MCB 2610 Microbe of the Day: Clostridium botulinum
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
is Clostridium botulinum Gram-positive or negative
Gram-positive
Is Clostridium botulinum aerobic or anaerobic?
obilgate anaerobe: oxygen is toxic to them, NO oxygen needed
what shape is Clostridium botulinum
bacillus: rod-shaped
what does Clostridium botulinum produce
heat resistant endospores
what does Clostridium botulinum ferment
sugars or amino acids
where is Clostridium botulinum found
in soil, lakes sediments, decaying vegetation
what is the causative agent of botulism
Clostridium botulinum
what is botulism
a paralytic illness caused by a nerve toxin produced by C. botulinum
what are the 5 types of botulism
1. food borne
2. wound
3. inadvertent botulism
4. infant botulism
5. adult intestinal colonization
what is food borne botulism
caused by eating foods that
contain the botulinum toxin: canned food or trying to ferment when no oxygen is present
what is wound botulism
caused by a wound infected with C. botulinum, inject drugs or traumatic injury
ex: car accidents
what is inadvertent botulism
accidental overdose of
botulinum toxin
what is infant botulism
caused by consuming spores
or bacteria, which germinate in the intestine and release toxin (honey: babies should not have)
- infants do not have fully developed guts, so a few spores could germinate and grow
what is adult intestinal colonization
caused by consuming spores, which germinate in the intestine and release toxin
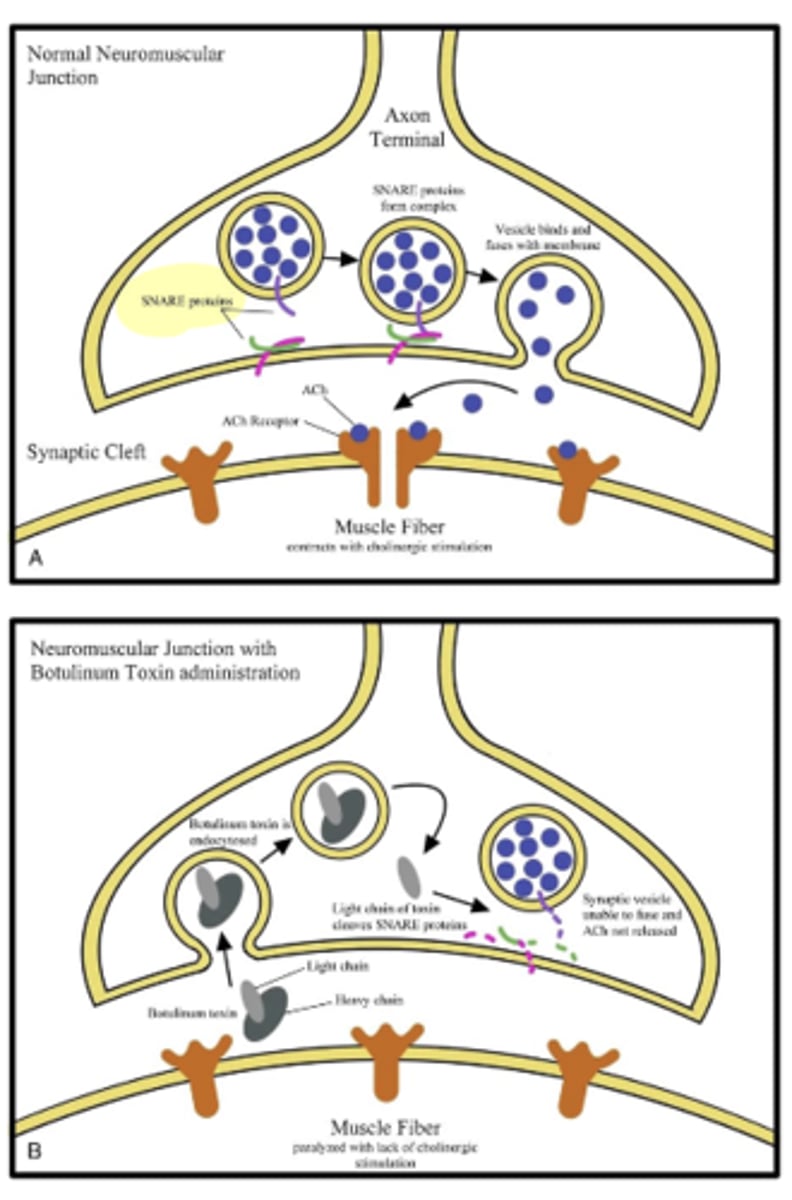
how does toxin act on Acetylcholine (Ach)
Ach causes muscles to contract
Toxin:
- Block Snare proteins from guiding Ach to the nerve membrane.
- Muscle is relaxed = Paralysis (do not contract)
- 8 known toxins A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and F/A hybrid (formerly H)
- A: Most common in the U.S., especially west of the Mississippi. Responsible for ~50% of foodborne outbreaks.
- Also widely used therapeutically (e.g., Botox).
- 2012: Toxin can get into the central nervous system
what are symptoms of botulism
- Double vision
- Blurred vision
- Drooping eyelids
- Slurred speech
- Difficulty swallowing
- Dry mouth
- Muscle weakness
what are specific symptoms of infant botulism
appear lethargic, feed poorly, are constipated, have a weak cry and poor muscle tone
If untreated botulism symptoms may progress to cause paralysis of respiratory muscles and airway obstructions, it could lead to
death
when do symptoms occur for foodborne botulism
symptoms can occur between 4 and 36 hours
what is the history of botulism
early 1800s- Dr. Justinus Andreas Christian Kerner
- Performed experiments on himself
- eating small amounts of so-called sour sausage- (Latin word for sausage, botulus)
- documented the signs and symptoms of botulism
- 1895- isolated from a Belgium scientist
- 1950- Dr. Vernon Brooks blocks the release of acetylcholine from motor nerve terminals
- BOTOX® was approved by the US FDA in December 1989- spasms
who discovered botulism and HOW
Dr. Justinus Andreas Christian
Kerner performed experiments on himself: eating small amounts of so-called sour sausage
epidemiology of botulism
rare 2024 (CDC):
- foodborne botulism: 9 cases
- infant botulism: 67 cases
- wound botulism: 12 cases
- other botulism (unknown): 5 cases
how do we diagnose botulism
- Serum analysis looking at BT toxin
- Needs to be caught early
what are treatments of botulism
- Treated with an antitoxin (NO HOSPITAL HAS IT, ONLY CDC) that blocks the action of the toxin circulating in the blood.
- If from food, inducing vomiting or enemas to remove contaminated food
- Antitoxin is available from the CDC
- Supportive care
- Antibiotics: depends on infection site (wounds)
- Can require several months of care in a hospital
- Patients who survive will have fatigue and shortness of breath for years
how to prevent botulism
1. boil home-canned foods for 10 minutes before eating, especially if you are unsure about the canning process
2. when in doubt, throw it out