Geography Paper 1 section C
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
River Processes and Landforms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What does a long profile of a river show?
The long profile of a river illustrates how the gradient of the land changes as the river flows from its source in the mountains to its mouth on the coast.
What does a cross profile show?
The cross profile illustrates how the shape of the valley changes as the river flows downstream.
Describe the upper course of a long profile river?
Steep gradient mostly verticle erosion.
Describe the middle cource of a long profile river?
lateral erosion and deposition
Describe the lower course of a long profile river
Gently gradient mostly deposition
Name three fluvial processes
Erosion and transportation and deposition
What is erosion
Erosion is the wearing away of the river bed and banks. Rivers erode vertically (downwards) and laterally (side to side)
Name the four types of erosion
Hydraulic action, abrasion, solution and attrition
What is hydraulic action?
The force of the water hitting the river banks. Faster flowing water has more hydraulic power.
What is abrasion?
Stones carried by the river scrape away at the river bed and banks
What is solution (erosion process)?
Slightly acidic river water dissolves alkaline rocks like limestone
What is attrition?
Stones within the water knock into each other and become smaller and rounder
Does attrition affect the river bank or bed?
No, it is an erosion process that does not affect the river bank or bed. It affects stones in the water.
4 methods of transporation in a river?
Solution, suspension, traction and saltation
What is solution (transportation process)
Minerals are dissolved in water carried by the river
What is suspension?
Mud and fine particles float in the water and are carried by the river
What is traction?
Heavy boulders are rolled along the river bed.
What is saltation?
Small stones bounce as they are moved by the river.
When does a river deposits the load with examples
A river deposits the load it is carrying when the flow of the water slows down. e.g. when it meets an obstacle, when it meanders (bends), when it meets the sea.
When are interlocking spurs formed?
Interlocking spurs are formed in the upper cource, when a river winds around bands or more resistant rocks.
Describe the formation of a waterfall?
A river meets a band of softer, less resistant rock
The softer, less resistant rock erodes more quickly through abrasion and hydraulic action
A plunge pool is formed and there is undercutting of the hard cap rock
The cap rock collapses and the waterfall retreats upstream, forming a gorge
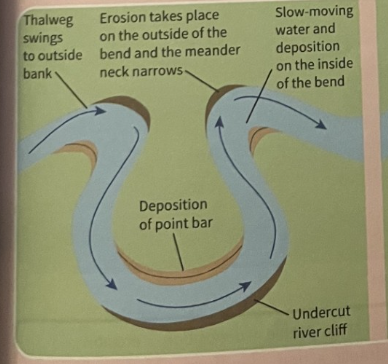
What is a meander and how is it formed?
Meanders are bends in the river. They form when a river moves away from a straight cource because of an obstacle, or shallow and deep sections, in the river channel. More erosion takes place where the water flows faster, and this becomes the outside of a meander. The line of fastest flow is called the thalweg.
Where does deposition take place and what does it form?
Deposition takes place where the water flow is slowest, forming the inside of the meander.
How does a river get bigger over time?
Continued erosion on the outside and deposition on the inside means the bend in the river gets bigger over time.
What are ox-bow lakes and how are they formed?
Ox-bow lakes are horeshoe-shaped lakes. They are formed when a meander is cut off from a river. This is because erosion takes place on the outside of a meander.
How do meanders exaggerate over time?
Thalweg swings to outside bank
deposition of point bar
Undercut river cliff
Erosion takes place on the outside of the bend and the meander neck narrows
Slow-moving water and deposition on the inside of the bend