Week 8B: Metabolic Toxins - Reactive Oxygen Species
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Describe the structure of the oxygen molecule
Oxygen has two single electrons in two different orbital shells, which makes it unable to react with bonds in organic compounds, usually requiring an enzyme
What are radicals?
Atoms that have one unpaired electron in their outer valence shell, making them very reactive
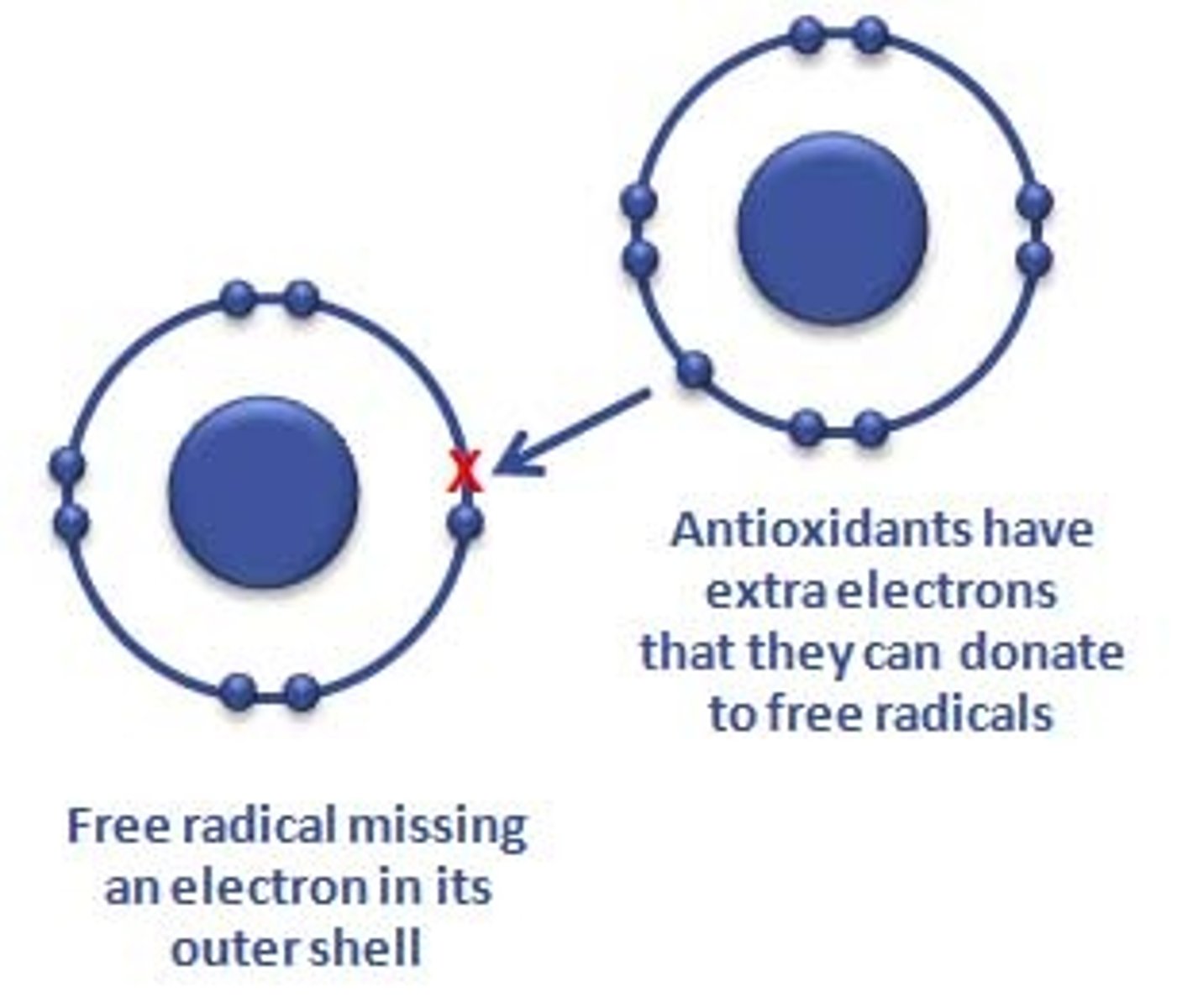
How does oxygen become a radical?
Oxygen has 2 electrons in two different orbitals. However, if oxygen gains an extra electron, it becomes very reactive and becomes a radical
What are free radicals?
Radicals that can exist independently from an enzyme (usually trapped in the enzyme)
How are radicals often generated?
Often generated during an enzymatic reactions since enzymes often move electrons when they are catalyzing reactions
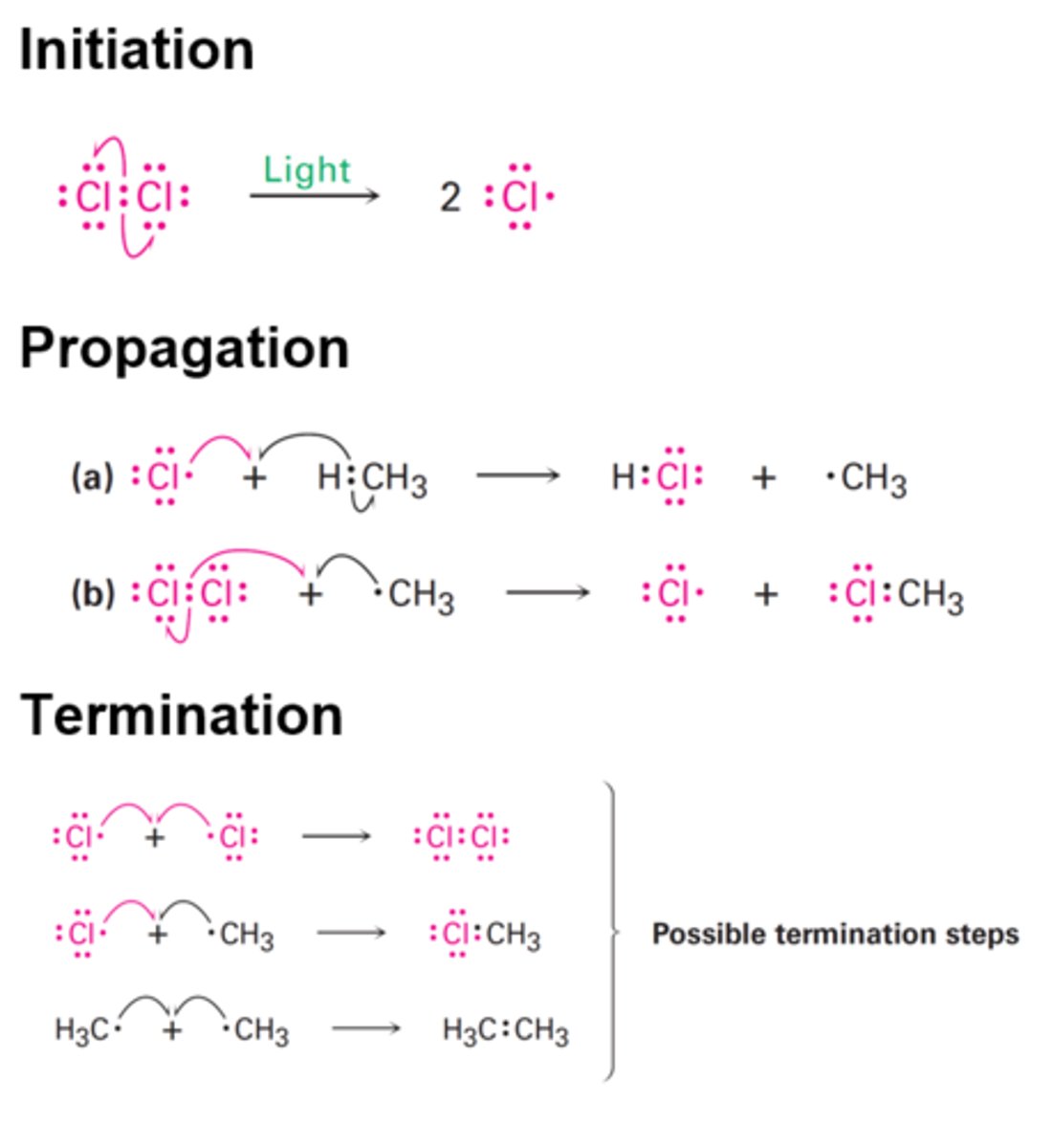
How can free radicals cause chain reactions that damages other substances?
