week 2 maternity: phys aspects of pregnancy
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
pt teaching of folic acid
it decreases neural tube defects
folic acid supplementation of 400 mcg of folic acid/day for childbearing aged women reduced the incidence of NTDs such as spina bifida
beneficial impact of folic acid supplementation is greatest between 1 month before pregnancy and through the first trimester, the period of neural tube development
sources of folic acid
dark green leafy vegetables
legumes (beans, peanuts)
orange juice
asparagus
spinach
fortified cereal and pasta
may be lost in cooking
what can iron supplementation aid in during pregnancy?
can reduce preeclampsia, PICA, premature rupture of membrane, higher risk of low birth weight
multigravida pts or short interconeption periods may lead to low FE in beginning of pregancy
sources of iron rich foods
shrimp
oysters
cream of wheat
peas
eggs
prunes
broccoli
beef and chicken
what should pregnant pts avoid doing exercise wise?
yoga poses on back for long periods
hot yoga or pilates causing overheating
contact sports, scuba diving, skydiving, anything risking injury or fall
pt should stop exercising and call her HCP if she experiences?
abd pain w or w/o nausea
calf pain or swelling
chest pain
dizziness, syncopre
headache
muscle weakness affecting balance
new dyspnea before exercising
regular, painful uteine contactions
vagginal bleeding or leaking fluid from the vagina
what is the length of gestation/human pregnancy
average 280 days or 40 wks
typically between 37 wks and 42 wks
what is trimester 1 week/month wise?
month 1: 1-4 wks
month 2: wks 5-8
month 3: wks 9-13
what is tri 3 week/month wise?
month 4: week 14-17
month 5: week 18-22
month 6: week 23-27
what is tri 3 month/week wise?
month 7: week 28-21
month 8: week 32-35
month 9: 36-40
what are preSUmptive indicators during pregnancy
subjective changes experienced and reported by the patient
amenorrhea
N/V
breast changes - end of first tri into third
fatigure
urinary frequency
vagianl and cervical color changes
quickening: first time mother feels fetal movement
what are probably indicators of pregnancy
objective findings that can be documented by an examiner
uterine growth and abdominal growth
what is chadwicks sign
increased congestion to the cervix because of increased estrogen
bluish purple coloration of the vaginal ucosa, cervix, and vulva seena t 6-8 weeks
what is goodells sign
softening of the servix and vagina with increased leukorrheal discharge; palpated at 8 wks
what is hegar’s sign
about 6 to 8 wks after the last menses, the lower uterine segment is so soft it can be compressed to the thinness of paper
what is melasma
mask of pregnancy
mask of darker skin tone
what is linea nigra
dark line in between belly button
what do pregnancy tests detect?
hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) or the beta subunit of hCG, in which is secreted by the placenta and present in maternal blood nd urine shortly after conception
what are some positive indicators of pregnancy
auscultation of fetal heart sounds
btwn 10-12 wks
normal FHR is 110-160 BPM
Observation and palpation of fetal movements by examiner
felt or visualized by examiner
observed after about 20 wks
visualization of embry or fetus
imagine such as ultrasonography
as early as 3-4 wks of gestation
what is quickening
first time that mother feels fetal movement usually around 18 wks-20 wks gestation
sometimes as early as 14 to 16 wks of gestation in multigravida
occasionally as late as 22 wks of gestation in some primigravidas
what is gravidity/gravida
refers to totqal numbers/times a woman has been pregnant without reference to how many fetuses there were with each pregnancy or when the pregnancy ended
simply how many times a woman has been pregnant, including the current pregnancy
what is parity or para
refers to the number of births after 20 wks gestation whether live births or still births
what is GTPAL?
G = # of pregnancies
T = # of term pregnancies (>= 37 wks and 0 days & beyond)
P = # of preterm pregnancies (>= 20 wks to 36 wks & 6 days0
A = # of abortions before 20 wks gestation
L = living children
what is nulligravida
a woman who has never been pregnant or given birth
what is primigravida
a woman who is pregnant for the first time
what is multigravida
more than 1 pregnancy
what are the goals for prenatal care?
maintenance of maternal fetal health
accurate determination of gestational age
ongoing assessment of risk status and implementation of risk-appropriate intervention
rapport built with the childbearing family
referrals to appropriate resources
frequency of prenatal care visits: conception to 28 wks
every 4 weeks
frequency of prenatal care visits: 29 to 36 wks
every 2 weeks
frequency of prenatal care visits: 37 weeks to birth
weekly
what are the prenatal lab tests?
