GHHS EARTH SCIENCE - Energy Resources Vocabulary
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
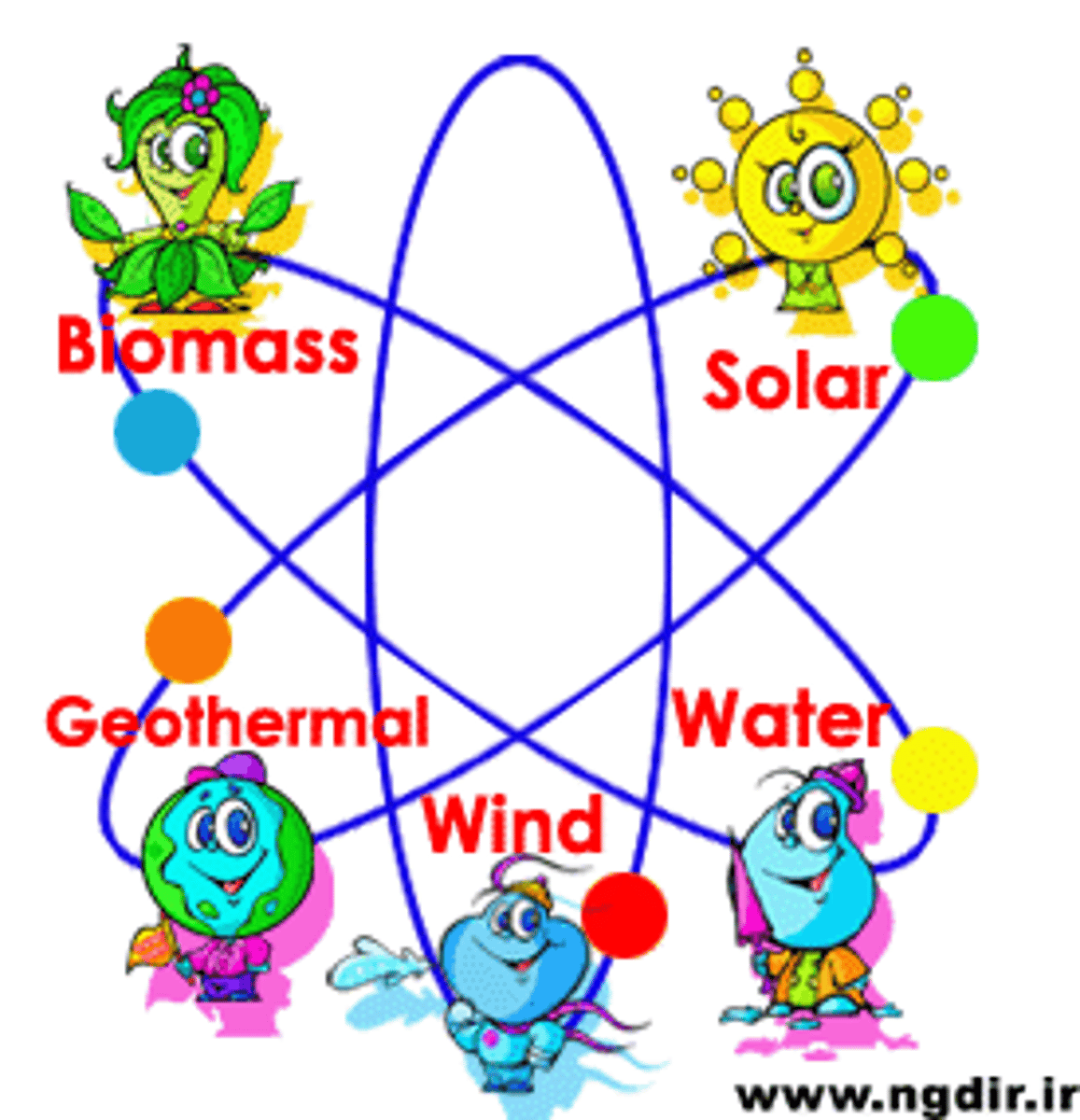
Renewable Resource
a resource that can be replenished (get more) within a human lifetime (~80 years)
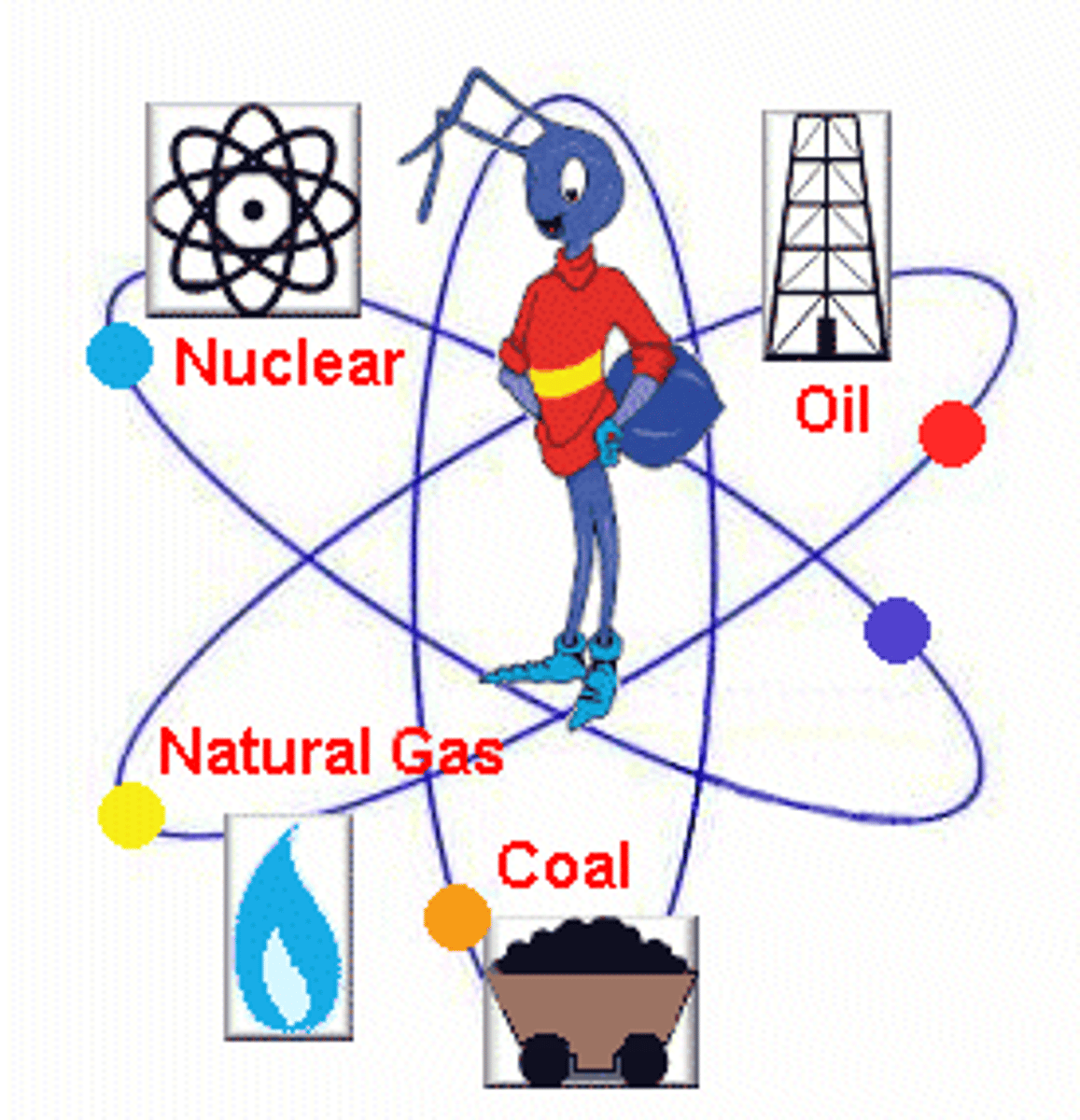
