Class 7. Human Psyche | Quizlet
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Borderline
very close to but not completely
your answer was ~ rude, so I would advise you to be more diplomatic in the future
She was a ~ candidate
After the exams, the teacher gave all ~ cases a spoken test.

Erratic
moving or behaving in a way that is not regular, certain, or expected SYN sporadic, random, bizarre
his pulse/heartbeat is ~
~ movement/driving/behavior/
the animal's ~ behavior made her wonder if it was ill
because of your ~ attendance at practice, you're in danger of being cut from the team

Coupled with
combined, joined
An oil spill ~ strong winds brought disaster.
The team's win, ~ a loss by their rivals, put them in first place.

Abandonment
ADJ. abandoned
the act of leaving someone or something, usually forever
memories of her father's complete ~t of her.
an ~ car/house
The child was found ~but unharmed.
There was an ~ supermarket trolley in the middle of the road.
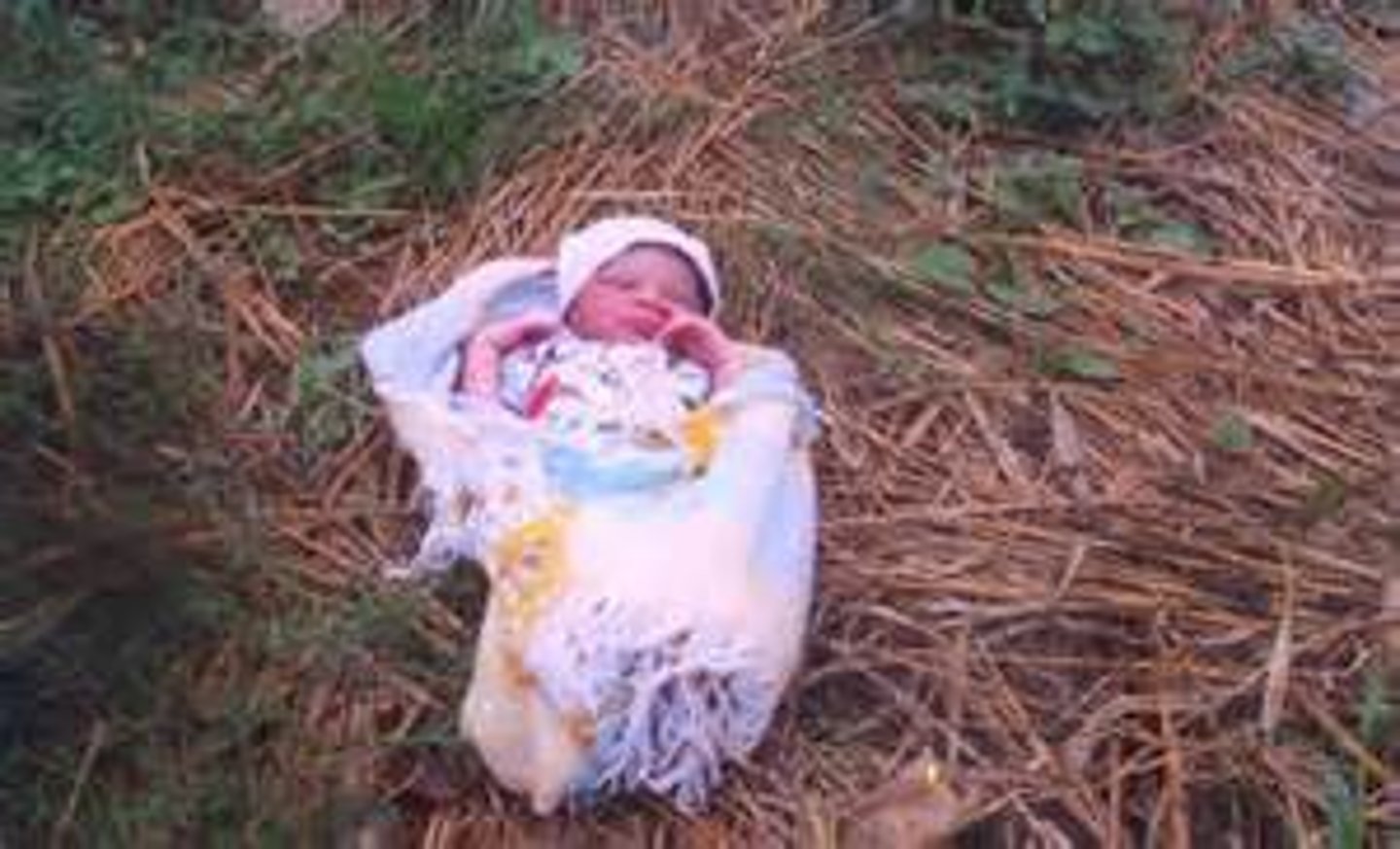

