Cardiac Physiology & Exercise: Regulation of Heart Function and Blood Flow
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is preload in cardiac physiology?
Preload is the initial stretching of cardiac myocytes prior to contraction, related to muscle sarcomere length.
How does increased venous return affect preload?
Increased venous return raises end-diastolic pressure (EDP) and end-diastolic volume (EDV), stretching sarcomeres and increasing preload.
What effect does hypovolemia have on preload?
Hypovolemia reduces ventricular filling, leading to shorter sarcomere length and decreased preload.
What factors affect preload?
Blood volume, posture, venous compliance, and atrial contraction.
Define afterload.
Afterload is the tension or stress developed in the wall of the left ventricle during ejection, representing the end load against which the heart contracts.
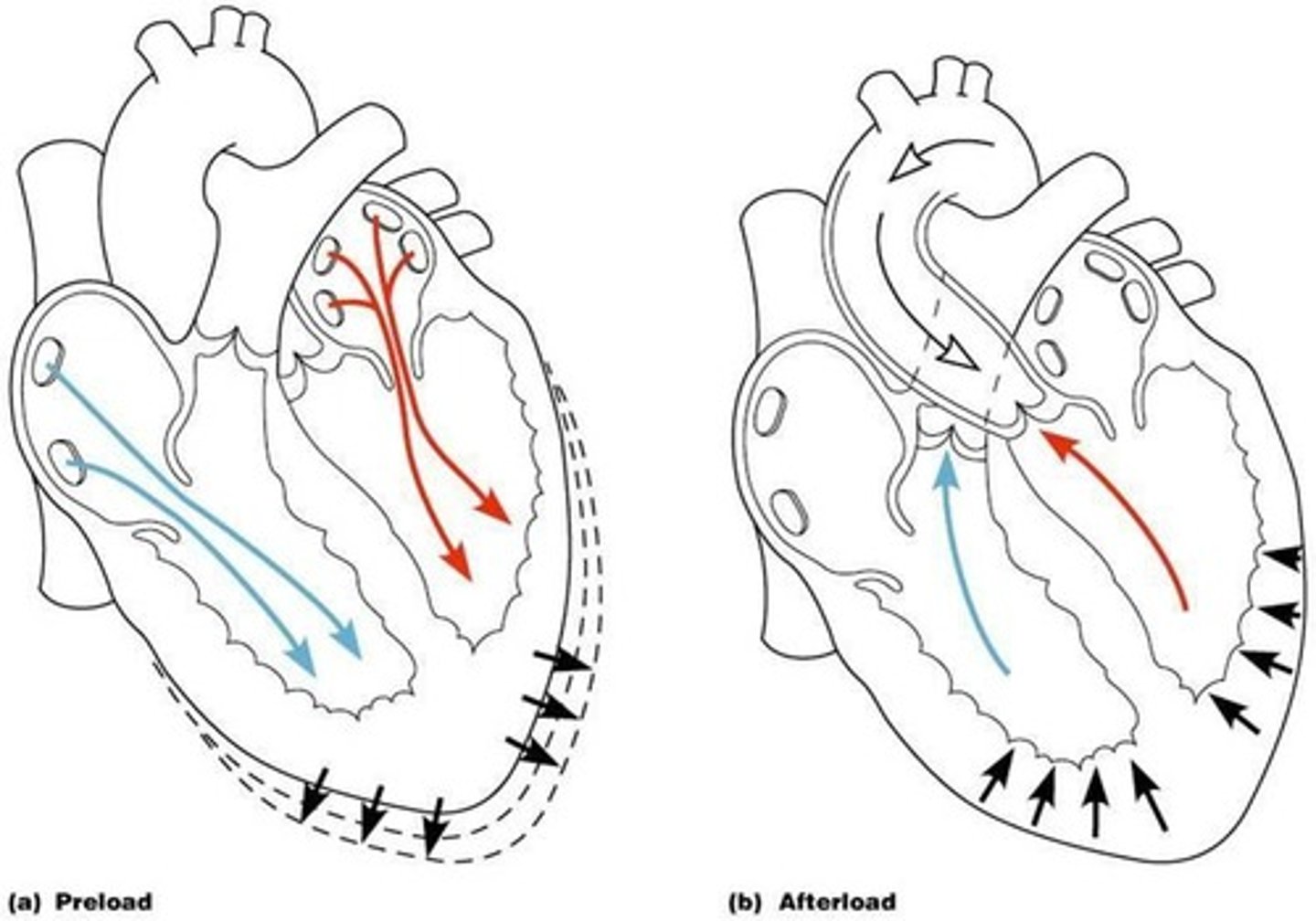
What components make up afterload?
