VCE unit 4 Biology - Immunity 2022
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
ability to resist infection by action of antibodies or lymphocytes
immunity

MHC I proteins that enable immune system to determine which cells belong
self
molecules not found on self cells which begin immune reaction to eradicate it
non-self

immune response mechanisms that are innate within the body to counteract pathogens
non-specific immunity
bodily structures and mechanisms that prevent pathogens from entering and infecting the body
first line of defence
special cellular layer which prevents entry (e.g. intact skin, stomach and intestinal lining)
physical barrier
secretion of chemicals that limit pathogen growth in parts of the body
chemical barrier

good bacteria which compete for space and nutrients with possible pathogens to restrict their growth
natural flora
the regular removal of pathogens out of the body
flushing

nonspecific resistance against pathogens in a generalised form
second line of defence
monocyte which engulfs and absorbs pathogens
phagocyte

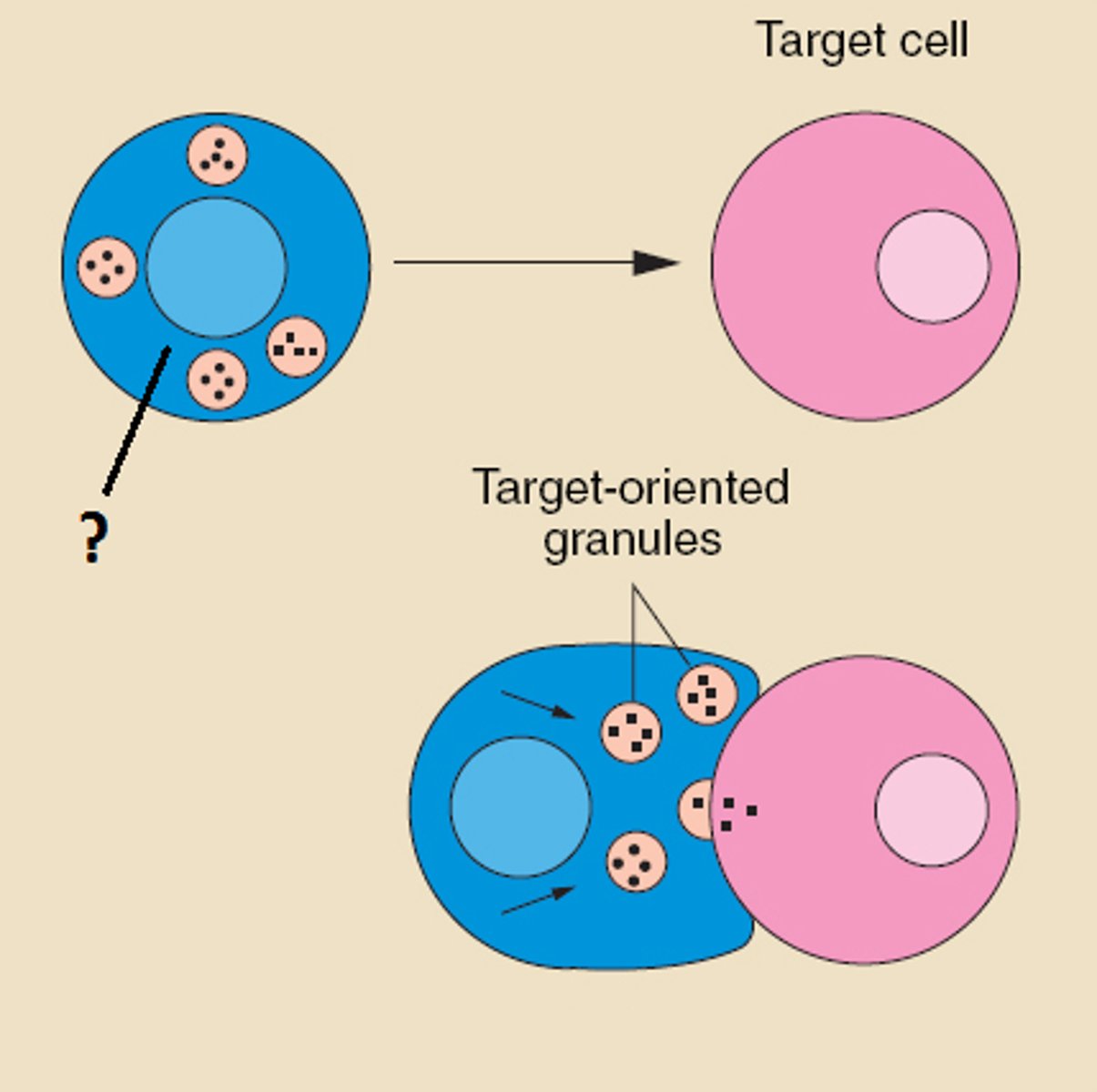
lymphocyte which destroys infected or cancerous cells through injection of cytotoxins into diseased cell
killer cell
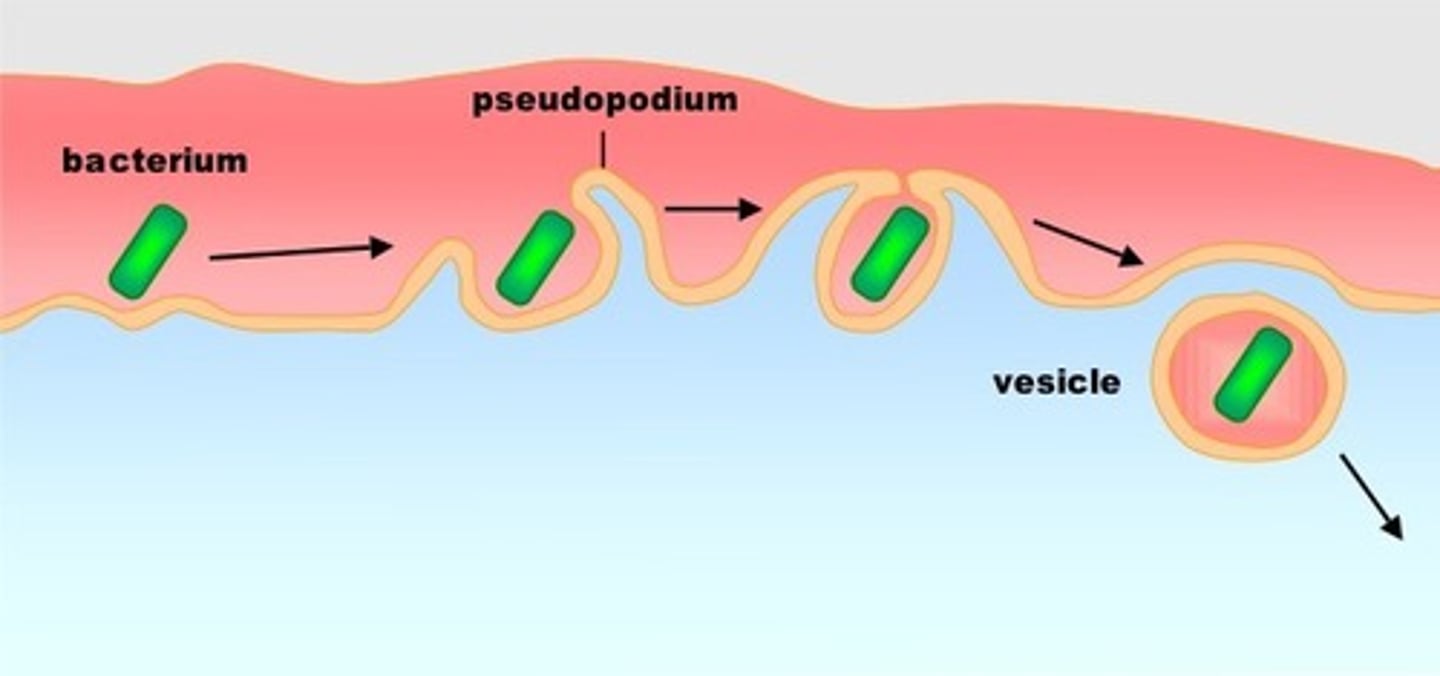
ingestion of pathogen by phagocytes
phagocytosis
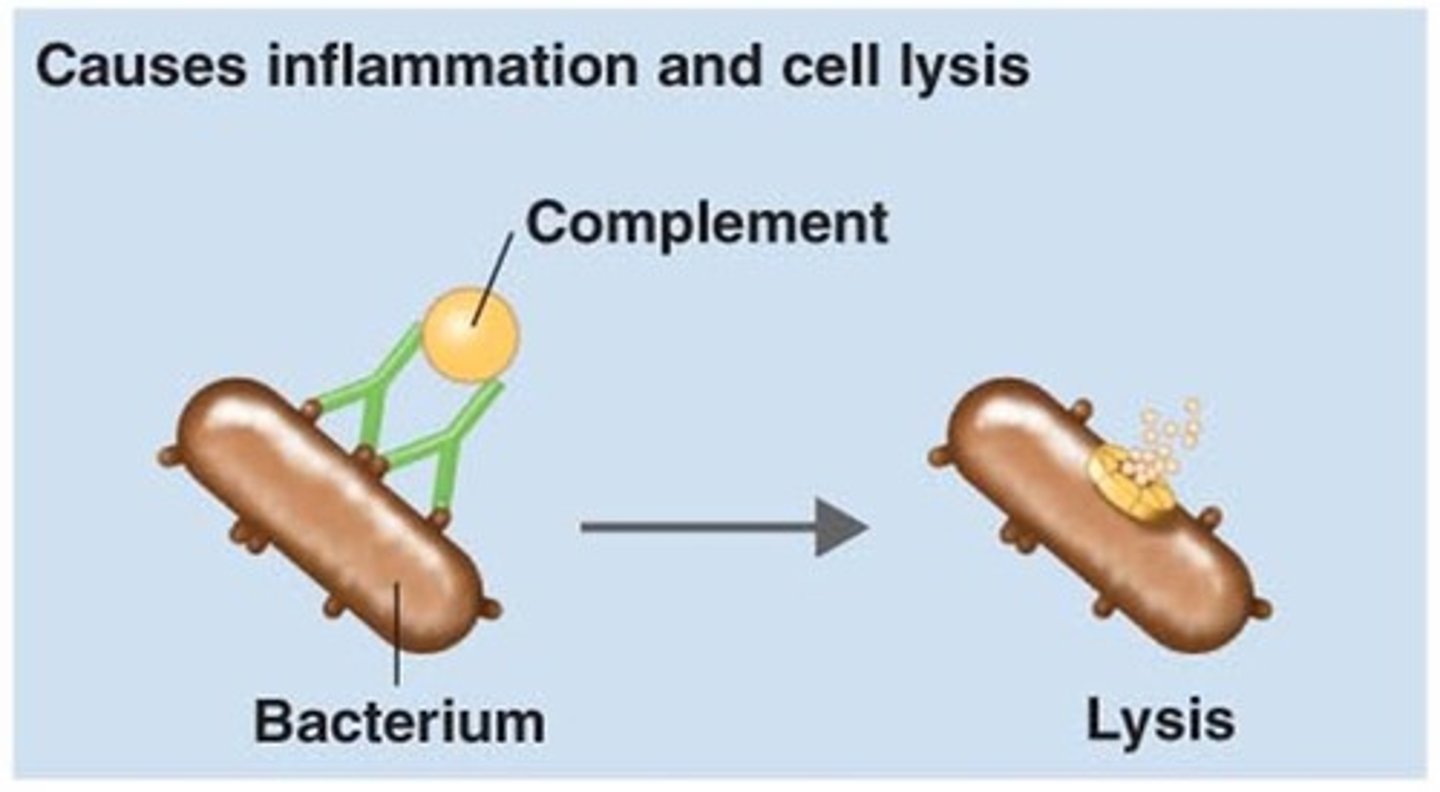
protein which binds to antigens to attract and stimulate phagocytosis
complement protein
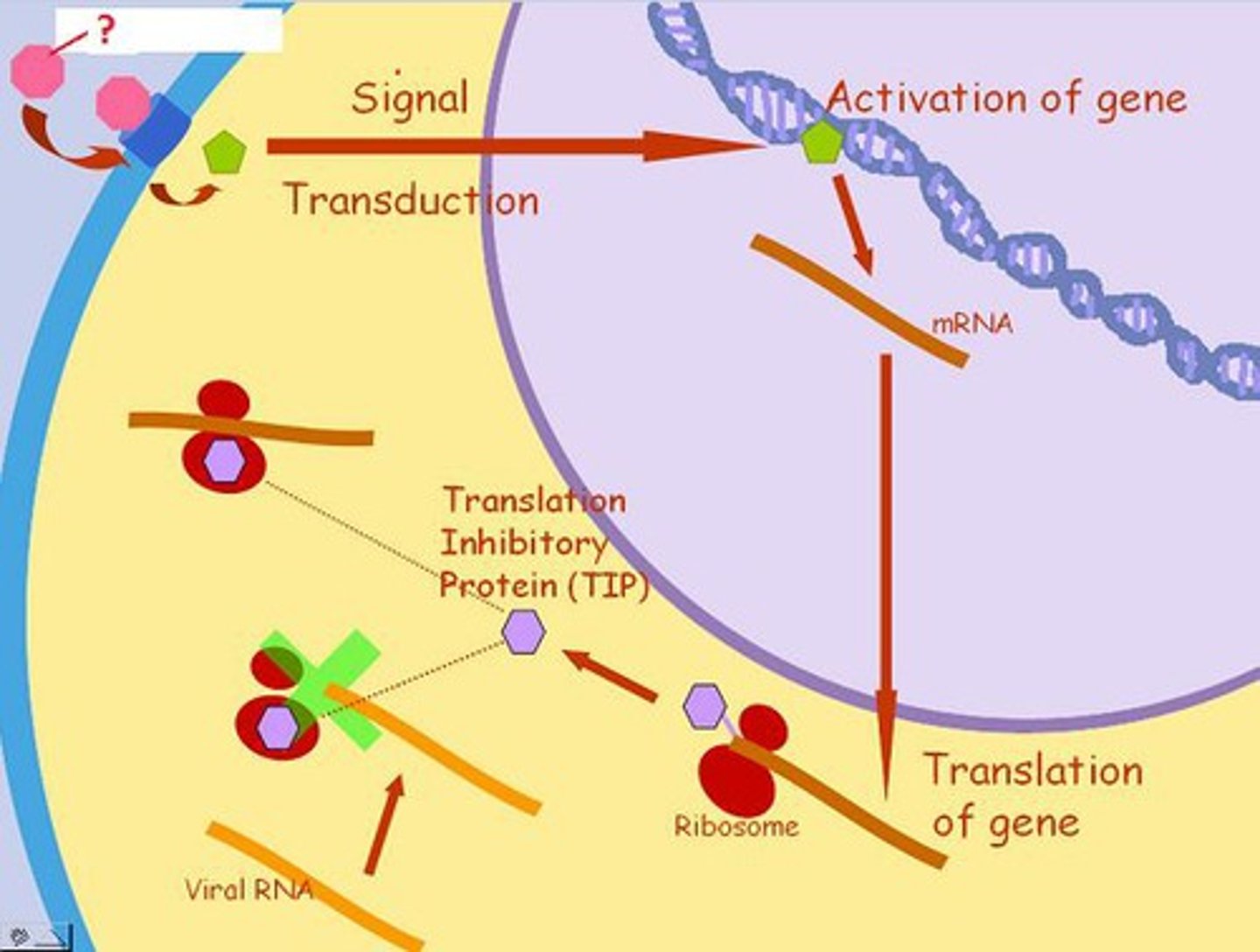
protein which inhibits virus replication
interferon
physical condition where region of body becomes red, swollen, hot and painful
inflammation

