Citterio Exam 3 (Mostly Review Session)
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to signal transduction and hormonal action, focusing on definitions, processes, and mechanisms involved.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Signal transduction is the transmission of ______________ from a cell’s ________ to its _______.
molecular signals, exterior, interior
Types of signals involved in signal transduction include:
Antigens, hormones, neurotransmitters, light, touch, and pheromones
These transduction signals cause changes in the cell:
__________ and __________
Gene __________ and _______
Change in an ____________, etc.
Differentiation, cell division, transcription, translation, enzymatic activity
Biological importance of Signal Transduction:
All cells have ______ and __________ signal-transducing mechanisms, which have been ________ during evolution.
____________ of the production and ______ of hormones and other regulatory signaling molecules is a major cause of ________.
specific, highly sensitive, conserved, dysregulation, release, disease
Receptors are membrane-bound or soluble proteins that exert a physiological effect after binding their ___________.
natural ligand
Binding interactions are:
________ and ________
________
______ and ______ states
_______
Target cell response depends on:
Ligand ________ at the receptor
__________ specific factors
specific, sensitive, reversible, active, inactive, saturable, concentration, target cell
Specificity in signal transduction refers to the _________ of a signaling ______ to its _____________ receptor.
binding, ligand, complementary
Explain the general sequence of events involved in signal transduction.
Reception, Transduction, Response, and End
Reception: A _______ interacts with a _________
Transduction: The _________ receptor interacts with _______ machinery
Response: A ____ signal is produced, or the activity of a _______ is altered, modifying the activity/behavior of the _________.
End: __________ event ends
ligand, receptor, activated, cellular, 2nd, protein, target cell, transduction
In amplification, when enzymes activate enzymes, the number of affected molecules ________ in an enzyme ________.
increases geometrically, cascade
Describe general features of signal transduction systems.
Specificity, amplification, desensitization, and integration
Specificity: _____________ first binding site on its ___________ receptor; other ligands ______ fit
Amplification: when enzymes _________ enzymes, the number of affected molecules ______ geometrically in an enzyme _________
Desensitization/Adaptation: receptor activation triggers a _________ circuit that ________ the receptor or ________ it from the cell _______
Integration: when 2 signals have ________ effects on a metabolic characteristic, such as the ________ of a ___ messenger X, or the _____________ Vmax, the regulatory outcome results from the integrated input from ____ receptors
signaling ligand, complementary, do not, activate, increases, cascade, feedback, shuts off, removes, surface, opposite, concentration, 2nd, membrane potential, both
Signal transduction often involves a _____________ feedback circuit that shuts off the receptor or removes it from the cell surface.
desensitization/adaptation
Explain the classification of signal-transduction systems according to the receptor type and signaling mechanism.
Nuclear Receptor: _______ binding allows the receptor to regulate the expression of specific _____ (Group _ hormones.)
G protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs): External ligand binding to a receptor activates an intracellular GTP-binding protein, which regulates an enzyme that generates an _________________ (Group _ hormones)
Receptor enzyme (__): ligand binding activates activity by _________________→ ______ activates ___________ factor, altering gene expression (Group _ hormones, ______, ______ factors, _________
Gated ion channel: channel opens/closes in response to the __________ of the signal ______ or the ________________ (not activated by __________)
hormone, genes, I, intracellular 2nd messenger, II, TK, autophosphorylation, kinase, transcription, II, cytokines, growth, interleukins, concentration, ligand, membrane potential, hormones
Group I hormones bind to ________ receptors and affect gene expression.
Receptors can be located in the ______ (e.g. gluco-corticoids) or in the _______ (e.g. thyroid hormone)
Cytosolic hormone-receptor complexes are translocated into the _______.
Once in the nucleus, the hormone-receptor complex binds to a ______________________ associated with a specific ___ sequence and acts as a _____________ factor.
The HRE may have up to __ proteins acting as coregulators and coactivators of gene transcription
intracellular, cytosol, nucleus, nucleus, hormone response element (HRE), DNA, transcription, 30
Three essential components define signal transduction through GPCRs:
a ___________________ with seven transmembrane helical segments,
a _______ that cycles between active (___-bound) and inactive (___-bound) forms, serving as the coupler, or transducer of the signal. The subunits of the heterotrimeric G-proteins are called the α, β, and γ subunits.
an ___________ (or ion channel) in the plasma membrane that is regulated by the activated G protein and produces the ____________.
plasma membrane receptor, G protein, GTP, GDP, effector enzyme, 2nd messenger
Cyclic GMP is generated by the enzyme ________, which can exist in soluble and membrane-bound forms.
guanylyl cyclase
Many Group _ hormones, such as epinephrine, bind to cell surface receptors that generate intracellular second messengers like ____ and _____.
