Genomics and Quantitative genetics
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SL22019
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What was the first whole organism to be sequenced
The bacteria Haemophilus influenzae (1995)
are changes in phenotype always due to changes in sequence?
not all changes in sequence causes changes in proteins
example is sickle cell anemia which is caused bu a single base pair point mutation in the b-globin gene
do synonymous mutation have no effect?
many studies suggest that non synonymous mutations can have no effect
can changes in a phenotype occur w out changes in sequence
yes
the position of a gene in a chromosome effect recombination and expression. potentially affecting its evolutionary rate
recent work suggests that chromosomes also have a specific neighbourhood and changes in this pattern can affect phenotypes.
when was the hunome genome project launched and how much did it cost
1990
3 billion dollars
how many base pairs in human genome
3 billion
strategy for sequencing the human genome
divide the task into smaller pieces: clone large pieces w known order and sequence them independently
identify genetic markers as landmarks
digest DNA into 300KB size
clone fragments, identify and order clones necessary to reconstruct
(when the human genome started there weren’t many genome markers)
genetic markers
DNA sequencd w a known physical location on a chromosome
location can be absolute, or relative to another marker
when there is a variation on that sequence it is a useful landmark for an allele
when the project started there was only 393 RFLP markers not sufficient to seq the human genome
celera and HGP
graig venters
1998joined w HGP
90% of human genome in 2001
150,000 gaps
“complete” human seq
2003
muhc improved and only 400 gaps
reduced number of coding genes to 2400
92% of genome
main outcome of HGP
the consortium model for tackling large projects
a reference genome that allows the identification of genetic variation in humans
technological changes have been truly revolutionary unleashing the power of genomics
finally complete human genome
2022
gapless - telomere to telomere
introduces nearly 200 million base pairs of seq containing 1956 gene predictions 99 are predicted to be protein coding
heritability and regression
galton : resemblance of offspring and parents can be measured by regression
quantitative vs mendelian variation
mendel described particulate inheritance (law of segregation and law of independent assortment)
focuses on qualitative traits (classify henotypes into discrete classes)
in modern genetics these are typically (genes of major effect, loss of function (KO) mutants)
molecular variation underlies trait variation
genetically based trait variation reflects effects of DNA sequence variation (link genotype to phenotype by measuring up effects of loci to add up and predict)
non genetic variation = the remainder
but inherited trait variation can arise from epigenetic effects
R.A Fisher
-1928
reconciled mendelian inheritance w biometrics (continuous inheritance)
quantitative traits ar epolygenic - each affected by many genes of small effect
showed that all previous results in biometrics were compatible w mendelian inheritance
developed the infinitesmal model (can approx inheritance and evolution using a model w an infinte no of loci each w an infinitesmillay small effect
heritability and regression
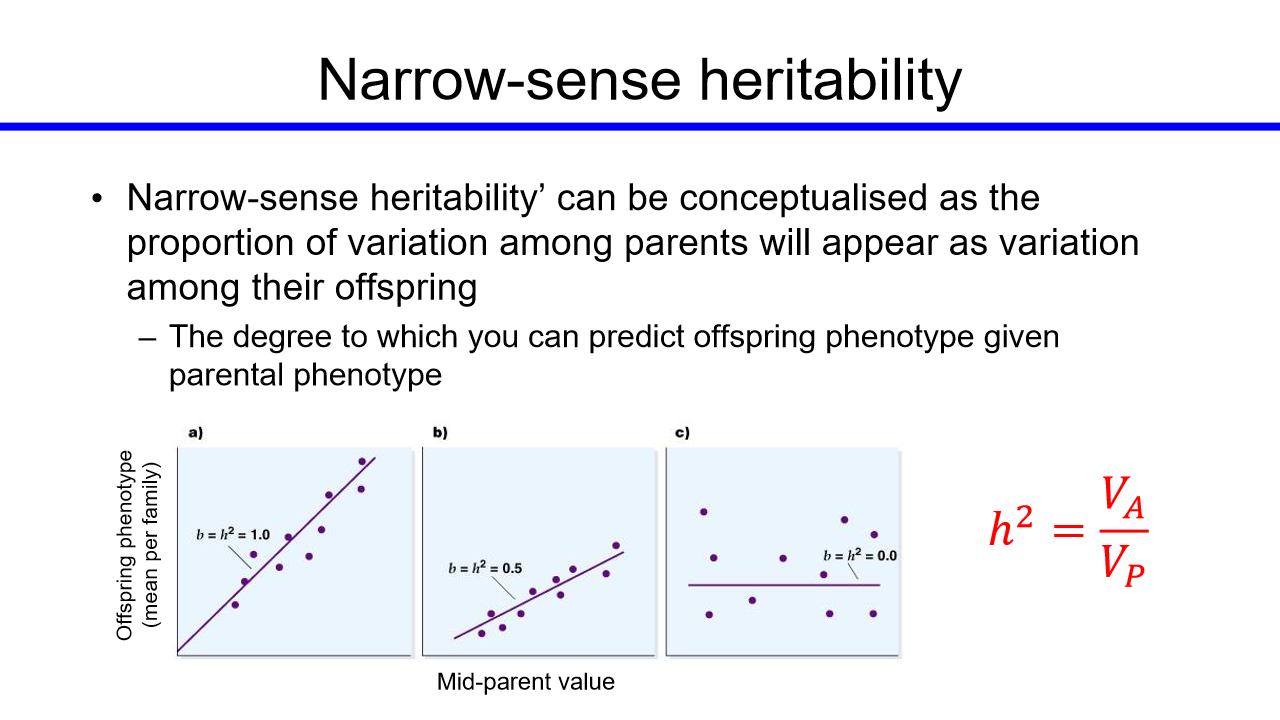
fisher denomstrated that the slope of the regression line (offspring on mid parent) provides an estimate of the proportiion of variation that is additive genetic (heritable)
narrow sense heritability
can be conceptualised as the porportion of variation among parents will appear as variation among their offspring
continuous distributions
a trait affected by alleles at some arbitraty number of loci where
each locus has 2 alleles w similar freqs and genotype freqs are in Hardy Weinberg proportions
the alleles are codominant (additive)
a locus w an additive effect
codominance