12. Place: Channels, supply chains, and retailing
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
P of Place
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Supply chain
= Set of three or more entities directly involved in the upstream/downstream flows of product, service, finances, and/or information from a source to a customer
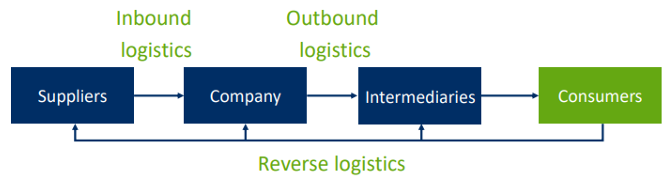
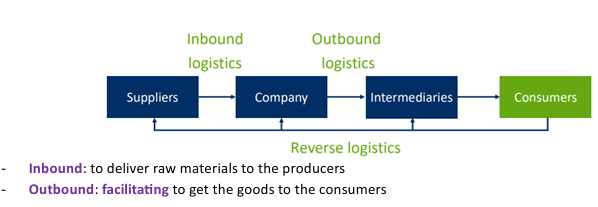
Inbound logistics
Involves the processes related to receiving, storing, and transporting raw materials from suppliers to a business
Outbound logistics
Processes of transporting goods from a business to the consumers
Reverse logistics
Moving goods from the customer back to the business
Distuptions during the logistics
Ex. Ship stuck in the Suez Canal, War in Ukraine
Marketing channel
= Distribution channel (distributes finished goods to end consumer)
= Set of interdependent organizations involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption
Main elements of marketing channels
Management of intangible aspects
Ownership
Control
Flow of communication (How well does information transfer to further entities?)
Management of tangible aspects
Logistics
Retailing
Access (Make sure customers have easy access to the desired products)

Value delivery network
= a network where every partner in the chain enhances and adds value to the goods
Interdependence: Rely/Depend on each other
Share/Reduce uncertainty
Work together, to have less risk
2 types of value delivery (win-win)
Upstream
Ensures smooth collaboration with those who provide input
Good relationship with suppliers
Downstream
Everything after manufacturing, who hande/recieve the finished product
Good relationship with who recieves the finished product
Reduced complexity
Fewer channel transactions (use an intermediary instead of direct contact)
Reduced cost: Each actor can focus on their core business
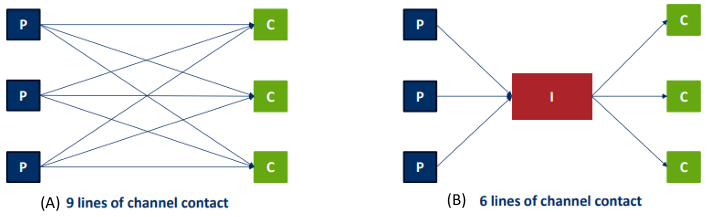
How channel members help reduce uncertainty
Increasing value and competitive advantage
Intermediaries are specialized in selling goods to customers
Routinization
Improving transaction efficiency
Allow distribution costs to be reduced
Specialization
Producers prefer to produce large quantities of a small range of goods
End users only want a limited quantity of a wide variety of goods
→ Sorting and smoothing
Focus on what they specialize in
Doing so via intermediaries
Specialization
Place utility
Bring products to a convenient location
Time utility
Provide time (storage) between manufacturing & consumption
Ownership utility
Ownership can be passed on easily
Information utility
Information about the product & usage

Disadvantages of using intermediaries
Lack of control
Unable to influence intermediaries (In-store merchandising, pricing…)
Intermediaries may be susceptible to competitor inducements
Time, money, and staff need to be invested in sustaining relationships with intermediaries
Types of intermediaries (!!!)
Agent/Broker
Between seller and buyers
No ownership → Brings customer and business together
Merchant
Same actions as an agent, but it does take ownership of a product
More control
Buying and selling products
Distributors/Dealers
Distribute the product
Offer value through services associated with selling inventory…
Franchisee
Contract to supply and market an offering to the requirements or blueprint of the franchisor
Wholesaler
Stocks goods before the next level of distribution takes both legal title and physical possession of the goods
Divide over different retailers
Retailers
Sell directly to end consumers
Infomediraries
Channel design
What’s the most effective and efficient way of getting the offering to the consumer?