Free radicals take electrons from other compounds to stabilize itself, resulting in the creation of a new free radical, which does the same thing
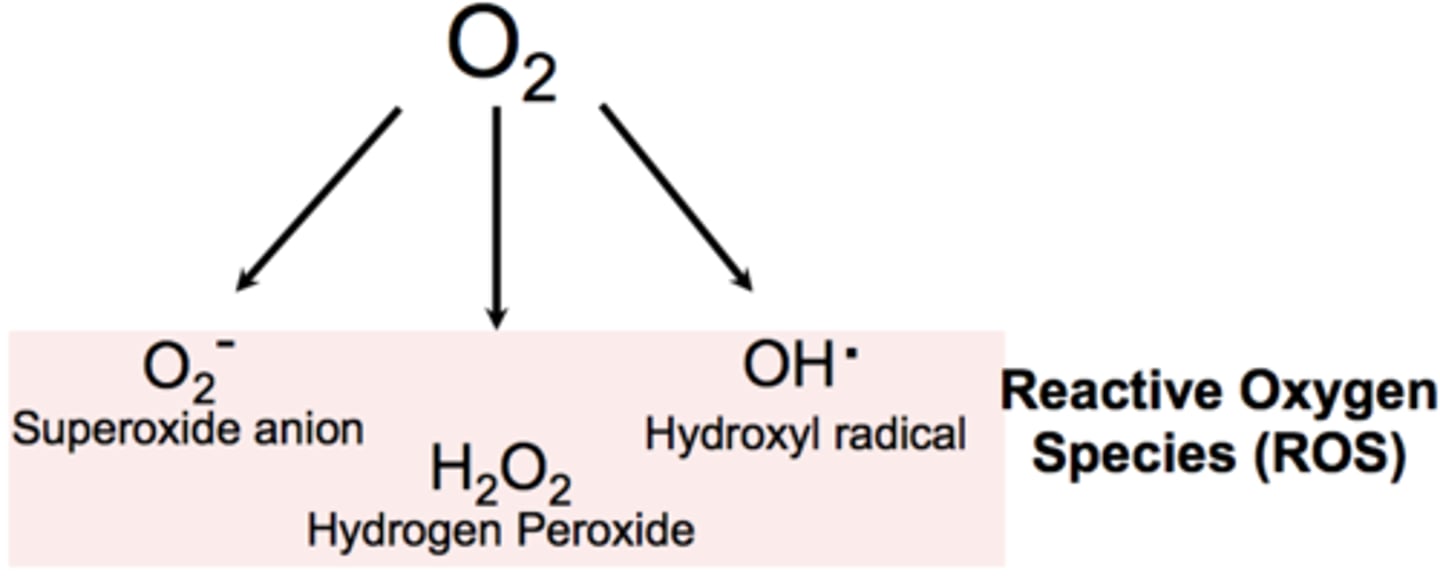
What are 4 common source of reactive oxygen species in aerobic cells?
1. Electron Transport Chain
2. Ionizing + UV Radiation
3. Drug Metabolism
4. Inflammation
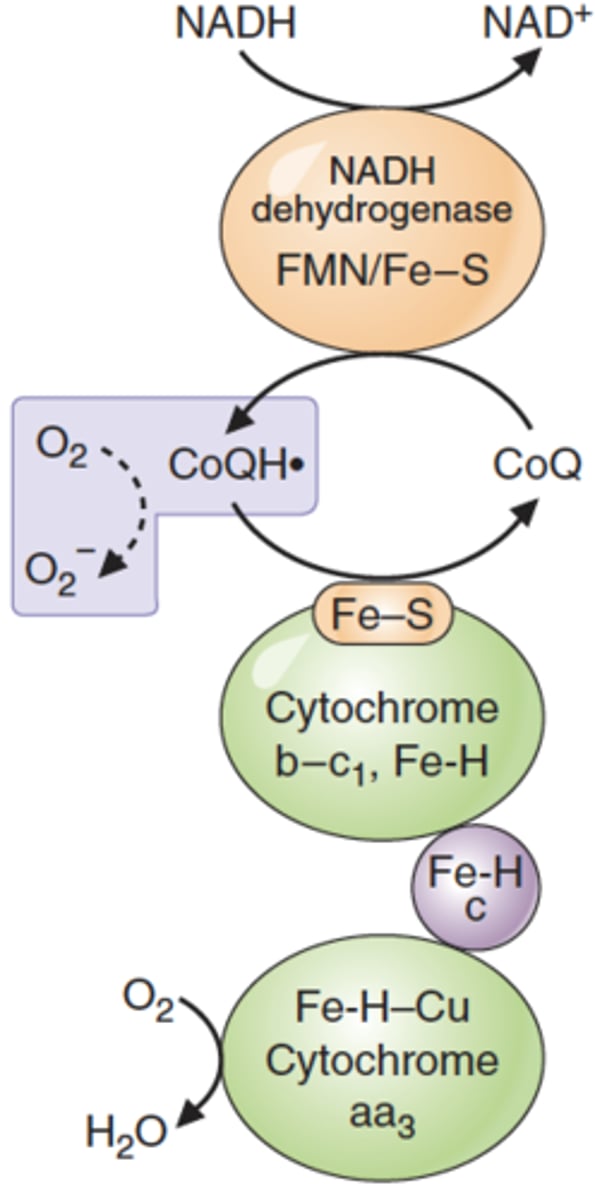
How are reactive oxygen species created by the electron transport chain?
