Biology - Chapter 11 FC
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
11.2
Cell division
process in which a cell divides into two new daughter cells
Chromosome vs. chromatin
Chromosome: threadlike structure within the nucleus that contains genetic info that is passed from generation to the next
Chromatin: substance found in eukaryotic chromosomes that consists of DNA tightly coiled around histones
11.4
Chromatids (sisters)
one of two identical “sister” parts of a duplicated chromosome
11.5
Centromere
region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
11.6
Cell Cycle (definition and phases)
Definition: series of events in which a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells
Phases: Interphase (G1,S,G2), Mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), and G0 phase
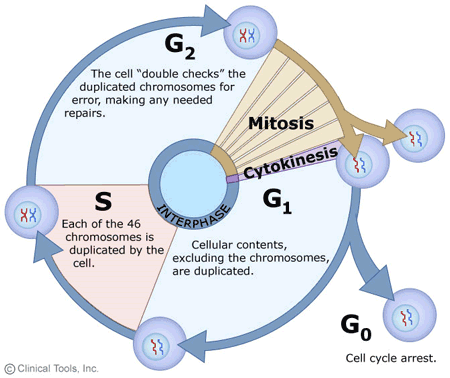
11.7
Interphase
period of the cell cycle in which the cell grows (cell spends most of time here)
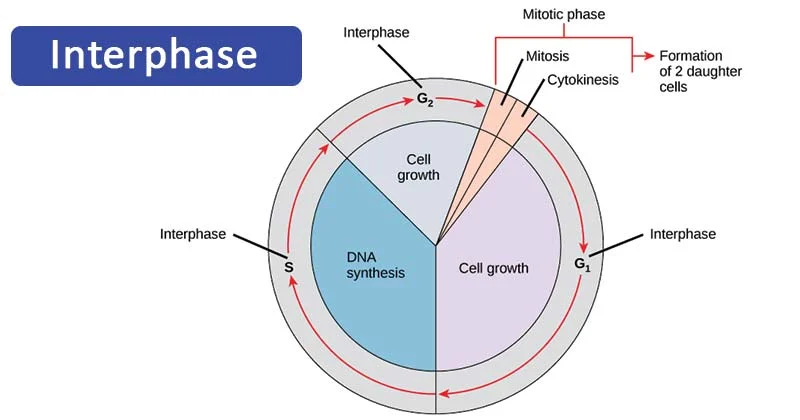
11.8
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cells division during which a cell nucleus divides
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
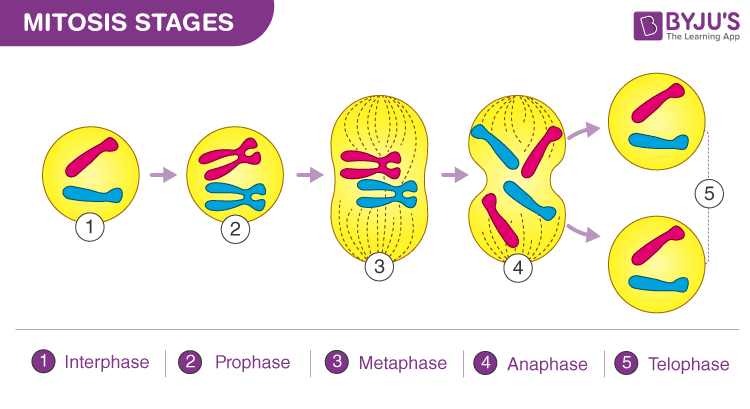
11.9
Prophase
