Understanding Management: Roles, Skills, and Challenges: CH1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Exceptional Manager
A manager who effectively integrates the work of people to achieve organizational goals.
Organization
A group of people who work together to achieve some specific purpose.
Management
The pursuit of organizational goals efficiently and effectively by integrating the work of people through planning, organizing, leading, and controlling the organization's resources.
Efficiency
Using resources—people, money, raw materials, and the like—wisely and cost-effectively.
Effectiveness
Achieving results, making the right decisions, and successfully carrying them out to achieve the organization's goals.
Rewards of Studying Management
Understanding how to deal with organizations from the outside, relate to supervisors, interact with co-workers, and manage oneself in the workplace.
Rewards of Practicing Management
Experiencing a sense of accomplishment, stretching abilities, building a catalog of successful products or services, and becoming a mentor.
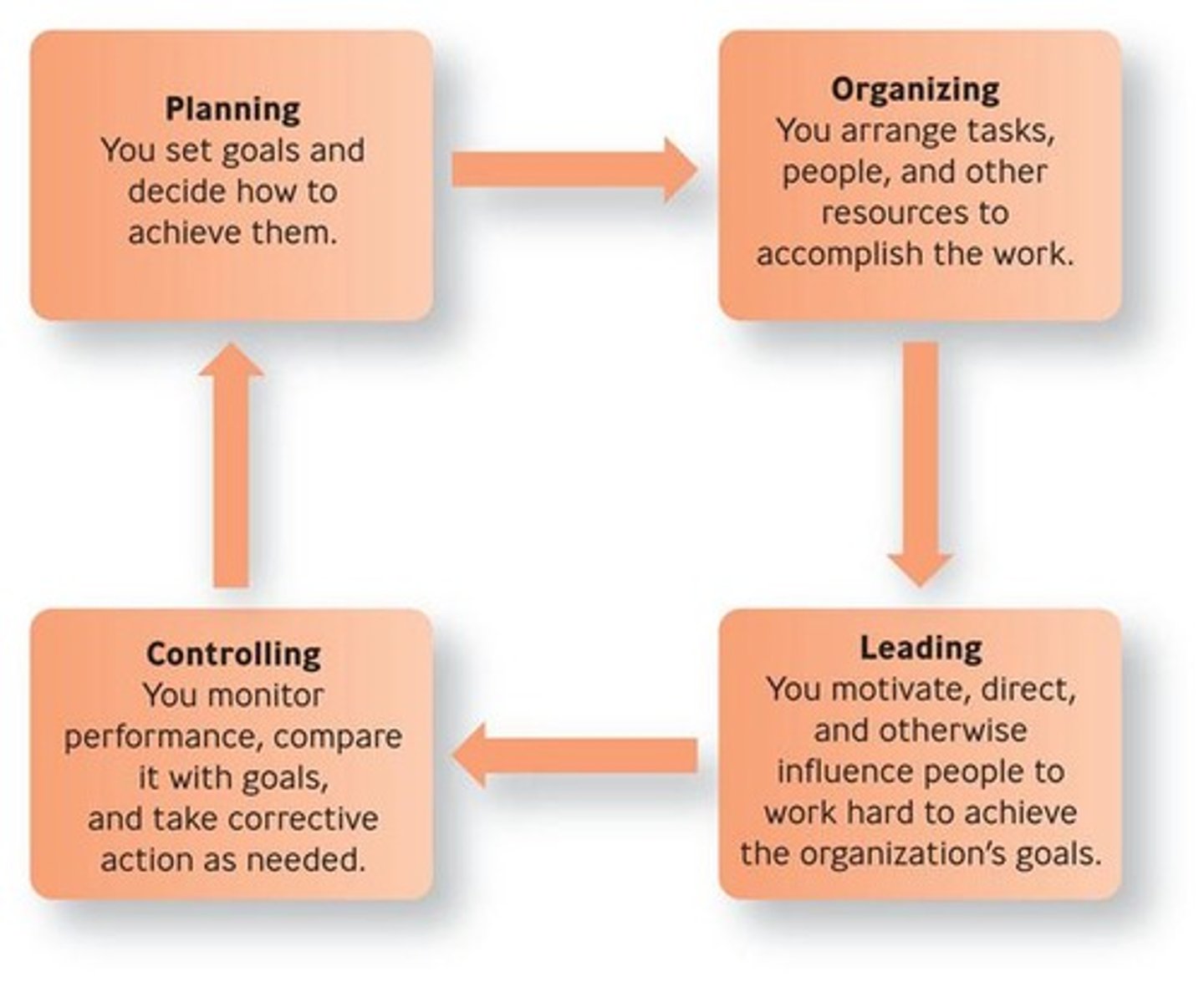
Management Process
The series of actions taken by managers to achieve organizational goals.
