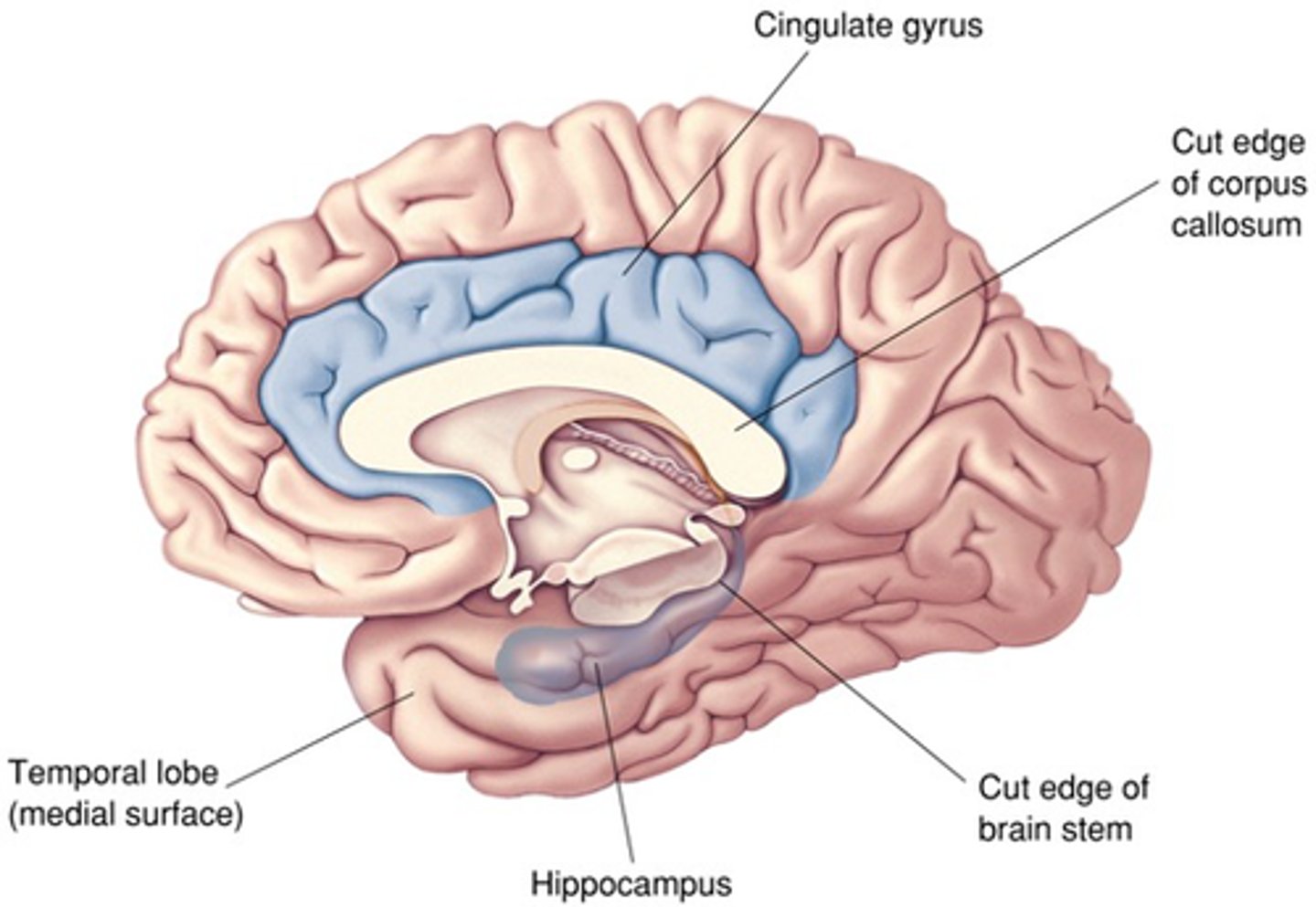
Cortex of cingulate gyrus, cortex on medial aspect of temporal lobe, hippocampus
What is included in the limbic lobe?