Electrons transferred during the ETC can escape and bind to the oxygen required for the chain to work. Often occurs due to coenzyme Q
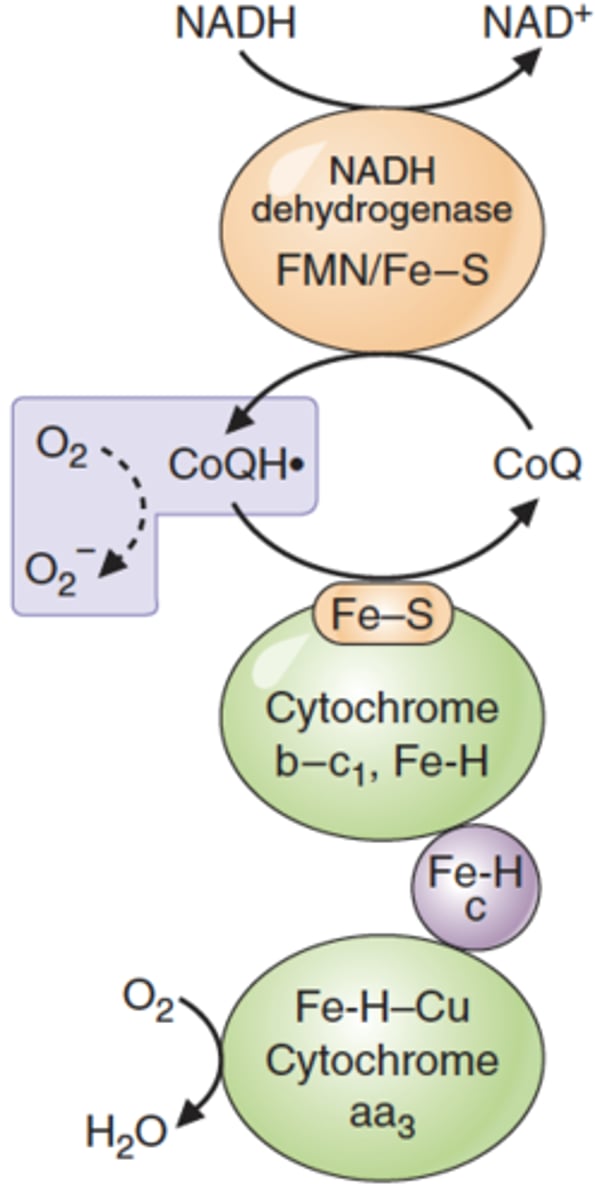
Which coenzyme is usually responsible for creating free radicals in the electron transport chain?
Coenzyme Q
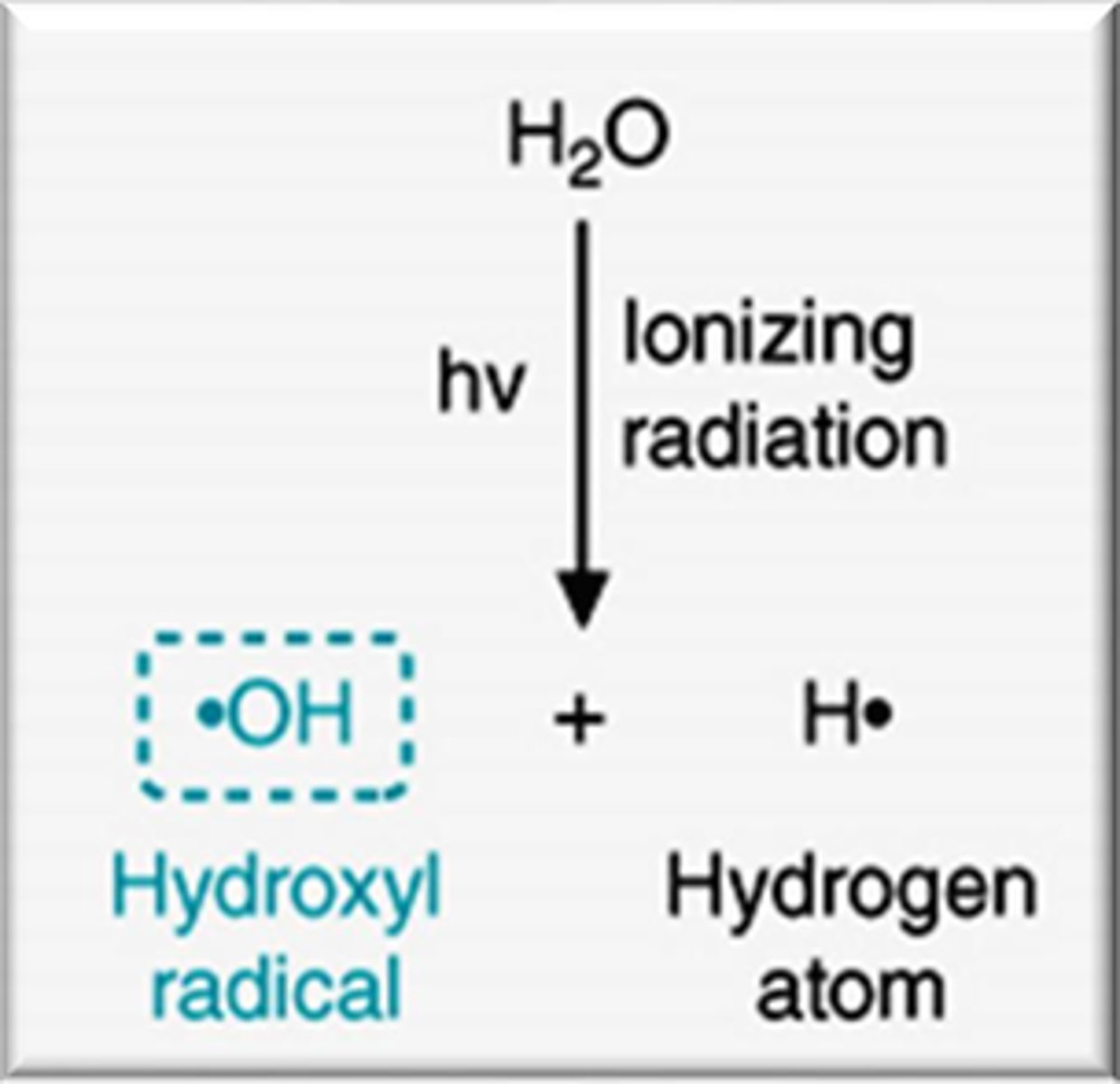
How are reactive oxygen species created by ionizing and UV radiation?
Ionizing and UV radiation can cause water to separate into a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl radical
How are reactive oxygen species created by drug metabolism?
