Unit 4: Monetary Policy & the Federal Reserve
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Monetary base (M0)
the total amount of currency and bank reserves in an economy. It is the most basic measure of a country's money supply
Fiat money
money that has no intrinsic value (paper money)
What are the uses of money?
Store of Value (putting money in accounts has value), Medium of Exchange (paying with cash), Unit of Account (currency conversions/exchanges)
M1
Cash, checking accounts
M1 is composed of currency in circulation, demand deposits, and other liquid deposits such as savings deposits. Does NOT include M0.
M2
M2 is composed of M1 and other small-denomination time deposits and balances in retail money market funds
M3
M1+M2+ larger time deposits + larger liquid assets
What money type is bank reserves?
M0
What money type is CD’s?
M2
Mia transferred $1,000 from her checking account to a certificate of deposit. How will the M1 and M2 measures of the money supply change?
M1 will decrease, M2 unaffected
Order of Asset Liquidity (Least to greatest)
M3 to M1
House, bonds, savings account, cash
How is money “created”?
By banks giving out loans
Bonds vs stocks
both financial assets
Bonds are basically long-term debts, interest-bearing assets.
Stocks are not interest-bearing, they are equity/stakes in a company
How to find real interest rate
Nominal interest rate - inflation rate
Discount Rate
Types of Monetary Policy
Limited Reserves and Ample Reserves
Limited Reserves Policy
Open Market Operations (buying/selling bonds), changing RRR, discount rate
Contractionary Monetary Policy in Limited Reserves
Sell bonds, increase rates/ratio
Ample Reserves Policy, and how they affect Monetary Policy
Administered Rate
When a central bank has "ample reserves," it means there is a large supply of funds available to banks, allowing them to readily lend money, which in turn gives the central bank greater control over short-term interest rates by primarily adjusting the interest rate paid on reserves, rather than manipulating the overall supply of reserves through open market operations; essentially, with ample reserves, the central bank can more precisely target the desired interest rate through administrative means.
Reserve Requirement
The percentage of deposits a bank must keep on hand as cash according to the Federal Reserve
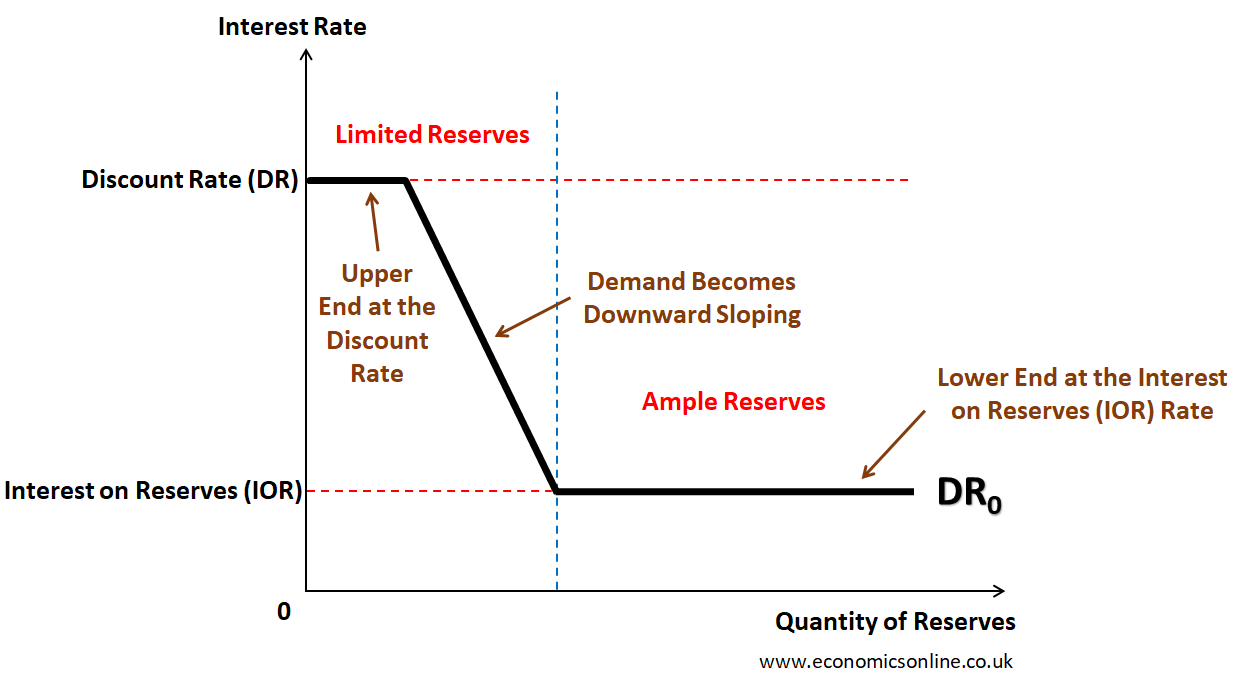
Simple Money Multiplier
1/RRR. How an amount of money put into the bank creates new money (kind of a trickle-down effect with each deposit and loan adding another piece)
How to calculate change in banking system money supply due to a deposit
Take that money, subtract off the RRR, then multiply by simple money multiplier
Excess reserves
What bank holds above Reserve Requirements, for loans
Which of the following explains why the amount predicted by the value of the simple money multiplier may be overstated?
It does not account for the bank’s desire to hold onto excess reserves.
Money Market Graph
quantity of money vs NOMINAL interest rate
MS is vertical, MD downward sloping.
Loanable Funds Market Graph
Investment is financed by national savings in a closed economy.
Shows REAL IR of private sector loans S/D
how does price level affect money market?
The nominal interest rate rises, and the price of previously issued bonds falls.
What is the Bond Market, and how is it affected?
Interest rates
Rising interest rates: Bond prices fall, and new bonds pay higher interest rates than older bonds
Falling interest rates: Bond prices rise, and older bonds pay higher interest rates than new bonds
Inflation
Rising inflation: Bond yields tend to rise
Low inflation: Bond yields tend to decline or remain low
Also Supply and Demand
If a question talks about deposits and excess reserves, what numbers can you use with the multiplier?
ONLY excess reserves and CHANGES in deposits, not the deposits themselves
What happens if there is an increase in household savings?
Supply of Loanable Funds increases, real interest rates decrease.
Discount Rate
Ceiling on Policy rate, what Federal Reserve charges banks for short-term loans
Part of LIMITED reserves
What happens when the Fed buys bonds?
Buy = bigger, so economy increases. This is because Money supply increases, interest rates decrease, investment increases, AD increases.
IOR
Interest on Reserves, part of ample reserves system. Pay banks to keep money in reserves
Transaction demand
Demand for money
What happens if adminstered rates decrease for ample reserves?
Decrease policy on ample reserves is for recession
Demand shifters of Loanable Funds Graph
FADE, foreign demand, All borrowing/lending/credir behaviors, deficit spending, expectations
Supply Shiffters of Loanable Funds
SELF: savings rate, expectations, lending at the discount window, foreign purchases of domestic assets
Liquidity Trap
An economic situation where interest rates are low, but consumers and investors hoard cash instead of spending.
What happens to money demand and IR_real when GDP increases?
money demand and real interest rates do too
what group is most affected by changes to interest rates?
businesses
Tight money policy….
contraction
Federal Funds Rate
Interest banks charge each other
Ample Reserves graph
backward logistic curve
Things that shift MS
reserve req, OMO/bonds, discount rate, administrated rates, feds lowering/raising interest rate
Federal Funds Rate
interest that banks charge each other, regulated bby the Fed. part of AMPLE reserve system