II, cAMP, cGMP
The process of signal transduction through _______________ involves three essential components: a ______________ receptor, a ________, and an _______ enzyme.
G protein-coupled receptors, plasma membrane, G protein, effector
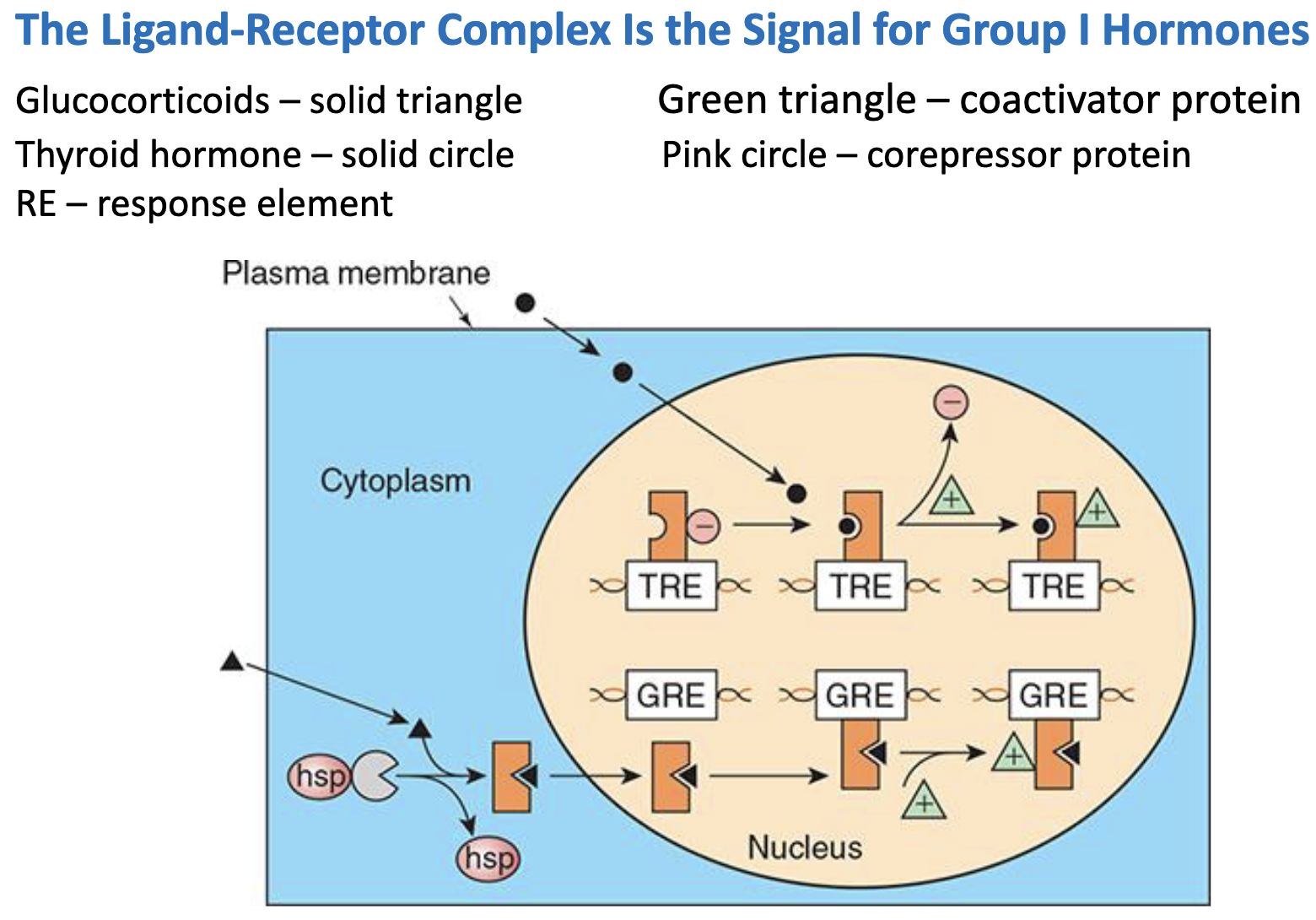
_________ hormones binding to Receptors in ___ → Release of __________ → ______________
Receptors bound to ___
hydrophobic, TRE, compressors, DNA transcription, TRE
Upon ligand binding, receptor tyrosine kinases ________, leading to the activation of __________- signaling pathways.
autophosphorylate, intracellular
The JAK/STAT pathway involves Janus kinase (JAK) and signal transducers (STATs) that translocate into the _______ to activate ___________.
