2. Biological Classification
1/237
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Comprehensive Biology flashcards that you would need for IAT or NCERT! Revise only from the "Answer with Definition" option, for question types, choose only "Flashcards". I've included both ways. Let me know if you would like to change or add something!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
238 Terms
Who is the father of Biology?
Aristotle
Who coined the term “Biology”? In what year?
Lamarck and Treviranus in 1802.
Who is the father of Botany?
Theophrastus
Who is the Father of Zoology?
Aristotle
What is Classification?
An arrangement of living organisms according to their common characteristics and placing the group within taxonomic hierarchy.
What is Taxonomy?
The branch of science which deals with characterisation, identification, classification, and nomenclature of organisms is called taxonomy.
What is the meaning of Monophyletic?
One Ancestry
What is the meaning of Polyphyletic?
the organism derived from two ancestors
What is the meaning of Paraphyletic?
the organism does not include all the descendents of common ancestor.
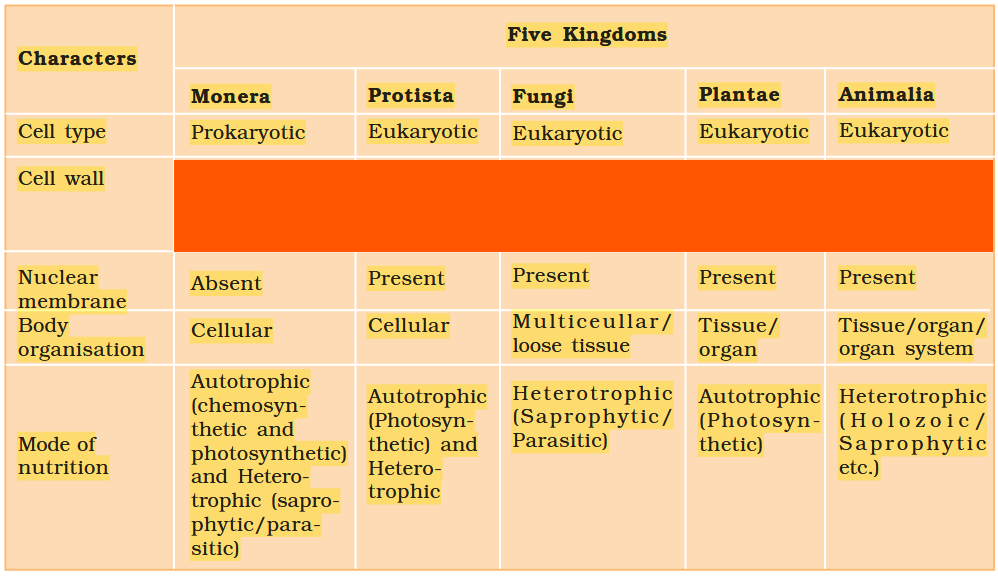
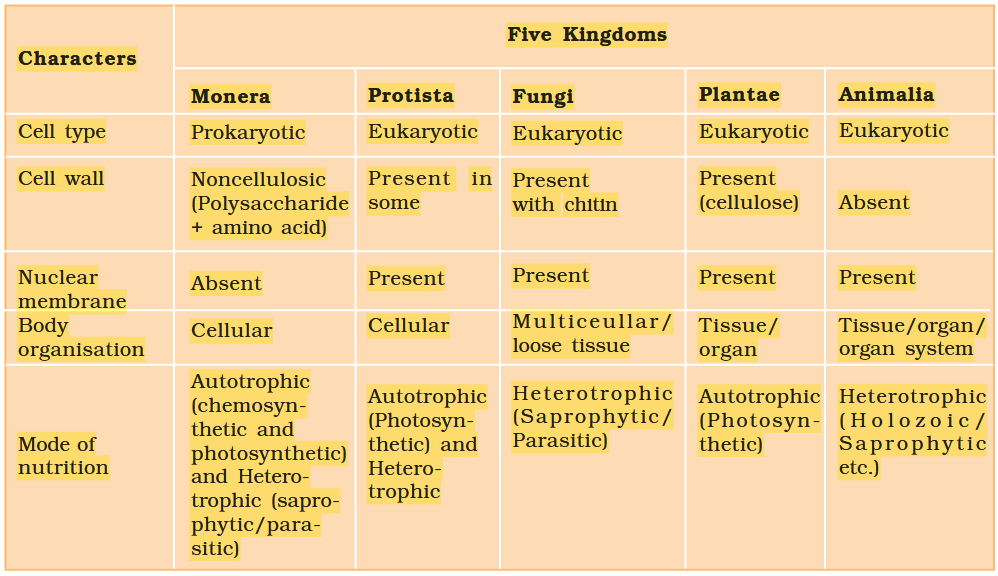
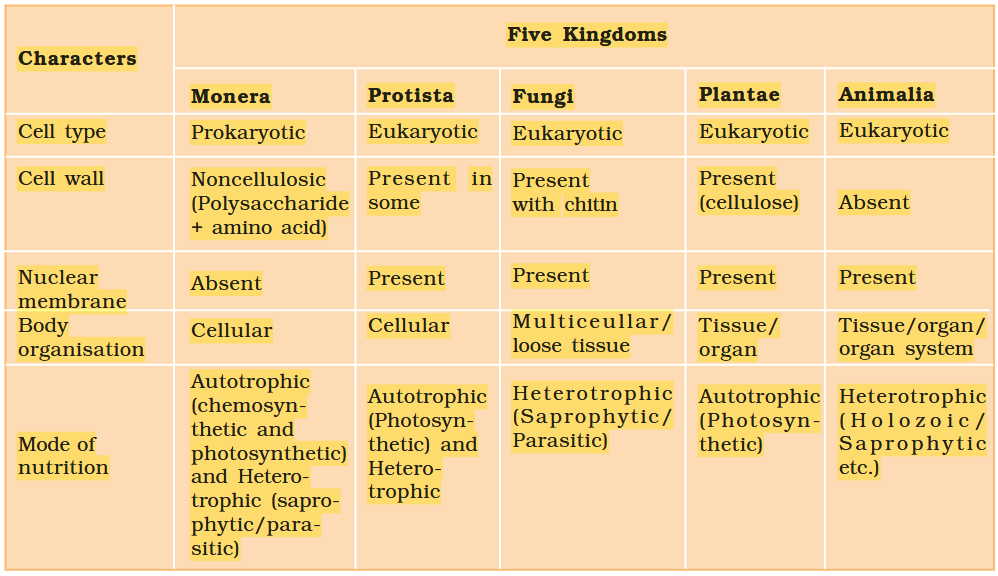
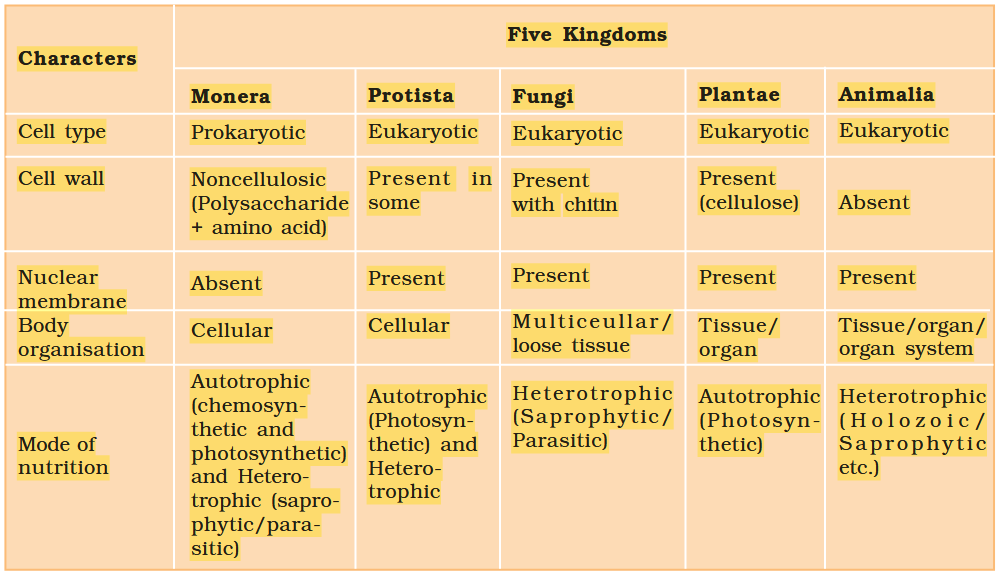
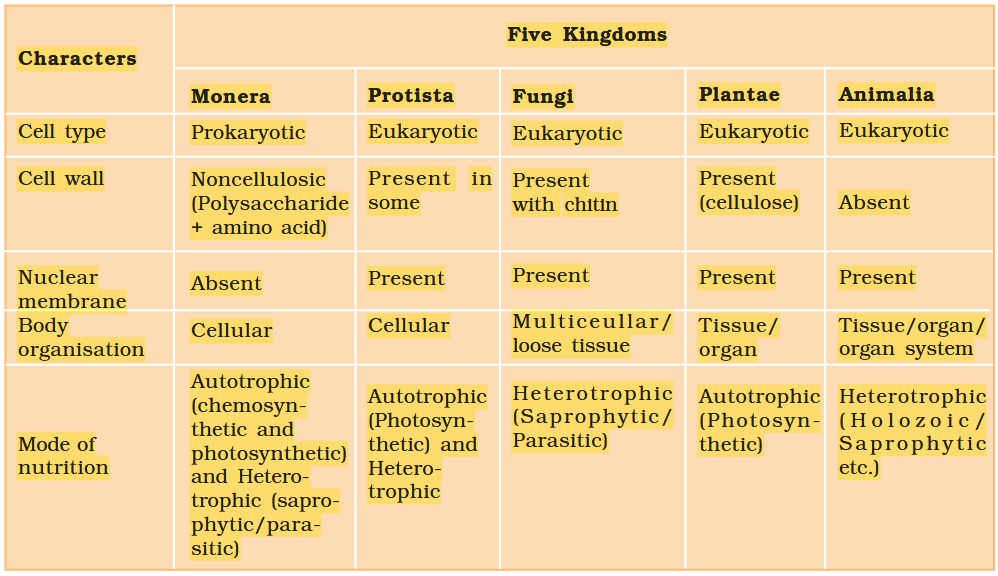
The Five-Kingdom Classification was proposed by?
RH Whittaker
What are the five kingdoms under Five-Kingdom Classification?
Monera
Protista
Fungi
Animalia
Plantae
The Two-Kingdom Classification was proposed by?
Carolus Linnaeus
What was the basis of the Two-Kingdom Classification?
Based on presence or absence of cell wall.
What were the merits of Two-Kingdom Classification?
Photosynthetic organisms were included into plant kingdom and non-photosynthetic organisms were included into animal kingdom.
What were the demerits of Two-Kingdom Classification?
Some organisms do not fall naturally either into plant or animal kingdom or share characteristics of both.
Who proposed the Three-Kingdom Classification?
