Week 1 Nurs 307
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Week 1 Objectives
Interpret how the Healthy People 2030 objectives will improve the health and welfare of the pediatric population and their families.
Describe the role of the nurse in the care of the pediatric patient and the expanding family.
Analyze the central role of therapeutic care relationship in providing nursing care to pediatric patients in all care settings and situations.
Evaluate the impact of cultural, ethical, legal, gender, and economic issues related to the health care of pediatric populations and their families.
Healthy People 2030 5 Steps
Attain healthy lives, free from preventable diseases and afflictions, and early death
Eliminate health inequity and achieve health literacy for all
Create great environments that promote great health
Promote healthy development and behaviors
Engage leaderships key constituents
General Role as a Pediatric Nurse
Promote the health and well-being of the child and family!
Therapeutic Relationships, Health Teaching, Research & EBP, Coordination & Collaboration, Promoter of Family Centered Care, Advocate, Support & Counseling, and Mandated Reporter
Family-Centered Care
Enabling
create opportunities
Empowerment
sense of control
foster strengths & abilities & actions
Family is a constant in child’s life —> taking care of the needs of the family members in relation to the care of the child is key
What is Family?
A family is what an individual considers it to be!
most family’s are consanguineous
Consanguineous, Affinal, Family of Origin
Blood Relationships
Marital Relationships
Family Unit someone is born into
Communal Families, Single-Parent, Homosexual families
Use the term “Household” for better description
Family Stress Theory
Stress = inevitable
Stressors can be expected or unexpected
Explains the reaction of a family to stressful events
Offers guidance for adapting to stress
Developmental Theory
Family = small group that interacts with the larger social system
Emphasis on similarities and consistencies in how families develop and change
Duvall’s family life cycle stages to describe changes a family goes through over time
how the family functions in one stage, directly affects how the family will function in the next stage
Duvall’s Family Life Cycle
Parenting Styles
Authoritarian, Authoritative, Permissive, Ignorant
Authoritarian
Focus on obedience, and punishment, instead of discipline
Authoritative
Create positive relationships, enforcing rules
Permissive
Has rules but does not enforce rules
‘kids will be kids’
Uninvolved
Little to no guidance, nurturing, or attention
Limit Setting & Discipline
establishing rules/guidelines for behavior &
to teach or a set of rules that govern conduct
the action taken to enforce rules after non-compliance
implementing discipline
consistency, timing, commitment, unity, flexibility, planning, behavior-orientation, privacy, termination
textbook pg 21
Childhood Injuries
Deaths by total (high to low):
Motor Vehicle (decreased)
Suffocation (increased)
Drowning (decreased)
Poisoning (decreased)
Burns (decreased)
Fall (increased!)

The Child in the Community: Nursing Care provided in
health centers, outpatient clinics
wellness centers / homeless shelters
schools, child care centers, homes
The Child in the Community: Nursing Role in these capacities
direct care
education and assessing for risks of infection, other health risks
promoting G/D
information about community resources for wellness
Influences on Children and Families
Poverty/Homelessness
Stress: positive or negative
Sedentary life / Lifestyle influences
Injury prevention: equipment, etc
Environments: School, family, community, culture
Tattoos/Body Art
Other Influences on Child Health
SOCIAL MEDIA / MASS MEDIA
race/ethnicity
parental education
land of origin and immigration status
religion and spiritual identity and culture
Child Maltreatment
Intentional physical abuse or neglect, emotional abuse or neglect, and sexual abuse
Child Neglect
Most common maltreatment
Failure of a parent to provide for their child’s basic needs
Physical Abuse
Deliberate infliction of physical injury!
each state defines this differently*
Abusive Head Trauma (AHT) — Shaken Baby Syndrome
Emotional abuse/neglect
Abuse through intentional or unintentional emotional hurt
Sexual Abuse
Devastating Type of Maltreatment
Incest, Molestation, Exhibitionism, Child Pornography, Child Prostitution, Pedophilia
Risk Factors for Child Abuse and Neglect
Factors for Physical Abuse
Poverty
Violence in Family | Parents were abused as children | Substance Abusers | Social Isolation
Prematurity/Low Birth weight | Younger than 3 y/o
Unrelated male primary caretaker
Child disability or condition that needs big gear
Factors for Sexual Abuse
Absence of natural father or having a stepfather
Being a female
Mother’s employment outside of home
Poor relationship w/ parent | Relationship with conflict
Parental substance abuse or social isolation
Nursing Management for Abuse
Protect from further abuse
Support the child and family
Prevent Abuse
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Deveopment
Sensorimotor
Pre-operational
Concrete Operational
Formal Operational
Sensorimotor
0-2 Years
Infant explores world through direct sensory and motor contact
Object permanence and separation anxiety develop during this stage
Preoperational
2-6 years
Child uses symbols to represent objects but does not reason logically!