Nonrenewable Resource
a resource that has limited amounts and no more can be made - within a human lifetime (~80 years)
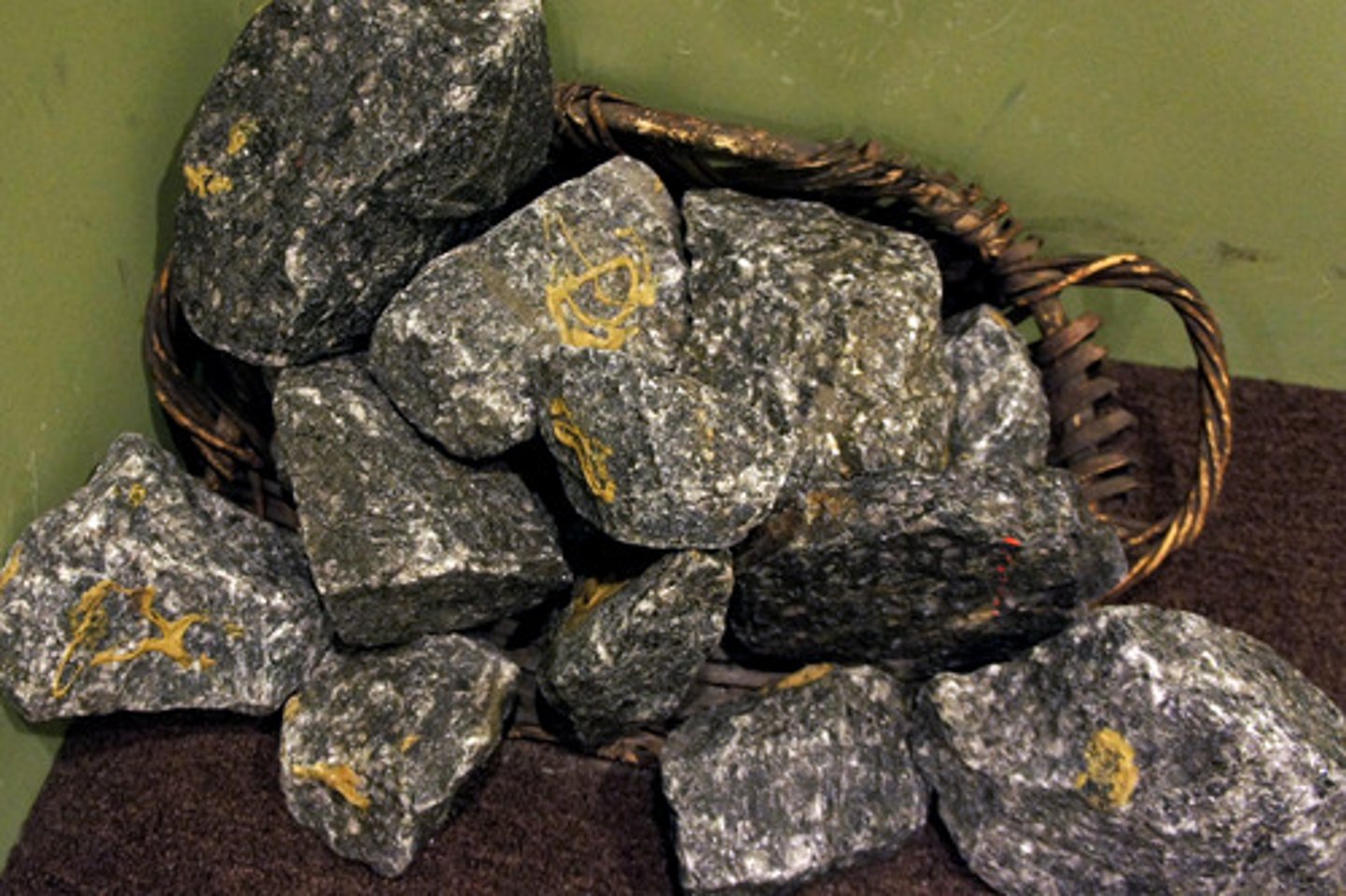
Ore
The desired mineral resource that is in its raw form, often mixed with surrounding materials