Ernst Haeckel
What were the three kingdoms under Three-Kingdom Classification?
Animalia
Plantae
Protista
What were the merits of Three-Kingdom Classification?
Created a third kingdom which includes unicellular eukaryotic microorganisms and some multicellular organisms.
What were the demerits of Three-Kingdom Classification?
Monerans were not placed correctly.
Who proposed the Four-Kingdom Classification?
Copeland
What were the four kingdoms under Four-Kingdom Classification?
Monera
Protista
Animalia
Plantae
What were the merits of Four-Kingdom Classification?
Monerans were placed separately along with other kingdoms.
What were the demerits of Four-Kingdom Classification?
Monerans were not subdivided in Archaebacteria and Eubacteria.
Who proposed Six-Kingdom Classification?
Carl Woese
What are the six kingdoms under Six-Kingdom Classification?
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Protista
Fungi
Animalia
Plantae
What were the three domains under the Three-Domain (Six-Kingdom) Classification?
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Eukarya
What are the merits of the Six-Kingdom Classification?
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria were separately placed.
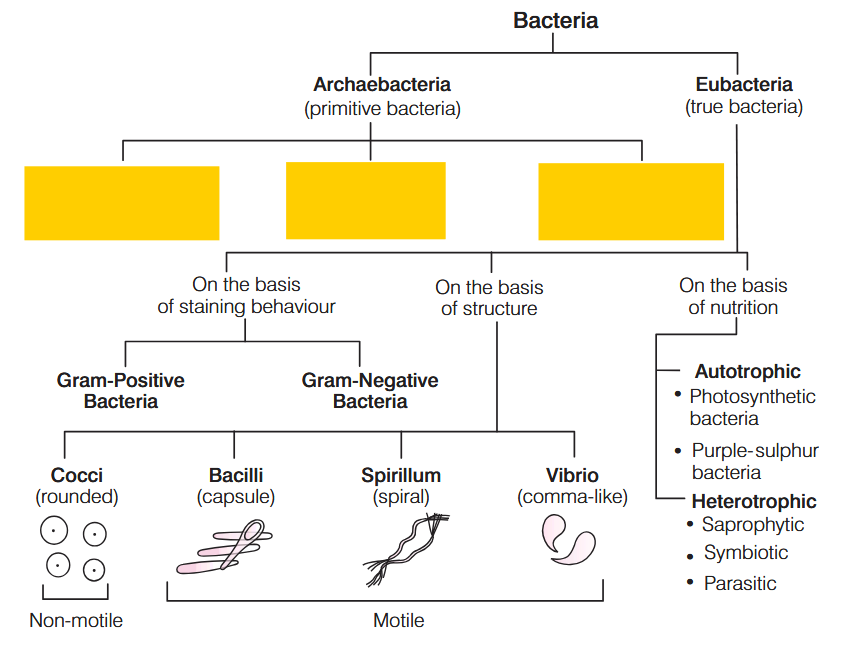
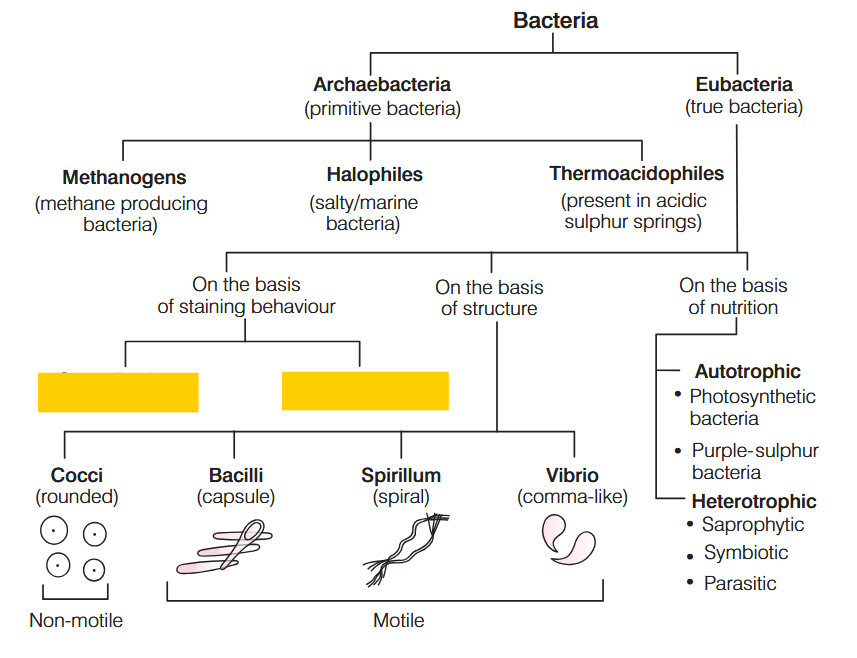
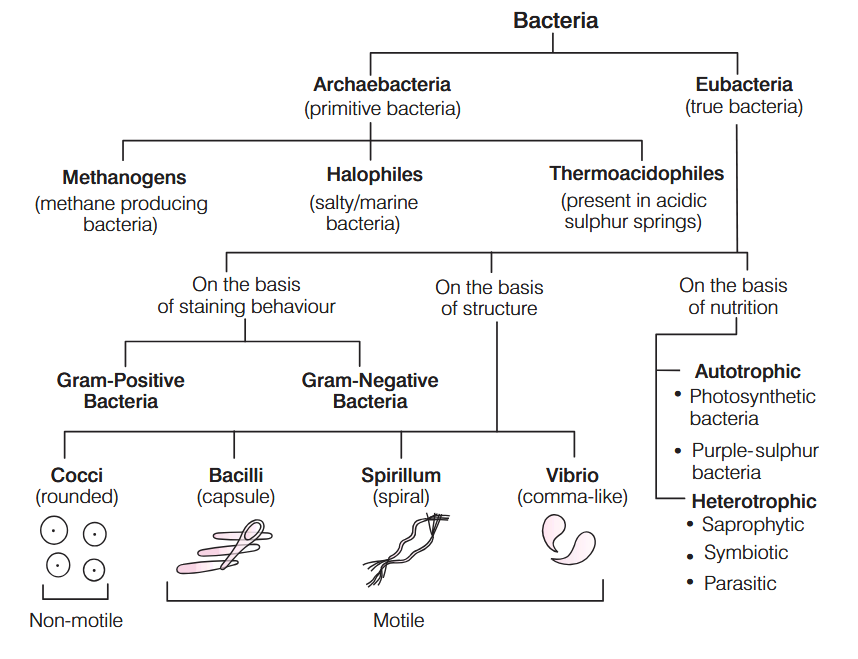
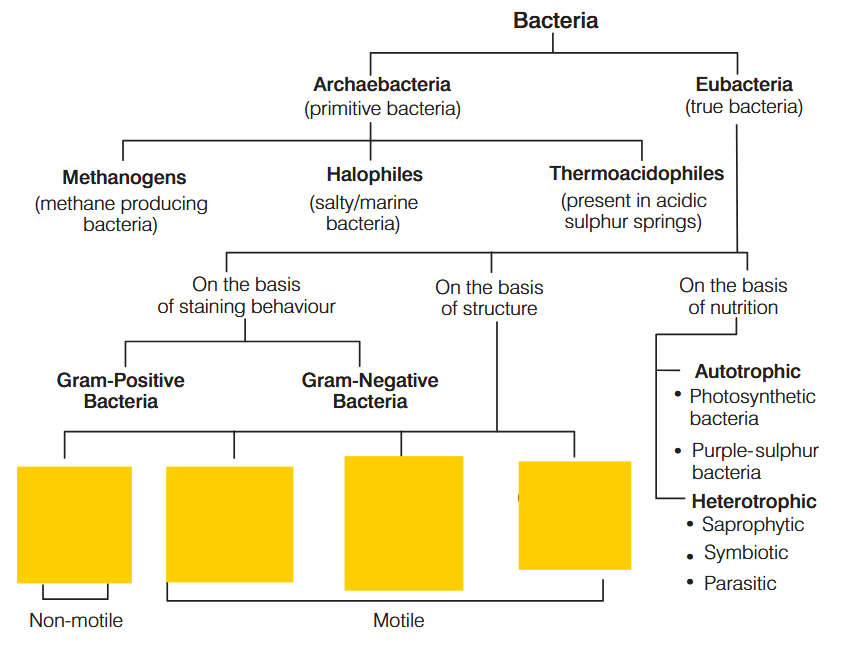
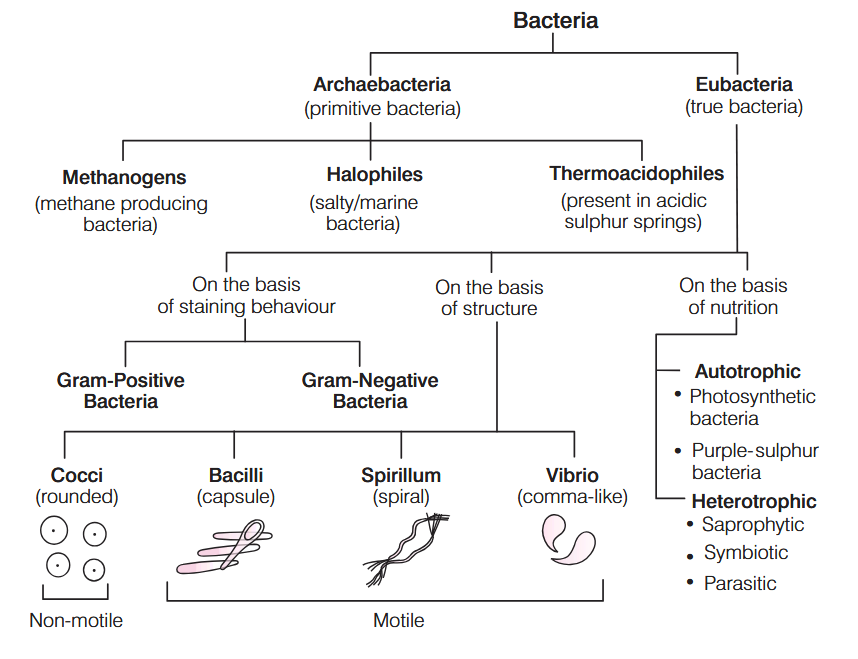
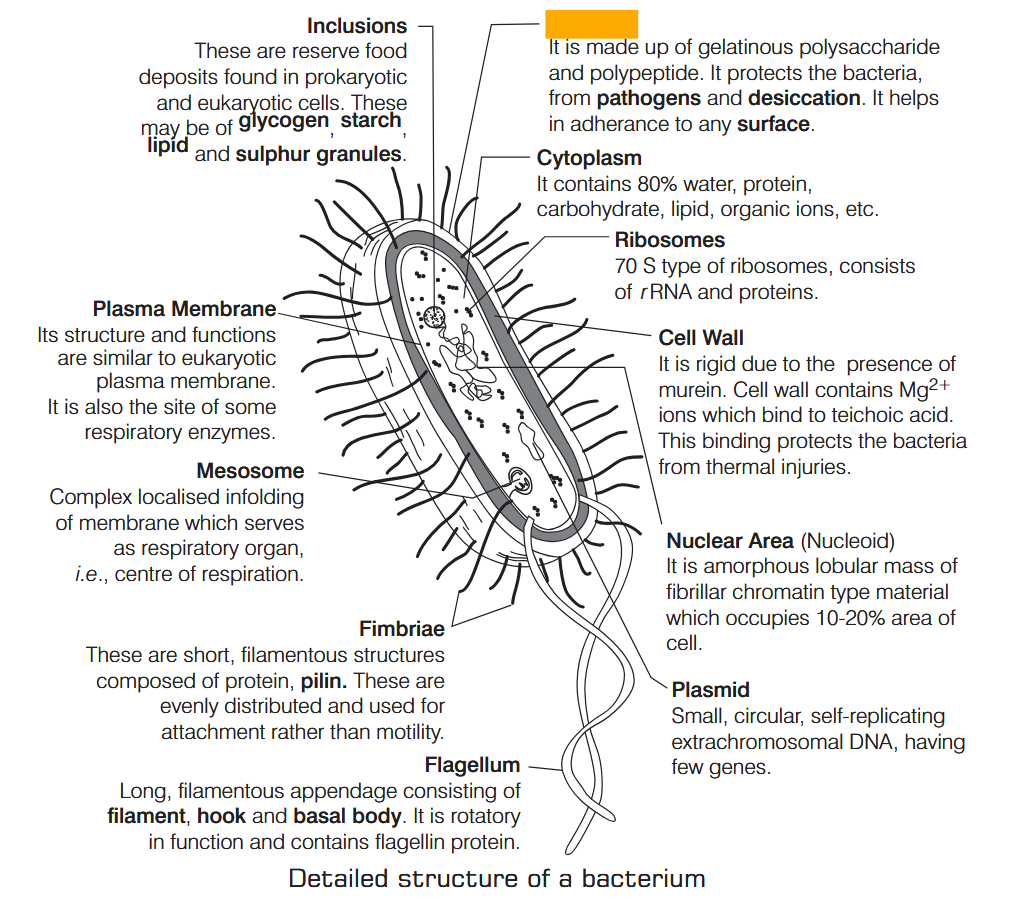
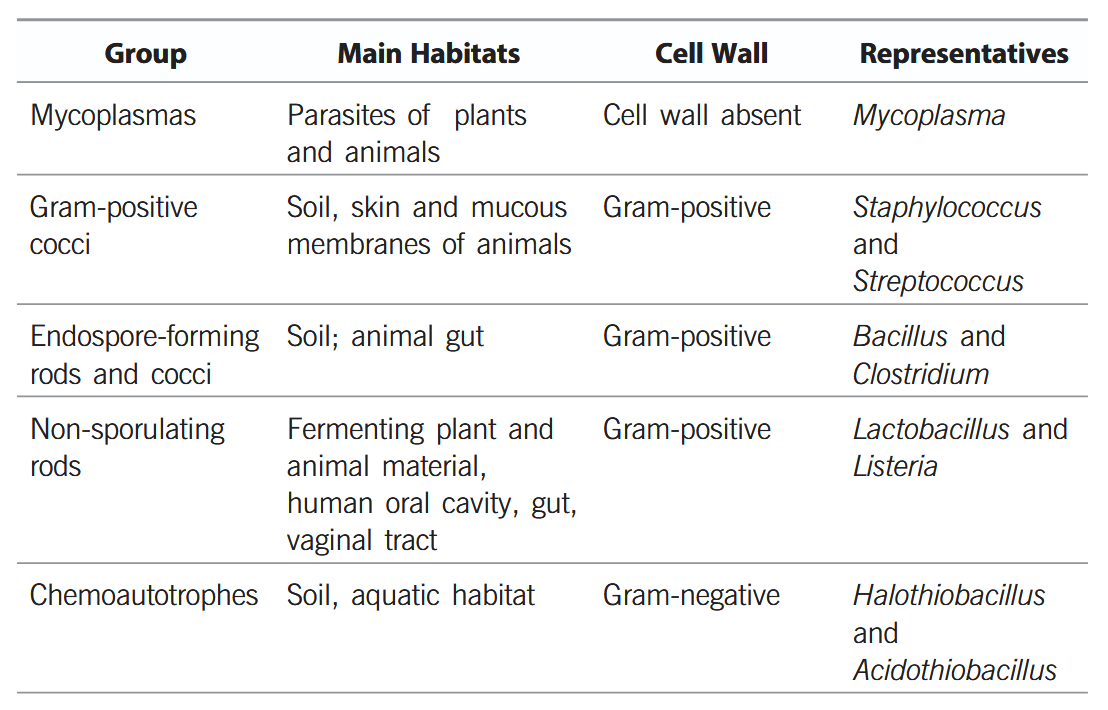
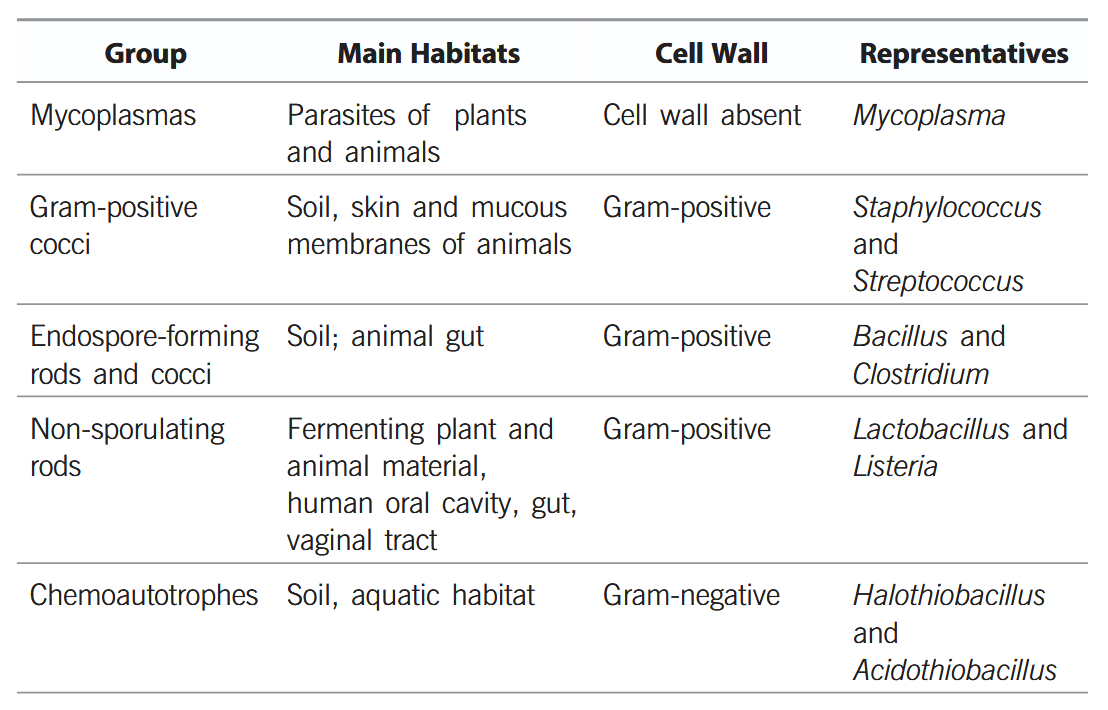
What is the characteristic of Kingdom Monera?
Prokaryotic, Unicellular Organisms
Bacteria do not contain cell wall. True or false?
False, bacteria DO contain cell wall.
