ORG CHEM LAB - STRUCTURAL EFFECTS ON MELTING POINT AND BOILING POINT
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Melting and Boiling Points
Physical properties of a compound’s structure
Depend largely on which bonds can hold three atoms together in a molecule
Useful for synthesizing a new compound
Melting Point
The range of temperature at which a substance changes from solid to liquid phase.
Frequently followed by decomposition
The value may not be an equilibrium temperature but a temperature of transition from solid to liquid only.
Boiling Point
Corresponds to the temperature at which thermal energy of the molecule is great enough to overcome the cohesive forces that hold them in the liquid state.
Employed for compounds having low melting points and compounds that are usually liquid at room temperature.
The range of this constant should not exceed 5 C except for extremely high boiling compounds.
Thee constant may also be decreased or increased depending on the volatility of the impurity present.
Factors Affecting Melting and Boiling Points
Molecular Weight
Structure and Intermolecular Forces
Impurities
Hydrogen Bonding
Attraction between a H atom that is bound to an electronegative atom and another molecule.
Functional groups: alcohols, amines (primary and secondary), carboxylic acids, amides (primary and secondary), and thiols
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Stronger than Van der Waals Interaction, but not as strong as H bonds
The positive part of one molecule is attracted to the negative part of another molecule
Functional groups: all polar compounds (alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, amides, esters, alkyl halides, and thioethers)
Induced Dipole-Induced Dipole (Van der Waals/London Dispersion Forces)
Weakest of all the intermolecular forces
A temporary polarized molecular causes its neighbor to become temporary polarized as well
Every molecule exhibits this attraction
Increase in chain length increases the attraction, whereas increase in branching decreases the attraction.
Hydrogen Bonding > Dipole-Dipole Interaction > Van der Waals
Intermolecular Forces Ranking
B. 1-propanol
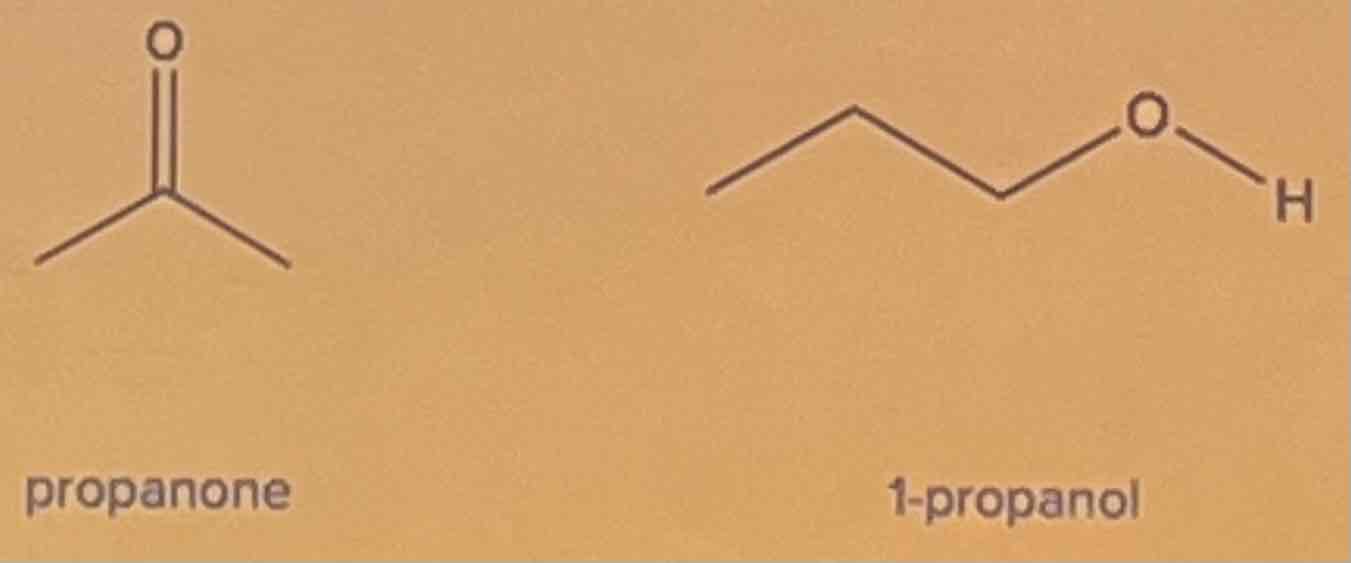
Exercise
Determine the intermolecular forces of attraction involved. Identify which of the given compounds has a higher boiling point.