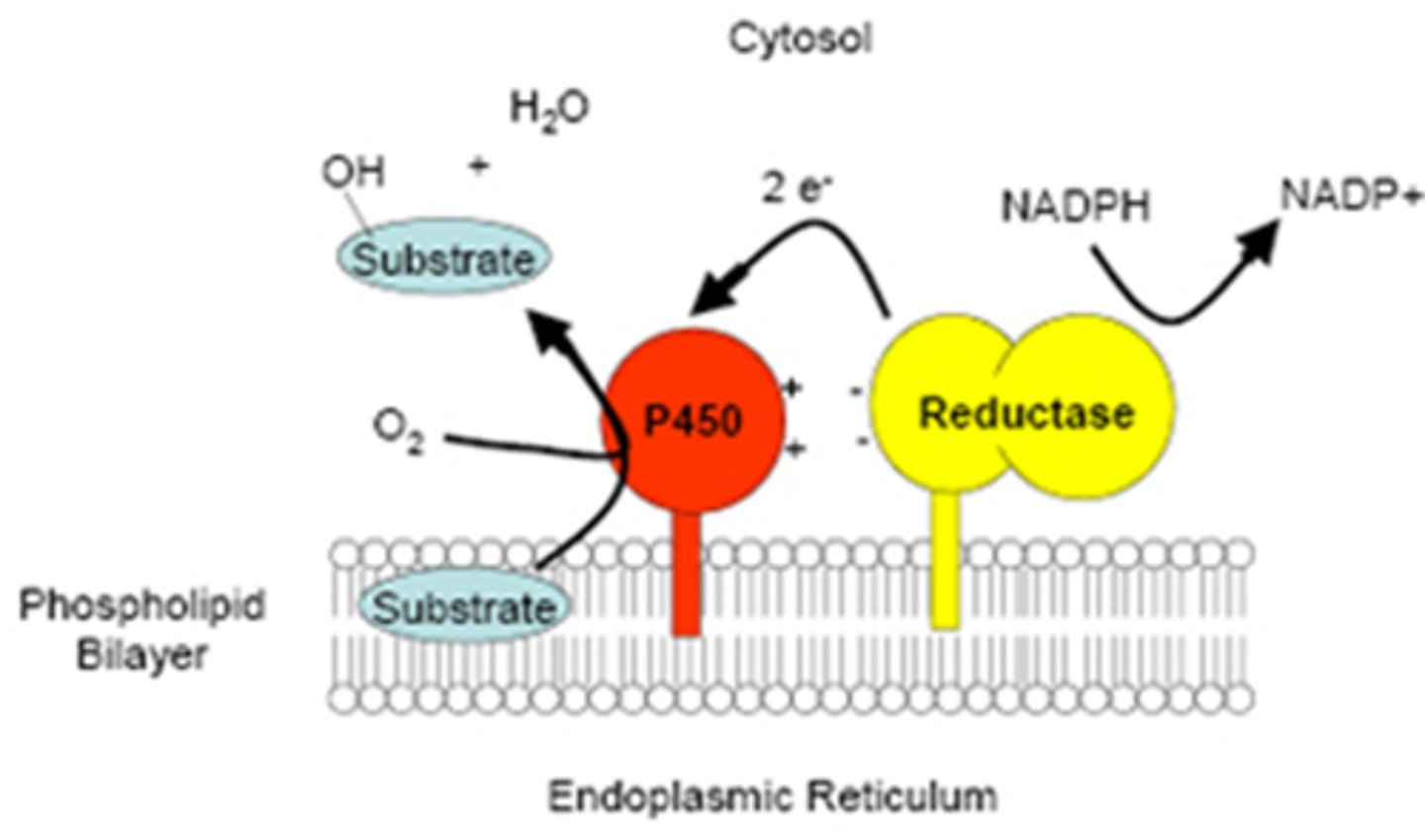
Cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for metabolizing/oxidizing drugs, can become leaky, causing radical intermediates that are involved in these enzymatic reactions to cause cell damage
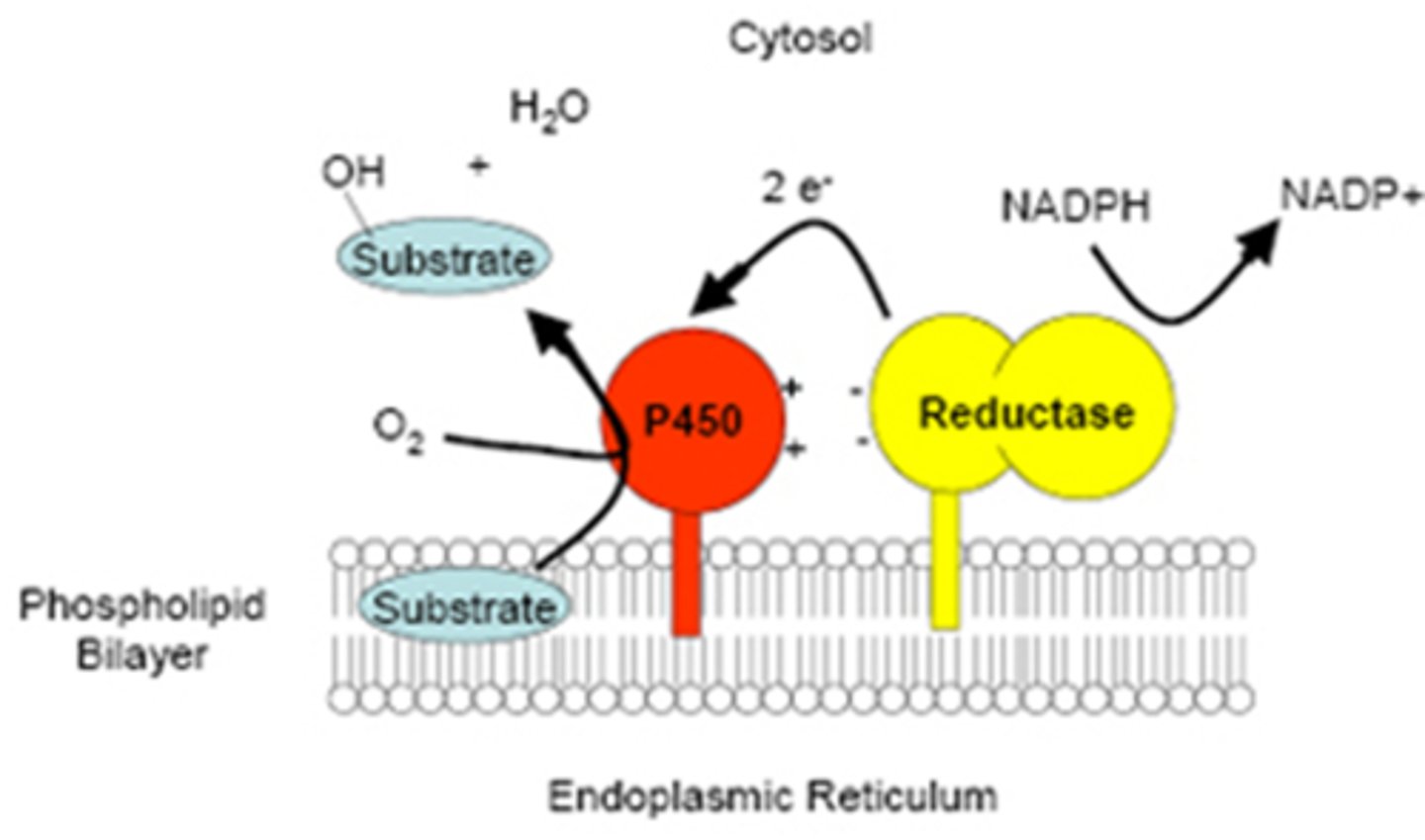
Which enzyme is responsible for metabolizing drugs and can become leaky to ROS?
Cytochrome P450
How are reactive oxygen species created by inflammation?