first and longest phase of mitosis; genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the chromosomes become visible
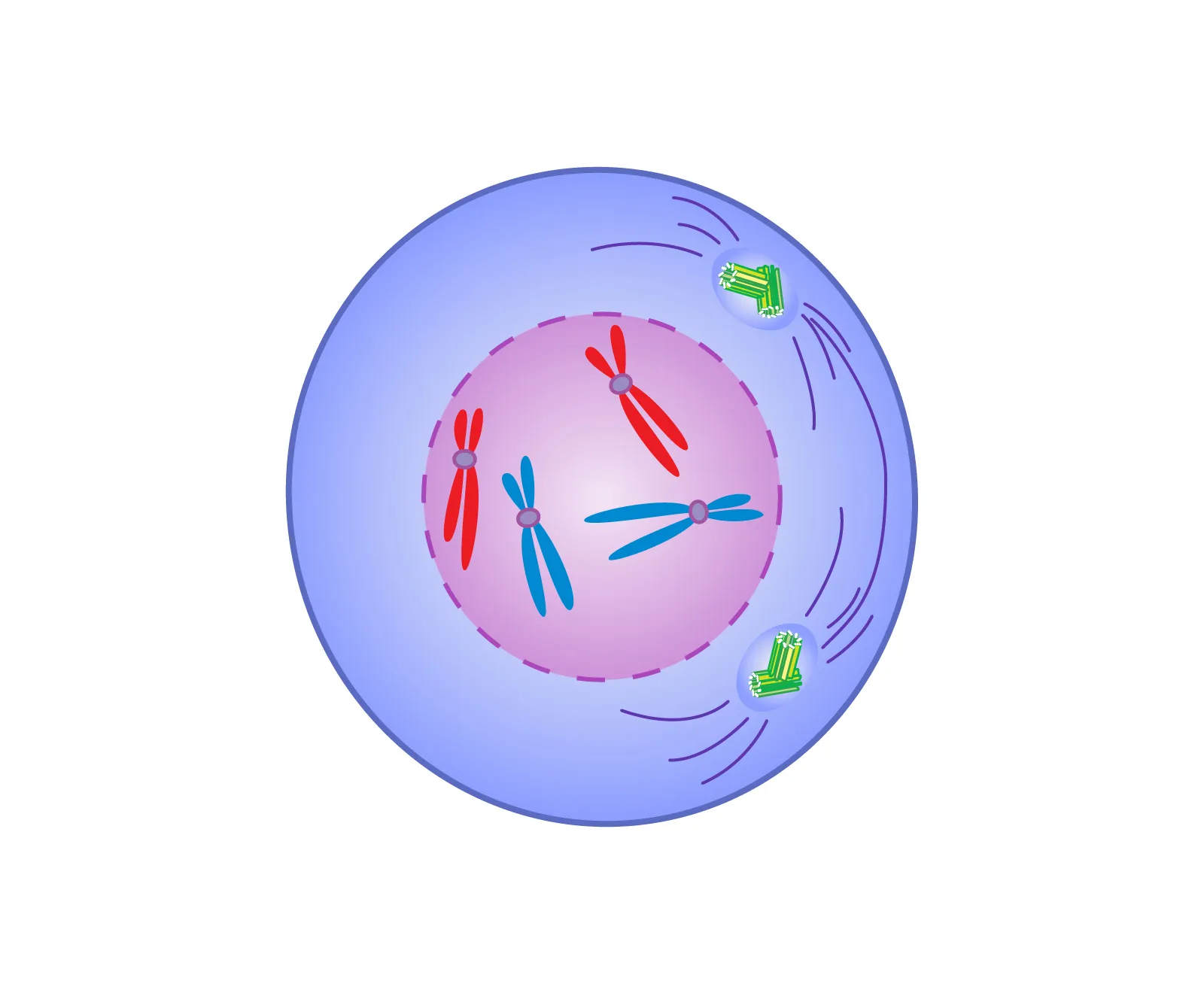
11.10
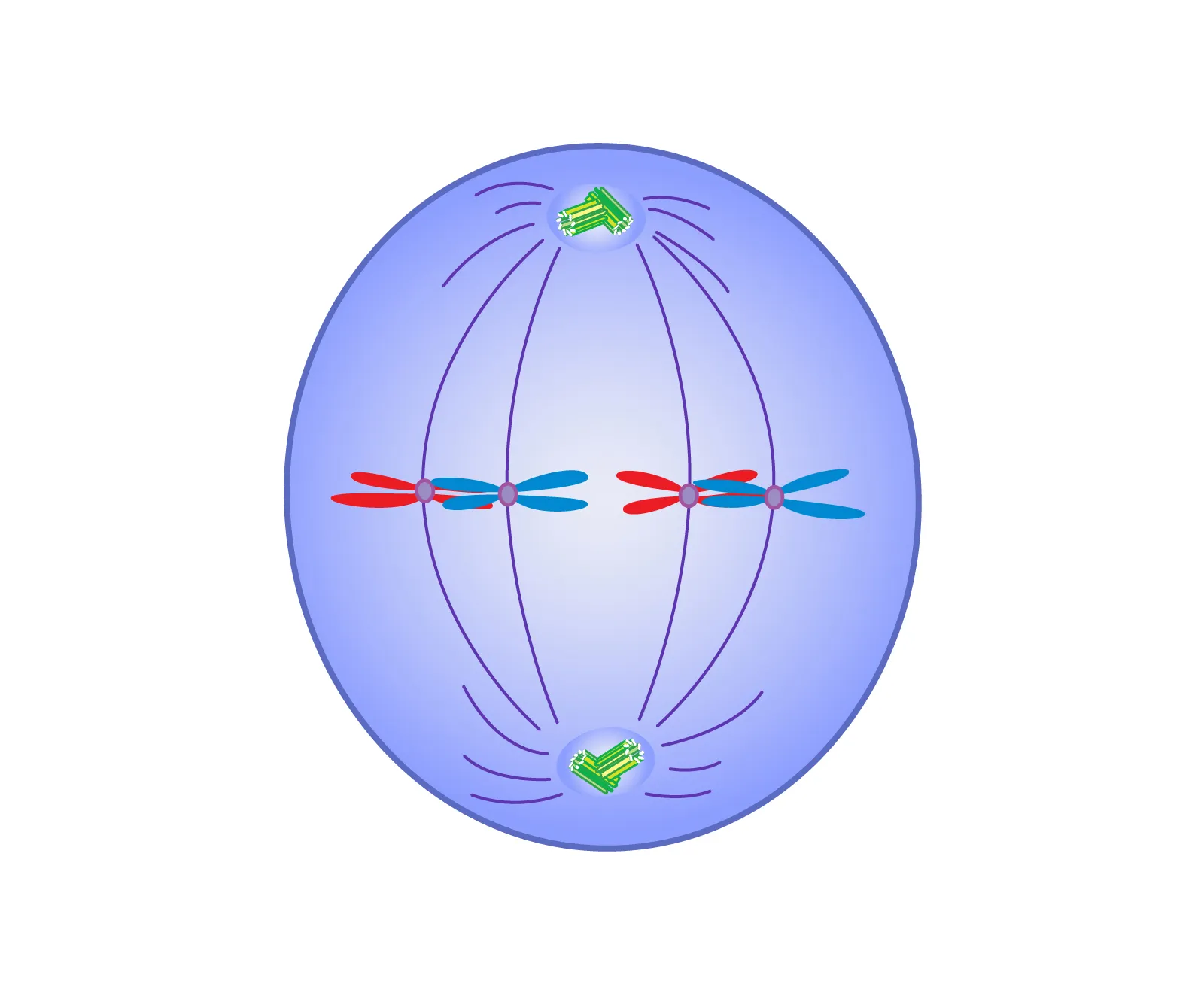
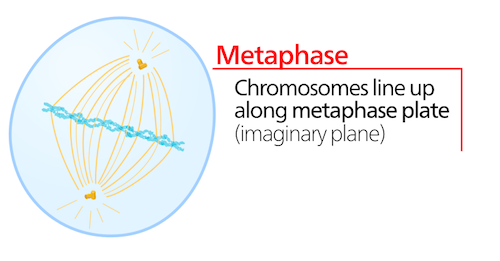
Metaphase
phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
11.11
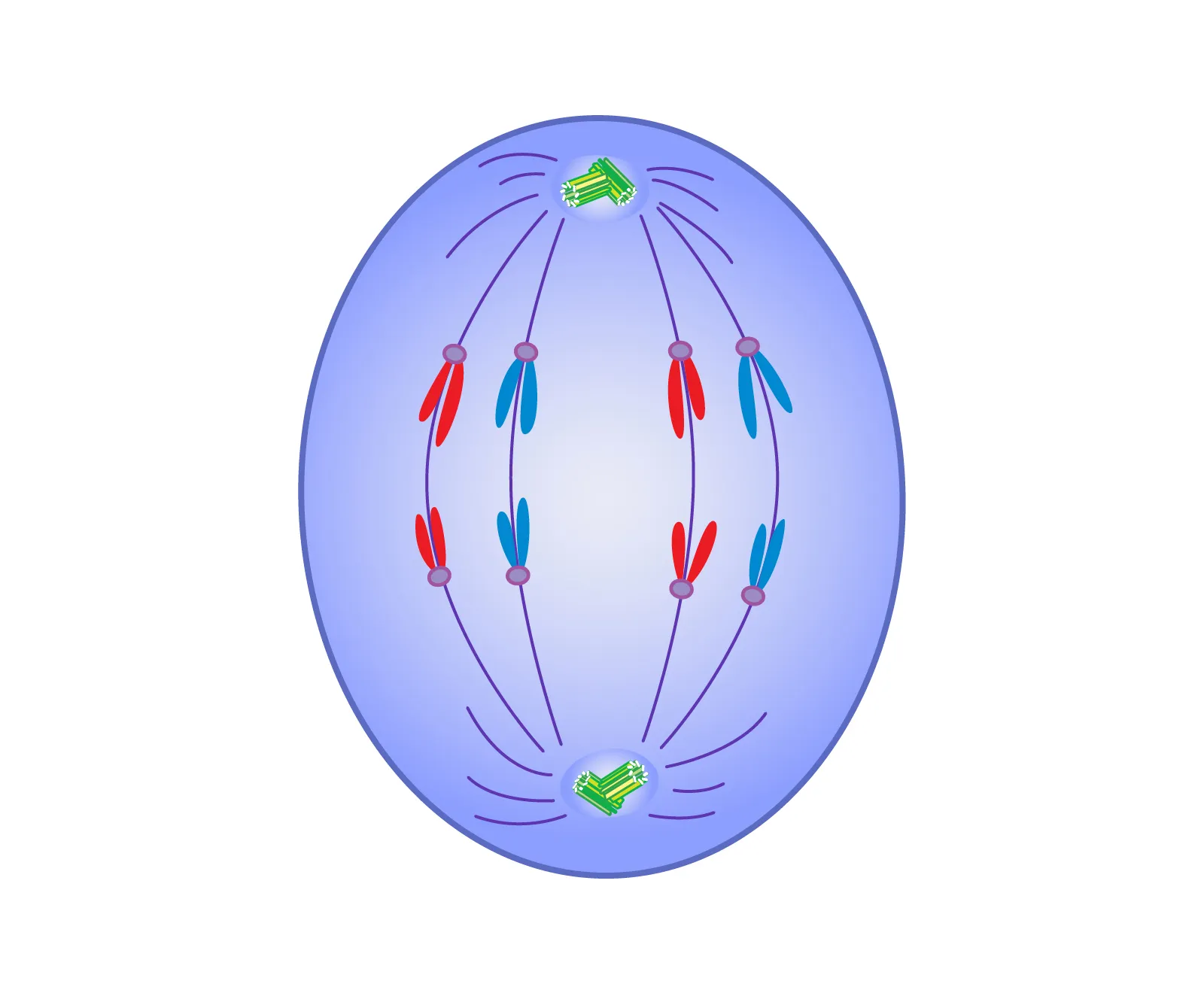
Anaphase
phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separated and move to opposite ends of the cell
11.12
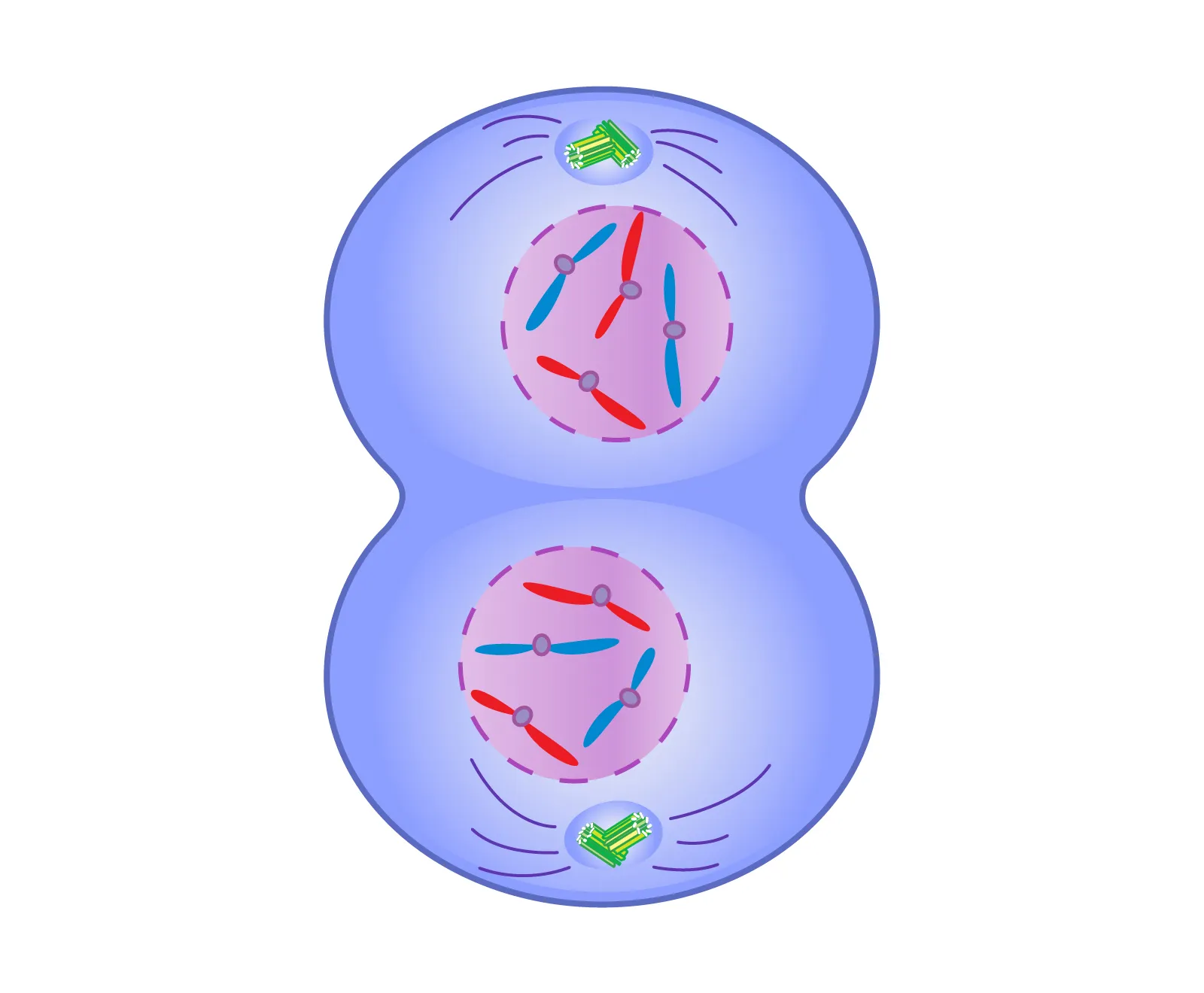
Telophase
phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin, cell starts to reform
11.13
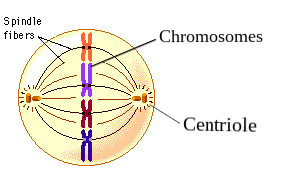