ABO & Rh type with antibody screen to identify isoimmunization
Hgb = anemia
Rubella = MMR vaccine if not immune pp
Varicella = if not immune, offer Varivax vaccine pp
VDRL or RPR = treatment for positive syphilis
Gonorrhea & chalmydia = treat
urine culture = if bacteruria
Hepatitis B surface antigen = immunoprophylaxis
HIV = treat w antiretrovirals if +
cervical screening = for HPV
TB skin test = for @ risk pts
prenatal screening = for abnormalities, diseases, defects
what is RhoGAM
antibody tests may be repeated in 3rd trimester in pts who are Rh-negative if the father of the baby is Rh-positive
if unsensitized, the pt should recieve Rho (D) immune globulin aka RhoGAM, prophylactically at 28 wks of gestation, after any invasive procedure such as amniocentesis, abdominal trauma
need give RhoGAM again within 72 hrs after birth if infants blood type is Rh positive
total weight gain for underweight BMI (<18.5)
28-40 lbs
total weight gain for normal BMI (18.5-24.9)
25-35lbs
37-54lbs for twin pregnancies
total weight gain for overweight BMI (25-29.9)
15-25lbs
31-50lbs for twin pregnancies
total weight gains for obese BMI (>=30)
11-20lbs
25-42lbs for twin pregnancies
what fish to avoid during pregnancy and why
bc of high levels of mercury
king mackerel
orange roughy
marlin
shark
swordfish
tilefish
tuna is safe but limit white (albacore) tuna to 6oz per week
foods to avoid in pregnancy
raw and unpasteurized - risk of listeria, parasites, bacteria
unpasterized juices or dairy products
raw sprouts of any kind
unpasteurized soft cheeses such as brie, camembert, or feta
refrigerated, smoked seafood
unheated deli meats or hot dogs
raw eggs
raw fish and shellfish
what teas promomte uterine contractions
teas with chamomile, peppermint, licorice, raspeberry leaf
what is PICA?
cravings for nonnutritive substances such as ice, clay, dirt, laundry starch
cause is unknown
iron deficiency is often associated with pica
substances may be contaminated with toxins or parasites
may cause dental problems
may cause nutritional deficiencies
warning signs for 1st trimester
abd cramping or pain indicates possible threatened abortion, UTI, appendicitis
vaginal spotting or bleeding indicates possible threatened abortion
absence of FH tone indicated missed abortion
dysuria, freq., urgency indicate possible UTI
fever or chills indicate infection
prolonged N/V indicated hyperemesis gravidarum, increased risk of dehydration
warning signs for 2nd trimester
abd. or pelvic pain indicates possible preterm labor, UTI, pyelonephritis, or appendicitis