Ability to pretend, and egocentric forms
Concrete Operational
7-12 years
Logical thinking begins about concrete objects
Can add and subtract
Conservation understanding increases
Formal Operational
12 years - Adult
Abstract thinking and hypothetical terms used
Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development
In this stage of development, when needs are met —> consequence is healthy, if not med, it is unhealthy
Trust vs Mistrust
0-1 year
Hope, basic needs being met
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt
1- 3 years
Will
Develop a sense of independence
Initiative vs Guilt
3 - 6 years
Purpose
Take initiative on some activities, can get guilty
Industry vs Inferiority
7 - 11 years
Competence
Develop self-confidence or sense of inferiority depending on if needs are met
Identity vs Role Confusion
12 - 18 years
Fideltity
Experiment with identity and roles
Intimacy vs Isolation
19 - 29 years
Love
Establish intimacy and relationship with others
Generativity vs Stagnation & Integrity vs Despair
30 - 64 yeras
64+ years
Care and Wisdom
Contribution to sciety and make life have meaning
Atraumatic Care (Stages)
Helping different development stages through trauma care
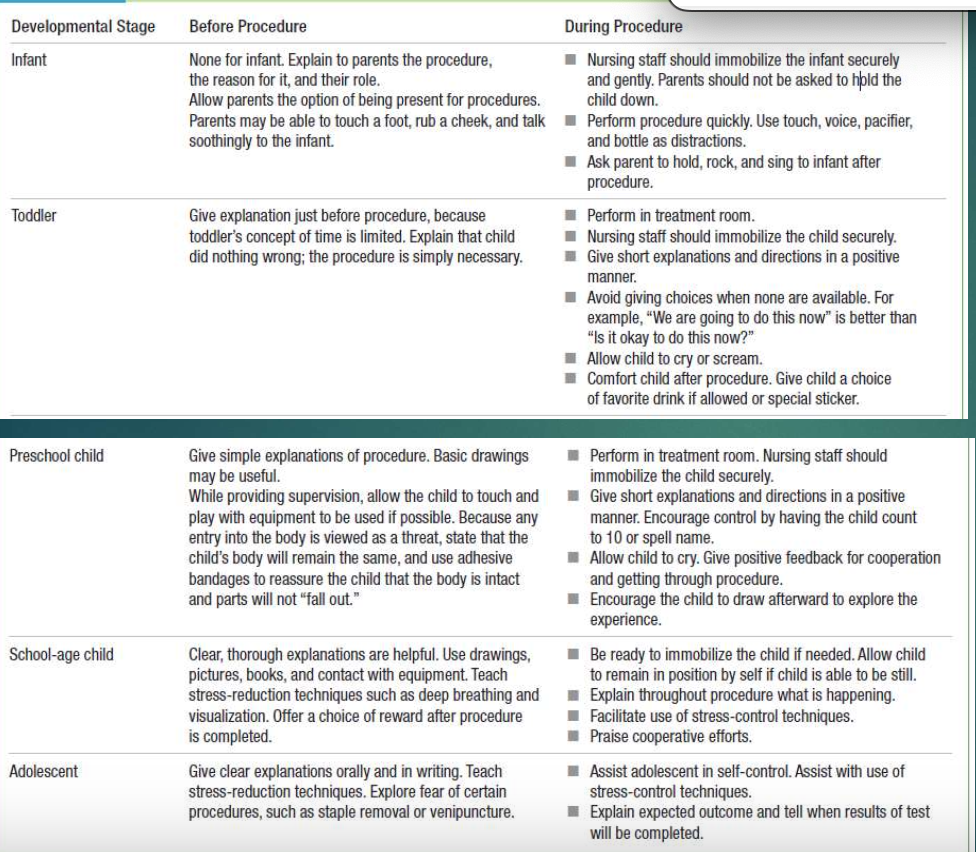
Atraumatic Care: Infant
Before Procedure
talk to parents, and keep them involved throughout the whole thing (optional)
During Procedure
secure and immobilize the infant, safely, parent is not doing it
Perform quickly
Parent can hold and rock infant post-procedure
Atraumatic Care: Toddler
Before Procedure
give explanation right before procedure
Child did nothing wrong!
