Chapter 10 Genetic Engineering
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Recombinant DNA technology
remove and combine gene into a different organism
A cloning host is usually a _____ or _____ that can ____ a gene and then ____ it into a protein.
bacterium, yeast, replicate, translate
What is the first step of recombinant DNA technology?
Gene inserted into plasmid
What is the second step of recombinant DNA technology?
Plasmid put into bacteria cell
What is the third step of recombinant DNA technology?
Host cell grown in culture
What is the fourth step of recombinant DNA technology?
Research and applications
What is involved in the first step of recombinant DNA technology?
restriction endonuclease, ligase
What is involved in the second step of recombinant DNA technology?
artificial transformation, competency
Restriction endonuclease
breaks bonds in DNA, creates sticky ends
What is the purpose of sticky ends?
join complementary DNA from other organisms
Ligase
seals plasmids back together
Artificial transformation
lab conditions that allow bacteria to take in DNA easily
Competence
ability of genes to cross plasma membrane
How do you make a gene more competent?
calcium chloride and heat shock
Transgenic plants
have DNA from other organism
BT gene
produce toxin to protect from caterpillars
Glyphosate resistance gene
protects food plants from specific herbicide
Glyphosate
herbicide kills weeds

What is shown in these images?
Argobacterium tumefaciens
Argobacterum tumefaciens causes what disease?
Crown-gall
Argobacterium tumefaciens is identified by what? What is this condition caused by?
tumor like growth, plasmid insertion
DNA profiling
specific DNA pattern obtained from person or sample
What are some examples of DNA profiling?
forensics, paternity, identifying human remains
List the 6 step procedure of DNA profiling.
collect sample, isolate DNA, cut fragments, replicate, separate and stain, analyze
Remember DNA profiling by:
CIC! RSA!
You can amplify DNA by PCR, which stands for ___ ____ ____. This _____ a segment of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of ____ of a particular ____ sequence.
polymerase chain reaction, amplifies, copies, DNA
How many steps are in the polymerase chain reaction cycle?
3
What are the steps of polymerase chain reaction?
Denaturation, priming, extending
In denaturation of PCR the DNA strands will _____, which causes what?
separate, exposes genes
Priming
DNA primers attach to 3’ end
During extending, the DNA polymerase is ____ ____ and extends the primers in a ? to ? direction.
heat stable, 5, 3

What is occurring in this step?
Denaturation
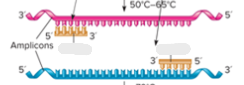
What is occurring in this step?
Priming
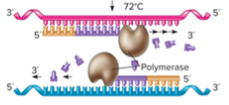
What is occurring in this step?
Extension
Thermocycler
amplifies DNA segments via PCR

What is this?
Thermocycler
Gel electrophoresis
separates DNA based on size

What is this device used for?
Gel electrophoresis
Where is the DNA sample placed in gel electrophoresis?
one end
In which direction do DNA molecules move in gel electrophoresis due to the current?
from negative to positive
What kind of fragments move the easiest through the gel matrix in electrophoresis?
shortest
DNA fragments appears as ____, each one is a collection of DNA molecules of the ____ length.
bands, same

The location of a band tells you what?
Fragment length

The width of a band tells you what?
Abundance

The shortest fragments travel the _____, the widest bands are the most ____.
fastest, abundant