As part of the immune response, neutrophils release ROSs "respiratory burst" to destroy pathogens and clean up dead cells
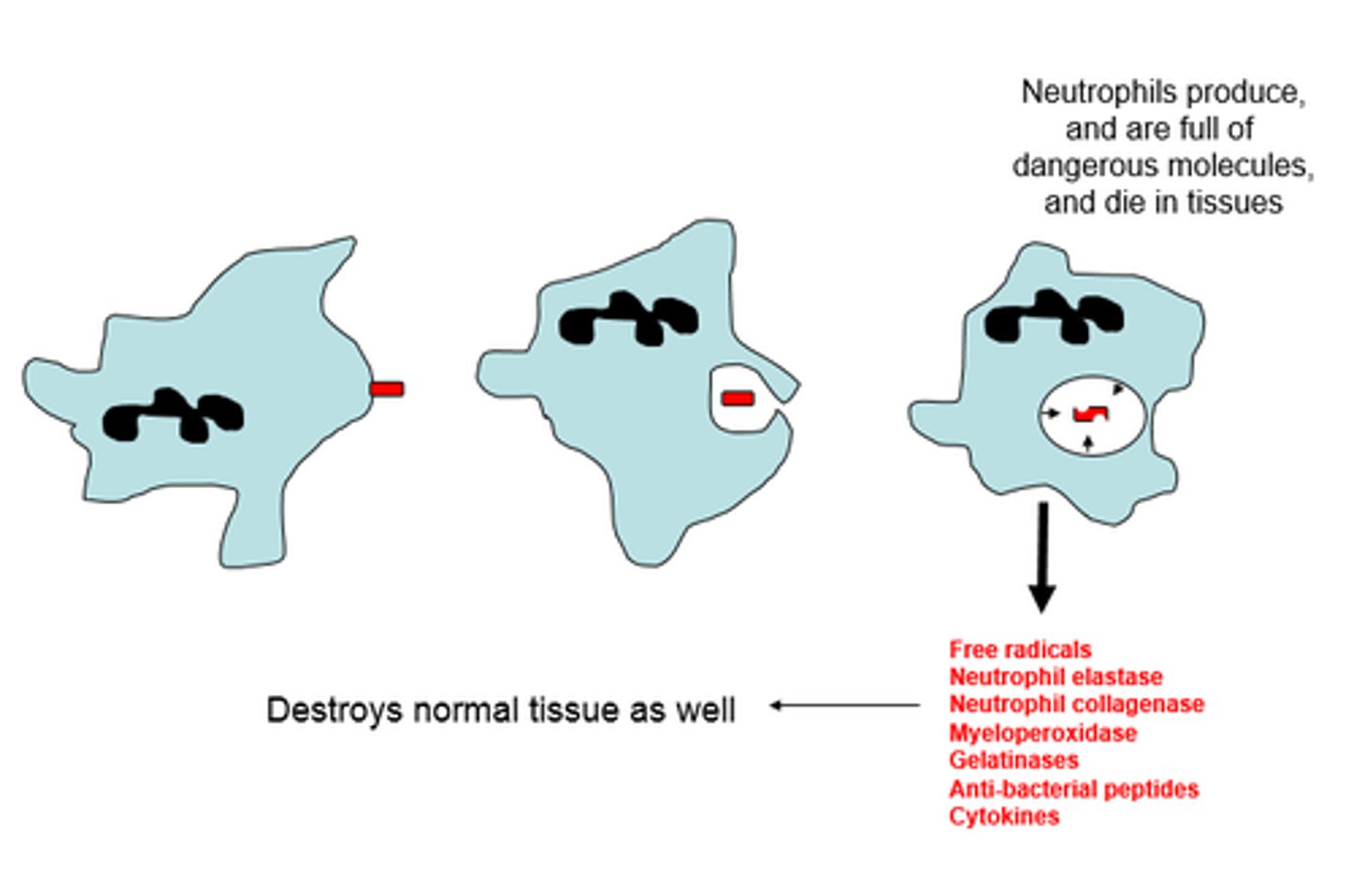
Which cells are responsible for destroying pathogens by releasing ROS?
Neutrophils
What are Reactive Nitrogen-Oxygen Species?
Free radicals that are produced inside and outside of the cell and can cause damage to cellular components
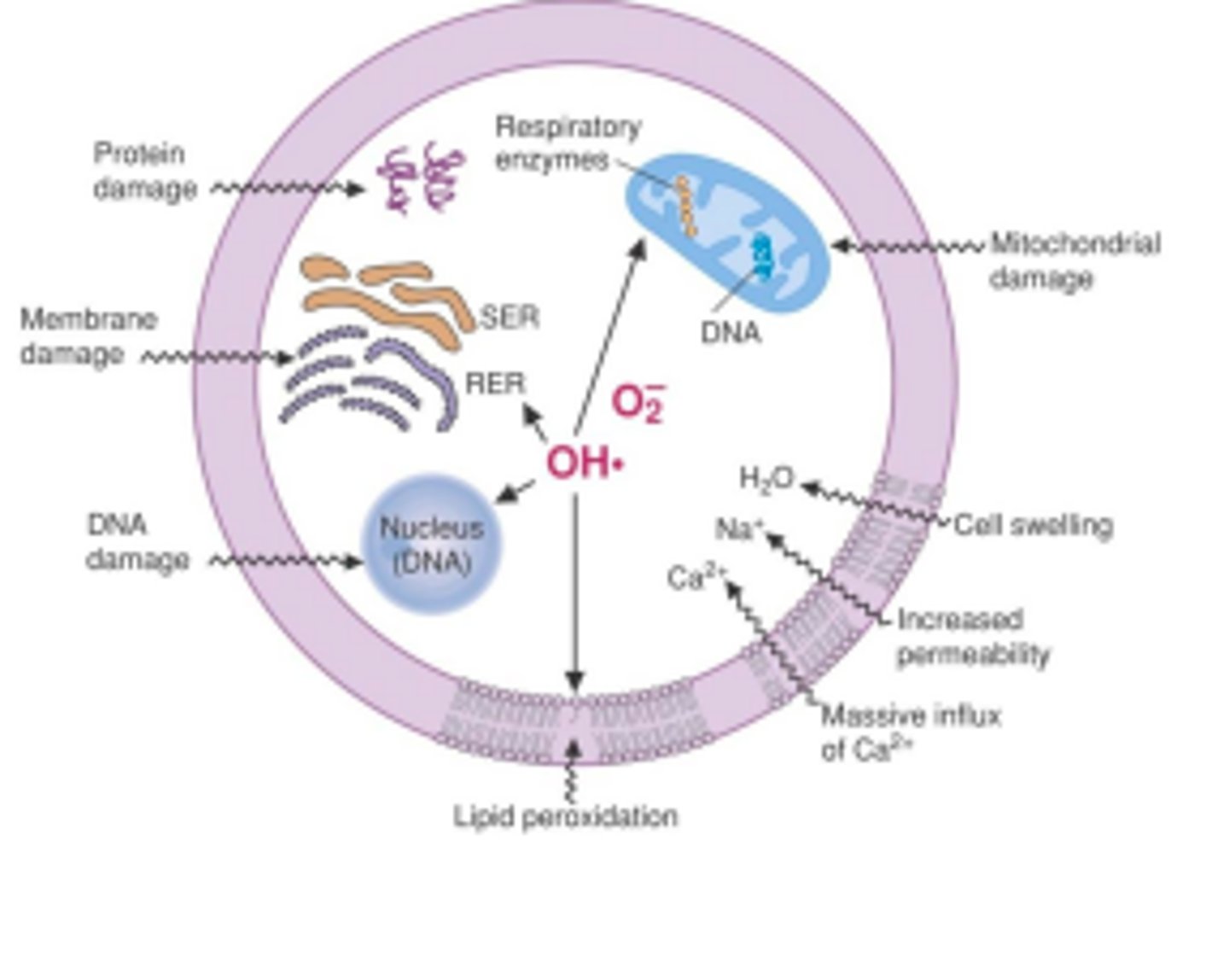
How does RNOS damage DNA?