absence of fetal movement ones the woman has been feeling daily movement indicates possible fetal distress or death
prolonged N/V indicates possible hyperemesis gravidarum, this woman is at risk for dehydration
fever and chills indicate possible infection
dysuria, freq., urgency indicate possible UTI
vaginal bleeding indicates possible infection, friable cervix caused by pregnancy changes, placenta previa, abruptio placeta, or PTL
what is leopolds 1st maneuver
abdomen
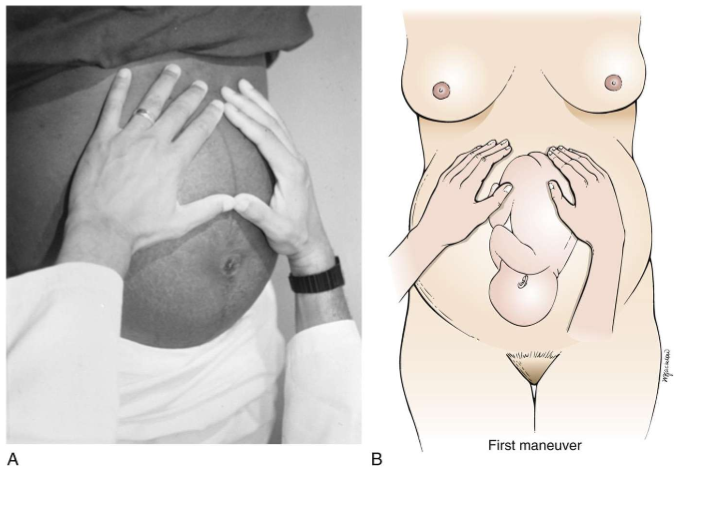
what is leopolds 2nd maneuver
abdomen
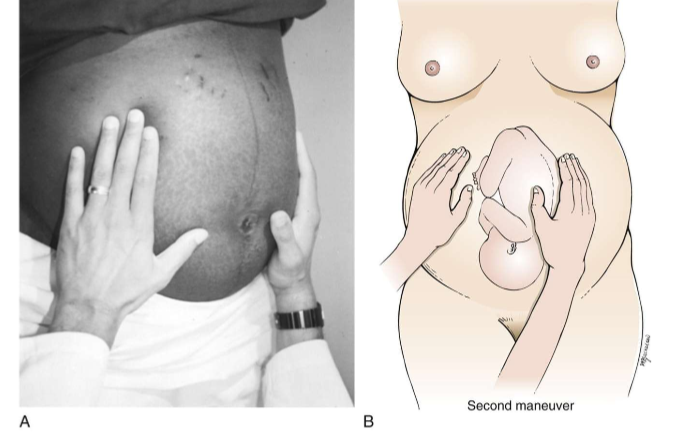
leopolds 3rd manuever
on fetal presenting part
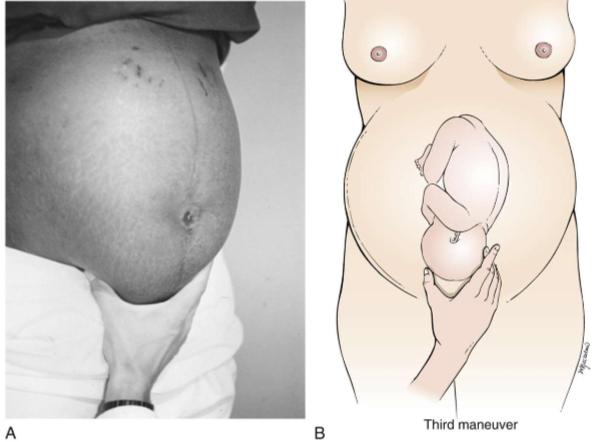
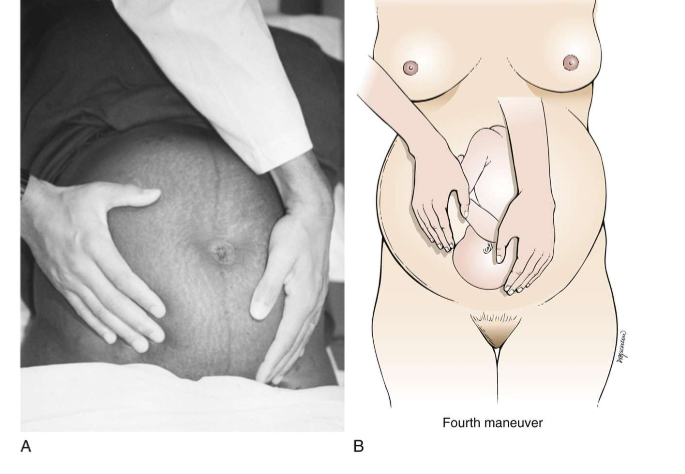
leopolds 4th maneuver
on fetal presenting part
what is the screening for group beta steptococcus for?
it is a 3rd tri lab
vaginal and rectal swab at around 35-37 wks gestation
if present bacteria, anticipate intapartum antibiotic treatment PRN
can be invasive and severe with potential longer term neurological sequelae
what is a 1hr glucose test for?
done at 24-28 wks gestation
third trimester lab
3hr glucose tolerance test is ordered if 1hr screen is elevated
determines gestational diabetes
warning symptoms in 3rd trimester to contact their provider immediately
abdominal or pelvic pain (PTL, UTI, pyelonephritis, appendicits)
decreased or absent fetal movement (Fetal hypoxia or death)
prolonged N/V (dehydration, hyperemesis, gravidarum)
fever chills (infection)
dysuria, frequency, urgency (UTI)
vaginal bleeding (infection, friable cervix caused by pregnancy changes or pathology, placenta previa, placenta abruptio, PTL)
signs and symptoms of PTL in 3rd tri
rhythmic lower abdominal cramping or pain
low backache
pelvic pressure
leaking of amniotic fluid
increased vaginal discharge
S/S of hypertensive disorders in third trimester
severe headache that does not respond to usual relief measures
visual changes
RUQ pain
facial or generalized edema
breast changes are normally caused by what hormone levels increasing?
estrogen and progesterone
produced by the corpus luteum and then by the placenta
how early is colostrum secreted?
as early as 16 wks
due to relwase of prolactin
what is lightening?
by 40 wks, fetal head descend into pelvic cavity
what is braxton hicks?
first contractions
uterus temporarily tightens and then returns to its original relaxed state
what is chadwicks sign?
bluish coloration of cervix, vaginal mucosa, and vulva
gives off blue hue
this is due to increased estrogen
what is goodell’s sign?