Metals
resources that are typically shiny in appearance and are also good conductors of heat and electricity
Nonmetals
resources that are typically not shiny (dull) in appearance and are also poor conductors of heat and electricity
Lode
term that refers to a large amount of a desired mineral found within the rock
Veins
a streak or band of a desired mineral that is located within a layer of rock
Placer deposits
deposits of a mineral resource that are often deposited at the base of a stream
Conservation
using resources in such a way that helps them to last longer. This can involve using less, making substitutions, or recycling.
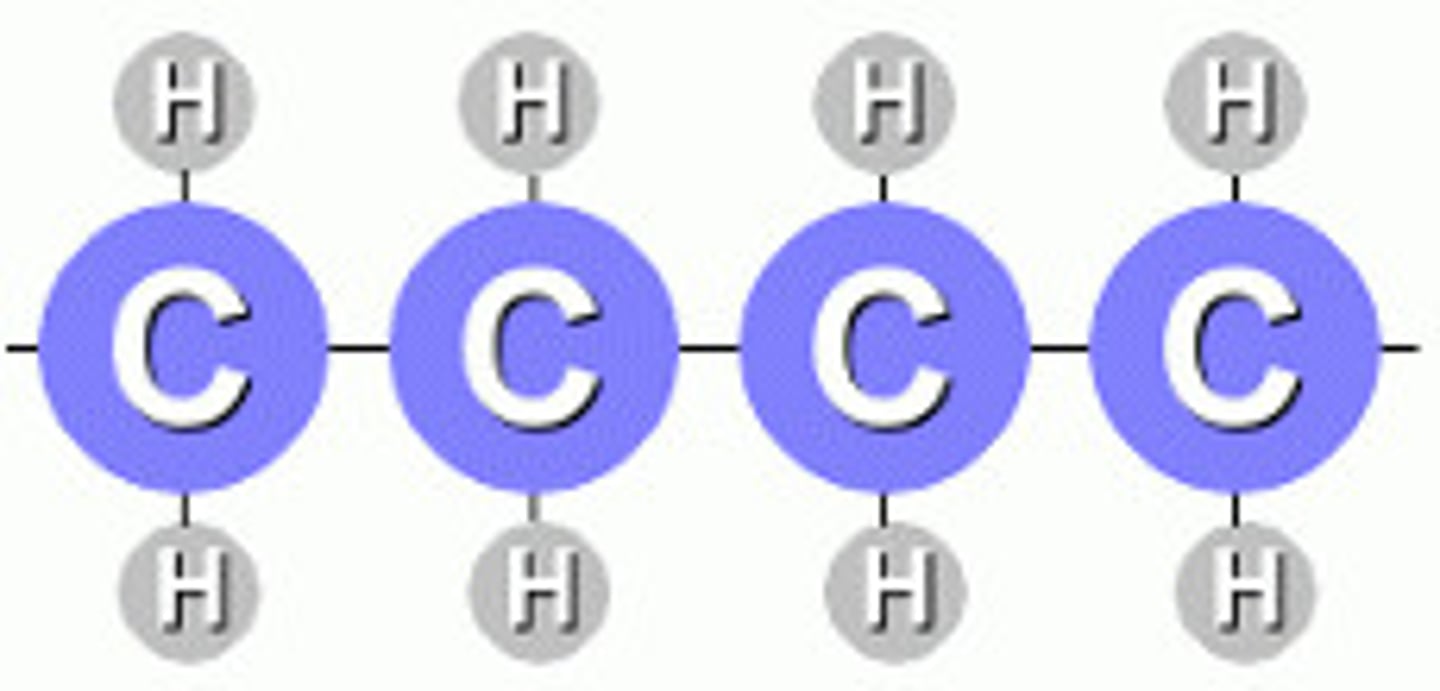
Hydrocarbon
substances made entirely out of carbon and hydrogen (often used as fuels)
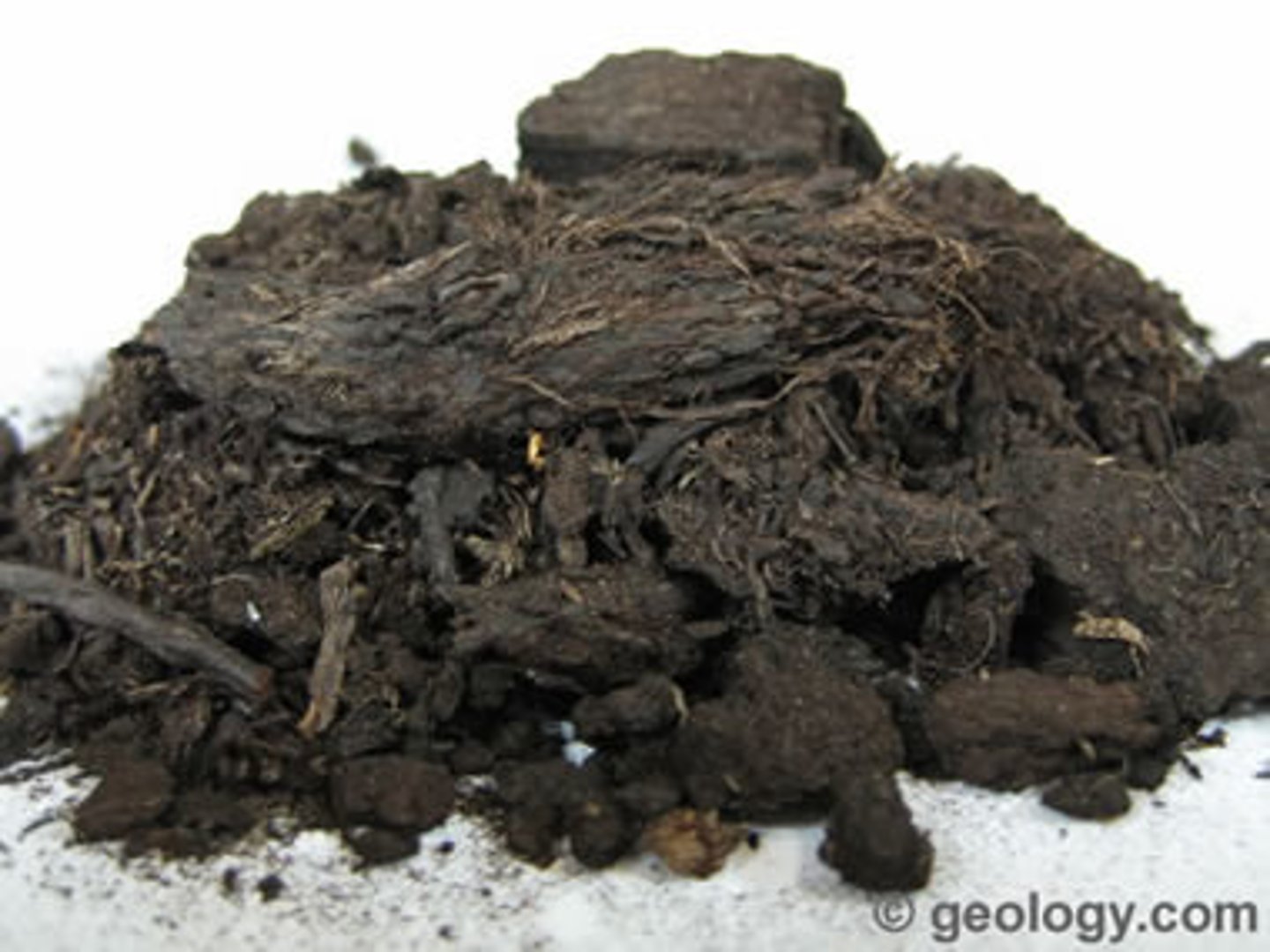
Coal: PEAT
earliest form of coal, not even considered a rock, but more like compacted soil

