Comprehensive Respiratory System Anatomy, Function, and Diseases
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
226 Terms
Respiratory System
The system that provides oxygen to the body and removes unwanted gases, such as carbon dioxide.
Lungs
The two organs of the respiratory system where gas exchange occurs.
Upper Respiratory System
Includes the nose, nasal cavity, and pharynx.
Lower Respiratory System
Includes the larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli.
Nose
A flap of cartilaginous tissue covered by skin that opens to the outside through nostrils.
Nasal Cavity
Divided into two halves by the nasal septum, made of cartilage and bone, and covered by mucus membranes.
Mucus Membranes
Tissues that produce mucus to humidify and warm the air.
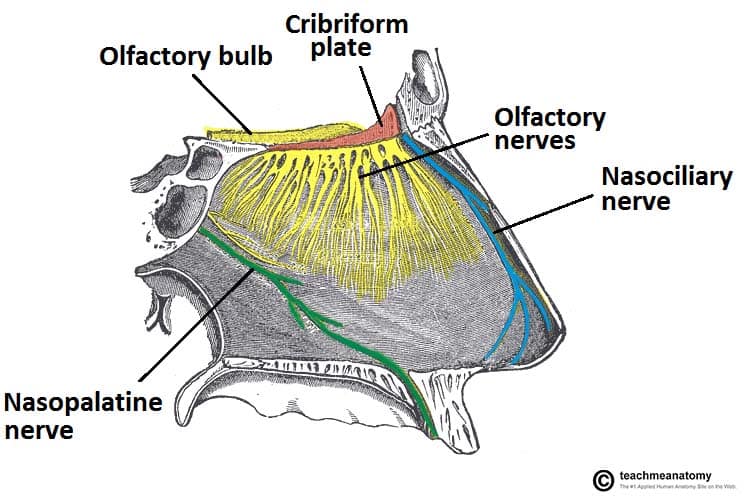
Olfactory Nerve
Located at the roof of the nasal cavity, involved with the sense of smell.
