3. Coping with Environmental Variation
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Phenotypes definition
product of genes interacting with environmental conditions
Genotype definition
Individual’s complete genetic makeupe
Phenotypes and the environment
traits have genetic basis but the environment turns on/off certain genes so different phenotypes develop
Phenotype fitness
phenotypes experiences higher fitness in one environment compared to challenging environments
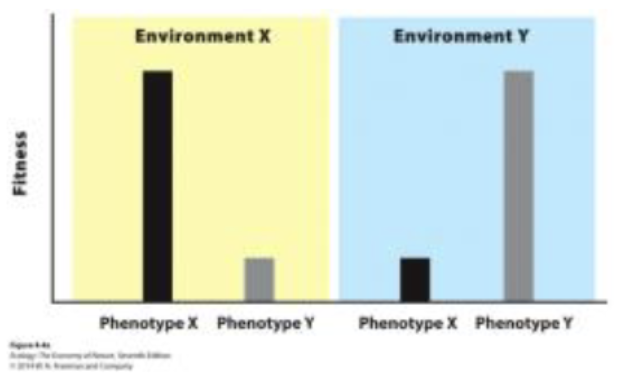
Phenotype plasticity
The ability of a single genotype to product phenotypes
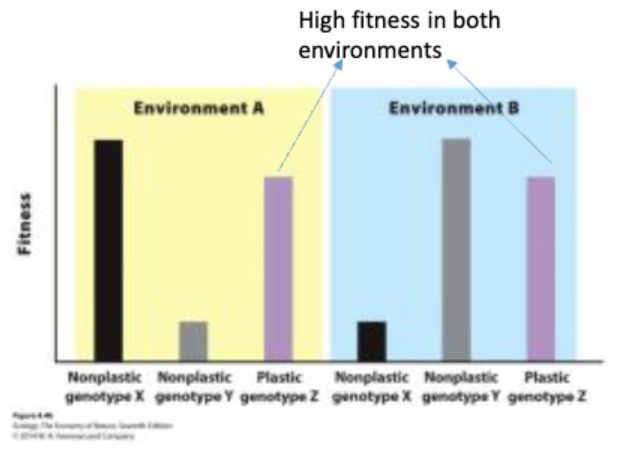
Types of phenotypic plasticity
morphology
physiology
behavior
life history
Phonology
Morphology def.
physical defenses, height, size of digestive tract to extract more nutrients
Physiology def.
digestive enzymes, chemical defenses
Behavior def.
habitat use, aggressiveness
Life history def.
sexual maturity, clutch size
Phonology def.
time to start reproduction
Metabolism def.
The sum of an organism’s biochemical reactions that acquire, use energy and tend to maintain homeostasis (steady internal conditions)
Catabolism def.
breaking down existing molecules
Anabolism def.
Building large molecules from smaller ones
Importance of temperature
Intensity of heat: average kinetic energy of the molecules in object/ system
Organism regulate internal temp in different ways
Thermal Neutral Zone Def.
The temperature range over which an endothermic animal at rest can maintain its metabolic rate and temperature without appreciable change
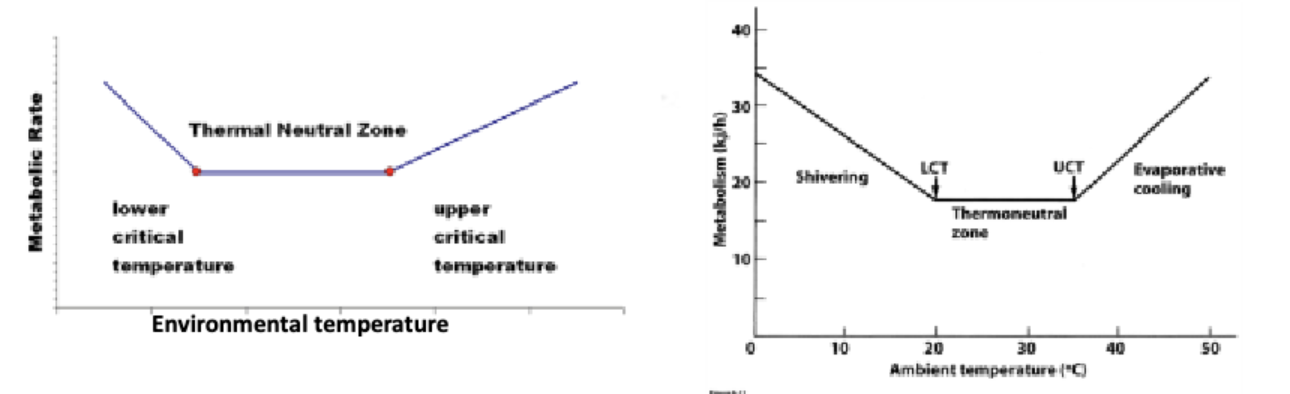
Critical upper / lower temperatures def.
