reproduction
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
when does mitosis and meiosis take place?
mitosis = grow, repair tissue
meiosis = to make gametes
during mitosis and meiosis, how do the resulting cells differ from the parent cell?
mitosis = genetically identical to parent cell
meiosis = genetically varied
during mitosis and meiosis, how many cells are produced from each parent cell?
mitosis = 2
meiosis = 4
during mitosis and meiosis, how many times does the parent cell divide?
mitosis = 1
meiosis = 2
after mitosis and meiosis, how many chromosomes are present in each daughter cell?
mitosis = 46 chromosomes (diploid)
meiosis = 23 chromosomes (haploid)
after mitosis and meiosis, how many pairs of chromosomes are present in each daughter cell?
mitosis = 23 pairs
meiosis = no pairs, chromosomes are unpaired
what are the 4 hormones and where are they released from in the menstrual cycle? (FOLP + POPO)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) = Pituitary Gland (brain)
Oestrogen = Ovary
Luteinising hormone (LH) = Pituitary Gland (brain)
Progesterone = Ovary
what is the function of the follicle stimulating hormone?
matures egg
what is the function of the oestrogen hormone?
builds up uterus lining
what is the function of the luteinising hormone?
stimulates ovulation
what is the function of the progesterone hormone?
keep lining maintained if pregnant
how long does the menstrual cycle last for?
28 days
what happens between 0-4 days of the menstrual cycle?
menstruation
what happens on day 14 of the menstrual cycle?
ovulation = egg released
what happens on day 28 of the menstrual cycle?
process restarts, lining sheds - if pregnant, lining is maintained
name all the charcateristics of asexual reproduction
doesn’t require gametes
no fertilisation
one parent cell required
genetically identical (clones produced)
name all the characteristics of sexual reproduction
requires gametes
fertilisation
usually 2 parents
offspring genetically different
define pollination
transfer of pollen, anther to stigma
name the characteristics of insect pollinated flowers
brightly coloured large petals
nectaries
small enclosed stamens and carpels
sticky stigma
name the characteristics of wind pollinated flowers
reduced/no petals
no nectaries
larger exposed stamens and carpels
feathery stigma
what are the conditions required for germination? (WOW)
Water
Oxygen
Warmth
why is water a condition required for germination?
to activate enzymes and processes in the seed
why is oxygen a condition required for germination?
the seed can do aerobic respiration, release energy to be able to grow
why is warmth a condition required for germination?
kinetic energy, for optimum enzyme activity in respiration
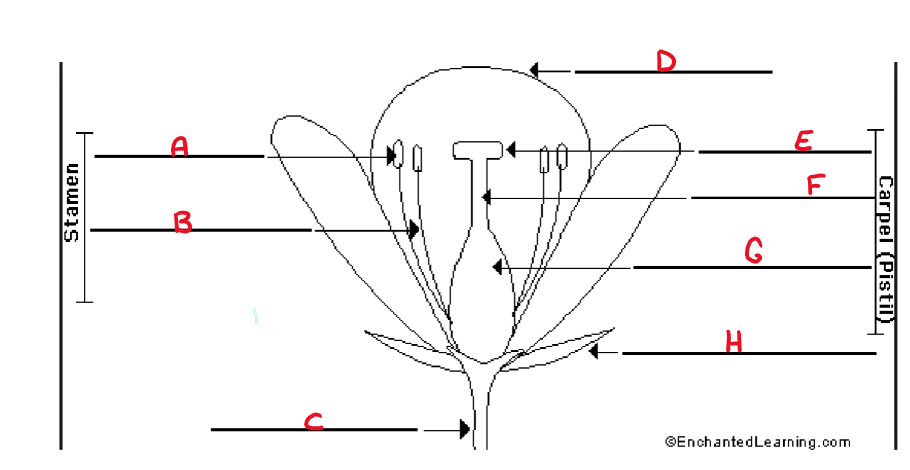
label the diagram
A = anther
B = filament
C = stem
D = petal
E = stigma
F = style
G = ovary
H = sepal
what is the difference between the ovary and ovule in plant reproduction?
ovary contains ovules which contains one egg cell each
what is a seed?
a fertilised ovule
how is a fruit formed?
a fruit forms when the ovary swells up after fertilisation
how do plants reproduce? (5 steps)
pollen grain lands on stigma
pollen cells germinate and produce digestive enzymes
a pollen tube is formed down the style and enters into the ovule
pollen and egg nuclei fuse (fertilisation) forming a zygote
the ovary swells and becomes a fruit and ovule becomes the seed coat
what are the adaptations of the placenta?
thin walls - for short diffusion distance
rich blood supply - maintain a large concentration gradient
large surface area - for maximum diffusion
what does the placenta do?
takes away waste products from baby like carbon dioxide and urea
delivers oxygen, glucose, amino acids, water, antibodies
where is sperm made?
testes
where are the eggs in human reproduction made?
ovary
name the stages after fertilisation
fertilisation (nuclei fuse) → zygote → embryo → foetus
what processes happen between the embryo and the foetus?
mitosis + differentiation
what is the cervix?
ring of muscle that holds the baby in place