Paranasal Sinuses
Air-filled spaces that open into the nasal cavity.
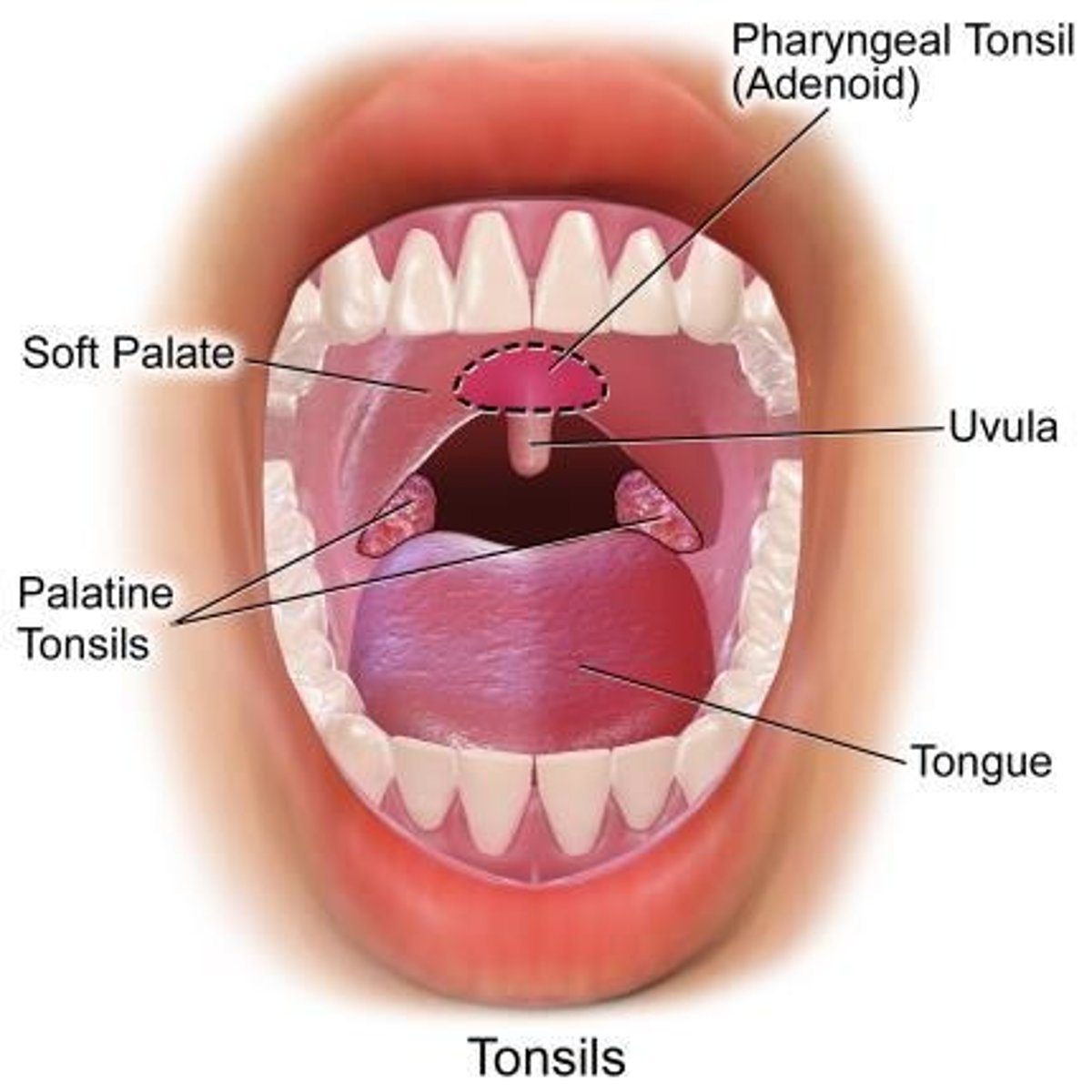
Pharynx
A common passageway for liquid, food, and air, divided into nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
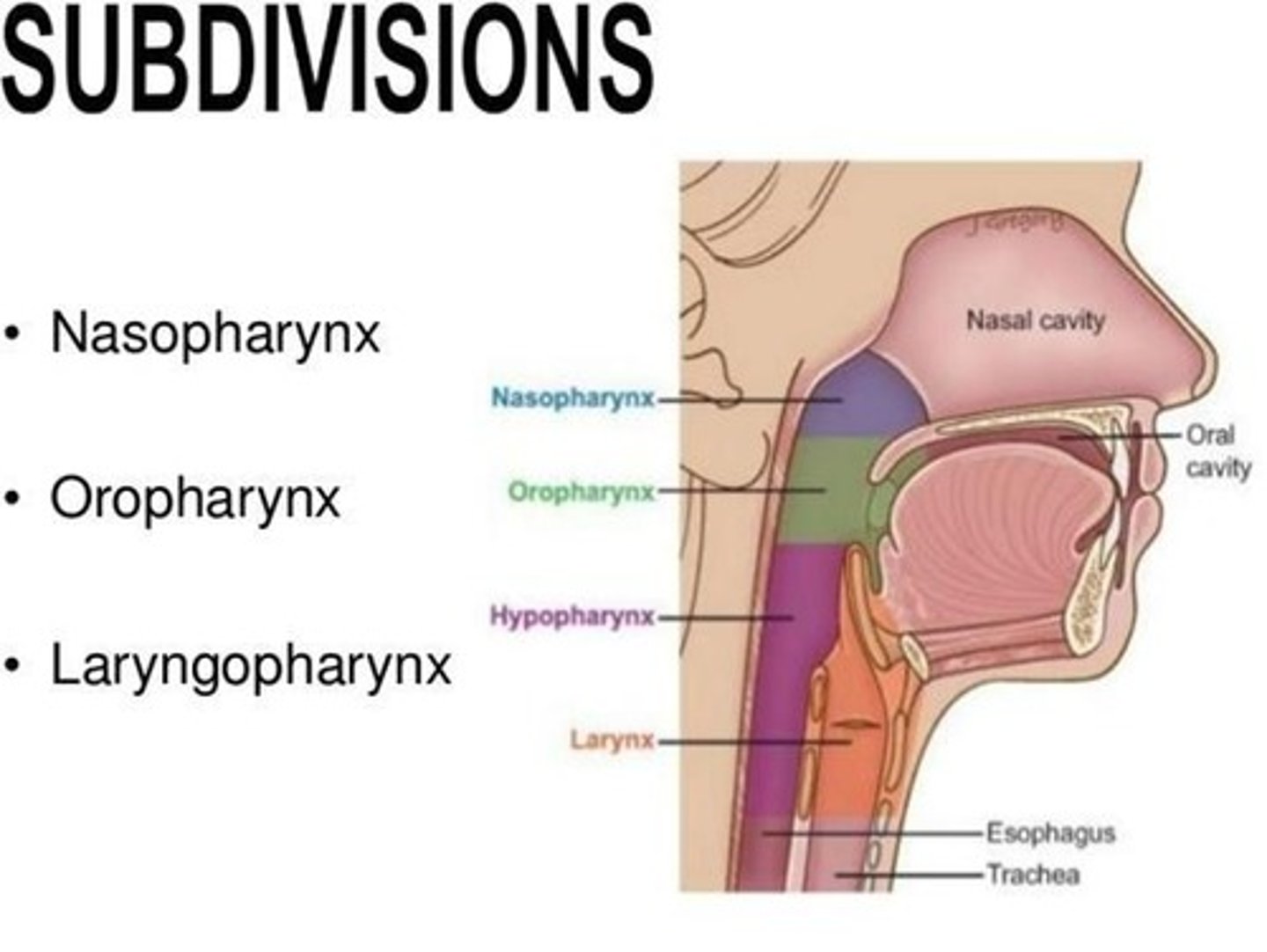
Nasopharynx
The part of the pharynx located behind the nasal cavity.
Oropharynx
The part of the pharynx located behind the oral cavity.
Laryngopharynx
The part of the pharynx located behind the larynx.
Larynx
The voice box that leads to the trachea and contains vocal cords.
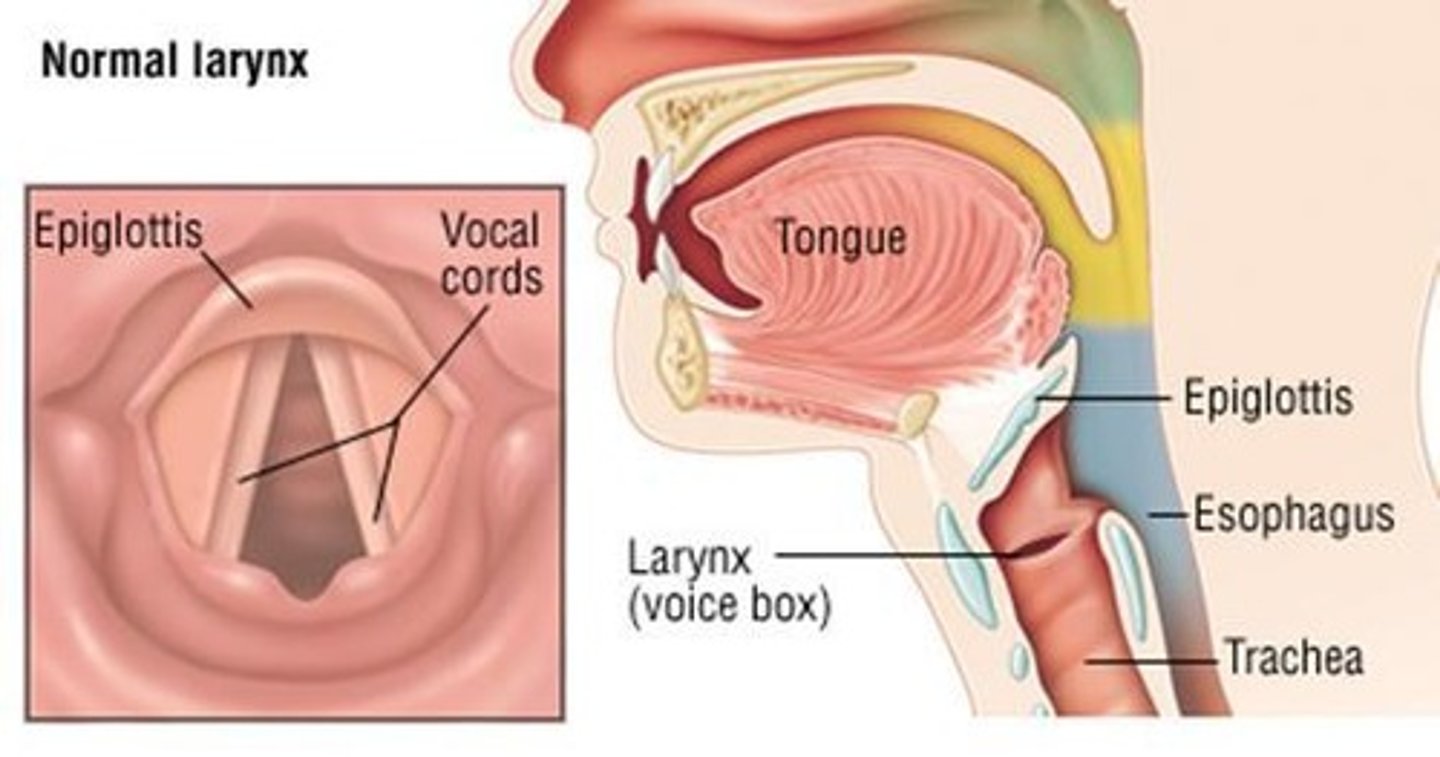
Glottis
The V-shaped opening in the larynx that allows air to be inhaled and exhaled.
Epiglottis
A flap-like structure that covers the glottis during swallowing to prevent aspiration.
Adam's Apple
The cartilaginous wall of the larynx in front.