Coal: LIGNITE
peat is compacted further to form this substance, which is also known as brown coal and is a sedimentary rock

Coal: BITUMINOUS
lignite is compacted further to form this substance, which is also known as soft coal and is a sedimentary rock

Coal: ANTHRACITE
bituminous coal is exposed to extreme pressure to form the metamorphic type of coal. often referred to as clean coal because it burns with less emissions than bituminous

Petroleum
This is a hydrocarbon formed from the remains of ancient animals. It can be refined into many different substances.

Natural gas
This product is also known as methane and is harvested through a process known as hydraulic fracturing (fracking)

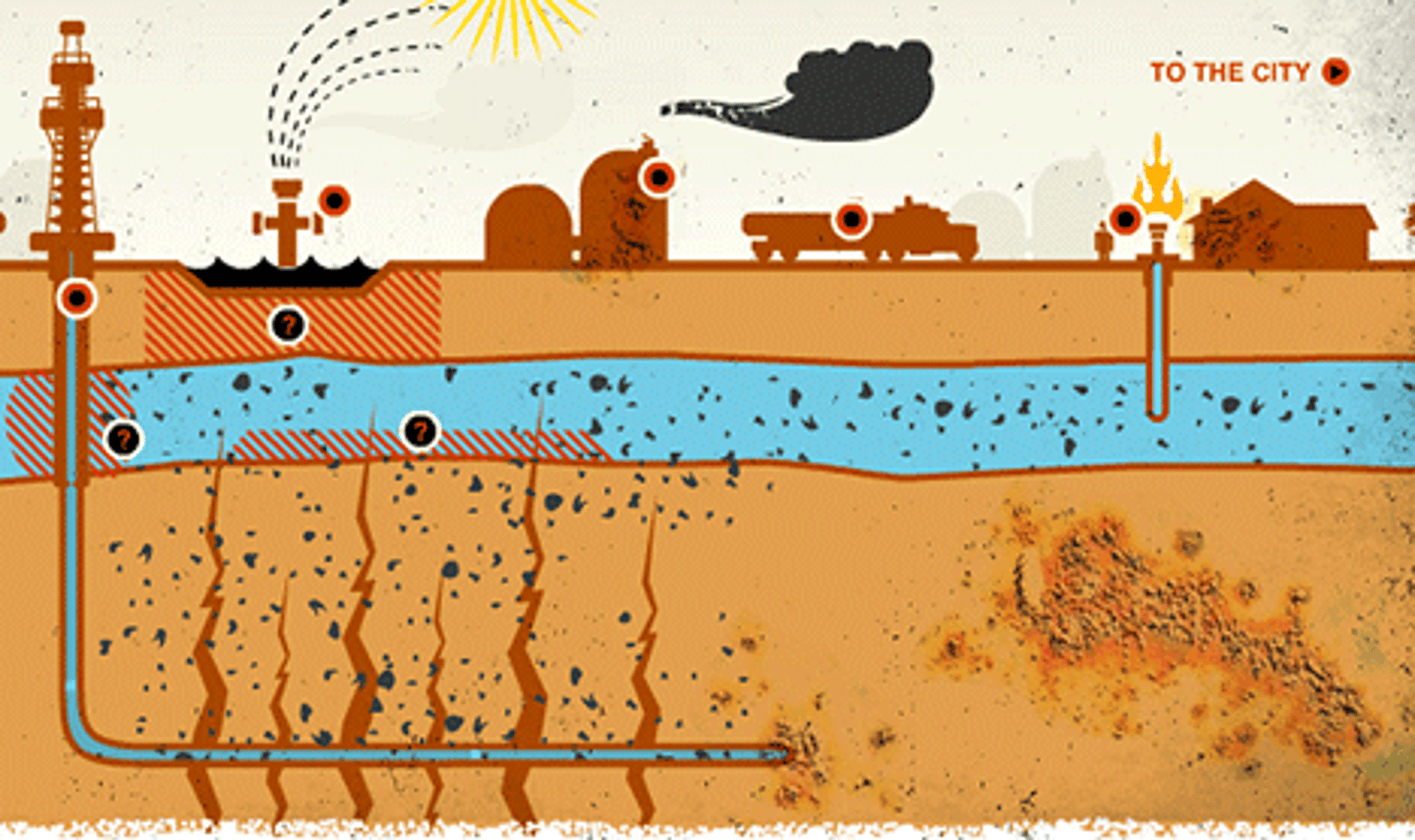
Fracking
this process (also known as hydraulic fracturing) involves injecting "water" deep into the ground to crack open the rock so that the natural gas trapped within the layers is released