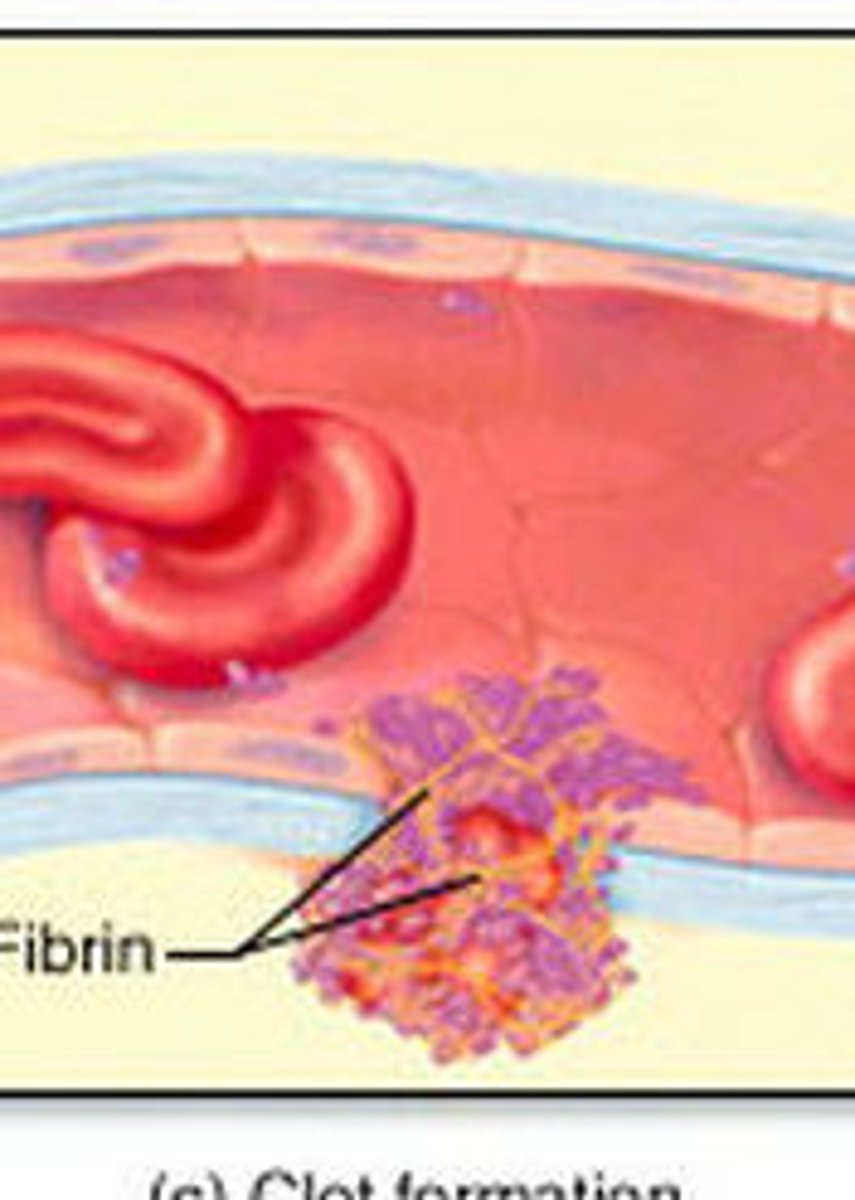
blood which has been converted into a solid state by platelets and fibrin
blood clotting
immune response mechanisms that are acquired by the body to counteract pathogens
specific immunity