nucleus, transcription
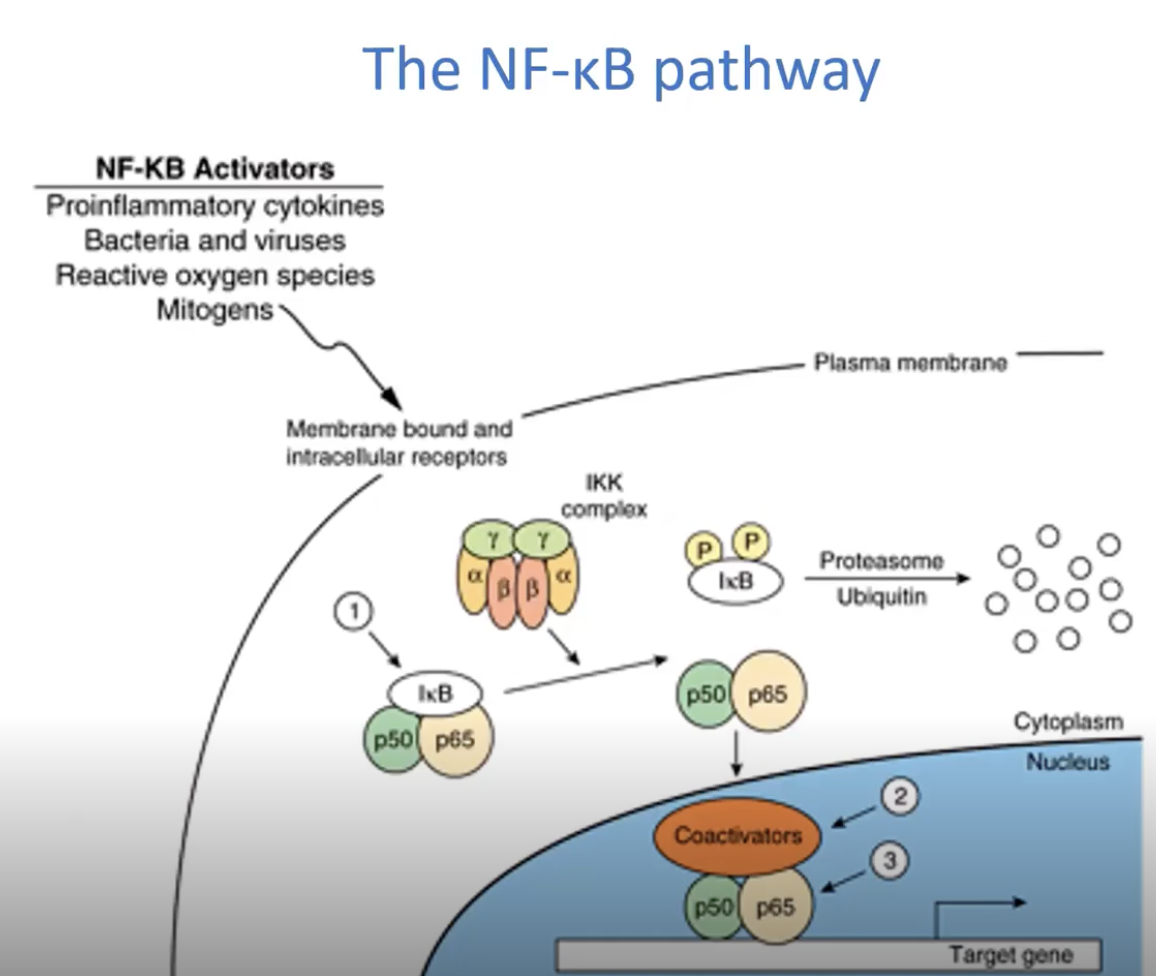
NF-κB is sequestered in the cytosol by an _________ protein known as ___.
inhibitory, IkB
_________ regulates the NF-κB pathway by inhibiting its activation and subsequent __________________.
Cortisol, gene transcription
Hydrolysis of cAMP to 5'-AMP is catalyzed by _____________, which can terminate the signal transduction response.
phosphodiesterases
Drug interventions affecting signaling can include receptor modulation, enzyme inhibition, and __________________.