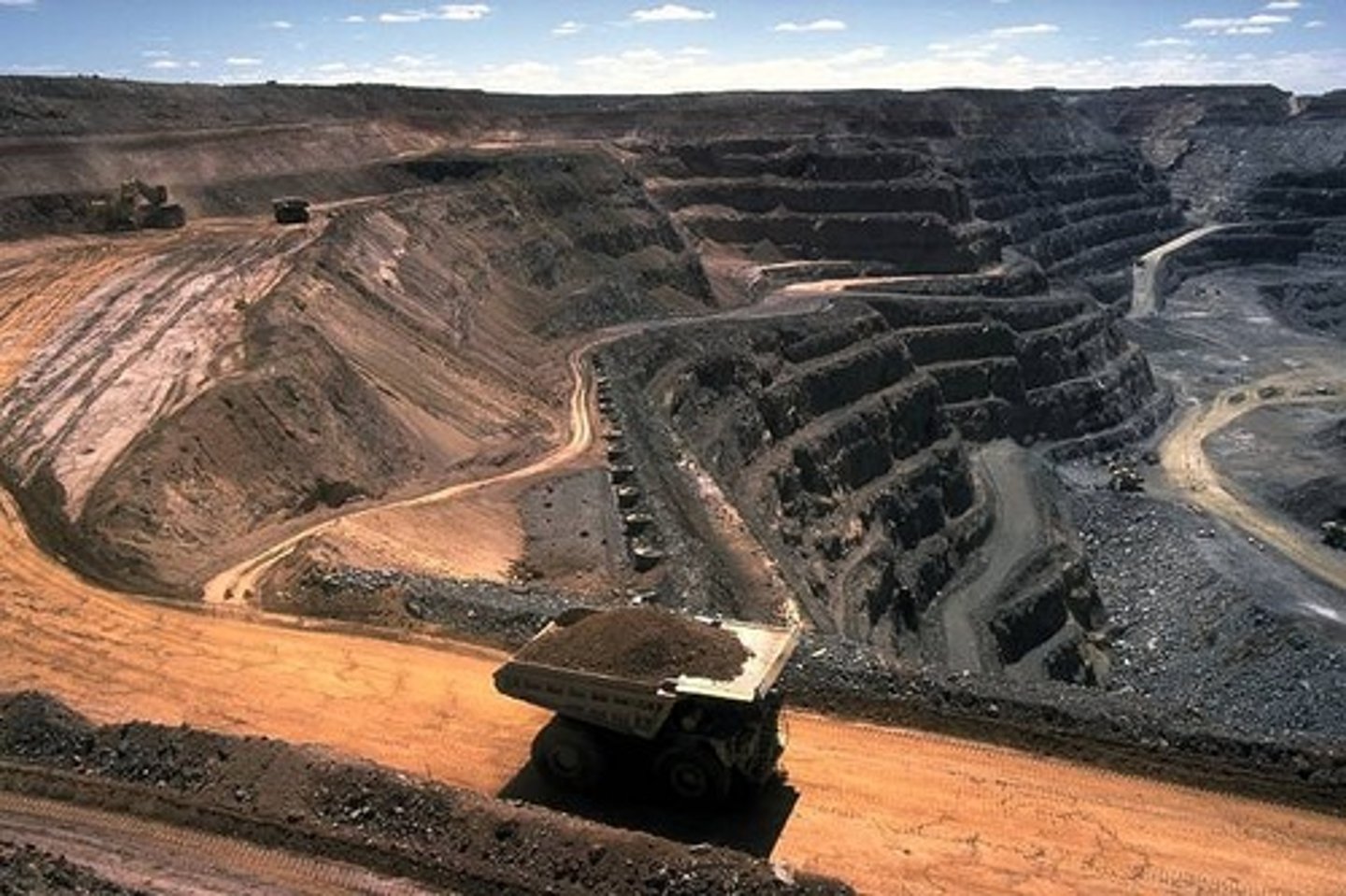
Mountaintop Mining
This type of coal mining involves removing the tops of mountains.
Strip Mining
This type of coal mining involves removing strips of coal at a time to gradually peel away layers that reveal the coal beneath