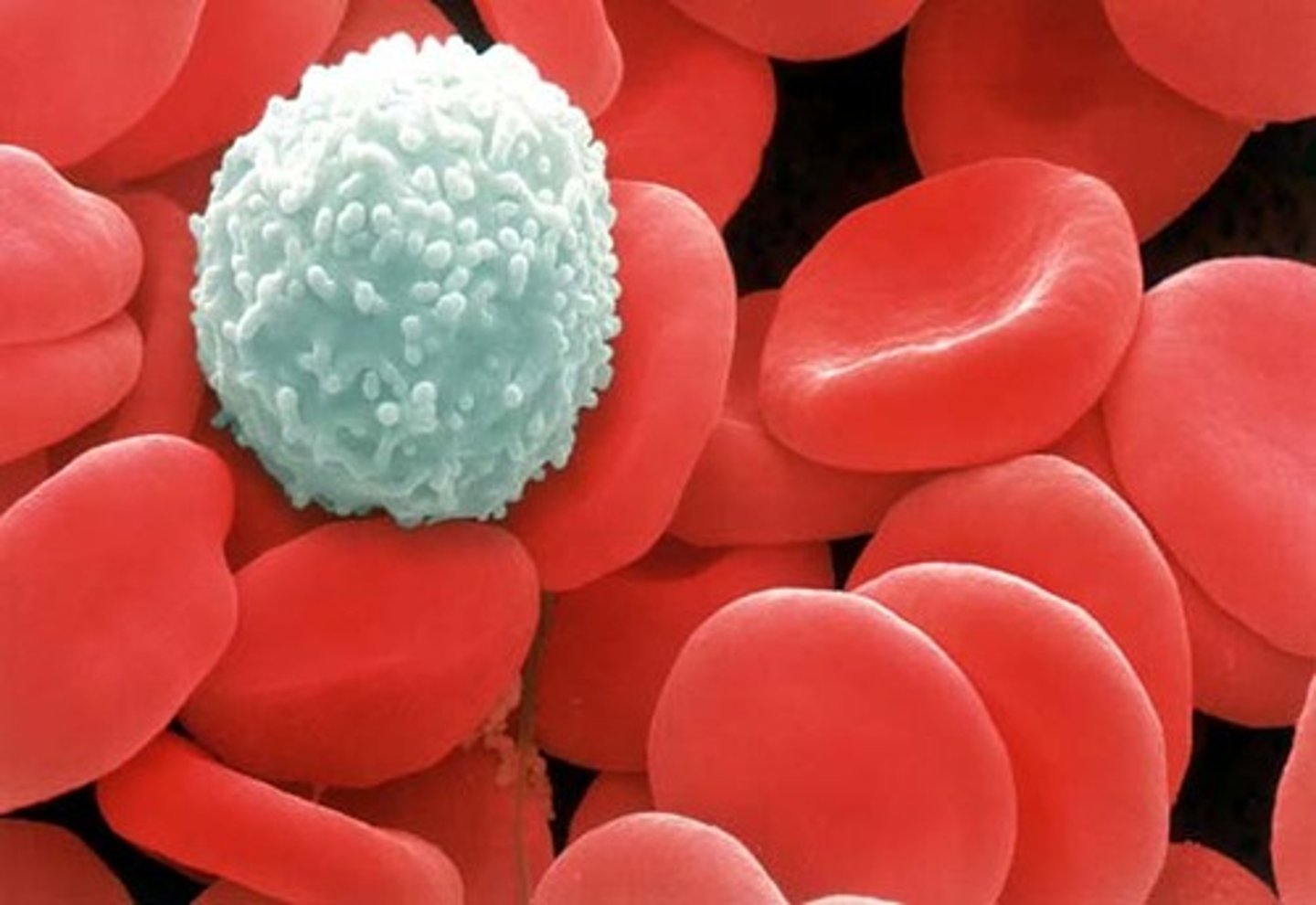
a leucocyte (white blood cell) which occurs in the lymphatic system that is largely responsible for immune responses
lymphoctye
lymphocyte processed in the bone marrow that is responsible for producing antibodies
B cell
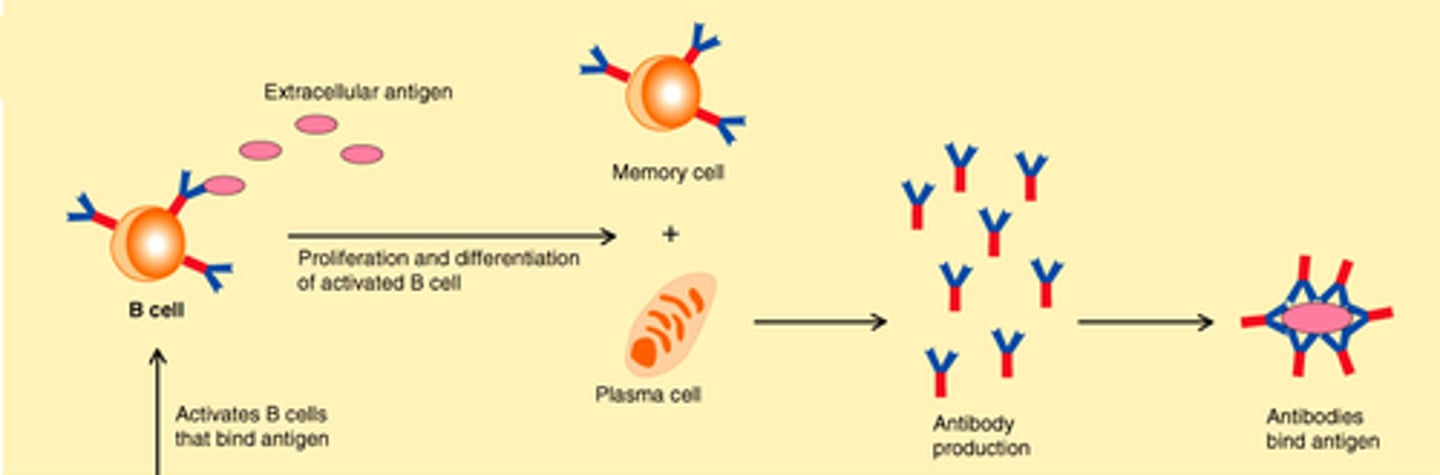
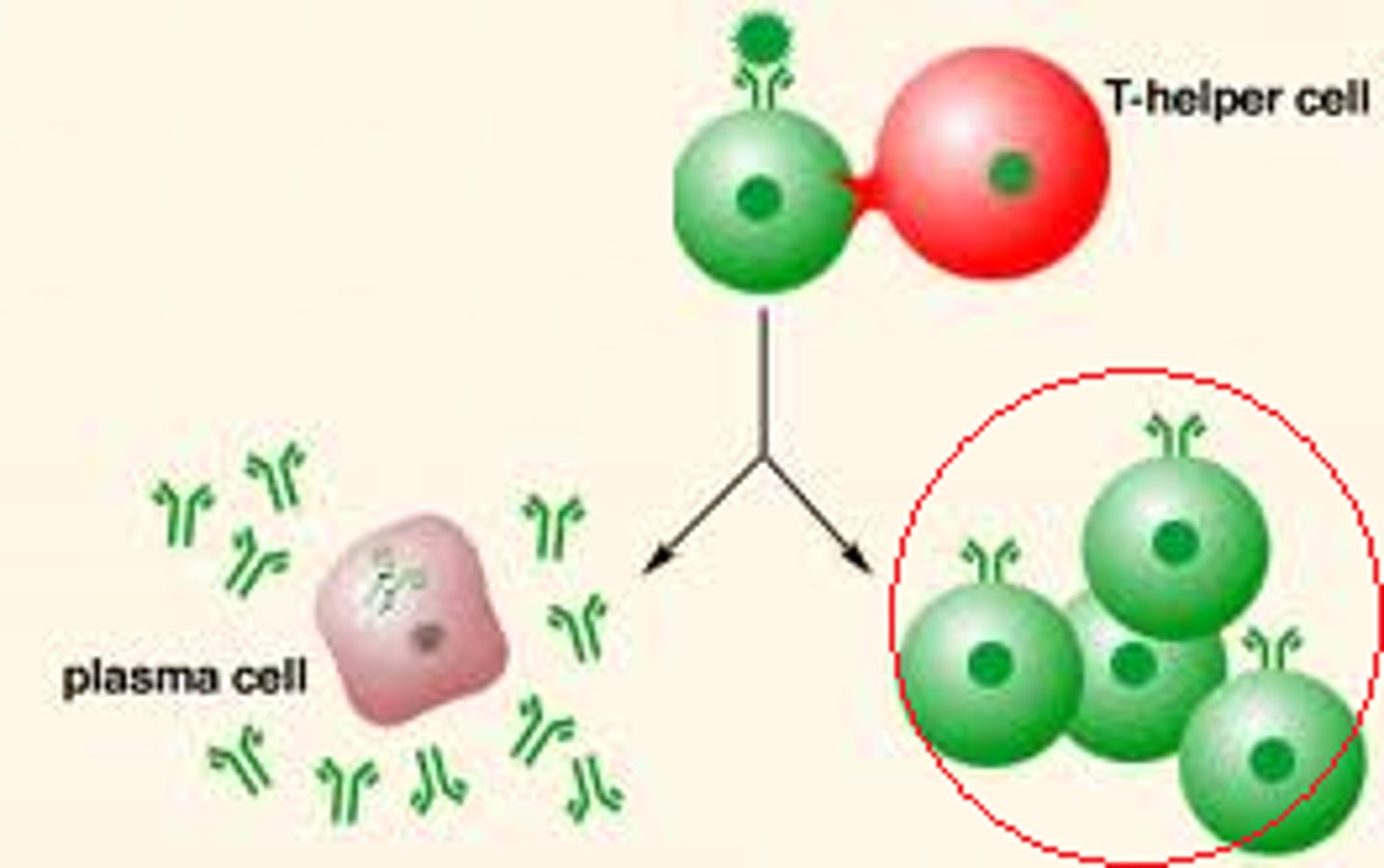
immune response involving the transformation of B cells into plasma cells that produce and secrete antibodies to a specific antigen
humoral response
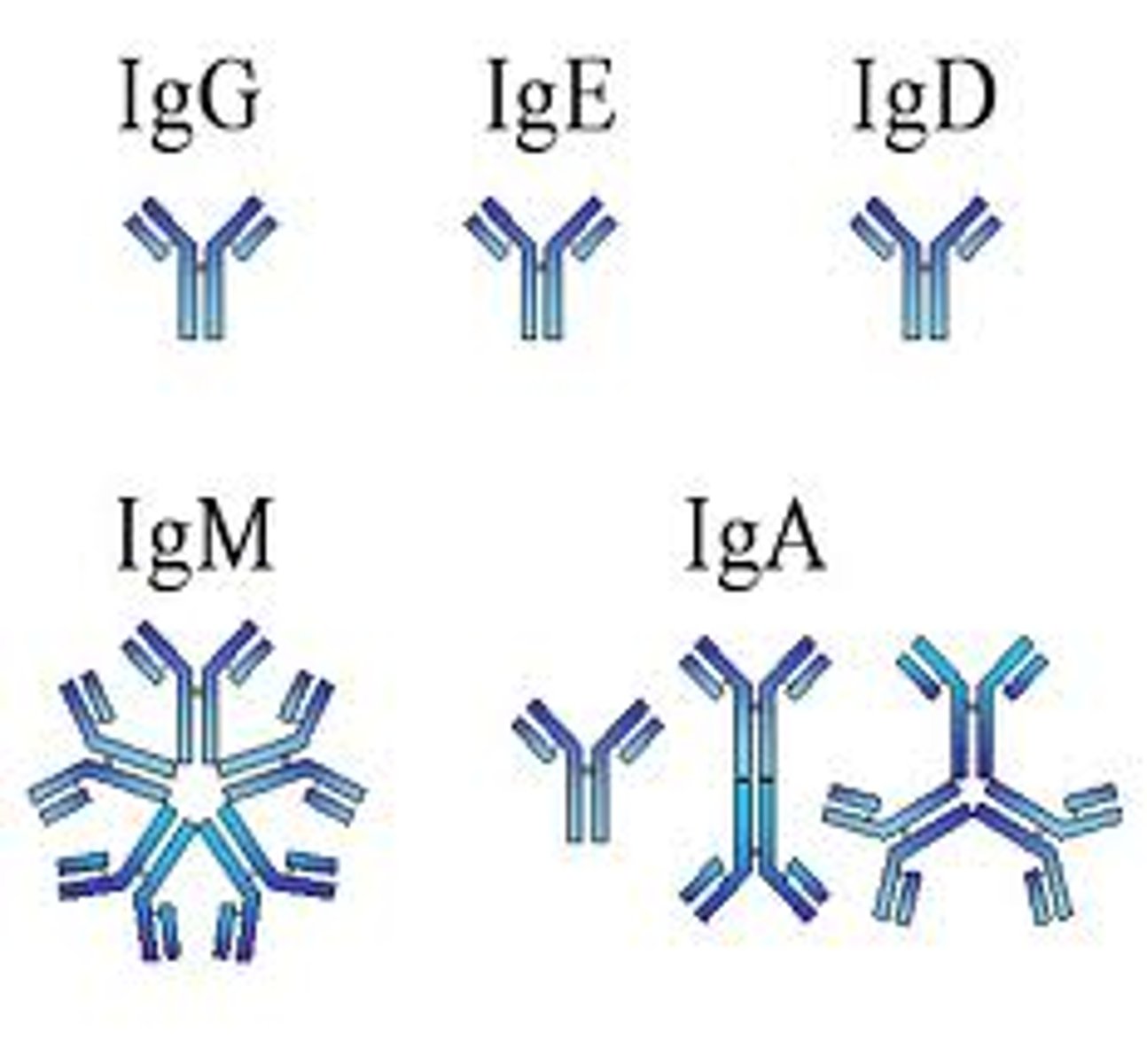