During Procedure
immobilize and secure safely
stay positive
Do not give “options” when options are available
Allow child to cry and scream
Offer favorite drink or sticker post-procedure
Atraumatic Care: Preschool Child
Before Procedure
Give simple explanations of procedure, basic drawings good
With supervision, let child touch and play with equipemtns (if able)
use adhesive tape, ensure body stays together
During Procedure
immobilize and secure safely
stay positive, have child count to 10
let them cry
encourage them to cry, offer treats
Atraumatic Care: School-Age Child
Before Procedure:
clear, thorough explanations are helpful (drawings, pictures, contact w/ equipment)
Teach deep breathing
offer a choice reward for post-procedure
After Procedure:
immobilize if needed, if they can be still let them
explain what is happening
use stress-control techinques
praise them!
Atraumatic Care: Adolescent
Before Procedure:
give clear explanations orally and in writing
teach stress-reduction techs
explore fear and discuss
During Procedure
Assist in self-control
Explain outcome and tell when results will be sent
Communication with Parents
Encourage parents to talk
Direct the focus
Listen and have cultural awareness, use silence if needed
be empathic
provide anticipatory guidance
avoid blocks to communication
Communication with Children
Consider the cognitive develpoment stage
play
be creative
Physical Assessment on Children
Review ATI chapter 2
Focus:
order of assessment
age-appropriate approaches to various parts
Gross motor milestones
Fine motor milestones
Language development for age
Key Points of the Assessment
Always Ask:
what’s going on?
what’s it going to look like?
how will i intervene?
Assessment is not in order, it is circular!
Assess, assess, assess!
Trend assessments: even slight changes make a difference!
Pain Assessment and Management
Age of Child
Box 5.1 (book)
Response to pain @ different ages
Pain Rating Scales
table 5.1 & 5.2 (book)
NIPS, FLACC, Faces/Wong-Baker
Interventions
Pharmacological
page 123-124 (book)
PCA Pump
Non-pharm/Complimentary
page 121
Health Promotion of Peds
Newborn, Infant, Toddler, Preschoolers, School-Age, Adolescent
Newborn: Adjustment to Extrauterine Life
Birth - 1 Month
Resp
Chemical, thermal, and tactile stimuli help w/ first breath
Circulatory System
changes to allow blood to flow through lungs
Closure of stunts! (PFO, PDA)
Thermoregulation
Quickly dry and place skin to skin w/ mom!
Warm, dry blankets
Infant Eval @ Birth
Table 7.1
APGAR @ 1 and 5
Measurements
Head: 33-35.5cm
Weight: 10% loss by day 3 or 4, 2 weeks = return, 6-9 lbs
Length: 48-53cm
Useful info for Newborn Health Promotion
Box 7.1 - Stool Patterns
Fig 7.6 - Sutures and Fontanels
Table 7.2 - Newborn Reflex
Table 7.3 - Newborn Sleep
Box 7.5 - Successful Breastfeeding
The Infant: Growth
Birth - 12 months
Physical development
RAPID!
Weight 2x = 5 months
3x = 12 months
dentition
X months - 6 months = # teeth
Table 9.1 MILESTONE! (STUDY)
Cognitive Development
Sensorimotor
Stimulation from surroundings
Stranger and Separation anxiety, attachement
Psychosocial Development
Erikson Trust vs MIstrust
Solitary Play
Nutrition
breastfeed/formula, progress to solids 4-6 months
iron-fortified form
nutrient-rich foods!
page 305 — Feeding During the First Year
H/H and Lead screening @ 12 months
Dental Health
good feeding practices
smear of toothpaste (once teeth there)
dental home by 1 year
Injury
falls, burns, MVA, drowning, choking, suffocation, strangulation
Teach injury prevention to parents!