Petrochemicals
all of the many substances that can be created from petroleum

BP Deepwater Horizon
the largest oil spill in the US. Oil from the bottom of the Gulf of Mexico leaked into the Gulf for more than one month. Chemical dispersants were used to break up the spill into tiny particles
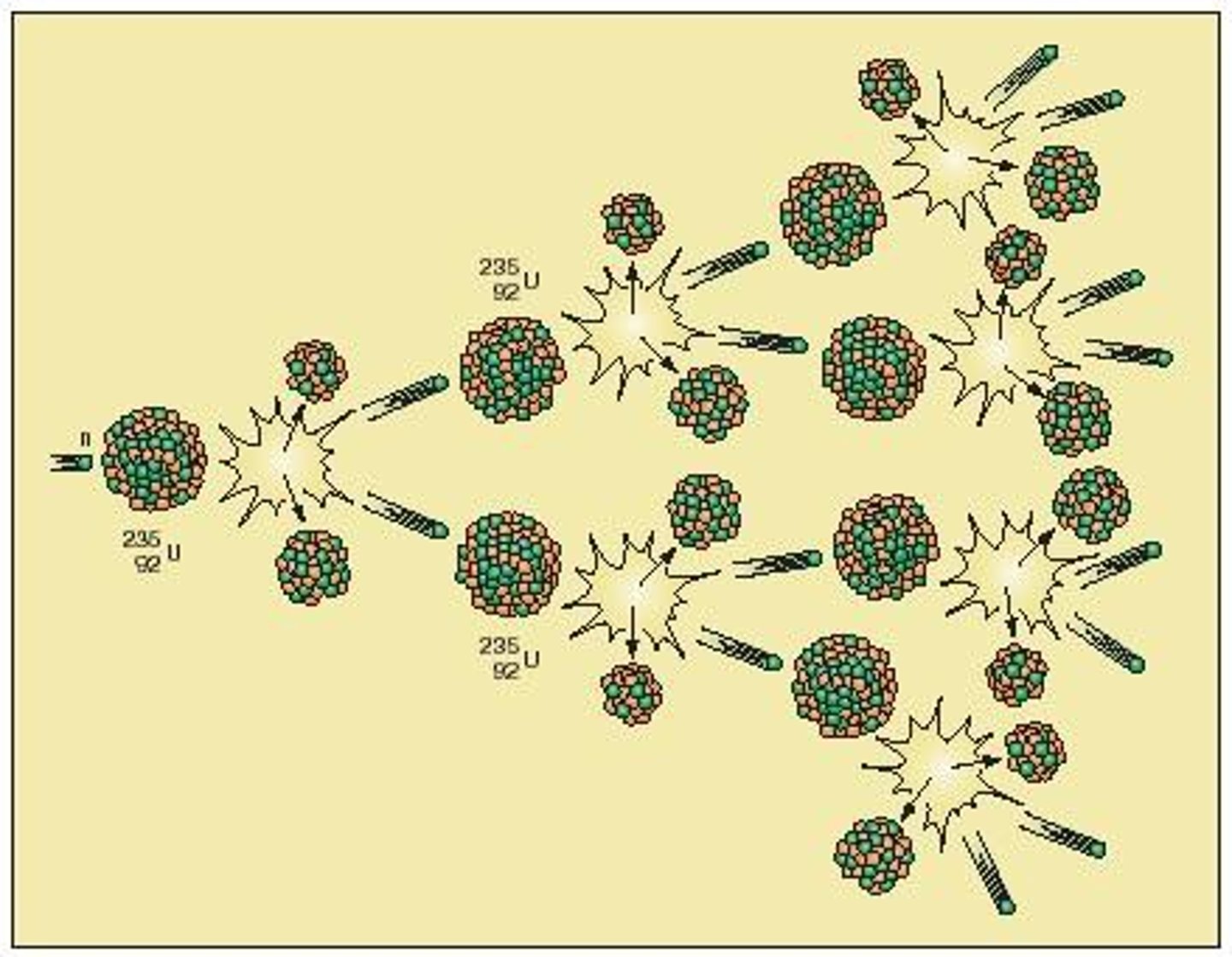
Nuclear Fission
the splitting of a uranium atom into 2 smaller atoms that generates large quantities of energy
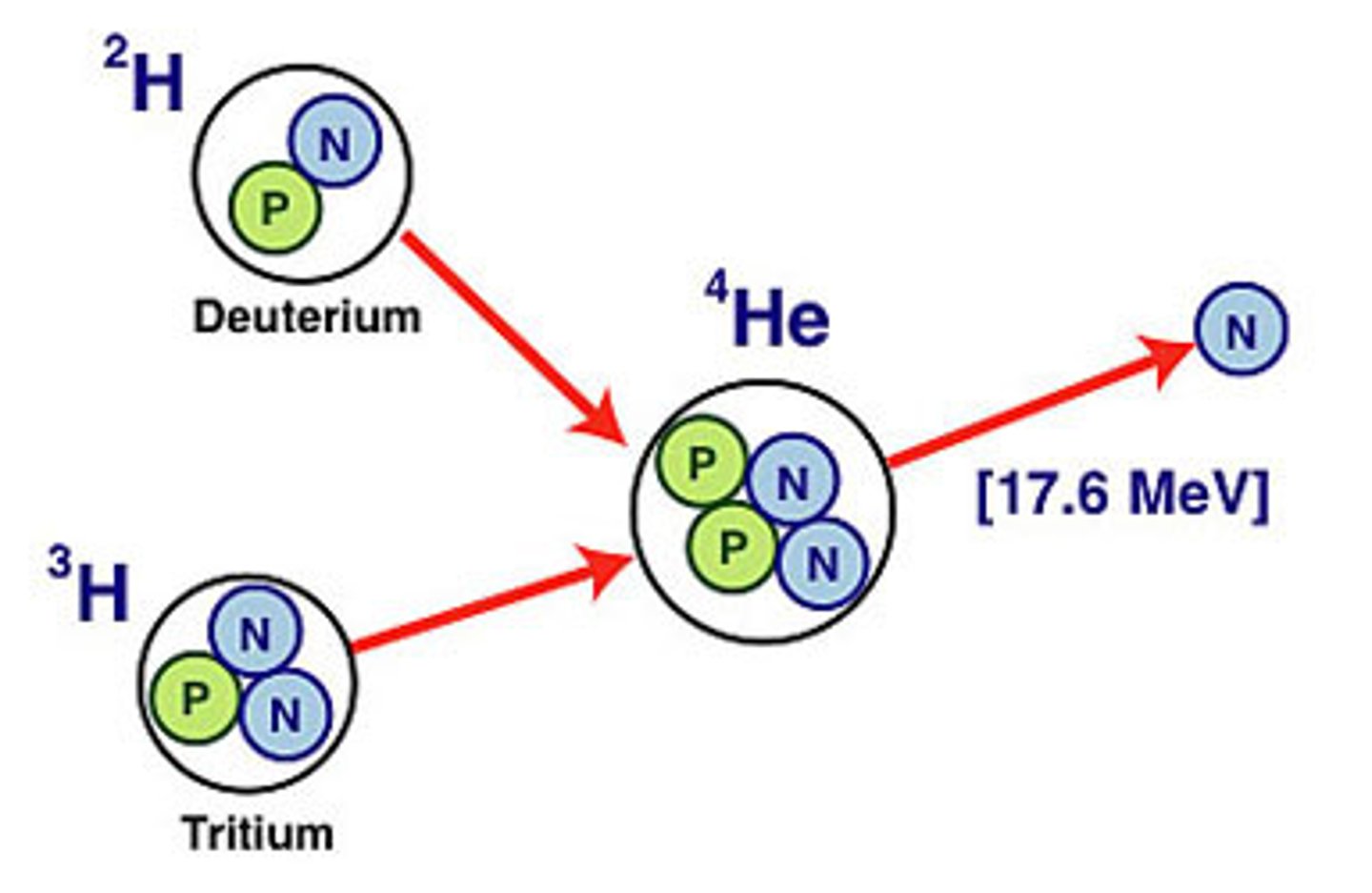
Nuclear Fusion
the process of combining two smaller atoms into one large atom. For example, stars combine two hydrogen atoms to create one helium atom and they glow with the energy created
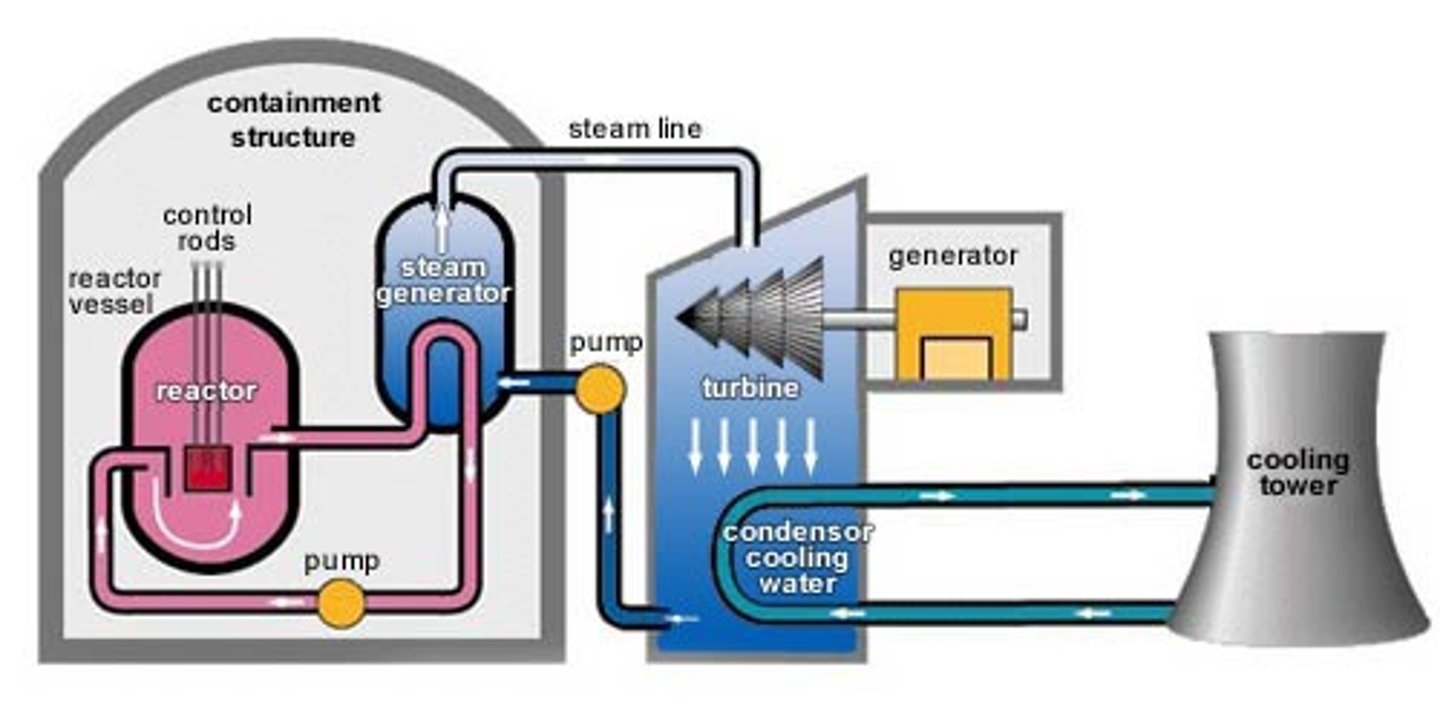
Nuclear Reactor
a facility that uses the energy from splitting uranium atoms to generate electricity
Fukushima, Japan
Site of a nuclear meltdown as a result of a tsunami that came onshore and flooded a nuclear powerplant
Chernobyl
Site of a nuclear meltdown in Russia
Three Mile Island
Site of a partial nuclear meltdown in the US

