Structure and Motion of the Knee PT 706
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What planes does tibiofemoral joint work in?
sagittal and transverse plane
Normal angle at the tibiofemoral joint?
valgus angle, about 5 degrees
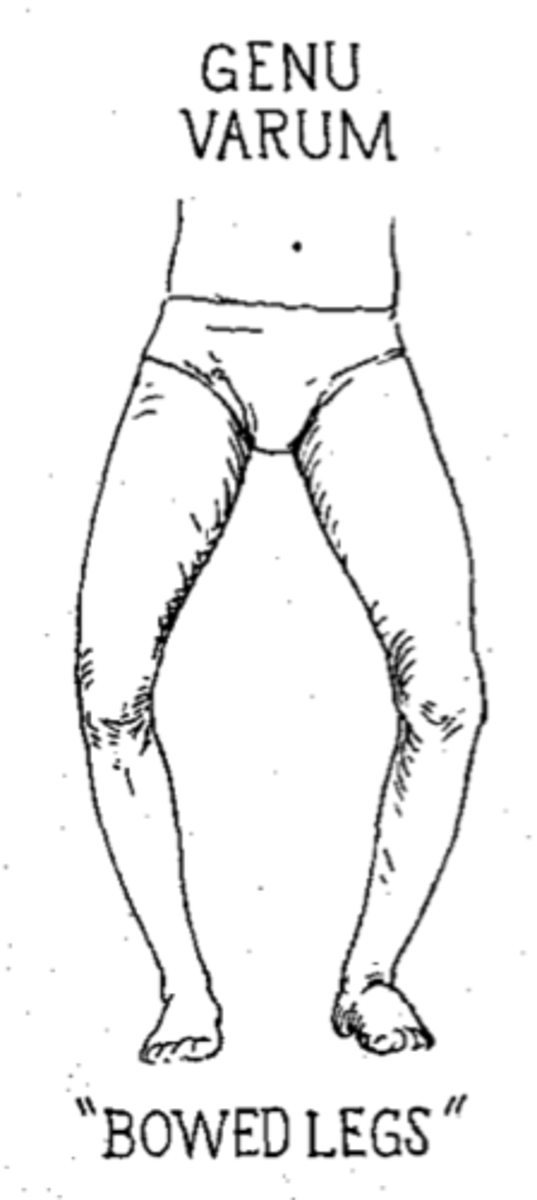
genu varum (varum)
decreased medial angle
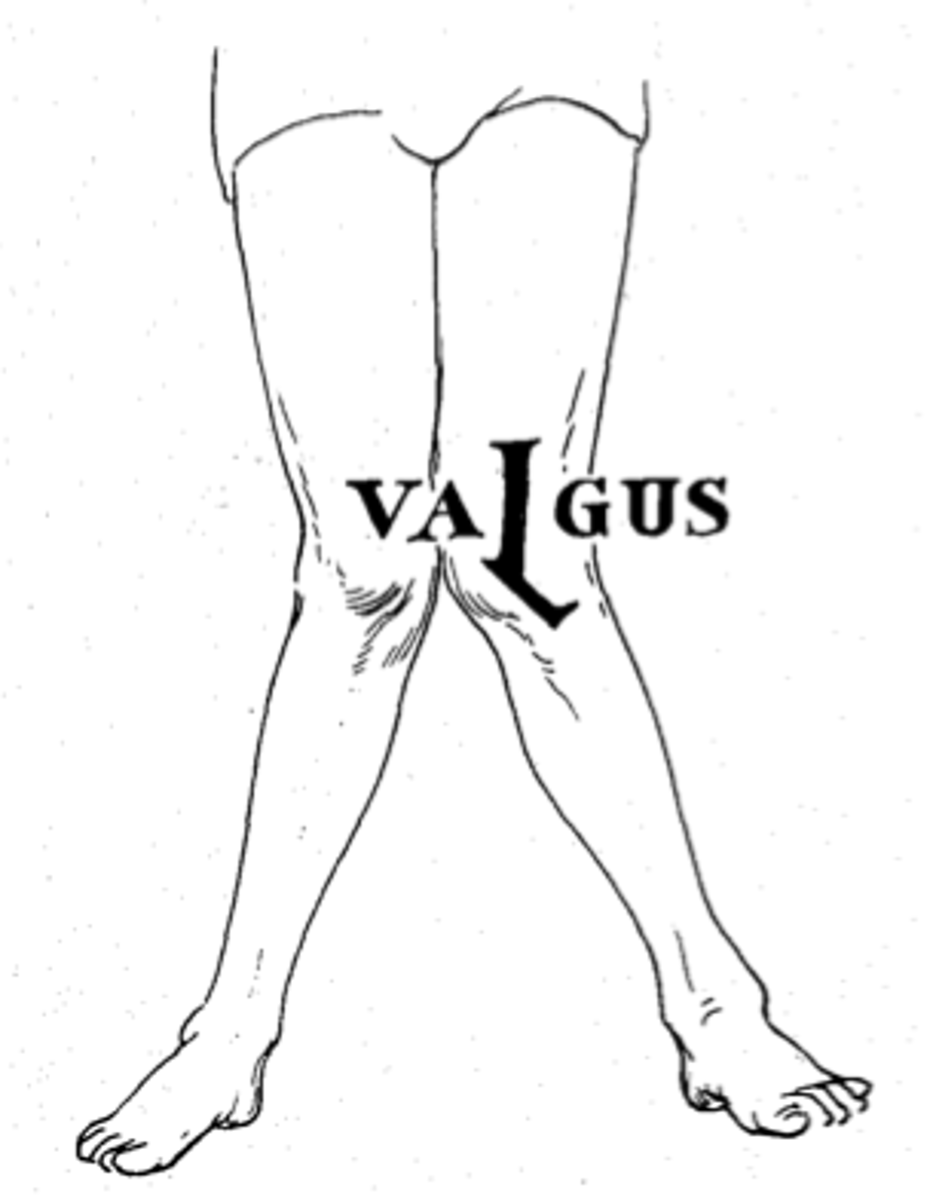
genu valgum (valgus)
increased medial angle
Forces during varus
medial is compressed, lateral tensile force (on stretch)
forces during valgus
lateral is compressed, medial tensile forces (on stretch)
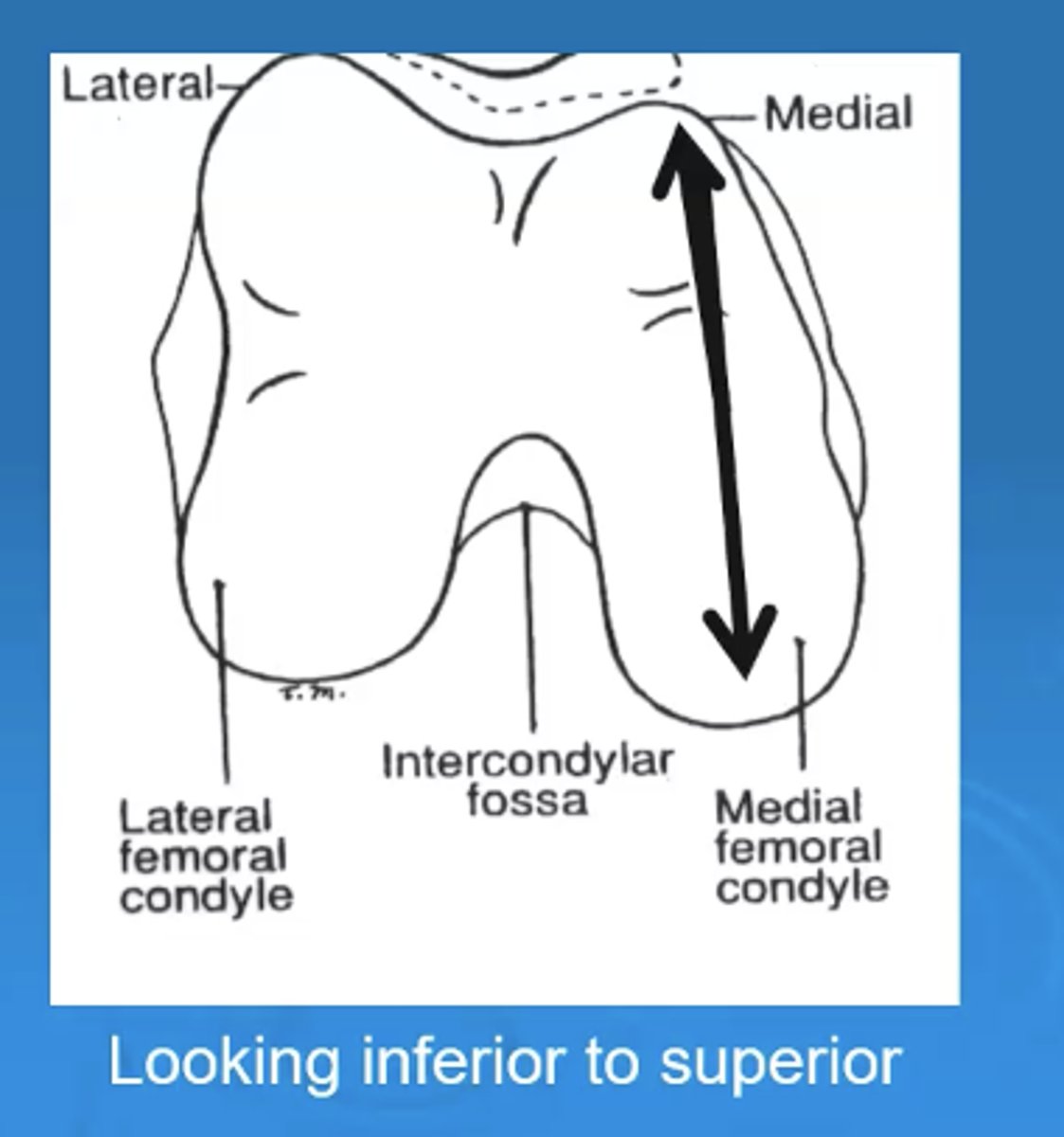
which femoral condyle is longer in the anterior/posterior direction
medial is longer in anterior/posterior direction
medial menisci shape
C shape
lateral menisci shape
O shape
how much of the load does the menisci absorb
50-70 percent
medial meniscus attaches to
MCL, semimembranosis
lateral meniscus attaches to
popliteus
menisci horns
anchor menisci to intercondylar region of tibia (anterior and posterior horns)
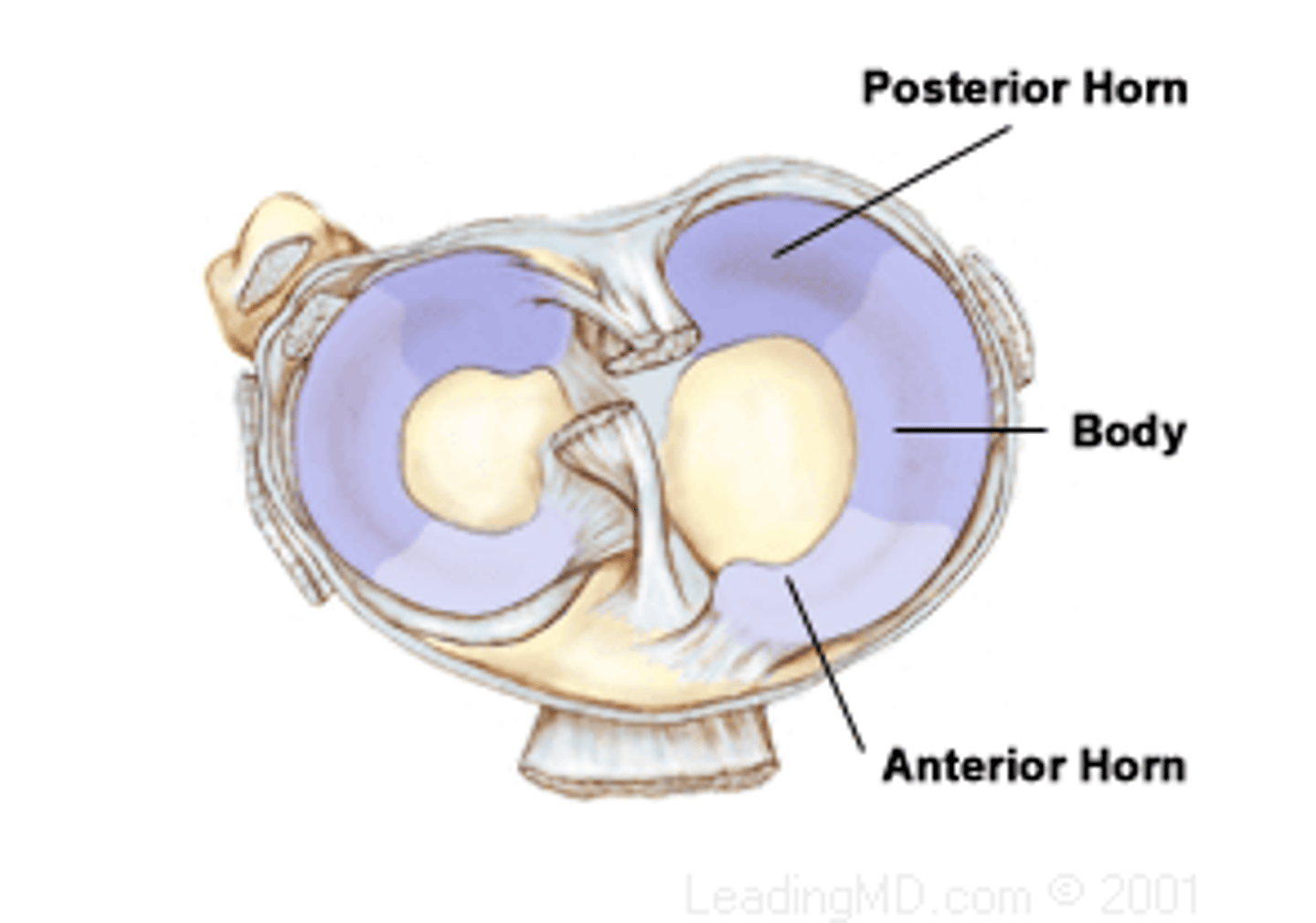
coronary ligament menisci
attach menisci to tibia condyles
vascularization of meniscus
