COMMERCE 1BA3 - Chapter 9
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Leadership
The influence that particular individuals exert on the goal achievement of others in an organizational context
Strategic leadership
Leadership that involves the ability to anticipate, envision, maintain flexibility, think strategically, and work with others to initiate changes that will create a viable future for the organization
Formal leadership
Individuals formally assigned to a leadership role
Ex: manager, executive, supervisor
Expected to influence others, and given specific authority to direct employees
Informal leadership
Individuals emerge to occupy informal leadership roles
NO formal authority
Rely on being perceived as highly skilled to exert influence
Shared leadership
Emergent phenomenon whereby leadership roles and influence are distributed among team members
Trait theory of leadership
The belief that leadership depends on the personal qualities or traits of the leader
Assumption that fuels the trait theory of leadership
The assumption that those who become leaders and do a good hob of it possess a special set of traits that distinguish them from the masses of followers
Which of the big five dimensions of personality are related to leadership
All five!
Extraversion and conscientiousness are the most consistent predictors of leadership effectiveness
Limitations of the trait theory of leadership
* We don't know if the traits make the leader or the leadership makes the traits
* Doesn't say what leaders actually do to be successful
* Doesn't take into account the situation in which leadership occurs
Leadership categorization theory
People are more likely to view somebody as a leader and to evaluate them as a more effective leader when they possess prototypical characteristics of leadership
Consideration (leader behaviour)
The extent to which a leader is approachable and shows personal concern and respect for employees
Considerate leaders are friendly, supportive, and protective of group welfare
Initiating structure (leader behaviour)
The degree to which a leader concentrates on group goal attainment