Three key decisions
Distribution intensity: Level of effort required of consumer to find the product
Channel configuration: Numbers/Types of intermediaries in supply chain
Multichannel decision: Number of differently used channels
Key considerations of channel design
Economics
Coverage: Be more available than competitors (not always: exclusiveness)
Control: More actors = less control about the product
Convencience & location
Where are we present?
Ex. McDonald’s being next to a highway
Different ordering options
Online, offline, department store?
Waiting time & delivery period
Try to reduce it by working with the best intermediaries
Purchase quantity
What and how much do the consumers actually require?

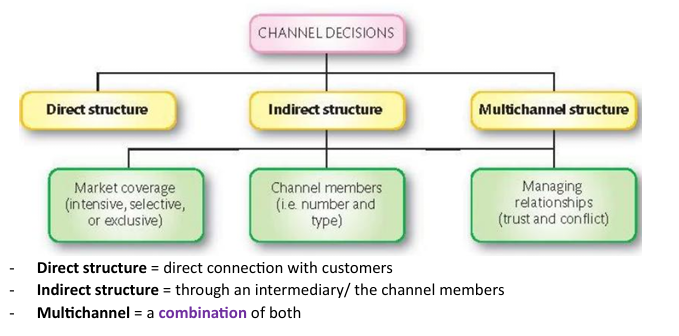
Distribution channel strategy
Direct structure: Direct connection with consumers
Indirect structure: Through intermediary
Multichannel structure: Combination
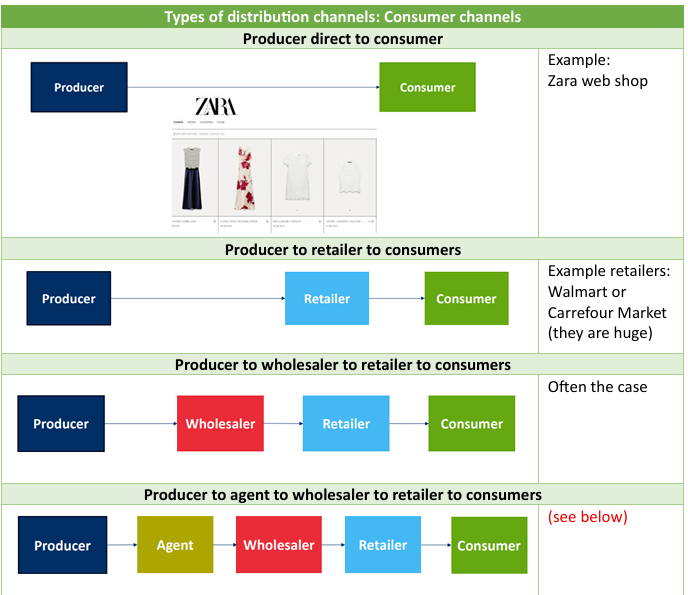
Types of distribution channels: Consumer channels
Producer → Customers (ex. Web shops)
Producer → Retailer → Customer (ex. Walmart) → ONLY when retailer is big
Producer → Wholesaler → Retailer → Customer (Usually the case)
Producer → Agent → Wholesaler → Retailer → Customer
When companies want to enter a foreign market → Agents possess knowledge about these things
Hybrid marketing system
= Benefit of multi-channel structure (indirect & direct)
Using 2 or more marketing channels to reach one or more customer segments
Ex. Make product available in your own stores, and other stores (ex. Nike)
Benefits of a multichannel structure
Increased reach
Producer control (Directly linked with customers)
Greater compliance (Part of a greater whole)
Optimized margins (The more intermediaries, the more divided margins)
Improved market insight (Working with only intermediaries → You don’t know the customer behavior)