Aortic pressure and the pressure the ventricle must overcome to eject blood.
What factors affect afterload?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation, and physical activity.
What is myocardial contractility?
The ability of the myocardium to contract, influenced by the binding between myosin and actin and calcium ion concentration.
What factors influence contractility?
Myocardial infarction (MI), sympathetic activity (increases), parasympathetic activity (decreases), and medication/drugs.
How does sympathetic activity affect heart rate?
Sympathetic activity increases heart rate, while parasympathetic activity decreases it.
What is Starling's Law?
Starling's Law states that increased chamber filling leads to increased myocyte fiber length, resulting in greater contraction and stroke volume.
How does limb movement during exercise affect stroke volume?
Limb movement enhances venous return, causing increased stroke volume.
What happens to cardiac output when standing?
Cardiac output falls because central venous pressure drops, leading to decreased stroke volume.
What is the relationship between preload and stroke volume?
Increased preload leads to increased stroke volume due to greater myocyte stretch and force generation.
Explain the effect of inotropy on the Frank-Starling curve.
Increased inotropy shifts the Frank-Starling curve upwards and leftwards, resulting in increased stroke volume and decreased left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP).
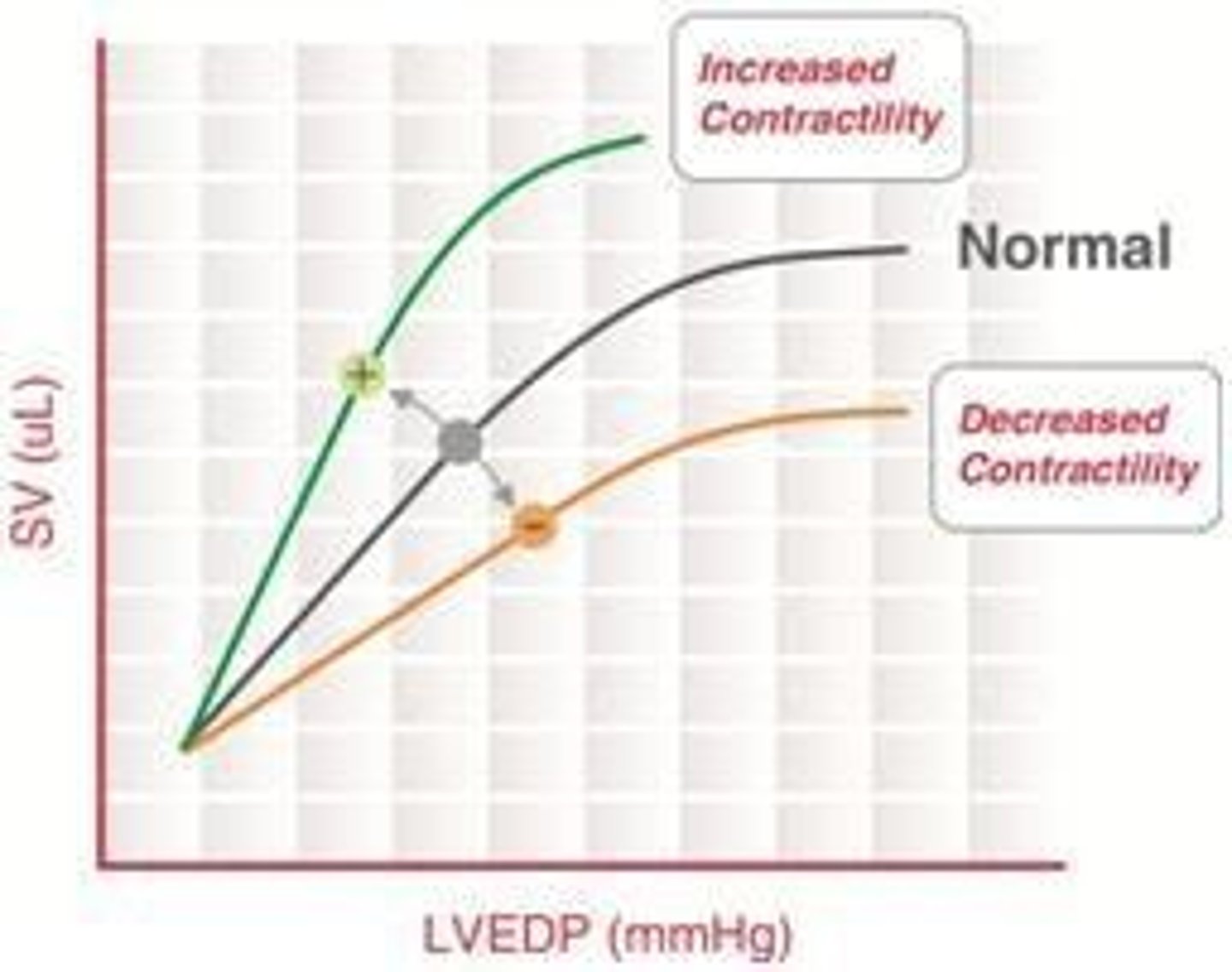
What is the Bowditch effect?
The Bowditch effect refers to the increase in inotropy with increased heart rate.
What is LaPlace's Law in relation to afterload?
LaPlace's Law states that larger vessel radius requires larger wall tension to withstand internal fluid pressure.
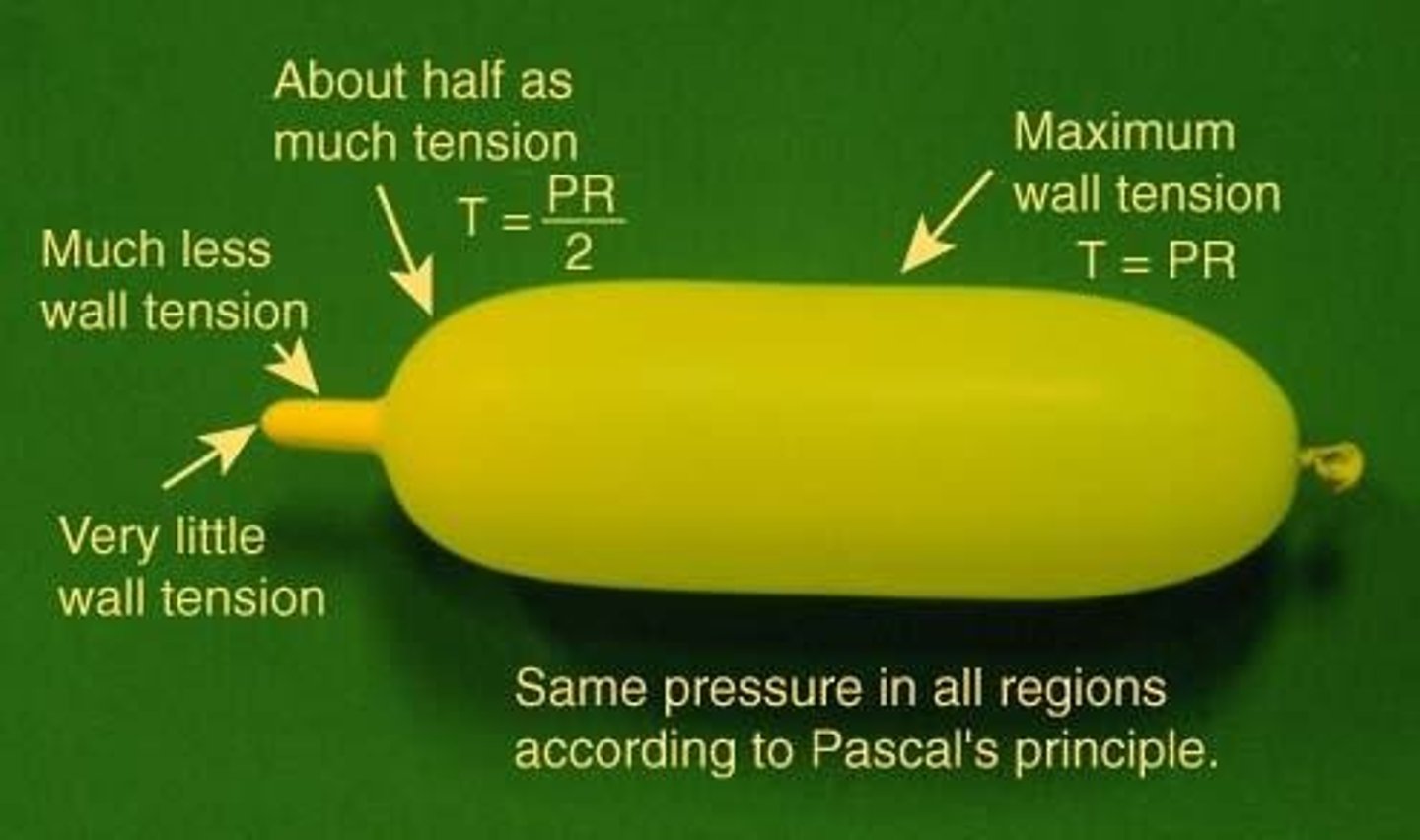
How does heart size affect energy requirements for contraction?
An increase in heart size increases the energy required for contraction; doubling the dimensions requires four times the tension to sustain systemic blood pressure (SBP).
What primarily contributes to increased cardiac output during exercise?
Most of the increase in cardiac output during exercise is due to increased heart rate rather than increased stroke volume.
What is the effect of increased afterload on stroke volume?
Increased afterload can decrease stroke volume if the heart cannot generate sufficient force to overcome the load.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system in regulating inotropy?
The sympathetic nervous system increases inotropy, while the parasympathetic nervous system has a negative inotropic effect in the atria.
What is the impact of exercise on myocardial contractility?
Exercise increases myocardial contractility due to increased sympathetic activity and calcium availability.
How does a loss of myocardium affect contractility?
Loss of myocardium, such as from myocardial infarction, results in decreased contractility.
What is the significance of the Frank-Starling mechanism during exercise?
The Frank-Starling mechanism ensures that increased venous return during exercise leads to a forceful contraction, matching right and left ventricular output.
How does increased heart rate affect intracellular calcium levels?
Increased heart rate leads to an accumulation of intracellular calcium due to the sodium-calcium exchanger, enhancing contractility.
What happens to stroke volume with decreased ejection velocity?
Decreased ejection velocity results in decreased stroke volume.
What is the relationship between sarcomere length and force generation?
Increased sarcomere length leads to increased force generation during contraction.
What system regulates local effects such as metabolites in vascular responses?
The Autonomic Nervous System
What is the role of adenosine in vascular control?
It acts as a local metabolite that influences vascular responses.
What is the function of nitric oxide in blood flow regulation?
It promotes vasodilation, enhancing blood flow.
What hormonal factors are involved in short-term blood pressure regulation?
Epinephrine, Vasopressin (ADH), and Angiotensin II.