Leaders with initiative are focused on accomplishing goals by organizing roles, planning, and dividing labour
Which of the two leader behaviour characteristics are more related to job performance and group performance?
Initiating structure
Rewards
Compliments, tangible benefits, and deserved special treatment
Effect of leader's reward behaviours on employee performance
When rewards are made contingent on performance, employees should perform at a high level and experience job satisfaction
Effect of leader's punishment behaviours on employee performance
When punishment is perceived as random, employees react negatively with great dissatisfaction
Punishment
Reprimands of unfavourable task assignments and the active withholding of raises, promotions, and other rewards
Situational theories of leadership
Argues that the effectiveness of a leadership style is contingent on the setting
Setting: characteristics of employees, nature of the task, characteristics of the organization
Two situational theories of leadership
Fielder's contingency theory
House's path-goal theory
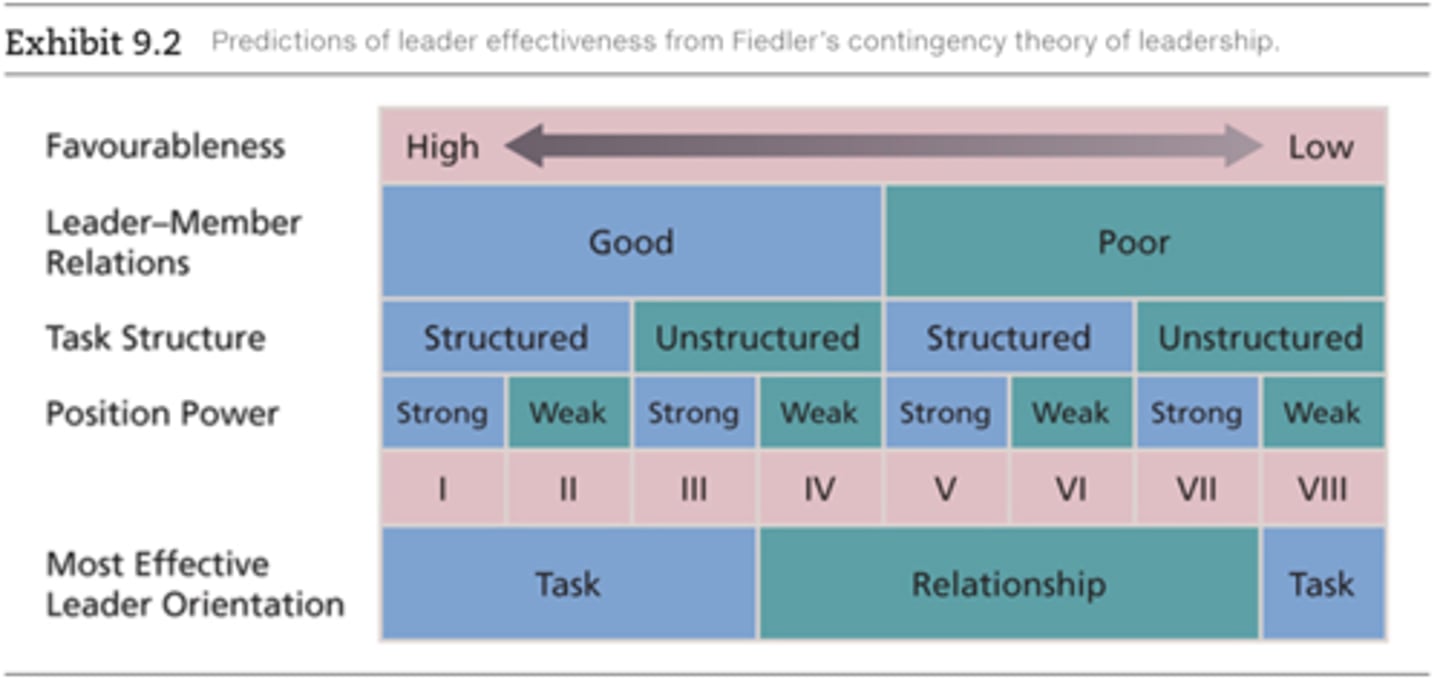
