lab 2 exam structures-- neuroanatomy
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
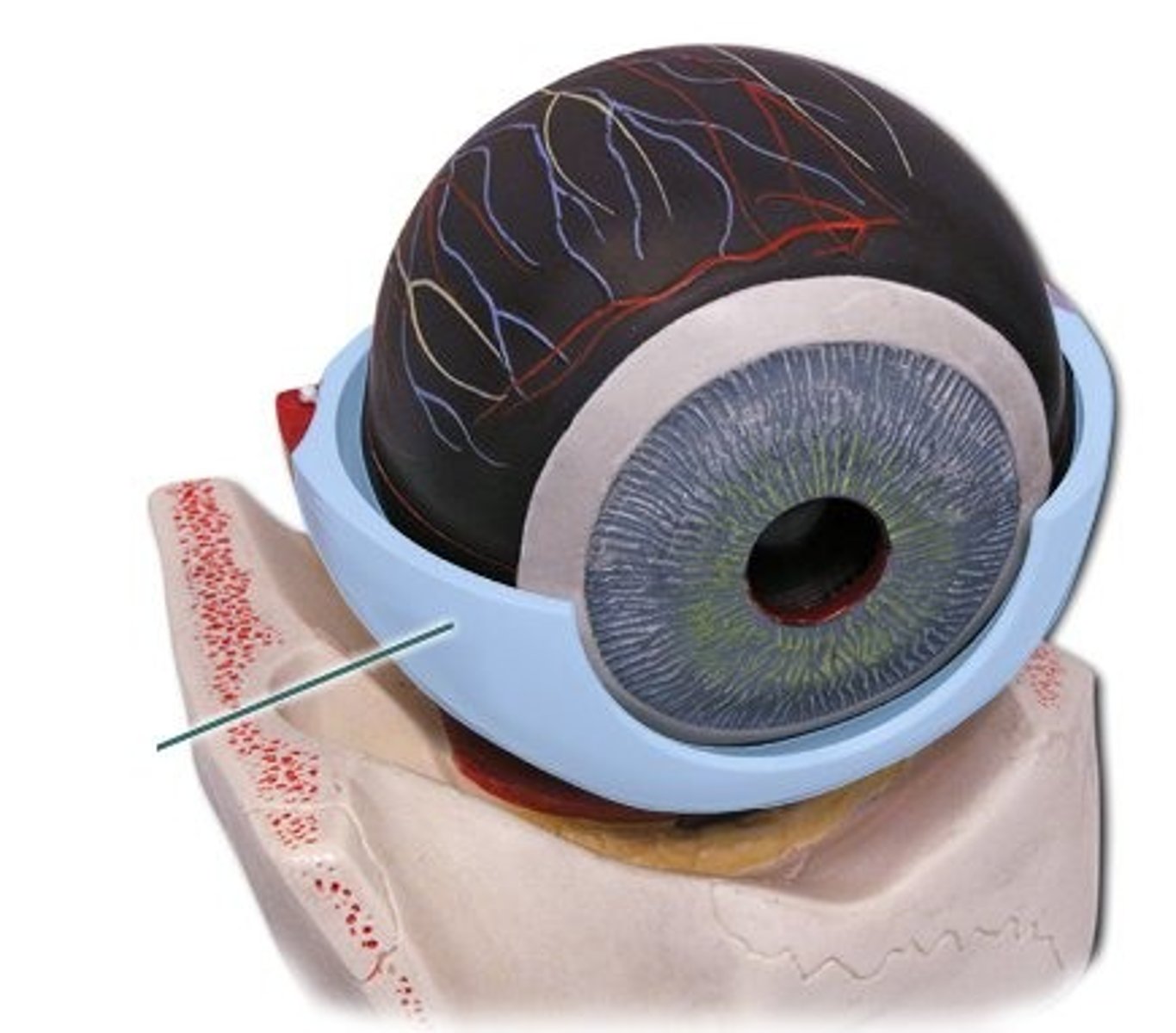
sclera-- white of the eye that provides structure
cornea-- directs light rays into eye and focuses light on retina
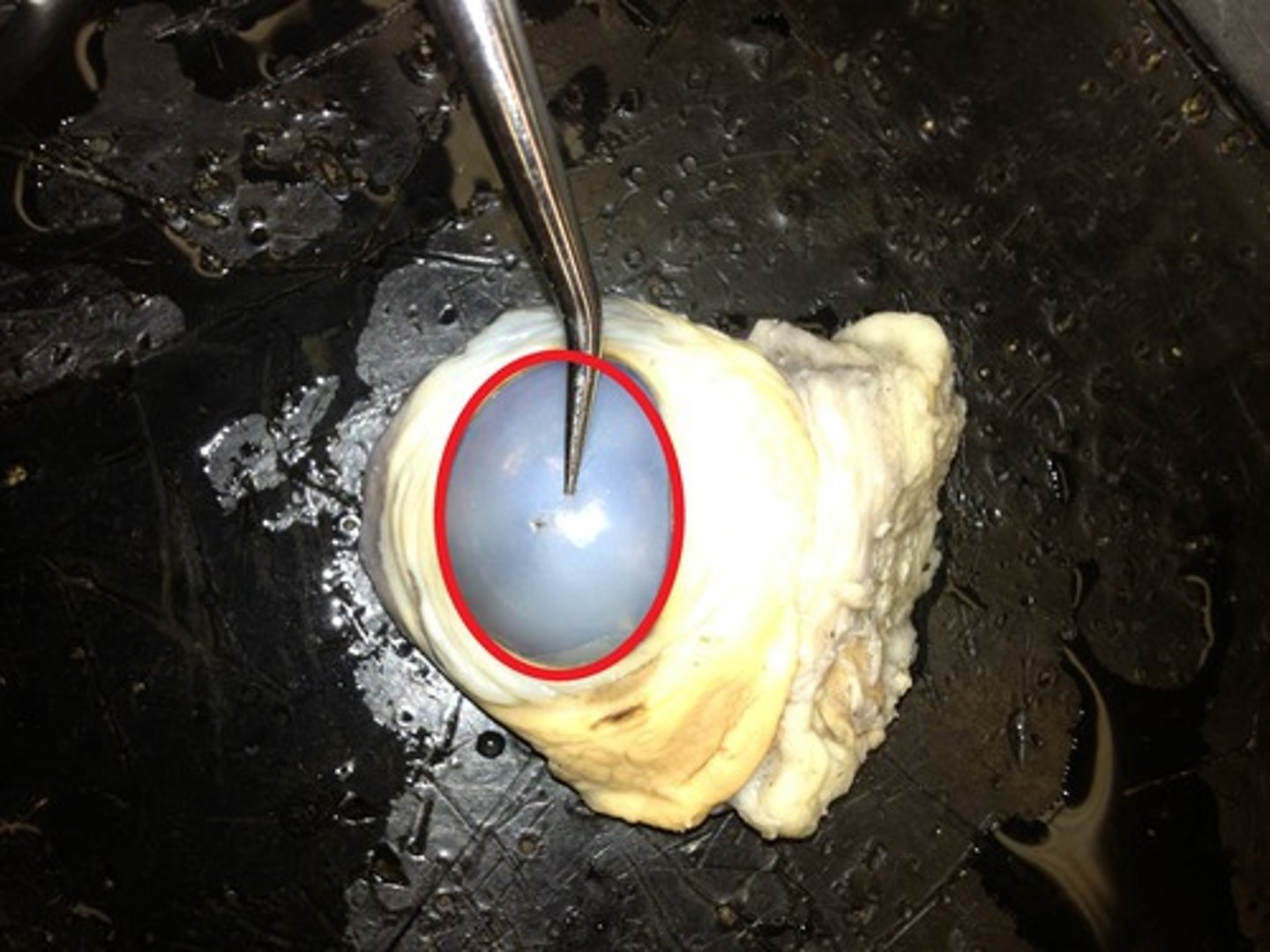
lens- Focuses light onto retina
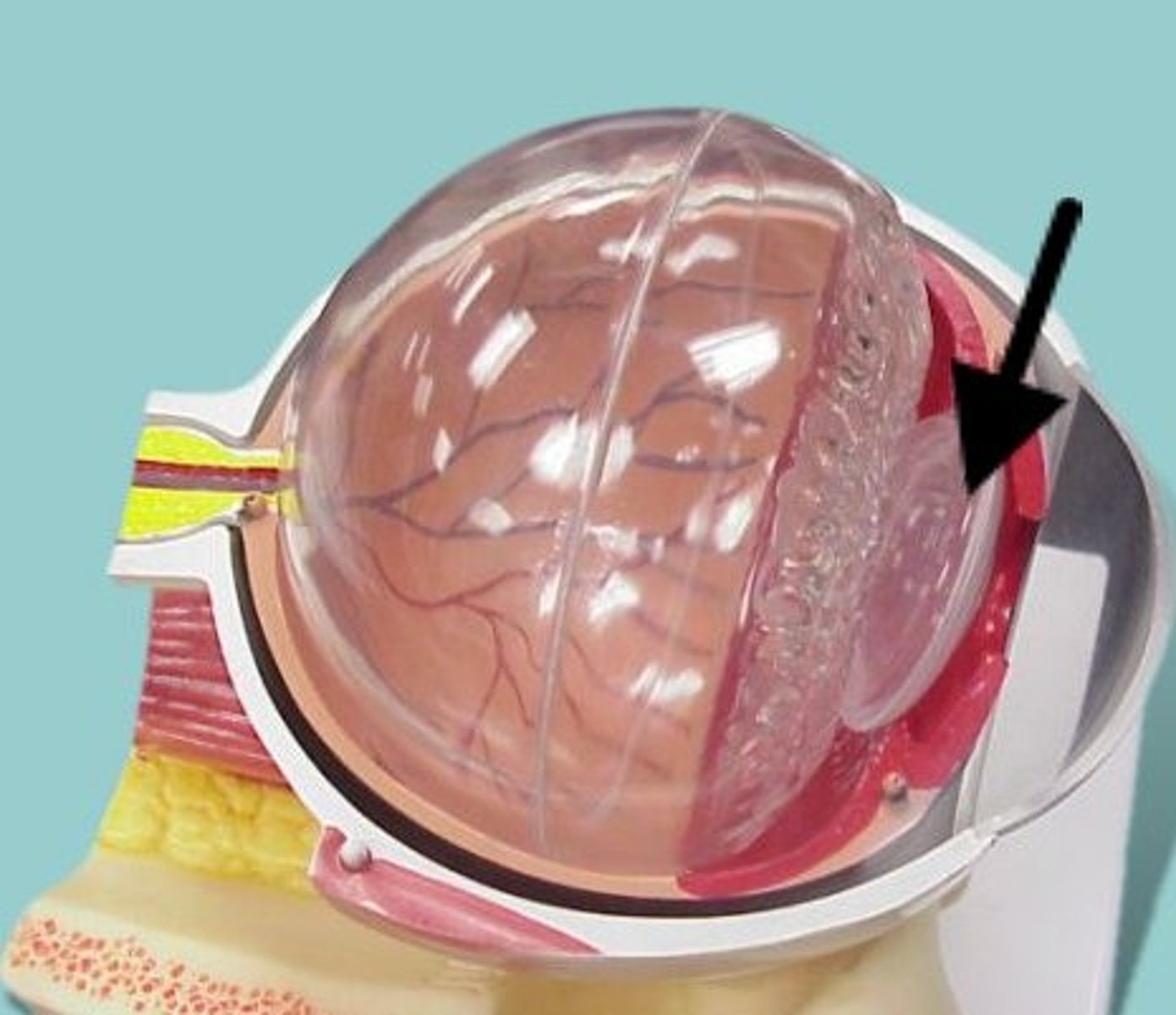
pupil-- opening in the center of the iris
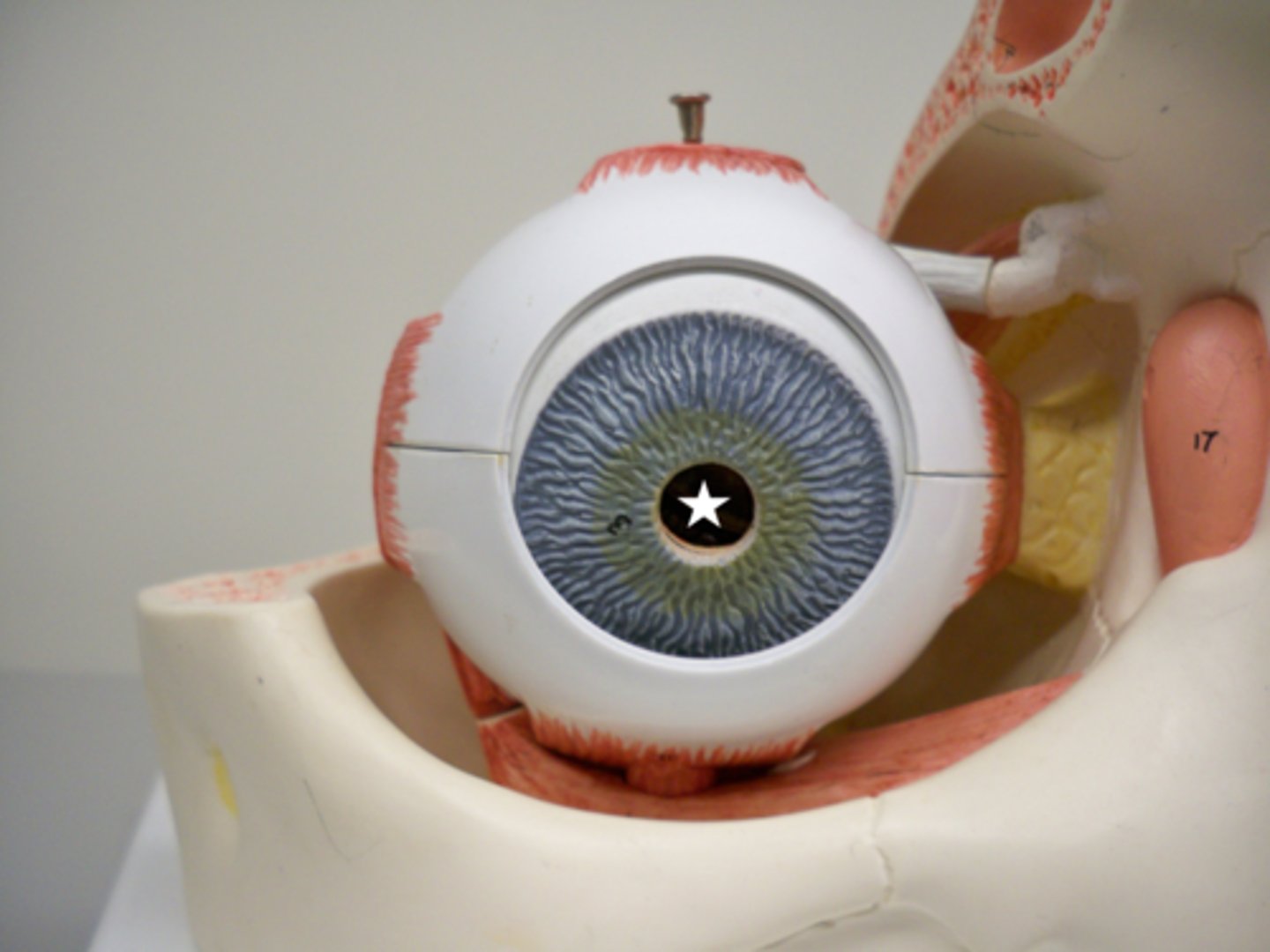
retina-- the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
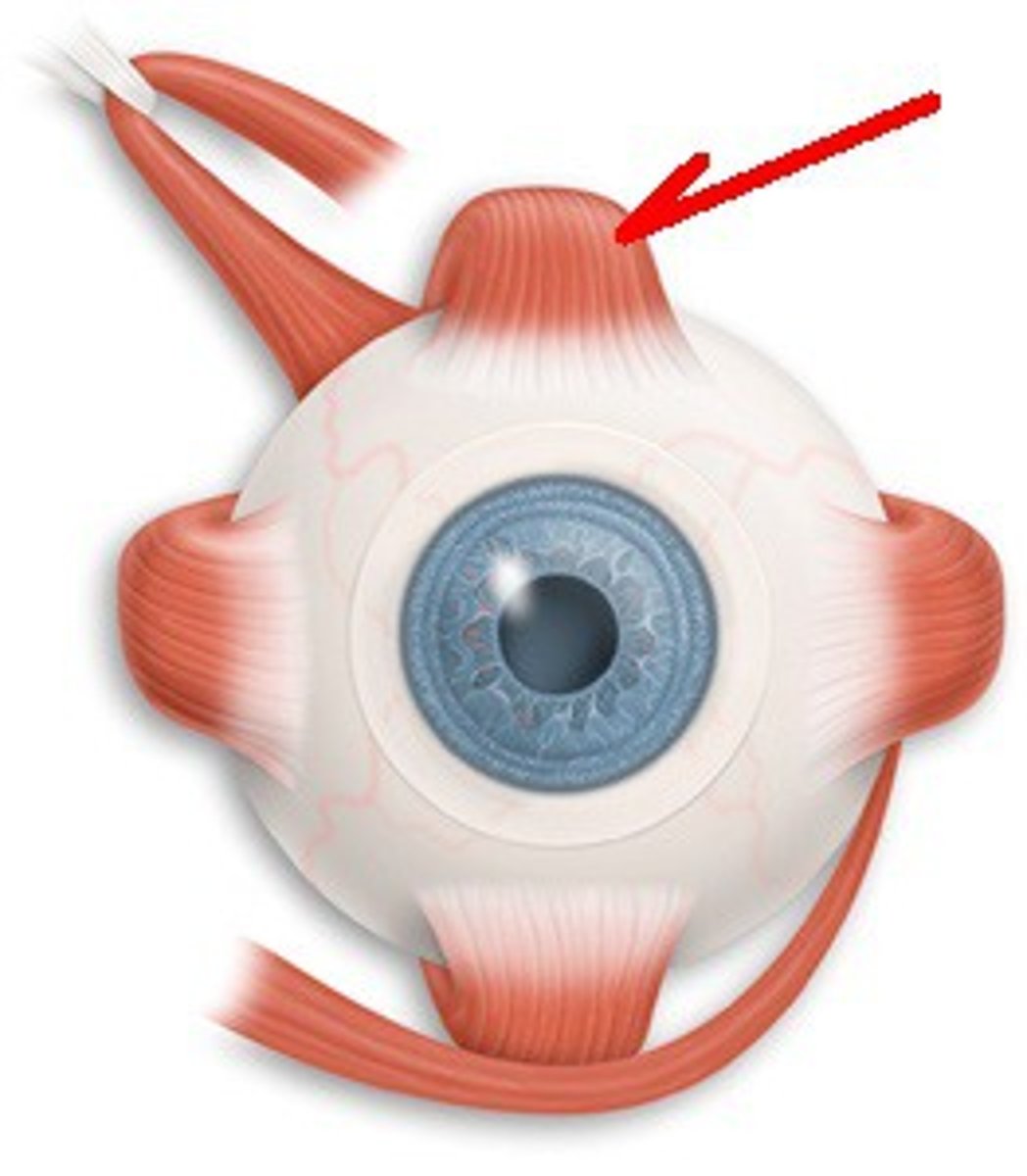
superior rectus-- elevates eye and turns it medially (III oculomotor)
inferior rectus-- depresses eye and turns it medially (III oculomotor)
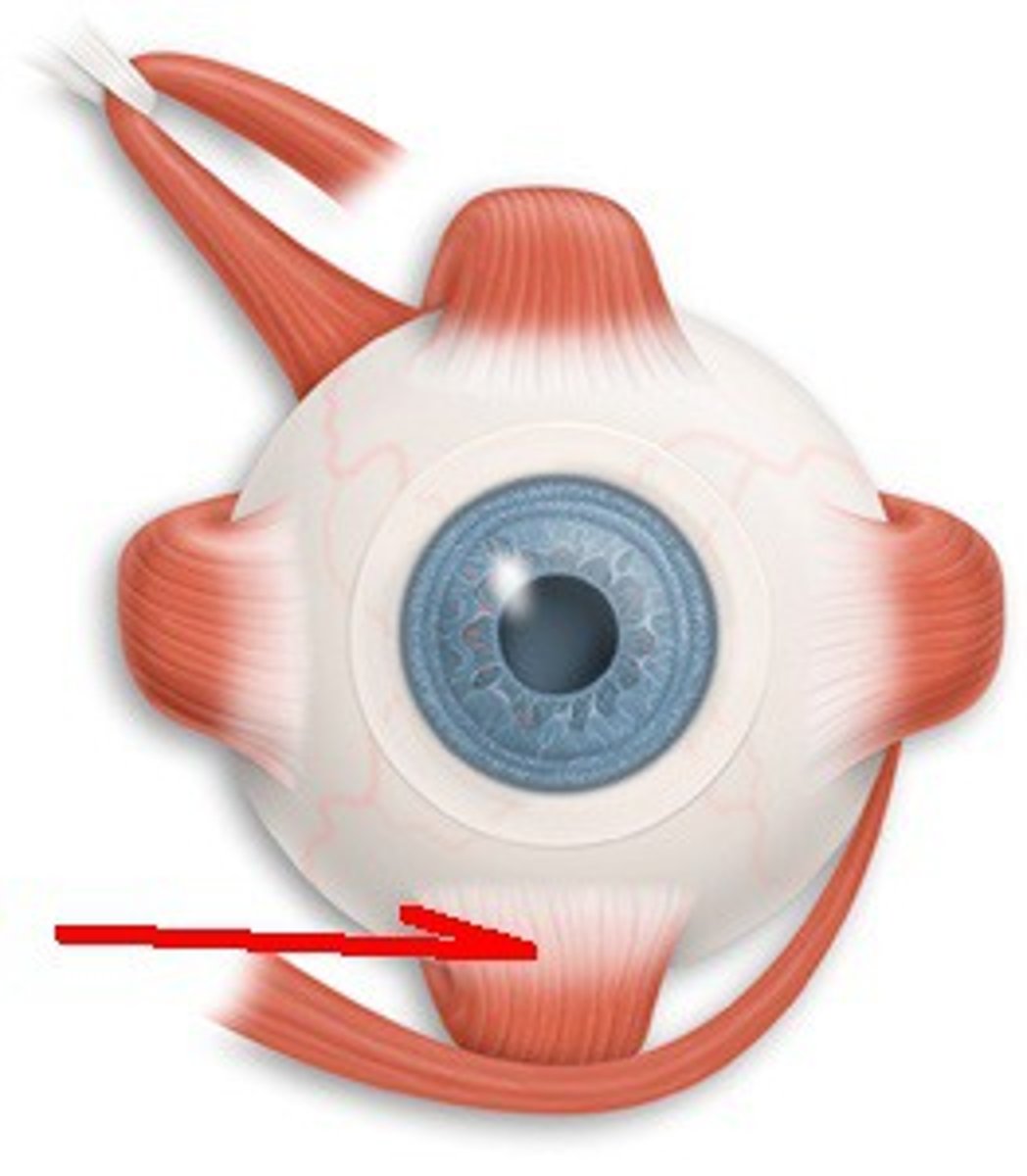
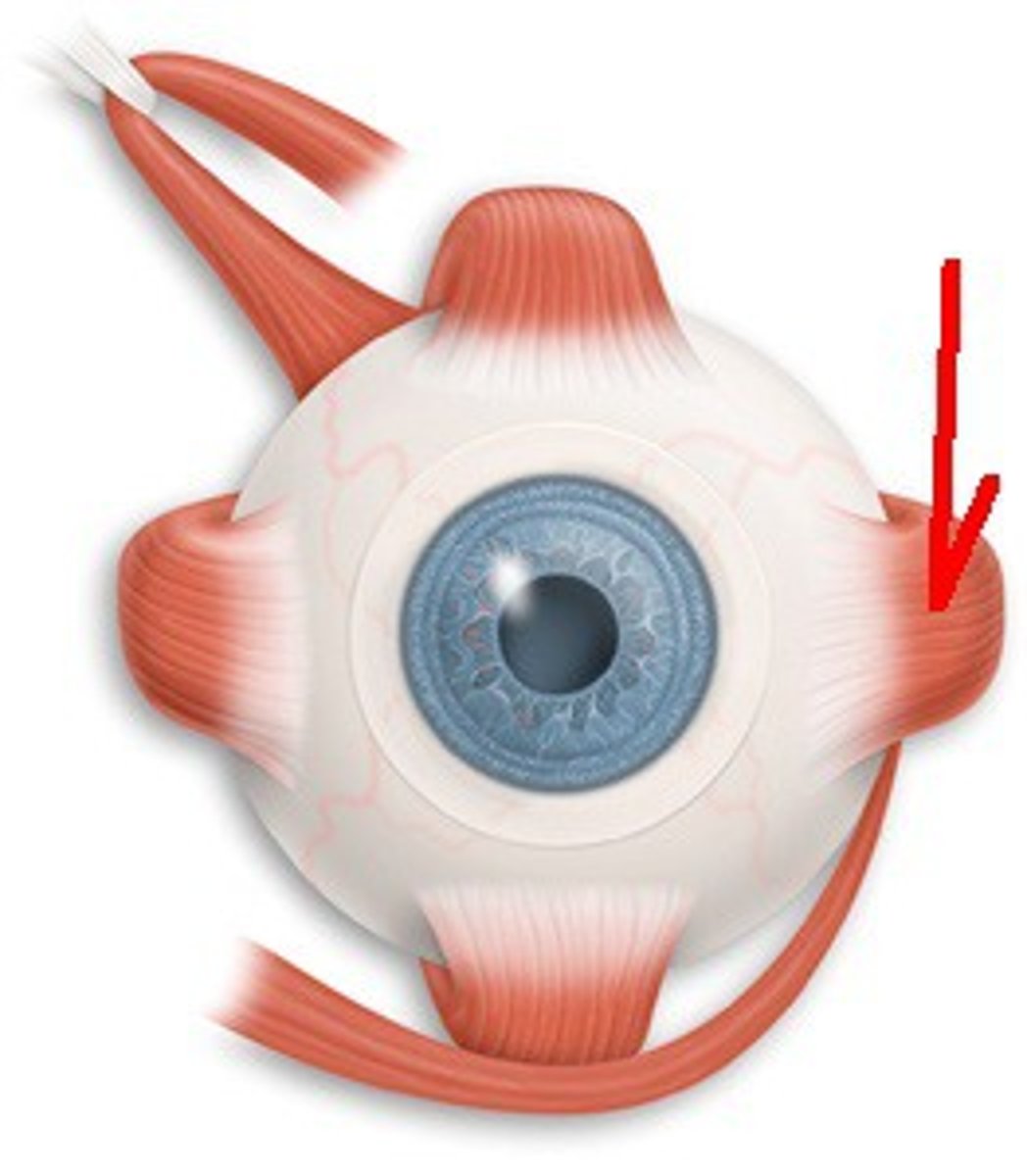
lateral rectus-- moves eye laterally (VI abducens)
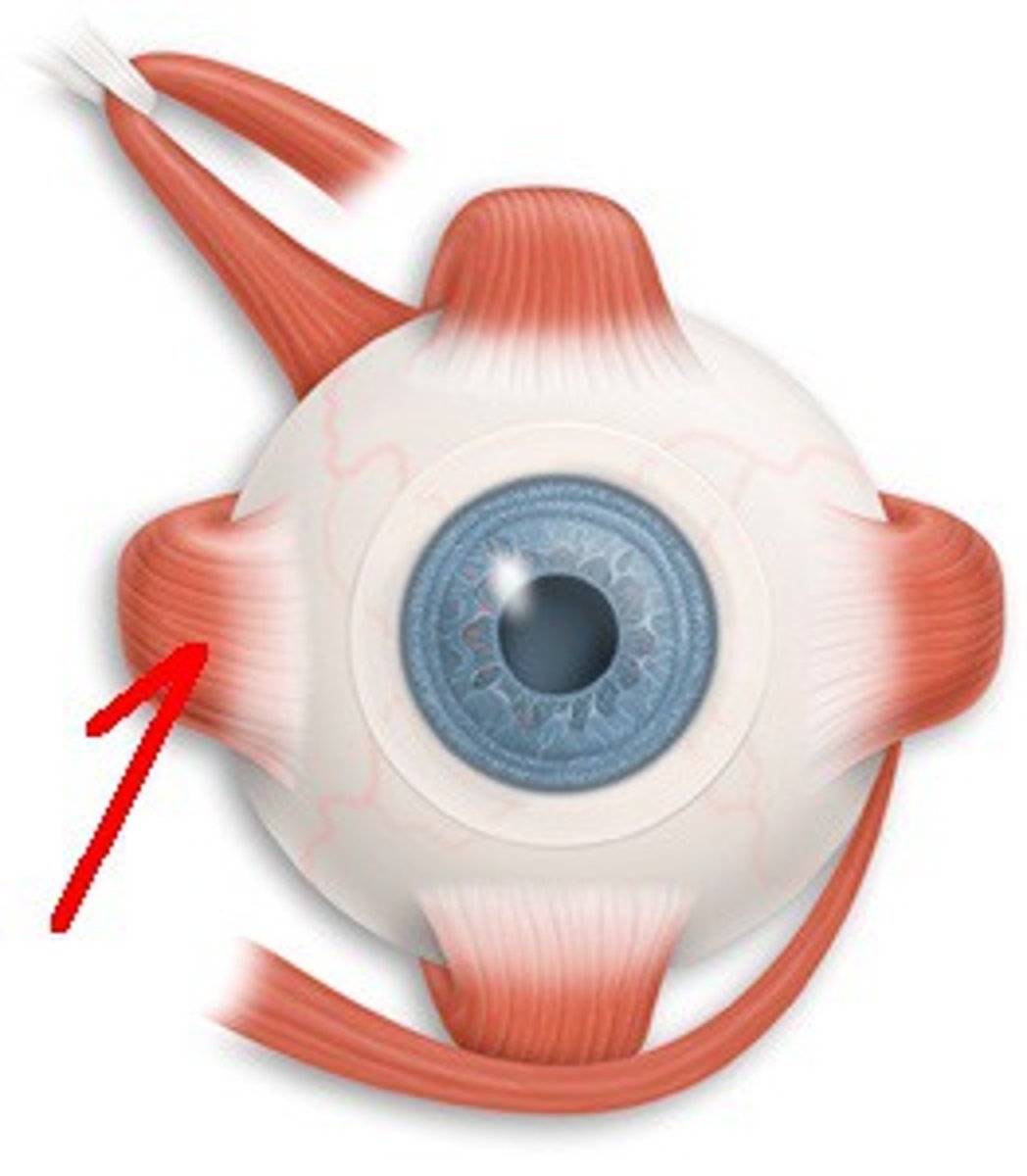
medial rectus-- moves eye medially (III oculomotor)