proteins which are present in antibodies that are secreted by plasma cells
immunoglobulin
unique molecule that can induce an immune response
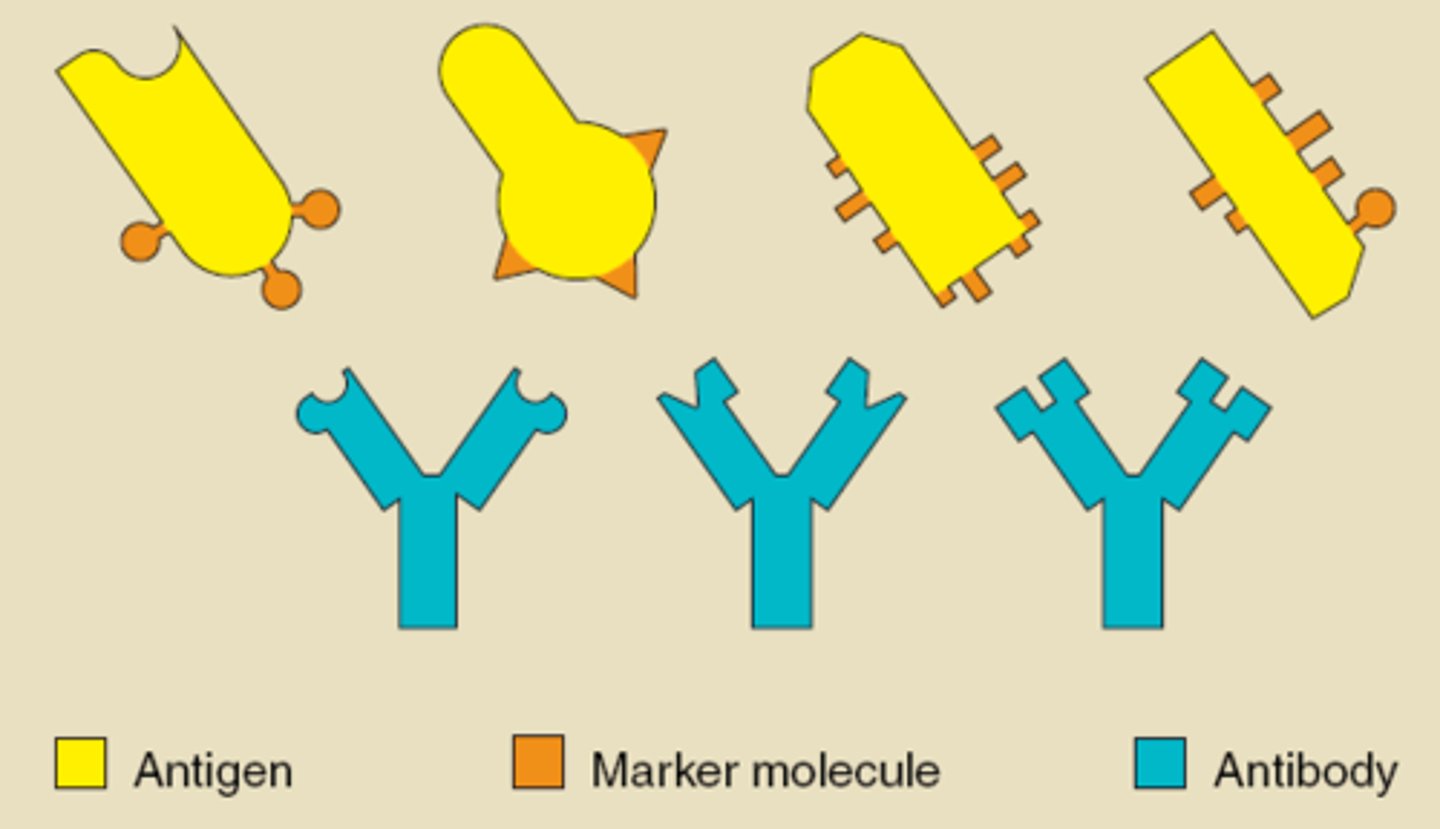
antigen
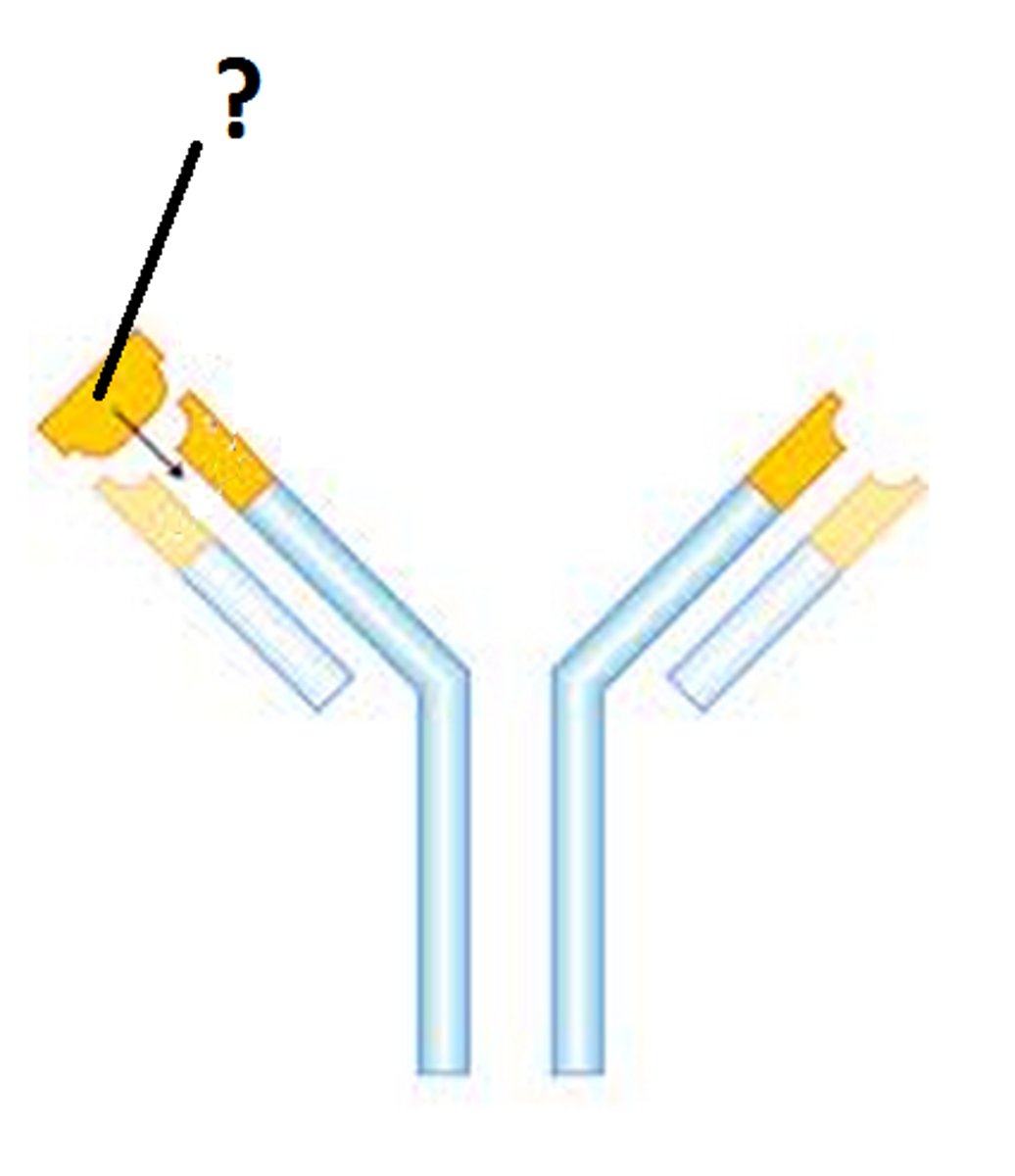
protein produced by plasma cells to counteract a specific antigen to recognise the pathogen as non-self
antibody
long-lived lymphocyte capable of responding a particular antigen on its reintroduction long after the exposure that prompted its production
memory cell
lymphocyte that is produced in the thymus that is activated when the MCHII proteins recognise specific antigens