second messenger regulation
Many Group _ hormones activate GPCRs
There are many ___-binding proteins
__, __, __, G12, Go
______ number of subtypes
II, GTP, Gs, Gi, Gq, large
Many different effector systems
____________ (9 isoforms)
Second messenger cAMP
__________________
Second messenger diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate
_______ and ____________
Second messenger calcium/potassium
______________
Second messenger cGMP
Adenyl cyclase, Phospholipase C, Calcium, potassium channels, Guanylate cyclase
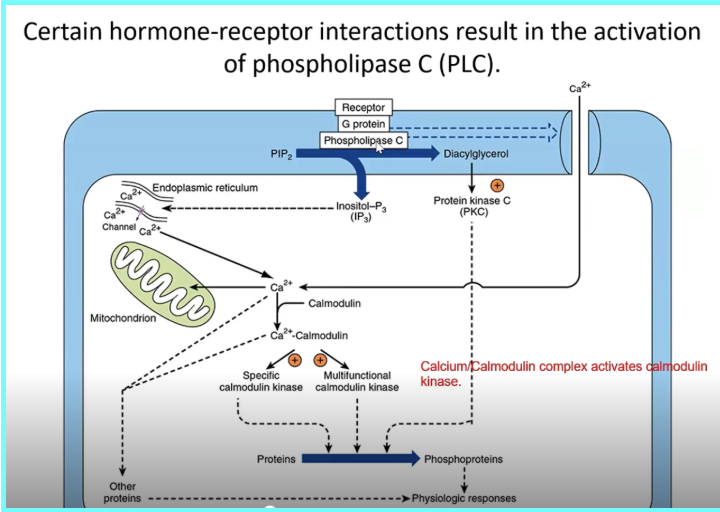
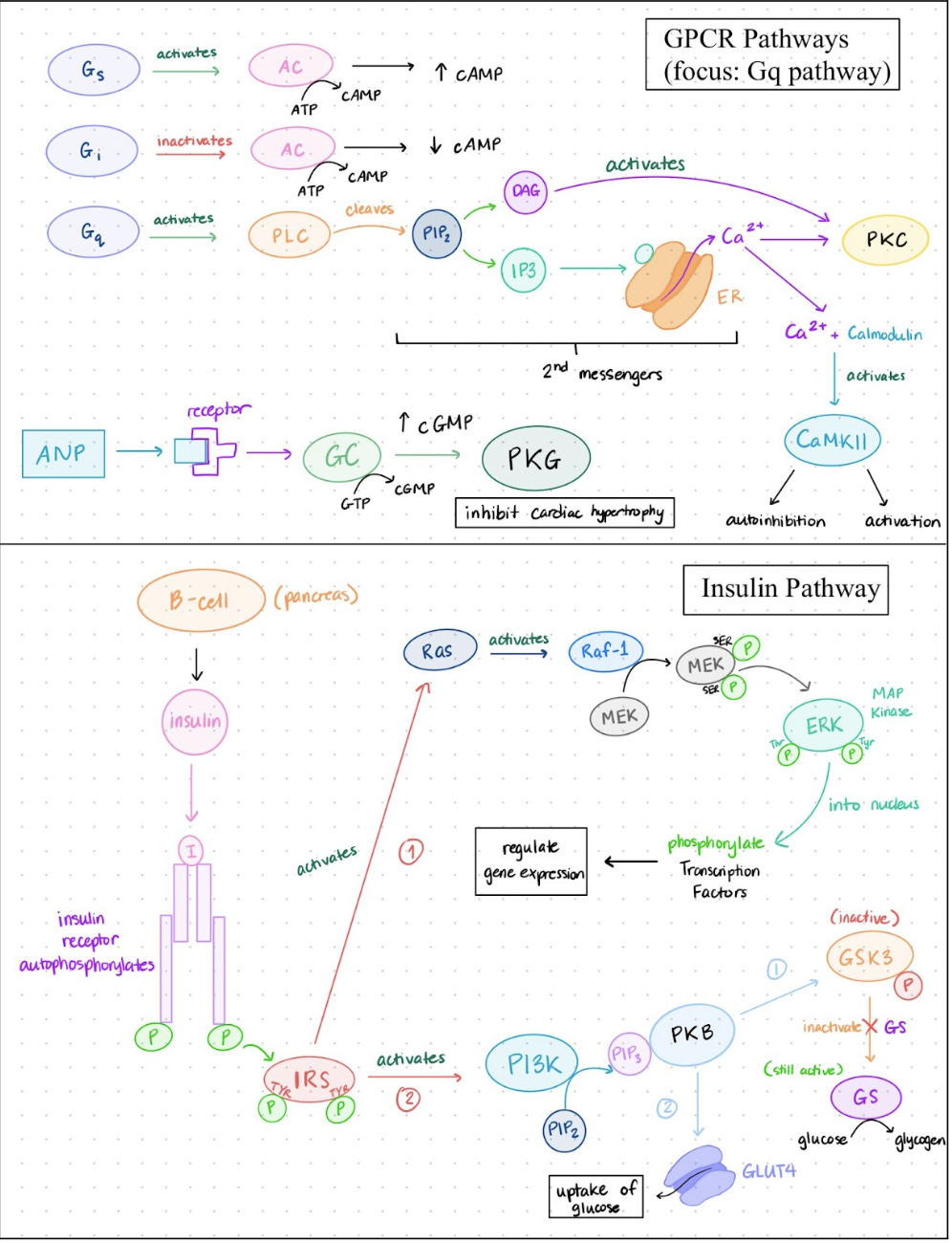
A hormone (ligand) binds to a _____ on the cell membrane. This activates a _______, which in turn activates ______________ (PLC)
___ acts on a membrane phospholipid called phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (____). ____ is cleaved into two important second messengers: Inositol trisphosphate (___) and Diacylglycerol (___)
___ releases Ca²⁺ from the __
Ca²⁺ binds to _________
DAG activates ____________ (PKC)