only periphery is vascularized, red and white zone (clinically important so surgeon can decide to do a repair), you need blood flow to region so it can heal
What bone does the menisci move/distort with
femoral condyles of femur. Even though they are on the tibia, they move with the femur
medial collateral ligament
primary resist to valgus
ER of tibia
anterior tibial translation
when is MCL taut
extension
when is optimal force resistance at for MCL
25 degrees of flexion (we care about this for testing the integrity of the ligament)
lateral collateral ligament
primarily resists varus forces
limits ER of tibia
When is LCL ligament taut
extension
What is optimal force resistance at for LCL?
35 degrees of flexion
anterior cruciate ligament
Limits anterior tibial translation
Hyperextension
Varus/valgus
Rotation
Max anterior translation occurs for ACL
30 degrees of flexion
Bands in ACL
anterior/medial band and posterior/lateral band
anterior medial band of ACL
becomes more slack at knee extension
posterior medial band of ACL
becomes more slack at knee flexion
Why we do the ACL test at 30 degrees?
Neither bands of the ACL are particularly taut
synergist with ACL
Hamstrings
(because they attach posteriorly to the tibia, and can pull the tibia posteriorly (resisting anterior tibial translation))
posterior cruciate ligament
*Primarily limits posterior tibial translation
Resists varus and valgus
Resists rotation
synergist with PCL
quads because they pull the tibia anteriorly
iliotibial band
thickened fascia
inserts on lateral tubercle of tibia (gerdys tubercle)
reinforces lateral knee= stability
some fibers attach to patella= lateral pull
AAOS knee flexion
135 degrees
AAOS knee extension
10 degrees
genu recurvatum
excessive extension
posterior tilt on tibia
plantar flexion of ankle
compression on the anterior side of tibiofemoral joint and length on the posterior side of tibiofemoral joint
axis of motion of knee
migrating axis due to incongruent surfaces, this is why we measure at lateral epicondyle (average of migrating axis that occurs)
when is there the greatest amount of axial rotation
90 degrees of flexion at the knee
ER to IR ratio of axial rotation
2:1
maximal restriction of axial rotation is when knee is in
full extension
Screw Home Mechanism
closed chain extension
IR of femur on fixed tibia
Screw home mechanism
open chain extension
ER of tibia on fixed femur
screw home mechanism
closed chain flexion
ER of femur occurs
screw home mechanism
open chain flexion
IR of tiba occurs
why does screw home mechanism occur
shape of medial femoral condyle, passive tension in ACL, slight lateral pull of quadriceps
open chain extension of knee
tibia rolls and glides anteriorly
open chain flexion of knee
tibia rolls and glides posteriorly
closed chain flexion of knee
femur rolls posteriorly and slides anteriorly
open chain extension of knee
femur rolls anteriorly and glides posteriorly
closed packed position of knee
full extension
resting position of knee
about 25 degrees of flexion
what way does the menisci roll
menisci rolls with the direction of roll
anterior deformation
during closed kinetic chain, the femur rolls anteriorly causing deformation on anterior menisci
posterior deformation
during closed kinetic chain, the femur rolls posteriorly causing deformation of posterior menisci
patella
largest sesamoid bone in the body, sits in a tendon and acts as a lever
covered with cartilage
joint of incongruency
Synovial joint
base of patella
superior surface
apex of patella
pointy inferior surface
which facet of the patella is the largest?