Temperatures disrupting metabolic functions and cellular components in the organisms, important changes can be detected (shivering, cooling)
Types of transfer of heat:
Radiation
Connection
Conduction
Evaporation (cooling)
Radiation def.
Heat transfer between two objects in absence of direct contact (NO CONTACT)
Convection def.
The transfer of heat energy by mass movement of a fluid (gas/liquid)
air, water, weather, etc.
Conduction def.
The transfer of energy (heat) from one place to another directly (by physical contact), Heat flows down a gradient from warmer to cooler areas
Evaporation def
Loss of water in the form of vapor. Heat is transferred from an organism to its surroundings as water evaporates from the organisms’s surface.
Energy exchange in terrestrial plants
heat convention & conduction
solar radiation
heat envirotranspiration
infrared out/in
Heat conduction
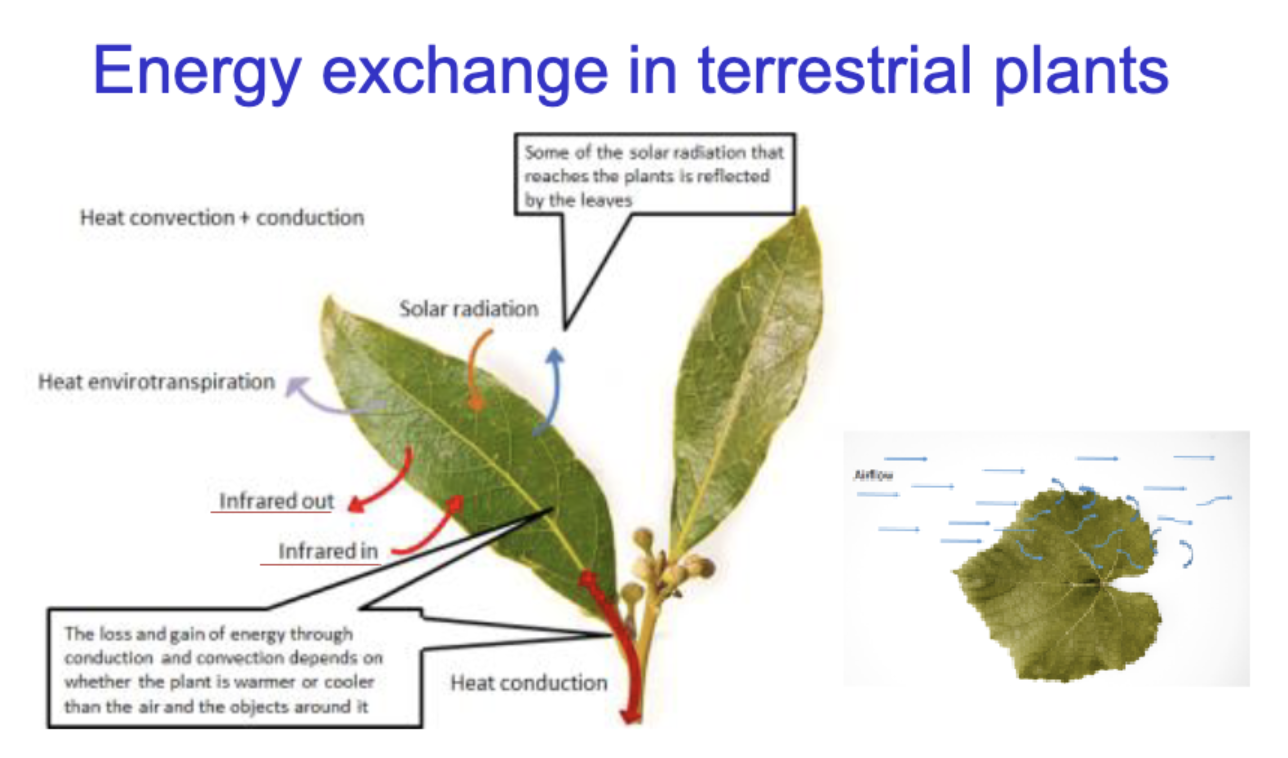
Change in heat equation for plant
ΔH plant = Solar + IR in - IR out +- H conv +- H cond - H evap
Physical Modifications In energy exchange
Hairs/ trichomes to increase pubesence and reflectance (thermoregulation)
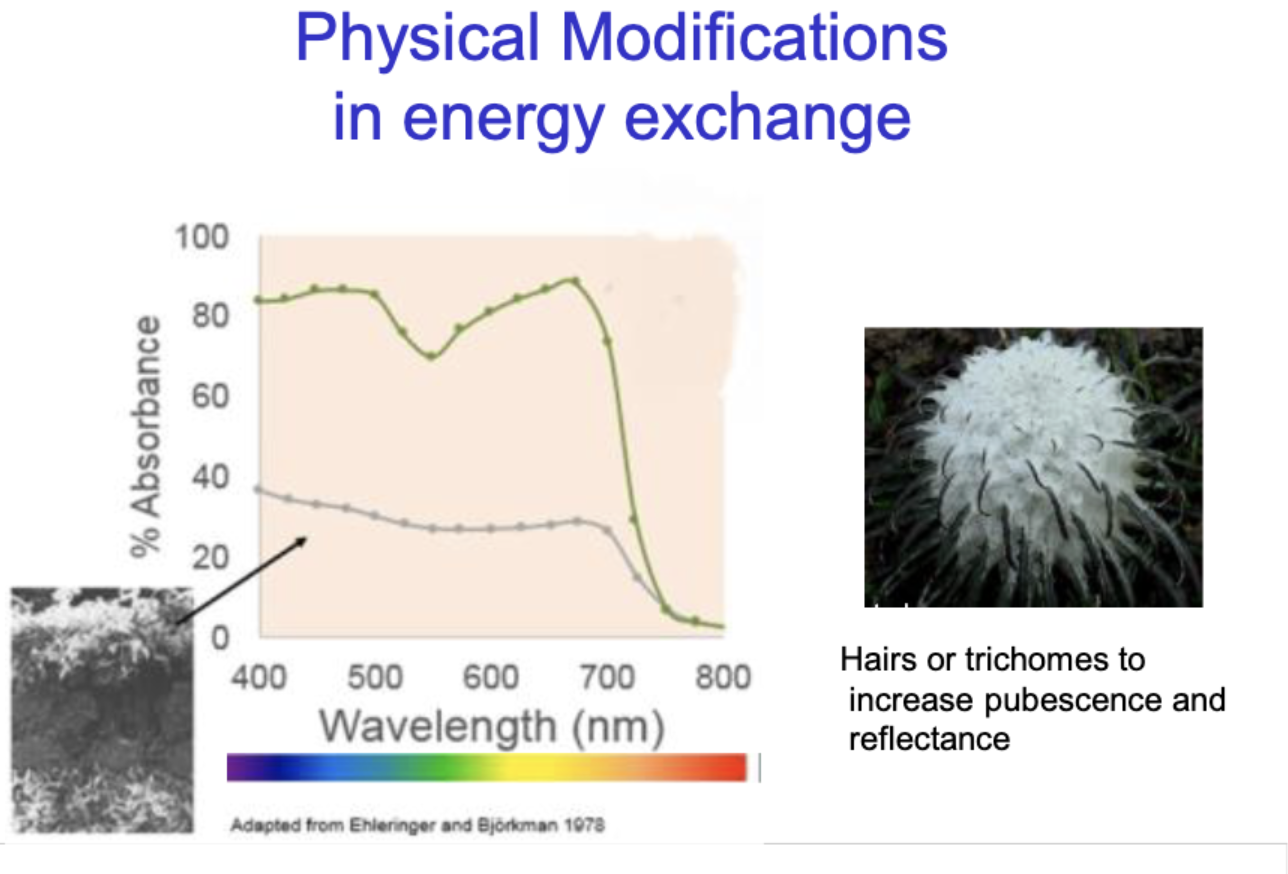
Thermoregulation
Regulation of temperature
Ecotohermes
Endotherms
Thermoregulation equation
ΔH animal = Solar + IR in - IR out +- H conv +- H cond - H evap + H met
Ectotherms def.