The combination of ___ activation and ______________ signaling modifies the activity of numerous proteins
GPCR, G protein, phospholipase C, PLC, PIP2, PIP2, IP3, DAG, IP3, ER, calmodulin, Protein kinase C, PKC, Calcium/calmodulin,
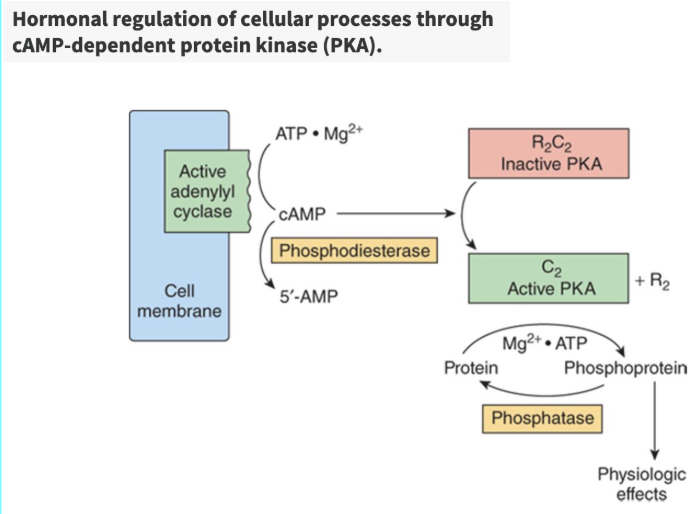
AC → ____ (___ messenger) from ATP → bind to subunits of ___ → releases the _______ part of ___ and makes it ______
cAMP, 2nd, PKA, catalytic, PKA, active
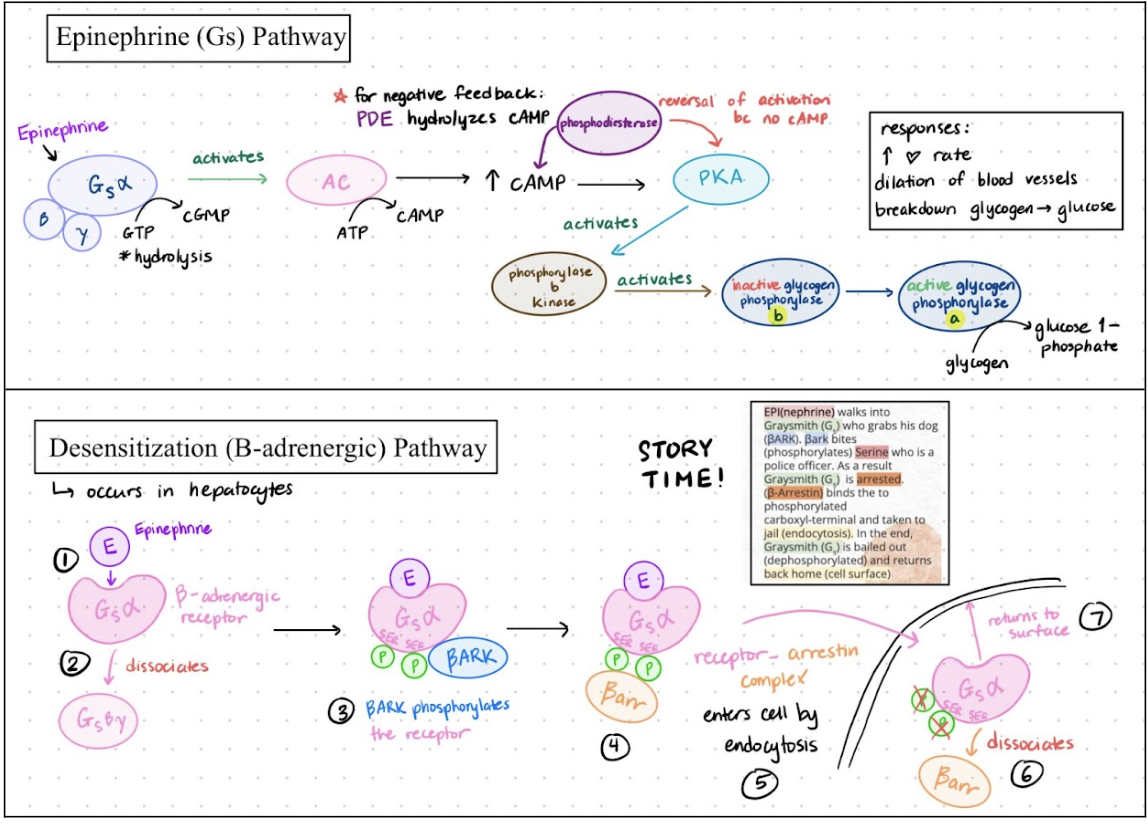
Gs: Epinephrine
Epinephrine binds to _________ receptor → allosteric change in hormone-receptor complex causes ___ bound to ______ to be replaced by ___ → activates _______, then separates to activate __ → AC catalyzes ____→ cAMP activates → ___ → _____________ of cellular proteins by ___ causes cellular response to epinephrine → cAMP is _______, reversing ___ activation
Beta-Adrenergic, GDP, Gs-alpha, GTP, Gs-alpha, AC, cAMP, PKA, phosphorylation, PKA, degraded, PKA
____________ is the process by which a small signal (1 molecule of epinephrine) is greatly increased in magnitude in a signaling cascade (lots of blood glucose molecules).