lateral facet
what helps prevent patellar dislocations
lateral ridge of femur
135 degrees of flexion
primary contact: superior pole
inferior to inter condylar groove
facets in contact: lateral edge of lateral facet and odd facet
90 degrees flexion
primary contact: starts to migrate towards inferior pole
engaged within the intercondylar groove from 90-60 flexion
facets in contact: medial and lateral facets
20 degrees flexion
priamary contact: inferior pole
superior to intercondylar groove
facets in contact: medial and lateral facets
external torque demands are greatest
open chain knee extension
and closed chain knee flexion
why do we not extend our knee all the way during knee extension exercise?
decreased the moment arm, but you are still working the quads effectively, this way you can avoid the high external moment arm
what is the role of the patella?
increases internal moment arm of knee extensor mechanism (making knee extension easier for us)
joint reaction forces are influenced by
the angle of knee flexion, force within the quad muscle
patella femoral joint reaction forces (PFJRF)
The deeper you go into a squat the compressive force into a joint goes higher, the contact area is higher from 60-90 degrees so it can help distribute this force
Q angle
ASIS to center of patella
tibial tuberosity to center of patella
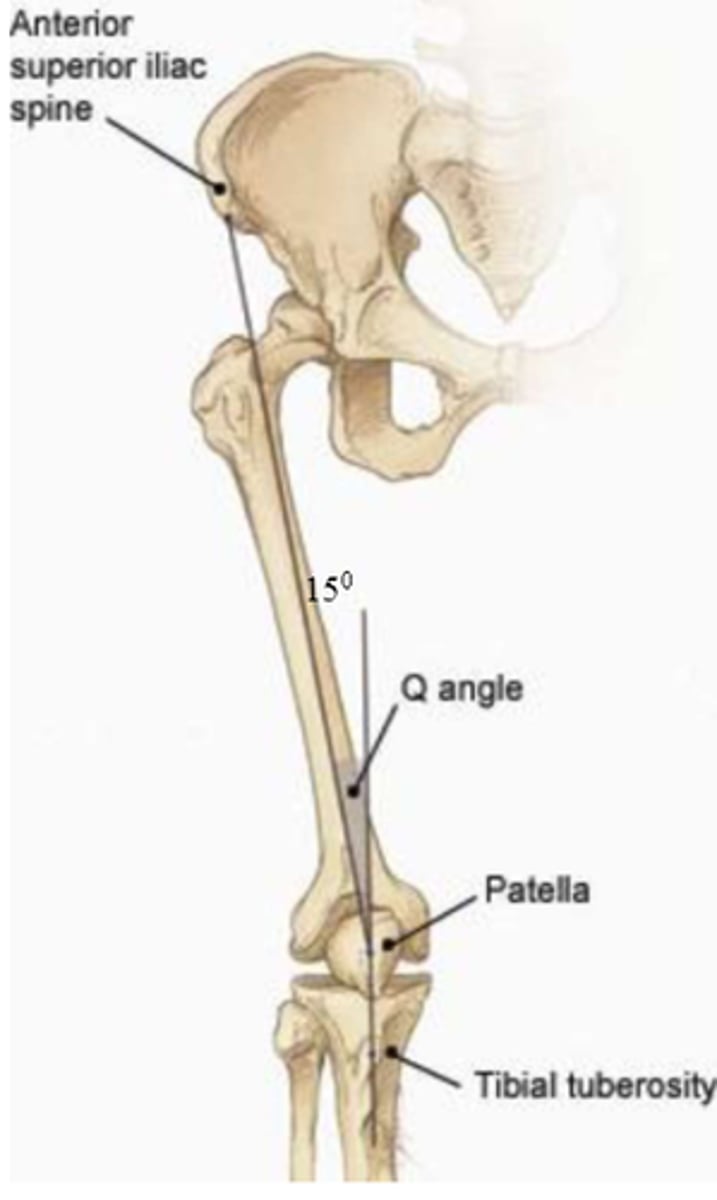
normal Q angle
10-15 degrees, larger in females due to wider pelvis
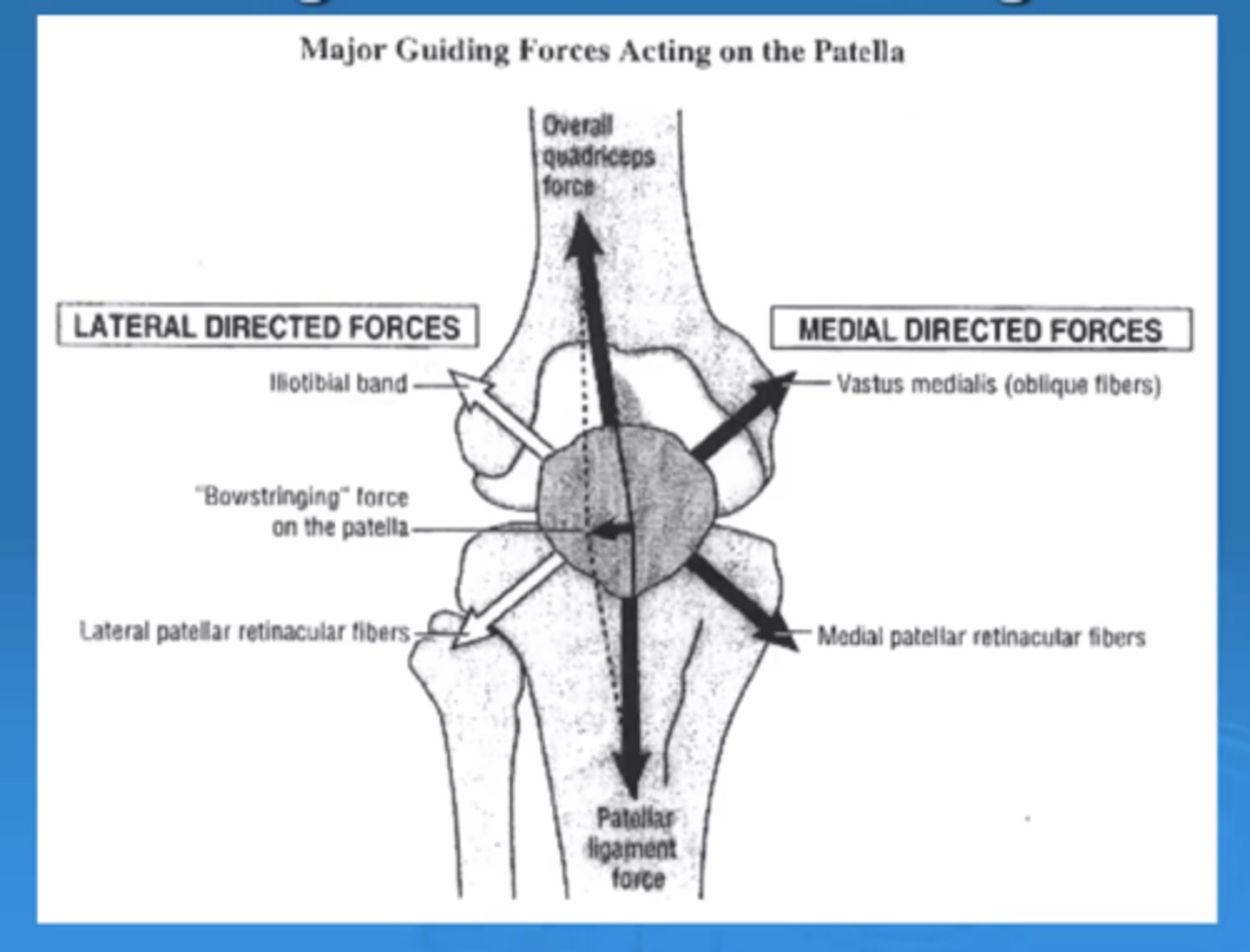
Is there more medial or lateral pull of the patella?
More lateral
This is why people dislocate more lateral, because we have more forces pulling laterally than medially.
Clinically, you want to have a more equal pull to prevent dislocatiom.
If you have a larger Q angle, you can have more lateral pull
patella movements
- tilited medially and laterally
- rotated medial and lateral based on ifnerior pole
- glide medial and lateral
- superior and inferior glide