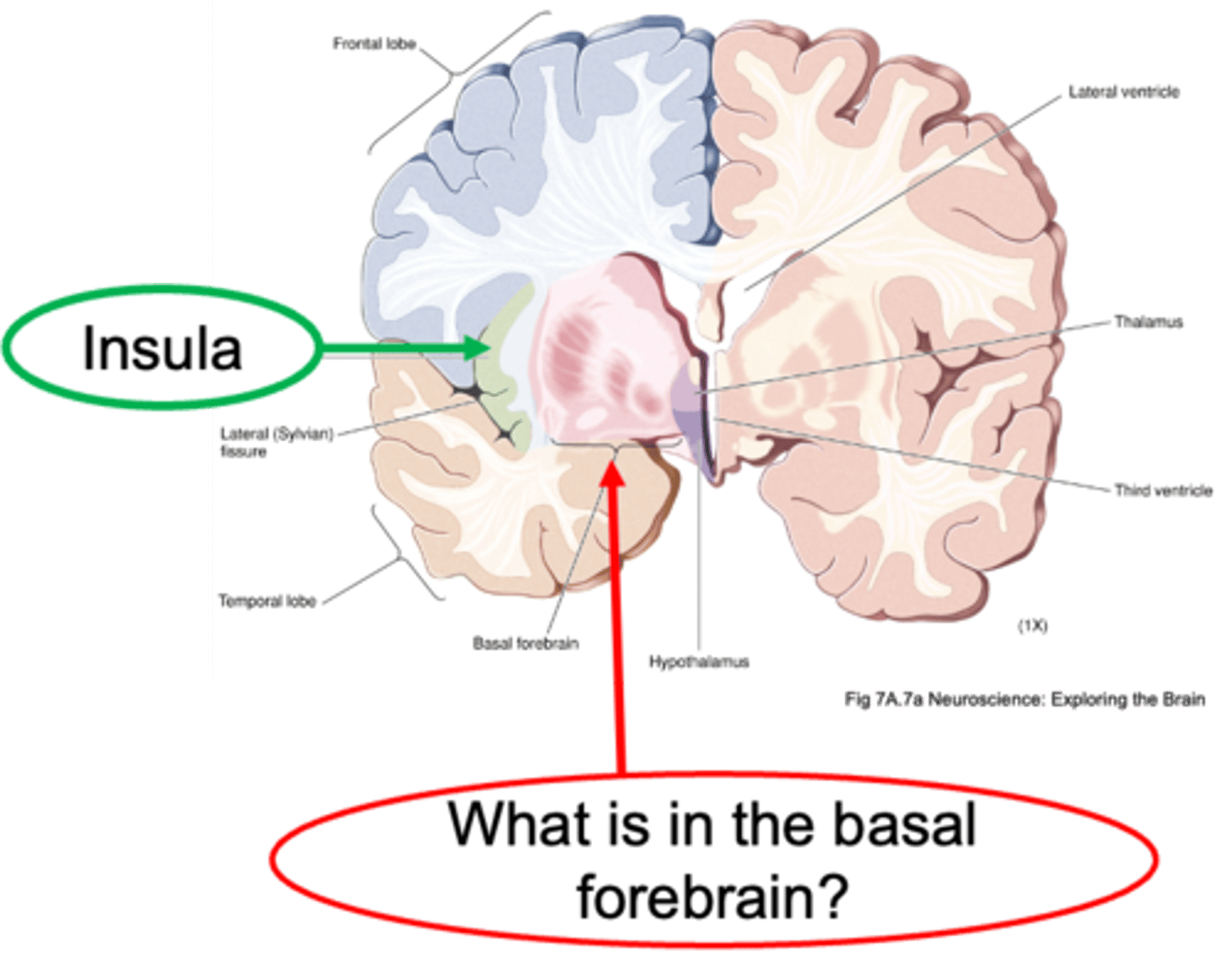
Insula
What is the name of the hidden area of the neocortex?