Amplification
Several Mechanisms Cause Termination of the β-Adrenergic Response
__________ of epinephrine in the blood drops.
________ of ___ bound to the ______ subunit, catalyzed by the intrinsic GTPase activity of the G protein.
_________ of ____ to 5′-___ (not active as a second messenger)
_________________________ reverse effects of PKA
Concentration, hydrolysis, GTP, G-alpha, hydrolyses, cAMP, AMP, Phosphoprotein phosphatases
_____________ is the reduction in responsiveness of the receptor to its ligand after prolonged exposure.
Epinephrine bound to ___________ receptors → triggers dissociation of ___________ from Gs-alpha → Gs-beta-gamma recruits ________ to the membrane → _________ Ser residues at the ____________ of the receptor → _________ (Beta-arr) binds to the phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal domain of the receptor → Receptor arrestin complex enters the cell by ________ → ______ dissociates → receptor is ____________ → returns to cell surface
Desensitization, beta-adrenergic, Gs-beta-gamma, Beta-ARK, phosphorylates, carboxyl terminus, Beta-arrestin, endocytosis, arrestin, dephosphorylated
STUDY
STUDY
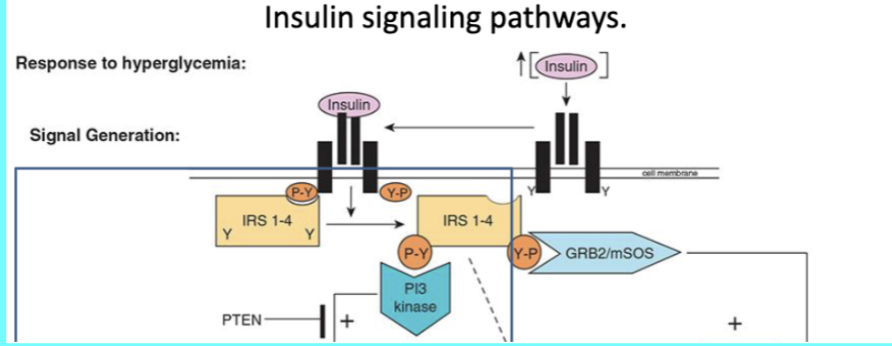
Features of Insulin Action:
Insulin is released from ____ cells in pancreas when blood glucose levels are ____.
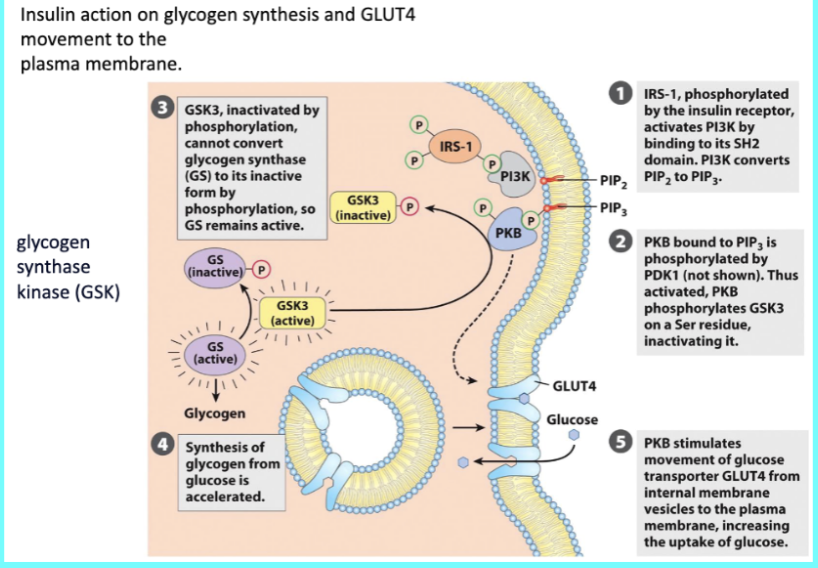
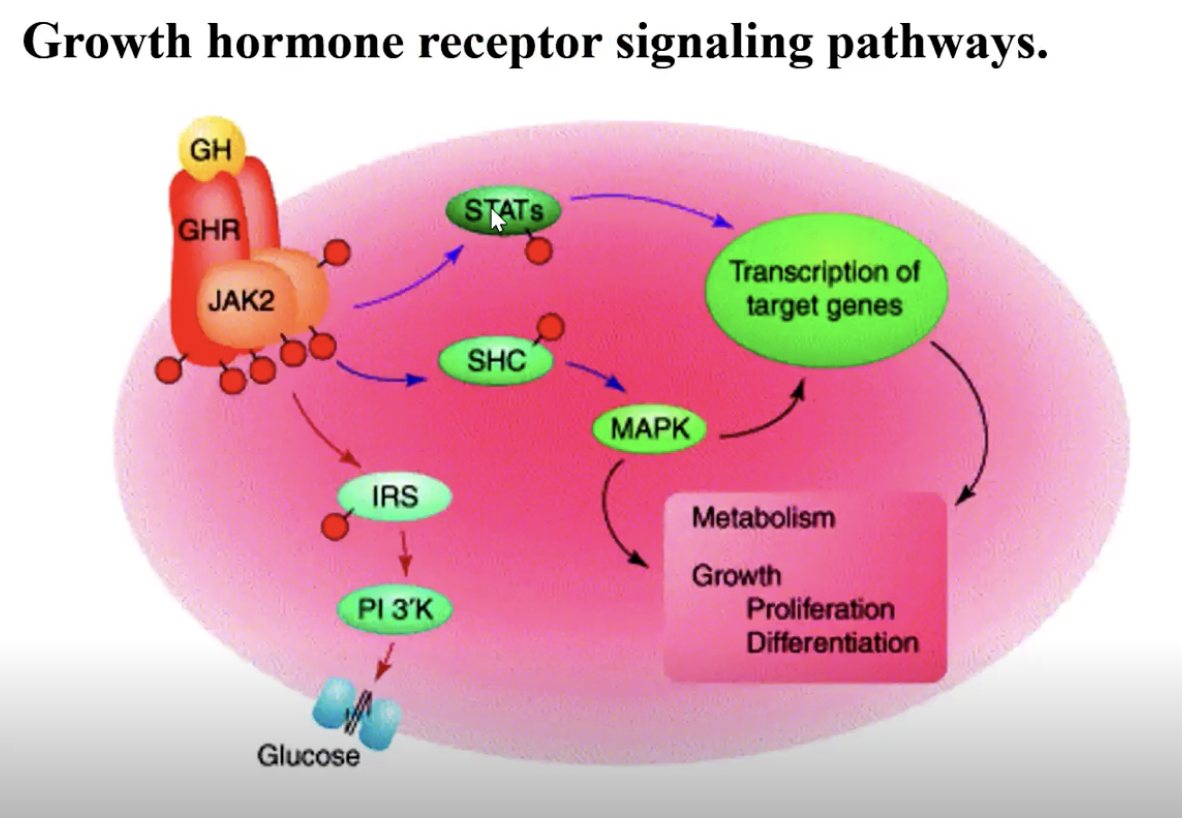
When insulin binds to receptors, an intrinsic ______________________. This recruits __________________ (IRS) which are also phosphorylated and activated.
___ activate a variety of proteins initiating kinase cascades
Protein kinase _ → increases glycogen synthesis and glucose uptake
___ and ___ kinase → cell growth and gene transcription
Beta, high, tyrosine kinase autophosphorylates, insulin receptor substrate proteins, IRS, B, MEK, MAP
STUDY