Solar Energy
using the energy from the sun to heat water, to make steam, to turn a turbine, to generate electricity

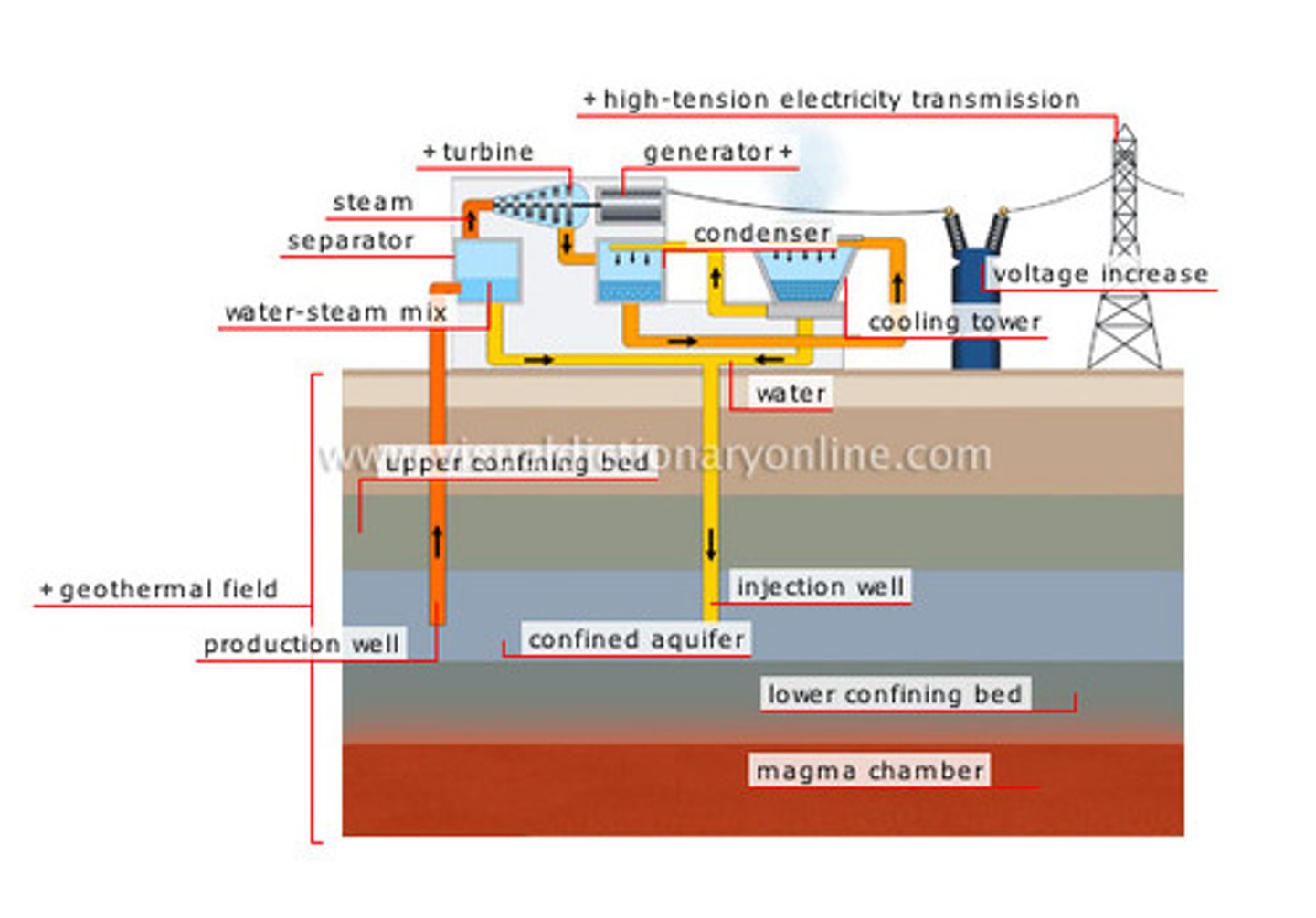
Geothermal Energy
using the energy from inside the earth (magma) to heat water, to make steam, to turn a turbine, to generate electricity
Hydroelectric Energy
using the energy of water falling over a dam to turn a turbine, to generate electricity