Theee are approximately ______ species of bacteria, with cosmopolitan occurrence.
4000
An average weight human (~ 70 kg) has about _____ kg of bacteria in the form of gut microflora to supplement the proper digestion and other metabolic functions.
2.5
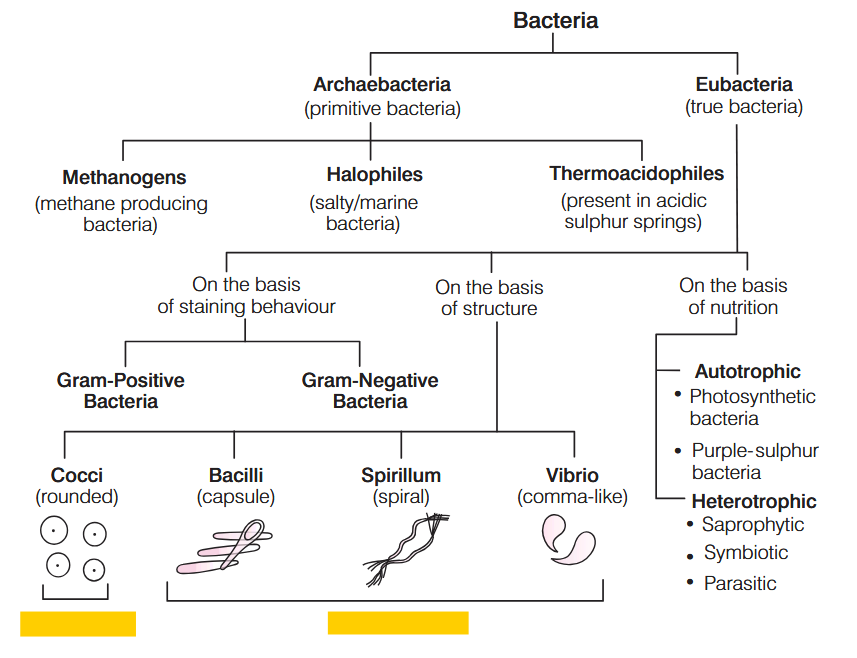

Archaebacteria have a cell wall made up of:
protein and non-cellulosic polysaccharides.
(pseudo-murein)
How does the cell wall in archaebacteria differ from other cell walls?
Most cell walls have ester-linkage, but cell walls in archaebacteria have ether-linkage.