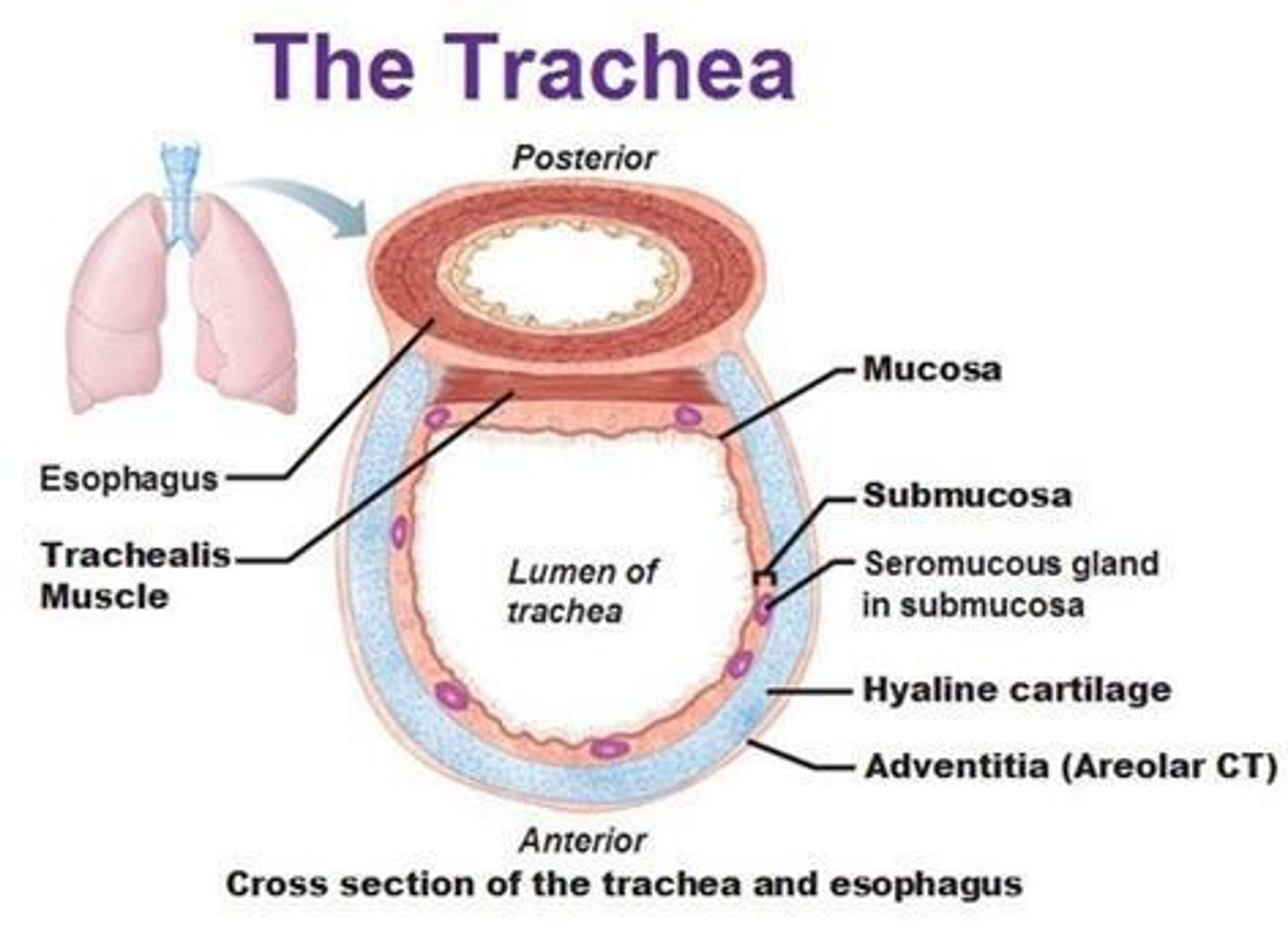
Trachea
The windpipe that is about 4 inches long and made up of C-shaped cartilage tissue.
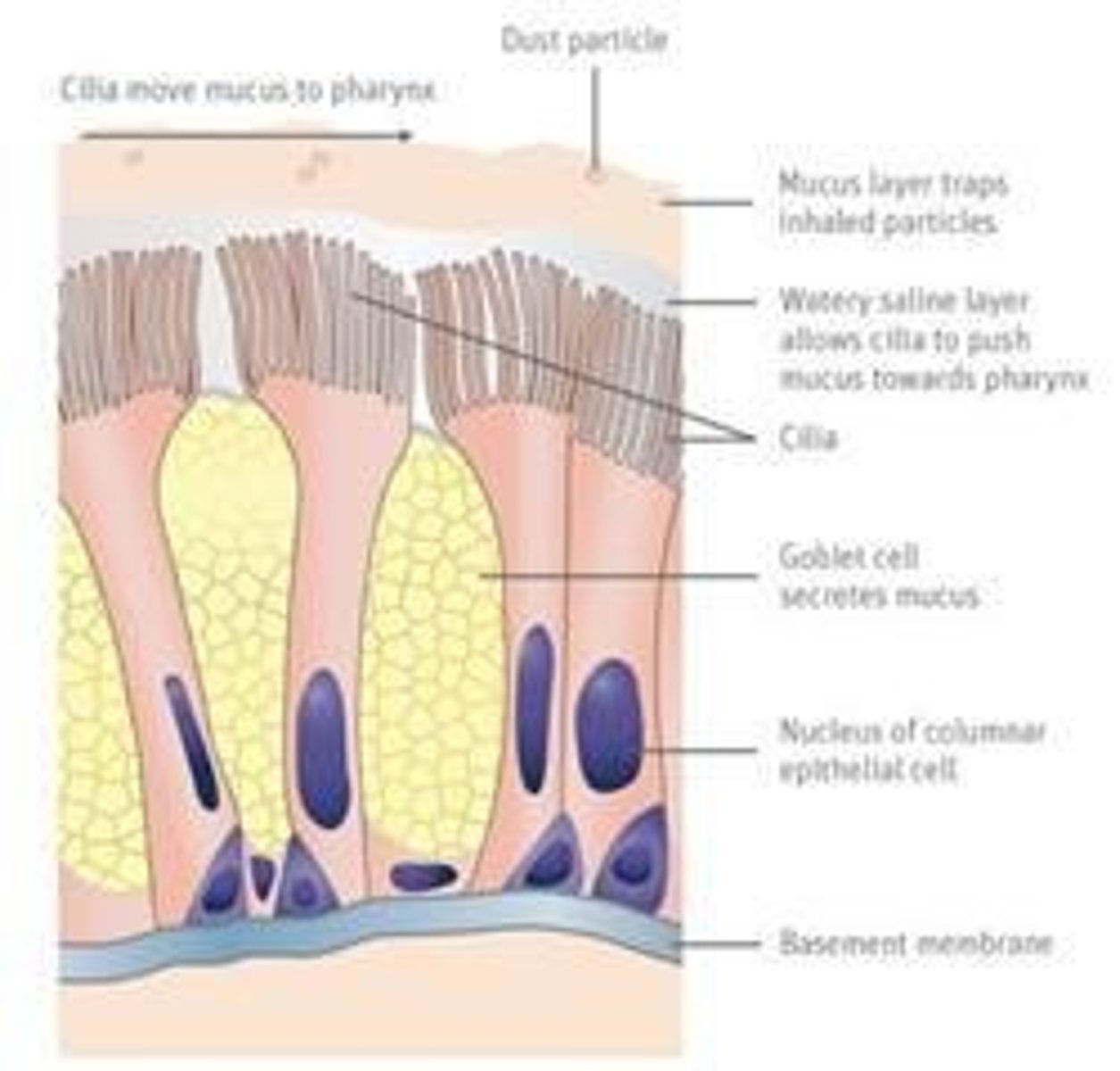
Cilia
Hairy-like structures in the trachea that sweep mucus with trapped particles toward the throat.