Challenges to Being an Exceptional Manager
Managing for competitive advantage, information technology, diversity, globalization, ethical standards, sustainability, and happiness and meaningfulness.
Competitive Advantage
The ability of an organization to produce goods or services more effectively than competitors do, thereby outperforming them.
Responsiveness to Customers
The ability to meet customer needs and preferences effectively.
Innovation
Finding ways to deliver better goods or services.
Quality
Making improvements in quality so that consumers choose your product.
Efficiency in Management
Avoiding overstaffing and overuse of raw materials to remain competitive.
Management Function: Controlling
The management function that involves monitoring and evaluating performance.
Management Function: Leading
The management function that involves motivating and directing people.
Management Function: Organizing
The management function that involves arranging tasks, people, and other resources to accomplish the work.
Management Function: Planning
The management function that involves setting objectives and determining a course of action for achieving those objectives.
Managing for Information Technology
The challenge of utilizing technology effectively within an organization.
Managing for Diversity
The challenge of managing a diverse workforce and creating an inclusive environment.
Managing for Globalization
The challenge of operating in a global market and understanding international dynamics.
Managing for Ethical Standards
The challenge of maintaining ethical practices within an organization.
Managing for Sustainability
The challenge of ensuring that organizational practices are environmentally sustainable.
Managing for Happiness and Meaningfulness
The challenge of creating a work environment that promotes employee well-being and fulfillment.
Information Technology
The use of the Internet to facilitate every aspect of running a business.
Global Online Consumer Spending
Estimated to be around $6.8 trillion, with projections showing it could reach $8 trillion by 2027.
Diversity
The changing demographic mix in the population, including a decrease in Non-Hispanic whites from 62% in 2014 to a projected 43% in 2060.
Aging Population
In 2030, nearly one in five U.S. residents is expected to be 65 and older.
Globalization
The phenomenon of American firms expanding globally while the world increasingly engages with the U.S.
Ethical Standards
Principles guiding behavior, highlighted by cases such as Bernie Madoff's $50 billion Ponzi scheme.
Sustainability
Economic development that meets present needs without compromising future generations' ability to meet their own needs.
Meaningfulness
A sense of purpose in life associated with better health, work satisfaction, and performance.
Top Managers
Individuals who make long-term decisions about the overall direction of the organization.
Middle Managers
Managers who implement policies and plans from top managers and supervise first-line managers.
First-Line Managers
Managers who make short-term operating decisions and direct daily tasks of nonmanagerial personnel.
Functional Manager
A manager responsible for just one organizational activity.
General Manager
A manager responsible for several organizational activities.
Team Leader
A first-line manager responsible for facilitating team activities toward achieving key results.
Bernie Madoff
Confessed to a $50 billion Ponzi scheme and was sentenced to 150 years in prison.
Dennis Kozlowski
Former Tyco International CEO who served prison time for grand larceny, securities fraud, and tax evasion.
Bernard Ebbers
WorldCom head serving 25 years for fraud.
Corporate Responsibility
The recognition by companies to address the causes of climate change.
Non-Hispanic Whites
Projected to decrease from 62% of the population in 2014 to 43% in 2060.
High-Touch Jobs
Jobs that involve dealing with people rather than computer screens or voice-response systems.
Food Assembly Line Supervisor
An example of a first-line manager responsible for overseeing nonmanagerial personnel.
Top manager
A high-level executive responsible for the overall direction and strategy of an organization.
Middle manager
An executive who manages the activities of other managers and is responsible for implementing organizational policies.
First-line manager
A manager who directly supervises nonmanagerial employees.
General manager
An executive responsible for all activities of a particular organization or a specific area within it.
For-profit organizations
Organizations that aim to make money (profits) by offering products or services.
Nonprofit organizations
Organizations that offer services to clients without the goal of making a profit, such as hospitals and colleges.
Mutual-benefit organizations
Organizations that aid members to advance their interests, such as political parties and labor unions.
Technical skills
The job-specific knowledge needed to perform well in a specialized field.
Conceptual skills
The ability to think analytically and visualize an organization as a whole, understanding how the parts work together.
Human skills
The ability to work well with others, motivating and inspiring trust and effective communication.
Valued traits in managers
Traits such as the ability to motivate and engage others, communicate effectively, and possess high energy levels.
Interpersonal roles
Roles that involve interacting with people inside and outside their work units, including figurehead, leader, and liaison.