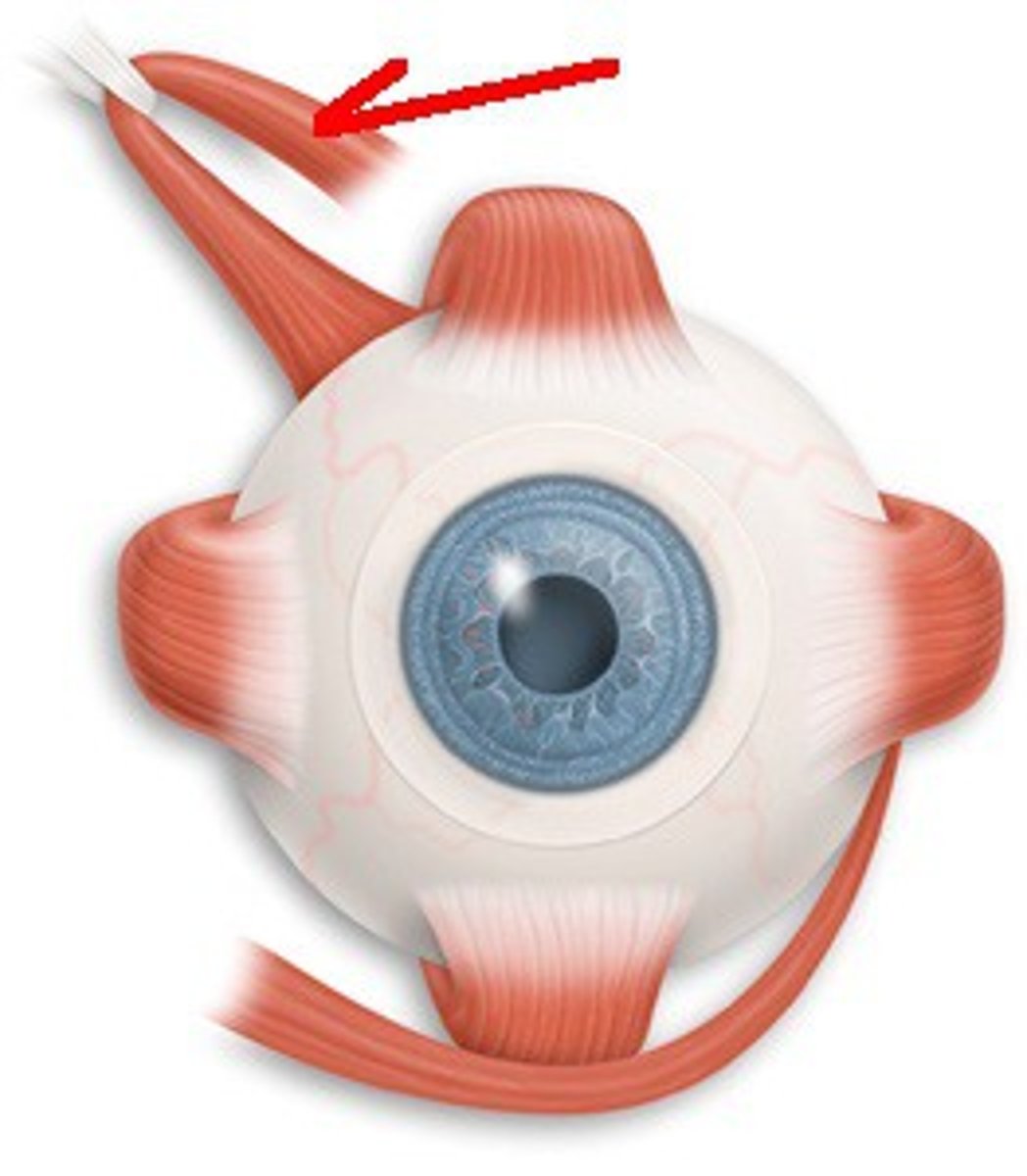
superior oblique-- Depresses eye and turns it laterally
IV (trochlear)
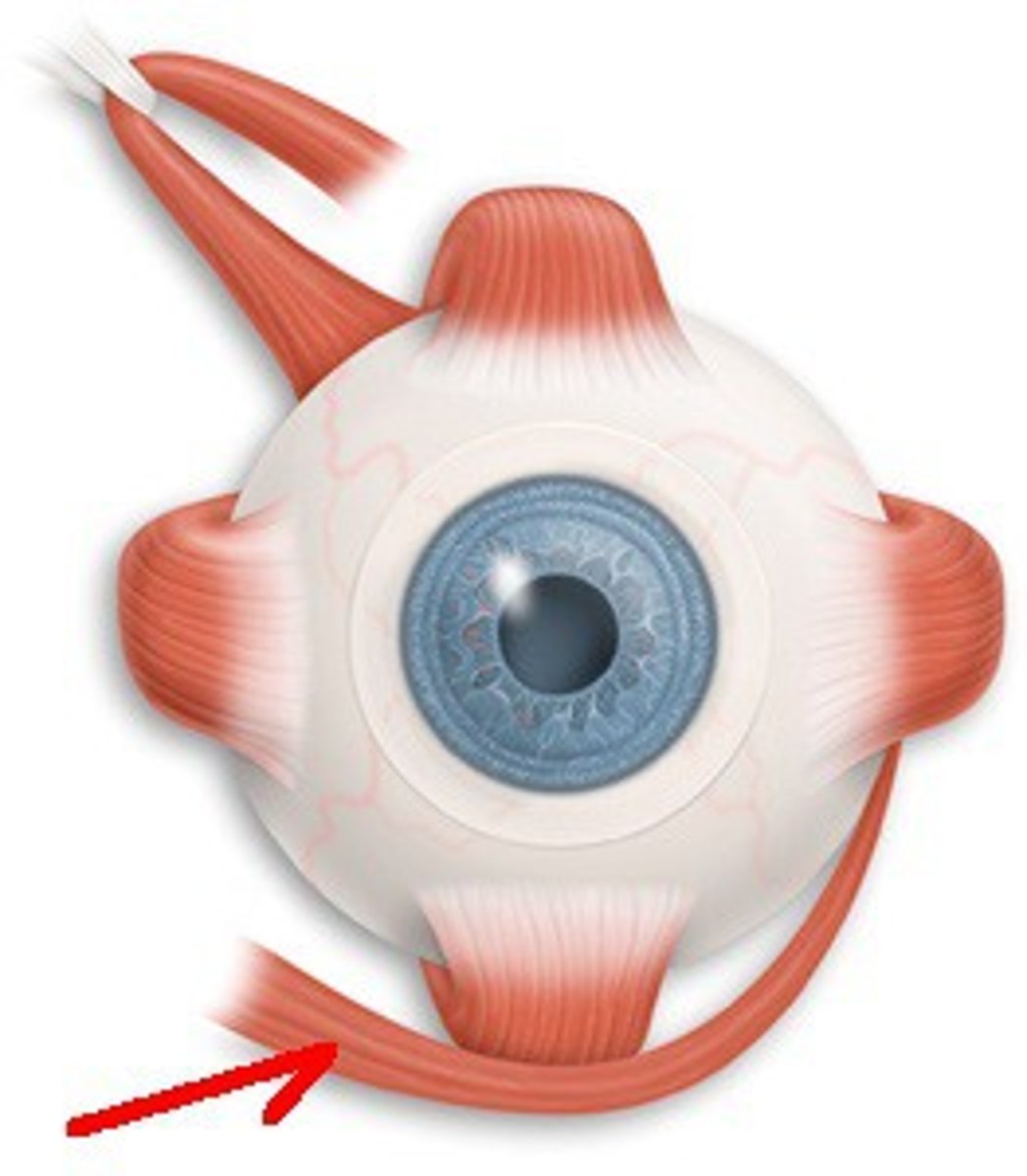
inferior oblique-- elevates eye and turns it laterally (oculomotor)
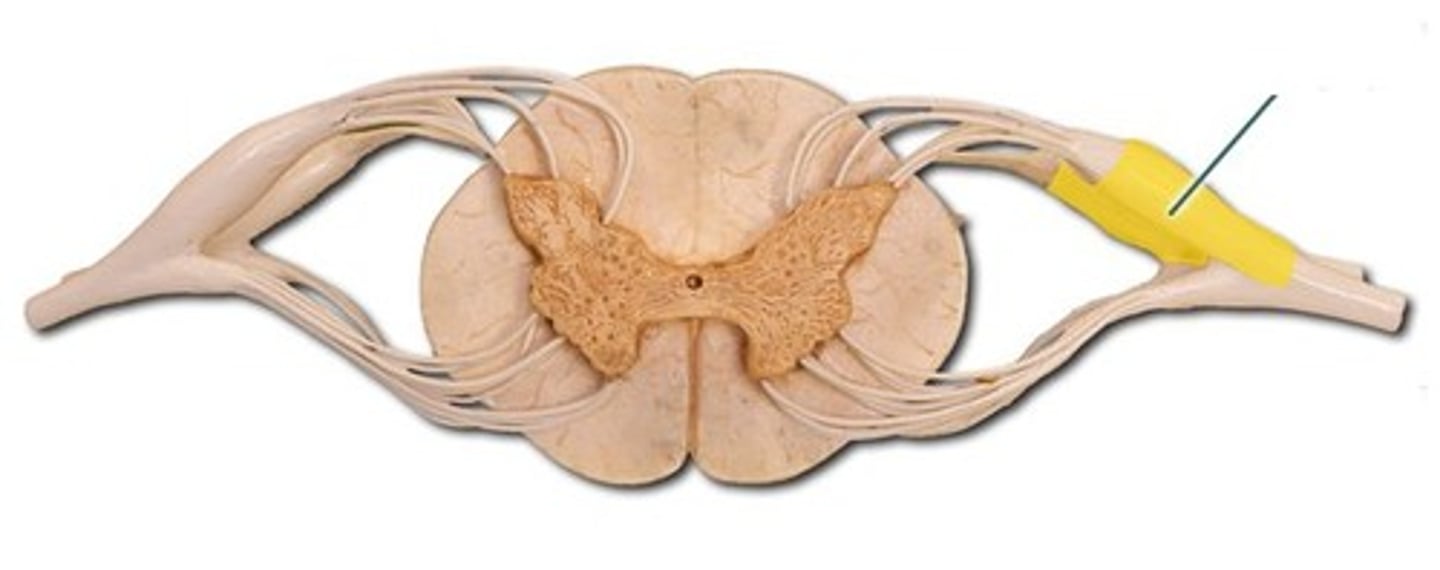
dorsal nerve roots-- Group of spinal nerve roots that enter the posterior (dorsal) part of the spinal cord and carry sensory nerve impulses from the body to the spinal cord.
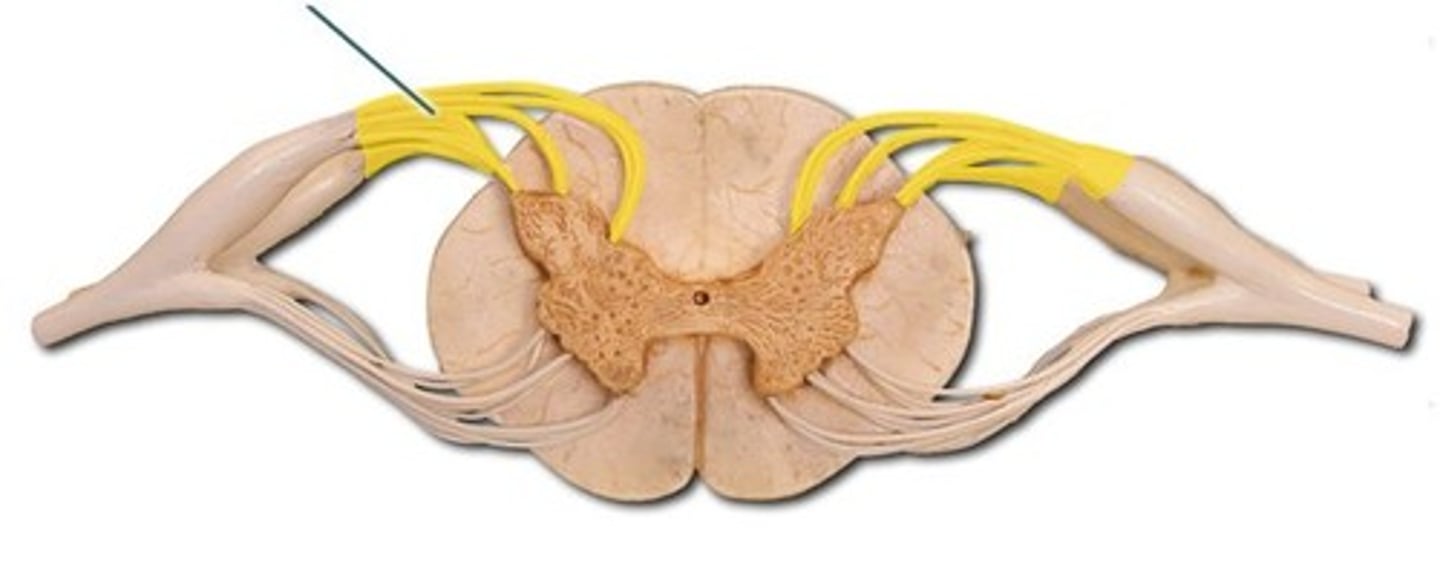
ventral nerve roots-- Group of spinal nerve roots that exit from the anterior (ventral) part of the spinal cord and carry motor nerve impulses to the body.
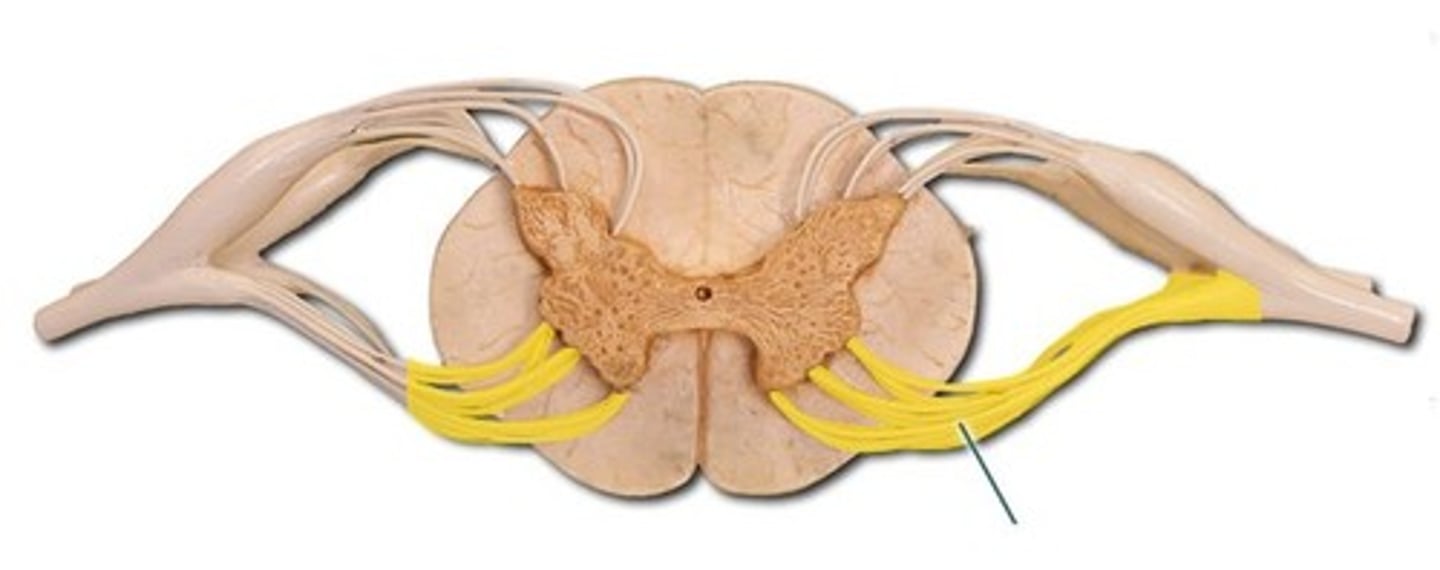
dorsal root ganglion-- contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons whose axons carry information to the spinal cord
anterior view of spinal cord
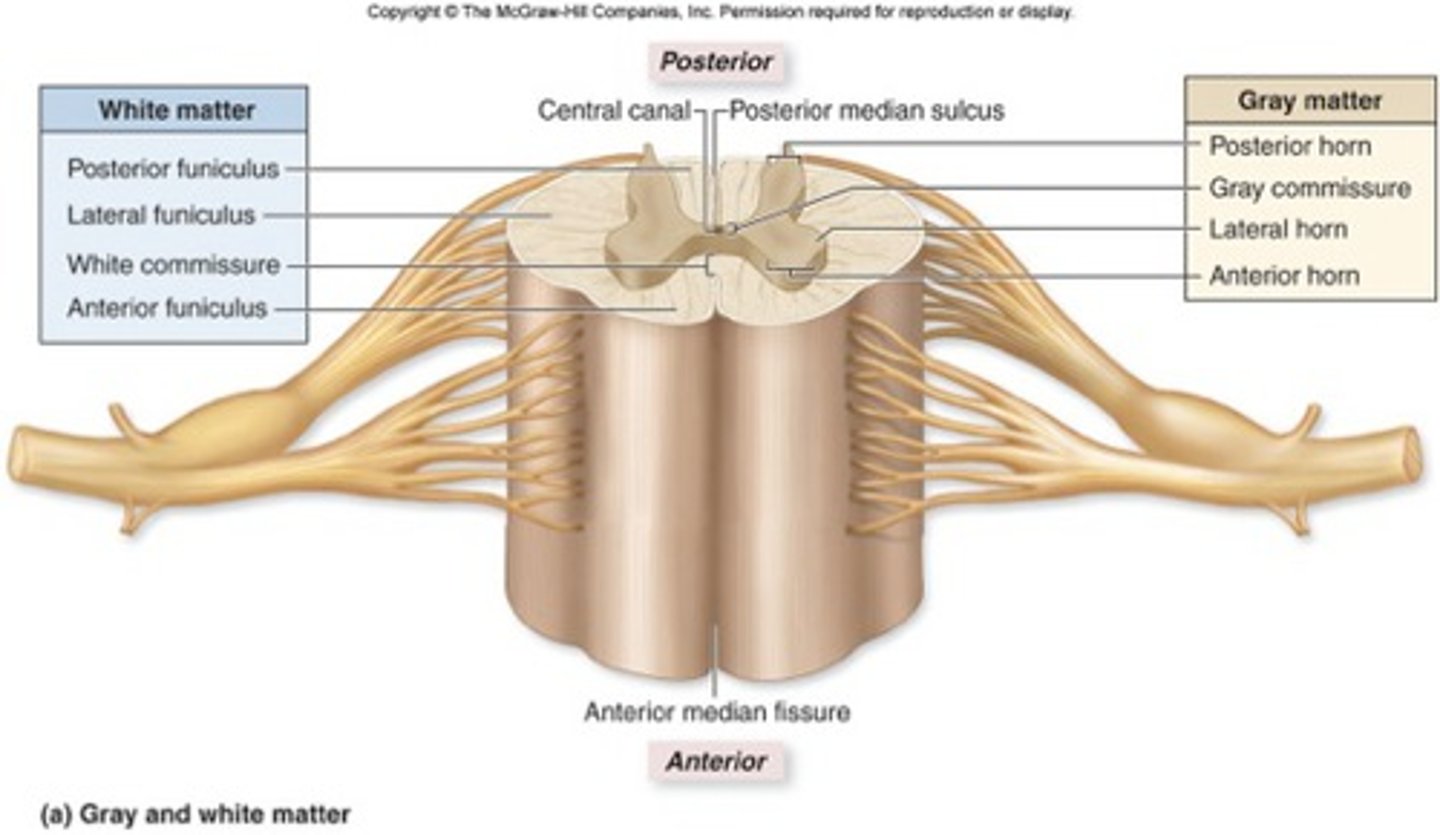
posterior view of spinal cord
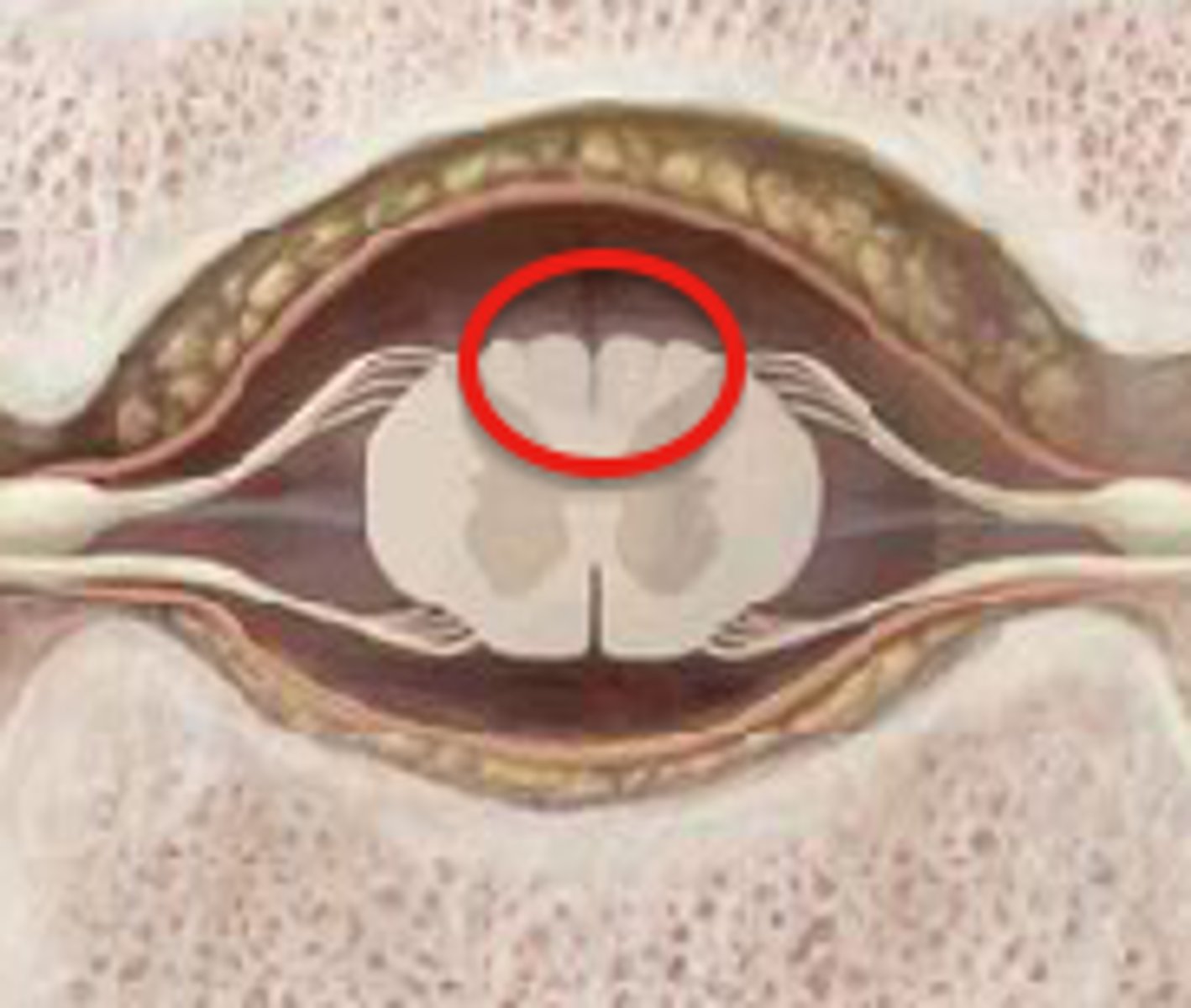