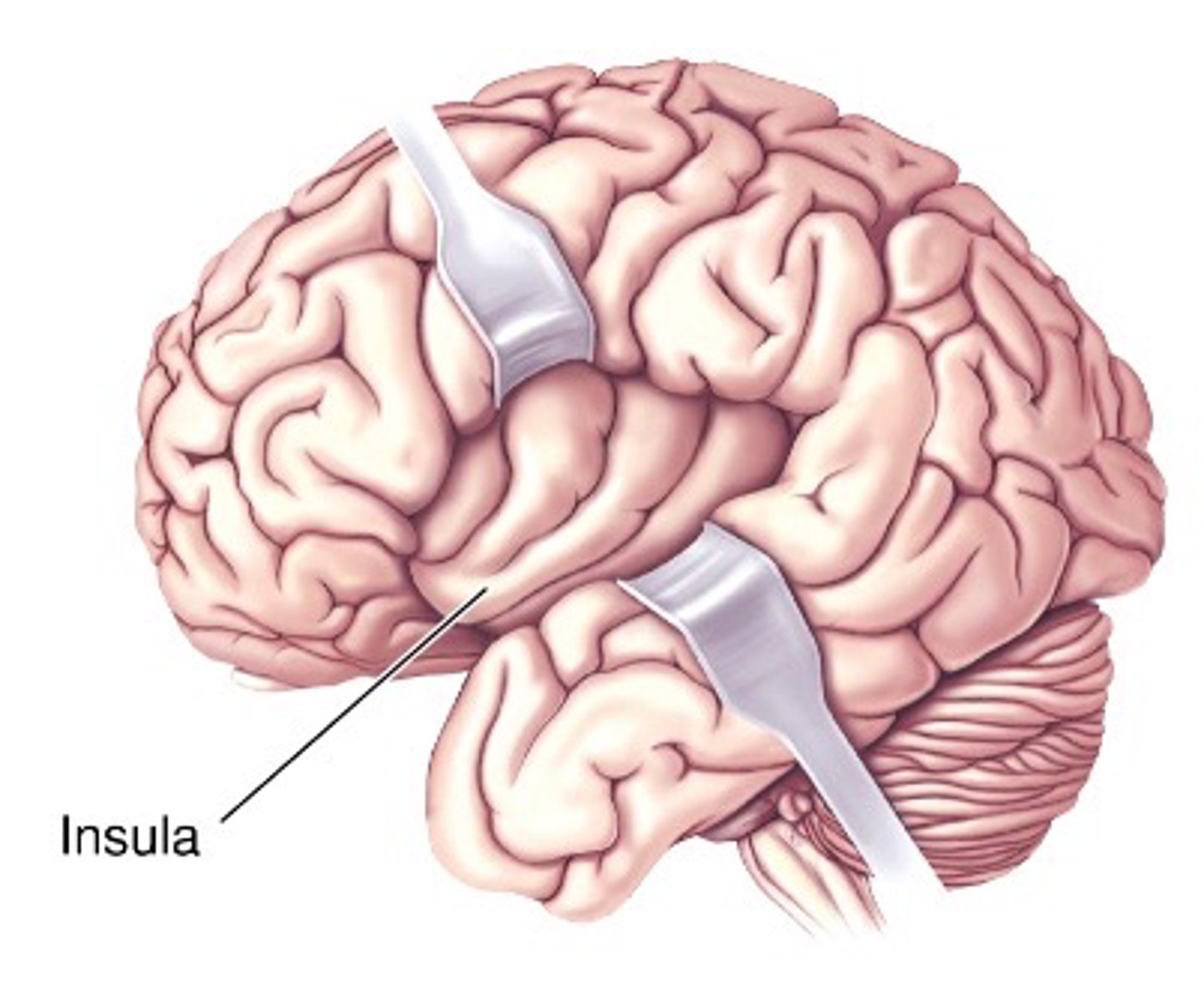
Sensorimotor processing to emotional regulation
What is the insula's functions range?
