Antimicrobial Drugs
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
antimicrobial agents
agents that kill microorganisms or inhibit their growth
antibacterials
inhibit cell wall synthesis, alter membrane permeability, inhibit protein synthesis, inhibit nucleic acid synthesis, and/or interferes with cellular metabolism.
types of antimicrobial drugs
antibacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoan, antihelminthic
acquired resistance
When bacteria become resistant to a drug that they were once susceptible to; develops through mutation or acquiring of new genes
antibacterial drug
an antimicrobial drug used to treat a disease caused by bacteria
antibiotic
a compound naturally produced by certain molds and bacteria that inhibits the growth of microorganisms
antimicrobial
a chemical that inhibits the growth of or kills microorganisms; this includes antibiotics and chemically synthesized drugs
antiviral drug
a drug that interferes with the replication of viruses; all antiviral drugs are chemical synthesized
bactericidal drug
an antimicrobial agent that kills bacteria; inhibit cell wall biosynthesis
bacteriostatic drug
an antimicrobial drug that inhibits the growth of bacteria
broad-spectrum antimicrobial
an antimicrobial that is effective against a wide range of microorganisms, often including both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
chemotherapeutic agent
a chemical used to treat a disease
intrinsic resistance
resistance due to an inherent characteristic of the microorganism
narrow-spectrum antimicrobial
an antimicrobial that is effective against a limited range of microorganisms
R plasmid
a plasmid that encodes resistance to one or more antimicrobial drugs
therapeutic index
a measure expressing the relative toxicity of a chemotherapeutic drug; it is the lowest dose toxic to the patient divided by the dose used for therapy
selective toxicity
this is what distinguishes antibiotics from disinfectants; cause greater harm to microorganisms than to host
features of antimicrobial drugs
selectively toxic for bacteria; bacteriostatic and/or bactericidal; minimize harm to patient; damage structures present in bacteria NOT present in host
antibiotics work together with the _______________________
immune system
minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
lowest concentration of an antibiotic that stops visible growth
Kirby Bauer
tests the effectiveness of antibiotics against pathogens; check for MIC
Dilution Technique
dilutes bacteria into broth tubes to check for MIC
synergistic
drugs that work together so the total effect is greater than if given separately
antagonistic
activity of one drug interferes with the action of another
Adverse Effects of Antimicrobial Drugs
Allergic Reactions; Toxic Effects; Suppression of normal flora
Development of resistance to antimicrobials
occurs through spontaneous mutations or acquisition of new genes (conjugative transfer of R plasmid)
Characteristics of an ideal antibiotic
selectively toxic to microbe but nontoxic to host; soluble in body; remains in body long enough to be effective; long shelf life; does not lead to resistance; not cost-prohibitive; hypoallergenic; microbiocidal rather than microbiostatic; does not suppress normal flora
mechanisms of action of antibacterial drugs
inhibit synthesis of protein nucleic acid, or essential metabolites; injure plasma membrane
antibiotics which inhibit cell wall synthesis
beta-lactam drugs such as-penicillin, ampilillin, amoxicillin, cephalosporins; also, drugs such as cycloserine, bacitracin, vancomycin
mechanism of antibiotics which inhibit cell wall synthesis
The peptidoglycan chains (mureins) are cross-linked by transpeptidases, located in the cytoplasmic membrane, closely associated with penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Beta-lactam antibiotics bind to PBPs and inhibit transpeptidation, the final step in cell wall synthesis.