dorsal horn-- sensory neurons in gray matter
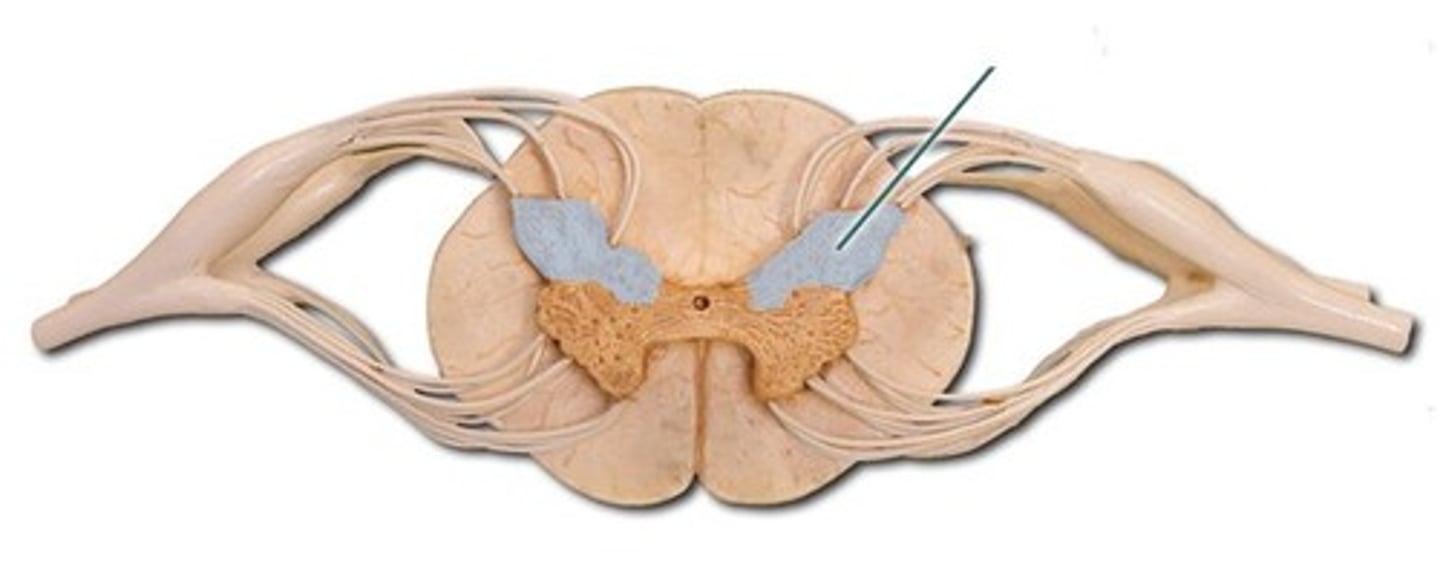
lateral horn-- (only in thoracic and lumbar regions)
- sympathetic neurons
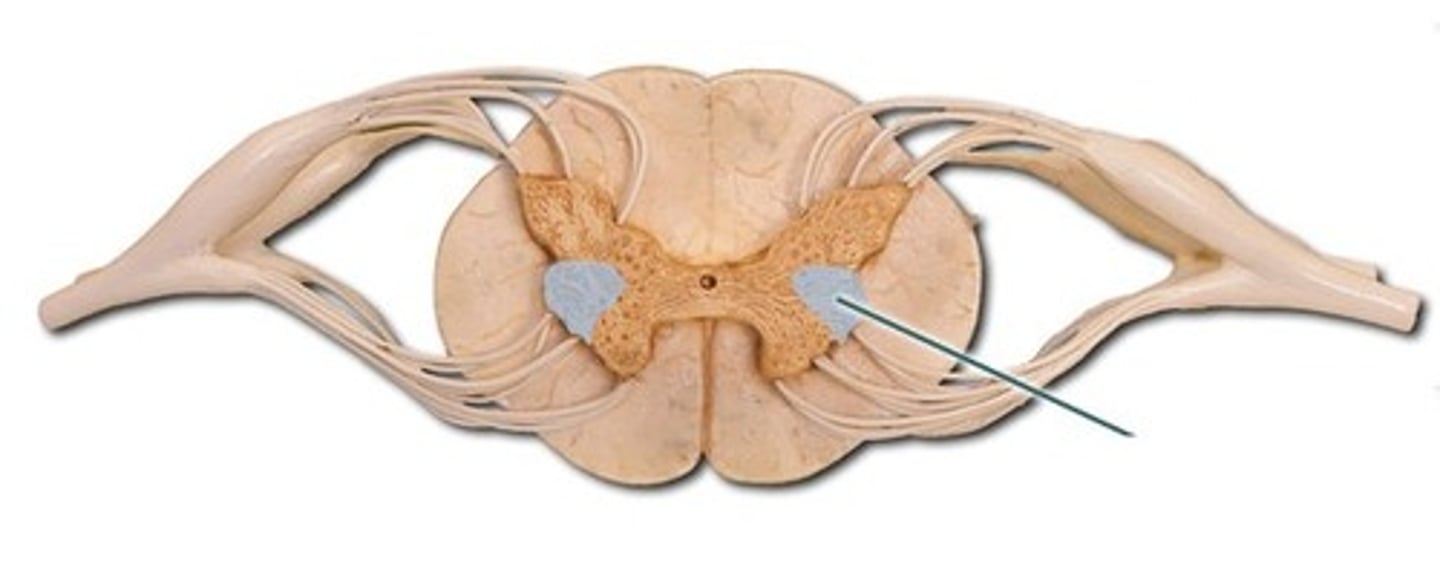
ventral horn-- motor neurons
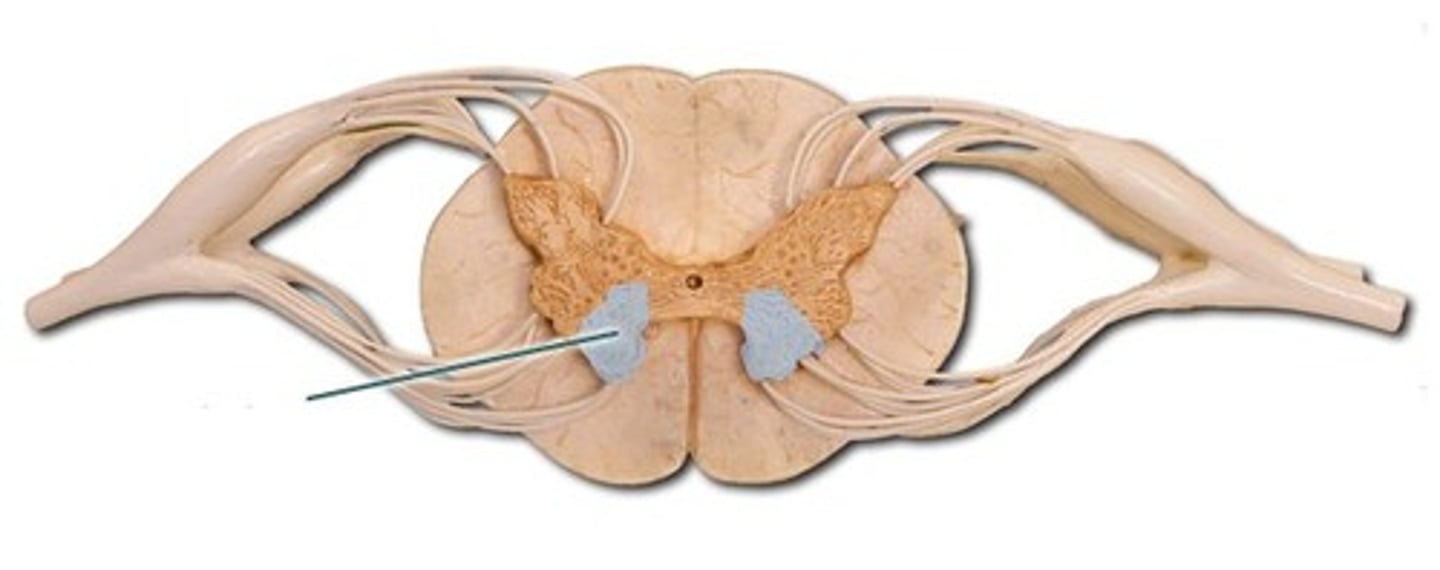
conus medullaris-- tapered end of spinal cord
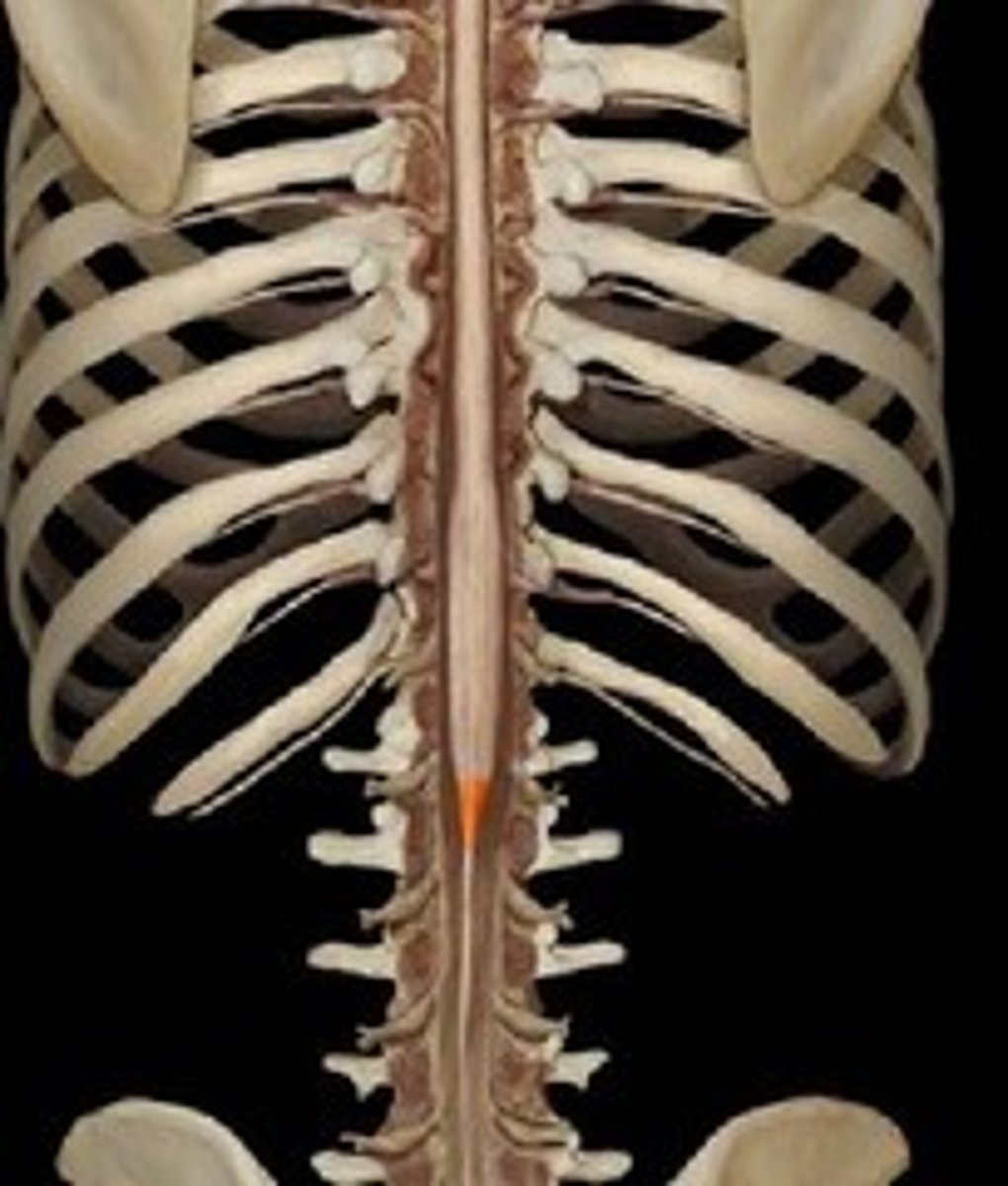
cuada equina-- collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
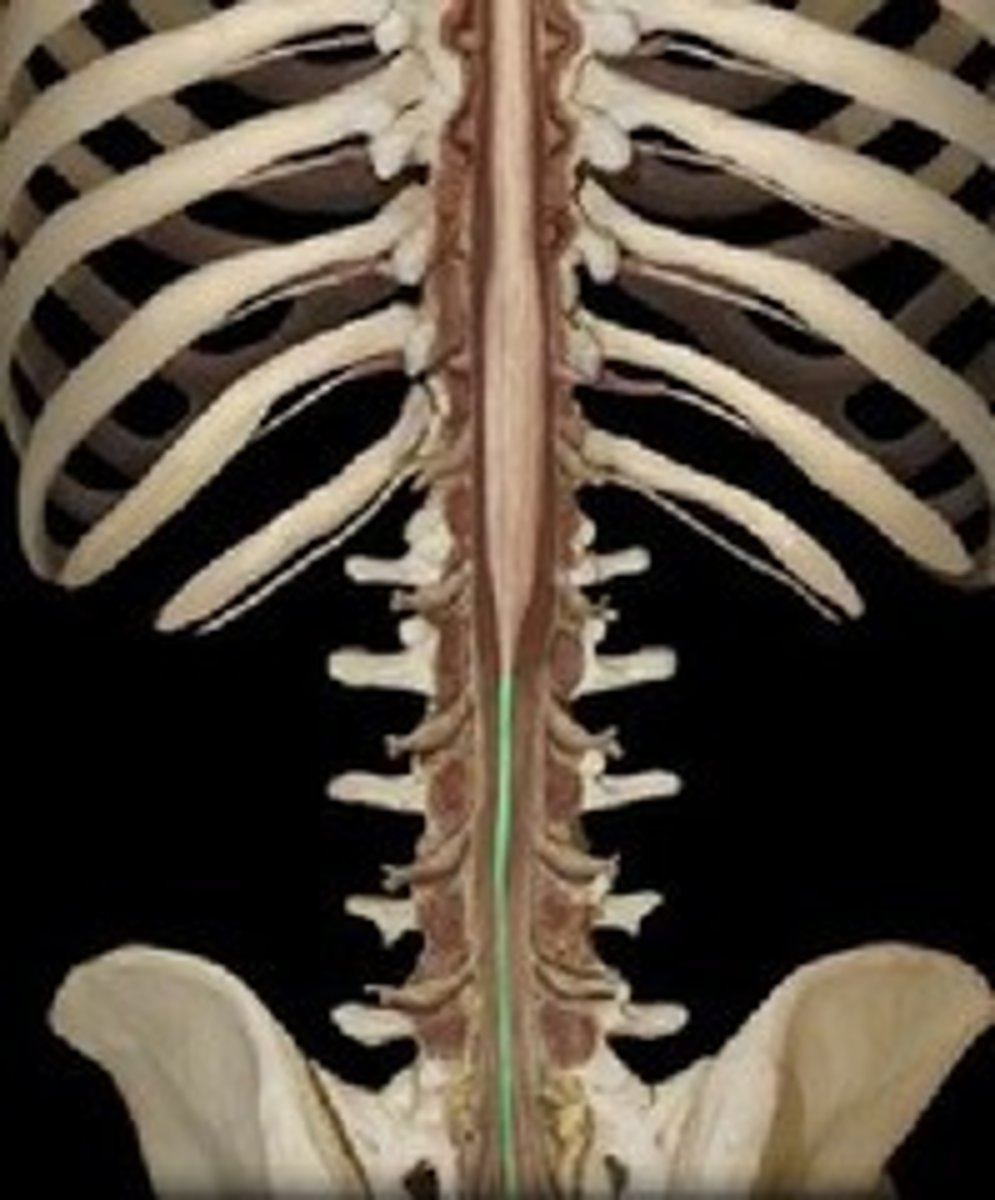
filum terminale-- thin thread of fibrous tissue at end of conus medullaris, attaches to coccygeal ligament
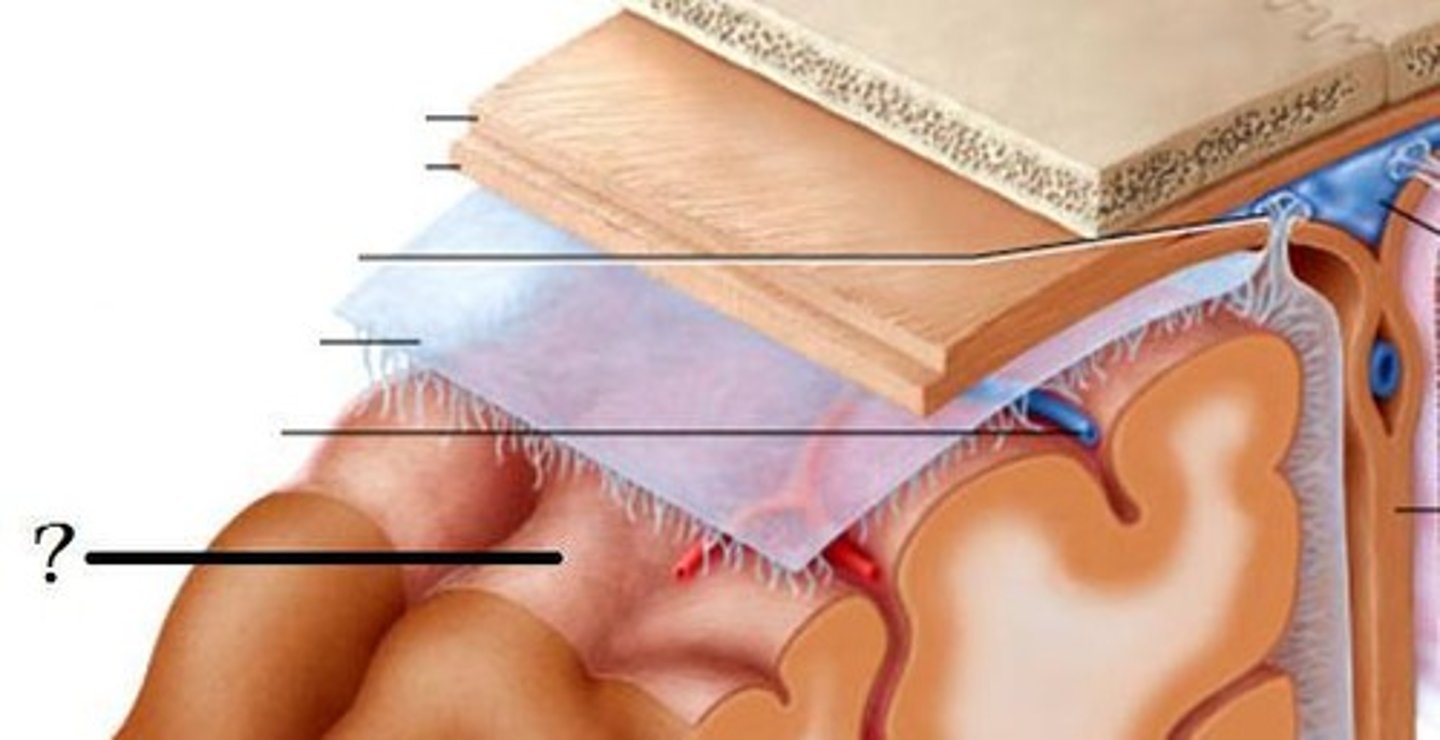
dura mater-- thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
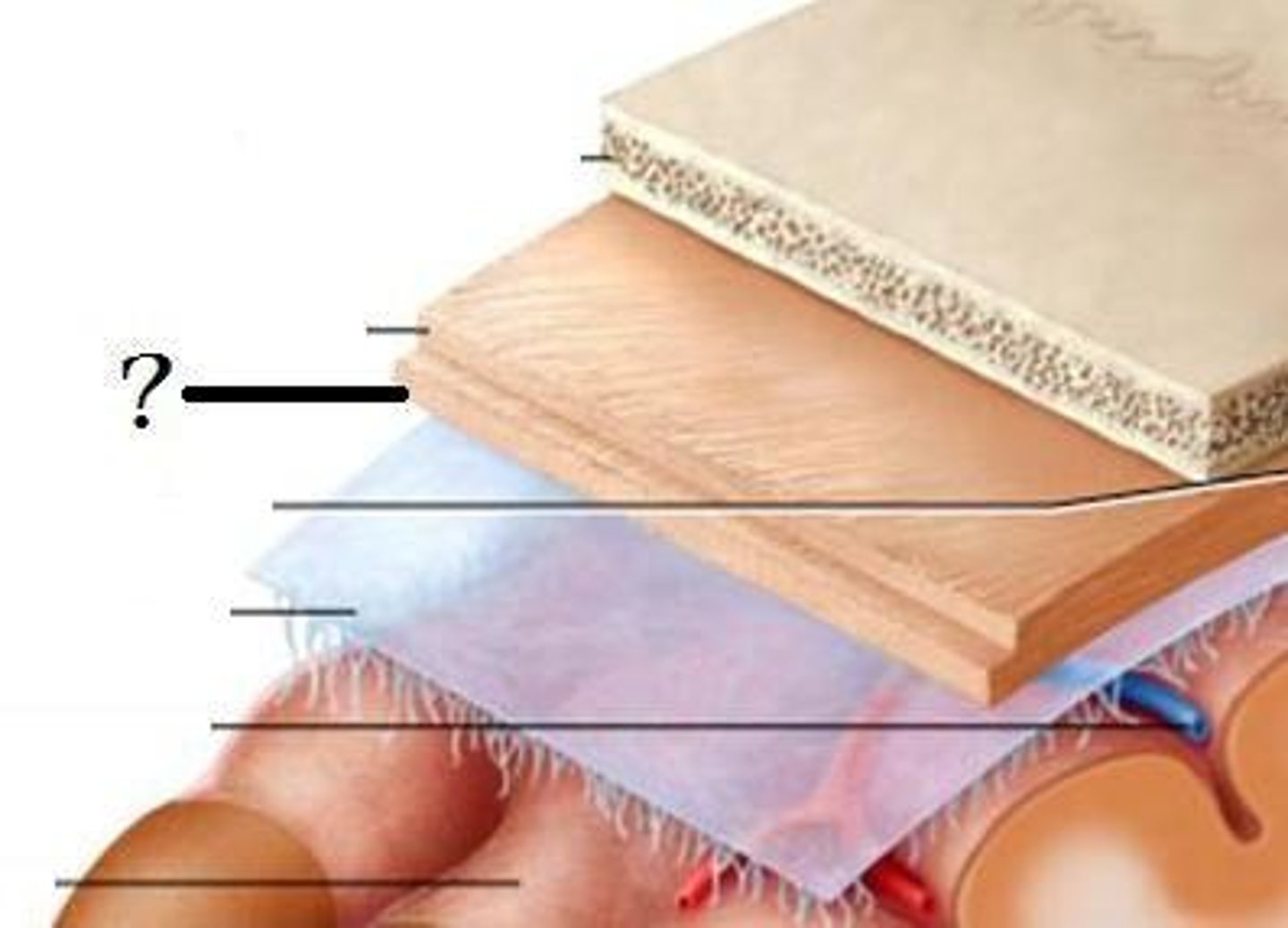
arachnoid mater-- middle layer of the meninges
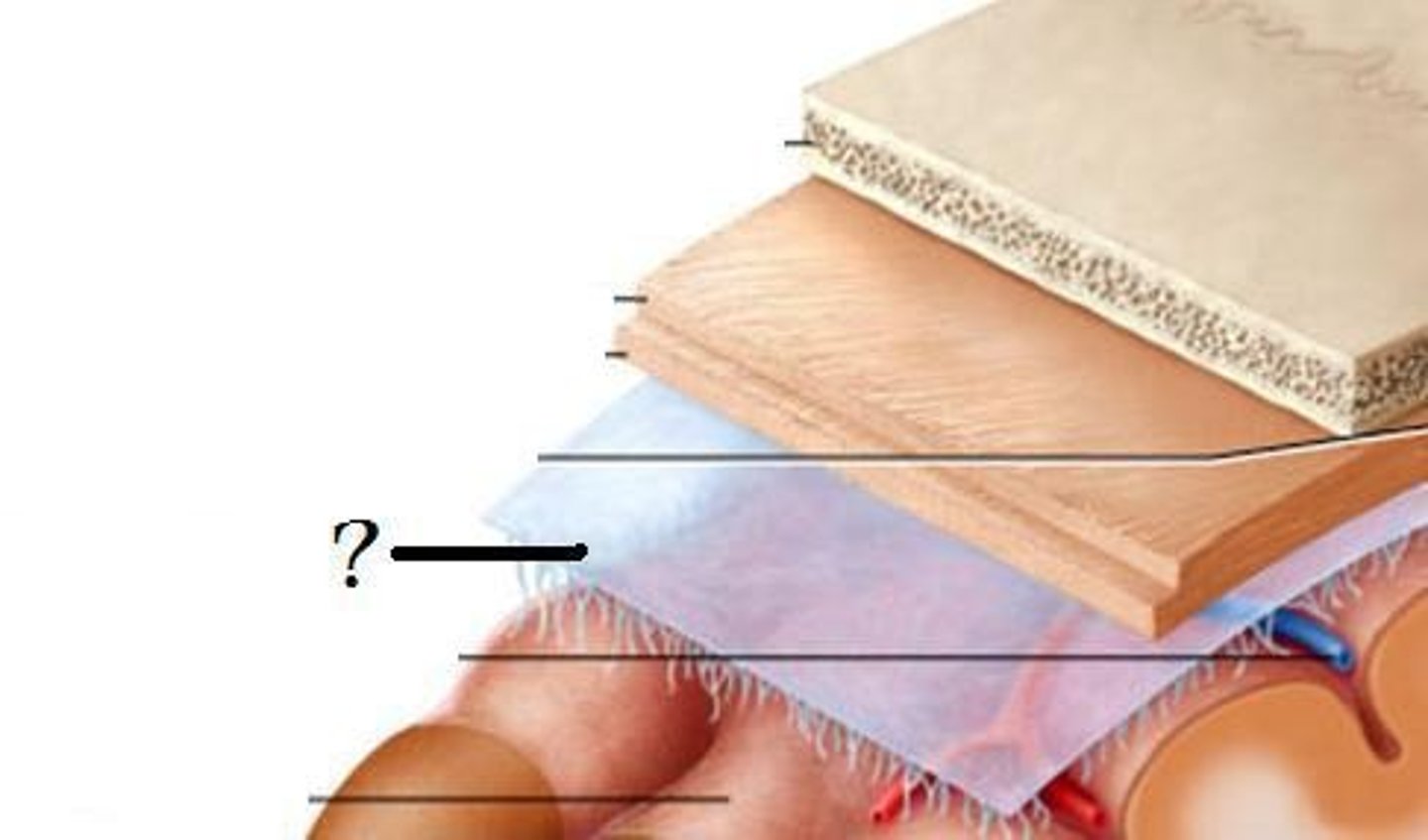
pia mater-- Innermost layer of the meninges
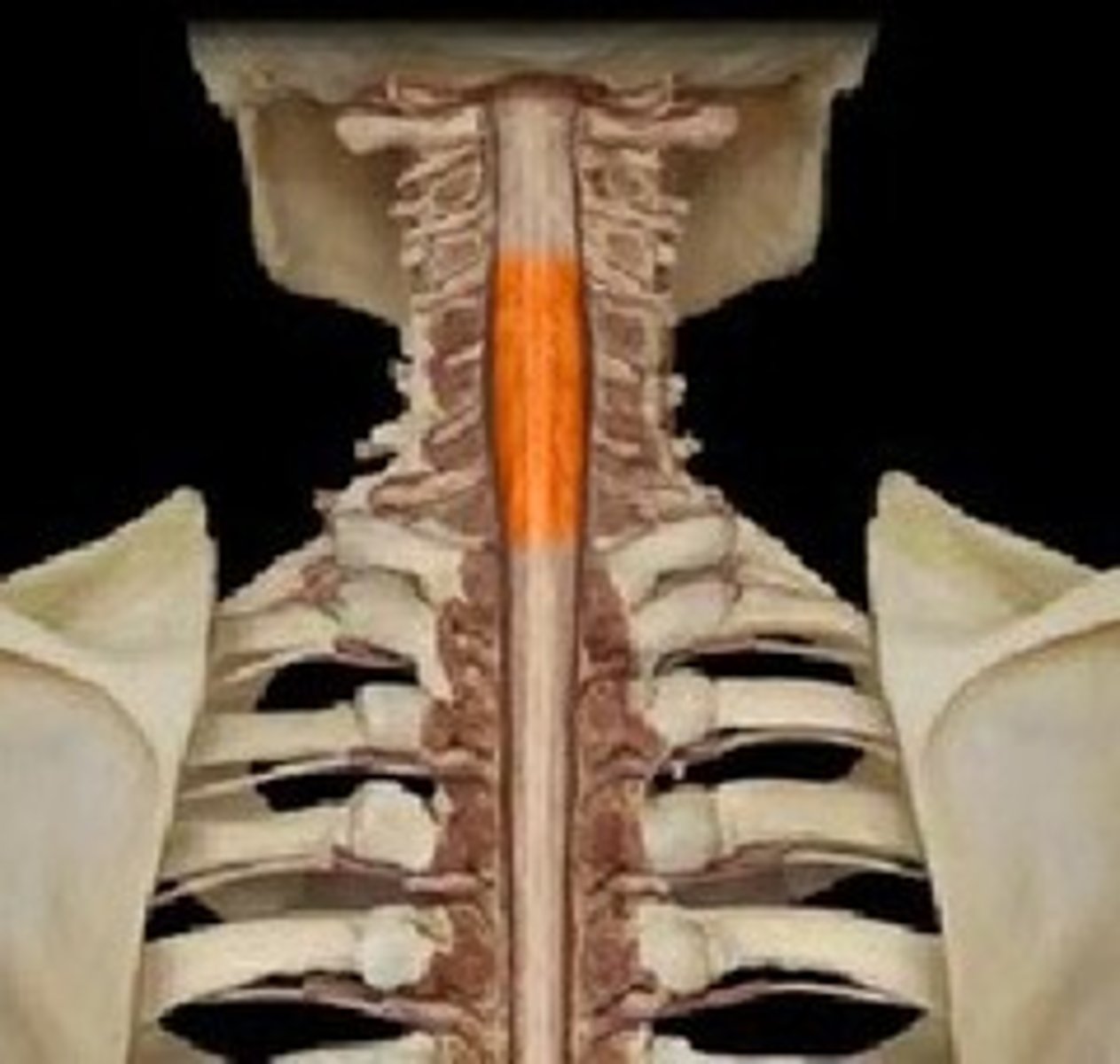
cervical enlargement-- supplies nerves to the shoulder and upper limbs