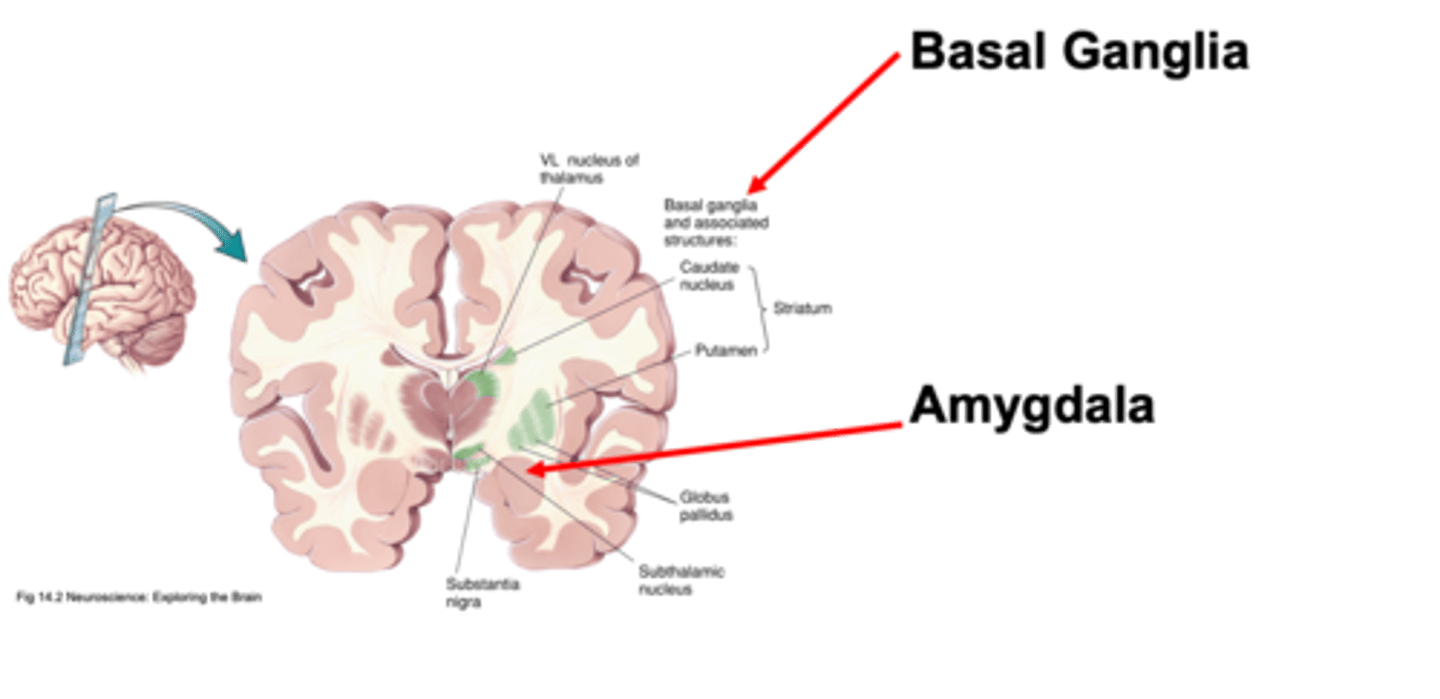
Initiation of movement
What is the basal ganglia involved in?
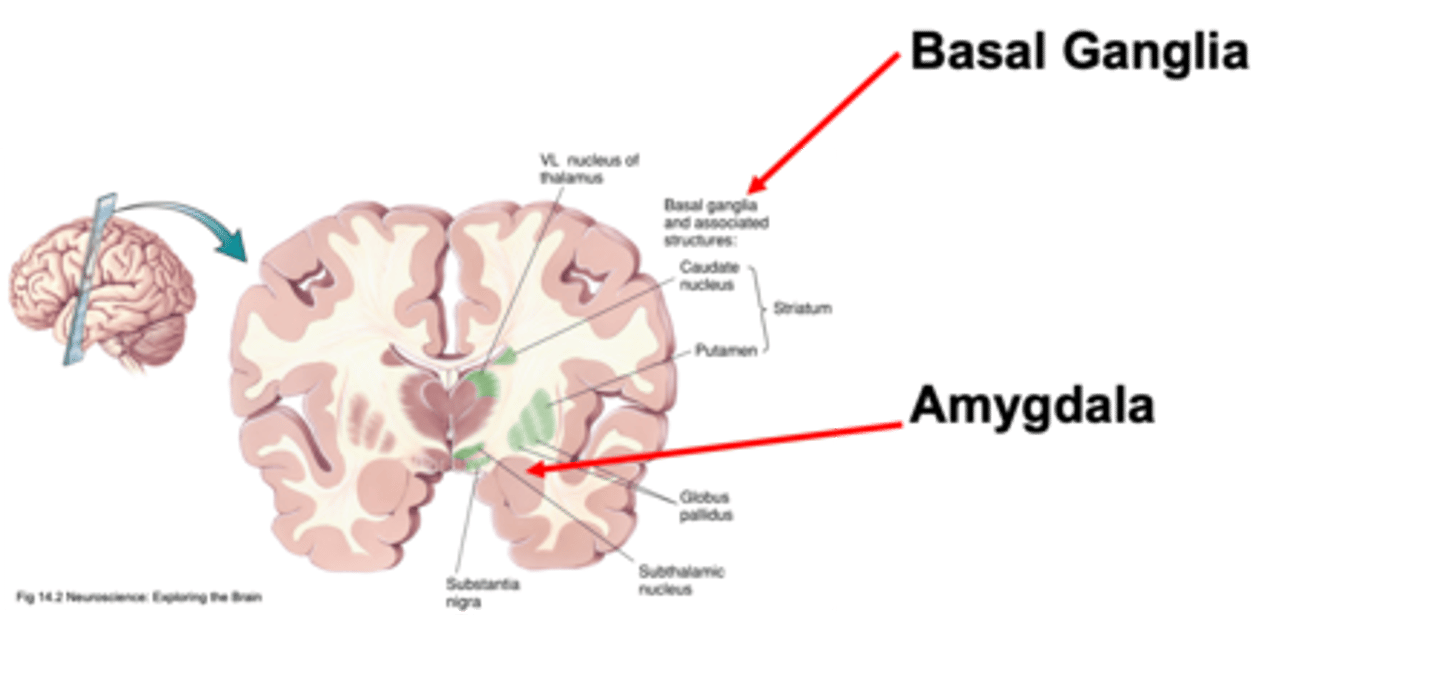
Fear
What is the amygdala involved with?