Bifurcation
The location where the trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi.
Primary Bronchi
The two branches that the trachea divides into, singular: bronchus.
Mediastinum
The area in the thoracic cavity where the trachea is located.
Vocal Cords
Structures in the larynx that vibrate to produce sound.
Mucosal Membranes
Membranes that humidify and warm the air in the pharynx.
Common Pathological Conditions
Health issues related to the respiratory system that can affect its function.
Bronchial Tree
The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, resembling an upside-down tree.
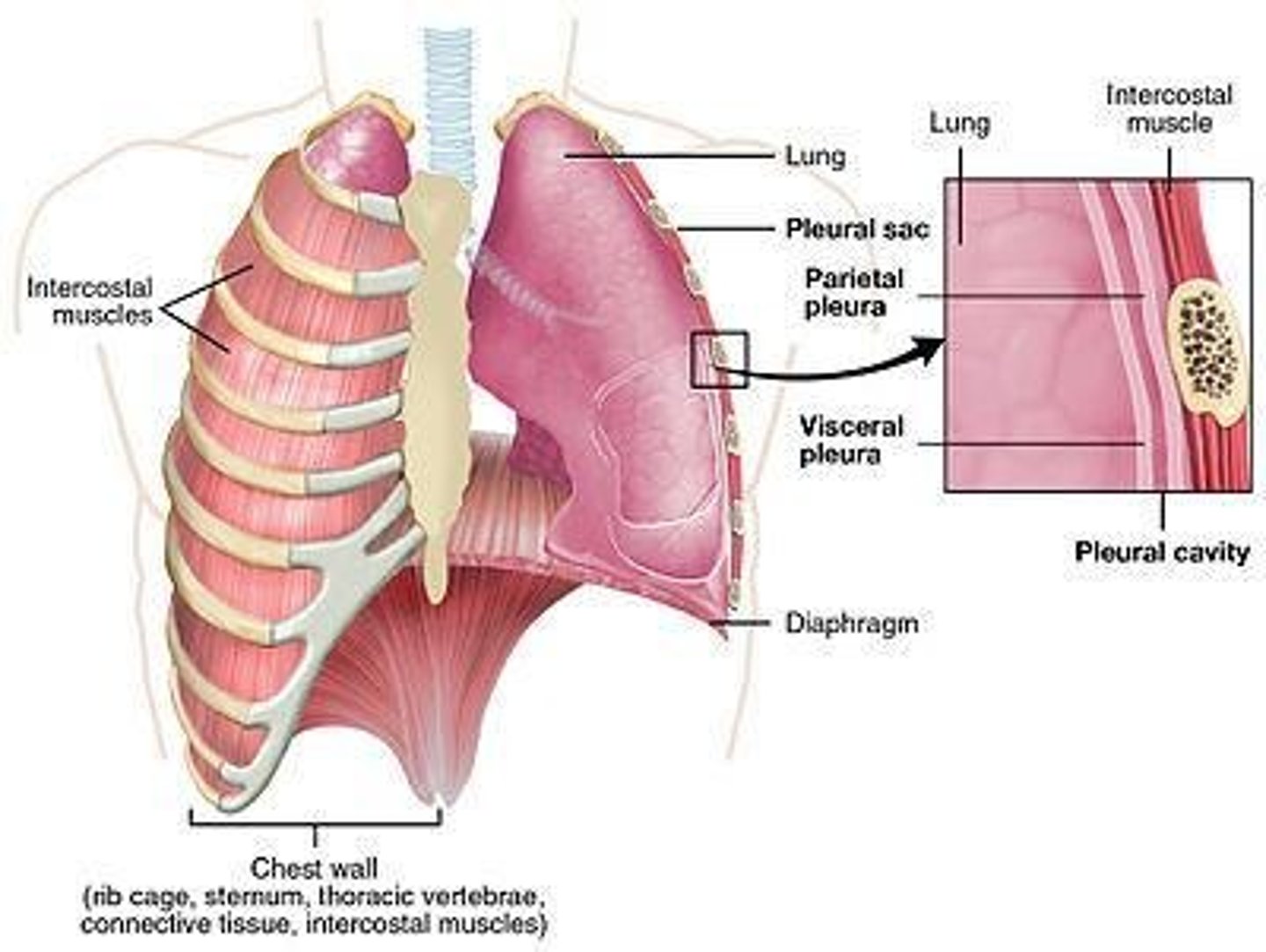
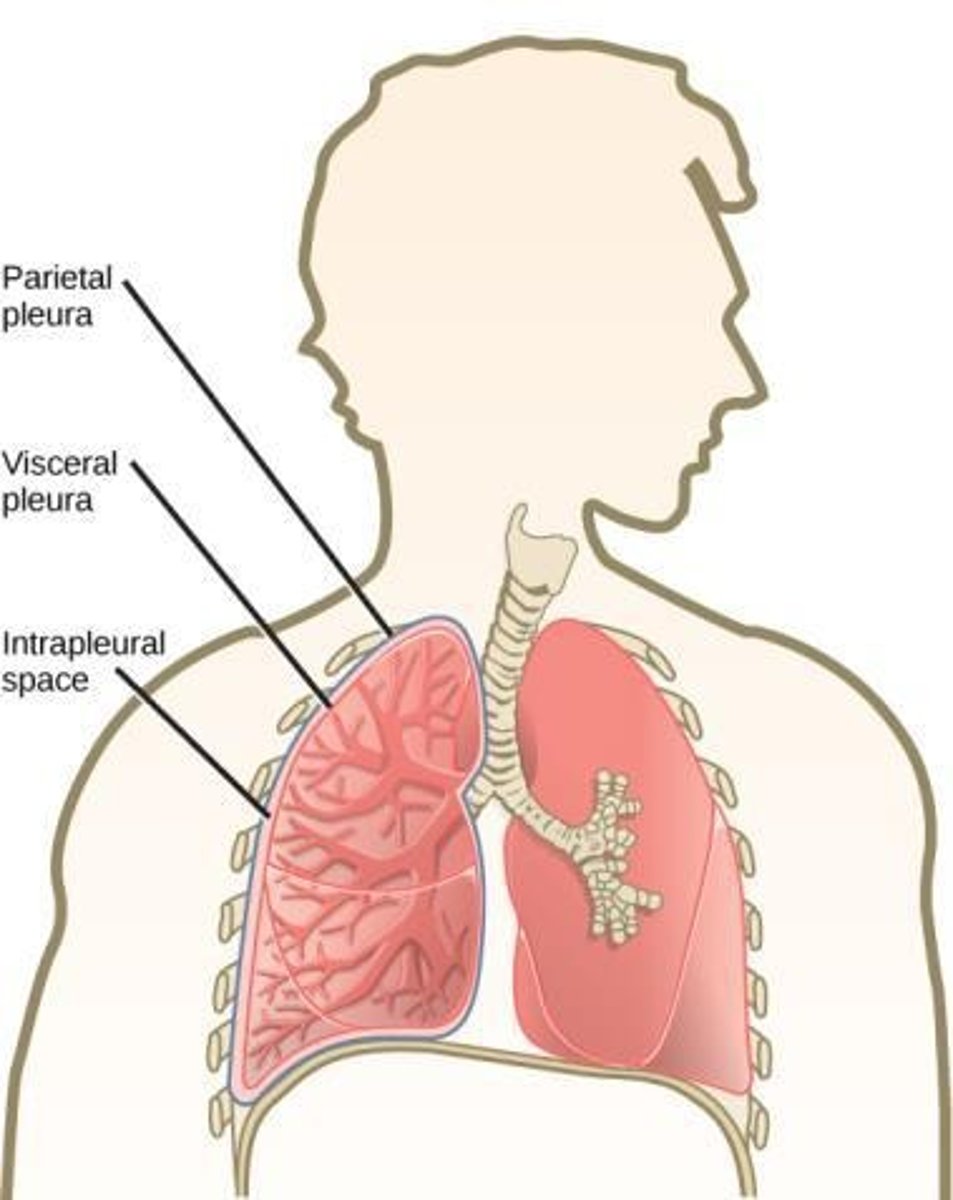
Pleura
A double folded membrane surrounding the lungs.