T cell
type of T cell which regulates and suppresses the immune response by releasing cytokines
helper T cell
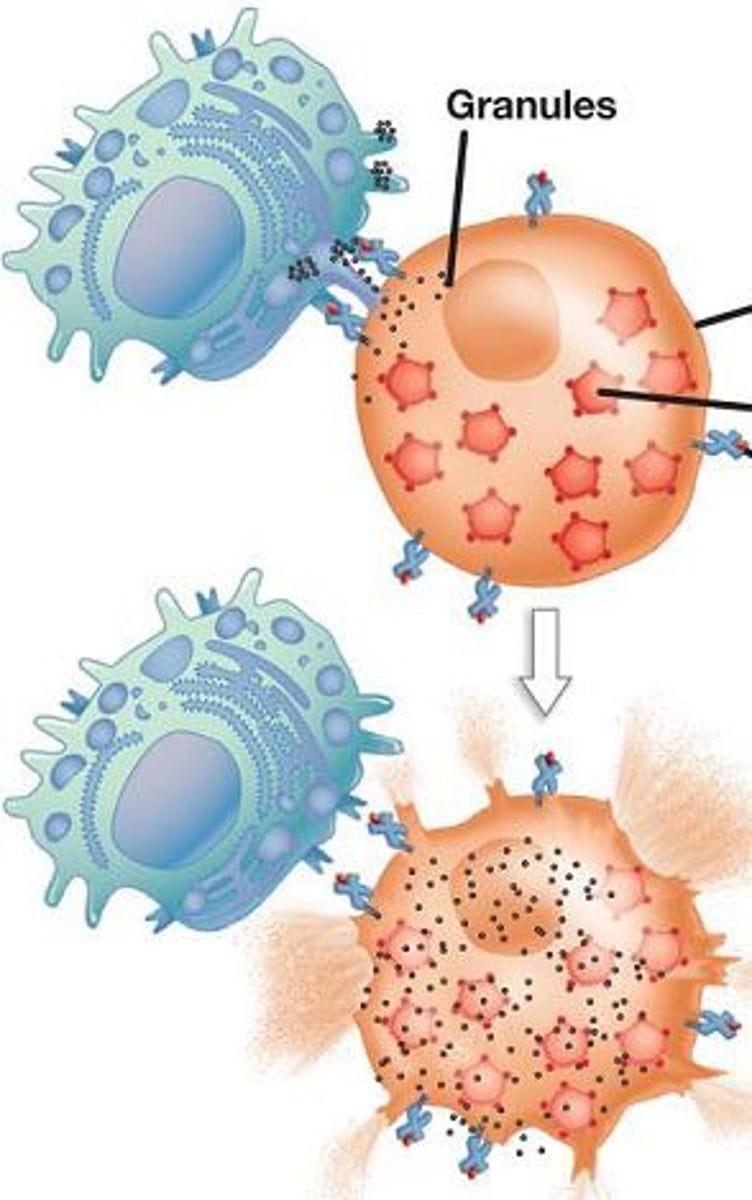
type of T cell which releases cytotoxic granules to apoptosize cancerous and infected cells.
cytotoxic T cell
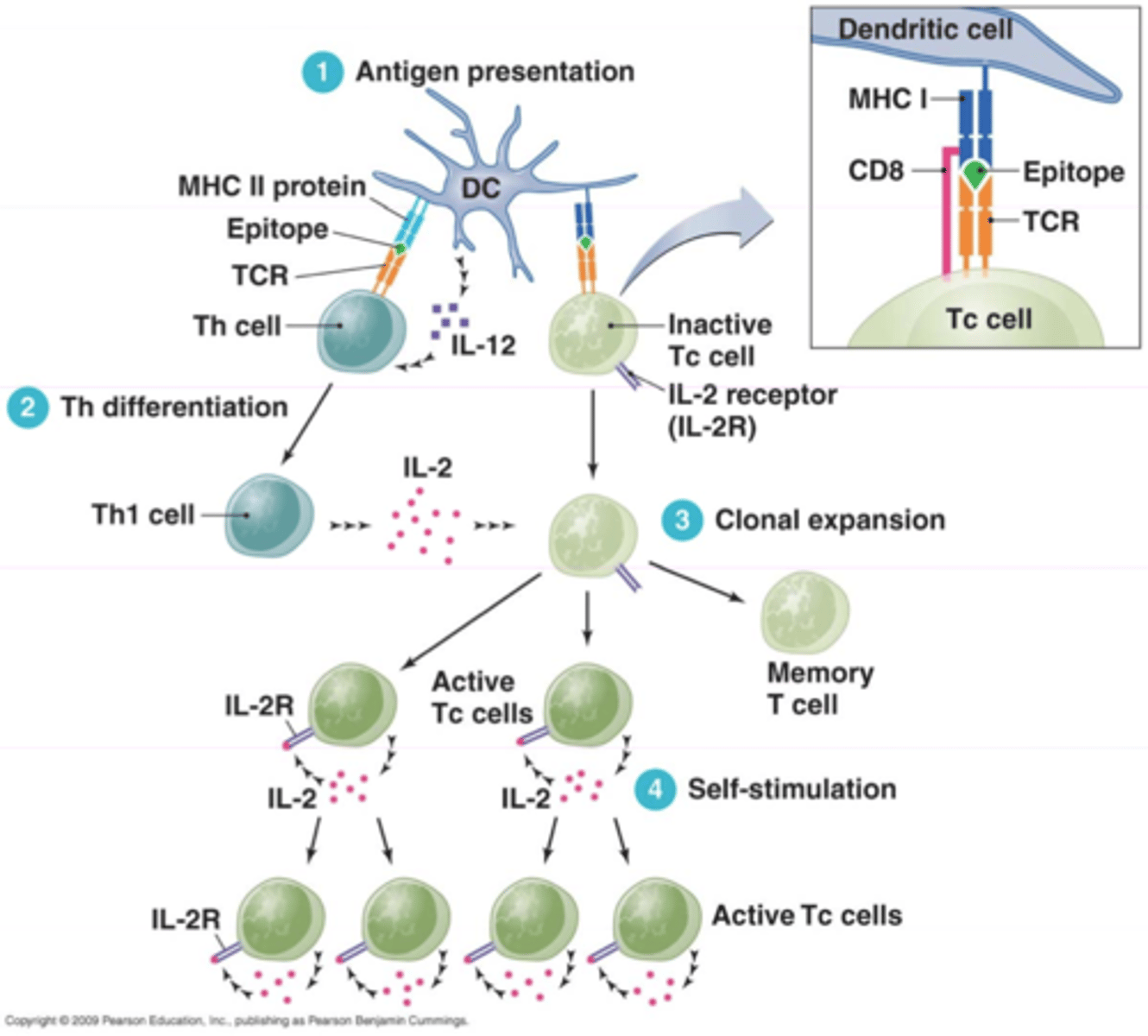
immune response which activates phagocytes and cytotoxic T cells and releases cytokines in response to an antigen
cell mediated response
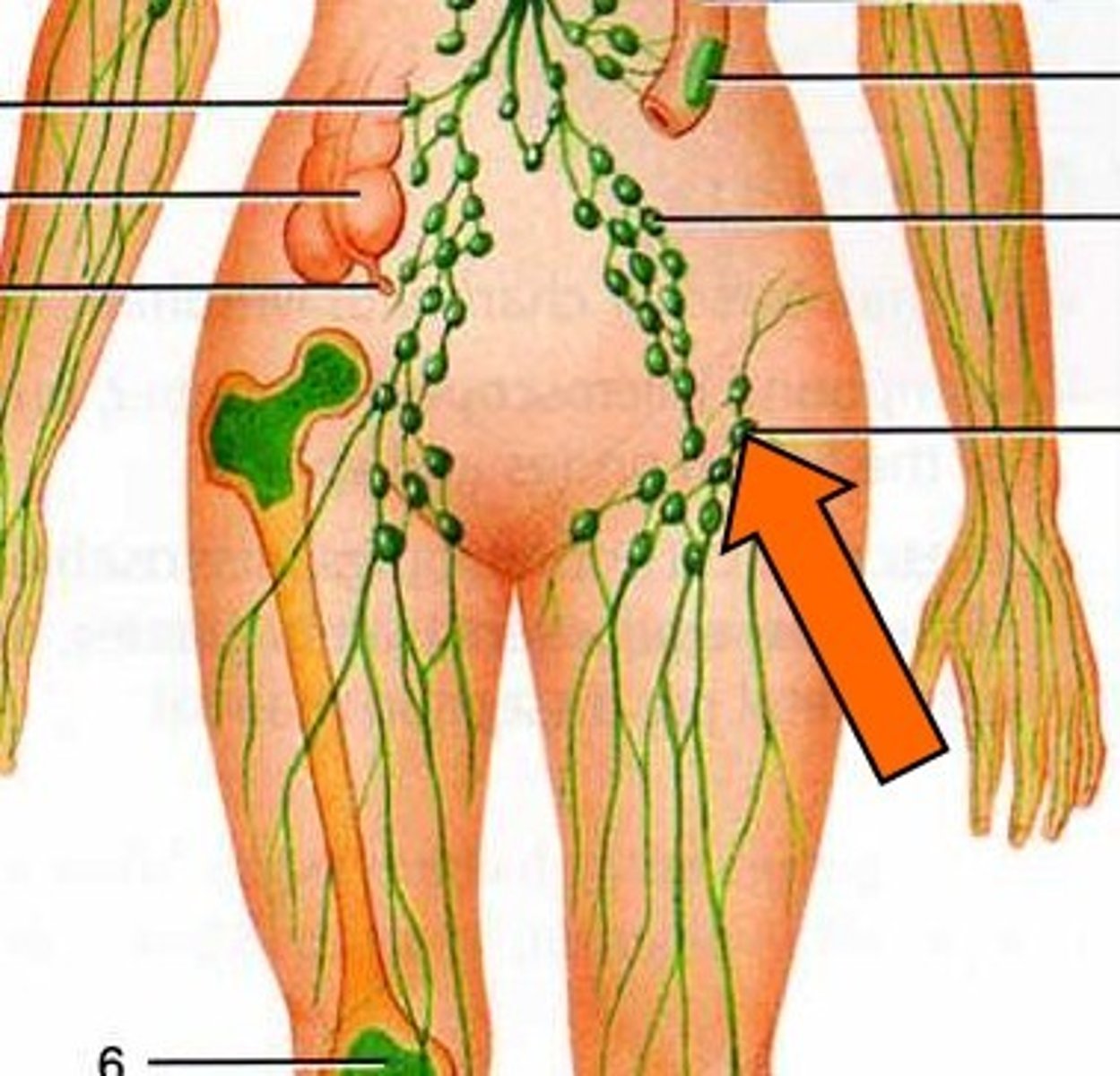
colourless fluid containing lymphocytes, which bathes the tissues and drains through the lymphatic system into the bloodstream