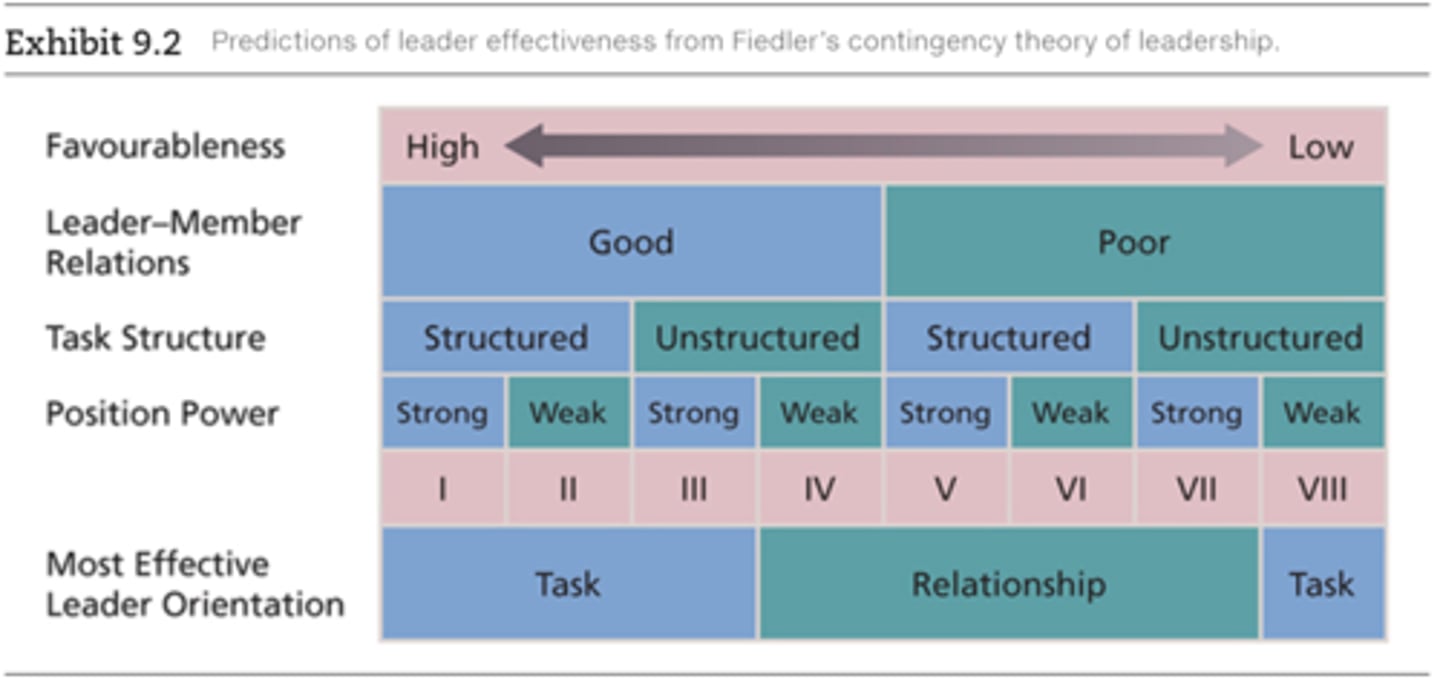
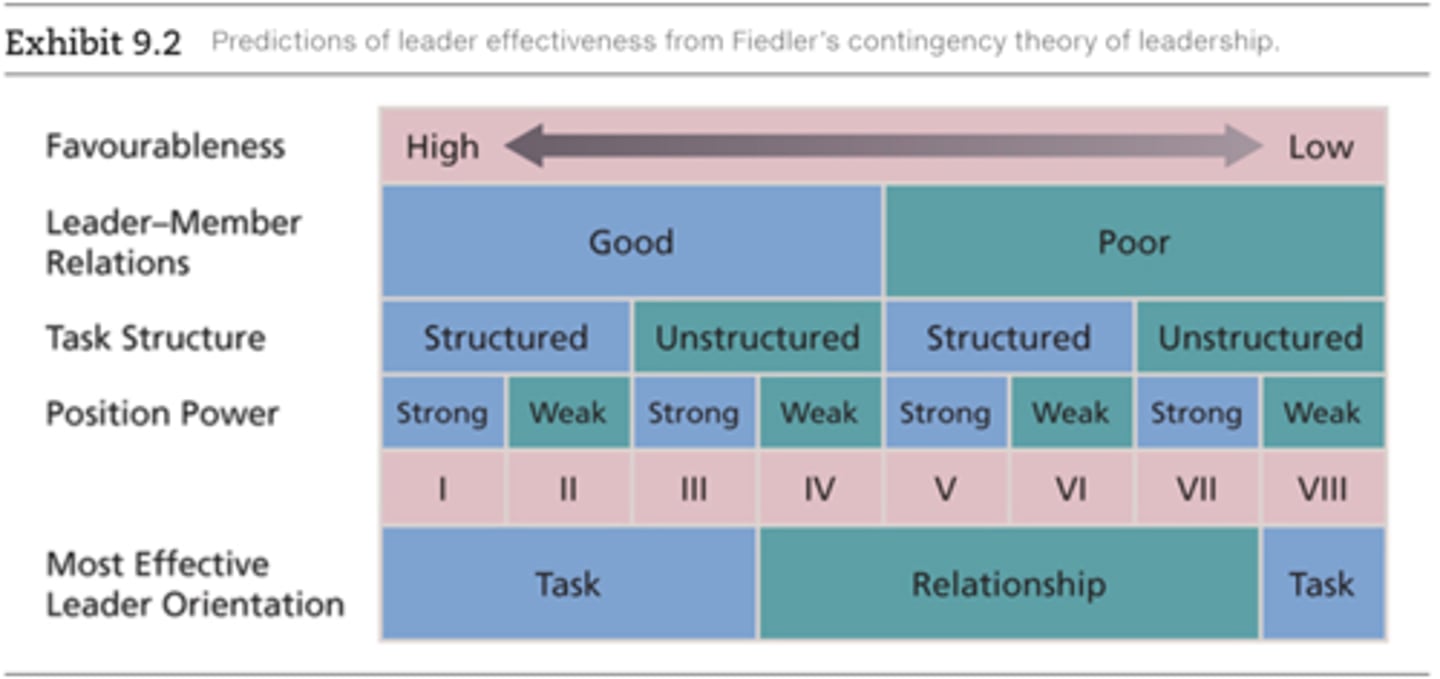
Fiedler's contingency theory
The association between leadership orientation and group effectiveness is contingent on the extent to which the situation is favourable for exerting influence
Least Preferred Coworker (LPC)
A measure that assesses leaders' task or relationship orientation by having them rate their most difficult fellow worker
The LPC score is an attitude of the leader toward work relationships
What do LPC ratings tell us
High on LPC: the leader is relationship oriented
Low on LPC: the leader is task oriented
Situational favourableness (fiedler)
Specifies when a particular LPC orientation should contribute most to group effectiveness
Factors that affect situational favourableness (most important first)
* leader-member relations
* task structure
* position power
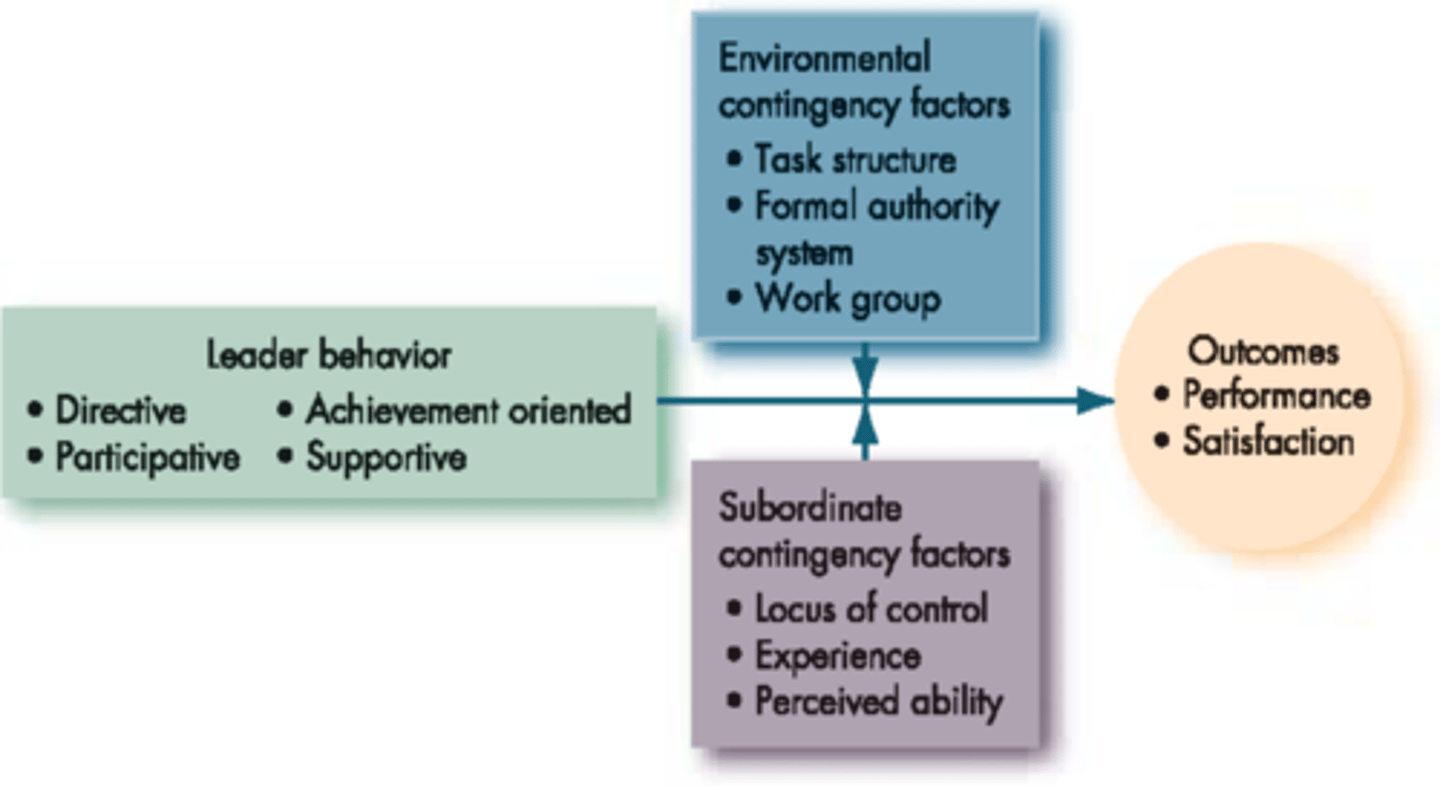
House's path-goal theory
Concerned with the situations under which various leader behaviours (directive, supportive, participative, achievement oriented) are most effective.

