Lecture 18: drug solubility and dissolution rate 3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what happens to weak bases and weak acids in the stomach?
a weak base has high dissolution rate in the stomach, dissolution rate falls as u continue down the GI
a weak acid has minimal dissolution in the stomach but its dissolution rate increases down the gut
what does the salt of a weak acid do to the pH of the diffusion layer
increases
what does the salt of a weak base do to the pH of the diffusion layer
decreases
the pH of the diffusion layer with free acid or salt
free acid: ph of bulk solution
salt: ph of salt
why does increasing the pH of a diffusion layer for a weak acid make it more soluble?
the salt of a weak acid increases the pH of the diffusion layer
this means that the acid can ionize and therefore is able to solubilise
this improves dissolution rate
why does decreasing the pH of a diffusion layer for a weak base make it more soluble?
the salt of a weak base decreases the pH of the diffusion layer
this means that the base can ionize and therefore is able to solubilise
this improves dissolution rate
what is cosolvency?
when 2 solvents are used in combination to increase the solubility of the solute
what is the purpose cosolvency?
a system where the drug solubility is higher than the aqueous solubility
improve stability of formulation
formulate higher concentrations of the drug
features of cosolvents:
organic compounds
miscible with water
better solvents than water for drugs due to low polarity
some solids are highly soluble in water
all polymers
what does hydrogen bond density give?
the amount of polarity of the solution
how do colsolvents decrease polarity of water?
they decrease the hydrogen bond density
reduces cohesive interactions of water
reduces polarity of the solution
We add cosolvents to water to make the solution less polar in order to increase the solubility of poorly water-soluble (hydrophobic) drugs.
what does reducing polarity do?
decreases:
surface tension
dielectric constant
solubility parameter
what is the formula for solubilisation by cosolvency?
the solubilisation slope increases with decreasing the polarity of the solvent
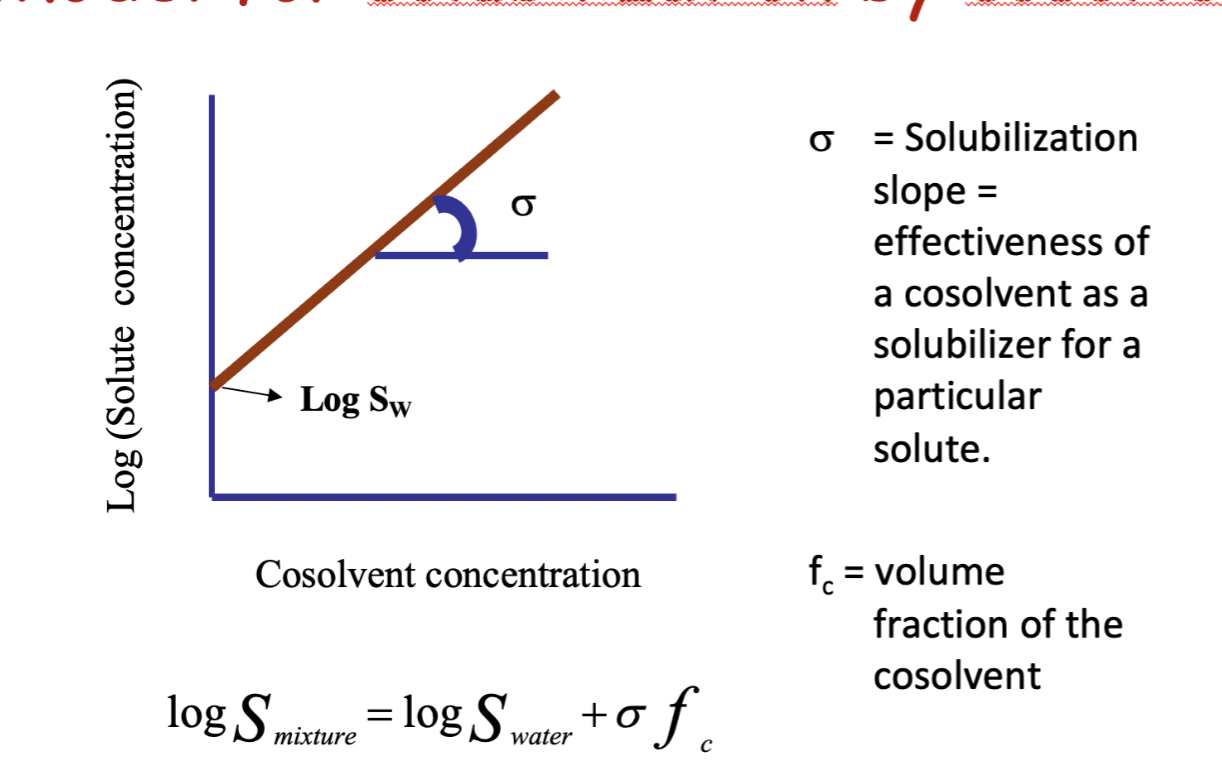
as the solute becomes more polar, cosolvency becomes less efficient, will eventually decrease solubility of a polar solute in water