softening of the cervix
what is hegars sign?
softening of the lower uterine segment
what is supine hypotension
weight of gravid uterus partially occludes vena cava and the aorta and diminish blood return to lower extremities and reduces cardiac return
dizziness, lightheadeness, nausea, syncope
light on side instead
what are respirstory system changes during pregnancy?
estrogen and progesterone causes vascular engorgement and smooth muscle relaxation leading to dyspnea, nasal and sinus congestion, epistaxis (nose bleeds)
this is due to estrogen and progesterone
causing upward displacement of diaphragm by enlarging uterus
renal system in pregnancy
increased GFR > increased urine output
urinary frequency and incontinence and increased risk of UTI may be asymptomatic
small proteinuria and glycosuria can be normal
increased progesterone levels = relaxation of smooth muscles
GI system in pregnancy
gingivits/bleeding gums
excessive salivation (ptyalsim)
increased progesterone levels relax smooth muscle, causing bloating, flatulence, and constipation
musculoskeletal system in pregnancy
increased progesterone and relaxin levels lead to softening of ligaments and increased joint mobility, resulting in widening and increased mobility of the sacroiliac and symphysis pubis to help facilitate birthing
can also lead to low back pain or pelvic discomfort
pelvis tilts forwarf, changing posture (increasing lordosis) and making a “waddle” gait
increased risk of falls due to shift in cent of gravity and change in gait and posture
distention of abdomen related to expanding uterus, reduced abdominal tone, and increased breast size leading to round ligament spasm
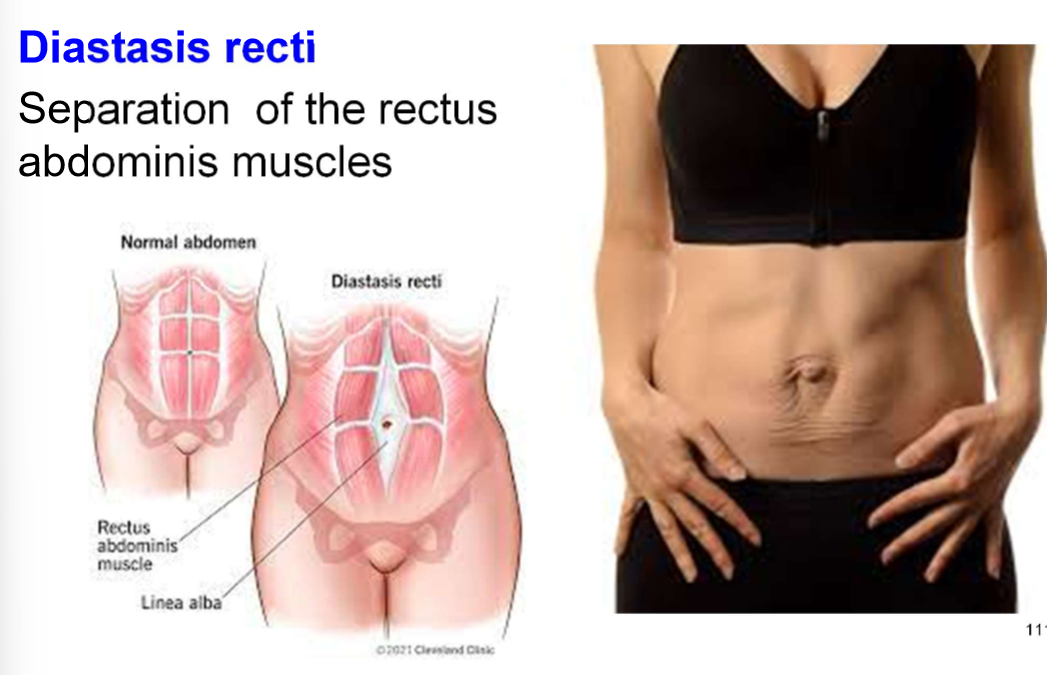
abdominal muscles stretch due to enlarging uterus causing diastasis recti
what is diastasis recti
seperation of the rectus abdominis muscles
integumentary system changes in pregnancy
linea nigra
melasma (chloasma)
increased prigmentation of nipples, areola, vulva, scars, and moles
due to estrogen and progesterone levels stimulating increased melanin deposition, causing light brown to dark brown pigmentation
what is the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
primary function of hCG in early pregnancy is to prevent deterioration of the corpus luteum so it can continue producing estrogen and progesterone until the placenta is sufficiently developed
hormone detected in pregnancy tests
how is the corpus luteum produced?