Regulate body temp through energy exchange with external sources (environment)
Endotherms def.
Rely primarily on internal heat generation, remain active below freezing temperatures, demand more energy (food) to support metabolism.
Physical modification and behaviors
lizard laying on hot wood for heat
elephant spraying itself with water with trunk to cool down
Bunny lifting ears to cool
Blood vessles vains and artiers can be
consturcted when cold causing less heat
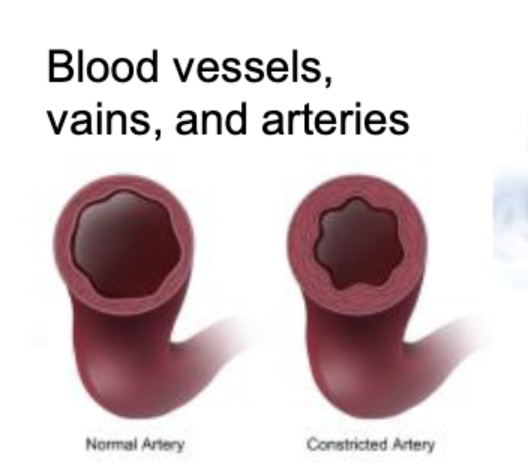
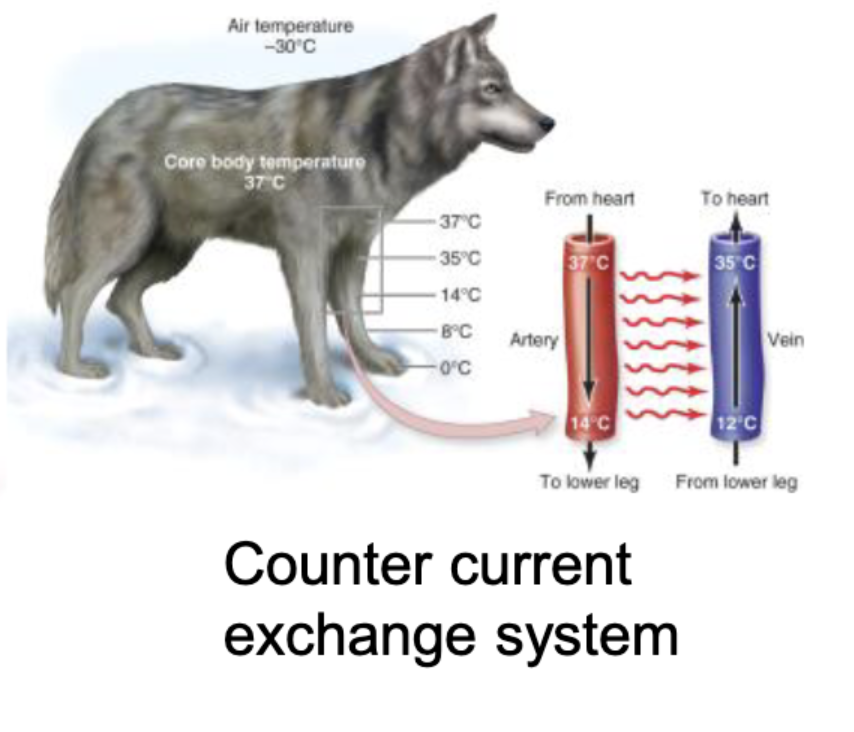
Core body temp is higher then external limbs bc
the counter current exchange system, heart to limbs coold limbs to hear heat, lets body be warmer then air temperature to survive in cold
Water internal balance def.