Connect between hemispheres
What do commissural fibres do in white matter?
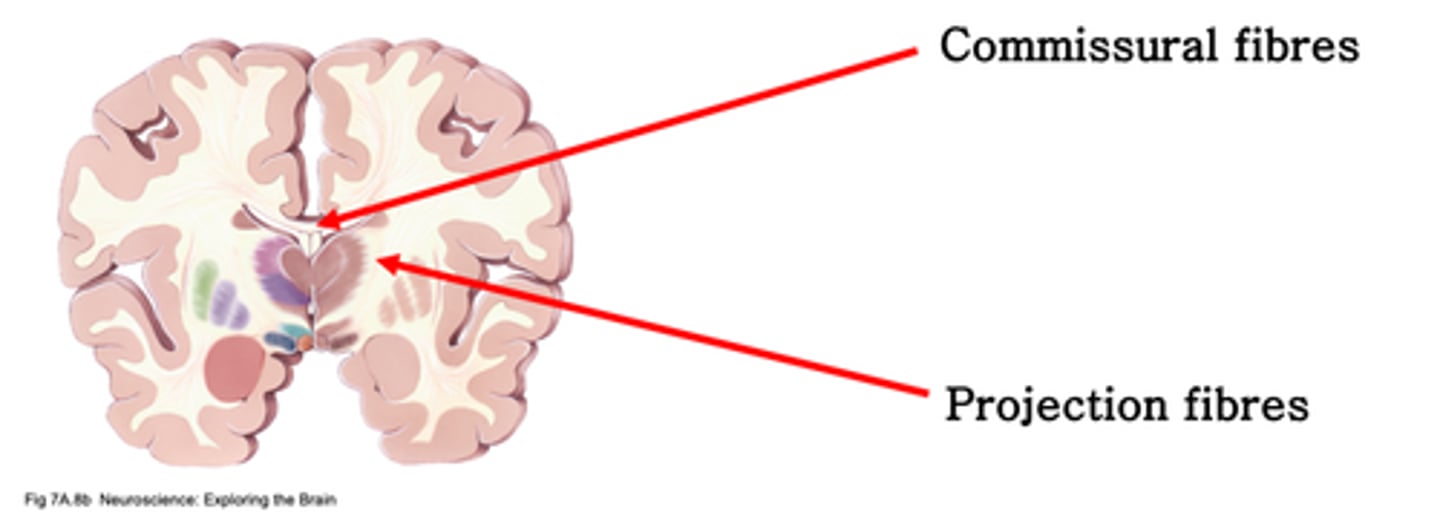
Link to non-cortical areas
What do projection fibres do in white matter?