Spindle fibers
a protein structure that helps divide the chromosomes by pulling them to opposite ends
11.14
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
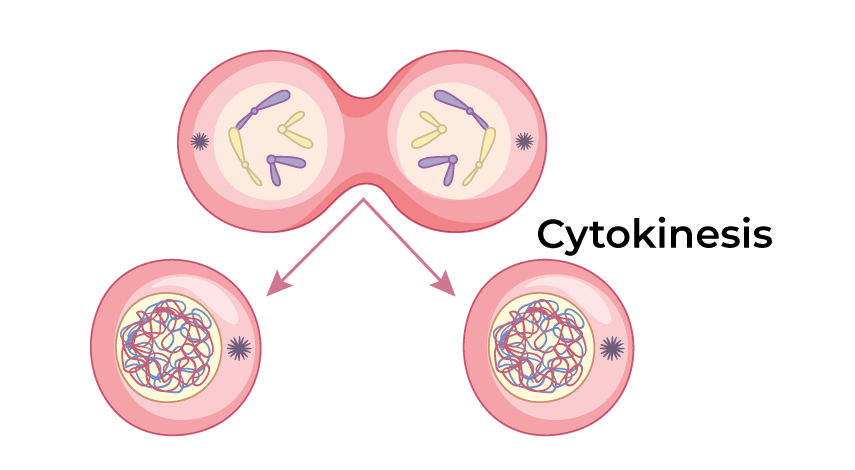
11.15
Metaphase plate/equator
the imaginary line that chromosomes line up on during metaphase
11.16
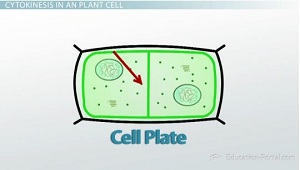
Cell plate
structure that forms when the cytoplasm of a plant cell divides
11.18
Internal regulators
Molecules within the cell, usually proteins such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent-kinases.
11.19
External regulators
Proteins that respond to events outside the cell, like growth factors and cell adhesion proteins.
11.20
Cancer
A term for diseases that shows abnormal cells divide without control and can divide nearby tissues
11.21
Tumor
An abnormal mass of tissue that forms when cells grow and divide more than they should or do not die when they should.
11.22
Apoptosis
form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death.
11.23
Centriole/centrosome
Centrioles duplicate in concert with chromosomes during the cell cycle
11.24
Sexual vs. Asexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves 2 parents, asexual only involves one (exact replica)