water content in most organisms represents a high percentage of their body mass
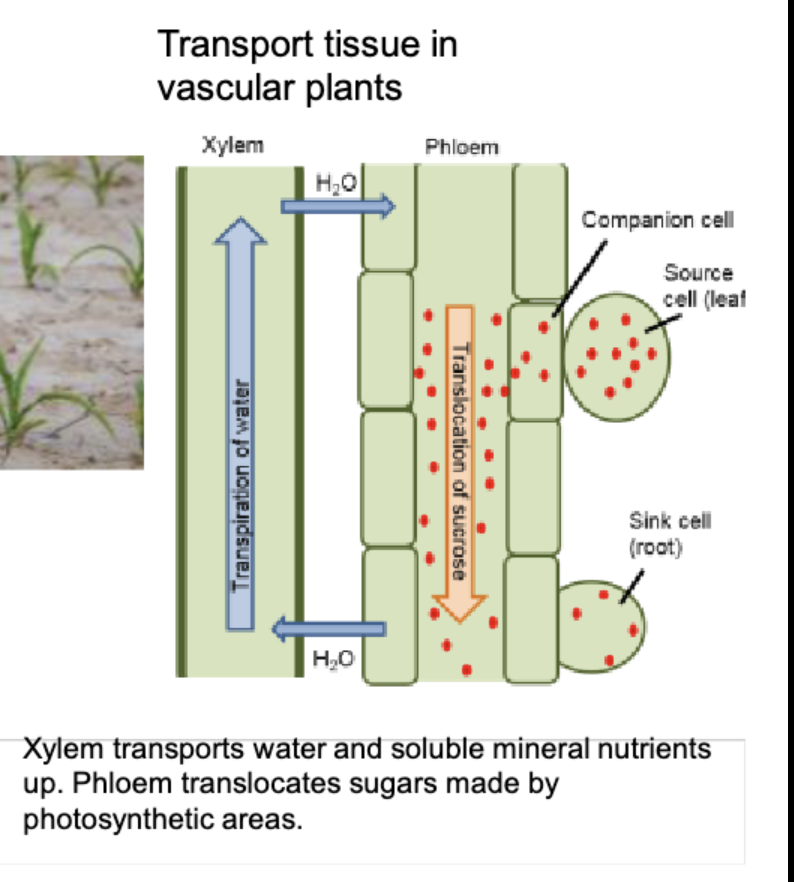
Transport tissues in vascular plants
Xylem: transports water and soluble mineral nutrients up
Phloem: translocates sugars made by photosynthetic areas
Variation in solutes
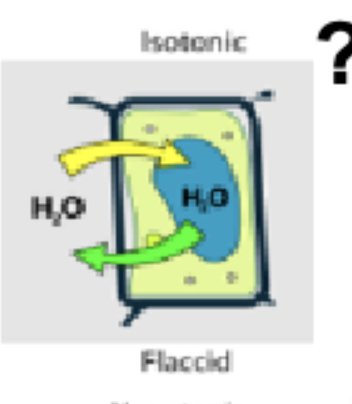
Isotonic
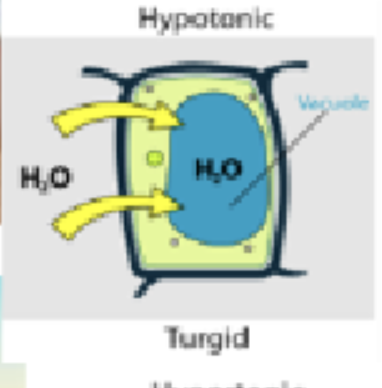
Hypotonic
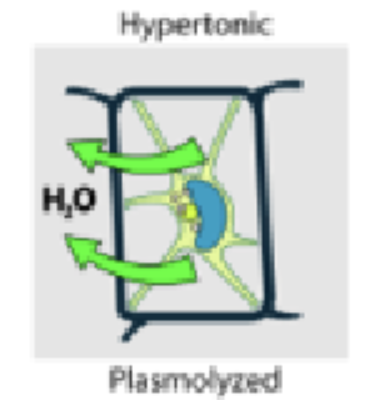
Hypertonic
Isotonic def.
Flaccid (neutral water in/out)
Hypotonic def.