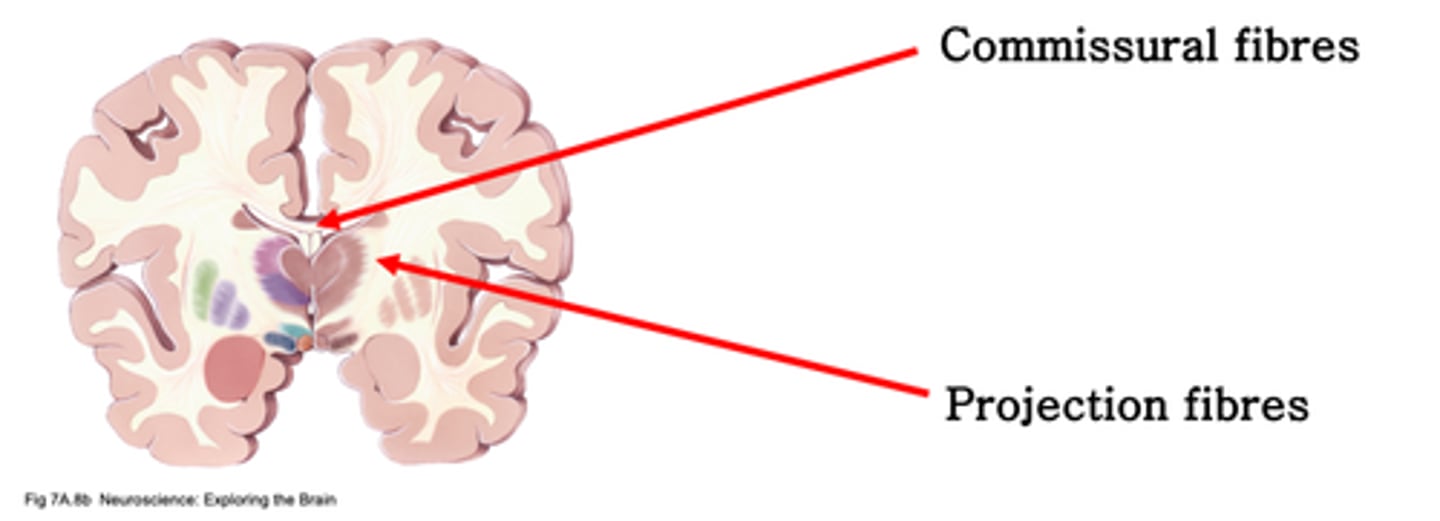
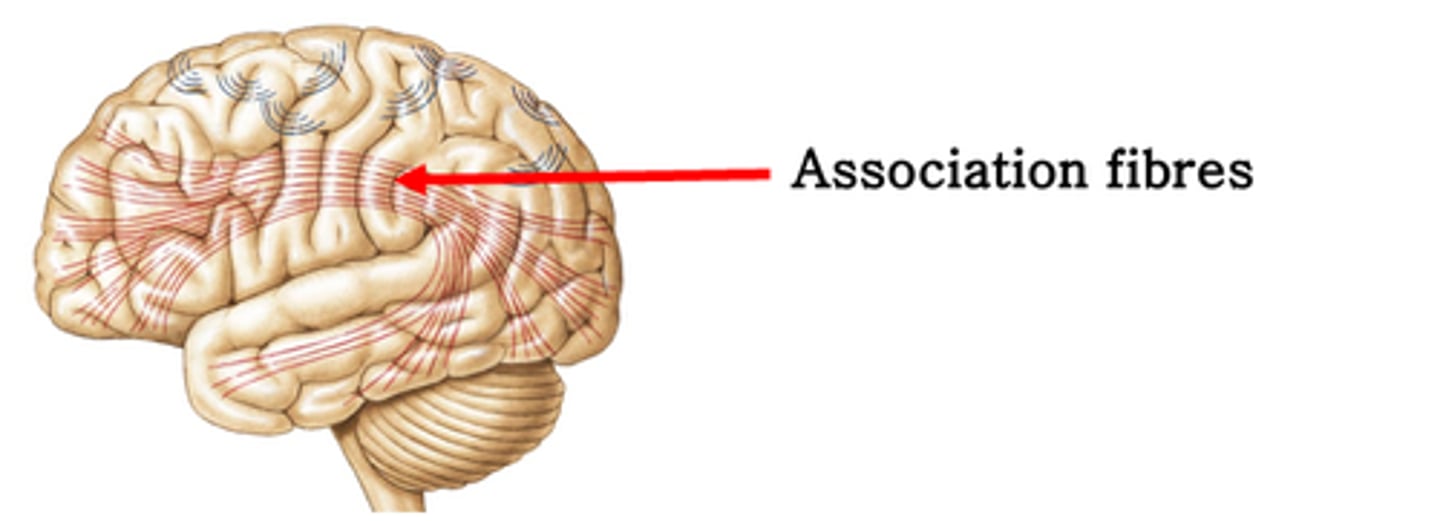
Link areas within a hemisphere
What do association fibres do in white matter?