Situational factors (house)
Employee characteristics
* level of authoritarianism
* locus of control
* level of ability
Environmental factors
* nature of the task
* formal authority
Look at slideshow for more information
Leader effectiveness equation (house)
Leader effectiveness = leader traits + leader behaviours + group member characteristics + situation
Participative leadership
A leadership style in which the leader consults employees for their suggestions and input before making work-related decisions
Diagram on class 9 slide 16
Advantages of participative leadership
* motivation
* quality
* acceptance
Disadvantages of participative leadership
* time and energy
* loss of power
* lack of receptivity or knowledge
Conditions for participation
* employees feel favourably toward it
* employees are intelligent and knowledgeable about the issue at hand
* when the task is complex enough to make participation useful
Vroom & Jago's situational model of participation
Suggests various degrees of participation that a leader can exhibit
A - autocratic
C - consultative
G - group
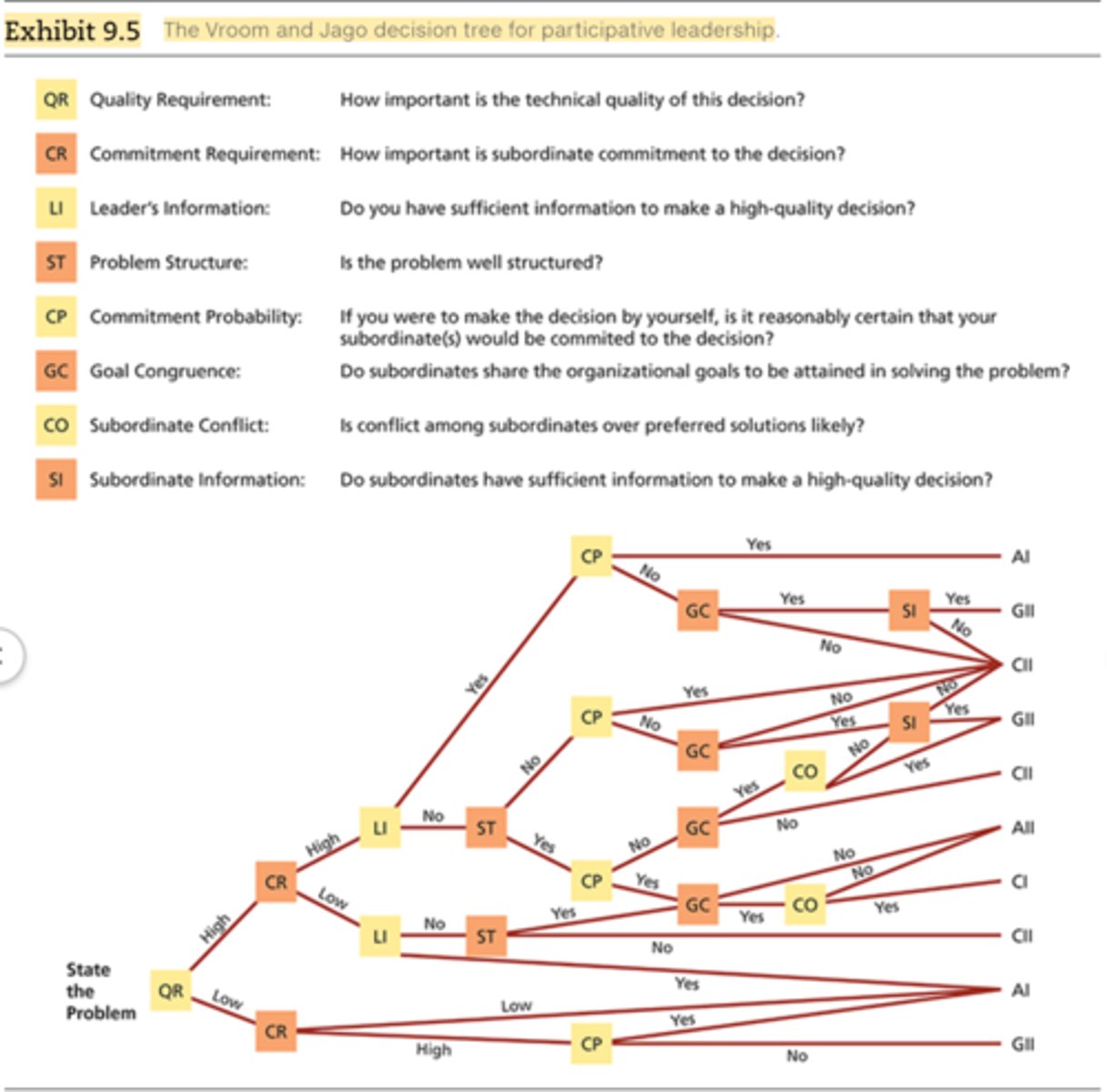
AI (Vroom & Jago)
You solve the problem or make the decision yourself
AII (Vroom & Jago)
You obtain the necessary information from your employees, then decide the solution to the problem yourself
CI (Vroom & Jago)
You share the problem with the relevant employees individually, getting their ideas and suggestions, then you make the decision
CII (Vroom & Jago)
You share the problem with your employees as a group, obtaining their collective ideas and suggestions, then you make the decision
GII (Vroom & Jago)
You share the problem with your employees as a group and together you generate and evaluate alternatives and attempt to reach consensus on a solution
Leader-member exchange (LMX) theory
A theory of leadership that focuses on the relationship that develops between a leader and an employee
Based on social exchange relationship-based and the norm of reciprocity
LMX differentiation
The variability in the quality of LMX relationships between members of the same workgroup
Relationship between LMX and performance
Higher LMX means higher commitment, better performance, higher self-efficacy, better attitudes, and better creativity
Relationship between LMX differentiation and group performance
Higher differentiation leads to worsened group harmony and poorer group performance
Transactional leadership
Leadership that is based on a straightforward exchange relationship between the leader and the followers
Involves contingent reward behaviour (leader reward behaviour) and management by exception
Management by exception
Leadership that involves the leader taking corrective action on the basis of the results of leader-follower transactions
Transformational leadership
Leadership that provides followers with a new vision that instills true commitment
Transformational leadership is a consistent predictor of effective leadership
Behaviours that transformational leaders use to encourage effort and dedication
* Intellectual stimulation
* individualized consideration
* inspirational motivation
* charisma (most important)
Charisma
The ability to command strong loyalty and devotion from followers and thus have the potential for strong influence among them
Implicit leadership theory
States that individuals hold a set of beliefs about the kinds of attributes, personality characteristics, skills, and behaviours that contribute to or impede outstanding leadership
GLOBE project cultural dimensions
Performance orientation, assertiveness, future orientation, humane orientation, institutional collectivism, in-group collectivism, gender egalitarianism, power distance, uncertainty avoidance
Performance orientation
The degree to which a collective encourages and rewards its members for improvement and excellence in their performance
Assertiveness