Regulation of Gene Expression by insulin through MAP protein kinase cascade
_____ binds to receptor → ____________ IRS-1 on Tyr residues → _______ of IRS-1 binds to mediator proteins → binding to ___ causes ___ release and ___ binding to ___ → activated Ras binds and activates _____ → Raf-1 phosphorylates ___ and _______ it → MEK phosphorylates __________ (on Thr and Tyr residue) and activates it → ____________ moves into the nucleus and __________ nuclear transcirption factors (_____) and activates them → _________________ joins SRF to stimulate transcription and translation genes for cell division
Insulin, autophosphorylates, Phosphate, Ras, GDP, GTP, Ras, Raf-1, MEK, activates, ERK/MAP kinase, ERK/MAP kinase, phosphorylates, Elk-1, phosphorylated Elk1
STUDY
Understand the patterns of signal transduction and pathway crosstalk in mediating physiological processes
Insulin receptor ________ → releases ___ (phosphorylate of β-Adrenergic receptor) → ____ internalization/desenstiization (reduced GPCR responsivness) → leads to recruitment of _______________ (SHC, Grb2, Sos, Ras, Raf-1) → activated ___ → ___ → alter _______________
activated, PKB, GPCR, mediator proteins, MEK, ERK, gene expression
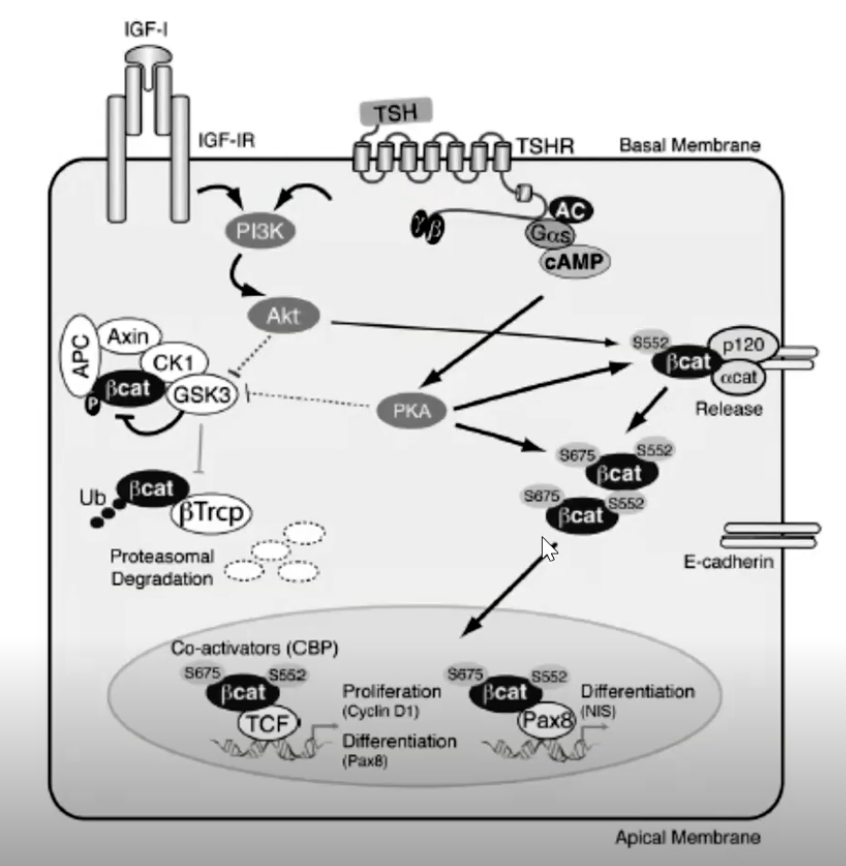
_____ receptor → activates ___ → ___
___ receptor activation → ___
PKA → phosphorylates _______ → goes to the ______ and alters gene transcription (cell __________ and cell _____________)
IGF-1, Akt, PKA, TSH, PKA, beta-cat, nucleus, proliferation, differentiation
JAK/STAT pathway is used by hormones and cytokines:
Some hormones (e.g. _____ hormone) and the ______ activate a __________ that is ___ an integral part of the ______ receptor.
___________ (JAK) is associated with, but not part of, the ______________ hormone receptor
Upon ligand binding, receptors _____ which activates ___
JAK ____________ the receptor attracting proteins called ______ (signal transducers and activators of transcription)