Infant Milestones TABLE 9.1
The Toddler: Growth and Development
1 to 3 years
Physical Development
rate of growth slows by age 2 weight 4x
4-6 lbs/year
body proportion changes
Cognitive Development
Preoperational
Language development
Psychosocial Development
autonomy vs shame and doubt
Parallel play!
Nutrition
may breastfeed
introduce cow’s milk (WHOLE!) and the limit amount consumed
picky eaters: QUALITY > QUANTITY
decrease caloric need
Dentition
Deciduous teeth good by 3 years
early childhood caries, by 1 year, should visit a dentist by then
Normal Changes in G&D
Table 11.1
Toilet training, sibling rivalry
temper tantrums, regressions
Injury
Table 11.2
The preschooler: Growth and Development
3-6 years
Physical Development
Growth in long bones, becoming more slender
4-6 lbs/pyear
Cognitive Development
Preoperational Stage
Table 4-16 (p.89)
Psychosocial Development
Initiative vs Guilt
Associative play, dramatic play
Nutrition
1-2% milk, teach normal food intake
decrease snacks
involve child in prep
Dentition
Education of good dental habits
Fluorinated toothpaste can be introduced
Normal Changes in G&D
Table 12-1
Preschool and kindergarten experience
Injury
MVA, pedestrian, drowning, burns, needle sticks, electrical
Teach prevention
School Age: Growth and Development
6-12 years
Physical Development
Boys and girls comparable in size/proportions
slow but steady growth
females preceding males in height
prepubescence
sexual awareness
Cognitive Development
concrete operational
conservations of altered forms
Psychosocial Development
industry vs inferiority
cooperative play (reliance on rules), team play
self-esteem, body image, sexuality
Nutrition
encourage balanced diets
take note of growth spurts
prevention/education of DM type 2
Dentition
loss of deciduous teeth commences
maintenance of good hygiene and practices
Normal Changes in G&D
table 14.1
school experiences
Injury
MVA/vs bike/vs pedestrian
firearms, burns, assault
Table 14.2 & FCC boxes on page 415
The Adolescent: Growth and Development
12 - 18
Physical Development
puberty/sexual maturity
box 15.2
girls 10, boys 13
Cognitive Development
formal operational
abstract thinking, critical thinking
Psychosocial Development
identity vs role confusion
sexual confusion
risk for depression
substance abuse
Nutrition
need for well-balanced diet
limit refined sugars and high fat foods
assess for any presence of eating disorders
Dentition
risk for damage from tobacco use and drugs
need for fluoridated water
dental care / maintenance
Normal Changes in G&D
Table 15.1
Injury
MVA, sporting injuries, drowning, box 15.3
intentional injury
Vital Signs for Infant (Birth to 1 year)
T
3 months = 99.5F / 37.5 C
6 monhts = 99.9F / 37.7 C
P/HR
110 - 160/min (newborn)
90 - 160/min (infant)
RR
30-60/min @ birth to 4 weeks
25-60/min @ 1 month - 1 year
BP
85/50 @ 1month - 1 year
64/41 @ Birth to 4 weeks
Vital Signs for Toddler (1 - 3 years)
T
1 year = 99.9F
3 year = 99.0F
HR
80 - 140/min
RR
25-30/min
BP
85-91/37-49
Vital Signs for Preschool (3 - 6 years)
T
5 year = 98.6F
P/HR
70 - 120 min
RR
20-25/min
BP
89-98/46/54
Vital Signs for School Age (6 - 12 years)
T
7 year = 98.2 F
9 -11 year = 98.1 F
P/HR
60-110/min
RR
20-25/min
BP
94-106/55-62
Vital Signs for Adolescents (12 - 18 years)
T
13 year = 97.9 F
P/HR
50-100/min
RR
16-20/min
BP
120/80
Sexual Maturation in Boys
1- Testicular Enlargement
2 - Pubic Hair Growth
3 - Penile Enlargement
4 - Axillary Hair Growth
5 - Facial Hair growth
6 - Vocal changes
Sexual Maturation in Girls
1- Breast development
2- Pubic Hair Growth (may occur before breasts)
3- Axillary Hair Growth
4- Menstruation