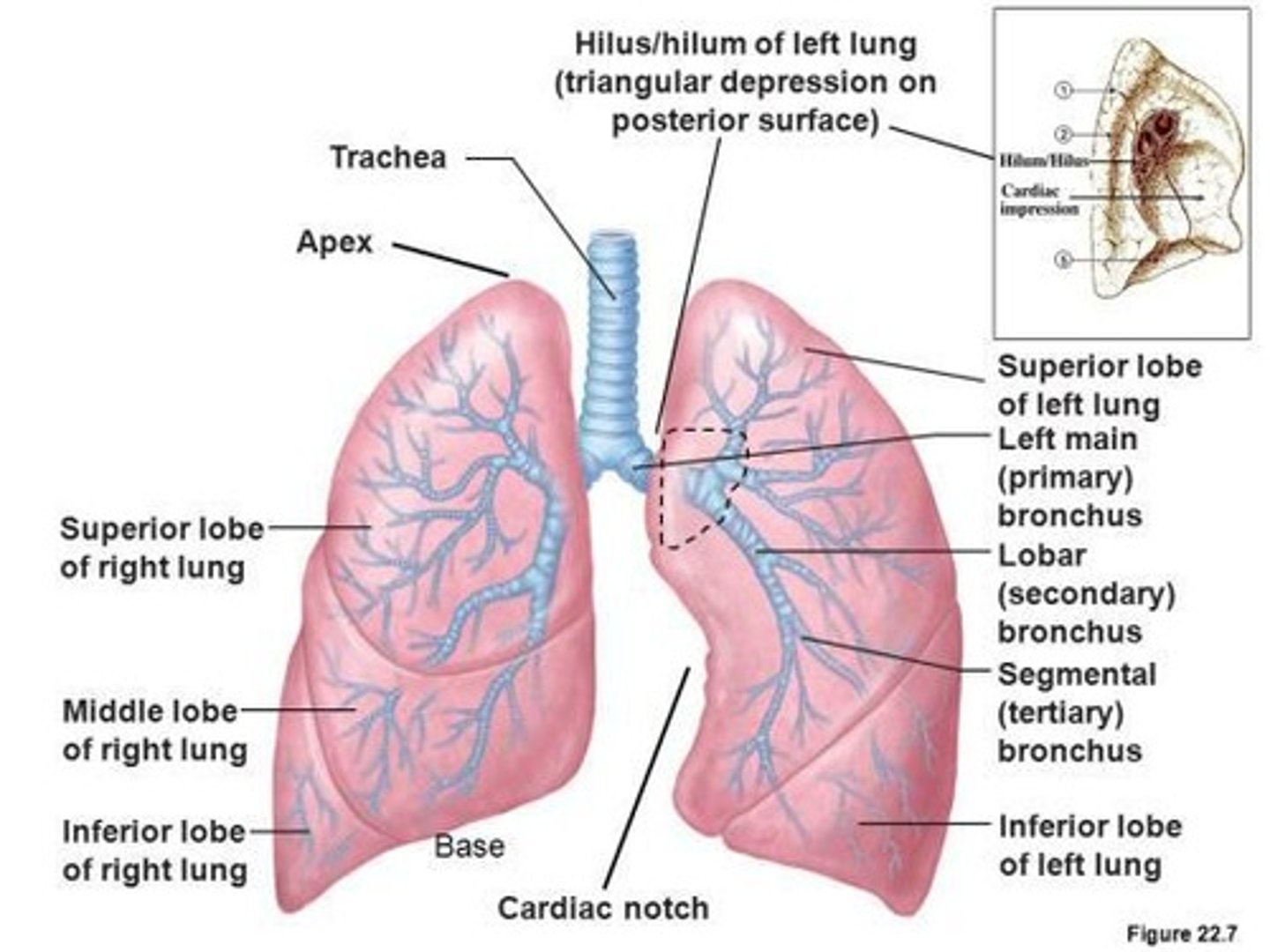
Apex of the Lung
The upper part of the lung.
Base of the Lung
The part of the lung that lies on the diaphragm.
Hilum
The depression on the medial border of the lung, the point of entrance for pulmonary arteries, veins, and bronchi.
Lobes of the Lung
The right lung has three lobes, and the left lung has two lobes.