lymph
structures which remove fluid leaked into tissues from the bloodstream to be returned to the circulatory system
lymph vessel
swellings in the lymphatic system that trap antigens and present them to the lymphocytes for immune response
lymph node
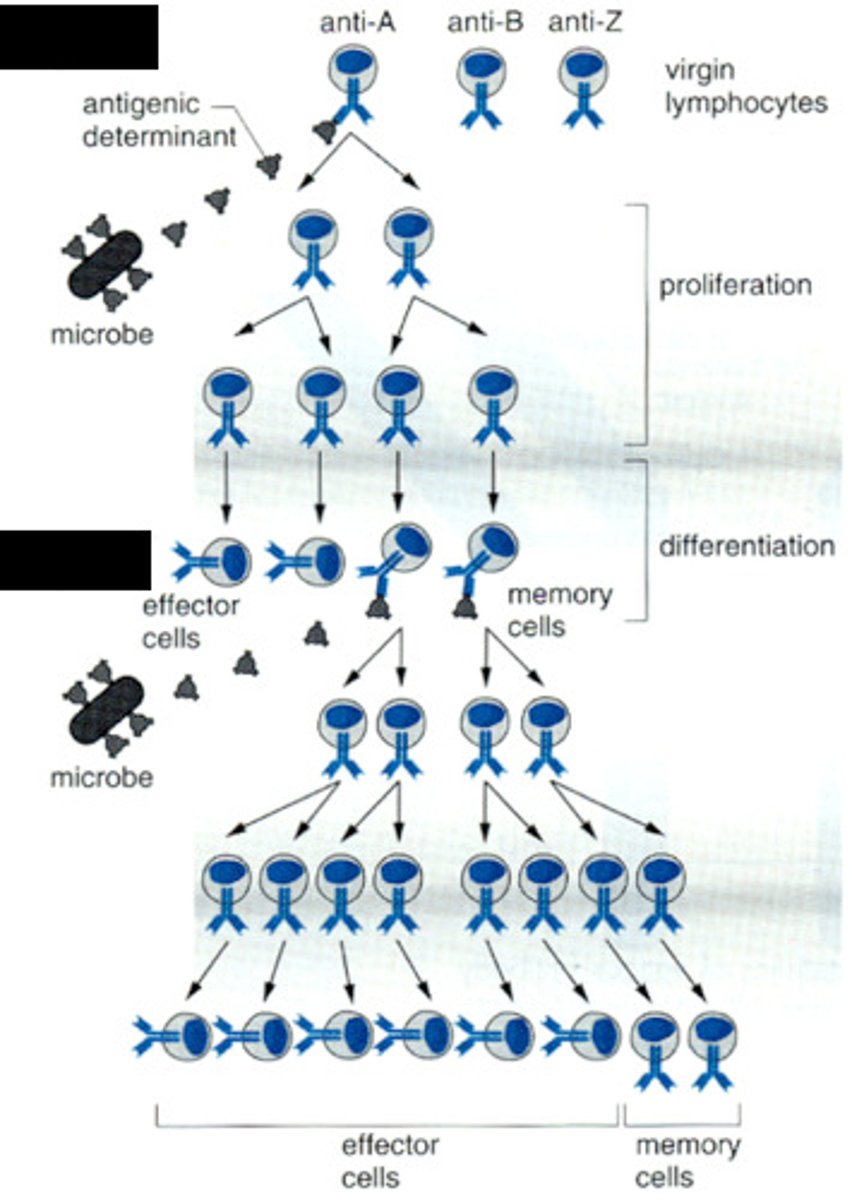
immune response which involves own immune system and creation of memory cells
active immunity
immune response and creation of memory cells are a result of exposure to a living pathogen
natural active immunity

