Physics 30 - Unit C: Chapter 13.1
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 13.1 - What is EMR?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
radiant energy that does not require a medium to travel.
produced by the acceleration of charged particles resulting in transverse waves of changing electric and magnetic fields.
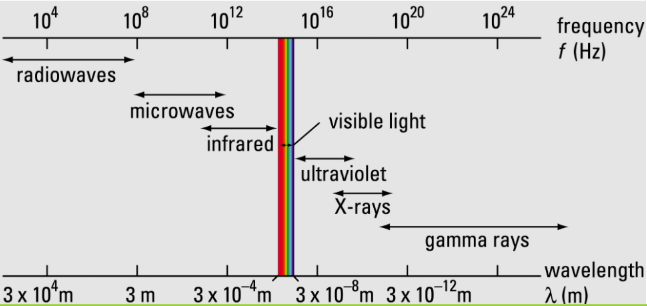
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
RMI → V → UXG
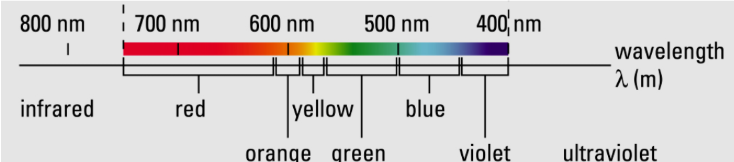
The Visible Spectrum
ROYGBV - (between 700nm - 400nm)
Transverse Waves
perpendicular waves
Propagation
the way waves or signals move through a medium or space.
it describes how energy or disturbances travel from one point to another.
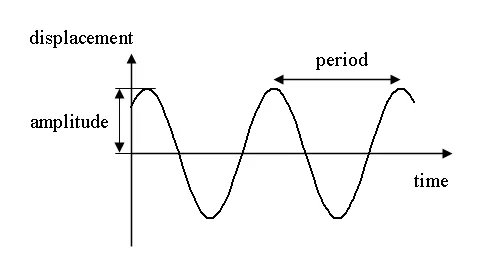
Periodic/Oscillatory Motion
a motion that repeats on a regular cycle
*IMPORTANT FACT ABOUT FREQUENCY*
frequency never changes once the waves leave the source vibration
Maxwell’s Electromagnetic Theory (1865)
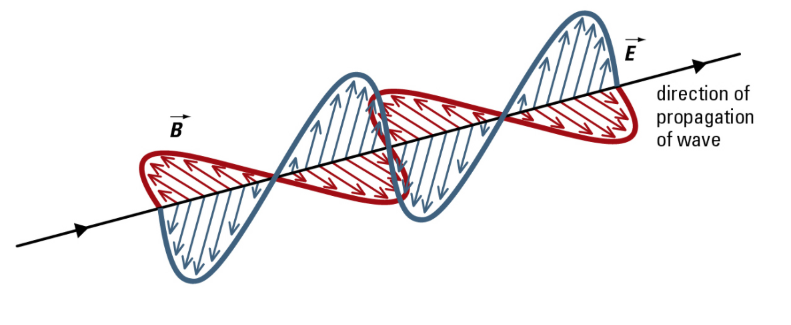
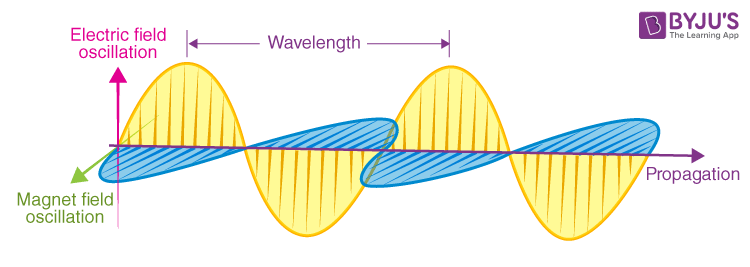
Maxwell proposed that EMR is an electromagnetic wave, which is made up of changing perpendicular electric and magnetic fields that regenerate each other.
Maxwell’s Property #1
Electromagnetic waves are produced whenever an electric charge is accelerating.
also determines the frequency (# of cycles per second of wave)
Maxwell’s Property #2
When the electric charge is accelerated in periodic motion, the frequency of oscillation of the charge will equal the frequency of the electromagnetic wave produced.
time for one period of blue wave = time for one period of yellow wave
Maxwell’s Property #3
All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light and obey the universal wave equation (c = f λ).
Maxwell’s Property #4
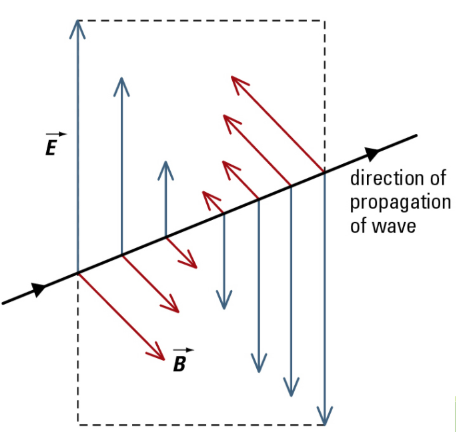
The oscillating electric and magnetic fields will always be perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
The electric and magnetic fields in a wave always move at right angles to each other and at right angles to the direction the wave is traveling
Maxwell’s Property #5
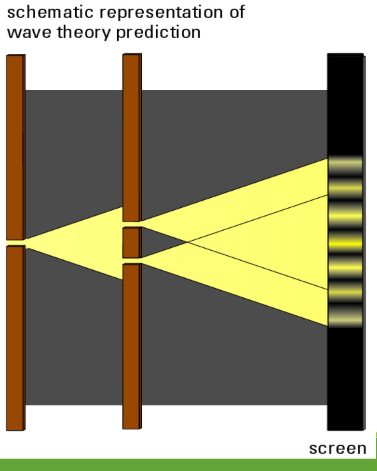
Electromagnetic waves should show all the phenomena associated with transverse waves:
interference
diffraction
refraction
polarization
Frequency Equation
Frequency (f) = number of times a wave or an oscillation repeats itself in one second
# of cycles in one second
Period (T) = amount of time it takes to complete one cycle
Frequency and Period are reciprocals of each other.