Tidal Energy
using the energy of the ocean tides to turn a turbine, to generate electricity

Wind Energy
using the energy of the wind to turn a turbine, to generate electricity

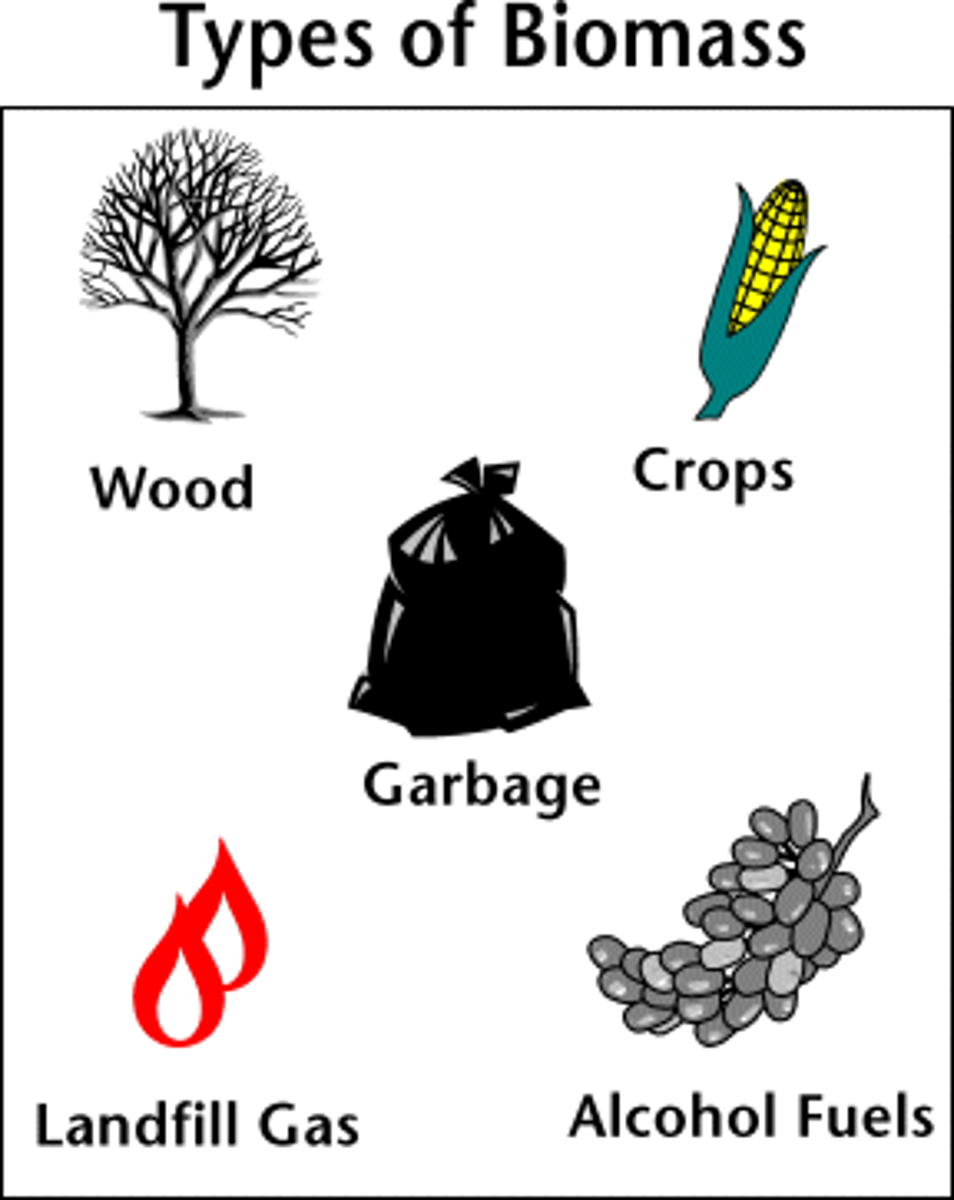
Biomass Energy
renewable energy that comes from an organic (once living) source. Could be from plants or even waste products.

Carbonization
conversion of an organic (once-living) substance into a carbon-based residue. this is how coal is formed
Crude Oil
naturally occurring, unrefined petroleum
Deforestation
the act of removing all trees from a forest
Fossil Fuels
fuel made from the remains of once-living organisms (coal, oil & natural gas are examples)
Fuel Rods
used in a nuclear reactor, typically made of Uranium 235
Mining
the act of removing valuable resources from Earth, consists of many different types
Radiation
form of energy given off during the decay of radioactive elements (namely uranium used as fuel in nuclear reactors)
Recycle
the process by which a substance is not discarded, but is used again - sometimes in a different way.
Organic
made of once living things (animals OR plants)