immune response and creation of memory cells are a result of exposure to a non-living pathogen
induced active immunity

treatment with a deceased or inactive pathogen to produce immunity against a disease
vaccination
resistance to the spread of a contagious disease within a population which results in a high proportion of individuals being immune to the disease, especially through vaccination
herd immunity

protection from pathogens through the antibodies produced from another human or animal
passive immunity

protection from pathogens through the antibodies produced from another human or animal who were exposed to living pathogen
natural passive immunity

protection from pathogens through the antibodies produced from another human or animal who were exposed to a non-living pathogen
induced passive immunity

blood serum containing antibodies and is used to pass on passive immunity for many diseases
antiserum

harmless substance which causes an allergic reaction
allergen
immune response to an allergen
allergic response
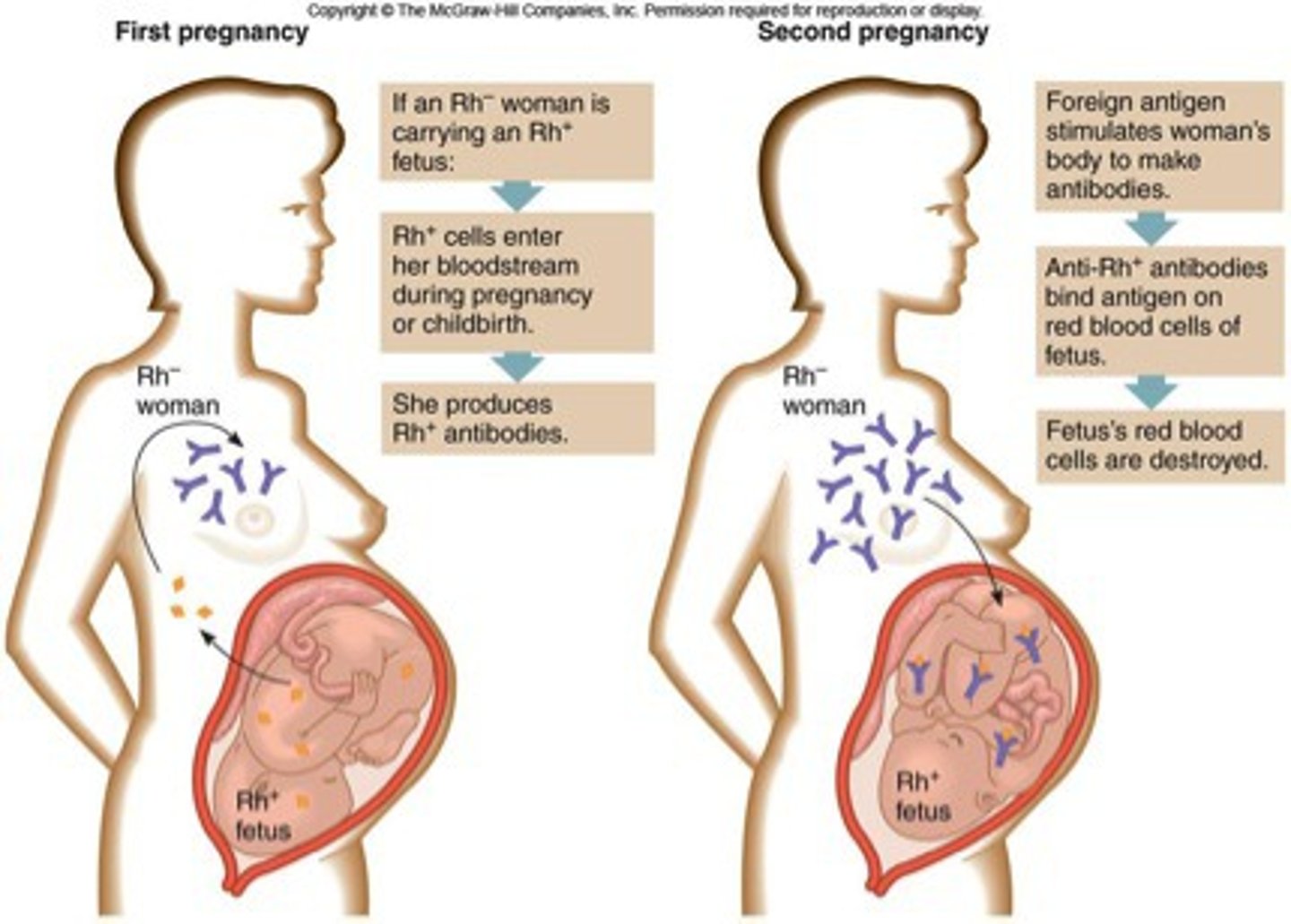
condition where mother has Rh- blood and child has Rh+ blood which can cause immune response against fetus
rhesus incompatibility
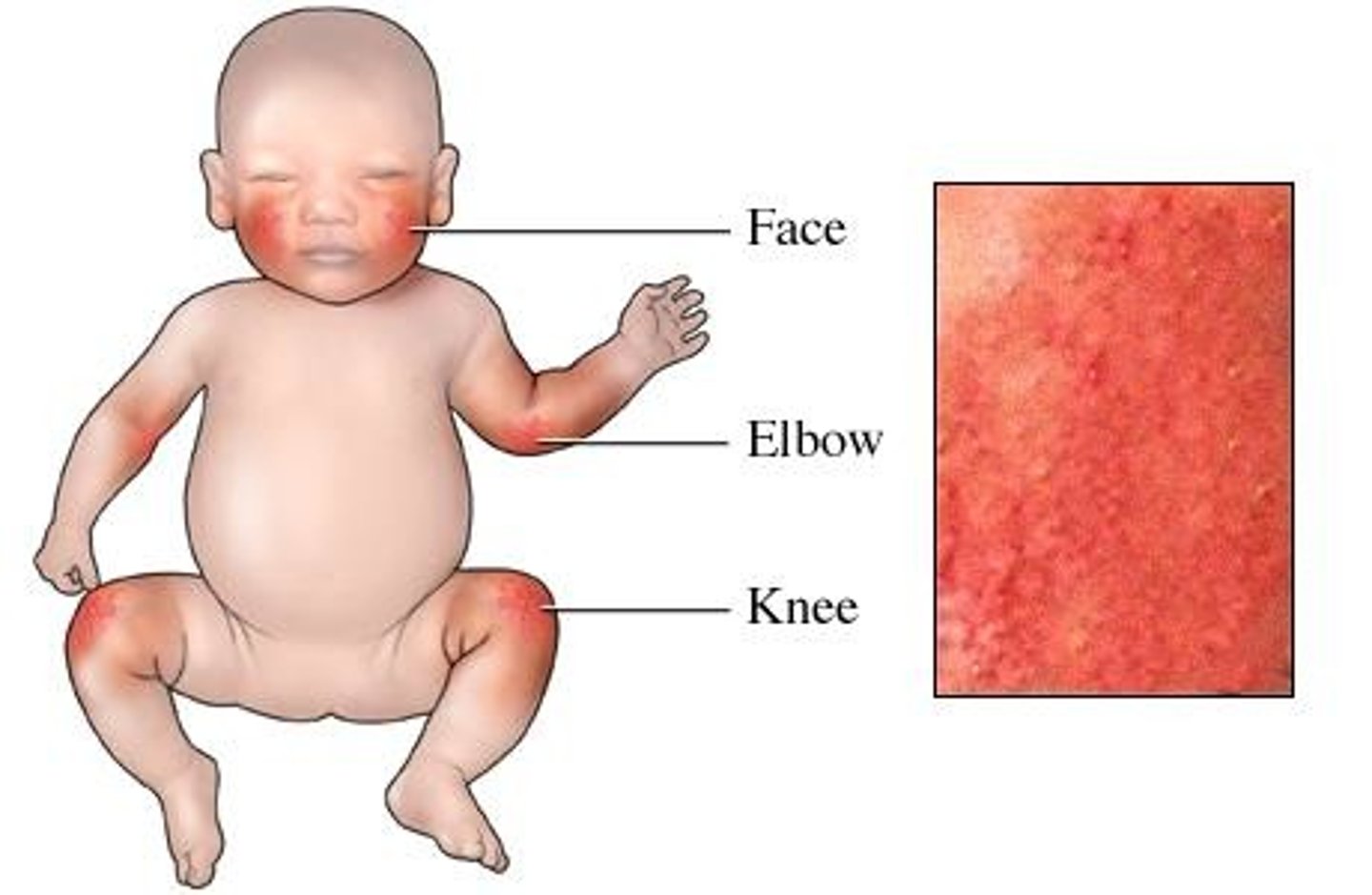
disease in which immune system recognises self as a non-self antigen, thus attacking it
autoimmune disease
when immune response overreacts and is highly sensitive to an harmless substance
hypersensitivity

