dementia,epilepsy,parkinsons drugs
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
dementia
progressive decline in cognition memory and behaviour
Types of dementia
Alzheimers,lewy body,Vascular,frontotemporal
Alzheimers
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and reasoning skills, leading to a gradual decline in cognitive function. It's the most common cause of dementia in older adult
lewy body
Clumps of protein forming inside brain cells a type of progressive dementia that leads to a decline in thinking, reasoning and independent function
vascular dementia
Vascular dementia is a form of dementia caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, damaging or killing brain cells
Frontotemporal
Frontotemporal dementia affects the front and sides of the brain (the frontal and temporal lobes).
Dementia is the name for problems with mental abilities caused by gradual changes and damage in the brain.
Cholinesterase inhibitors drug eg
Donepezil,Rivastigimine,Galantamine
Cholinestare inhibitors indications
GI issuses,Insomnia,bradycardia
cholinesterase affects
Cholinesterase is an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine (ACh), a neurotransmitter essential for nerve impulse transmission
NMDA Receptor antigonist eg
memantine
NMDA Receptor antigonist side effects
hallucinations, delusions, confusion
nmda receptor antagonist effects
a process where excessive glutamate stimulation leads to neuronal damage or deathGlutamate excitotoxity
Antidepressants eg
SSRIs
Antipsychotics egs
Risperidone,Quetiapine
sleep disturbances
Melatonin,avoid benzodiazepines
antipsychotics
behavioural issues a class of medications primarily used to treat psychosis, particularly schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
Parkinsons disease
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement.
Parkinsons cause
Dopamine loss in substantia nigra
Motor signs
Tremor,rigidity,bradykinesia
Non-motor signs
mood,cognition,autono,ic,dysfunction
TRAP acronym
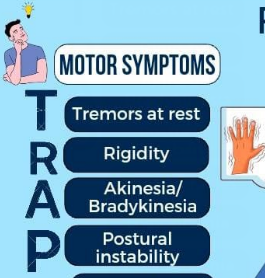
Parkinsons medication eg
Levodopa+carbidopa
Levodopa and carbidopa
mainstay therapy
Levodopa and carbidopa side effects
dyskinesia,hypotension,hallucinations
Dopamine agonists eg
Pramipexole,Ropinirole
Pramipexole,Ropinirole job
direct stimulation
Pramipexole,Ropinirole side effects
Impulse control disorders,sleep attacks
benzodiazepines
continue to be used for a variety of conditions, including the management of neuropsychiatric symptoms associated with dementia.
MAO-B inhibitors eg
Selehiline,rasagiline
MAO-B inhibitors role
prolong dopamine
COMT Inhibitors eg
Entacapone
COMT Inhibitors role
extend levodopa effects
Anticholinegics eg
help with sympyoms in younger people
Amantadine
treat Parkinson's disease (sometimes called "paralysis agitans" or "shaking palsy")
Depression
SSRIS,SSRNIS
Psychosis
Pimavanserin,clozapine
Sleep and autonomic
tailored approaches(eg melatonin,midodrine)
3cs epilepsy
Calm, Cushion, Call
3 s’s
Stay, Safe, Side
epilepsy
recurrent unprovoked seizures
epilepsy types
focal vs generalized types
epilepsy causes
genetic ,structural, metabolic
tonic seizure
tone = muscle a tonic seizure, the tone is greatly increased: the body, arms, or legs become suddenly stiff or tense.
Clonic seizures
means fast stiffening and relaxing of a muscle that happens repeatedly. In other words, it is repeated jerking
Antiepileptic drugs
prevent seizures with minimal side effects
Monotherapy
preferred initially
Levetiracetam
Levetiracetam is a medicine used to treat epilepsy
Levetiracetam side effects
A blocked nose or itchy throat. If it's bothering you, ask your pharmacist for something to help your symptoms. ...
Feeling drowsy, sleepy or dizzy. ...
Headaches. ...
Aggression, or feeling irritable or agitated. ...
Feeling sick or being sick (nausea or vomiting)
sodium valproate eg
gaba,Na + blocker
pregnant women should
avoid valproate
Elderly,
favour lamotrigine,levetiracetam
drug interactions
Enzyme inducers (e.g,carbamazepine)vs inhibitors
Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine is a medicine used to treat epilepsy. It can also help prevent low mood (depression) in adults with bipolar disorder.
Lamotrigine side effects
headaches
drowsy
sleepy
tremors
sleeping difficulties
Diarrhoea
Mild skin rash
challenges
side effects are they a burden or benefit
polypharmacy and drig interactions
disease progression
medication adjustments
focal seizures
Focal seizures are a type of seizure that affects only one side of your brain and body.
what to do to help
individualised therapy
monior side effects and cognitive mood
educate and involve caregivers