The degree to which individuals are assertive, confrontational, and aggressive in their interactions with others
Future orientation
The extent to which individuals prepare for the future, for example, by delaying gratification, planning ahead, and investing in the future
Humane orientation
The degree to which a collective encourages and rewards individuals for their fairness, altruism, generosity, caring, and kindness to others
Institutional collectivism
The degree to which the institutional practices of organizations and society encourage and reward collective distribution of resources and collective action
In-group collectivism
The degree to which individuals express pride, loyalty, and cohesiveness in their families or organizations
Gender egalitarianism
The degree to which a collective minimizes gender inequality
Power distance
The degree to which members of a collective expect power to be distributed evenly
Uncertainty avoidance
The extent to which a society, organization, or group relies on social norms, rules, and procedures to lessen the unpredictability of future events
Six global leadership dimensions
* charismatic/value-based
* team-oriented
* participative
* humane-oriented
* autonomous
* self-protective
Universal facilitators of leadership
* trustworthiness, justice, and honesty
* foresight
* encouraging, motivating, confidence, positivity
* communication and team builder
Universal impediments to leadership
* loner and asocial
* irritable and uncooperative
* imposing views on others
Culturally contingent endorsement of leader attributes
* individualism
* being conscious of status
* taking risks
Global leadership
A set of leadership capabilities required to function effectively in different cultures and the ability to cross language, social, economic, and political borders
Glass ceiling
Invisible barrier that prevents women from advancing to senior leadership positions in organizations
Role congruity theory
Prejudice against female leaders is the result of an incongruity between the perceived characteristics of women and the perceived requirements of leadership roles
Communion
the aspect of belonging to a larger group and the well-being of others
* associated with femininity
Agency
Individual, personal self-improvement, and goal attainment
Glass cliff
When women and minorities are promoted to top management only when companies are failing (set up to fail without support)
How we can reduce gender inequality in leadership
* mentoring programs
* increasing awareness of drivers of prejudice
* avoiding tokenism
* ensure women are given appropriately demanding tasks
* encourage male participation in family-friendly benefits
List the new and emerging theories of leadership (positive leadership)
* empowering leadership
* ethical leadership
* authentic leadership
* servant leadership
Positive leadership
A group of theories that focus on leader behaviours and interpersonal dynamics that increase followers' confidence and result in positive outcomes
Empowering leadership
Implementing conditions that enable power to be shared with employees
* participation and autonomy in decision making
* employees experience feelings of meaning, competence, and impact
Ethical leadership
The demonstration of normatively appropriate conduct through personal actions and interpersonal relationships
* relationships of trust
* increases group ethical voice and psychological well-being
Authentic leadership
Leadership that involves being true to oneself
* act upon true values, beliefs, and strengths
* creates trust and well-being
* promotes self awareness, transparency, internalized moral perspective
Servant leadership
A form of leadership that involves going beyond one's own self-interests and having a genuine concern to serve others and a motivation to lead
* focuses on the needs of followers and their growth and development
* creates trust in management, positive perceptions of organizational justice, work attitudes, high OCBs