Informational roles
Roles that involve receiving and communicating information, including monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson.
Decisional roles
Roles that involve using information to make decisions to solve problems or take advantage of opportunities.
Entrepreneurship
The process of taking risks to create a new enterprise.
Entrepreneur
Someone who sees a new opportunity for a product or service and launches a business to realize it.
Intrapreneur
Someone who works inside an existing organization to mobilize resources for a new product or service opportunity.
Management process
A circular process involving planning, organizing, leading, and controlling to achieve organizational goals.
Levels of management
The hierarchical structure of management, including top managers, middle managers, first-line managers, and nonmanagerial personnel.
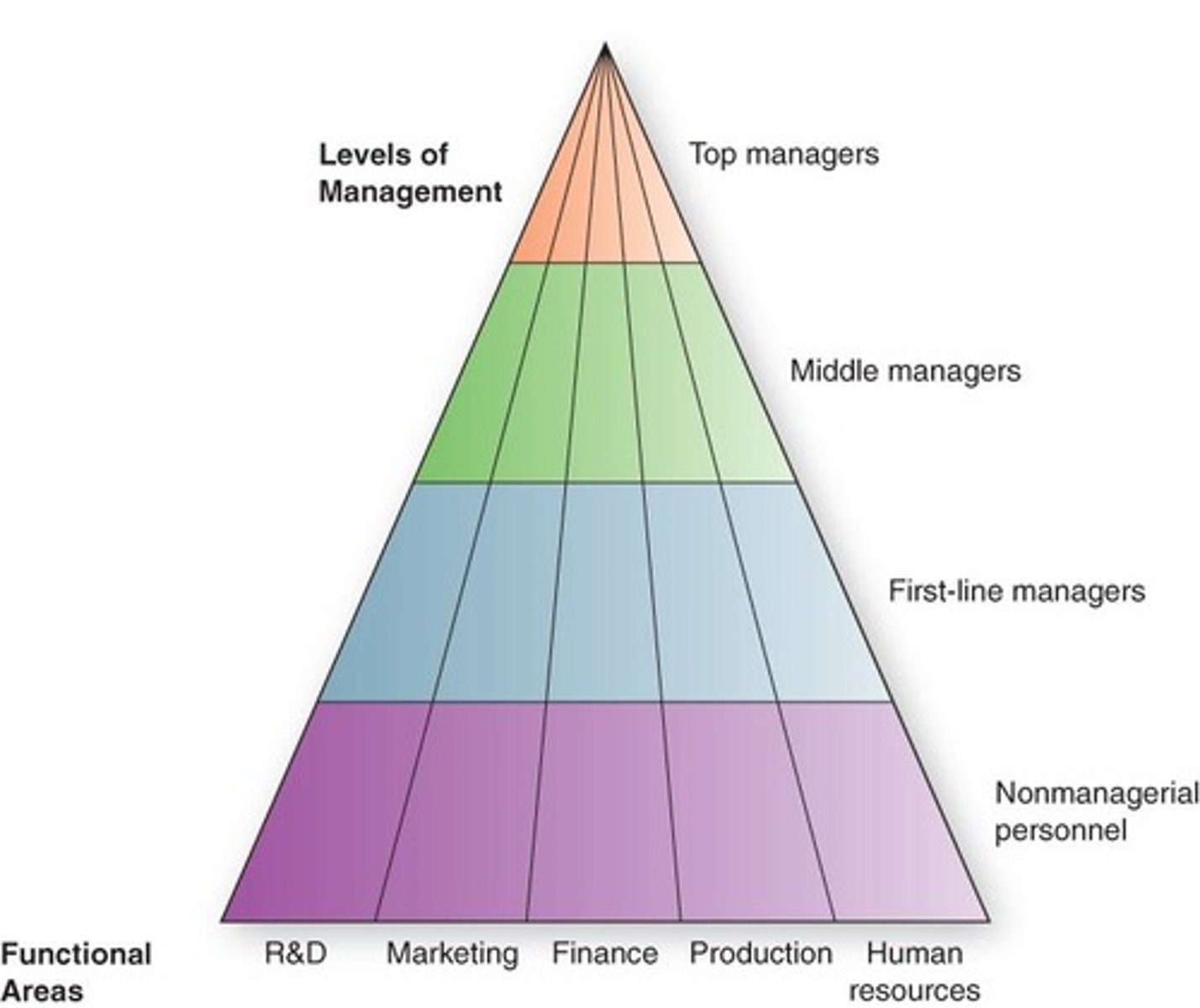
Functional areas
Different departments within an organization, such as research and development, marketing, finance, production, and human resources.