Turgid (bursting) (too much water in)
Hypertonic
Plasmolyze (shrinked up, hyper in small water amount) (too much water out)
Trade offs with photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O (Light(energy) →) C6H12O6 + 6O2
Stooma opened vs stoma closed
Stoma open during day
stoamtes open
Water travels up
more water flow in leaf, stem, roots
carbon doxide intake allowed
Stoma closed during night
stoamtes closed
more water still, to prevent water loss
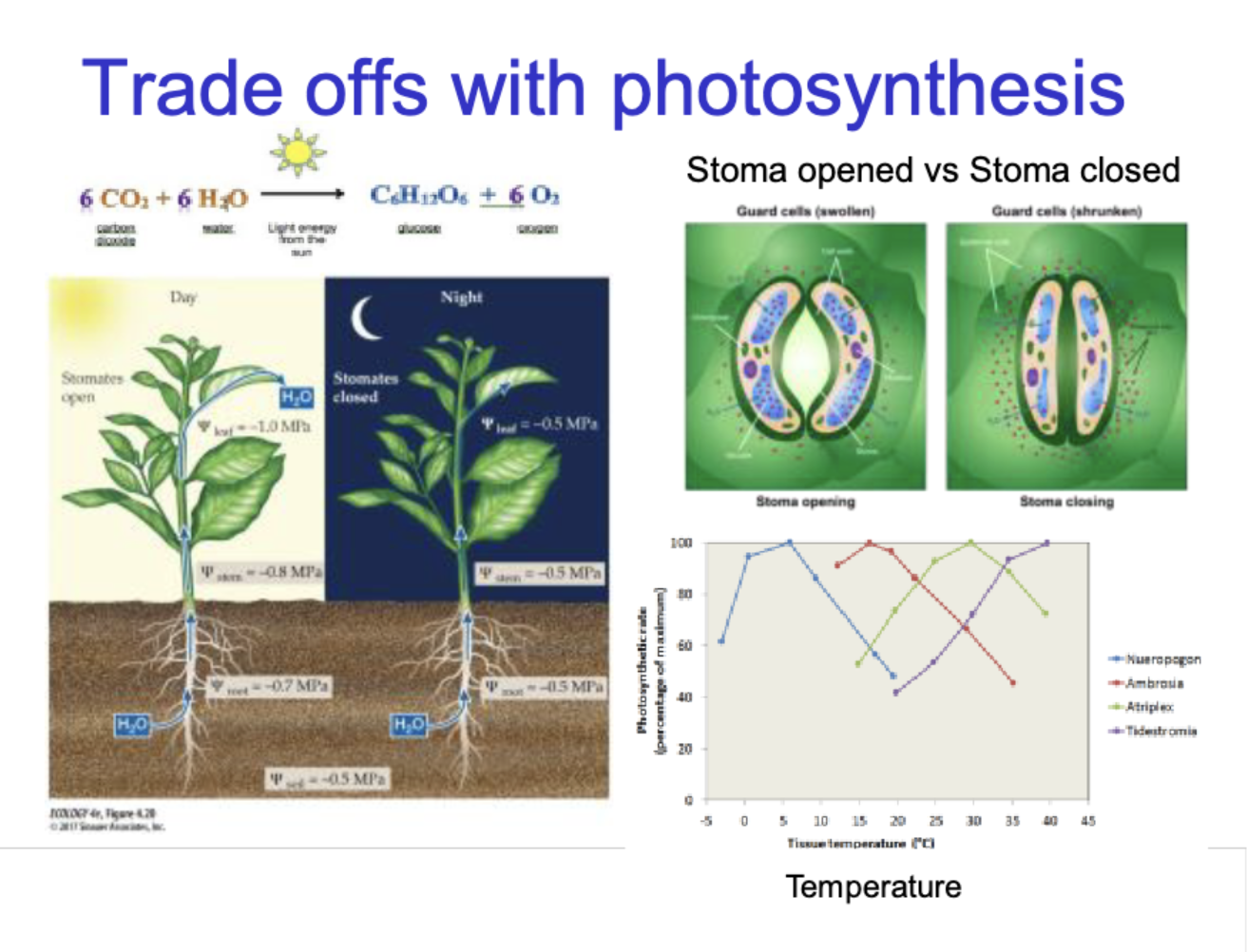
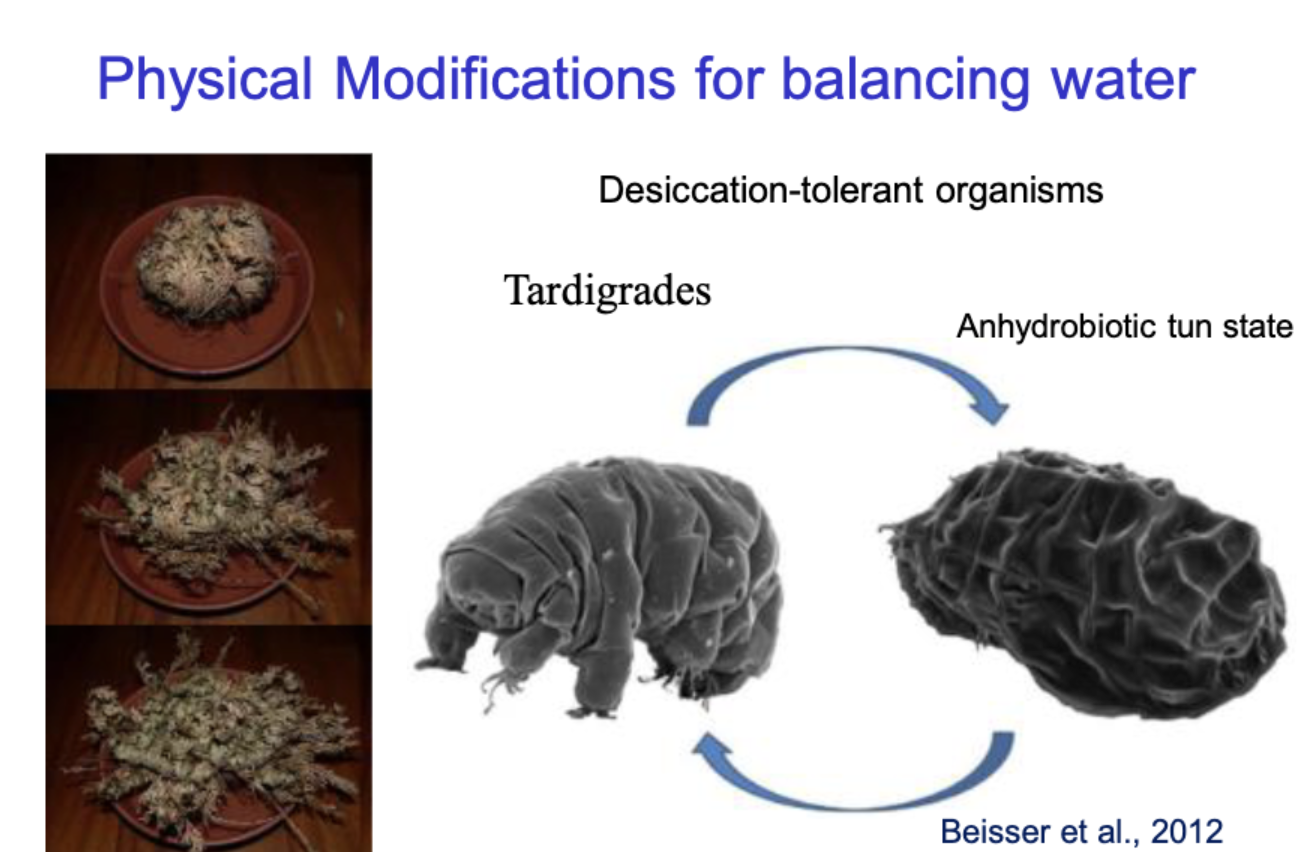
Physical modifications for balancing water