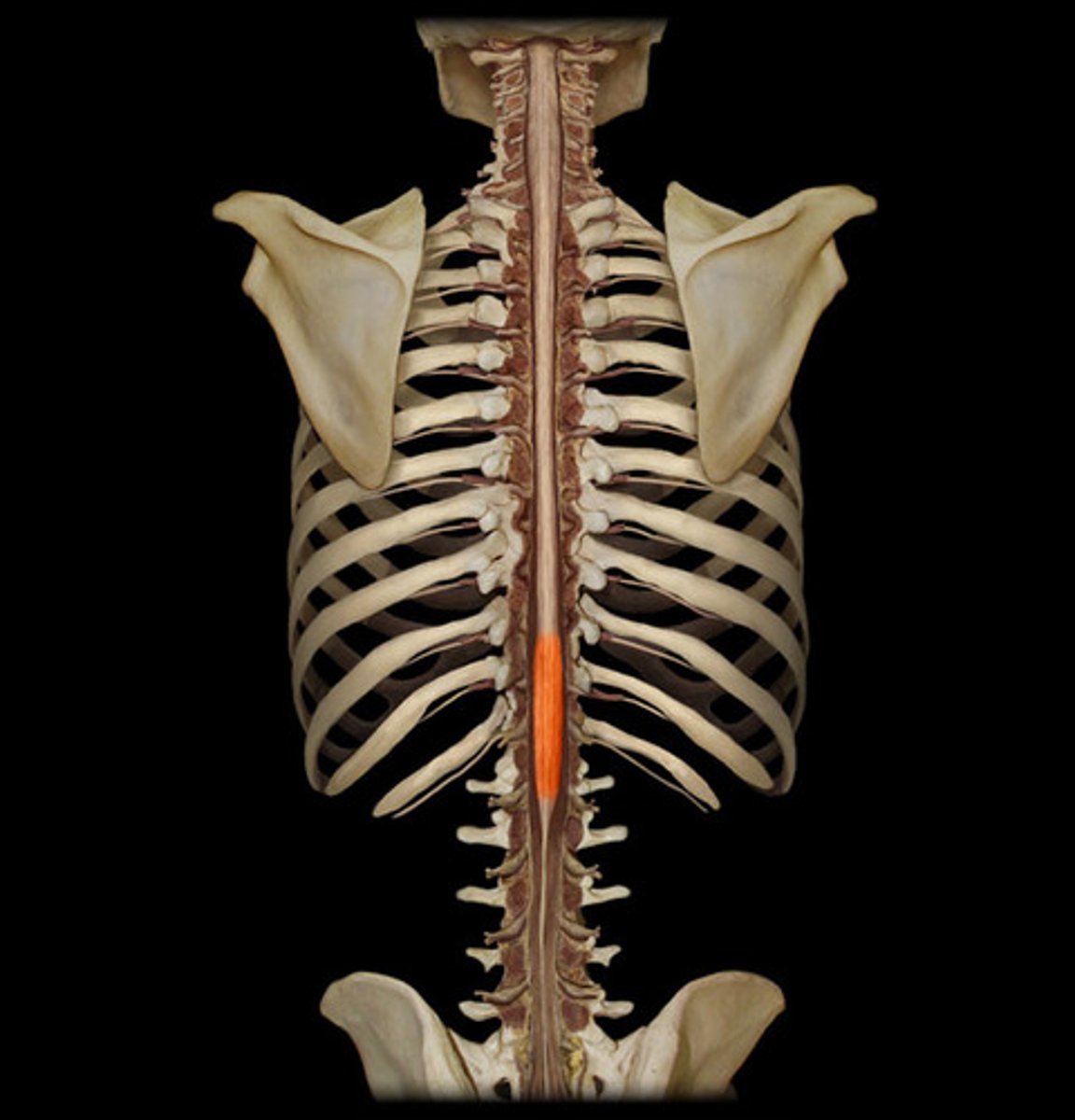
lumbar enlargement-- nerves to pelvic region and lower limbs
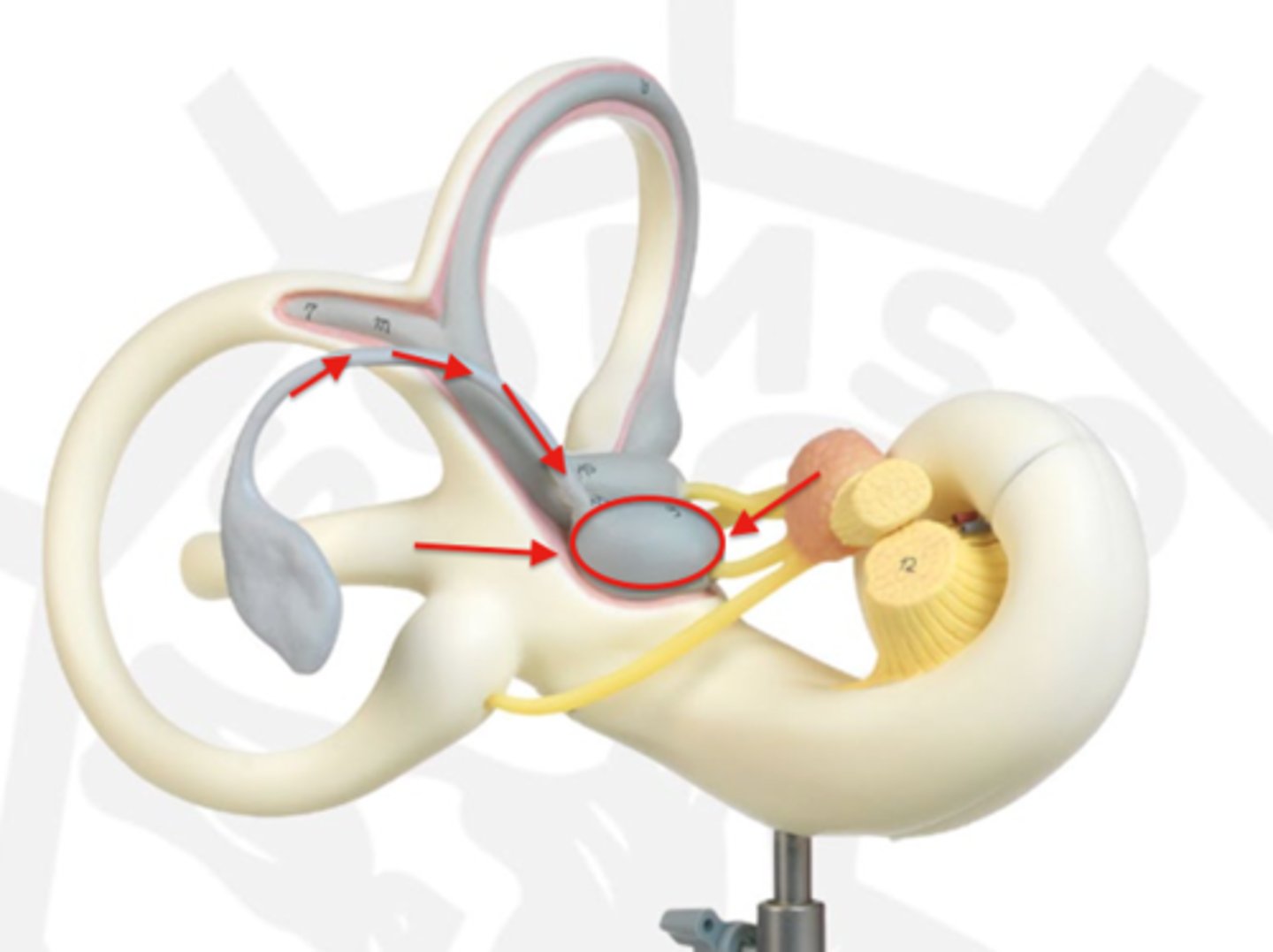
posterior semicircular canal-- Detects tilting the head to the side (or cartwheels)
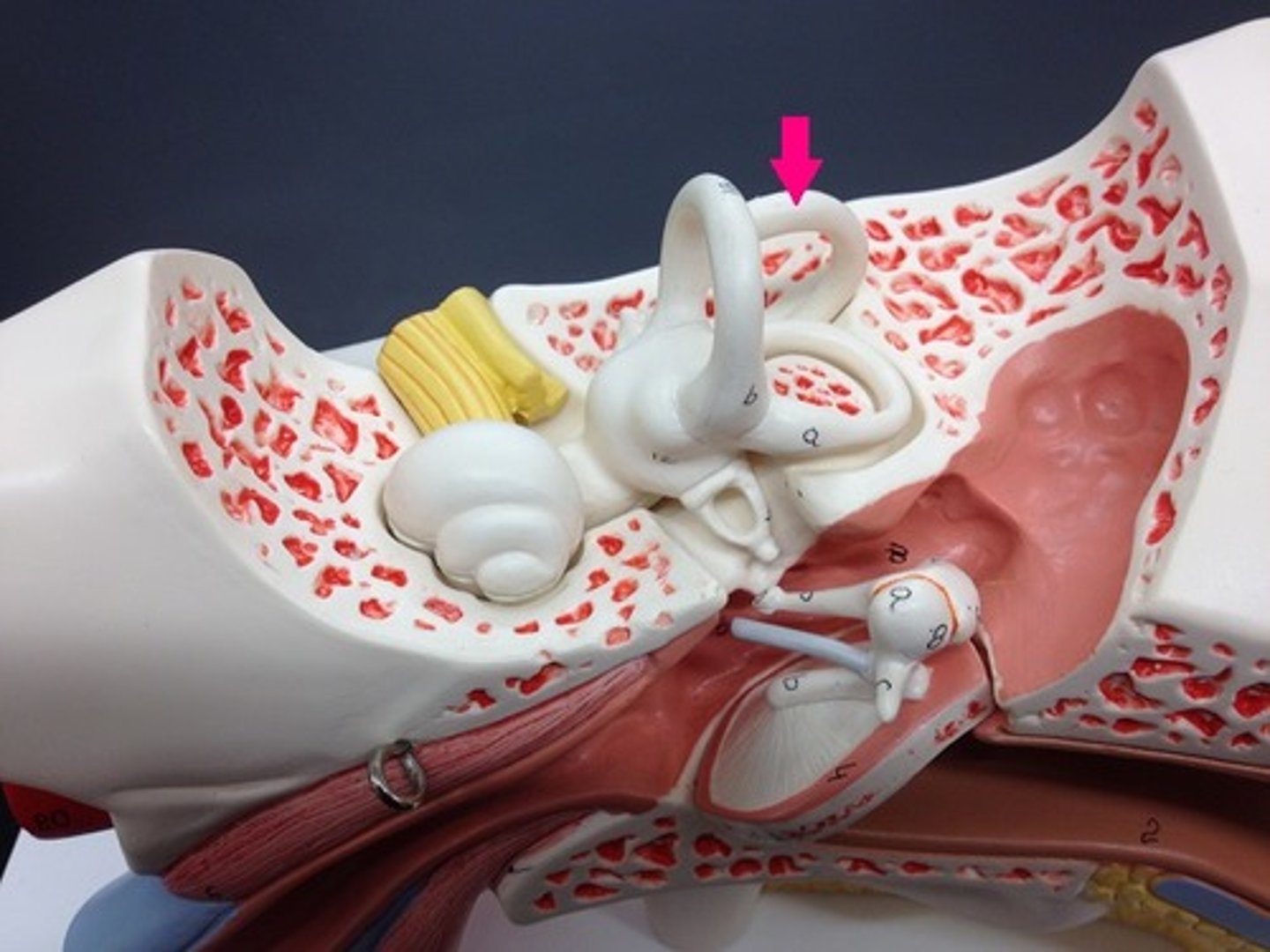
lateral semicircular canal-- no motions
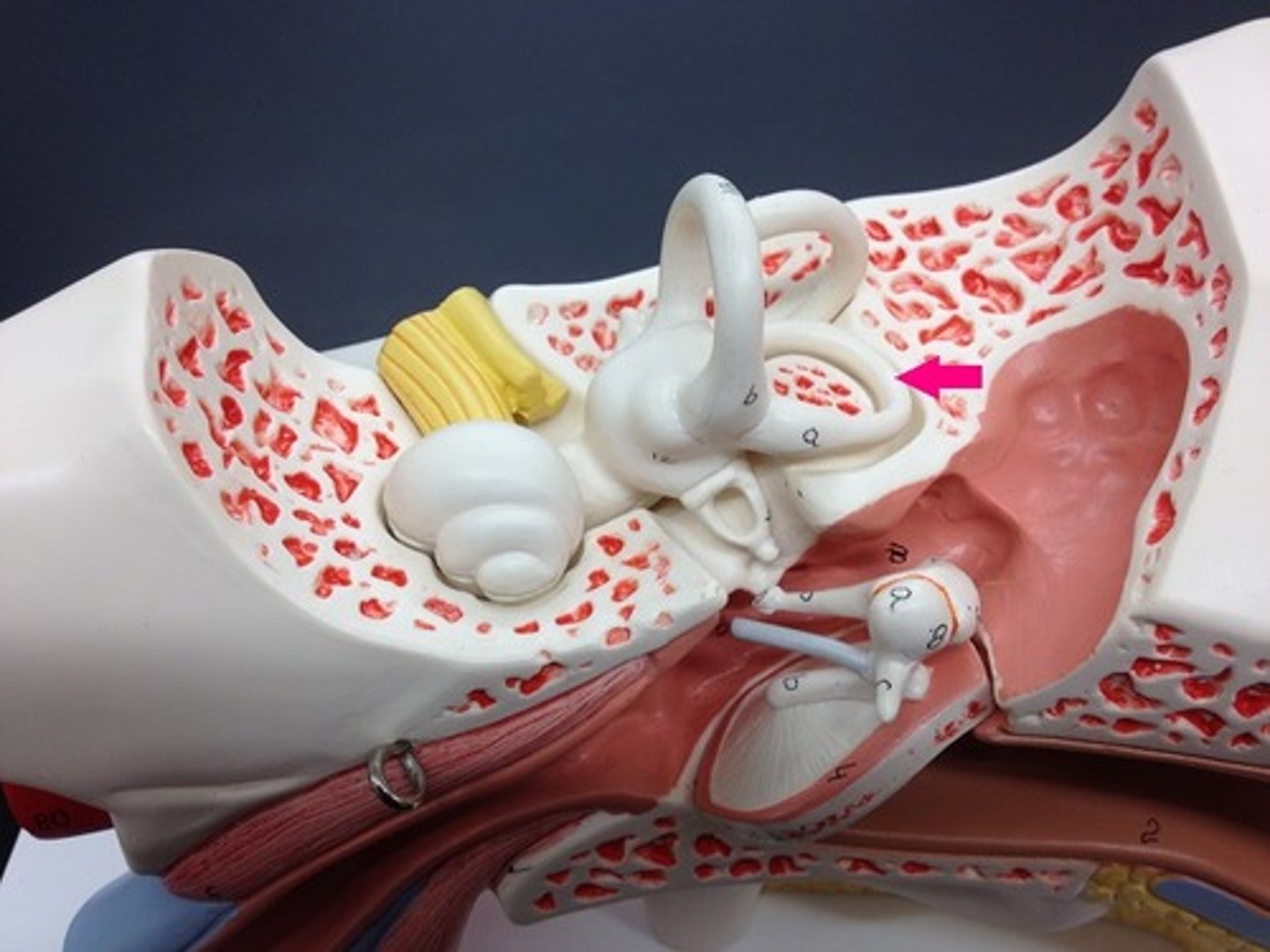
utricle-- detects front to back motions
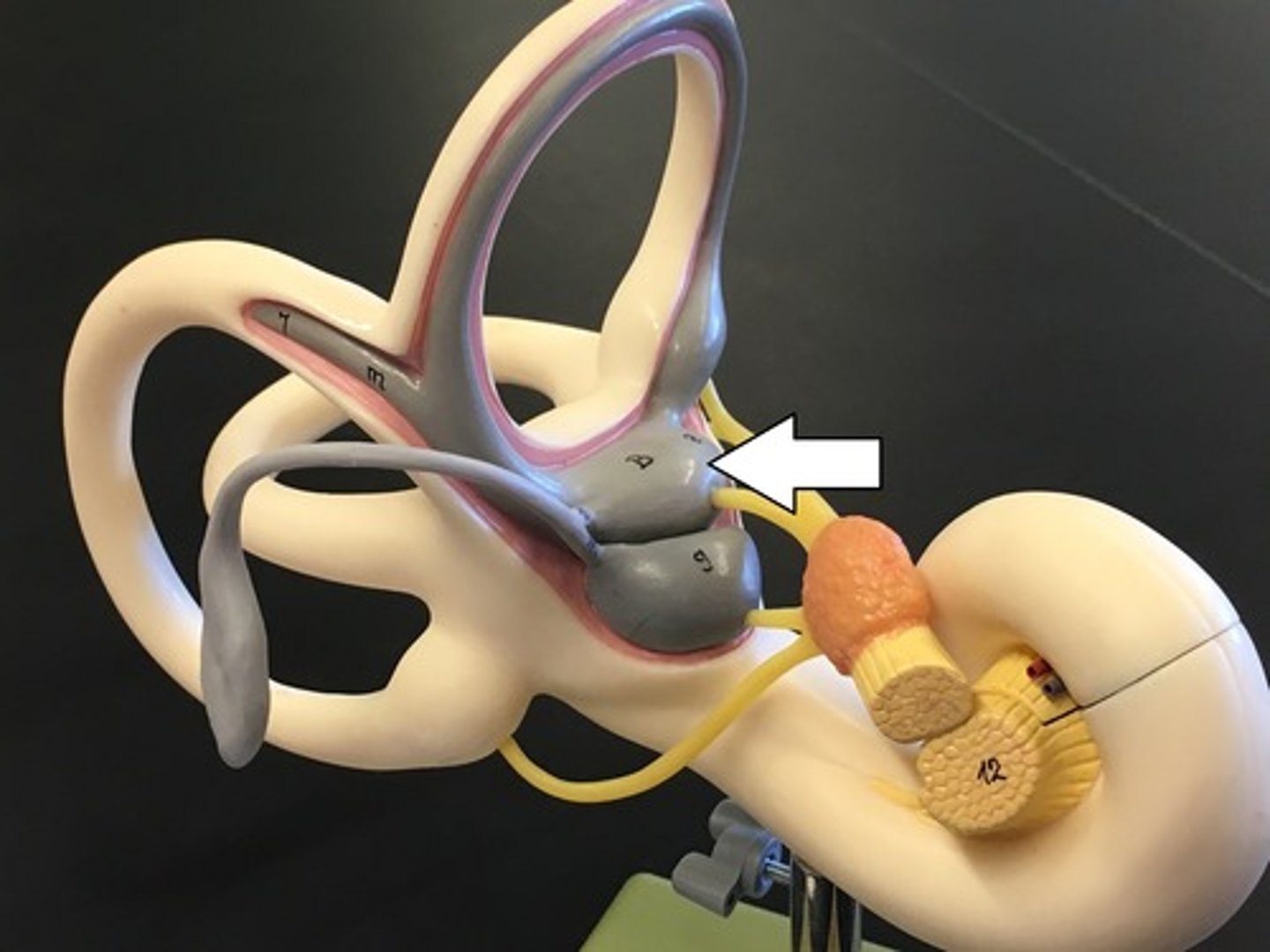
saccule-- detects up and down motions
vestibulocochlear nerve-- hearing and balance (CN8)
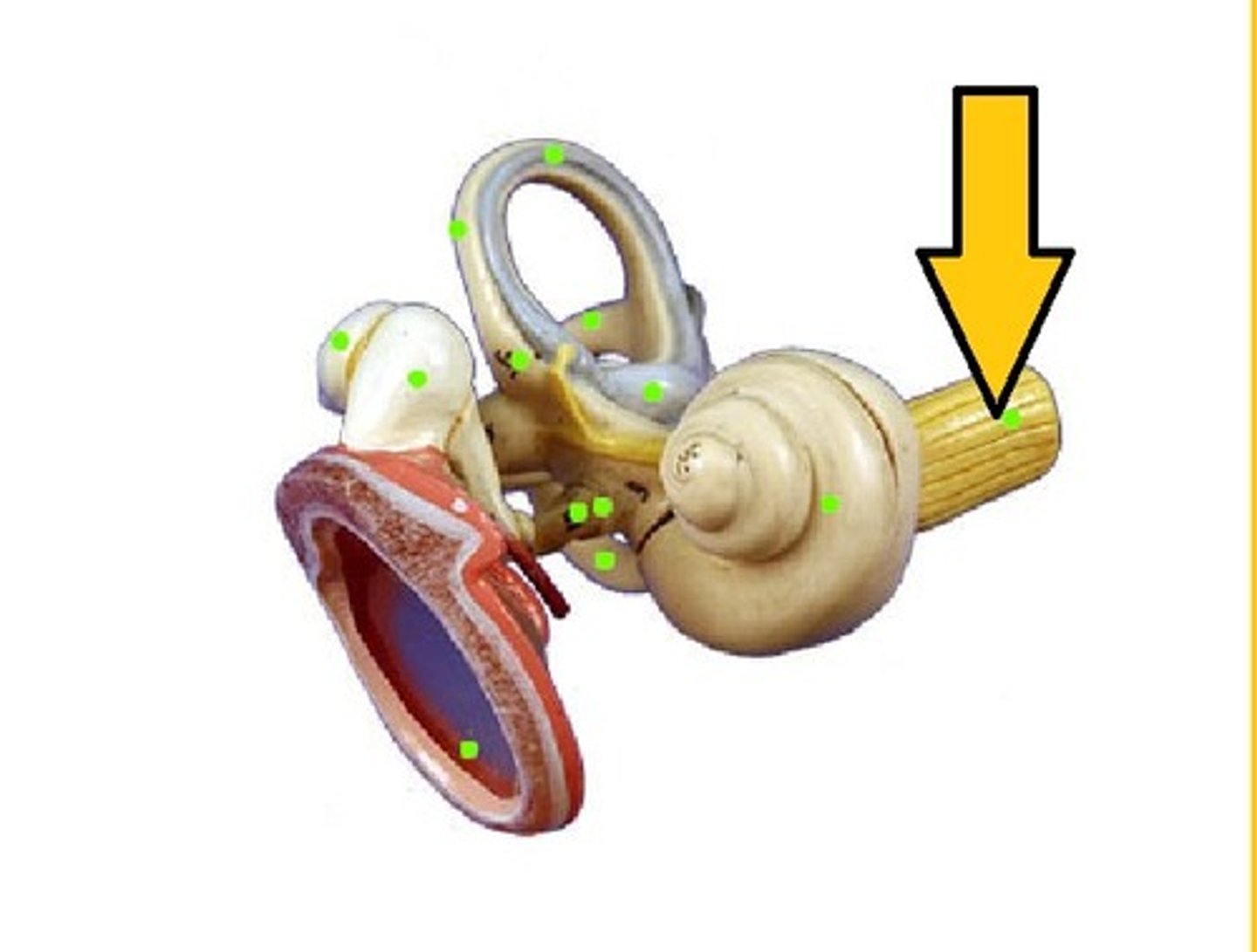
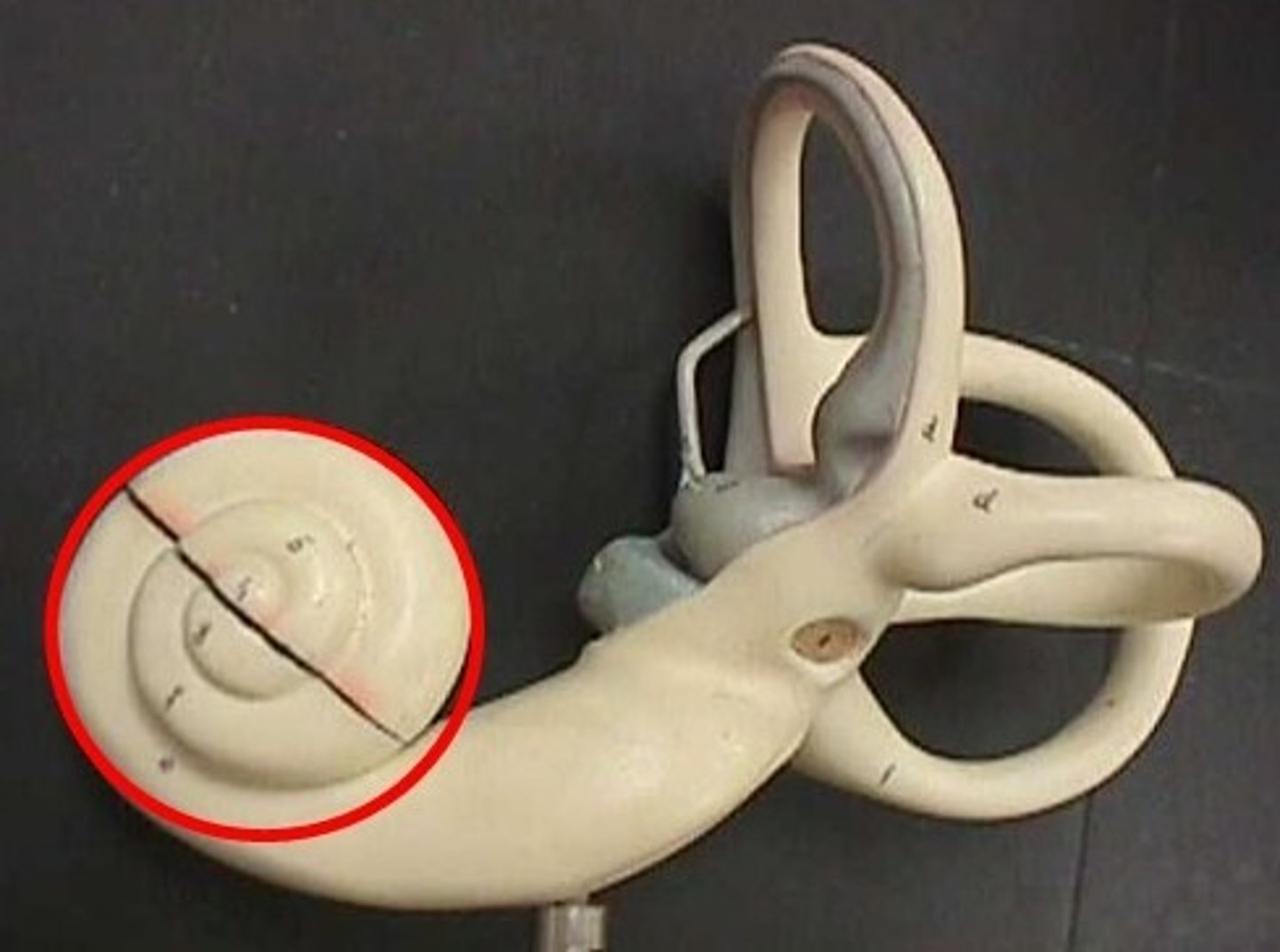
cochlea-- fluid moves and sound waves trigger nerve impulses
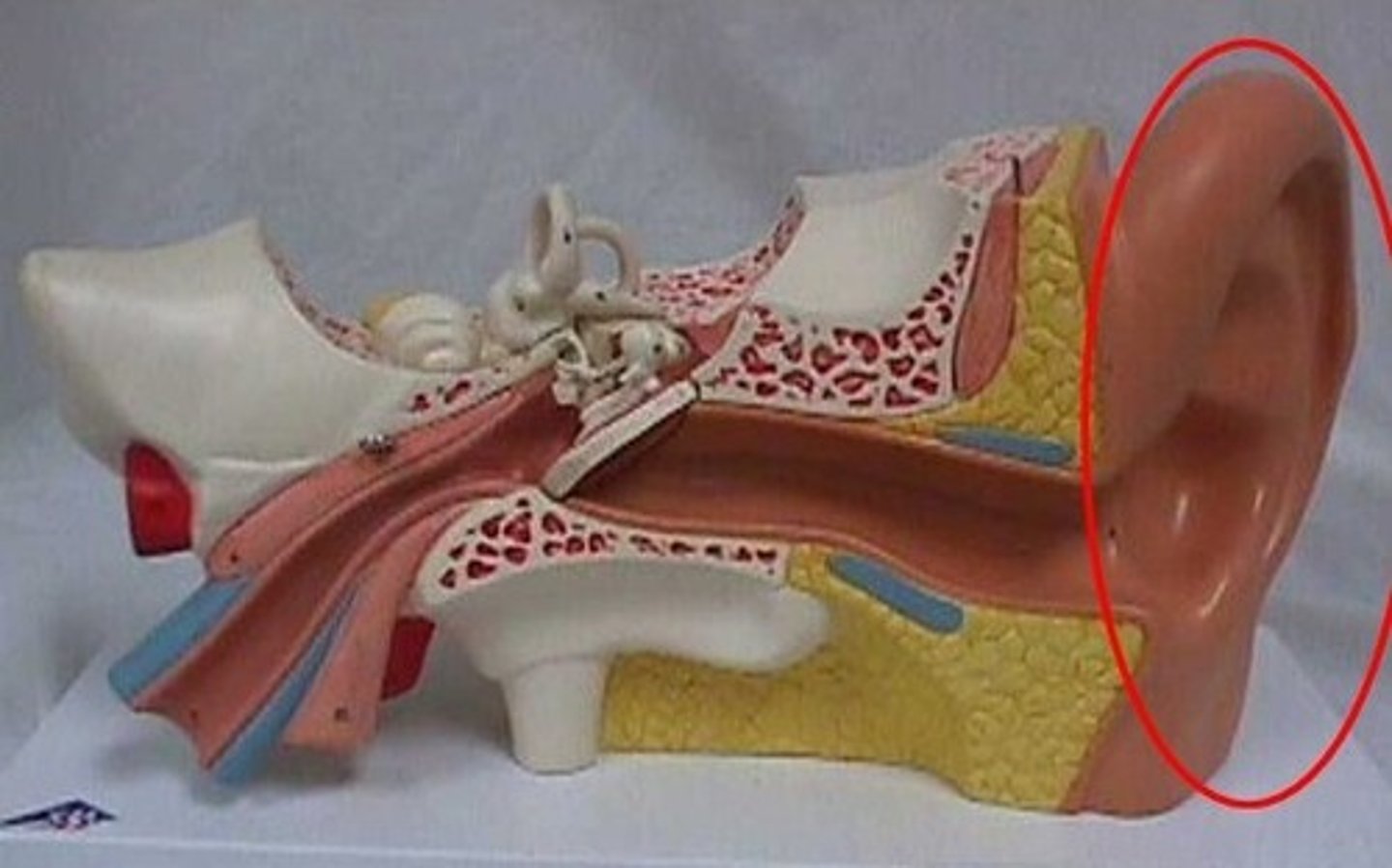
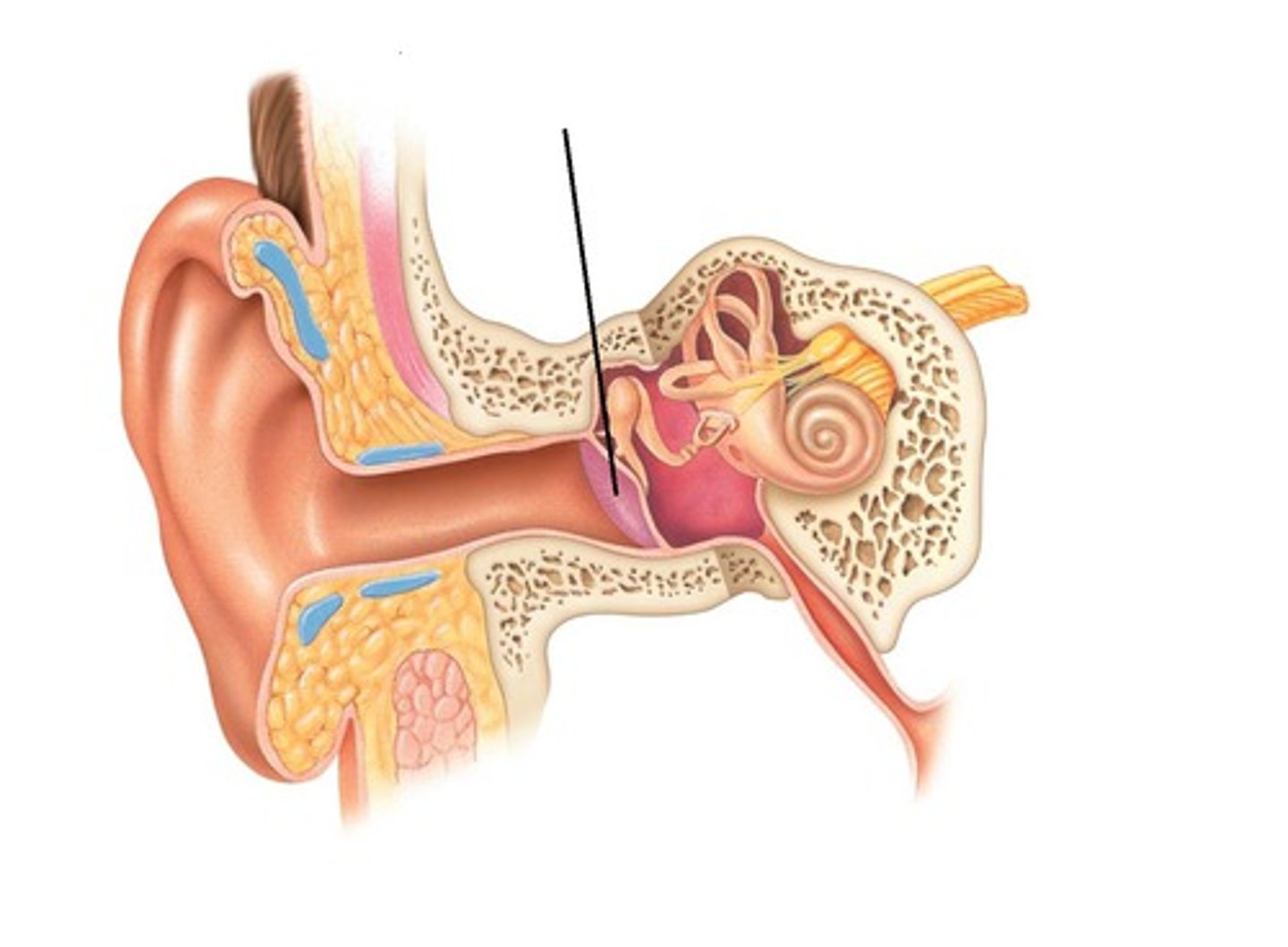
pinna
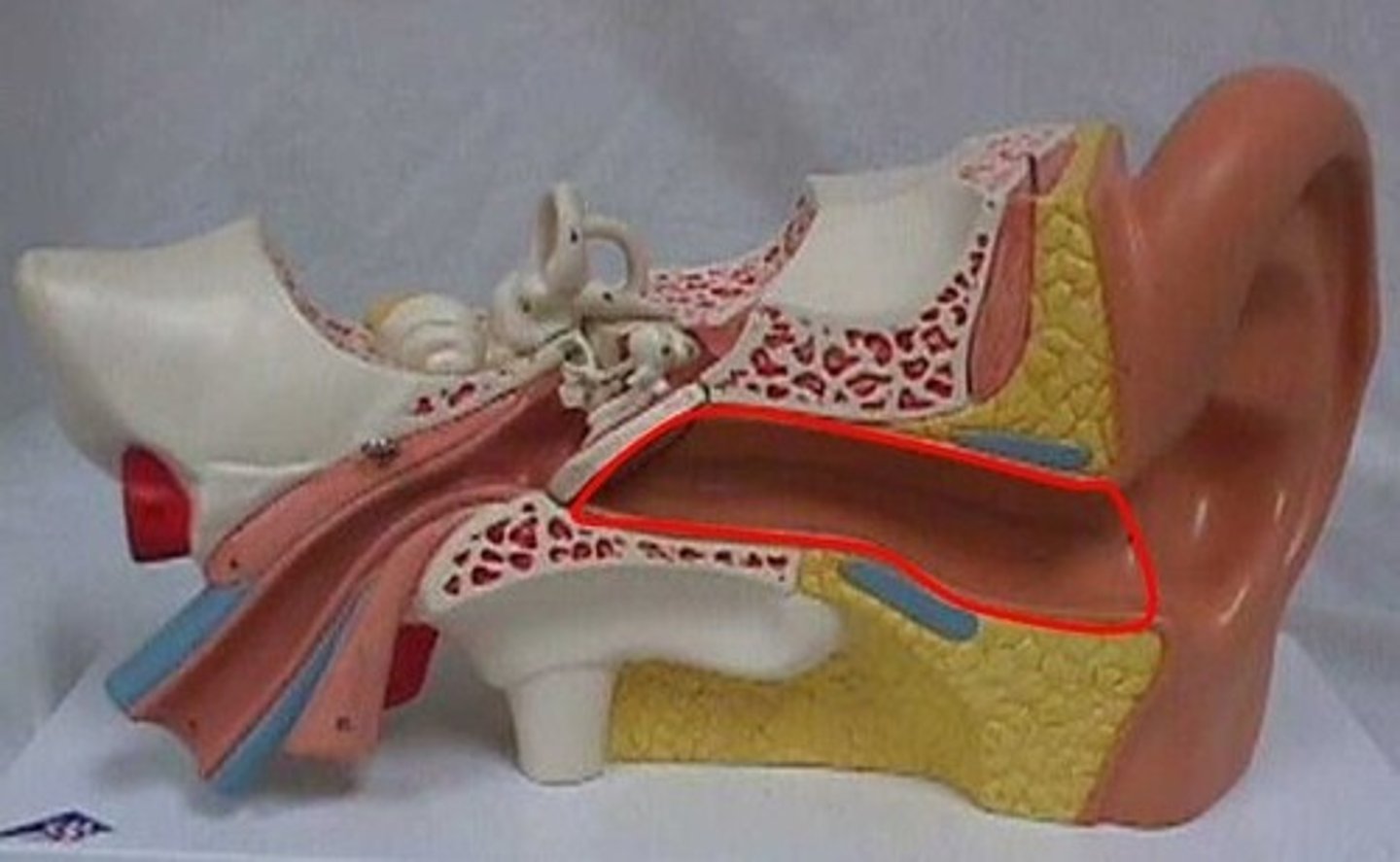
external auditory meatus
ossicles-- three tiny bones in the middle ear that transport sound to inner ear