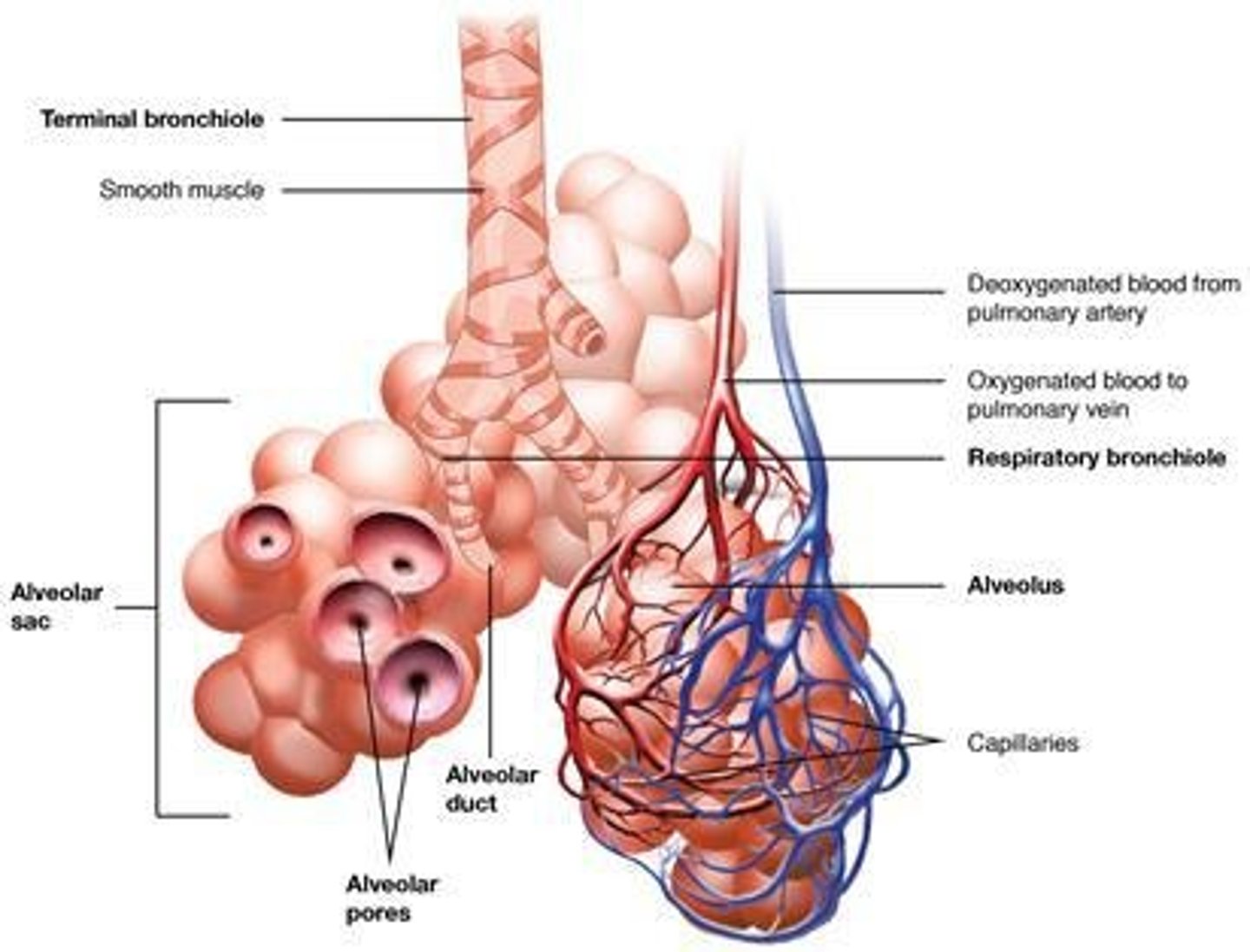
Bronchioles
Smaller branches of the bronchi that lead to air sacs or alveoli.
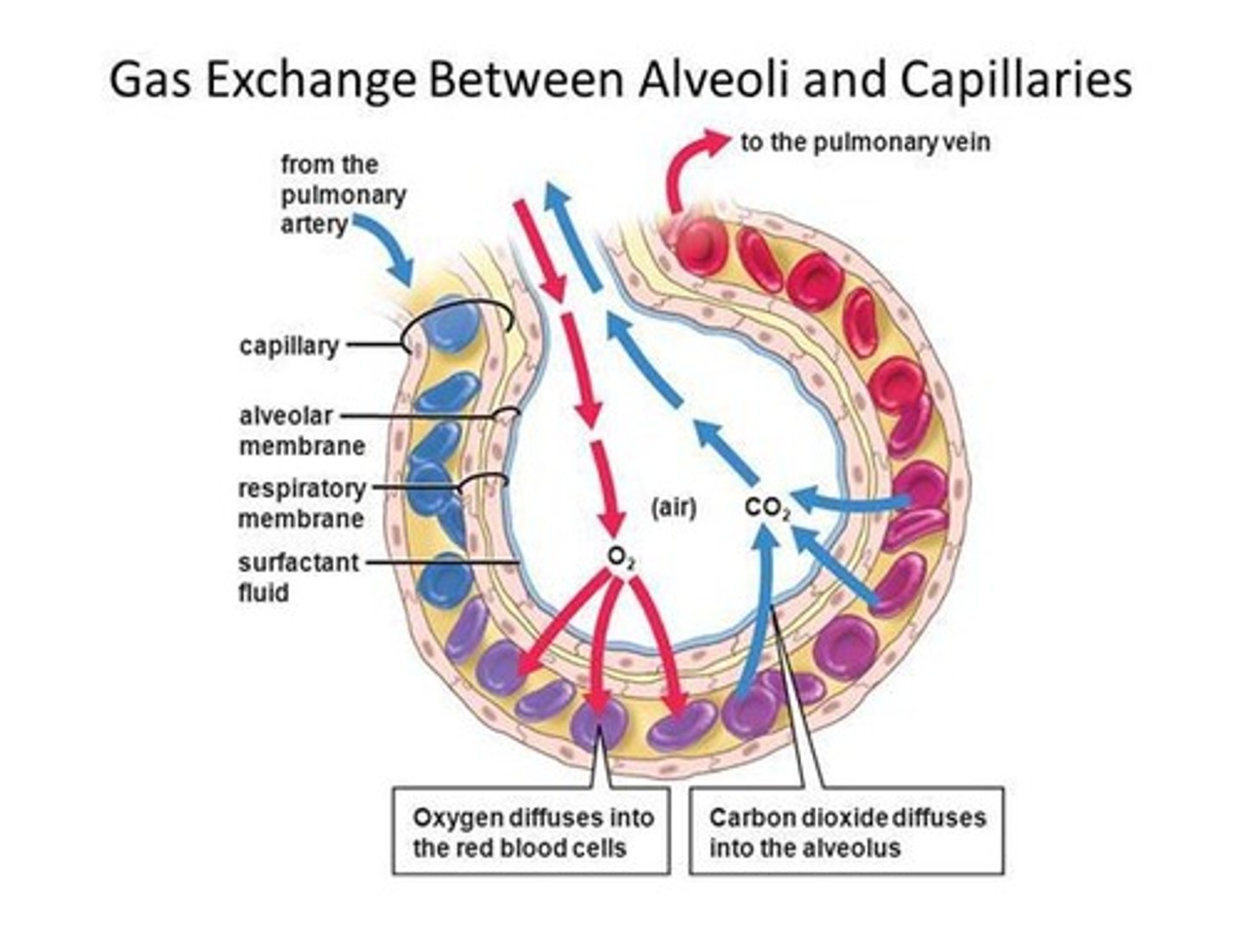
Alveoli
Air sacs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.
Alveolar Cell Type 1
Cells that make up the wall of the alveoli.
Alveolar Cell Type 2
Cells that secrete surfactant in the alveoli.
Surfactant
A protein-fat substance that reduces surface tension inside the alveolus and prevents collapse.
Visceral Pleura
The inner layer of the pleura that covers the outside of the lung.
Parietal Pleura
The outer layer of the pleura that attaches to the inside of the rib cage.
Pleural Space
The space between the visceral and parietal pleura.