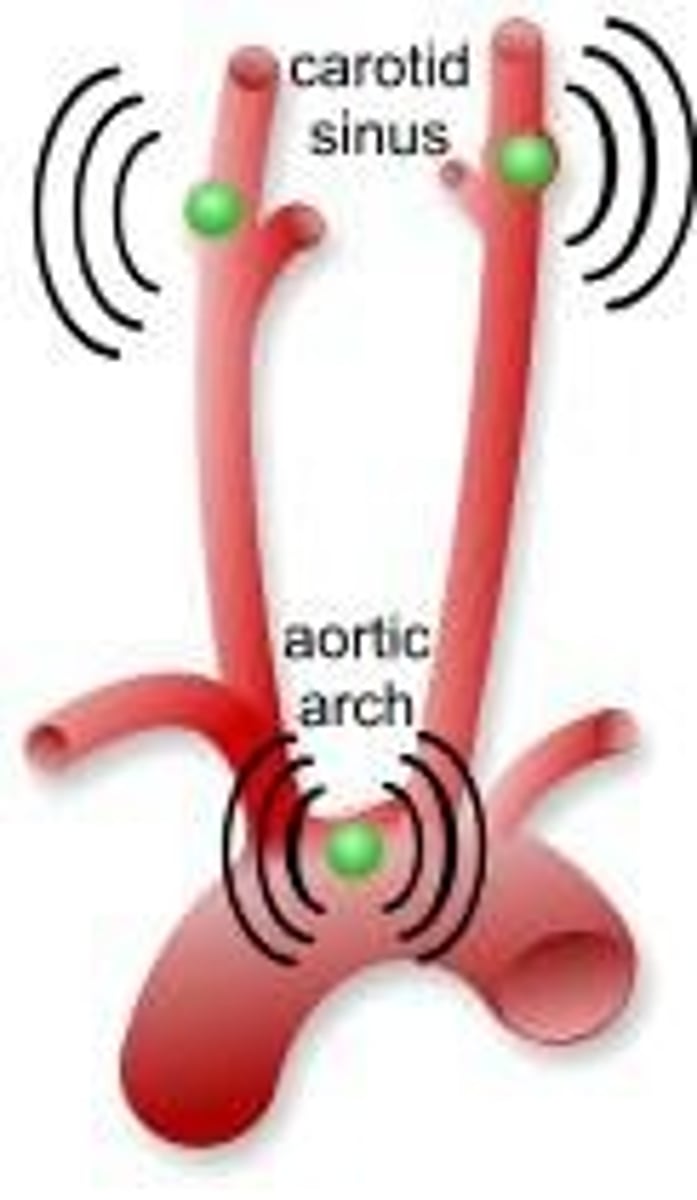
What is the Baroreceptor Reflex Pathway's response to high blood pressure?
It decreases heart rate (HR) and cardiac output (CO).
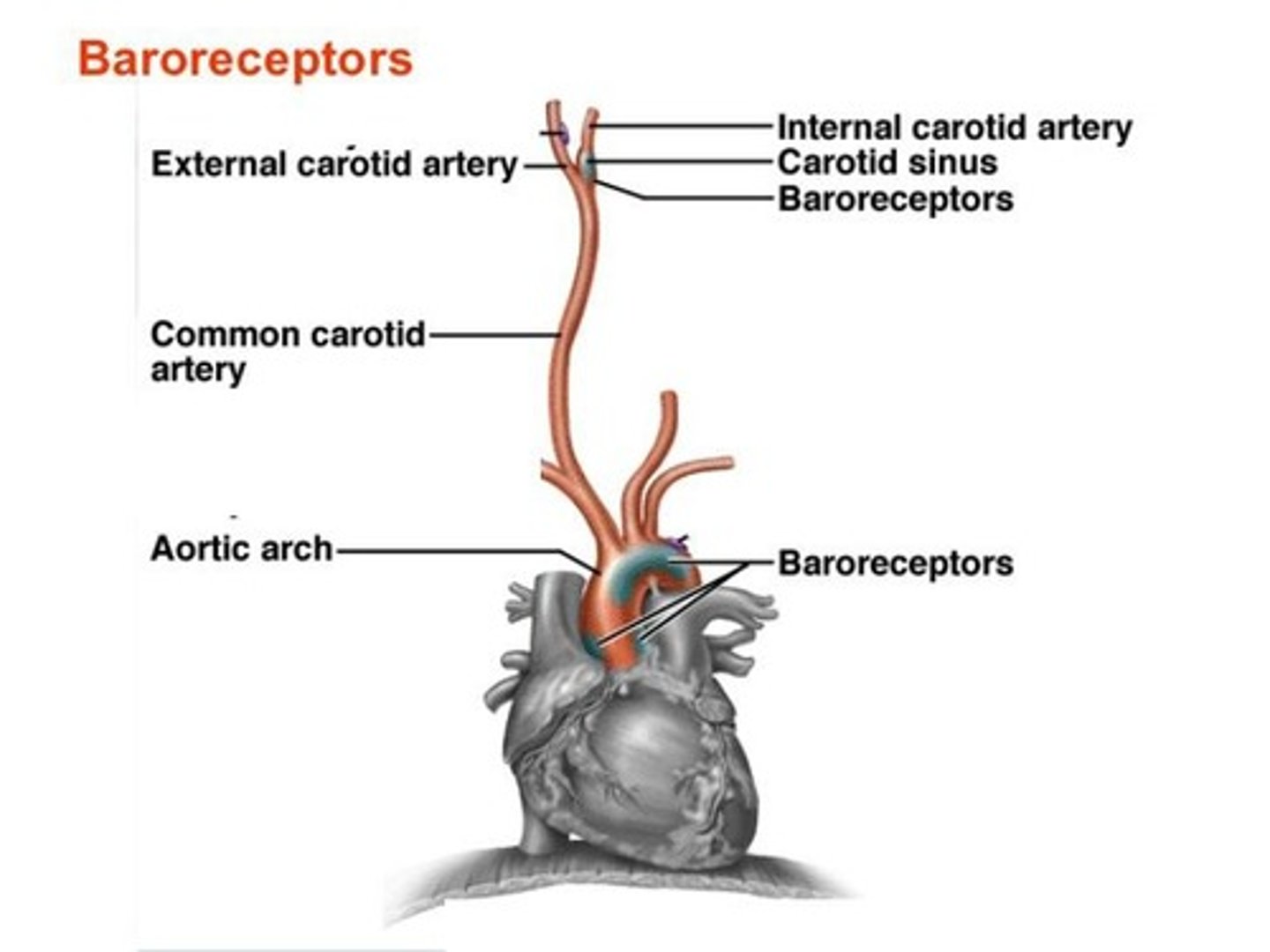
What happens in the Baroreceptor Reflex Pathway when blood pressure is too low?
It increases heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), and causes vasoconstriction.
What does the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) regulate?
It regulates sodium (Na+) levels in the blood and plasma volume.
What is the effect of Angiotensin II?
It causes vasoconstriction and stimulates thirst.
How does exercise affect heart rate?
It increases heart rate and stroke volume.
What are the three challenges imposed on circulation during muscular exercise?
Increased pulmonary blood flow, raised blood flow through exercising muscle, and stable blood pressure maintenance.
What is the formula for cardiac output (CO)?
CO = Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR).
How does cardiac output change in untrained adults during exercise?
It can increase from 5 liters/min to 20 liters/min.
What physiological changes occur to oxygen uptake during exercise?
Increased respiratory rate, tidal volume, and diffusion of oxygen at the alveolar level.
What is VO2 max?
The maximum rate of oxygen consumption attainable during physical exertion.
What happens to coronary blood flow during exercise?
It increases in proportion to cardiac work due to metabolic vasodilation.
What is the effect of prolonged heavy exercise on stroke volume?
Stroke volume tends to decline, requiring increased heart rate to maintain cardiac output.