____________________ dimerize and translocate into the nucleus where they bind to ____________ and activate transcription.
The phosphotyrosine residues of the receptor also activate proteins of the __________ pathway as well as G protein- mediated activation of ___ demonstrating “__________.
growth, cytokines, tyrosine kinase, not, hormone, Janus kinase, cell surface growth, dimerize, JAK, phosphorylates, STATs, Phosphorylated STATs, response elements, MAP kinase, PLC, cross-talk
STUDY
NF-κB pathway:
__________ RESPONSE
___ phosphorylated to ___ and ___ and activate transcription that leads to inflammation, regulated by ___________
INFLAMMATORY, IkB, p50, p65, glucocorticoids
The NF-κB Pathway is regulated by Glucocorticoids:
The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory action of _______ are explained in part by a 3-fold inhibition of _____ pathway.
_______ increases _______ and therefore IκB protein and more efficient sequestration of NF-κB in the ________.
The ____________ receptor competes with NF-κB for binding to _________
The glucocorticoid receptor directly binds to the ___ subunit of NF-κB and ______ its action.
cortisol, NF-kB, Cortisol, IkB mRNA, cytoplasm, glucocorticoid, coactivators, p65, inhibits
Development of Protein Kinase Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment
In all types of cancer, the normal regulation of cell division has become __________ due to defects in one or more genes such as ____________
The simplest protein kinase inhibitors are _________ that occupy the ATP binding site but cannot serve as ___________________
For example, _______, which targets ____, is effective against advanced ____________________ (NSCLC)
dysfunctional, protein kinases, ATP analogs, phosphoryl group donors, Erlotinib, EGFR, non-small cell lung cancer