Pleural Fluid
A small amount of watery, slippery fluid secreted by the pleura that prevents friction during breathing.
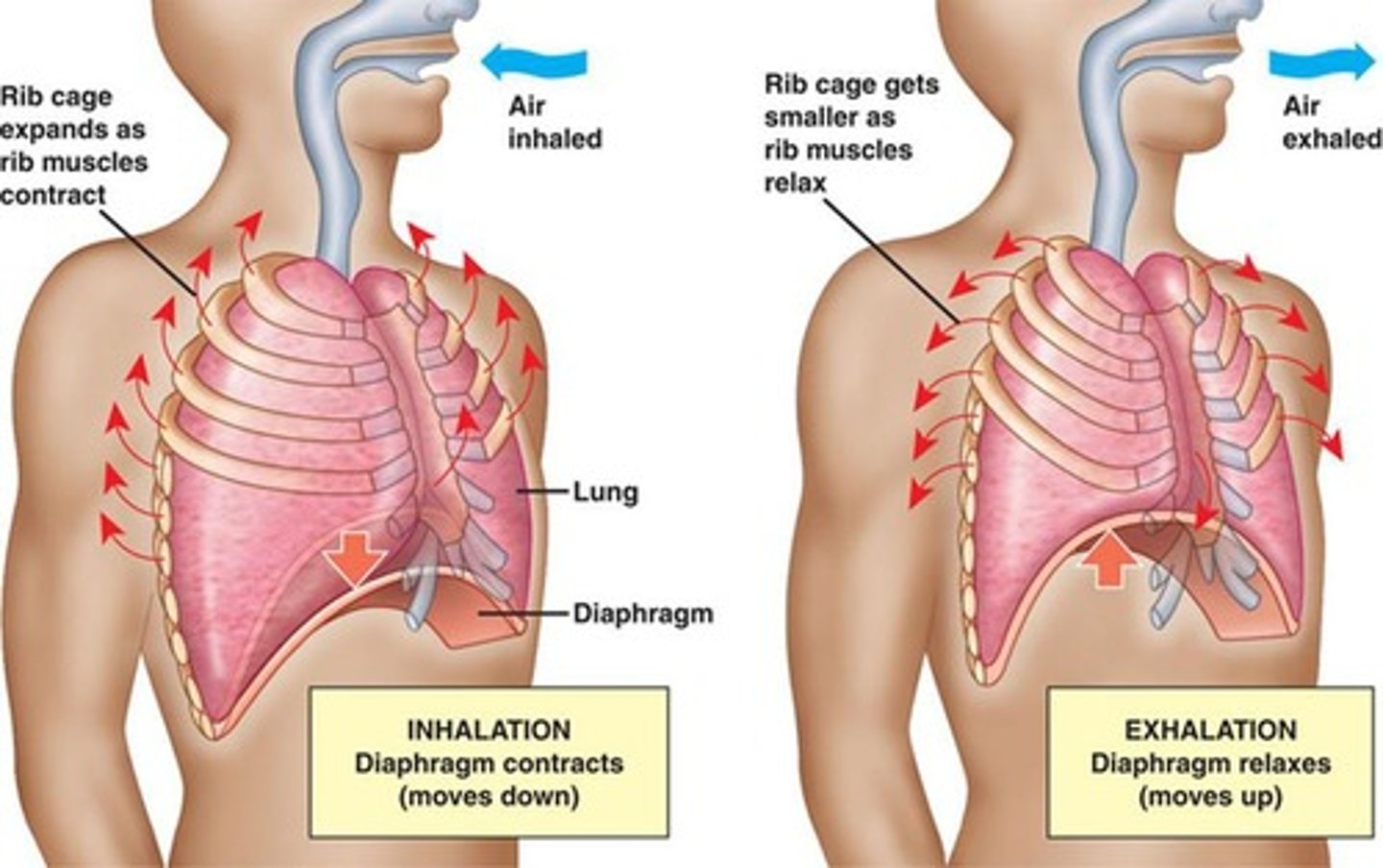
Respiration
The process of supplying the body with oxygen, consisting of inspiration and expiration.
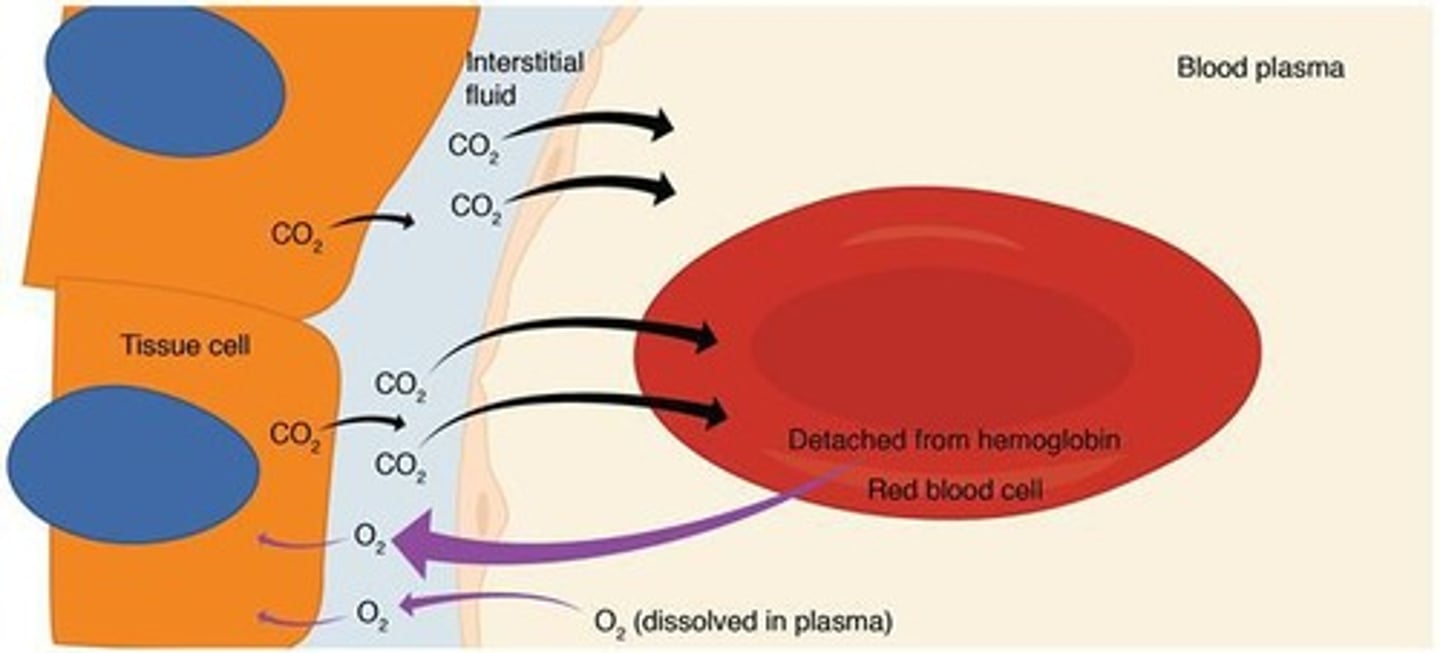
External Respiration
The exchange of air between the lungs and blood, involving inhalation, oxygen exchange, and exhalation.