Cell walls in archaebacteria also have branched lipids
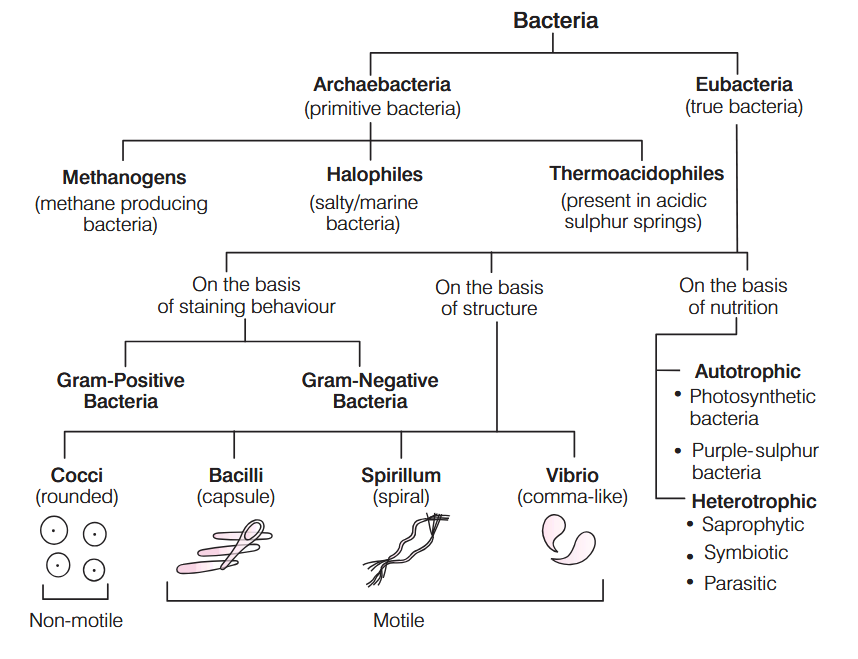
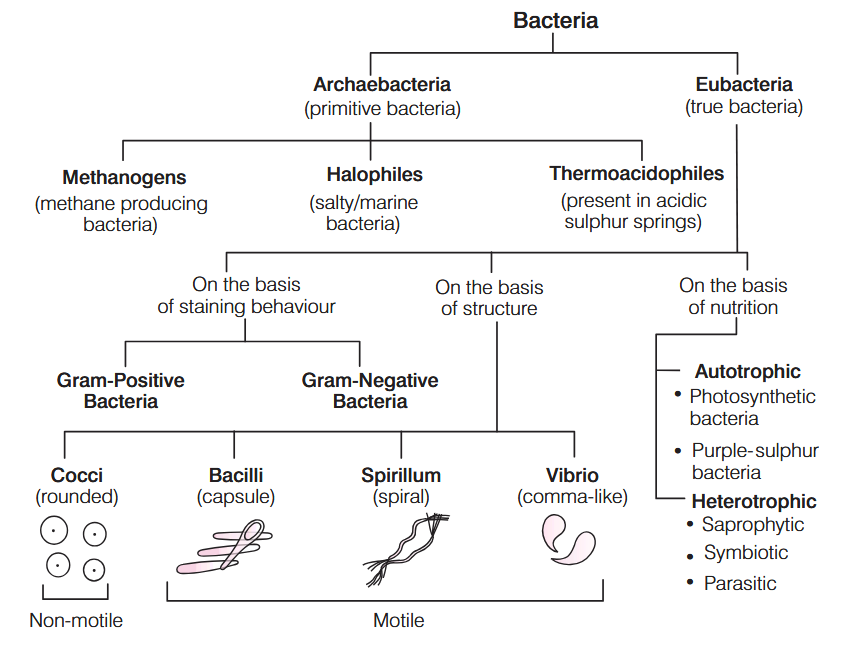
Which bacteria help in the production of biogas?
Methanogens
Where are methanogens found?
in marshy areas
in guts of people/cows/whatever
Archaebacteria are the group of most primitive prokaryote. True or false?
true.
What makes Archaebacteria a unique subsection of Bacteria?
The presence of 16 srRNA, makes them unique and helps in placing in a separate domain called archaea between bacteria and eukarya.
Archaebacteria are also known as __________, because they represent the earliest form of life on earth.
living fossils
Why are archaebacteria known as living fossils?
because they represent the earliest form of life on earth.
Name three things Archaebacteria can be used for.
Experimentation for absorption of solar radiation.
Production of gobar gas from dung and sewage.
Fermentation of cellulose in ruminants.
Why are Eubacteria known as “true bacteria”?
Eubacteria are ‘true bacteria’ which lack nucleus and membrane bound organalles like mitochondria, chloroplasts, etc.
What is the mode of nutrition of cyanobacteria?
they are photosynthetic autotrophs
Why are cyanobacteria photosynthetic autotrophs?
they have chlorophyll-a pigment similar to plants
What habitats are cyanobacteria found in?
freshwater/marine/terrestrial
What are heterocysts?
specialised cells in cyanobacteria that fix nitrogen
why do heterocysts have thick cell walls?
To prevent oxygen from entering the cells, as the enzyme nitrogenase is sensitive to oxygen
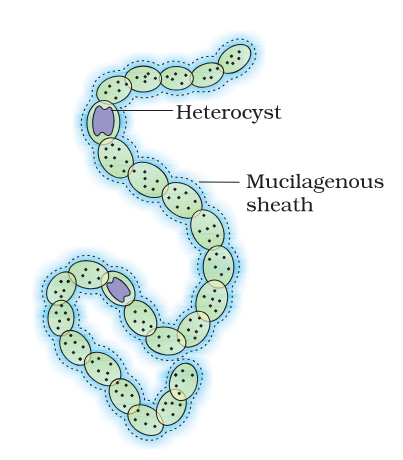
What is this organism called?