Mood swings
an abrupt and unaccountable change of mood
He is liable to abrupt ~
his sudden ~ of ~
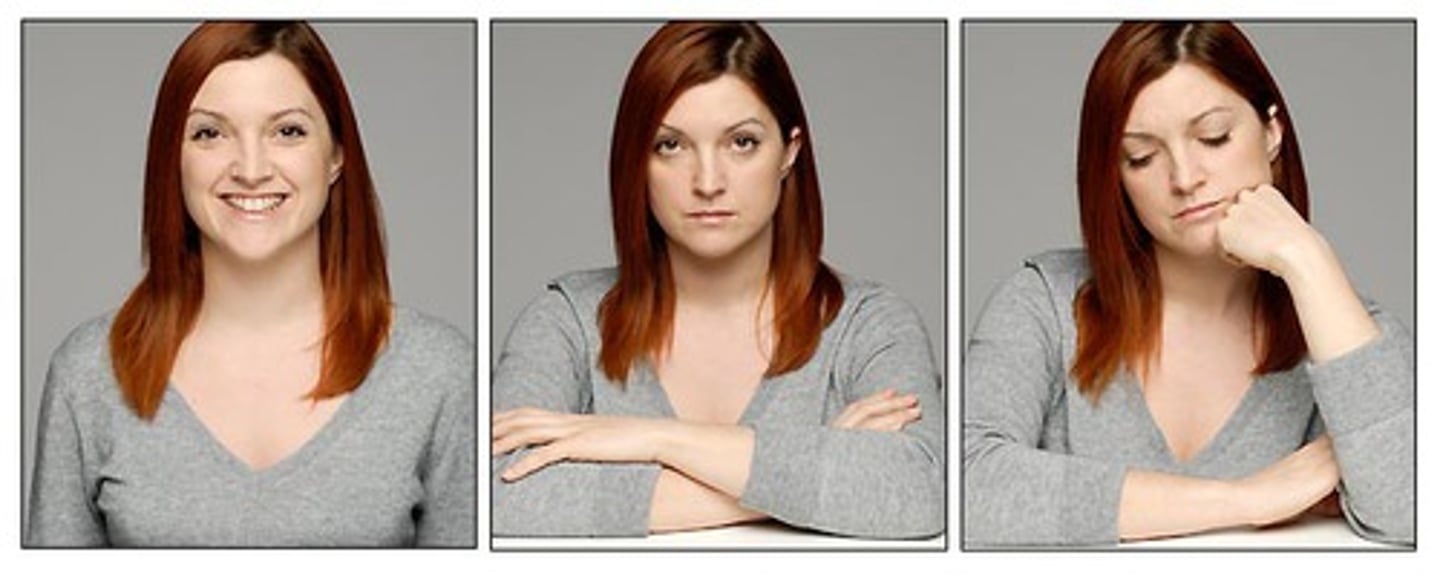