Internal Respiration
The process where oxygen is carried by lung blood vessels to the heart and then to body cells for gas exchange.
Respiratory Control Center
The part of the brain that regulates the process of breathing, including depth and rate.
Chemoreceptors
Receptors that monitor levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body, located close to the aorta and carotid arteries.
Phrenic Nerve
The nerve that sends messages from the respiratory control center to the diaphragm.
Expiration
process of breathing out
Ventilation
movement of air in and out of lungs
Gas transport
after exchange of gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide are carried by the blood to the lung (CO2) and body cells (O2)
Cellular respiration
Body cells use oxygen for the metabolism and production of energy, and they result in creation of waste carbon dioxide.
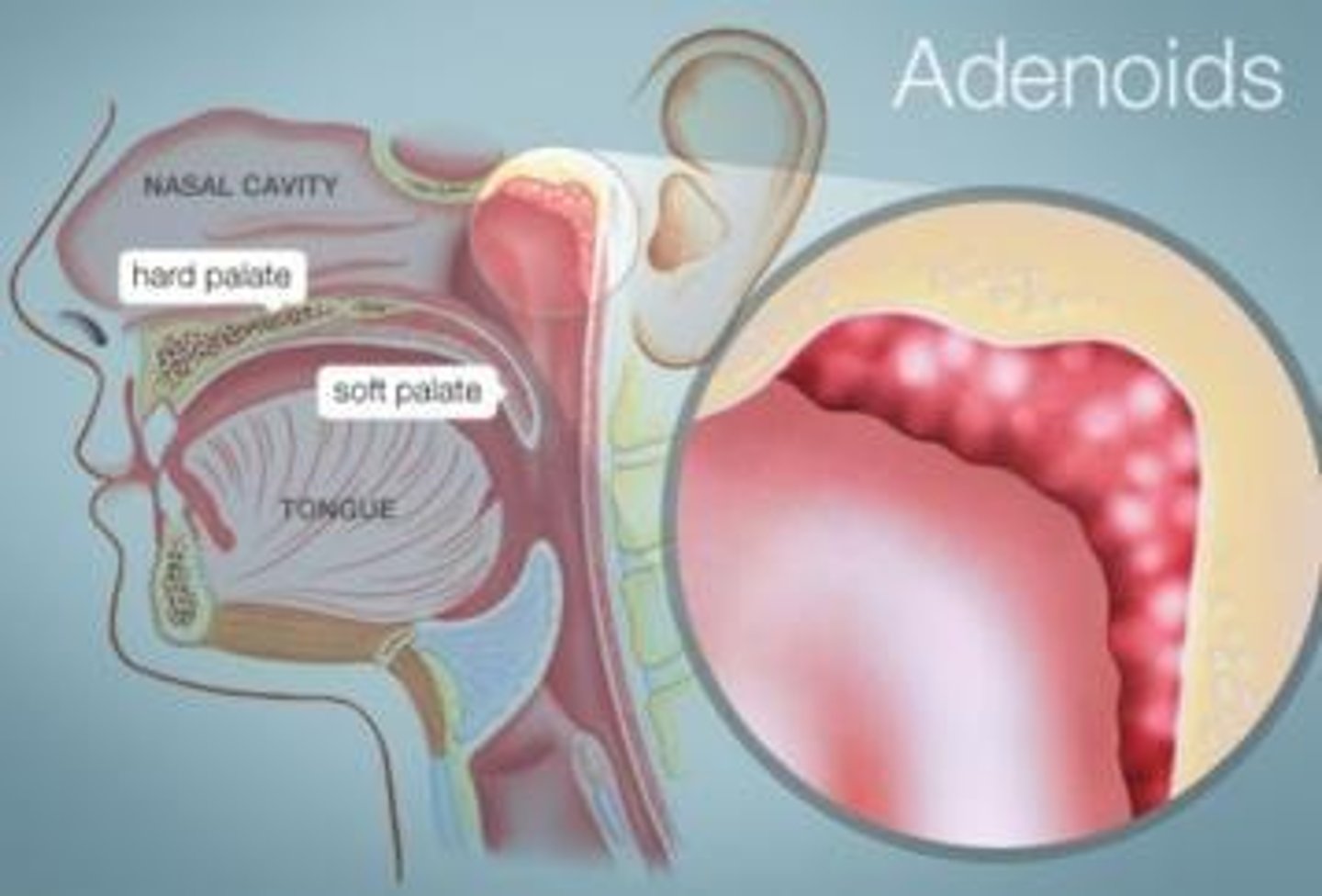
Adenoids
A mass of lymphatic tissue in the back of the nose within the nasopharynx (posterior aspect) and is larger in children and gradually becomes smaller in adults.
Alveolus (alveoli)
are air sacs in the lungs that allow exchange of gases through the tiny walls. There are about 480 millions alveoli in the lungs that creates a surface area of 100 square meter.
Bronchus (bronchi)
two branches of the trachea that enter the lung through the hilum.
Carbon dioxide
waste gas produced by body cells through the process of metabolism.
Diaphragm
is the muscular membrane separating the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, and along with the intercostal muscles help the process of breathing.
Inspiration (inhalation)
process of the breathing in.
Larynx (voice box)
part of the airways that contain the vocal cords and allows air in and out of the lungs.
Lobe
large division of the lung. The left lung has two lobes and right lung contains three lobes.
Lumen
is the inside opening of the airways that allows air in and out.
Metabolism
process of using oxygen to change the food and release energy in the cell.
Nostril (Nares)
nasal opening.
Oxygen
gas that helps to release energy from the food and passes into the bloodstream by the lungs and then travels to all body cells.
Palatine tonsil
small mass of lymphatic tissue in the oropharynx.
Paranasal sinus
four pairs of air cavities in the facial and cranial bones near the nose.
Pharynx (throat)
common passageway for food and air.
Pleural cavity
is a tiny space between the two layers of the pleura.
Pulmonary parenchyma
essential tissue of the lung that is responsible for exchange of gases and contains bronchioles and alveoli.
Trachea (windpipe)
is a cartilaginous tube that connects pharynx and larynx to the bronchi and allows air in and out
adenoid/o
Adenoid
alveol/o
alveolus, air sac
bronch/o
bronchial tube
bronchi/o
bronchus
bronchiol/o
bronchiole
capn/o
carbon dioxide
coni/o
dust
cost/o
Rib
cyan/o
blue
epiglott/o
epiglottis
hal/o
breathe
laryng/o
larynx, voice box
lob/o
lobe of the lung
mediastin/o
mediastinum
nas/o
nose
orth/o
straight, upright
ox/o
oxygen
pector/o
chest
pharyng/o
pharynx, throat
phon/o
voice
phren/o
diaphragm
pleur/o
pleura
pneum/o
air, lung
pneumon/o
lung
pulmon/o
lung
rhin/o
nose
sinus/o
sinus cavity
spir/o
breathing
steth/o
chest
tel/o
complete
thorac/o
chest
tonsill/o
tonsils