Can cause strand breaks in DNA
Can cause 20 different alterations that can lead to mutations
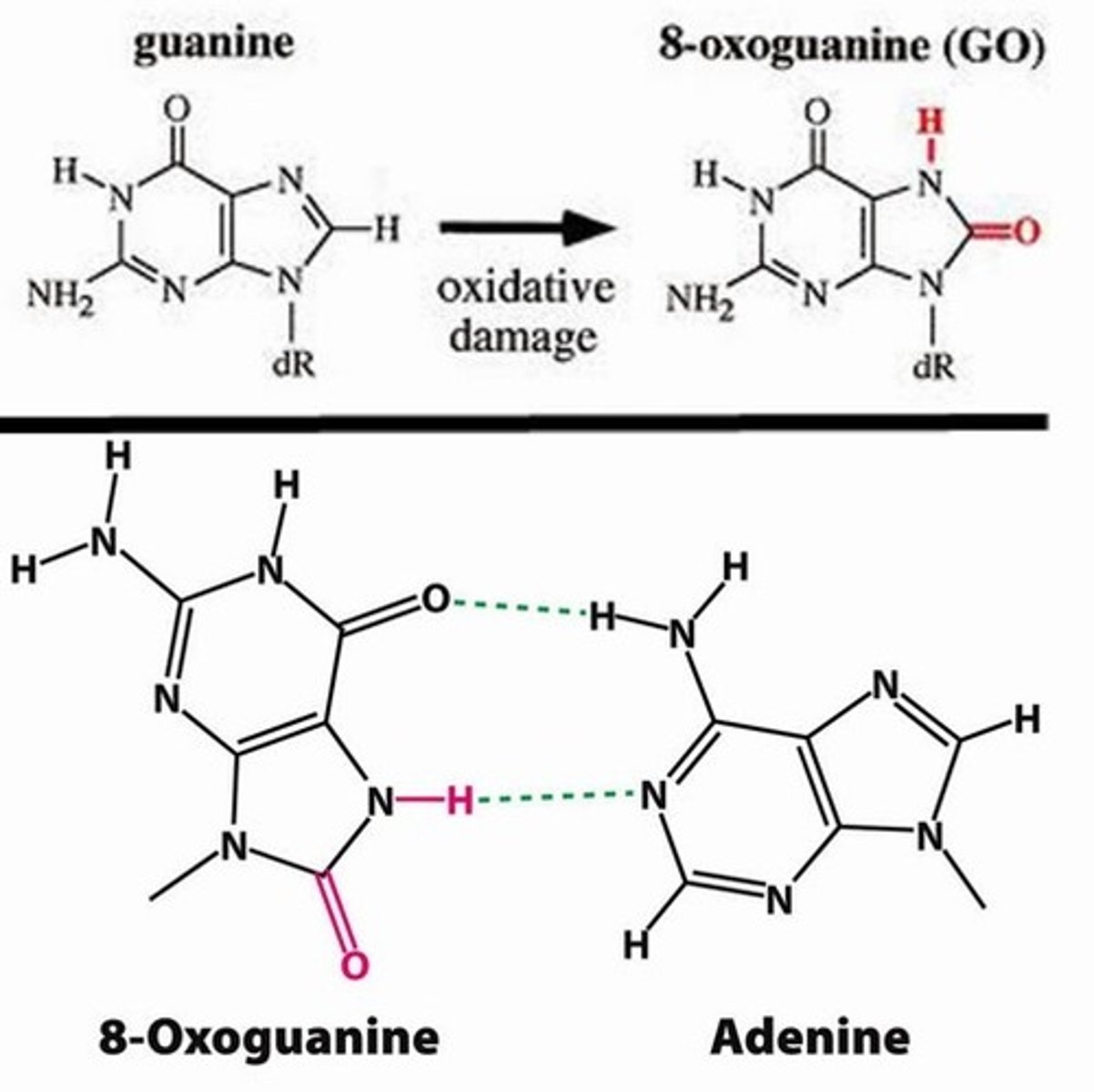
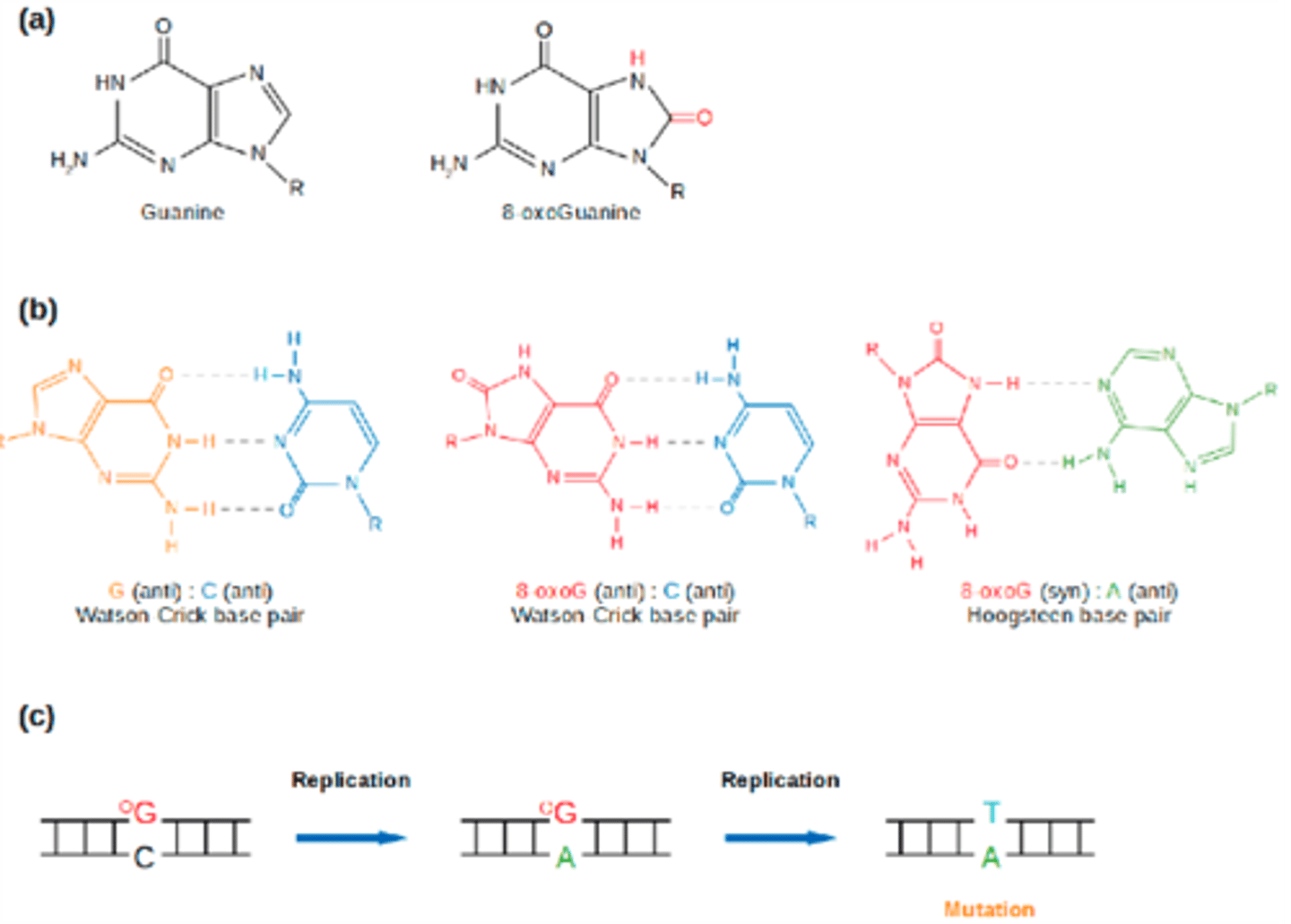
What is the 8-hydroxyguanine/8-oxyguanine modification of DNA?