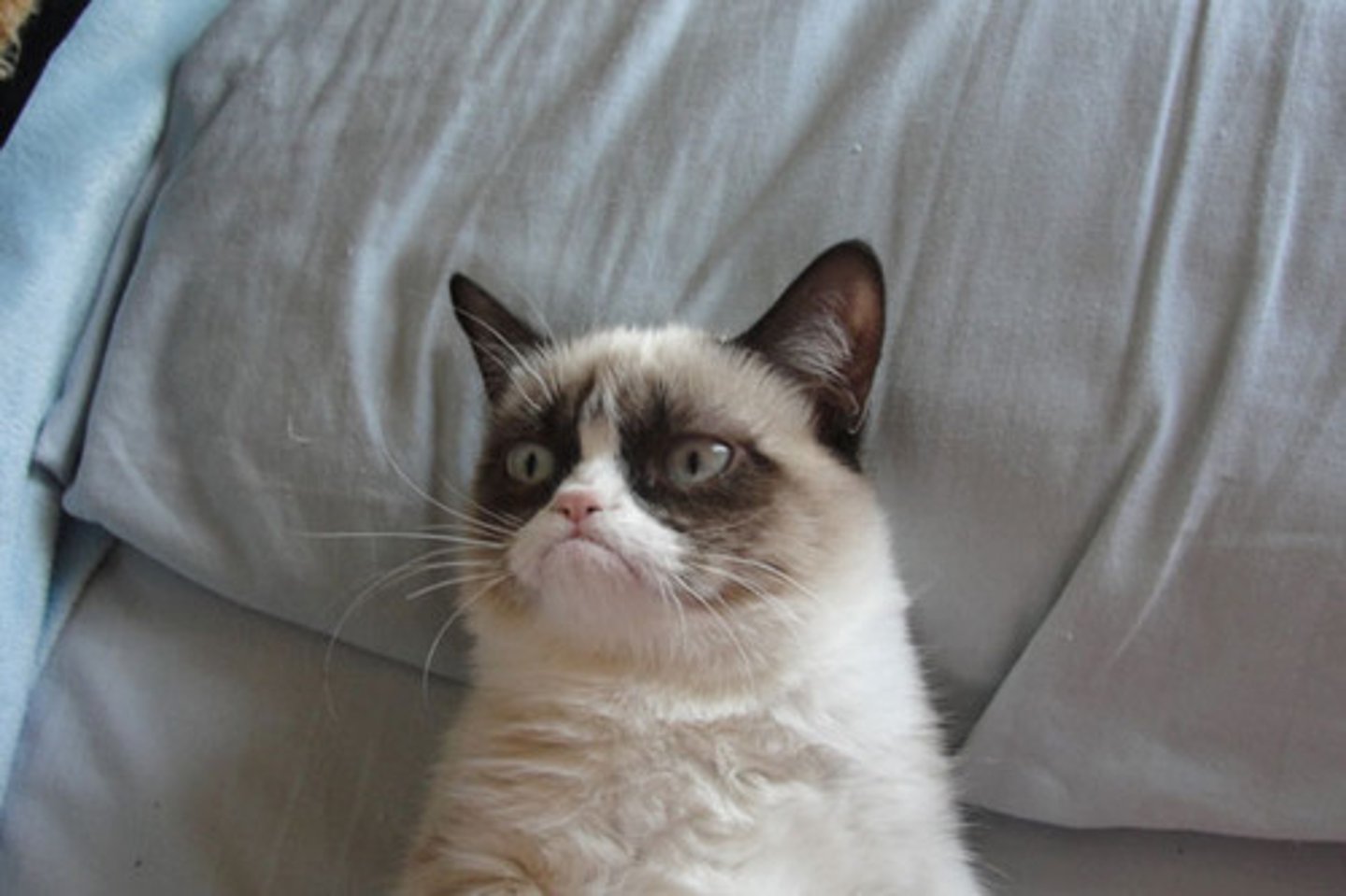
Grumpy
being in a slightly angry mood because you are annoyed at something or are feeling tired
a ~ neighbor whose yard we had long ago learned not to trespass
a ~ old man/lady
the baby's sure to be ~ if she doesn't get her afternoon nap