A. propanone
B. 1-propanol
B. 1-butanol
Exercise
Determine the intermolecular forces of attraction involved. Identify which of the given compounds has a higher boiling point.
A. Ethanol
B. 1-butanol

B. 1-butanol
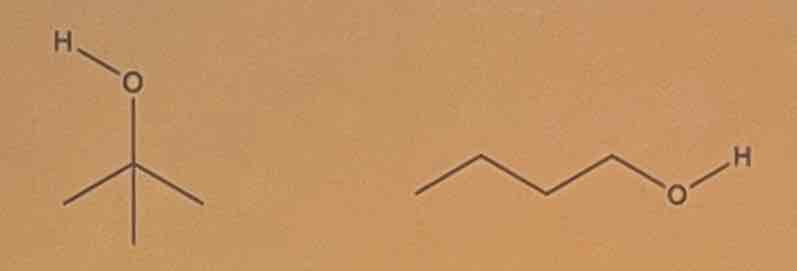
Exercise
Determine the intermolecular forces of attraction involved. Identify which of the given compounds has a higher boiling point.
A. t-butyl alcohol
B. 1-butanol
B. 1-propanol
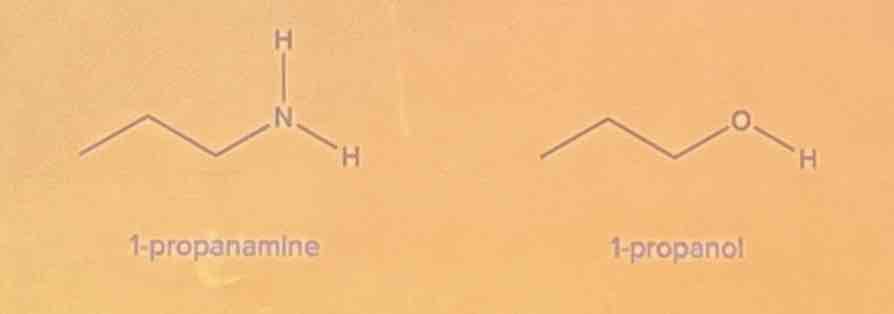
Exercise
Determine the intermolecular forces of attraction involved. Identify which of the given compounds has a higher boiling point.
A. 1-propanamine
B. 1-propanol
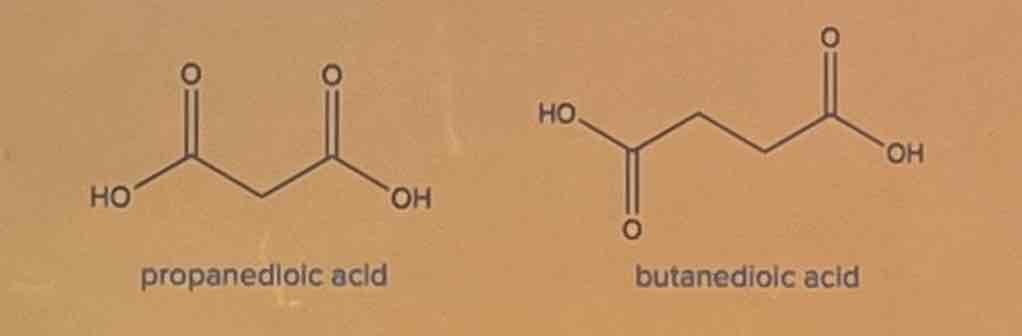
B. butanedioic acid
Exercise
Determine the intermolecular forces of attraction involved. Identify which of the given compounds has a higher boiling point.
A. propanedioic acid
B. butanedioic acid