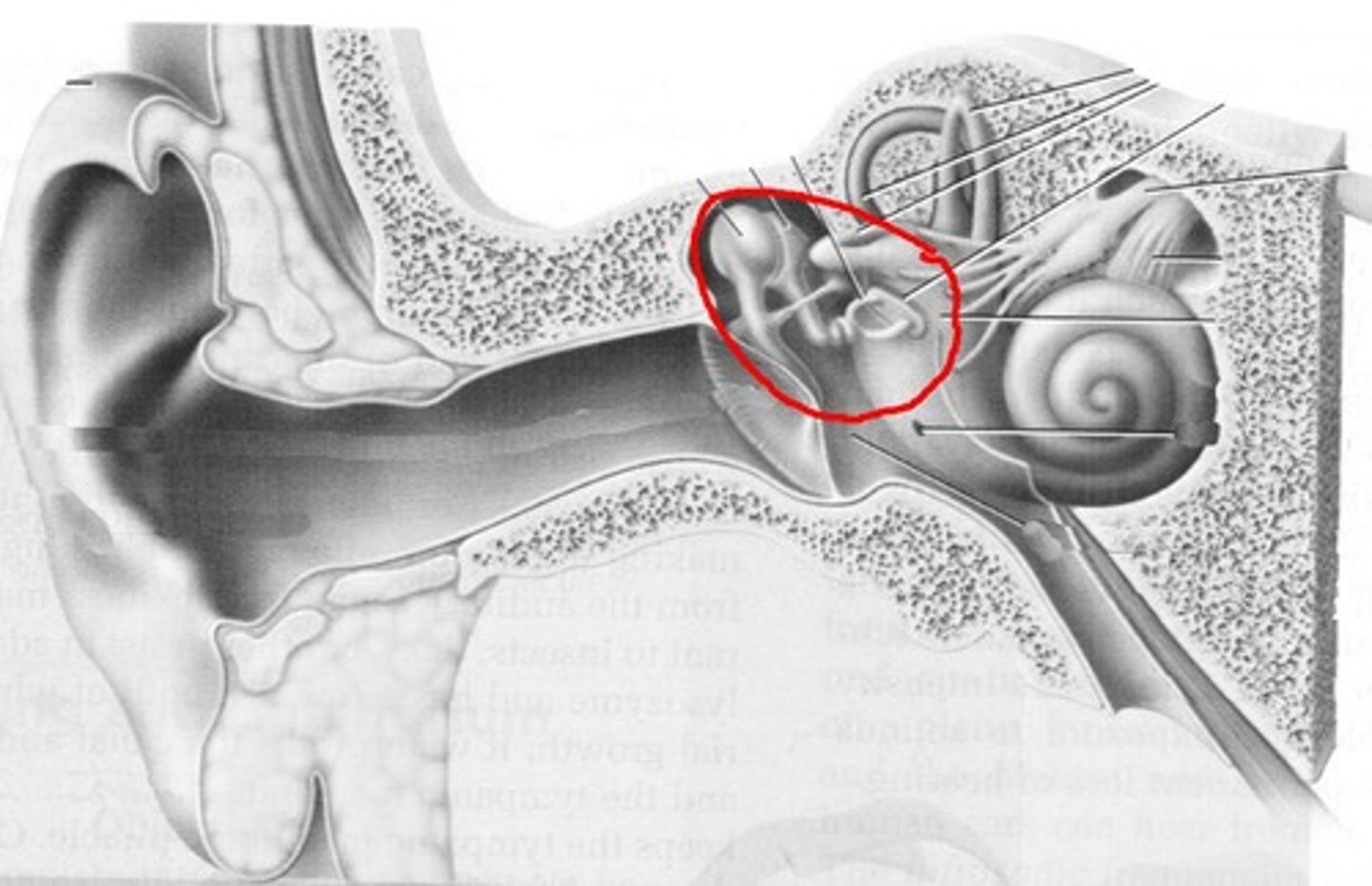
ear drum-- a tightly stretched membrane at the end of the ear canal that vibrates when hit by sound waves
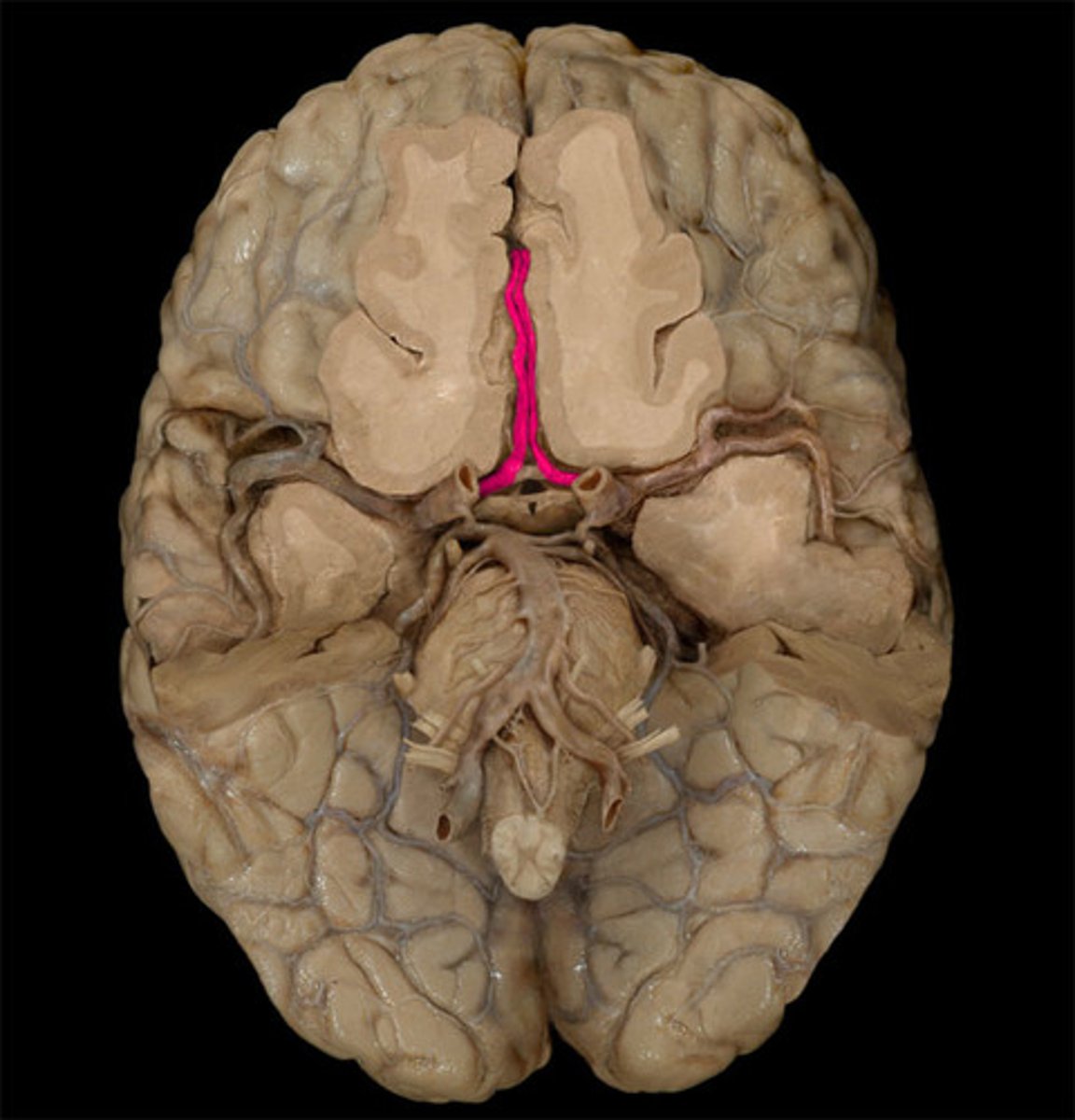
anterior cerebral artery-- The arteries that supply oxygen to most medial portions of frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes; strokes here can affect leg use
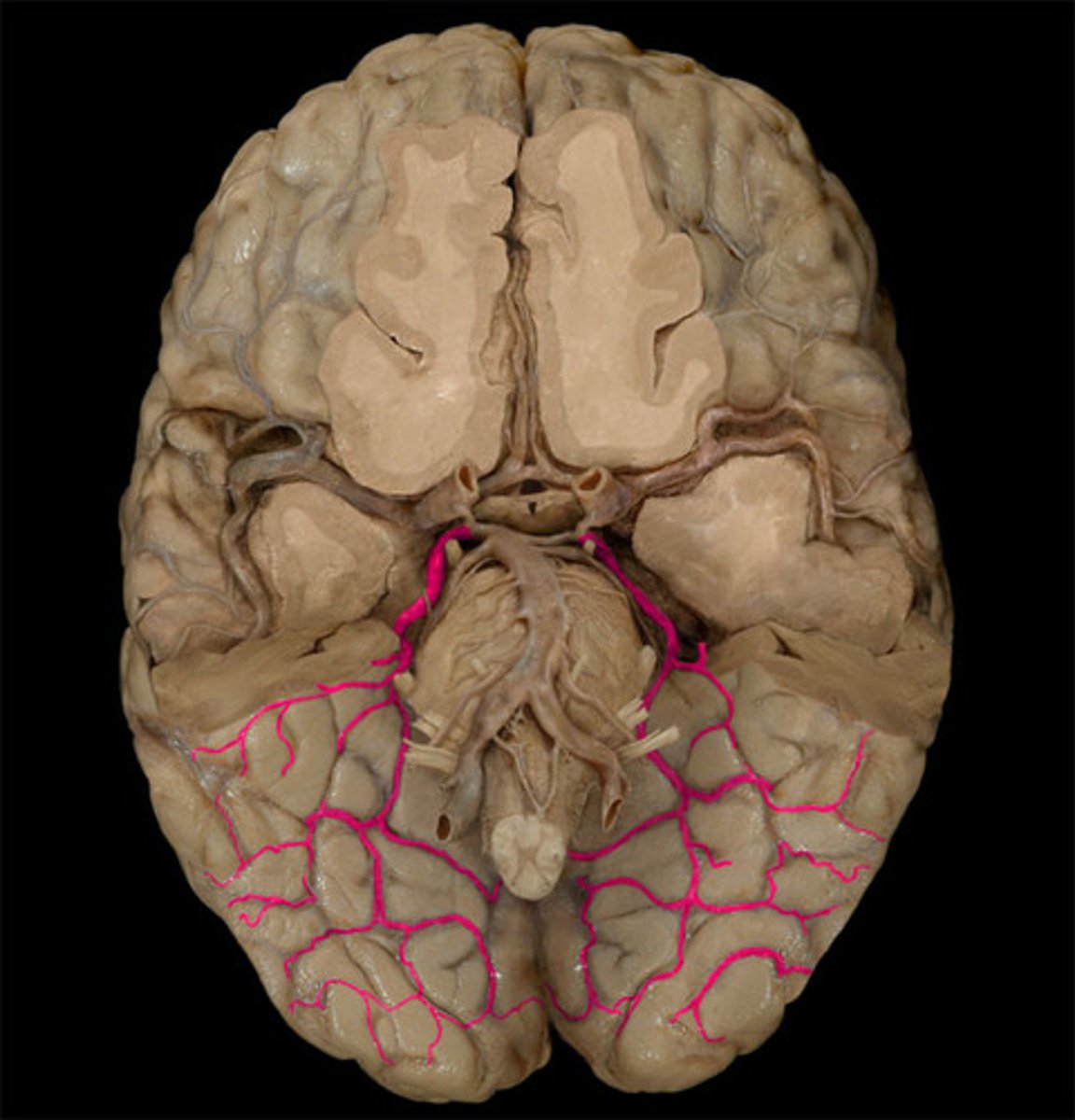
posterior cerebral artery-- supplies occipital lobe and inferior temporal lobe
middle cerebral artery-- Supplies entire lateral cortex
Largest branch of internal carotid artery
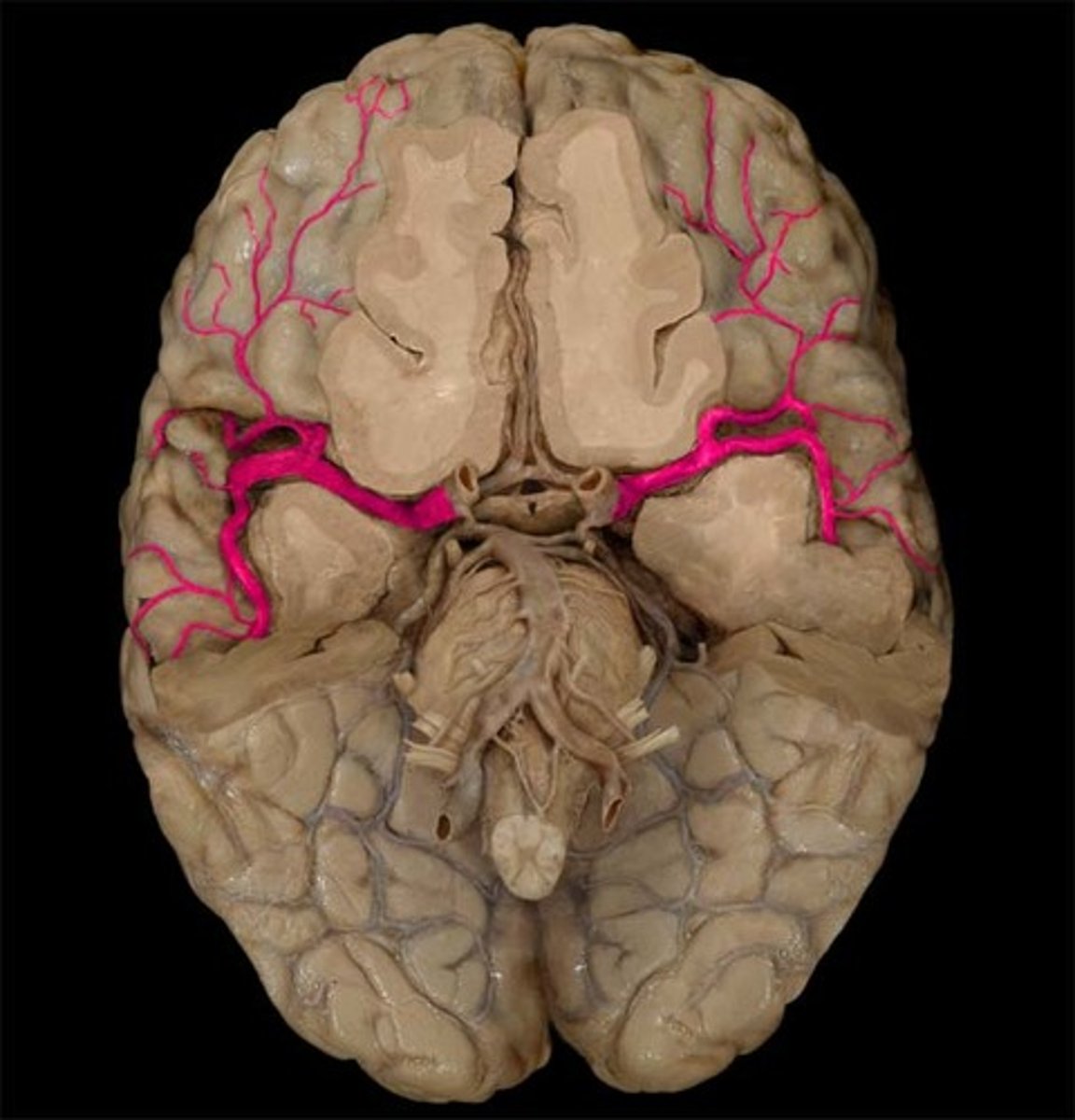
vertebral artery-- 1 of 2 arteries that branch off subclavian arteries, then course up vertebrae into brain
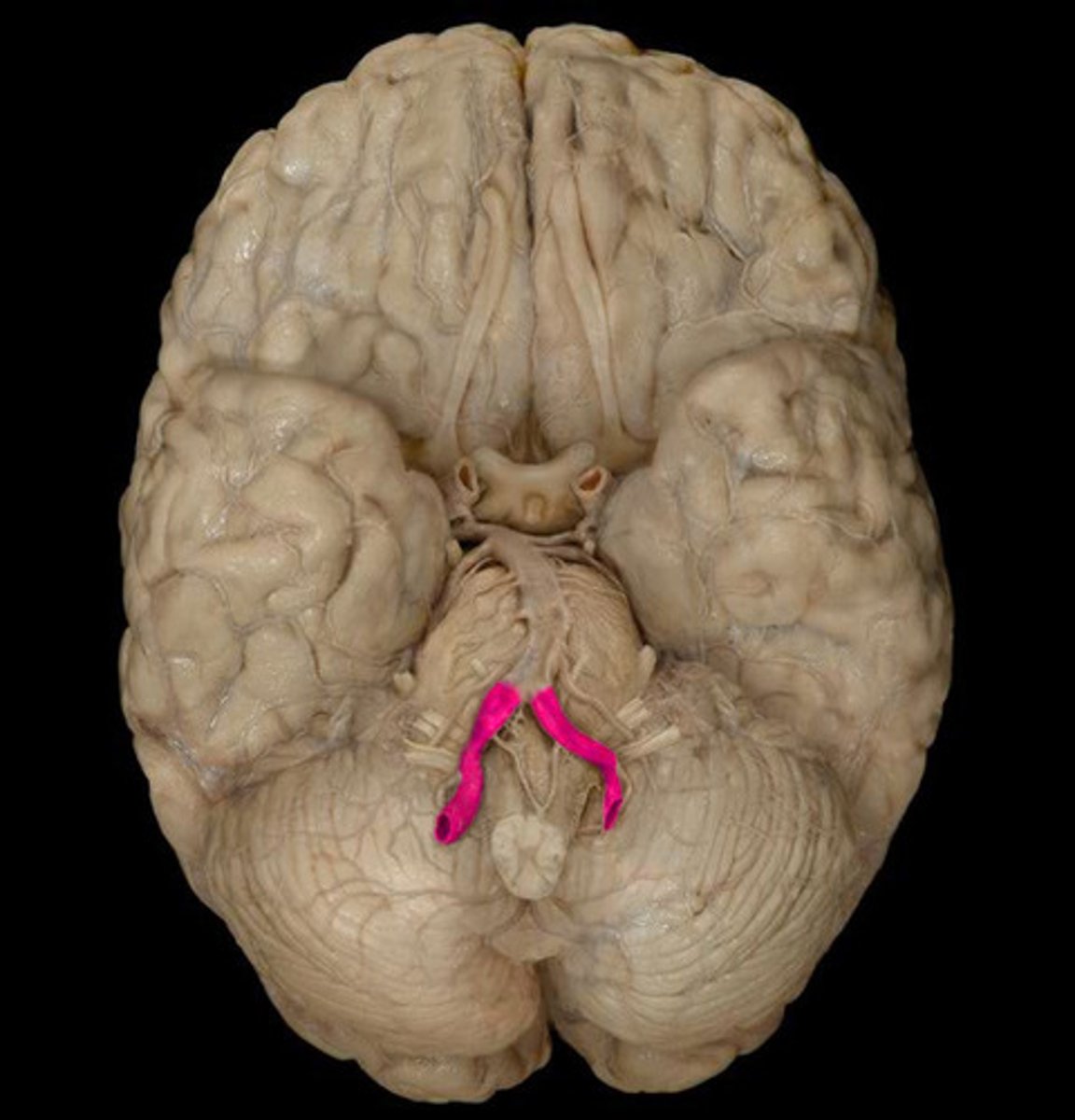
basilar artery
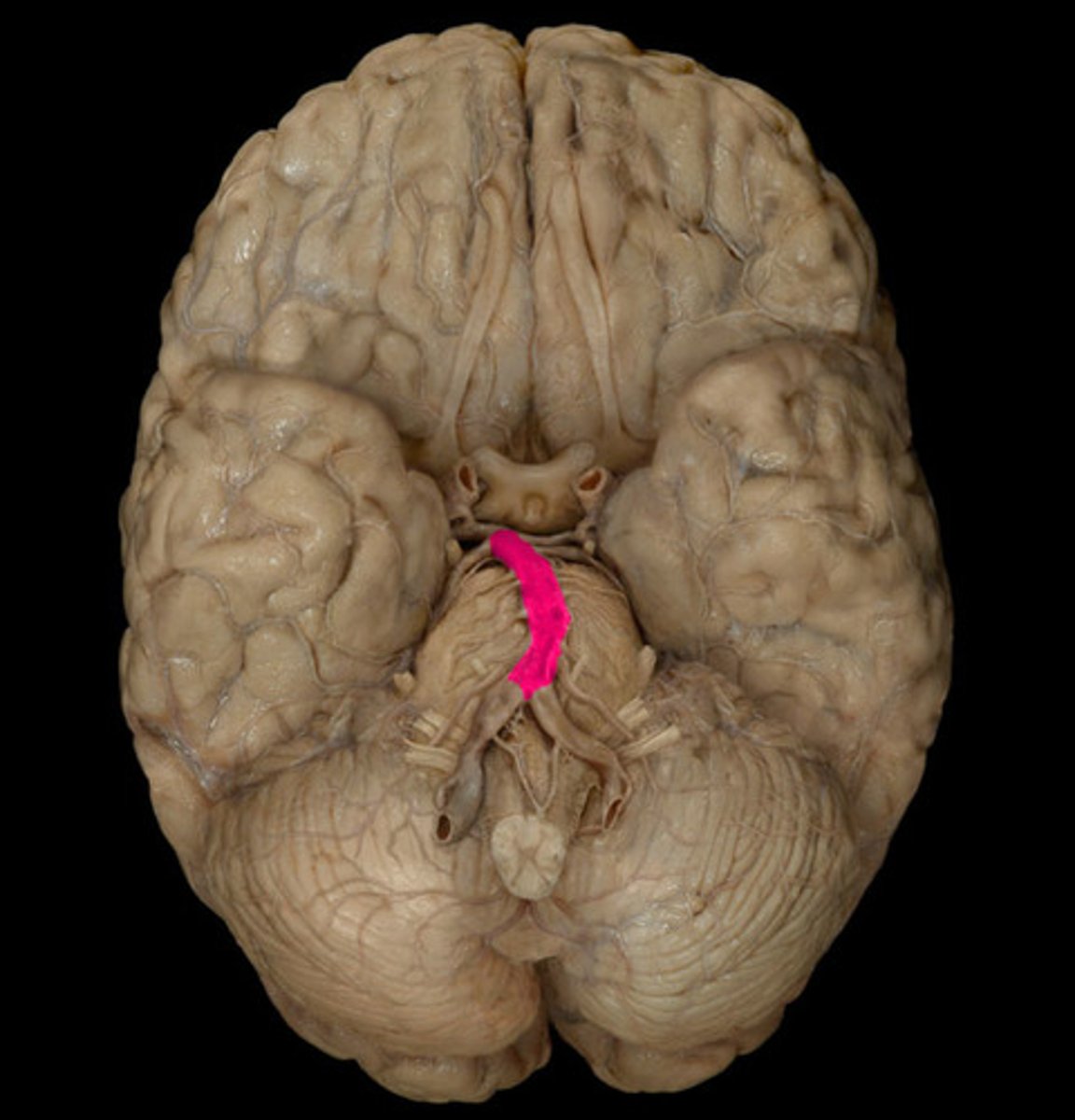
internal carotid artery-- Artery that supplies blood to the brain, eyes, eyelids, forehead, nose, and internal ear.