Flex shopping
Switching channels to find the best prices
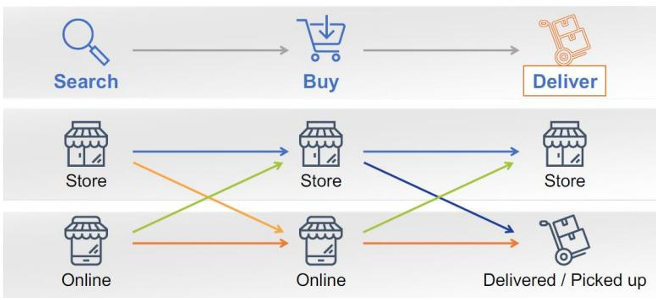
Omnichannel marketing
Better compared to multichannel (Different channels live separately)
Create a seamless experience for customers across channels
Ex. Disney
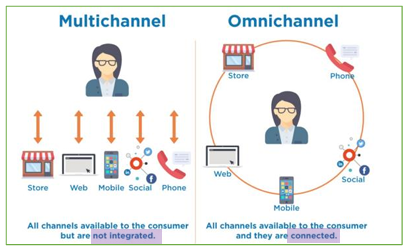
Why omnichannel marketing?
Customer-centric
Data integration
Flexibility (Multiple outlets to find your product)
Channel intensity
Intensity
Available everywhere (ex. Coca Cola)
Use all available outlets
When there are many alternatives
Selective
Specialized stores (ex. Washing machinesà
Distributions through multiple but not all reasonable outlets
Exclusive
Small amount in different stores (ex. Versace)

Disintermediation
Elimination of intermediaries
Re-intermediation
Introduction of additional intermediaries into the distribution channel
Channel conflict
Disagreement with channel members on goals, task, division or reward
Horizontal channel conflict
Conflict between two or more players at the same level of the supply chain
Price conflicts
Sell the cheapest: Race to the bottom
Turf wars
Outlets located in the same customer segment
Policy variations
Different intermediaries → Different discounts or promotions
Grey marketing
One of the outlets selling in an illegal way
Vertical channel conflict
Conflict between two or more parties at different levels of the supply chain
Ex. A retailer that stops selling a certain producer’s products
Supply chain
Set of three or more entities directly involved in the upstream or downstream flows of product, service, finances, and/or information from a source to a customer
Supply chain management activities and goals
Fulfilment—Delivering the products in a reasonable time frame
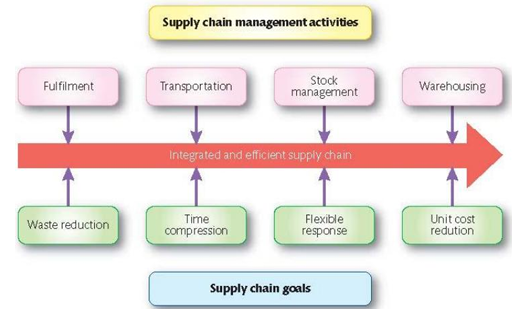
Sypply chain management goals
Competitive advantages
Doing the right things (quality, availability…)