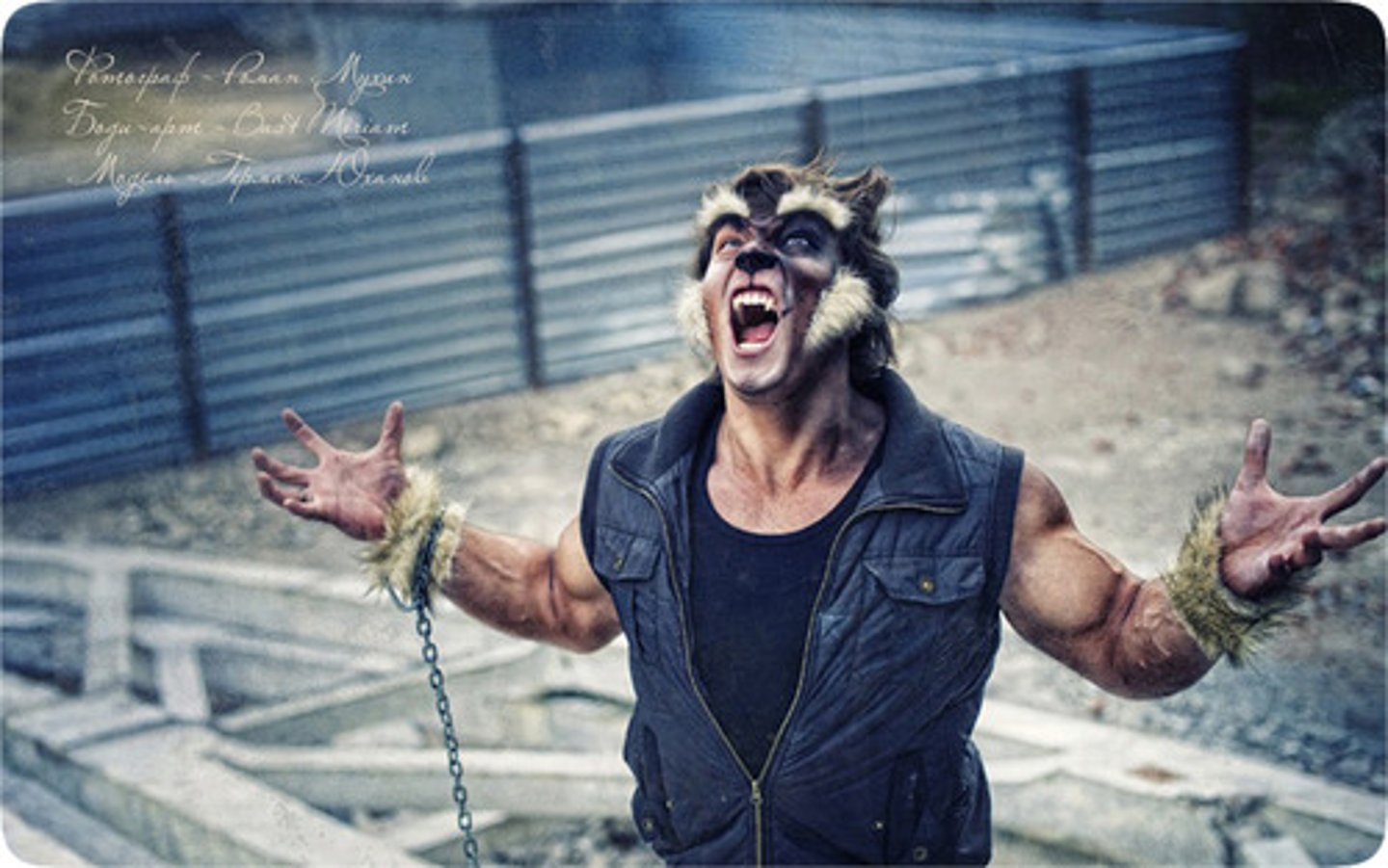
Shapeshift
to undergo a noticeable change (in character for example), to metamorphose
A werewolf is a mythological or folkloric human with the ability to ~ into a wolf

Clingy
Cling like a leech
Her younger brother clings like a leech, always hanging around us and asking for money.
too emotionally dependent SYN needy
a ~ child
a ~ plastic wrap
~ fabrics dress/clothes

Pervasive
Pervasive is most often used of things we don't really want spreading throughout all parts of something:
But pervasive can occasionally also be found in neutral and even positive contexts: a pervasive rhythm, a pervasive sense of calm
existing in or spreading through every part of something
~ atmosphere of/sense/fear/attitude/influence/corruption
a ~ problem
a stench that is ~
Her influence is all-~

Fetch
go or come after and bring or take back
~ help/a doctor
If you throw the ball the dog will ~ it.
She's gone to ~ the kids from school.
Could you ~ my bag for me?

Startling
very surprising, astonishing, or remarkable
~ new evidence came to light during the trial.
He made a ~ discovery.
It is a city of ~ contrasts.
~ beauty/effect/results/insight/speed

Misconception
a view or opinion that is incorrect because based on faulty thinking or understanding
a common/popular ~
There's this ~ that you get famous and everything is perfect.
Many gardeners are under the ~ that bamboos grow only in mild climates.
an attempt to clear up ~s about the disorder
frequently held ~s about the disease

Offer a perspective
to suggest a particular way of considering something; to think about a situation or problem in a wise and reasonable way
The aim is to ~ a fresh ~.
The exhibition provides us with a unique ~ on her work.
a report that looks at the education system from the ~ of deaf people

Needy
wanting too much attention and love
~ families
... where ~ children from the community could come to get free, nutritious meals.emotionally ~
The girl was ~ for her mother's affection.

equipped
qualified
she is well ~ for the job
he was ideally ~ for this task
I am perfectly well ~ to look after myself.
Some students have emotional problems that teachers are ill ~ to handle.

deemed
to be regarded or considered in a specified way
~ it wise to go slow
those whom she ~ worthy
a movie ~ appropriate for all ages
The evening was ~ a great success.
I ~ it an honor to be invited.
They would take any action ~ necessary.