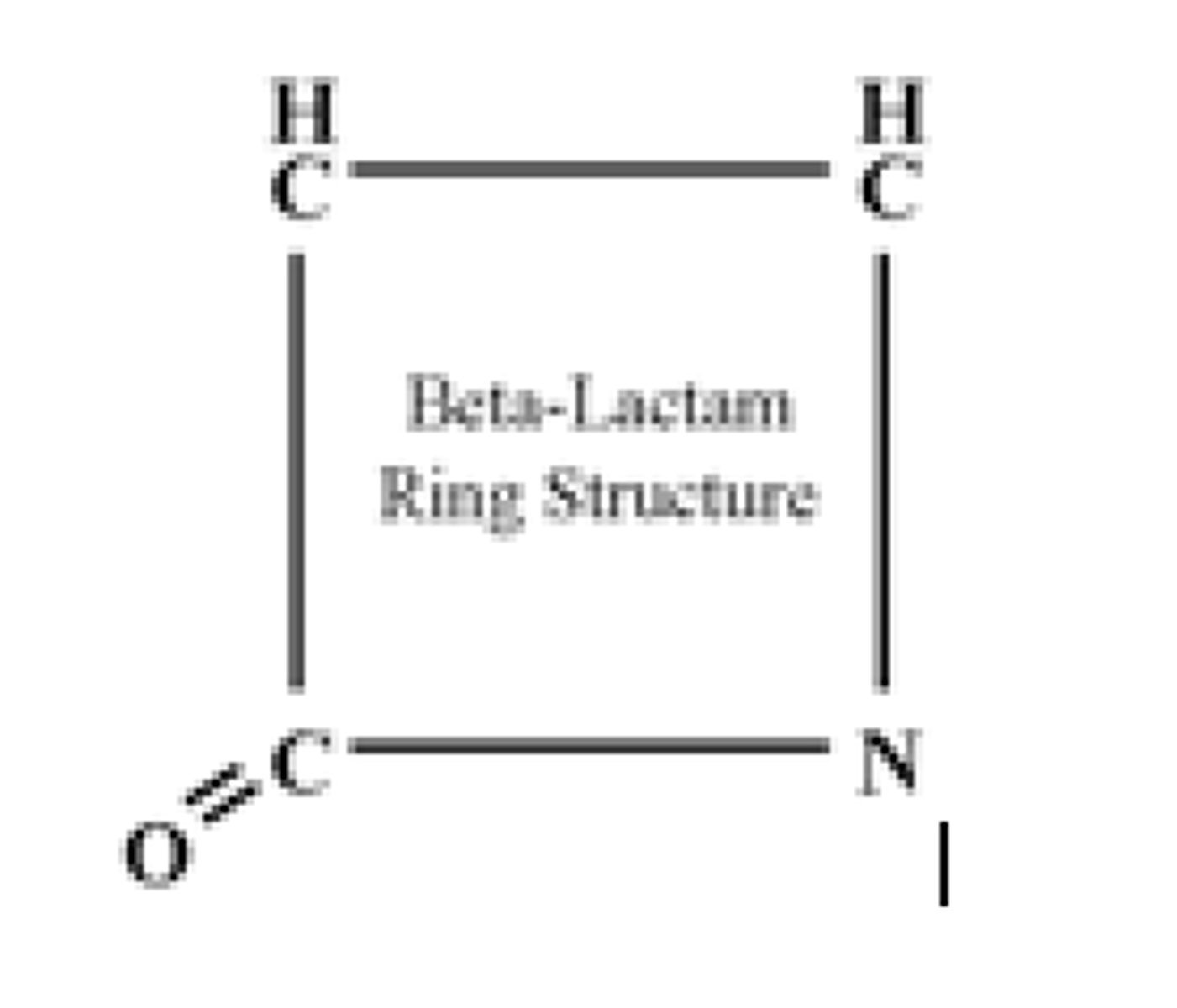
beta lactam ring
common in all antibiotics that are cell wall synthesis inhibitors.
beta lactam drugs
Penicillin G.
Amoxicillin.
Cephalosporin C.
Cefoxitin.
Thienamycin.
Aztreonam.
Clavulanic Acid.
Penicillins
generally effective against gram-positive bacteria; broad-spectrum penicillins such as amoxicillin and ampicillin are more hydrophilic and can be effective against gram-negatives
Cephalosporins
used for treatment of meningitis, pneumonia, and septicemia
Cycloserine
used in treatment of tuberculosis
Bacitracin
generally effective against gram-positive bacteria; used for topical treatment of a variety of localized skin and eye infections, as well as for the prevention of wound infections.