A modified version of guanine due to reaction with a RNOS, causing it to base pair with an adenine instead of a guanine
This can cause an A-T pair to be replicated during DNA replication and cause further mutations
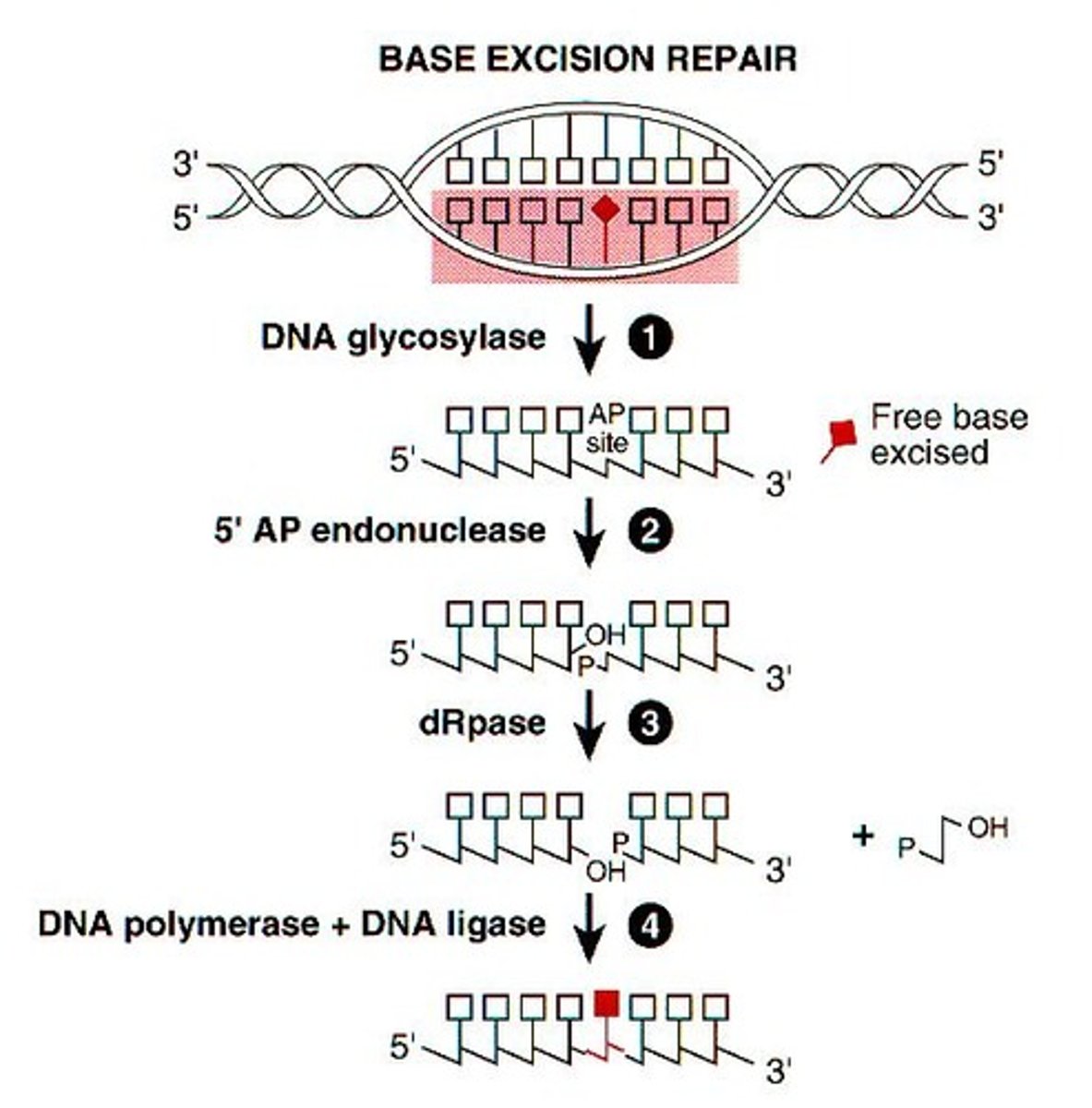
What DNA repair method can be employed to fix RNOS damage?
Base excision repair system (DNA exonuclease relies on lack of H-bond formation to recognize mismatched DNA, which does occur with RNOS damage)
What are three defenses that protect against free radicals?
1. Enzymes
2. Anti-oxidants
How do enzymes protect against free radicals?
Enzymes neutralize radicals by breaking them down or donating/accepting electrons
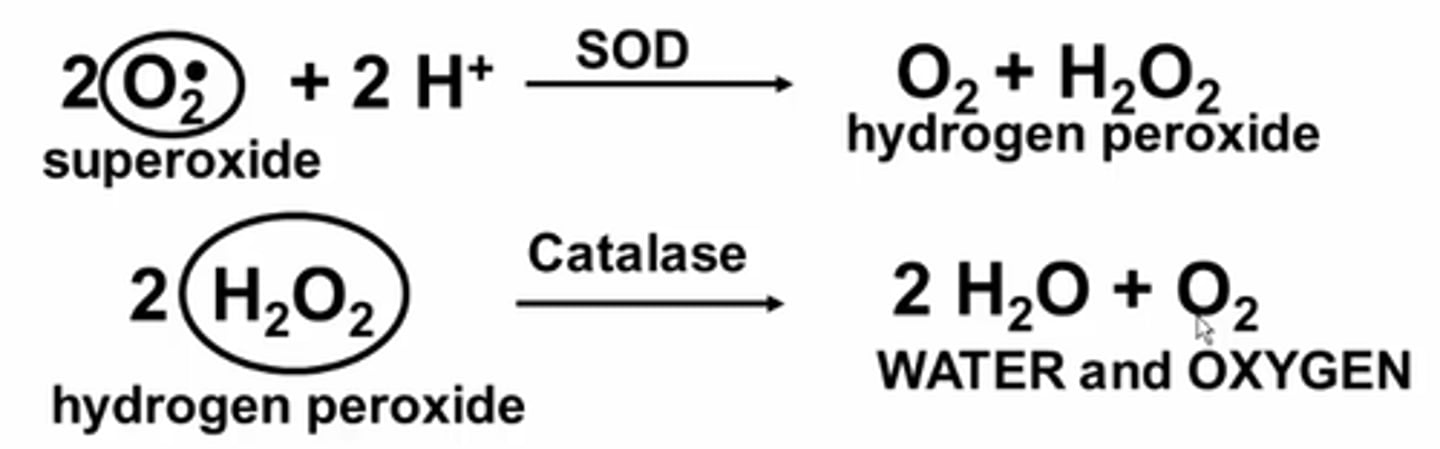
What are examples of enzymes that breakdown free radicals?
Superoxide dismutases
Catalases
Glutathione peroxidases
What do enzymes that protect against free radicals require in order for them to work?
These enzymes contain metals Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, which are required in our diet for them to work
What are common forms of anti-oxidants found in our diet?