Resistant
1. opposed to it and wants to prevent it; 2. not harmed or affected by something
wrinkle-~ clothes
a drug-~ strain of virus
These plants are ~ to cold temperatures.
He became ~ to the medication.
Mosquitoes are becoming ~ to insecticides.
Come by
manage to acquire or obtain
a good job is hard to ~
In rural France, English language magazines are rather hard to ~
do you ever ~ any old books?
On and off
happen occasionally, or only for part of a period of time, not in a regular or continuous way
It rained ~ all day.

Saving grace
a good quality that something or someone has that stops it, him, or her from being completely bad
His one ~ is his sense of humor.
It's expensive, but the machine's ~ is its ease of operation.
Beautiful photography was the ~ of the otherwise awful film

Work wonders/miracles
to produce very good effects
Her new diet and exercise program has ~ for her.
That will ~ for their motivation.
You'll love this new face cream. It ~ on my wrinkles.
This new medicine ~ with my headaches.

Exacerbate /ɪɡˈzæsərbeɪt/
to make (pain, disease, emotion, etc) more intense; aggravate
The new law only ~s the problem.
His aggressive reaction only ~d the situation.
~ a condition/crisis/shortage/situation/symptoms

Meltdown
a breakdown of self-control (as from fatigue or overstimulation); a rapid or disastrous decline or collapse
fears that an accident could cause ~
a company experiencing financial ~
After a long day at the beach, our toddler had a major ~ in the car on the way home.

Overwhelmed
to be overcome completely in mind or feeling by a certain emotion
~ by a task/the amount of/the size of/the enormity of
She was ~ by feelings of guilt.

Sustain
to give support or relief to
Hope ~ed us during that difficult time.
The roof, unable to ~ the weight of all the snow, collapsed.
The army ~ed heavy losses. (suffer, undergo)
He ~ed serious injuries in the accident.

Come out
make a public appearance (If something comes out, it becomes known publicly after it has been kept secret)
everything ~ all right
~ as bisexual
decided to ~ to her family
blew his cover and ~ as a CIA agent

grounded
mentally and emotionally stable : admirably sensible, realistic, and unpretentious
remains ~ despite all the praise and attention

Malicious
having or showing a desire to cause harm to someone
There is no truth whatsoever to the ~ rumors.
His observations were funny without being ~.
Vandals may take ~ pleasure in destroying and defacing property but usually don't truly hate the owners.

Weed out
to remove (people or things that are not wanted) from a group
They will review the applications to ~ the less qualified candidates.
He is keen to ~ the many applicants he believes may be frauds.
Curb
to control or limit something that is not wanted
trying to ~ her curiosity
pills designed to ~ your appetite
He needs to learn to ~ his temper.
New measures should ~ the speed of cars traveling through the village.
~ an epidemic

Cultivate
to develop or improve by education or training
The land around here has never been ~d.
He has carefully ~d his image.
She ~d a taste for fine wines.
~ a passion/reputation

Trigger
sensations, images, or experiences that spark a negative emotional response
Smoke ~ed the fire alarm.
The timer was set to ~ the bomb in exactly one hour.
His remarks ~ed a public outcry.
Certain foods ~ his headaches.
The power outage was ~ed by heavy rains.

a lost cause
a person or thing that can no longer hope to succeed or be changed for the better
She decided her acting career was ~.
I'm ~ when it comes to anything technical.
Finishing the project on time seemed like ~.

invade
to enter by force in order to take over
The troops ~d at dawn.
When tourists ~, the town is a very different place.
The cancer eventually ~d the brain.
Do the press have the right to ~ her privacy in this way?
You feel tense with worrying thoughts constantly ~ing your sleep.

Hygge (pronounced hue-gah)
the act of creating intimacy with yourself, friends and home
To live the ~ way, focus on friendship, wholesomeness, and happiness.