Vancomycin
generally effective against most gram-positive organisms; used as IV treatment for septicemia or endocarditis caused by MRSA, as well as pseudomembranous colitis
Antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis
aminoglycosides; tetracyclines; macrolides
mechanism of antibiotics which inhibit protein synthesis
target either 30s or 50s subunit of ribosome
Aminoglycosides
effective against many gram-negative and some gram-positive organisms
Types of aminoglycosides
gentamycin, amikacin, netilmicin, neomycin, streptomycin, rifampicin, tobramycin, kanamycin
Macrolides
effective against gram-negative bacteria; can be used as alternative to penicillin-sensitive patients for gram-positives, such as streptococci, staphylococci, and pneumococci; very safe drugs; usually given orally
Types of macrolides
erythromycin, clarithomycin, azithromycin
Tetracycline
broad-spectrum antibiotic; used to treat many different bacterial infections of the skin, intestines, respiratory tract, urinary tract, genitals, lymph nodes, and other body systems. It is often used in treating severe acne, or sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or chlamydia.
Chloramphenicol
broad-spectrum antibiotic; known to have serious side-effects; used as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis, and to treat meningitis, plague, cholera, and typhoid fever.
Antibiotics that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
quinolones (fluoroquinolones) and rifamycins
mechanism of antibiotics that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
inhibit topoisomeraes (wind/unwind DNA, such as DNA gyrase) or inhibiting RNA polymerase
Quinolones
Fluoroquinolones are broad-spectrum antibiotics (effective for both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria) that play an important role in treatment of serious bacterial infections, especially hospital-acquired infections and others in which resistance to older antibacterial classes is suspected.
Rifamycins
particularly effective against mycobacteria, and are therefore used to treat tuberculosis, leprosy, and mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections.
Antibiotics that injure plasma membranes
Polymyxin B
mechanism of antibiotics that injure plasma membranes
binds membrane of grm-negative bacteria and alters permeability; specifically binds to LIPID A (also binds to phospholipids). Therefore, can be quite toxic because host membranes are composed of phospholipids.
Disrupts outer membranes (has to be a GN). This leads to leakage of cellular contents and cell death.
Not typically a first-line drug.
Antibiotics that inhibit synthesis of essential metabolites
Sulfonamides
mechanism of antibiotics that inhibit synthesis of essential metabolites
impair the function of folic acid, mimic the structure of metabolic pyrimidines, or mimic the structure of metabolic purines.
Sulfonamides
Sulfa drugs were the first chemical substances systematically used to treat and prevent bacterial infections in humans;They may be prescribed to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), bronchitis, eye infections, bacterial meningitis, pneumonia, ear infections, severe burns, traveler's diarrhea, and other conditions
Anaerobic & Parasitic Drugs
5-Nitroimidazoles; wide-spectrum; Metronidazole - against anaerobic bacteria and protozoan infections; Tinidazole - against amoebic/parasitic infection; longer duration of action.
Diffuses into the organism where the nitro group is reduced chemically reactive intermediates are formed that inhibit DNA synthesis and/or damage DNA.
Antiviral Drugs
Designing safe and effective antiviral drugs is difficult, because viruses use the host's cells to replicate. It must attach to and enter a host cell. This makes it difficult to find targets for the drug that would interfere with the virus without also harming the host organism's cells.
mechanism of antiviral drugs
targets are various points of viral reproduction
Types of antiviral drugs
(wide-spectrum); metronidazole; tinidazole, amantadine, zanamivir, immunoglobulins, acyclovir, cidofovir, lamivudine, alpha-interferon, ganciclovir, famciclovir, fosarnet
Anti-tuberculosis drugs
blocks mycelia acid synthesis
isoniazid, ethionamide, ethambutol, cycloserine