failure of the immune system to protect the body from infection, due to the absence of immune response cells and mechanisms
immune deficiency disease
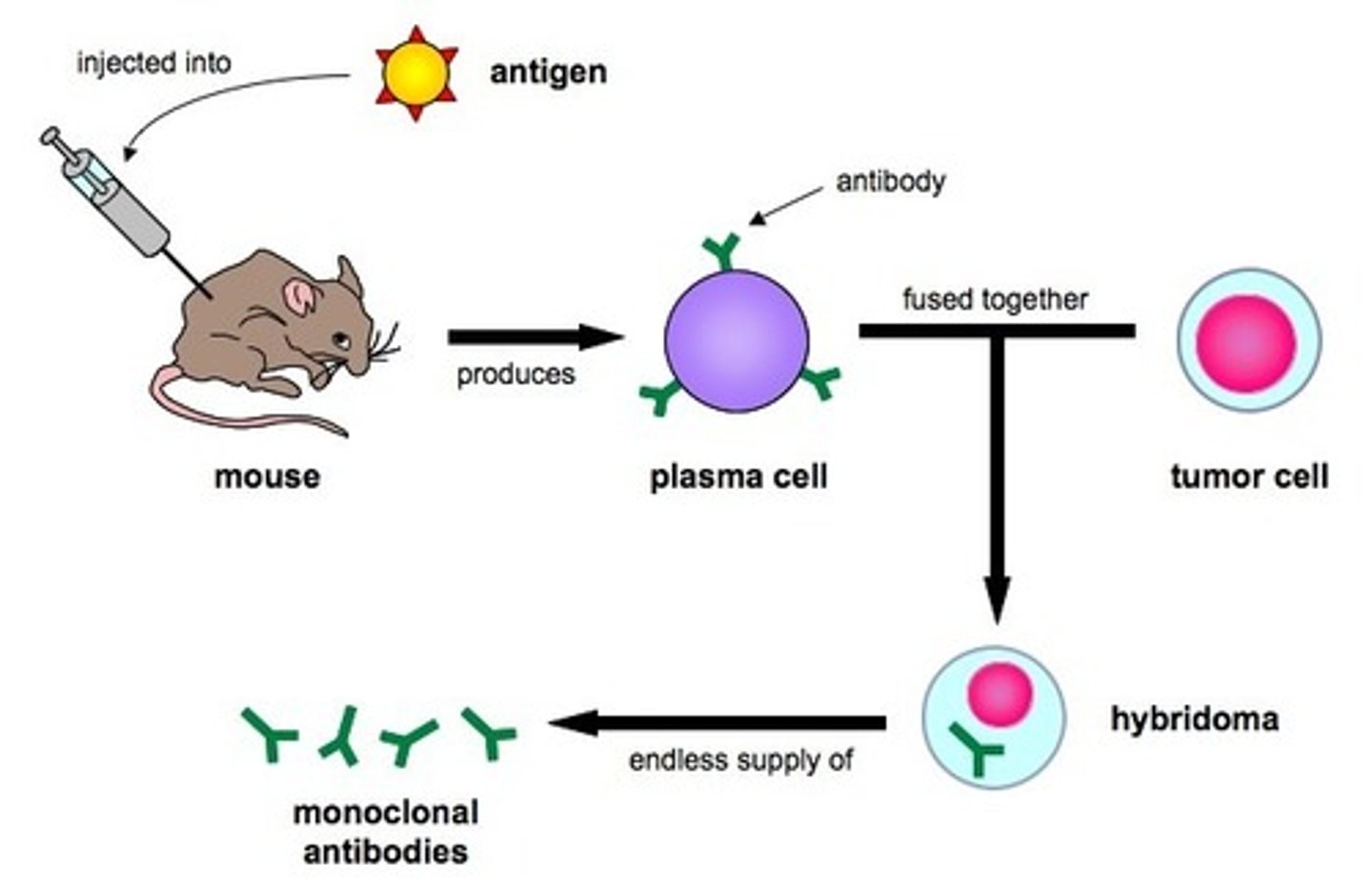
antibody produced by single clone of cells and consisting of identical antibodies
monoclonal antibody
Inflammation
Increased blood flow to damaged areas, increased permeability of blood vessels allows white blood cells to be attracted to the site.
Fever
Increase in body temperature to cause pathogen growth to slow and improves the inflammatory response.
Cytokines
Signaling molecules that indicate the presence of damage or of an invader triggering various responses from the immune system.
Interferons
A cytokine that is produced by virus infected cells signaling to the immune system the presence of a virus.
Complement Proteins
An array of blood proteins which can kill cells recognize as non-self.
Phagocytes
Large groups of white blood cells that engulf and digest foreign cells.
Natural Killer T cells
Detect infected or diseases body cells and release chemicals that cause the cell to lyse.
Neutrophils
A type of phagocyte that rapidly enter the cell and engulf the pathogen then die in large numbers. (pus is made up from the debris of neutrophils)
Mast cells
These cells produce and release histamines, they are found in the respiratory and gastrointestinal track.
Dendritic cells
Are phagocytes with membranous extensions that engulf pathogens, process them, then present them to other cells to allow for recognition to occur.
Antigen
A unique molecule or part of a molecule that initiates an immune response.
Self-antigen
A molecule that defines the cell as belonging to the organism.
Non-self-antigen
A molecule that is not recognised by the host cell as belonging.
Antibodies
Molecules produced by the lymphocytes to bind to specific antigens on pathogens preventing the action of the pathogen.
B lymphocytes (B - Cells)
They are capable of making antibodies when presented with a pathogen that they mark for engulfment and destruction by a phagocyte. They then activate and turn into plasma and memory cells.
Plasma Cells
Specialized to produce large amounts of antibodies to fight infection.
Memory B cells
They remember the antigens of the pathogens and respond to later infections. They live in the bone marrow. They are activated by b lymphocytes and produce antibody 'tags' to allow for the phagocytes to destroy the 'tagged' cell.
T lymphocytes (T - Cells)
Produced in the bone marrow and the thymus gland, they have antibody like molecules on their surface which bind with foreign antigens. There are 4 main types.
Helper T cells
Part of the T lymphocytes, they produce and release cytokines in response to antigens activation other immune cells.
Cytotoxic T cells
Part of the T lymphocytes, When stimulated they target foreign/infected cells and kill (lyse) them with lethal chemicals that they make.
Regulatory T cells
Part of the T lymphocytes, When the threat has passed they turn off or suppress the activity of the other cells.
Memory T cells
Part of the T lymphocytes, They have previously encountered and responded to the antigen, they can recognise foreign invaders and act like memory B cells. They do not 'tag' infected cells but signal effective killer T or cytotoxic cells to destroy the infected cell.