Vitamin E, C, and Carotenoids
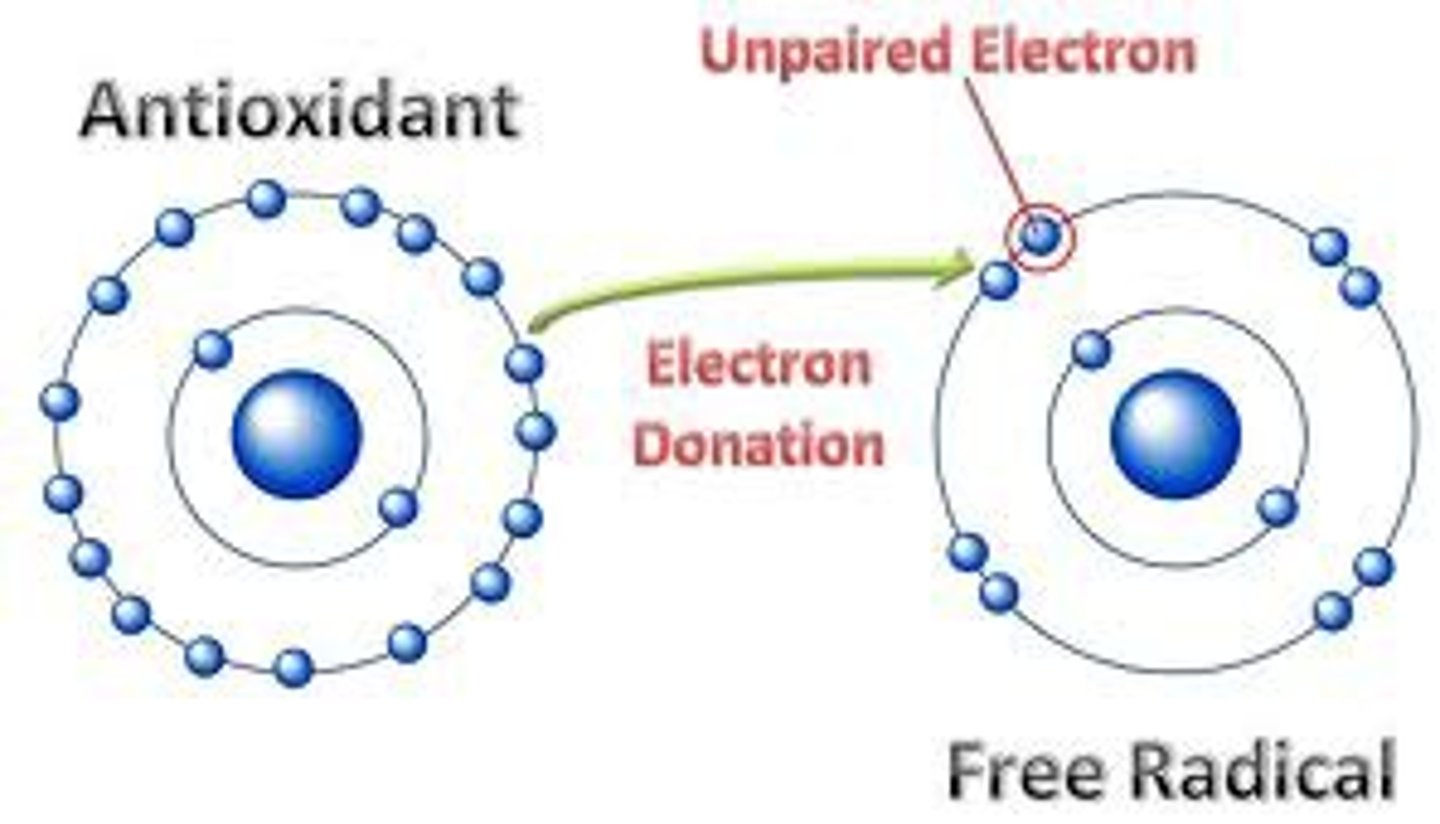
How does vitamin C and E work as antioxidants to neutralize free radicals?
Vitamin E donates an electron to radicals to fill their electron shells and make them stable. The loss of electron from the Vitamin E does not cause it to be unstable and that electron can be regenerated by Vitamin C
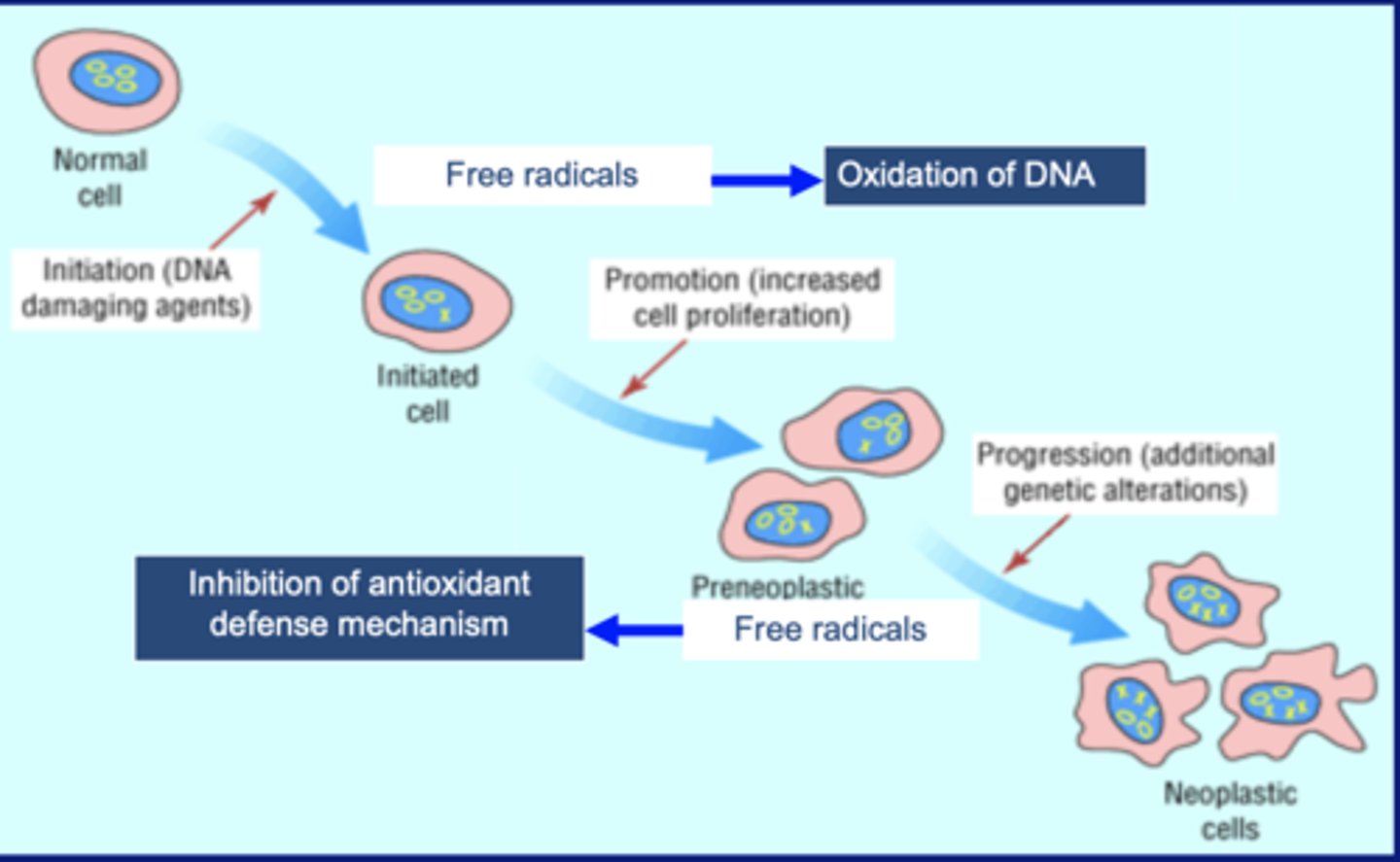
How does cancer form from increased oxidative stress?
Increase of RNOS causes damage/mutations to DNA. These mutations can cause uncontrolled cell proliferation. which can results in cancer