Doing things fast
Doing things on time
Being able to change
Being low-cist
Just-in-time management (JIT)
Circular supply chains

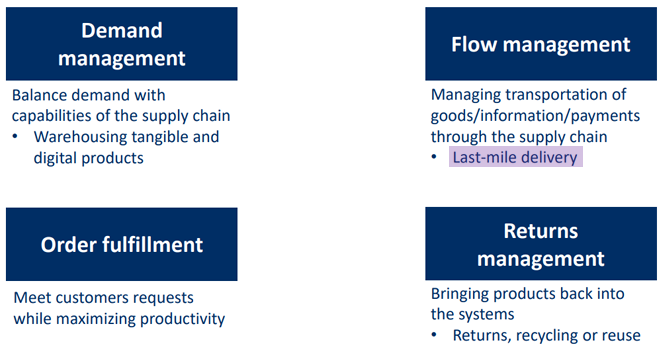
Supply chain management activities
Demand management
Flow management
Good transportation of goods
Returns management
Order fulfillment
Retailing
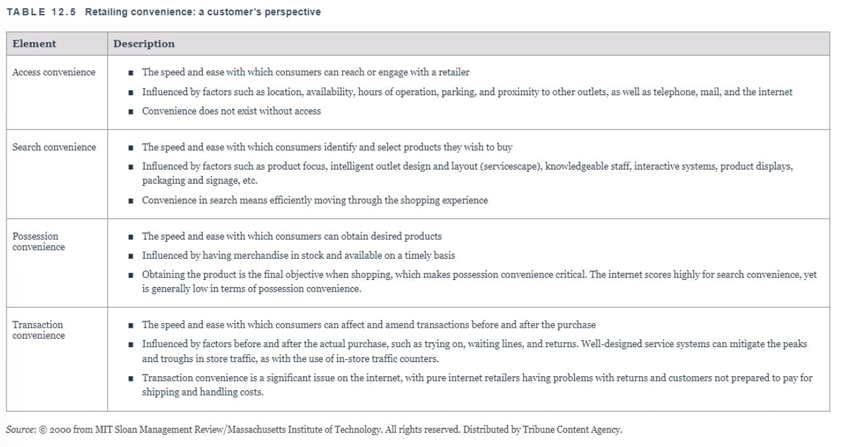
= All the activities directly related to the sale of products and services to consumers for personal use
4 key elements of convenient product acquisition (retailing)
Access—Being easy to reach
Search—Customers can easily identify what they want
Possession—Easy to obtain, immediate ownership
Trabsactions—Different payment methods
Difference retailer and wholesaler (!!!!)
Retailers sell tp customers
Wholesalers sell to different businesses (who in turn sell to customers)
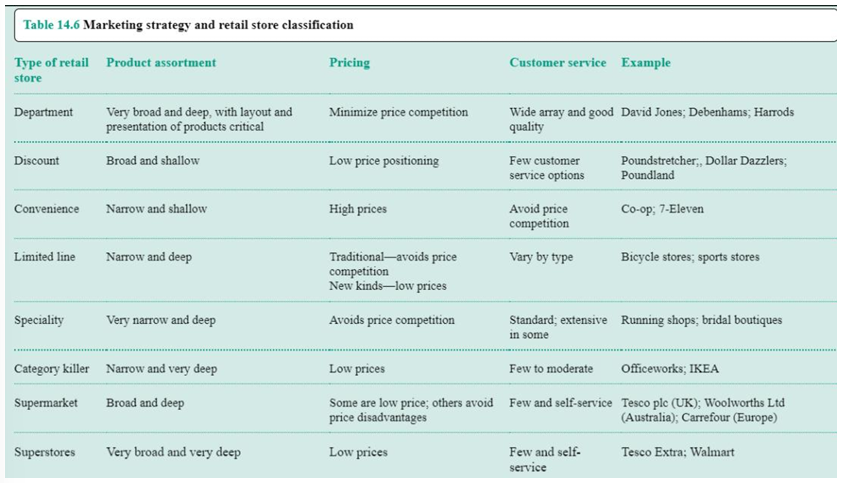
Retail store classification
Department stores: huge variety of products
Convenience store: smaller stores, open at specific times
Limited lines: specific for a certain category
Customer needs in online stores
Conveniece
User-friendly interface: Has to look professional (otherwise, it might be perceived as low quality)
Sorting & filtering products: find goods according to your own criteria
Search function: able to find a specific item
Multiple delivery options
Trust
Safe payment
Free delivery: no transportation cost
Free returns: if it doesn’t suit you
Customer needs in physical stores
Experience: providing sensations (touch, feel, smell)
Service & advice: interaction with in-store staff
Time utility: ex. no lines
Lightning speed of change
= Businesses need to invest in innovation and be ahead using new tech to improve their products
Consolidation
= Different businesses are coming together: joint ventures
Advantages:
Scaling up
More professionalism
Global expansion