early in pregnancy
due to estrogen
what are the effects of estrogen during pregnancy regarindg the endocrine system?
placenta continues to produce estrogen for the remainder of pregnancy
facilitates uterine and breast development
facilitates increases in vasculariy
facilitates hyperpigmentation
alters metabolic processes and fluid and electrolyte balance
how is progesterone produced?
first produced by the corpus luterume and then by the fully developed placenta
what major fx does progesterone have?
suppresion of FSH and LH
maintenance of the endometrial layer for implantation of the fetilized ovum and prevention of menstruation
maintains pregnancy by relaxation of smooth muscles leading to decreased uterine activity which results in decreased risk of spontaneous abortions
decreases GI motility and slows digestive processes
why is glucose needed in pregnancy? why is insulin needed?
increased need for glucose due to developing fetus leading to increased production of insulin
increase in circulating cortisol leading to increase in maternal rsistance to insulin leads to increased risk of hyperglycemia
pt teaching is experiencing N/V (nutrition/food wise)
eat crackers, dry toast, or dry cereal before arising in the morning, then get out of bed slowly
eat small amounts of high carbohydrate, low fat foods, q2 hrs and a total of 5-6 small meals per day to prevent an empty stomach
eat a protein snack before bedtime
suck on hard candy
what is hyperemesis gravidarum?
a condition associated with severe vomiting leading to weight loss, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and ketosis
N/V pt teaching (nonpharm/ cannot PO wise)
wear a P6 acupressure wrist band
take vitamins at bedtime with snack (not in the morning)
suggest vitamin B6, 25 mg by mouth 3 times daily or ginger, 250 mg by mouth four times daily
oral or rectal meds may be prescribed for management of troublesome symptoms
pt teaching for heartburn
eat small meals q2/q3 and avoid fatty, acidic, or spicy foods
eliminate or curtail smoking and drinking coffee and carbonated beverages, which stimulate acid formation in the stomach
avoid citrus fruits and juices, tomato based products, chocolate, and peppermint if they increase symptoms
try chewing gum
remain upright for 30-45 mins after eating
avoid bending over or lying flat
refrain from eating atleast 3 hrs before bedtime
what may be causing backache in pregnancy
increased joint mobility, lumbar lordosis, and relaxed ligaments contribute to the problem
pt teaching for backache
teaching correct psture and body mechanics can help prevent back pain
stooping or bending puts a great deal of strain on the muscles of the lower back
instruction should include correct and incorrect methods of lifting
what exercises can you do to relieve backaches ?
pelvic tilt/pelvic rocking (cow position)
tailor sitting (almost like criss cross applesauce)
shoulder circling
what is round ligament pain?
sharp pain in the inguinal area or on the side, usually on the right
results from softening and stretching of the ligament from hormones and uternie growth
may be difficult for woman to distinguish from uterine contractions
careful assessment to rule out contractions followed by reassurance are appropriate measures
pt teaching for round ligament pain
lie on her side and flex the knees up to the abdomen
bend toward pain
do pelvic tilt and pelvic rock exercises
use warm baths or compresses
use side lying in exaggerated sim’s position with pillows for additional support of the abdomen and in btwn legs
use maternity belt
when is urinary frequency and nocturia most common?
1st and 3rd trimester
pt teaching of urinary frequency and nocturia
reassure the woman of the normalcy of response
encourage the owman to empty her bladder frequenctly, front to back
kegel exercises may help maintain bladder control
constipation in pregnancy
can casue abd. fullness and flatulence and hemorrhoids
hard, dry stools, decreased frew. of bowel movements
iron supplementation can caus e
what happens to intestinal motility during pregnancy
decreased during pregnancy as a result of progesterone, pressure from the enlarged uterus and decreased activity
‘pt teaching of constipation
maintain adequate fluid intake
engage in regular exercise such as walking
increased fiber in diet through veggies, fruits, and whole grians
maintain regular bowel habirs
maintain good posture and body mechanics
pt teaching of hemmorhoids
avoid bearing down with bowel movements
comfort meassures (ice packs, warm baths or sitx baths, witch hazel compresses)
elevate hips and lover extremeities during rest periods throughout day
gently reinsert hemorrhoid into rectume while doing kegel exercises
pt teaching of leg cramps
dorsiflex foot to stretch calf (towards body)
apply warm compress to area
change positions slowly
massage
engage in regular exercise and muscle conditioning
relaxin
one of the hormones that causes gradual softening of pelvic cartilage and connective tissues
after ovulation, this is the remaining cells of an old follicle thsy prrsists for ~12 days
corpus luteum
folic acid
supplementation decreases risk of neural tube defects