How does sympathetic drive affect blood pressure during exercise?
It overcomes the baroreceptor reflex, leading to a linear increase in blood pressure.
What occurs to diastolic blood pressure at VO2 max?
Diastolic blood pressure can drop slightly due to decreased peripheral vascular resistance.
What is the role of the skeletal muscle pump during exercise?
It increases filling pressure, enhancing stroke volume.
What happens to blood flow in exercising muscle during heavy dynamic exercise?
Blood flow can increase from 1 liter/minute to 19 liters/minute.
What is the impact of metabolic vasodilation during exercise?
It reduces muscle vascular resistance, preventing a huge rise in arterial pressure.
What is the relationship between sympathetic activity and exercise intensity?
Sympathetic activity increases during exercise intensities exceeding 50% of maximal capacity.
What physiological changes occur in skin blood flow during exercise?
Initially, there is vasoconstriction, followed by vasodilation if temperature rises.
What happens to peripheral resistance during exercise?
It falls due to vasodilation in exercising muscle, coronary arteries, and skin.
What is the effect of posture on stroke volume during exercise?
In supine exercise, increases are largely due to heart rate; in upright exercise, stroke volume increases significantly.
What happens to ejection fraction during sympathetic stimulation?
Ejection fraction and ejection velocity increase due to enhanced myocardial contractility.
What can limit VO2 max in ischaemic patients?
Individuals can be limited to a VO2 max of less than 14 mls/kg/min.