Properties and Effects of Solutions: Chemistry Solutions, Vapor Pressure, Colligative Properties
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Molarity
Molarity = moles of solute / liters of solution
Mass Percent
Mass percent = (mass of solute / mass of solution) × 100
Mole Fraction
Mole fraction of component A (xA) = nA / (nA + nB)
Molality
Molality = moles of solute / kg of solvent
Normality
Normality = equivalents of solute / liters of solution
Equivalents of acids and bases
Mass that donates or accepts a mole of protons
Equivalents of oxidizing and reducing agents
Mass that provides or accepts a mole of electrons
Like Dissolves Like
Polar molecules and ionic compounds tend to dissolve in polar solvents; nonpolar molecules dissolve in nonpolar compounds.
Steps of Solution Formation
1. Breaking up the solute into individual components (endothermic). 2. Overcoming intermolecular forces in the solvent (endothermic). 3. Allowing the solute and solvent to interact to form the solution (often exothermic).
Enthalpy (Heat) of Solution
ΔHsol'n may have a positive sign or a negative sign.
Enthalpy (Heat) of Hydration
Includes ΔH of step 2 and step 3.
Factors Favoring the Solution Process
1. Negative value for ΔHsol'n. 2. Increase in entropy. 3. For positive values of ΔHsol'n, the increase in entropy outweighs the increase in energy.
Structure Effects
Polar (hydrophilic) dissolves in polar; nonpolar (hydrophobic) dissolves in nonpolar.
Henry's Law
The amount of a gas dissolved in a solution is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the solution.
Henry's Law Equation
P = kC, where P = partial pressure of the gaseous solute, C = concentration of the dissolved gas, k = constant characteristic of a particular solution.
Temperature Effects on Solids
Increases in temperature usually increase solubility (the amount that can be dissolved).
Temperature Effects on Gases
Solubility of gases always decreases with increasing temperature.
Nonvolatile Solutes
Nonvolatile electrolytes lower the vapor pressure of a solute.
Raoult's Law
Psolvent = P0solvent × Xsolvent, where Xsolvent is the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution.
Ionic Solutes
Dissociation of ionic compounds has nearly two, three or more times the vapor pressure lowering of nonionic (nonelectrolyte) solutes.
Non-ideal Solutions
Liquid-liquid solutions in which both components are volatile.
Modified Raoult's Law
Ptotal = PA + PB, where PA and PB are the partial pressures.
Ideal Solutions
Liquid-liquid solution that obeys Raoult's law; no solution is perfectly ideal, though some are close.
Negative deviations from Raoult's law
Lower than predicted vapor pressure for the solution.
Positive deviations from Raoult's law
Higher than predicted vapor pressure for the solution.
Colligative Properties
Properties dependent on the number of solute particles but not on their identity.
Boiling-Point elevation
Nonvolatile solutes elevate the boiling point of the solvent.
Freezing-Point depression
Solutes depress the freezing point of the solvent.
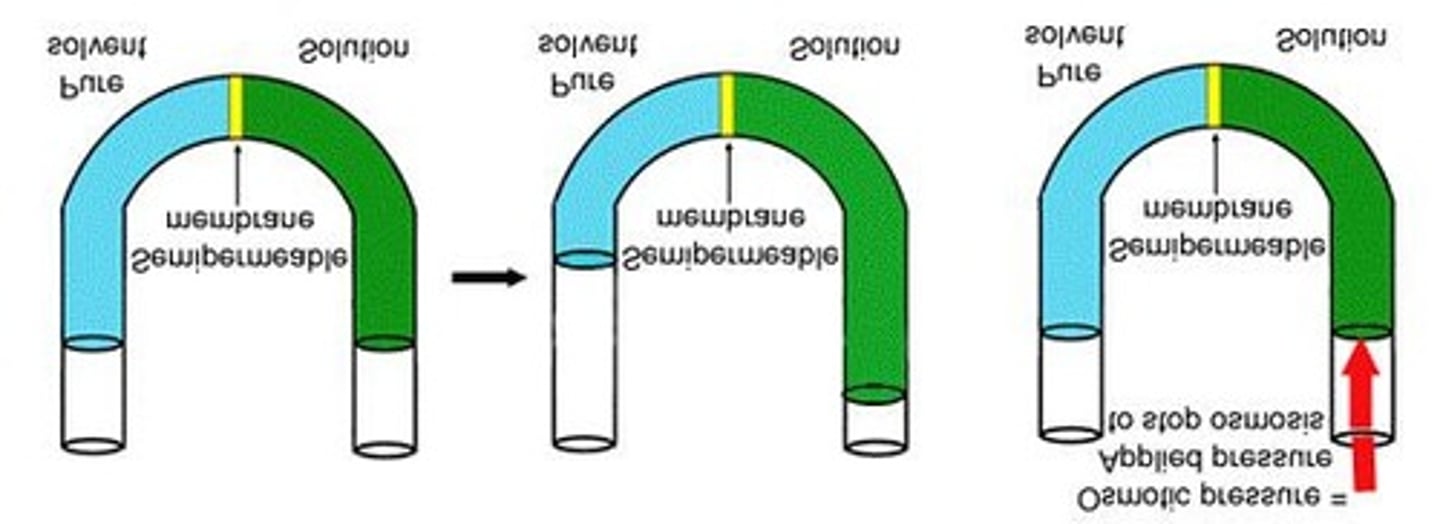
Osmotic Pressure
The pressure necessary to keep water from flowing across a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis
The flow of solvent molecules into a solution through a semipermeable membrane.
Dialysis
Transfer of solvent molecules as well as small solute molecules and ions.
Isotonic Solutions
Solutions that have the same osmotic pressure.
Crenation
Cells placed in a hypertonic solution lose water to the solution, and shrink.
Hemolysis
Cells placed in a hypotonic solution gain water from the solution and swell, possibly bursting.
Reverse Osmosis
External pressure applied to a solution can cause water to leave the solution.
van't Hoff factor i
The number of particles in solution divided by the number of moles of dissolved solute.
Expected value of i for NaCl
i = 2.
Expected value of i for BaCl2
i = 3.
Expected value of i for Al2(SO4)3
i = 5.
Actual values of i
Values of i are less than expected due to ion pairing (clustering).
Boiling-elevation and freezing-point depression formula
∆T = imK.
Osmotic pressure formula
π = iMRT.
Colloidal Dispersions (Colloids)
Tiny particles suspended in some medium.
Tyndall Effect
Scattering of light by particles.
Size range of colloidal particles
Particles range in size from 1 to 1000 nm.
Aerosol
Gas dispersing medium with liquid dispersed substance.
Foam
Liquid dispersing medium with gas dispersed substance.
Emulsion
Liquid dispersing medium with liquid dispersed substance.