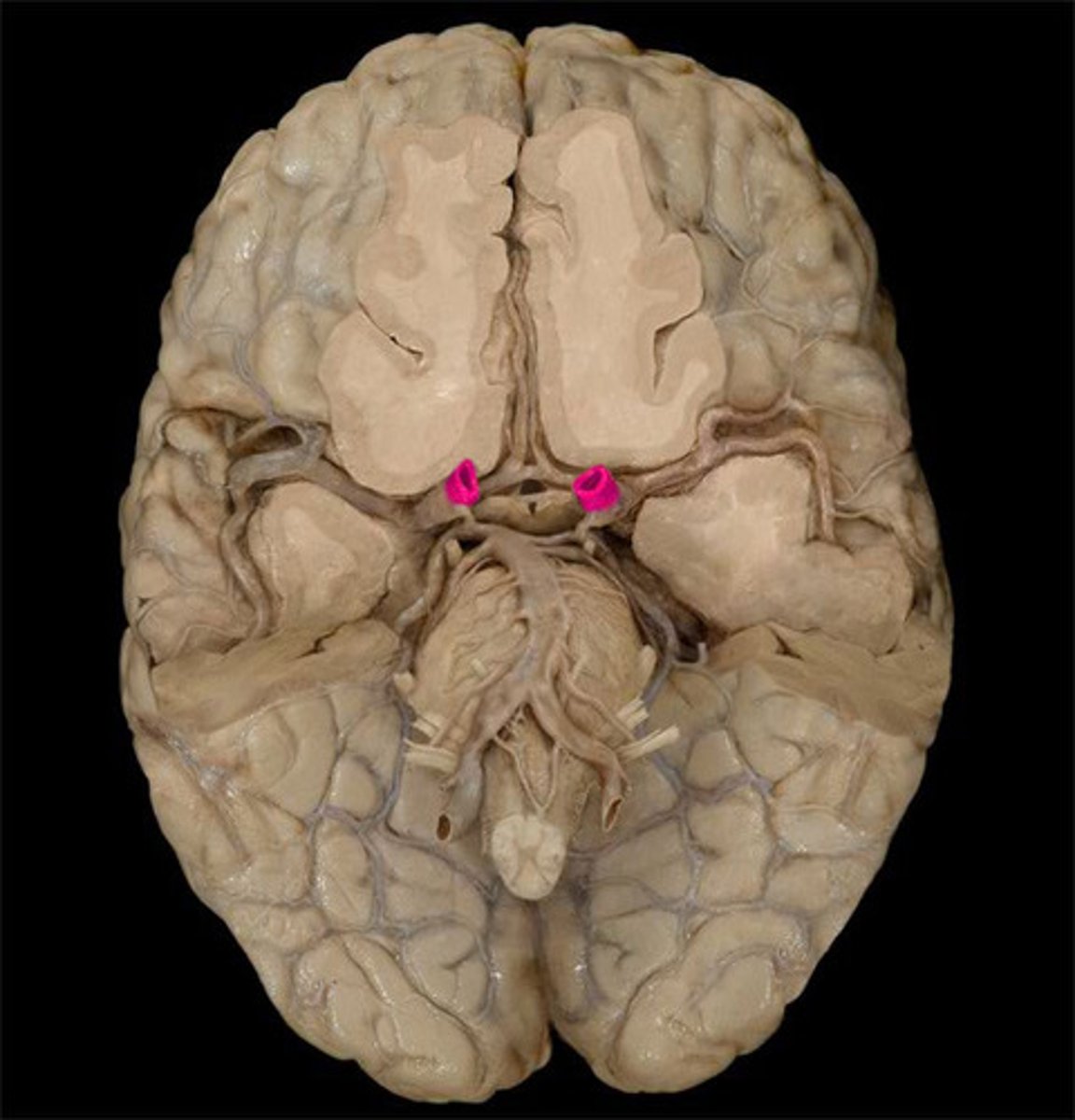
posterior communicating artery Connects posterior cerebral artery to the internal carotid artery
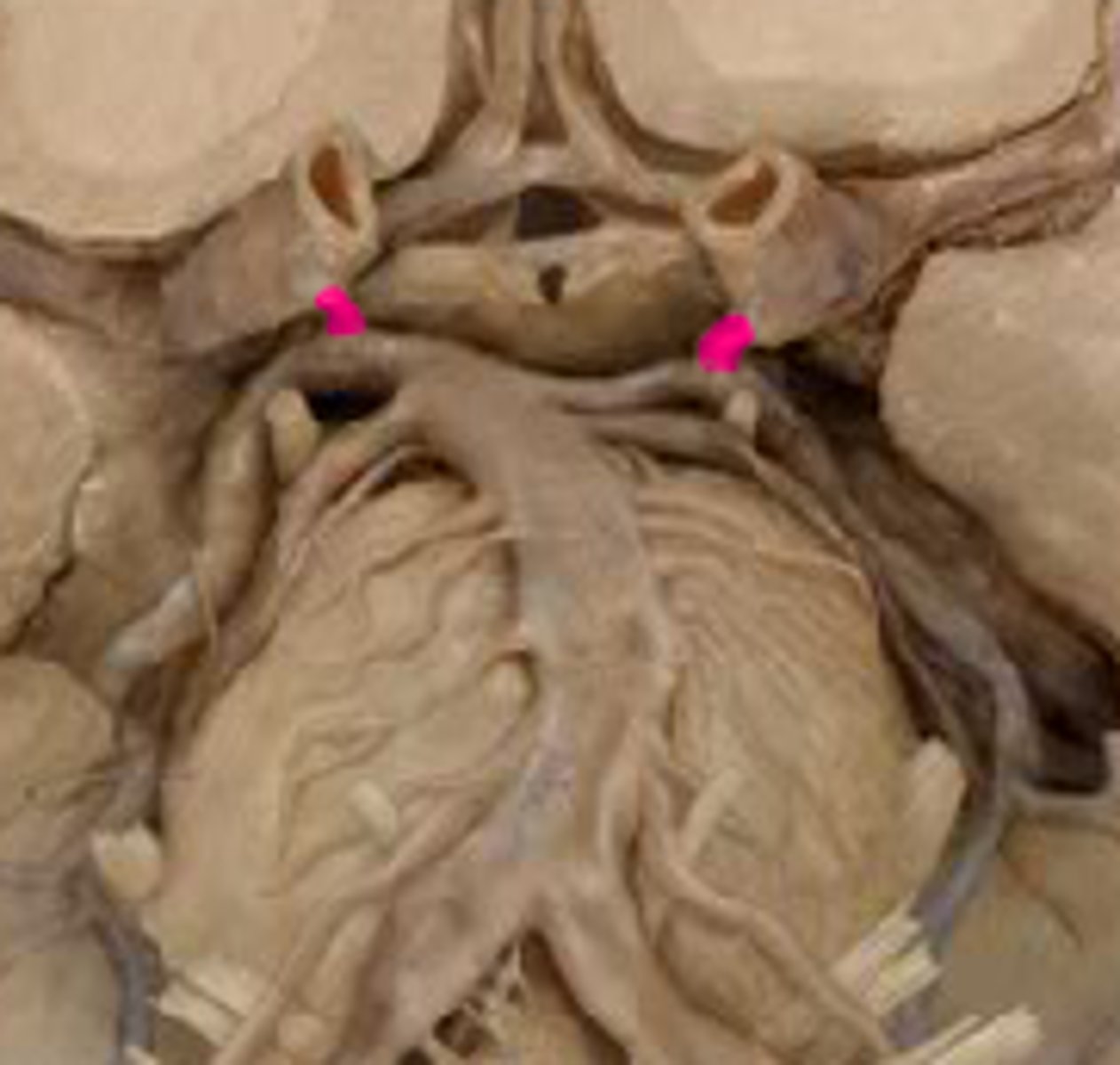
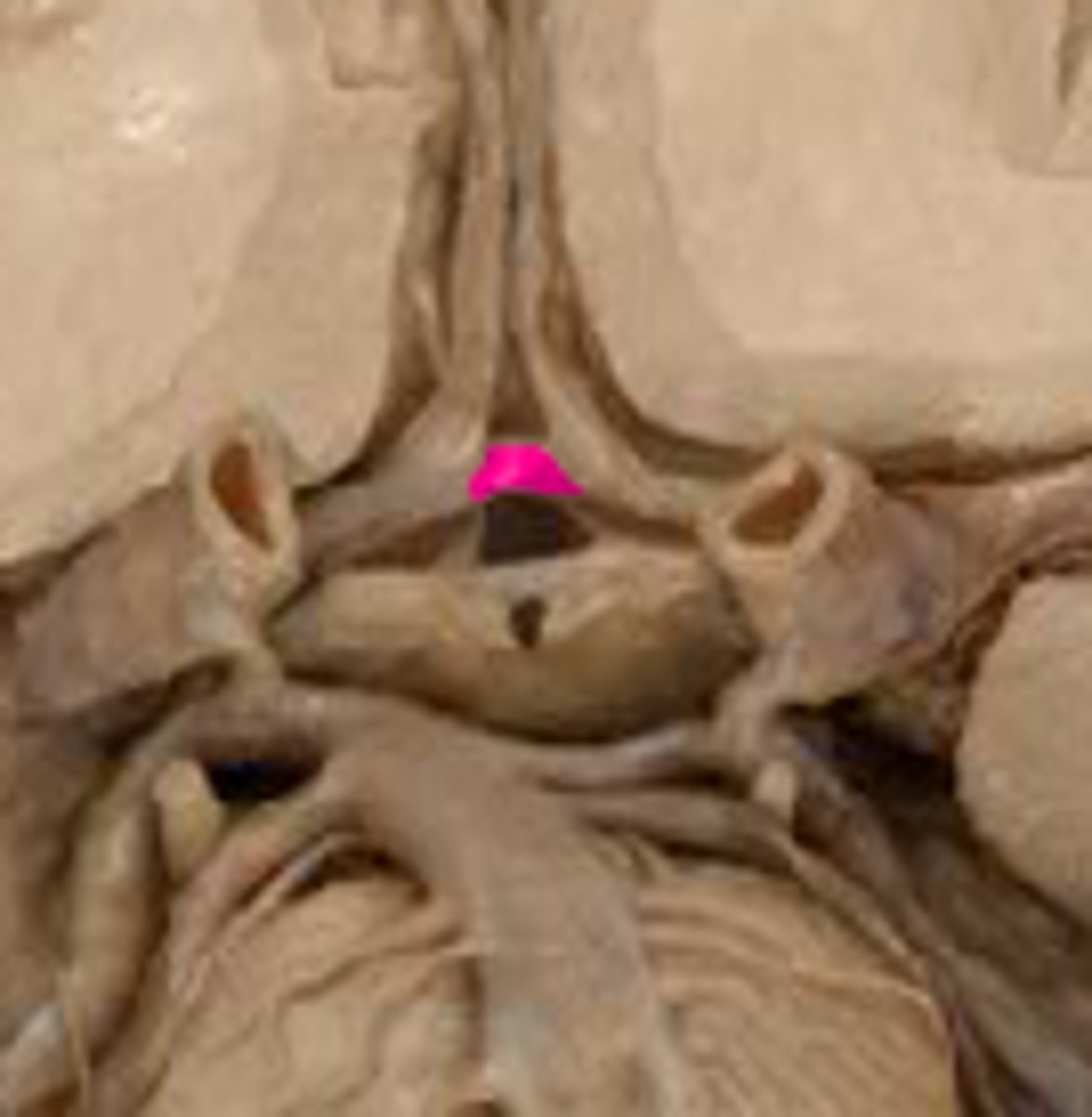
anterior communicating artery connects left and right anterior cerebral arteries
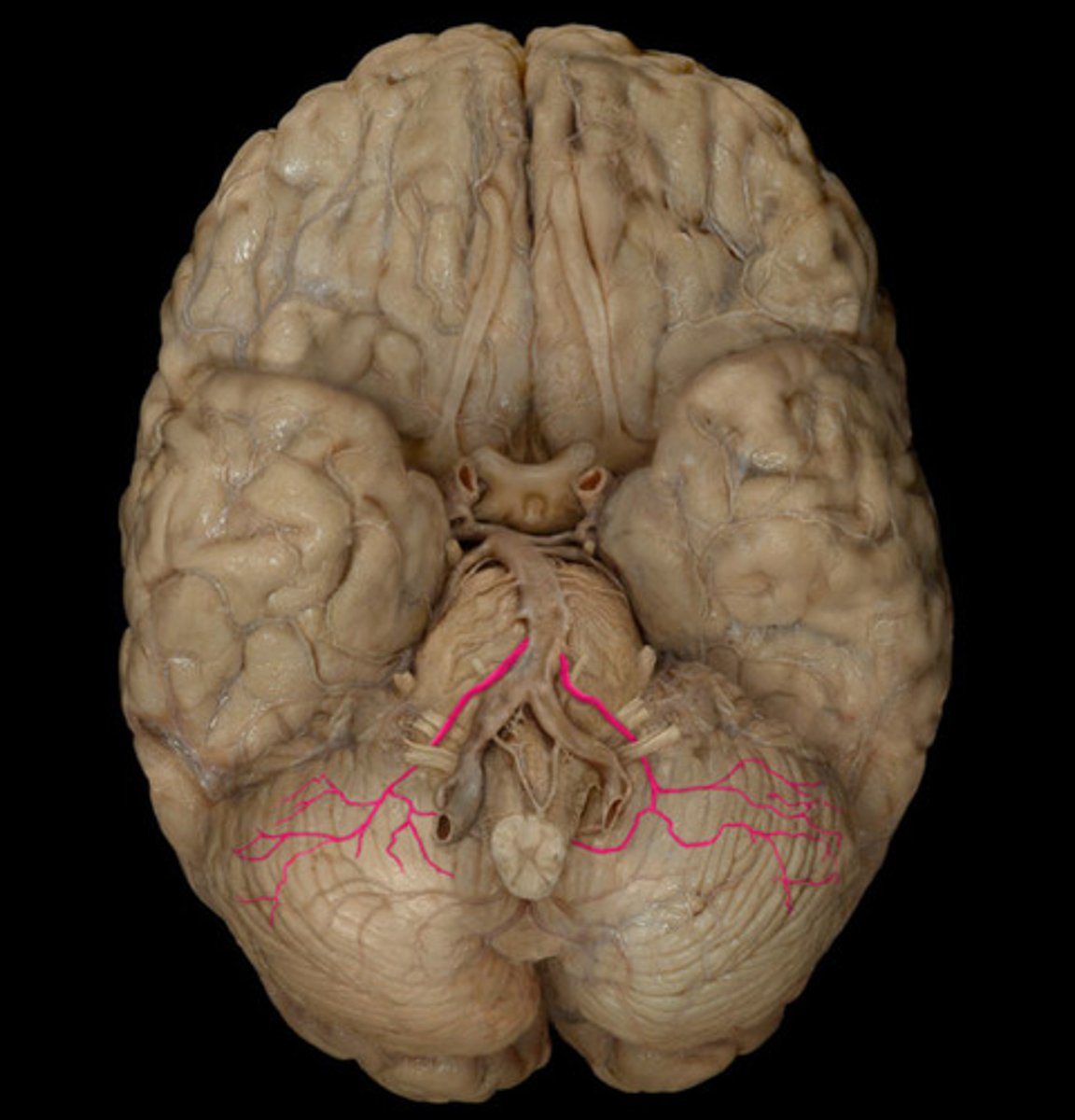
pontine arteries-- supplies the pons

anterior inferior cerebral artery-- Serves the lateral pons (vestibular nuclei, facial nucleus, spinal trigeminal nucleus, cochlear nuclei, and the sympathetic fibers)
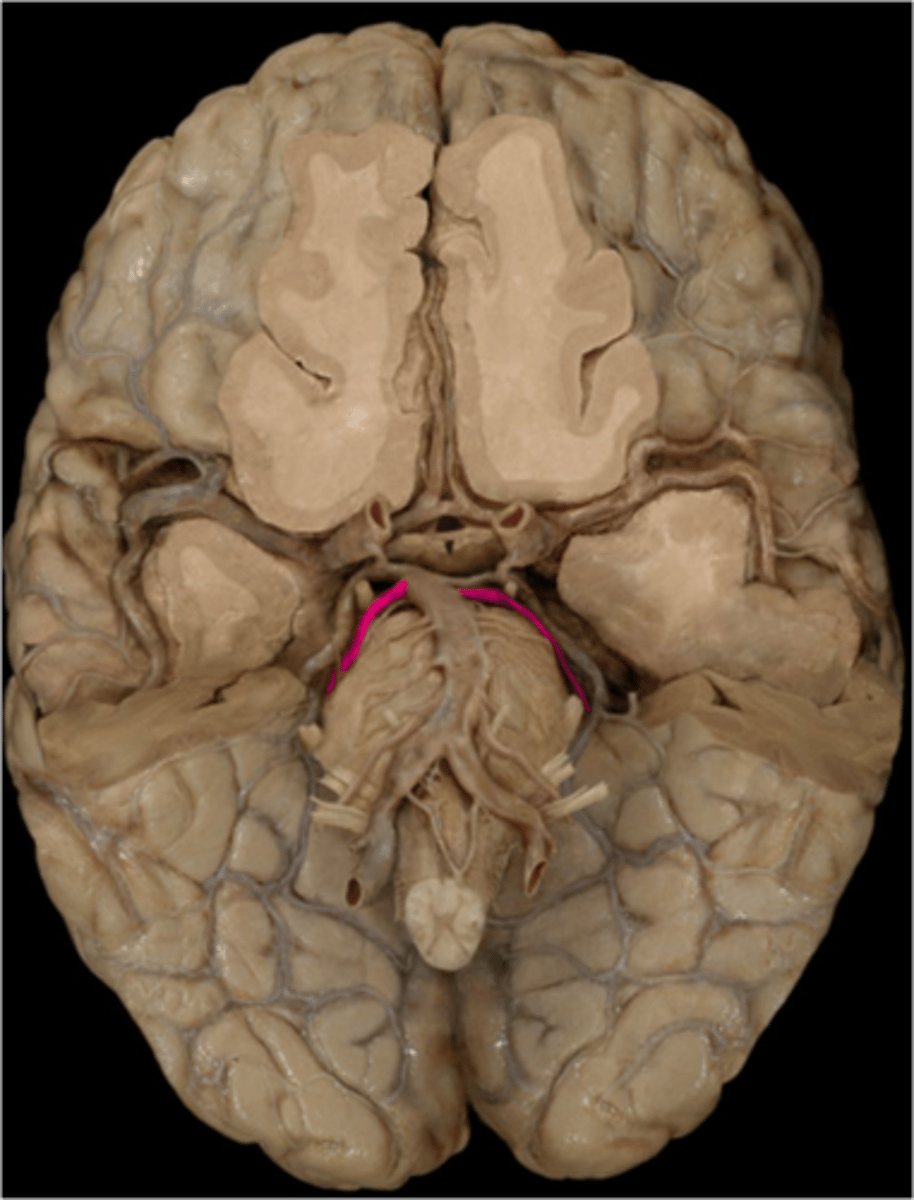
superior cerebellar artery-- supplies cerebellum and midbrain
lateral ventricle-- C-shaped lateral portion of the ventricular system within each hemisphere of the brain
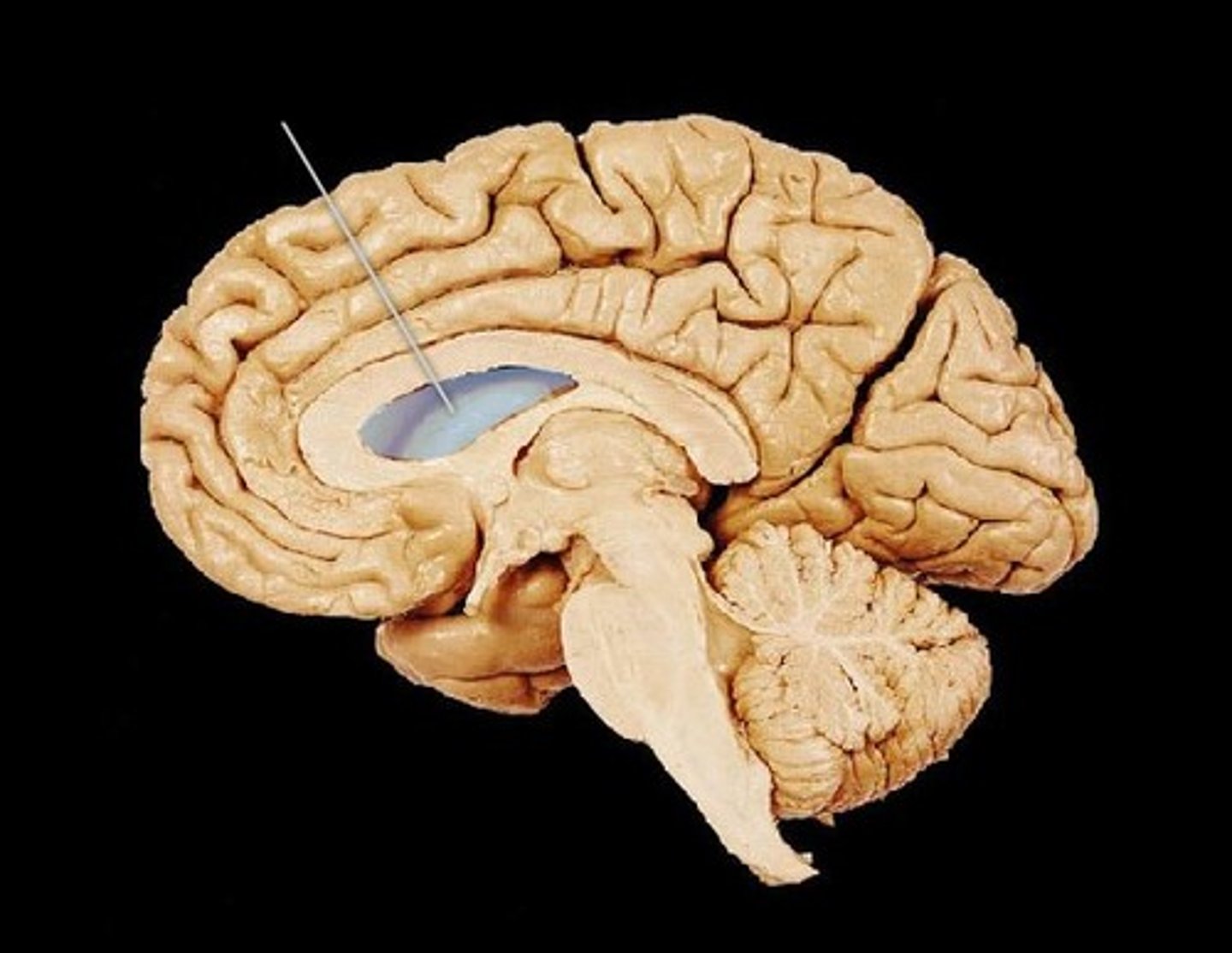
interventricular foramen-- connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
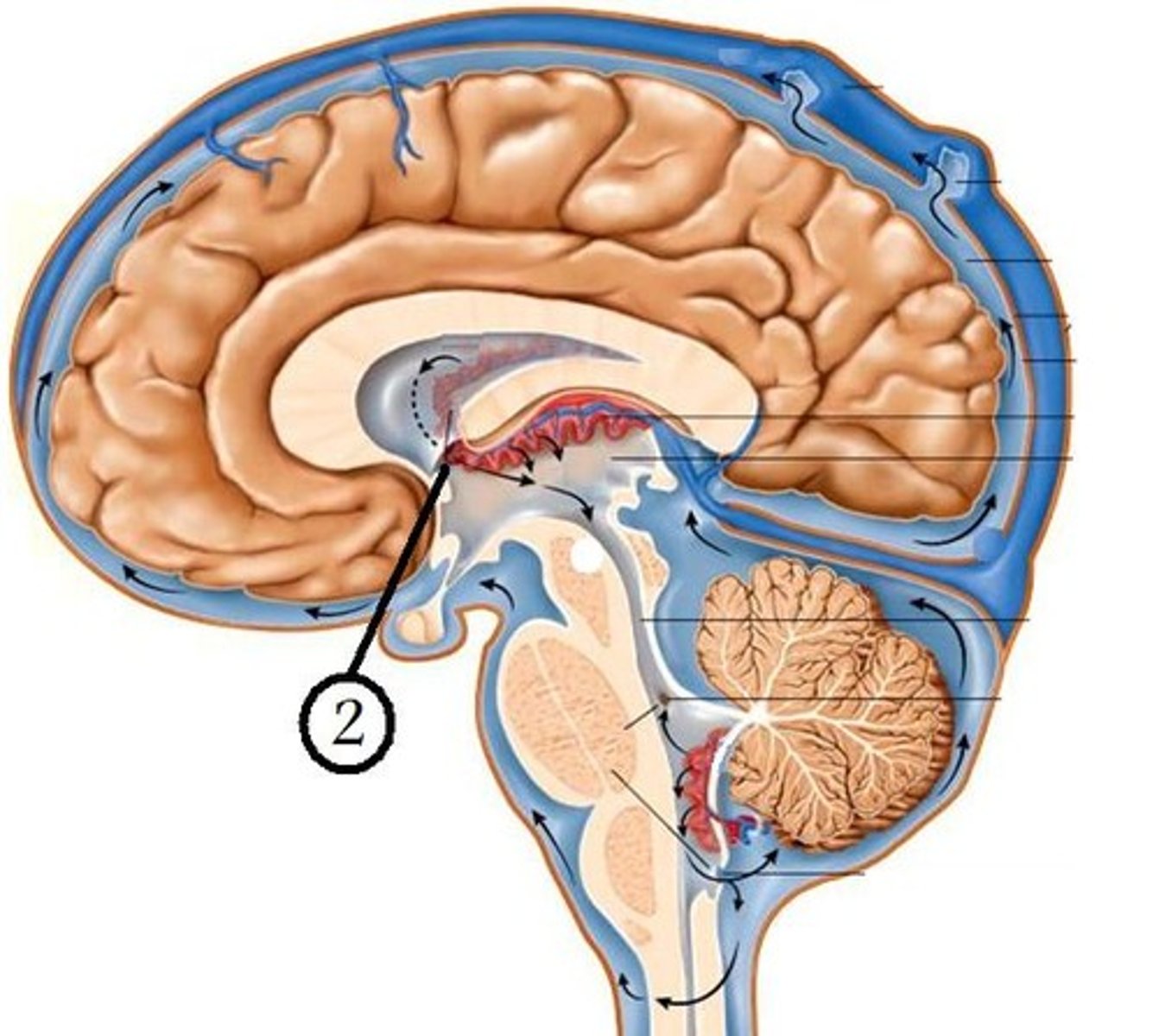
third ventricle-- the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
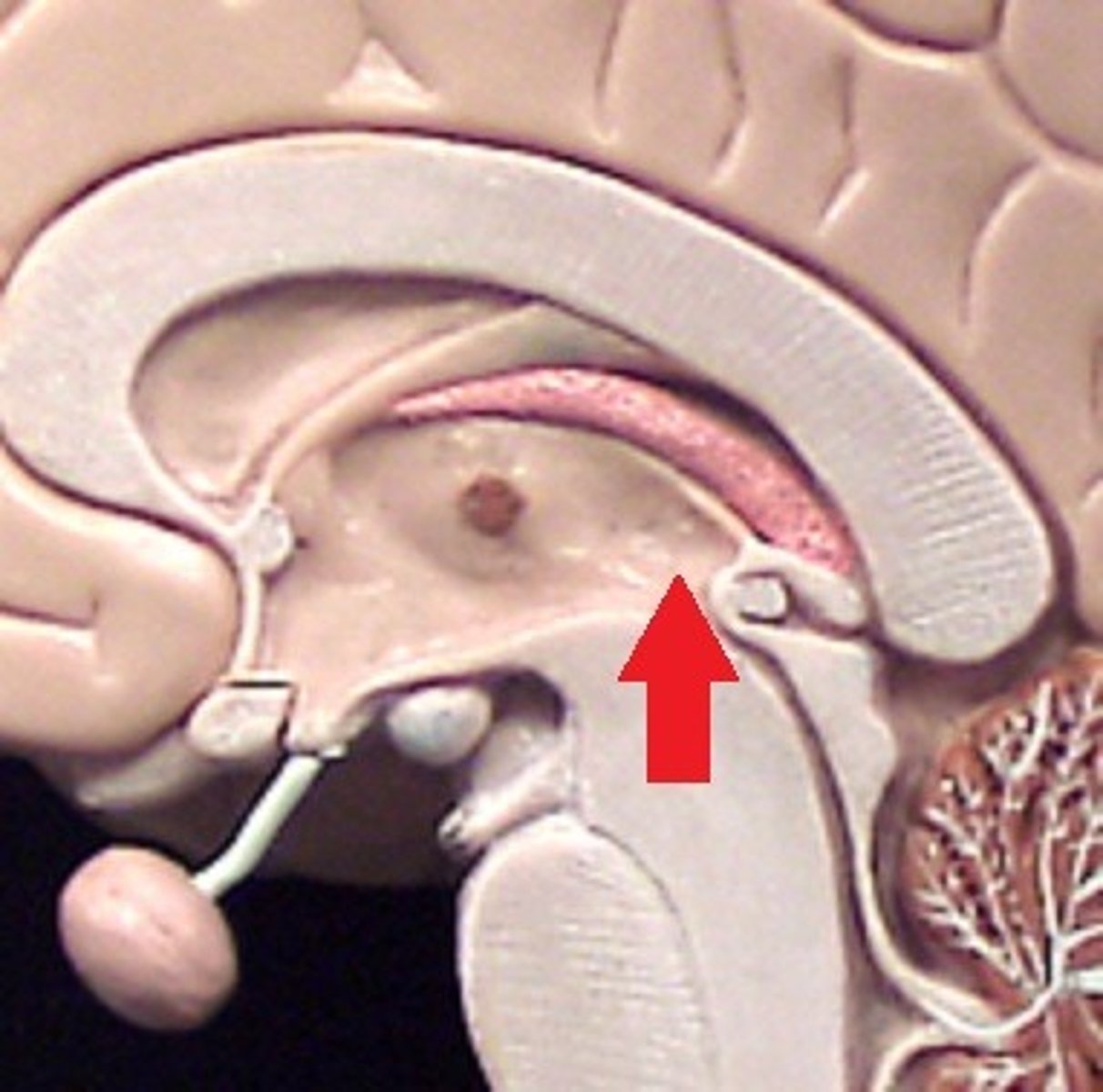
cerebral aqueduct-- connects the third and fourth ventricles
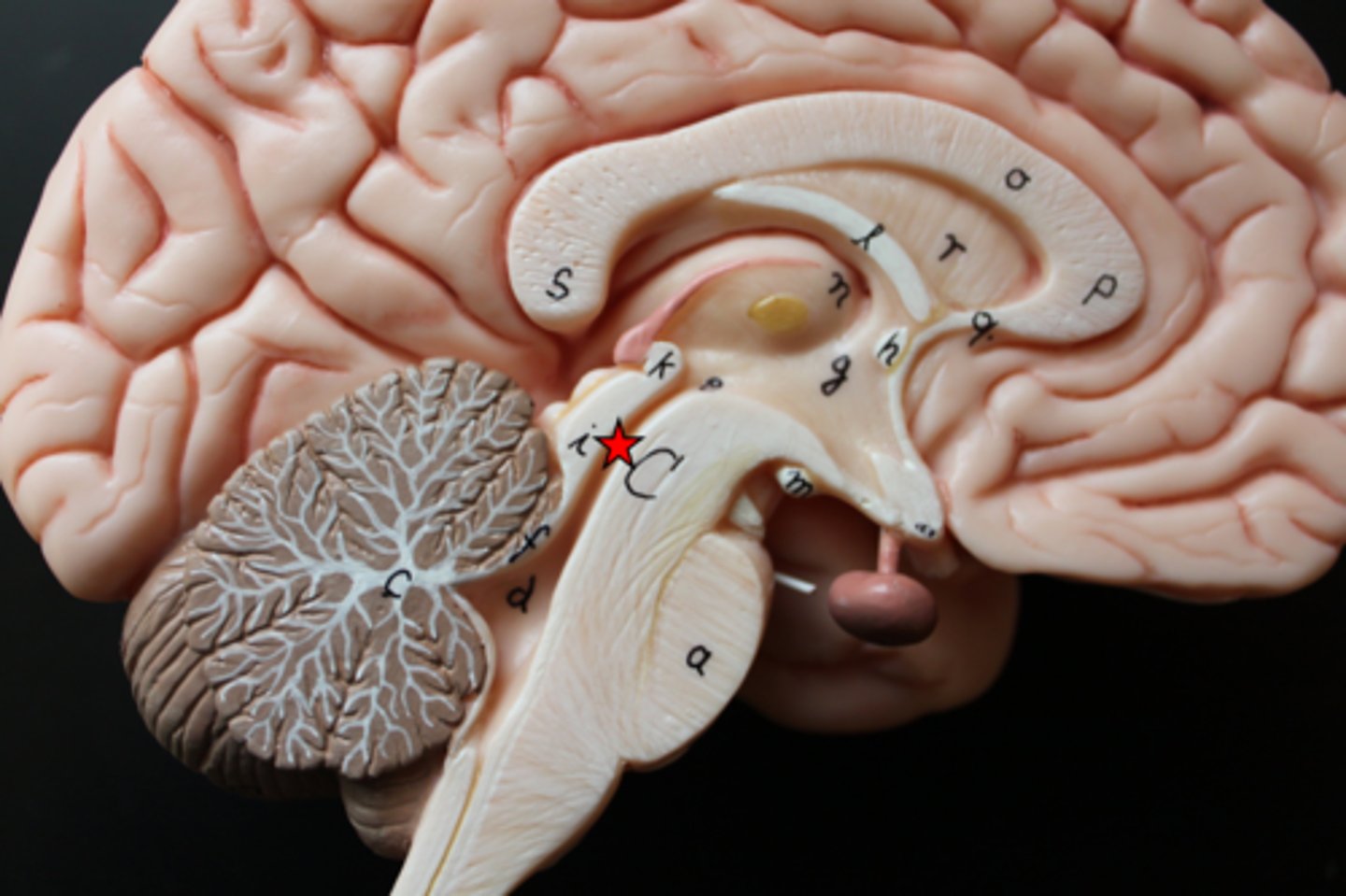
fourth ventricle-- the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons
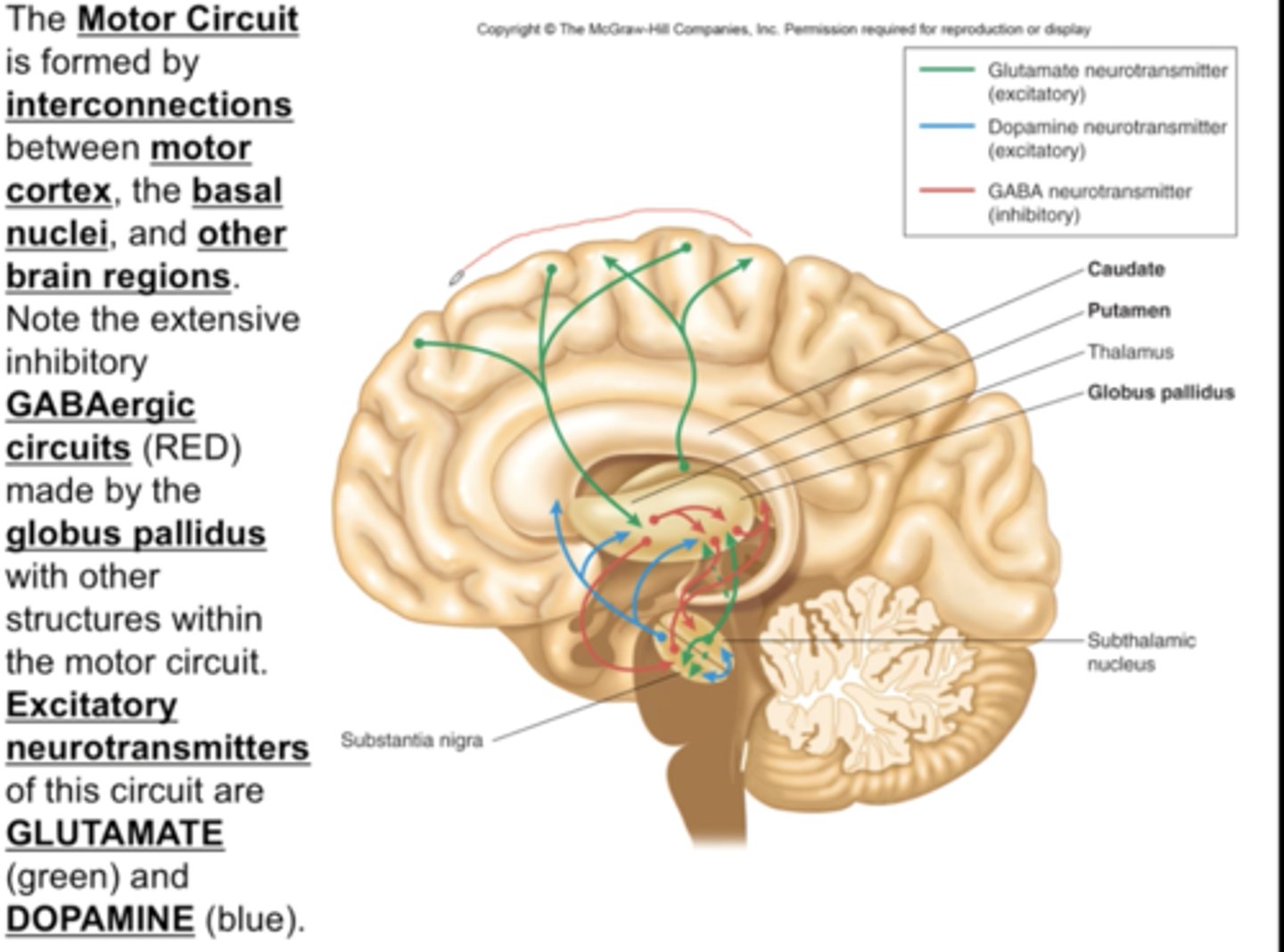
motor circuit-- allows intended movements to occur while inhibiting unintended movements
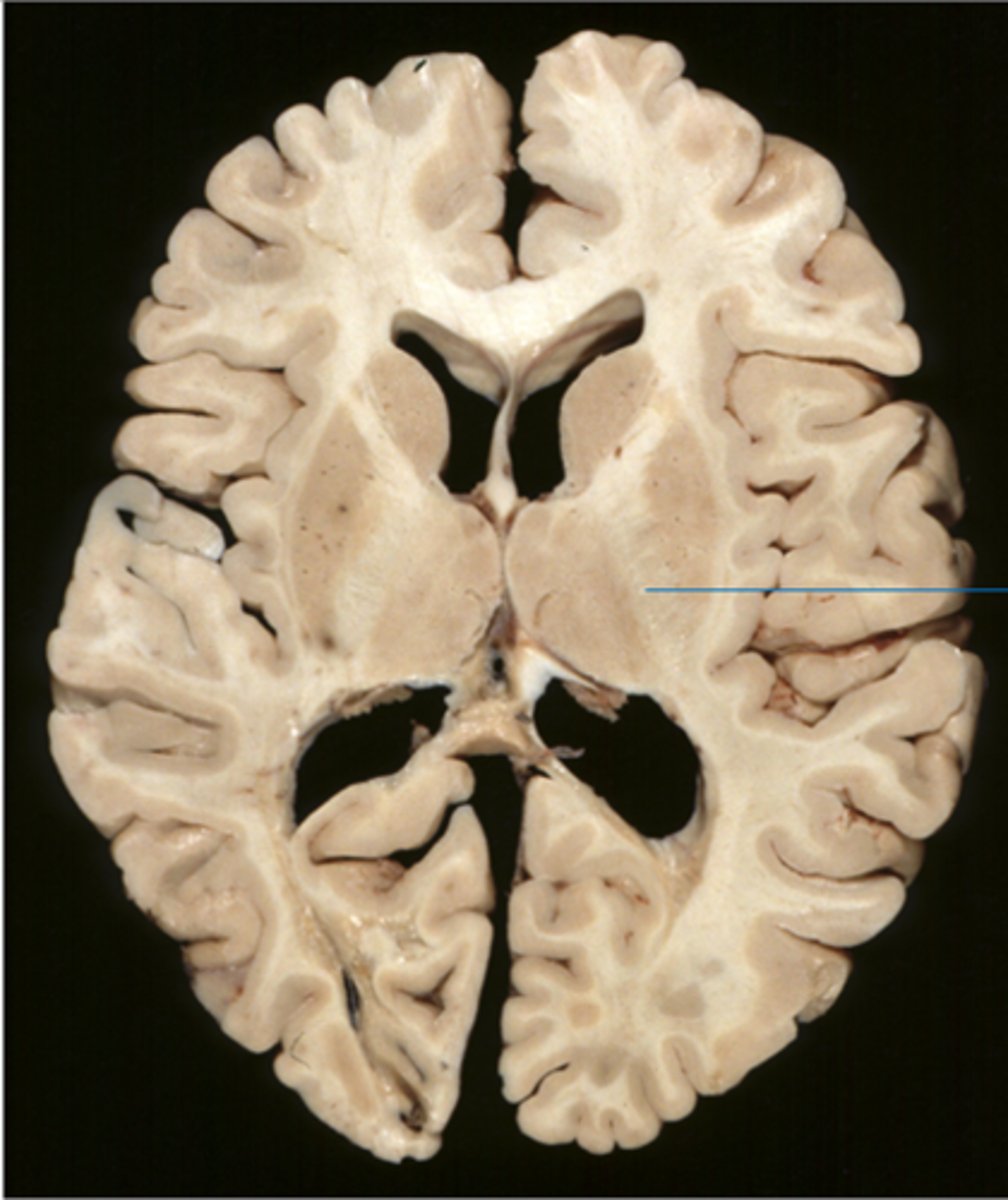
projection fibers-- tracts between the cerebrum and other parts of the brain and spinal cord
internal capsule-- band of projection fibers that runs between the basal nuclei and the thalamus
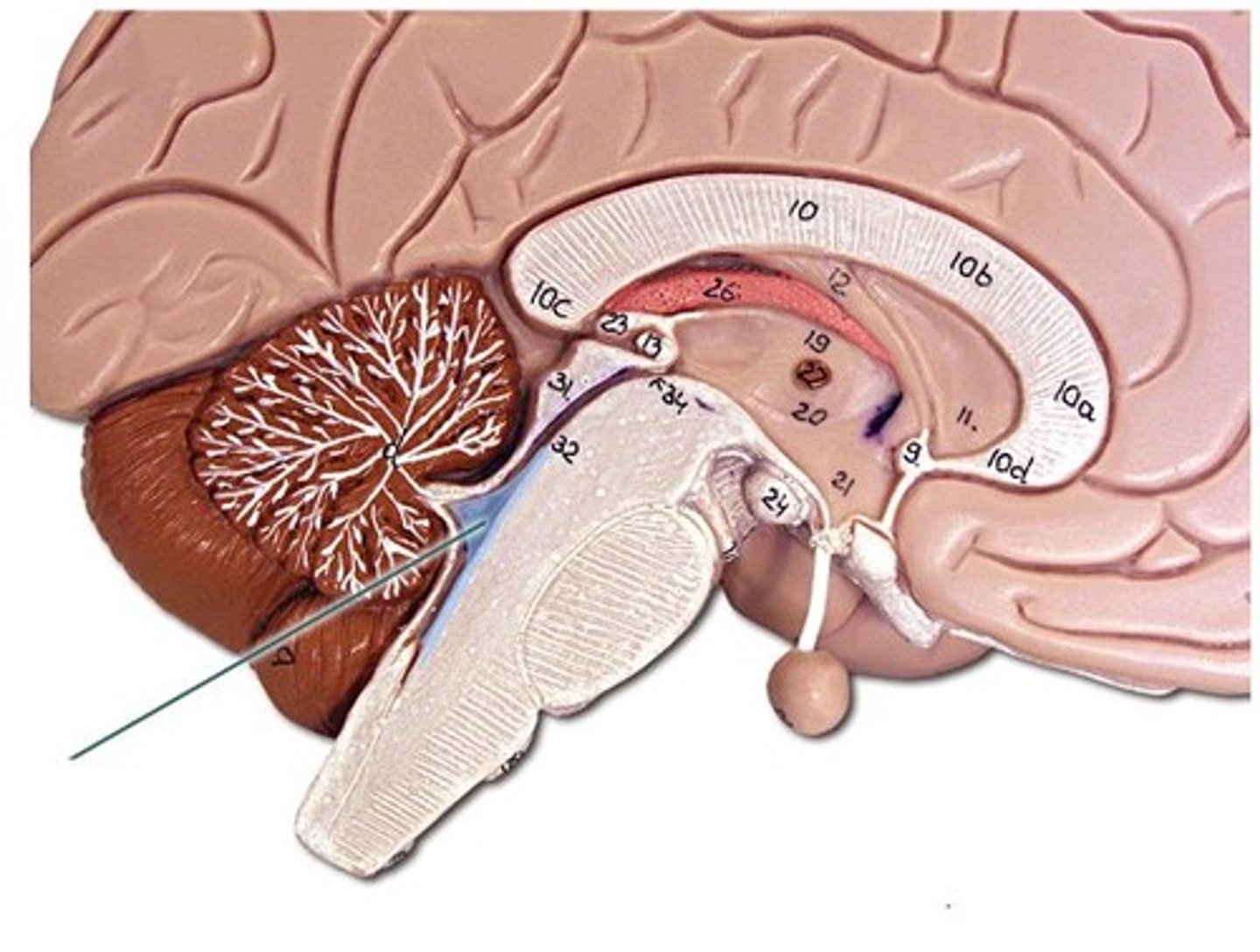
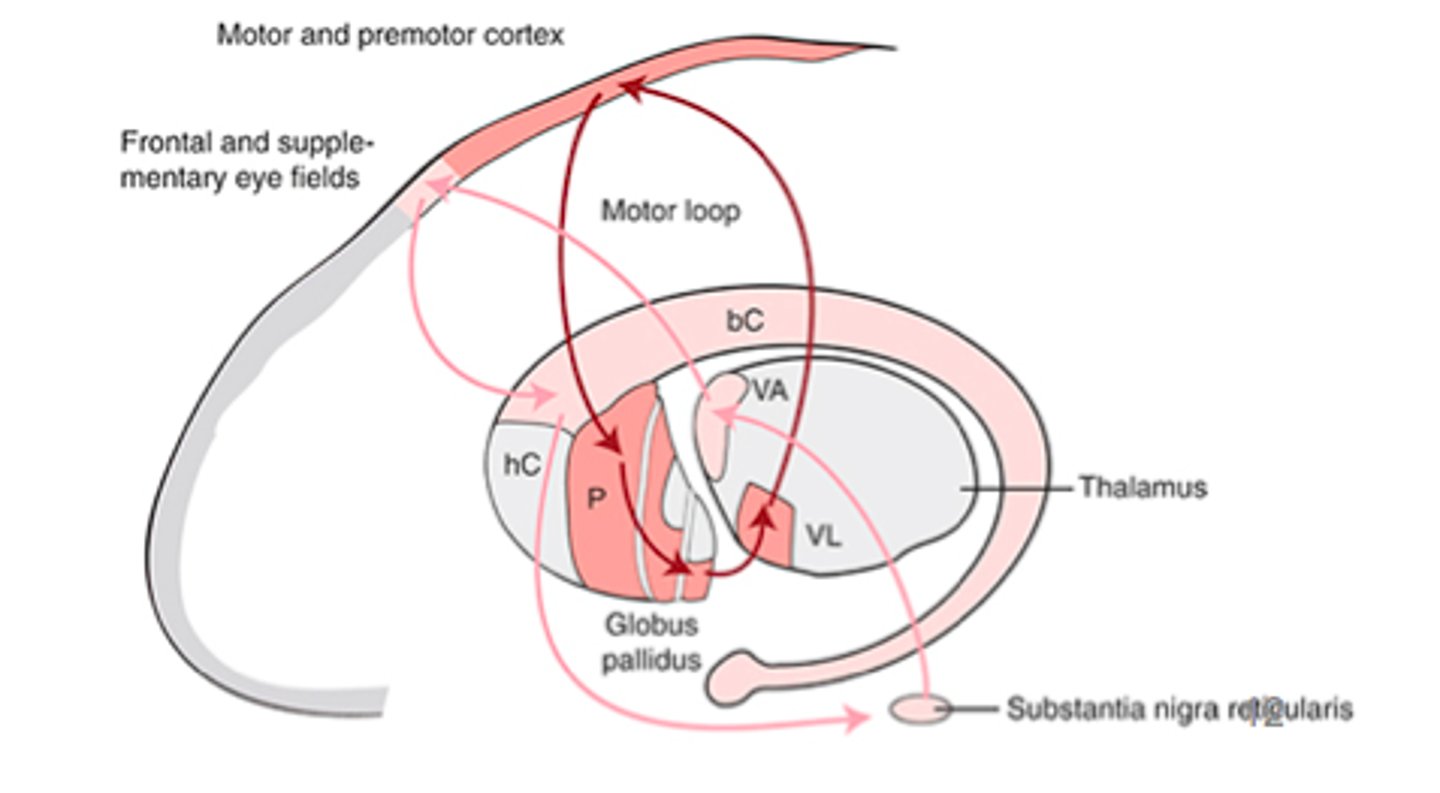
oculomotor loop-- decisions about eye movements and spatial attention; initiation of fast eye movements
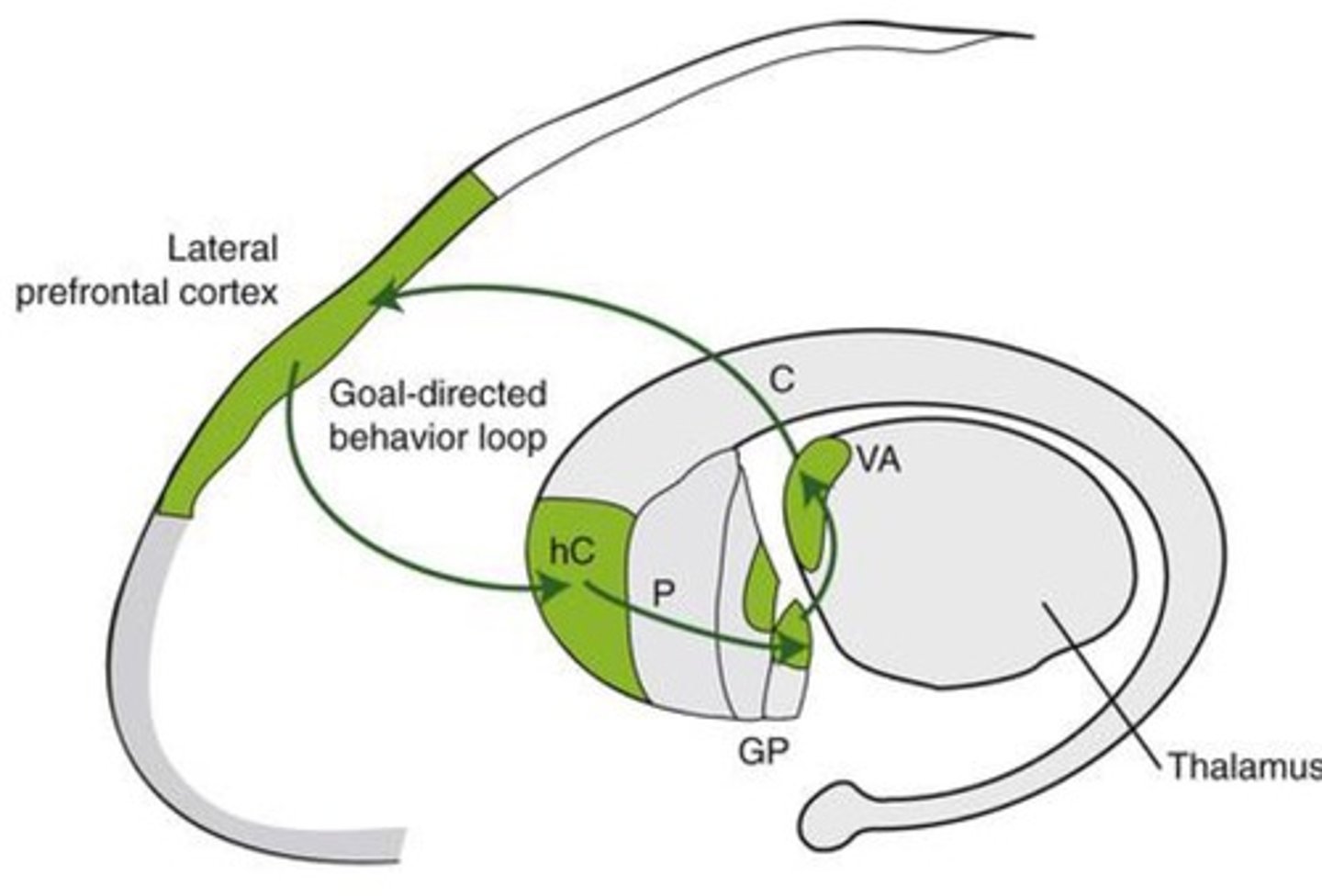
goal directed behavior loop-- Goal-directed behavior; makes perceptual decisions, plans, and decides upon actions in context; divergent thinking
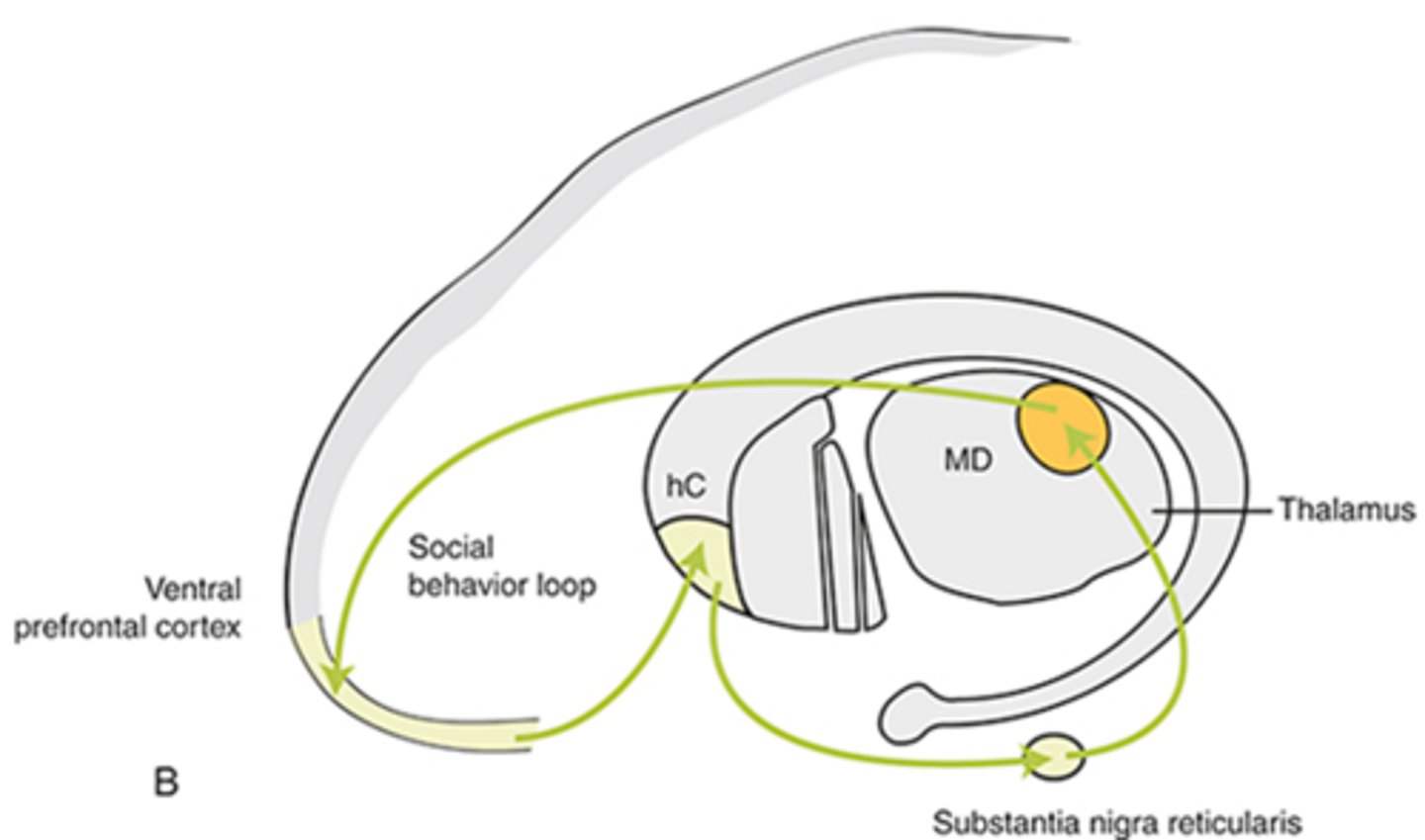
social behavior loop-- Head of the caudate is part of the loop that recognizes social cues, regulates self-control, and parses out relevant from irrelevant information.
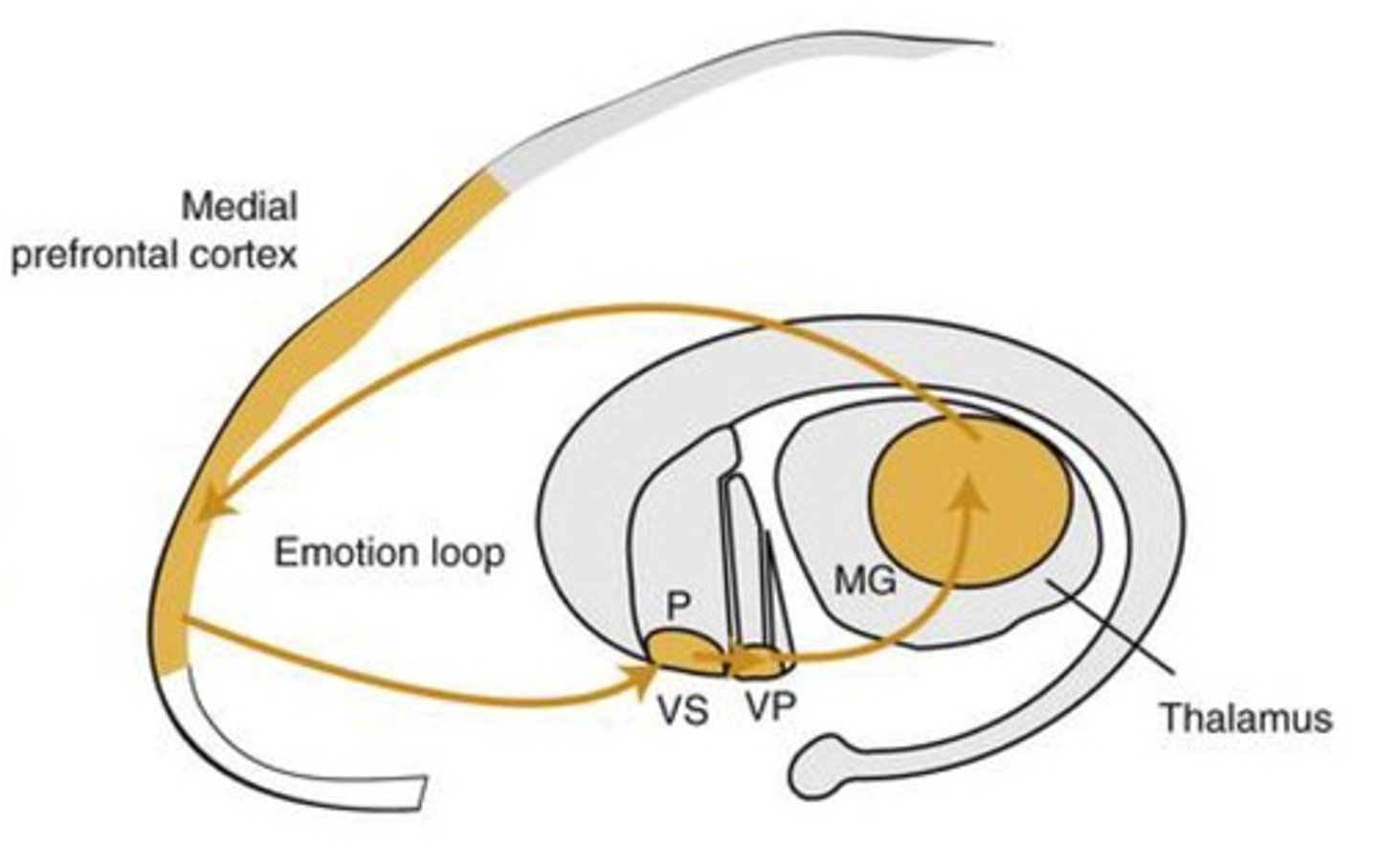
emotion loop-- Emotions; concerned with seeking rewards; involved in reward-guided behaviors; self-awareness; identifies value; monitors predictions
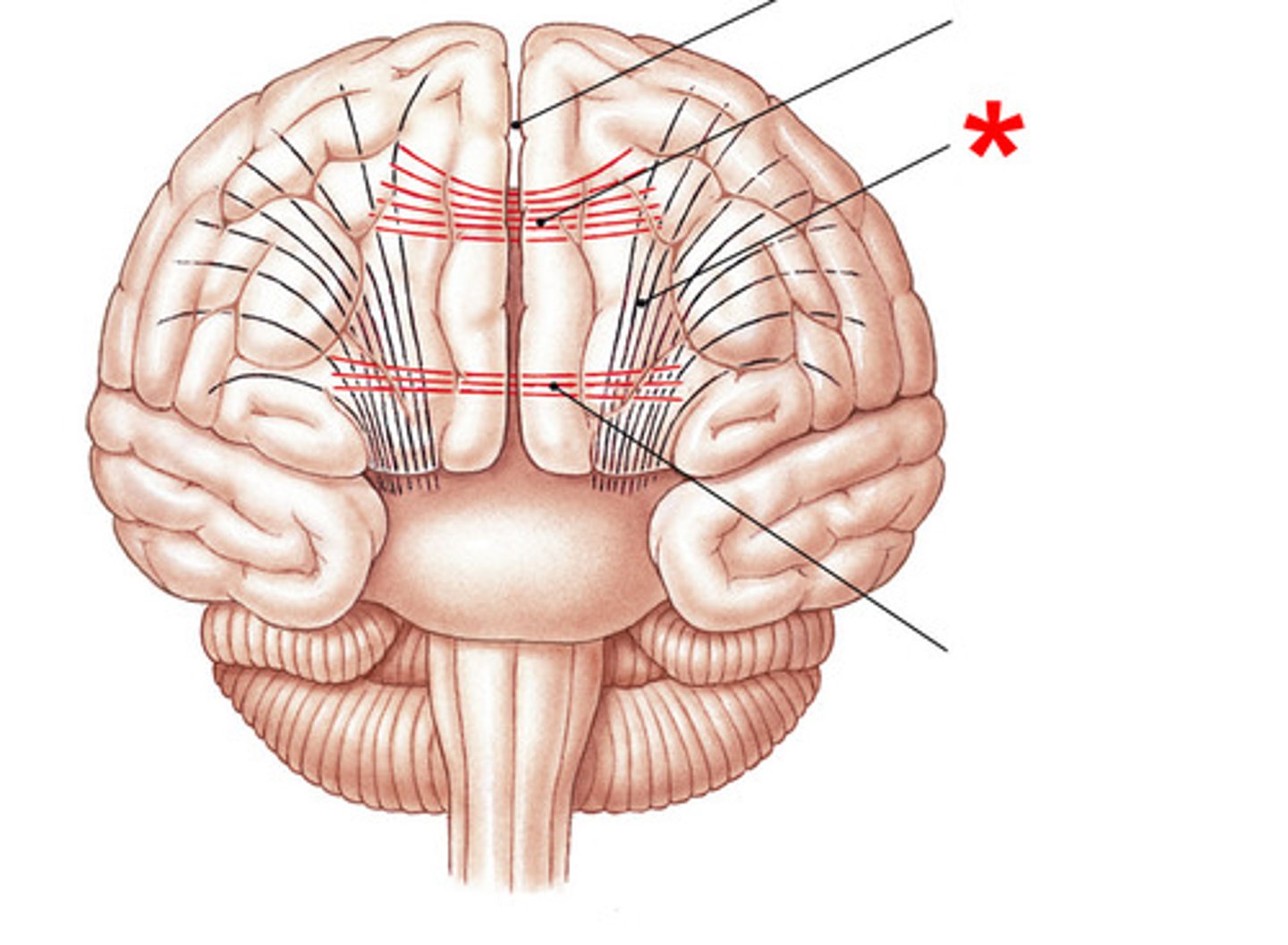
commissural fiber-- Connects the left & right hemispheres.