Corpus callosum
Which of the following is an example of a structure through which a large amount of commissural fibres project: internal capsule, hypothalamus, corpus callosum or lateral ventricle?
Diencephalon
The thalamus is part of the ...?
50
The thalamus has over __ nuclei
A relay station
What does the thalamus act as? (not its only purpose)
Movement
The thalamus is also an important step in the initiation of ______________
Neocortex, projection
The thalamus connects to the __________ via ______________ fibres
11
The hypothalamus has __ major nuclei
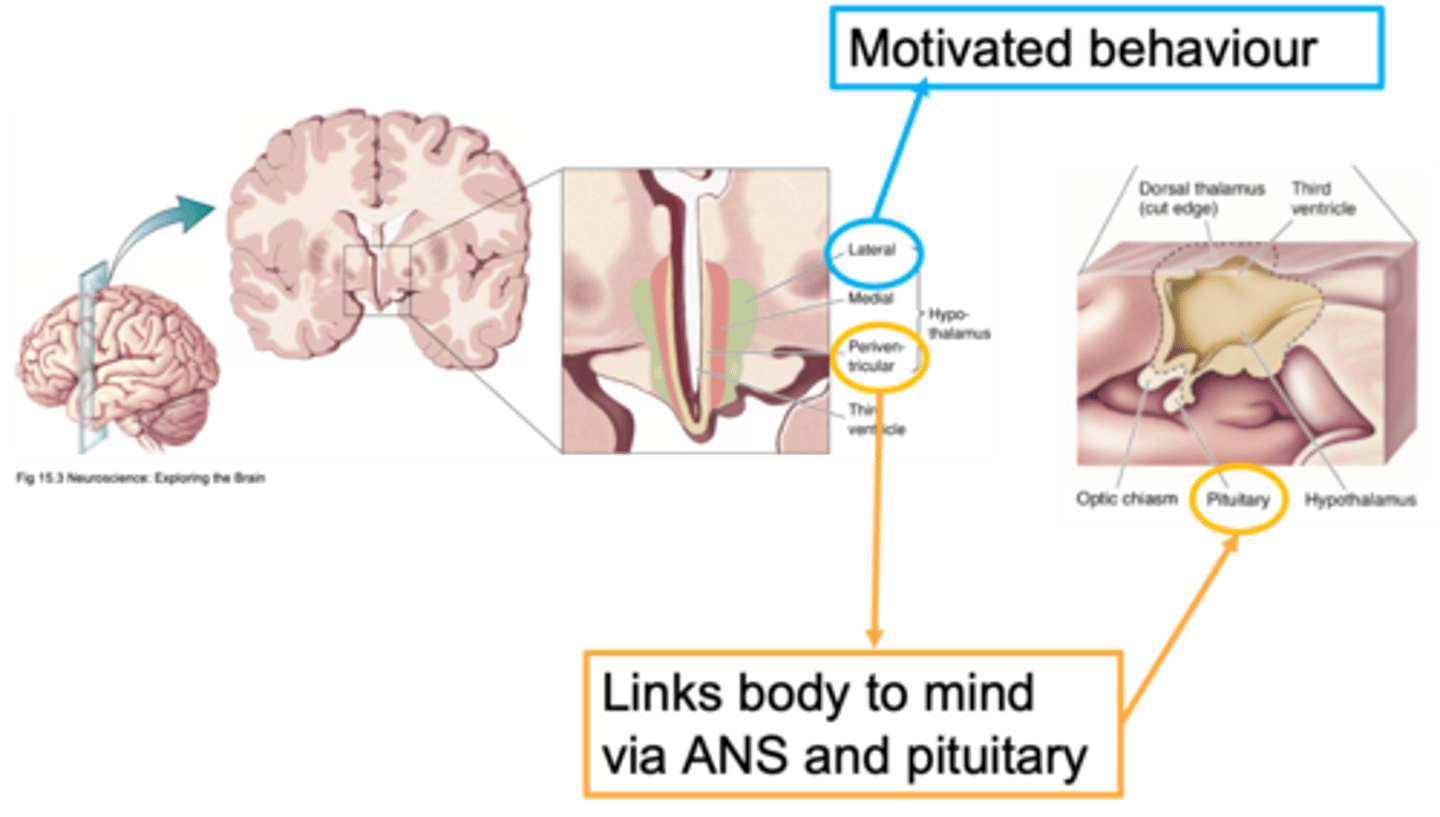
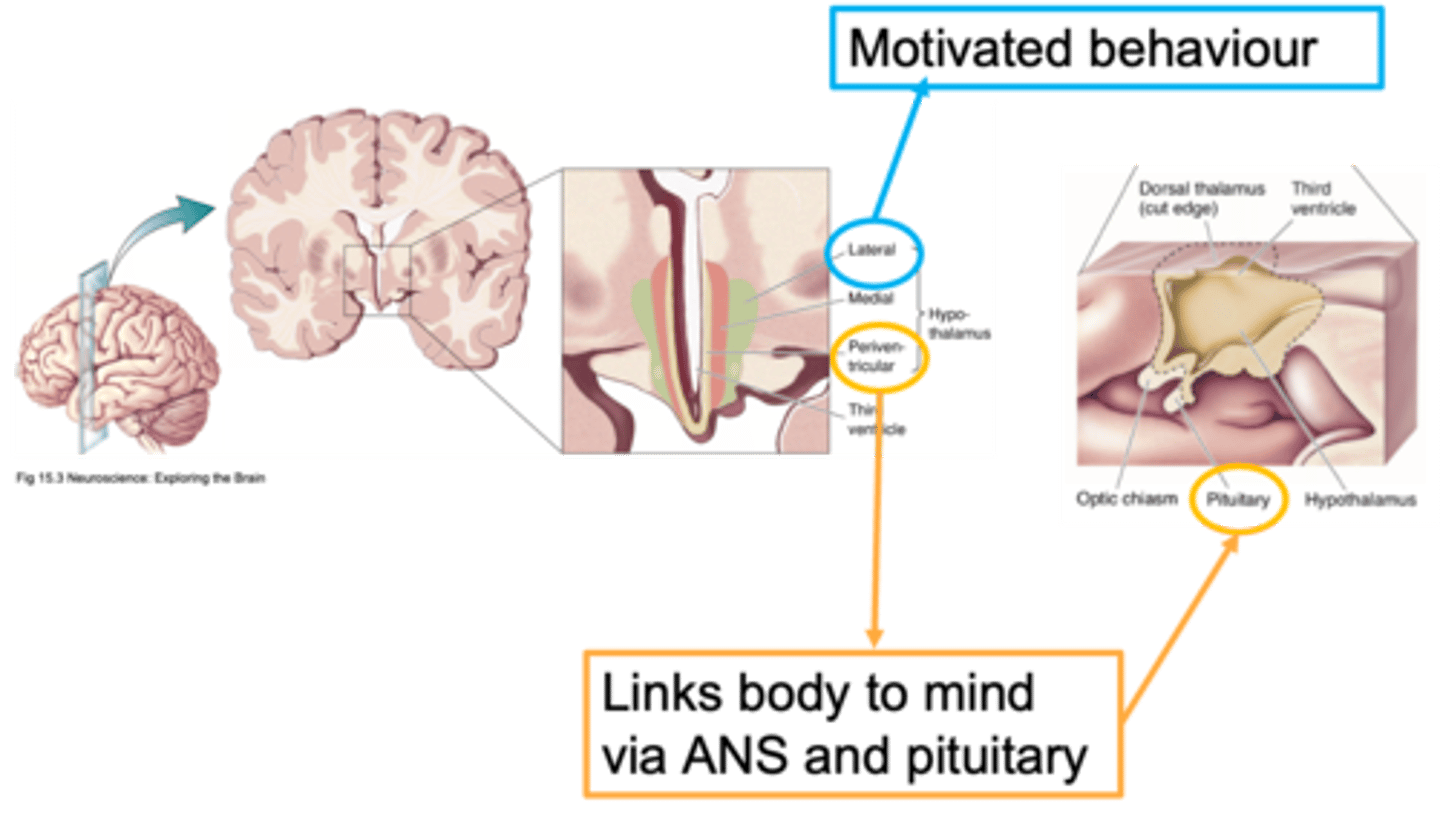
Homeostasis
The hypothalamus is massive regulator of ...?