Desiccation-tolerant organisms
tardigerades can curl up into a ball - anhydxroobotic tun state when in extreme dehydration
Moss having water and not
Barriers to desiccation (dryness, dehydration)
Cuticle
Skin
Hair
Trichomes (hair like outgrowths on plants)
wax
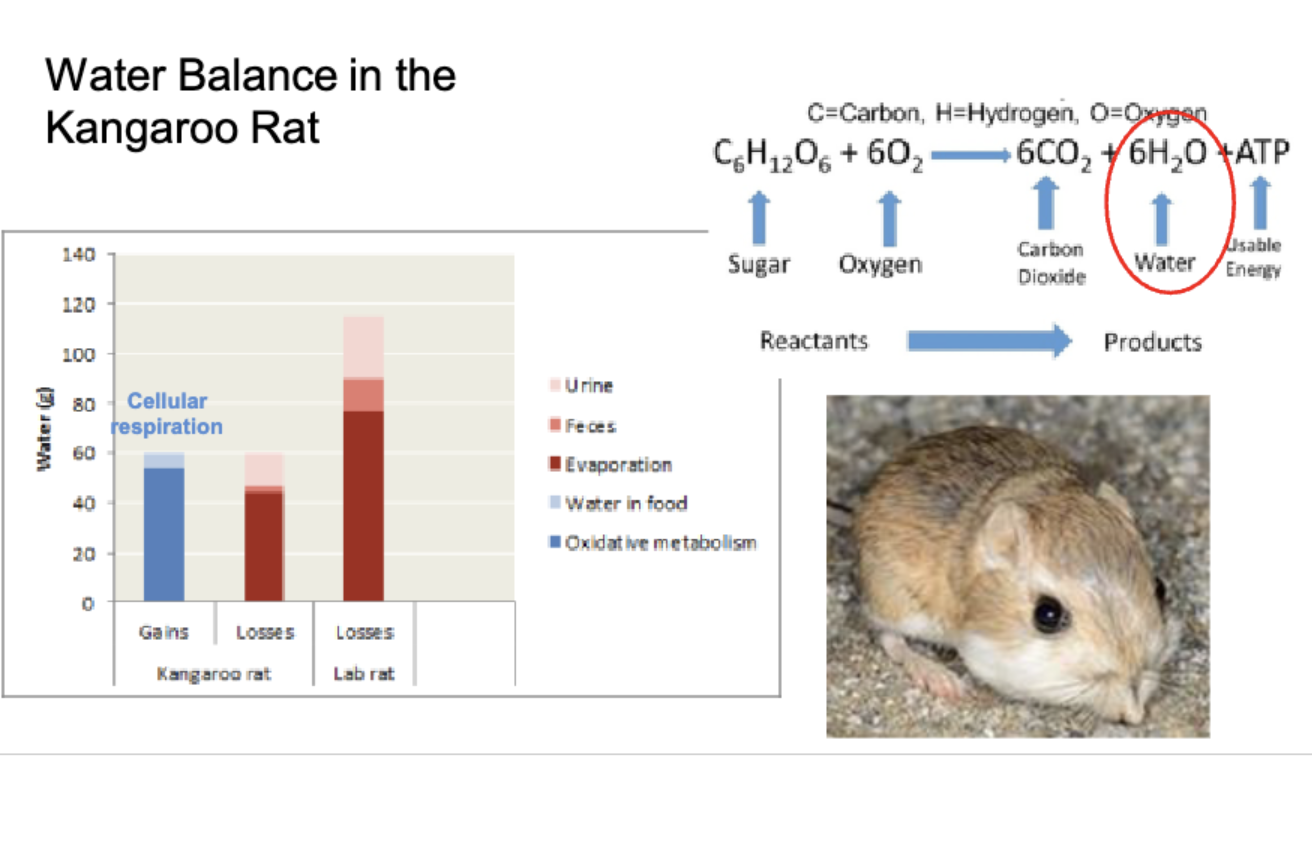
Water balance in kangaroo rat
even between gains and losses
Salinity def.
The state of having high water aka high saline
Adaptations to salinity
Rapid changes of salinity:
Copeped trigous sp - synthesis amino acids to increase the osmotic (osmosis: flow of water) potential to the body fluids and match the environment

When have extreme condtions an organism often….
Migrates to survive
Migration def and ex.
The seasonal movement of animals from one region to another
Temperature
darkness
flood supplies
water supplies
Reproduction
predation
Storage of rescues def.
reserve of enegy in the tissues: roots of organisms
Dormancy def.
Dramatic reduction of the metabolic processes (physiological shutdown)
Diapause: insects
Hibernation: mammals
Torpor: small birds and mammals
Aestivation: snails, desert tortoises, nile crocodiles