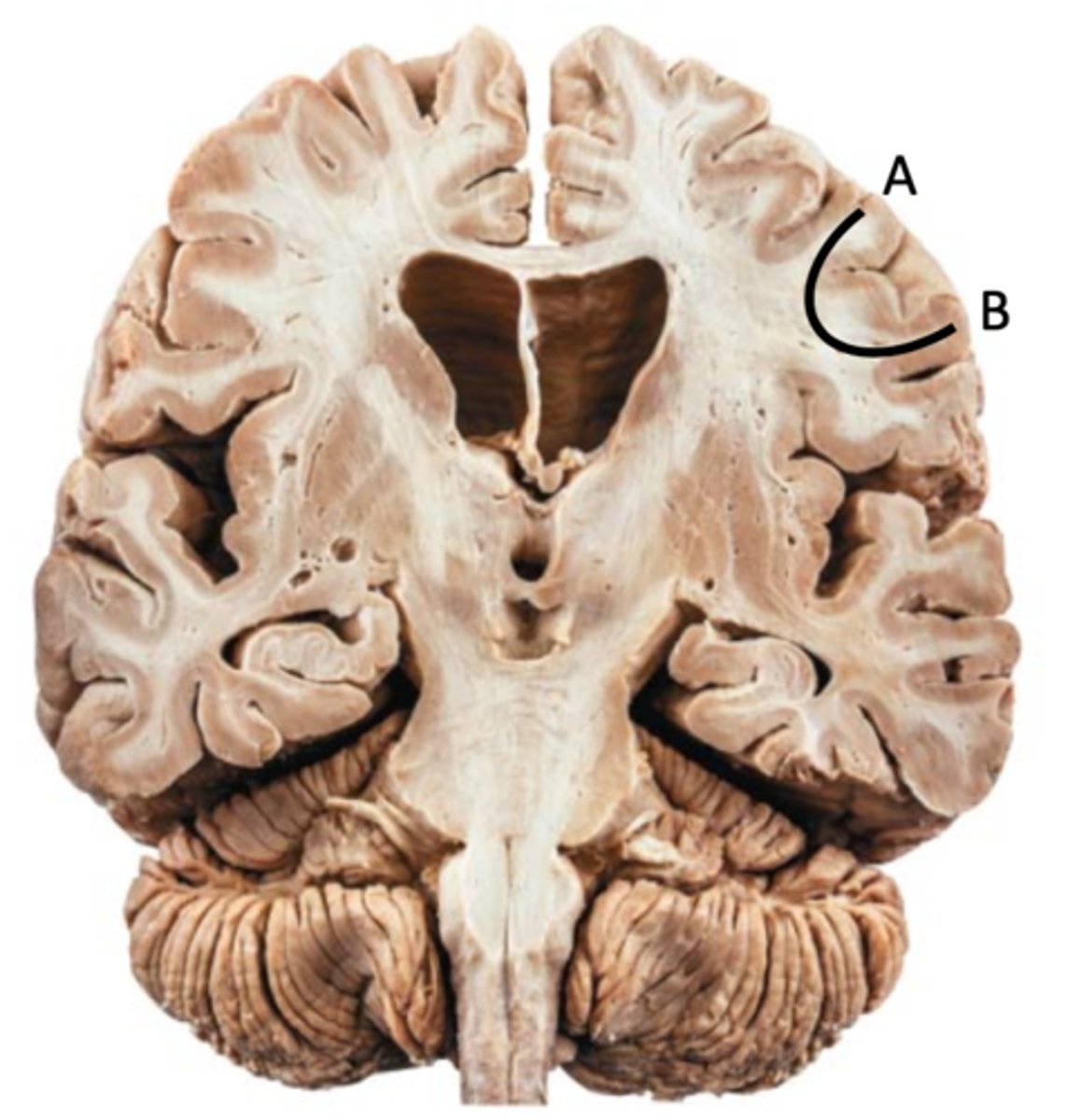
short association fiber-- connect adjacent gyri
long association fiber
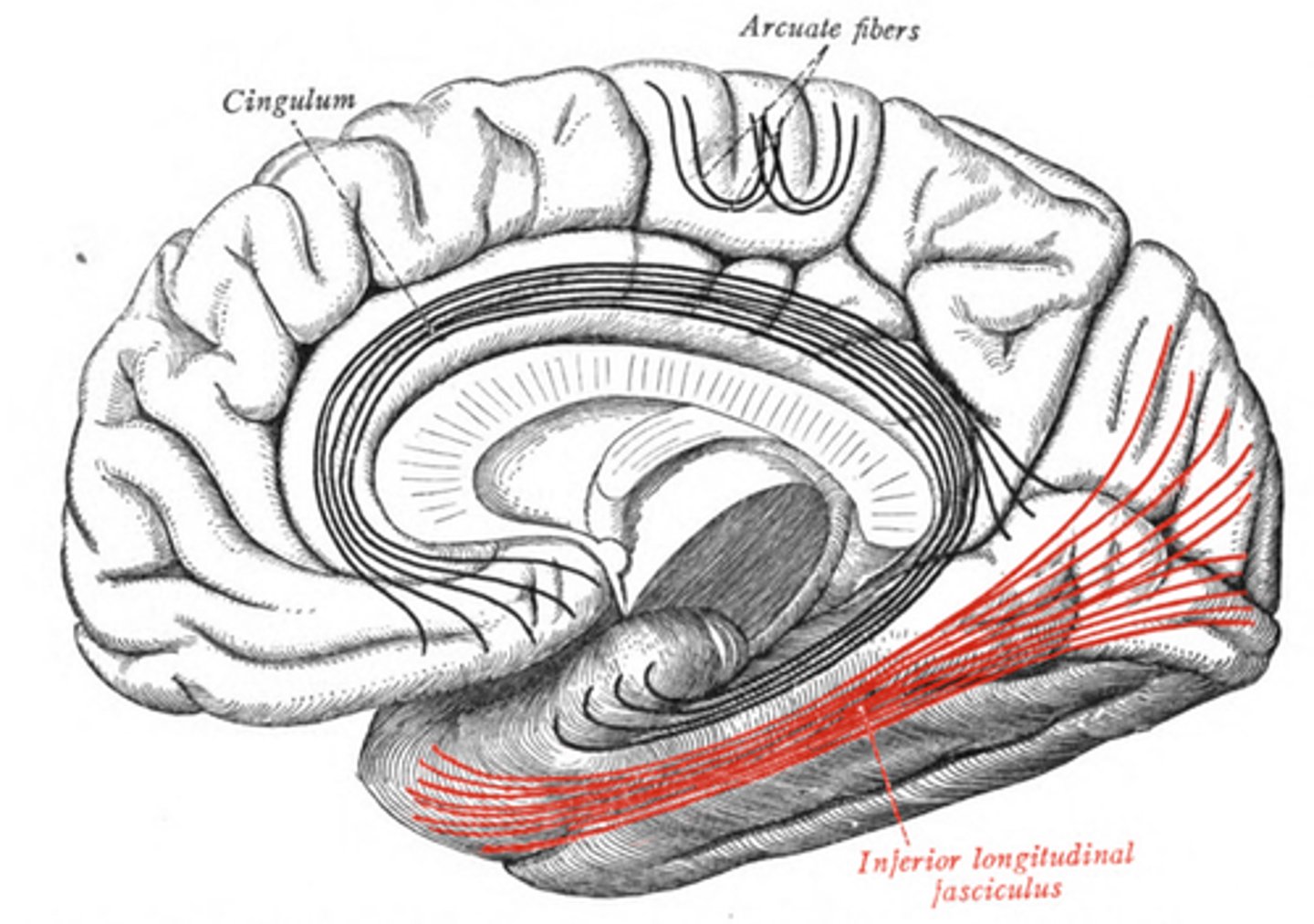
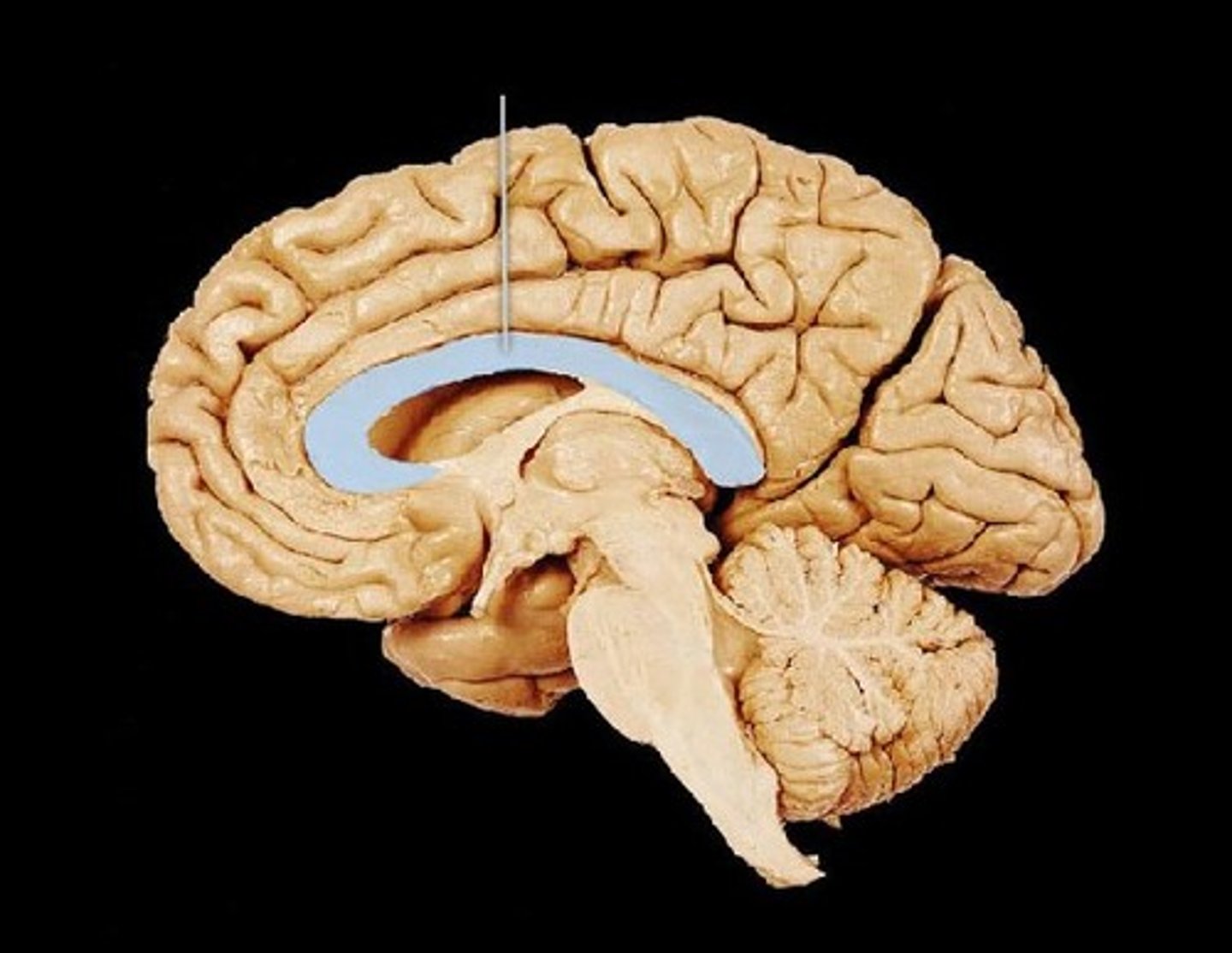
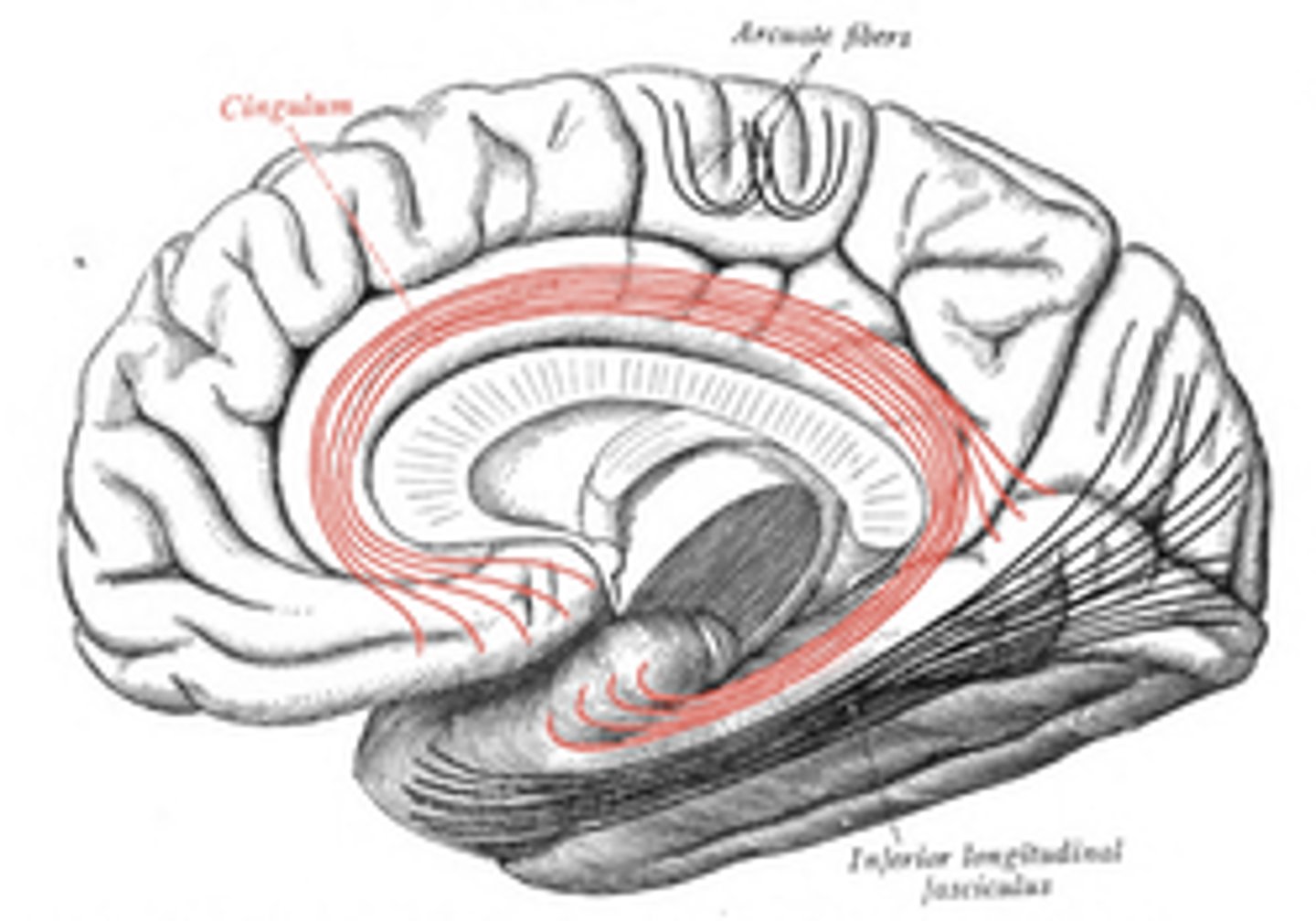
cingulum-- connects frontal, parietal, and temporal lobe
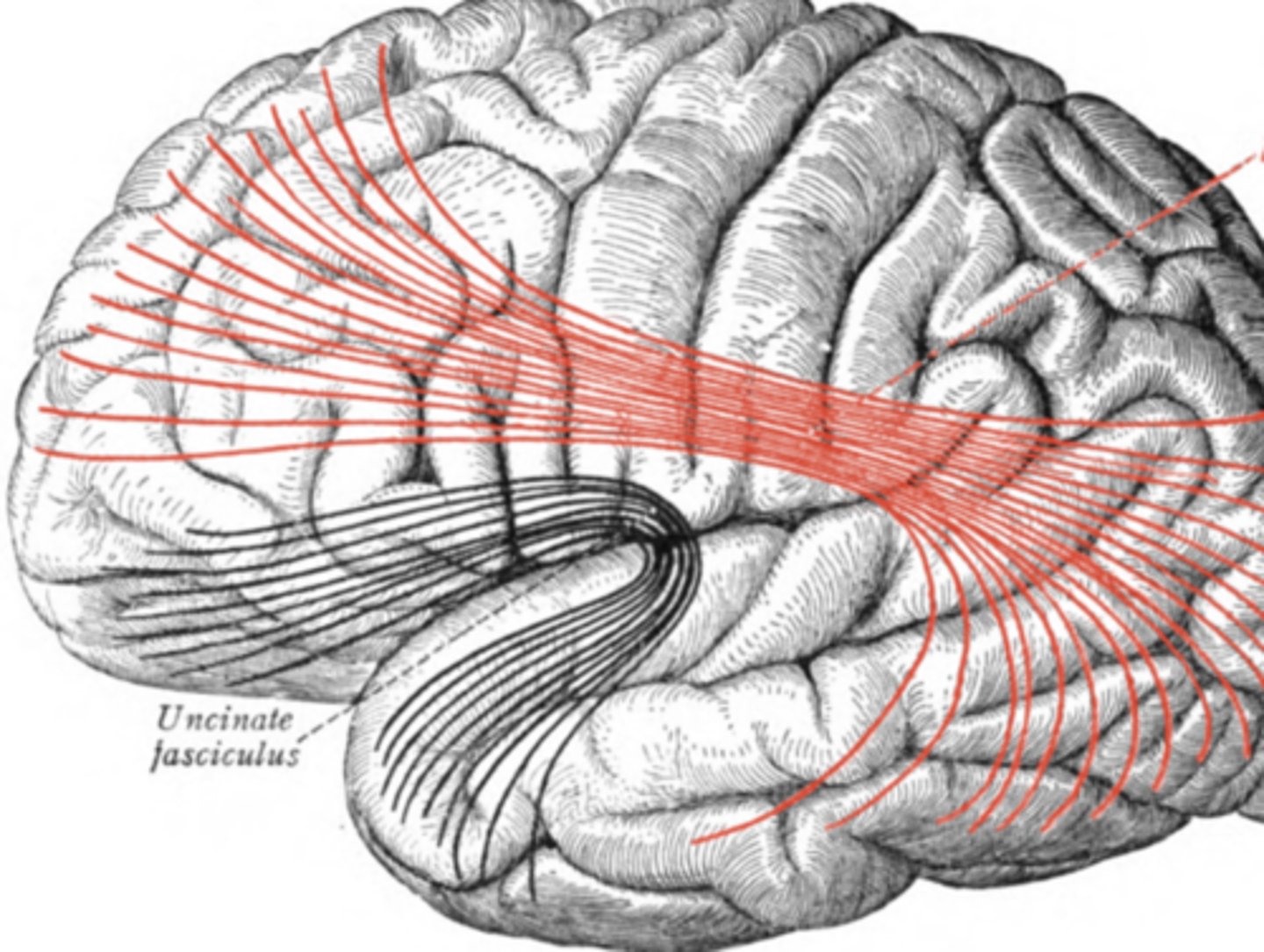
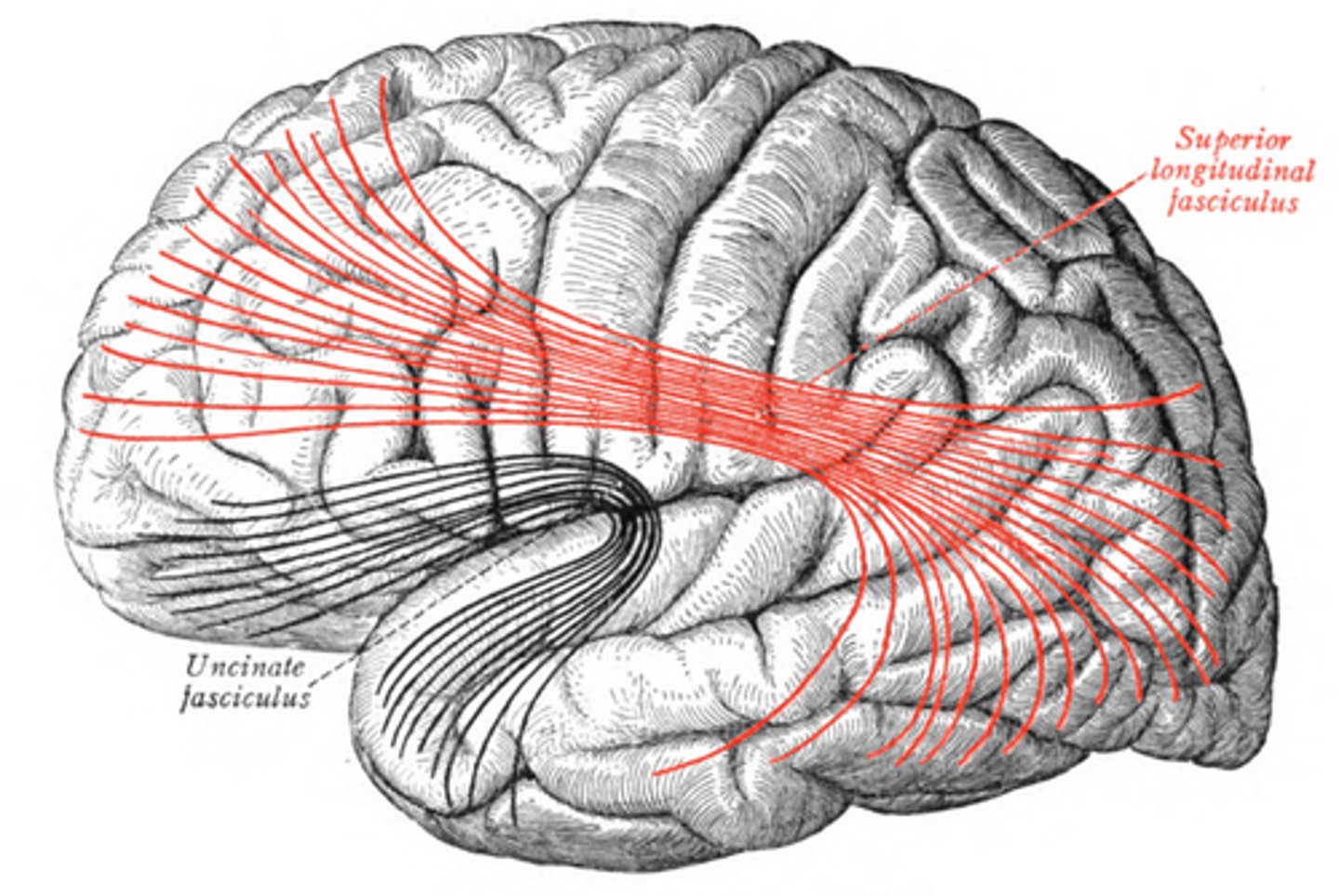
uncinate-- connects frontal to temporal
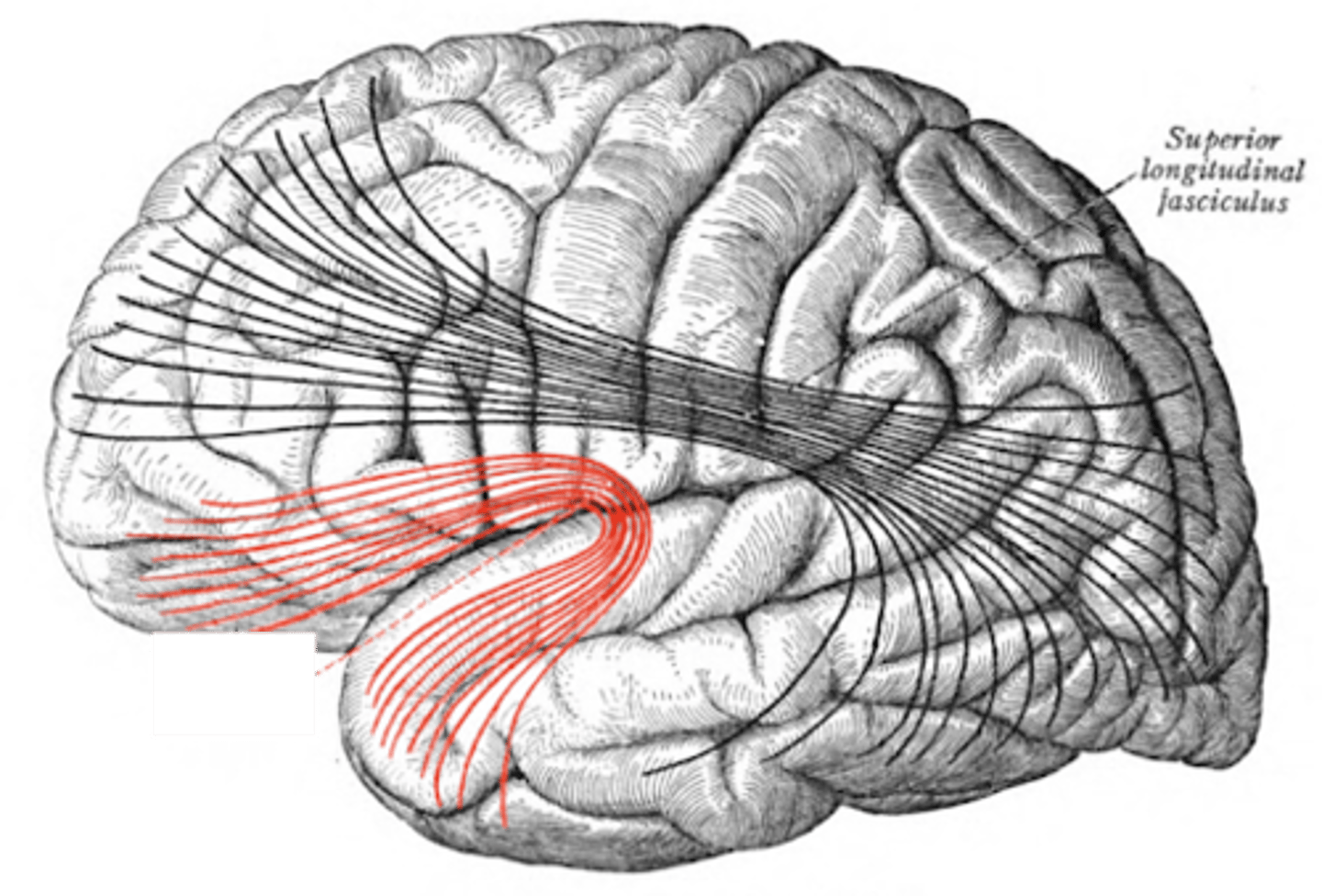
superior longitudinal fasciculus-- connects all lobes
inferior longitudinal fasciculus-- connects occipital and temporal lobes