Nostoc
Imagine a diagram of Nostoc
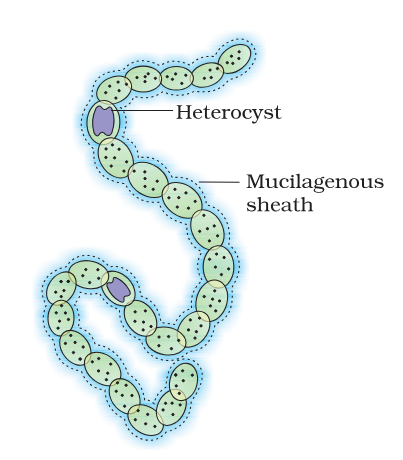
Which two cyanobacteria contain heterocysts?
anabaena
nostoc
How do saprophytic bacteria contribute to nutrient cycling?
they break down organic matter into smaller compounds
they oxidise aforementioned smaller compounds, using the energy released for themselves and letting the byproducts (nutrients) release into the soil
the nutrients in the soil are then used by other plants when growing
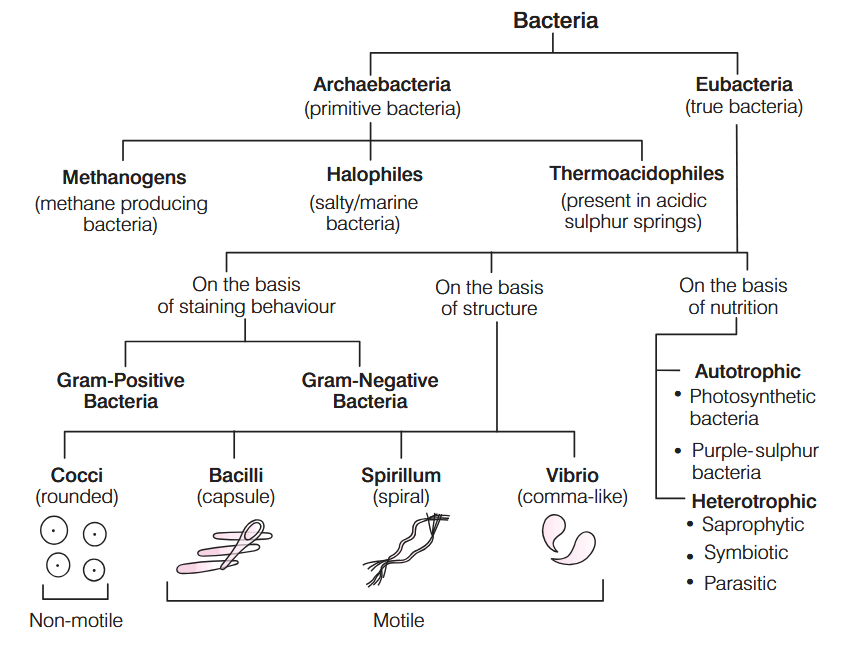
What are these bacteria called?
cocci
imagine cocci
What are these bacteria called?
bacilli
imagine bacilli
what are these bacteria called?
spirilla
imagine spirilla

what are these bacteria called?
vibrio
imagine vibrio

name 4 diseases caused by heterotrophic eubacteria
Cholera
Typhoid
Citrus Canker
Tetanus
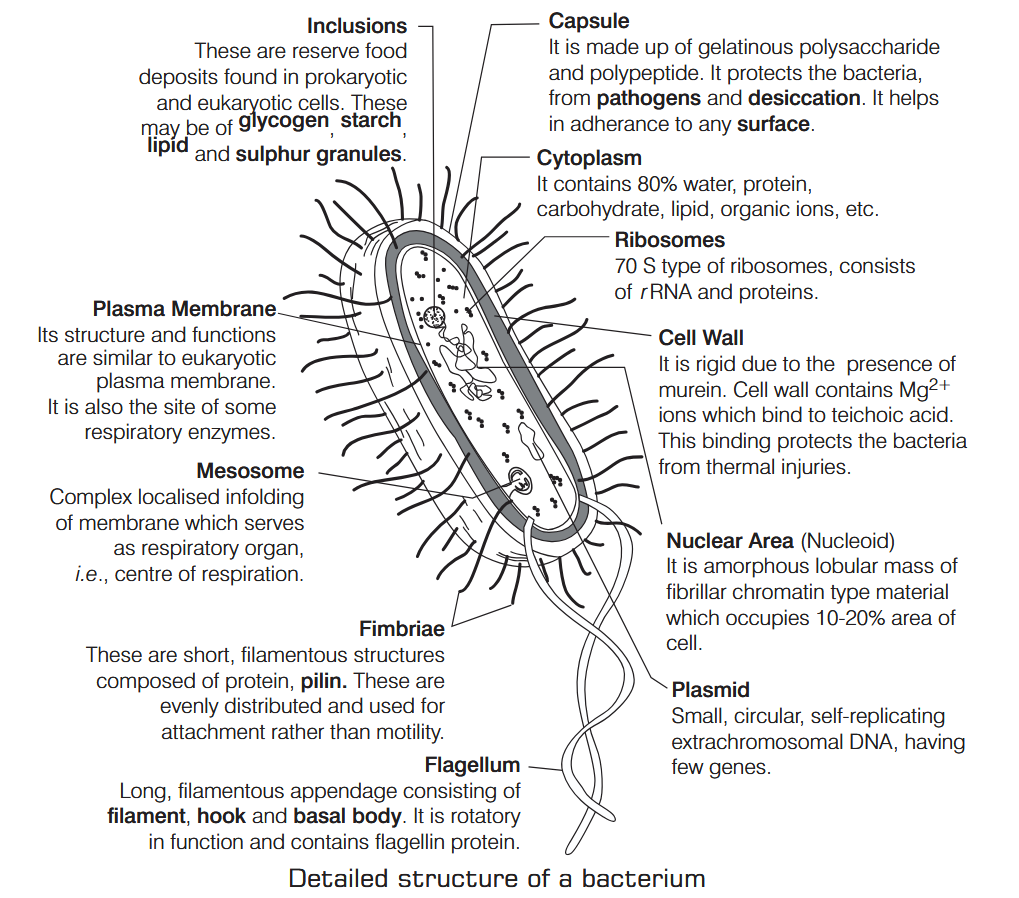
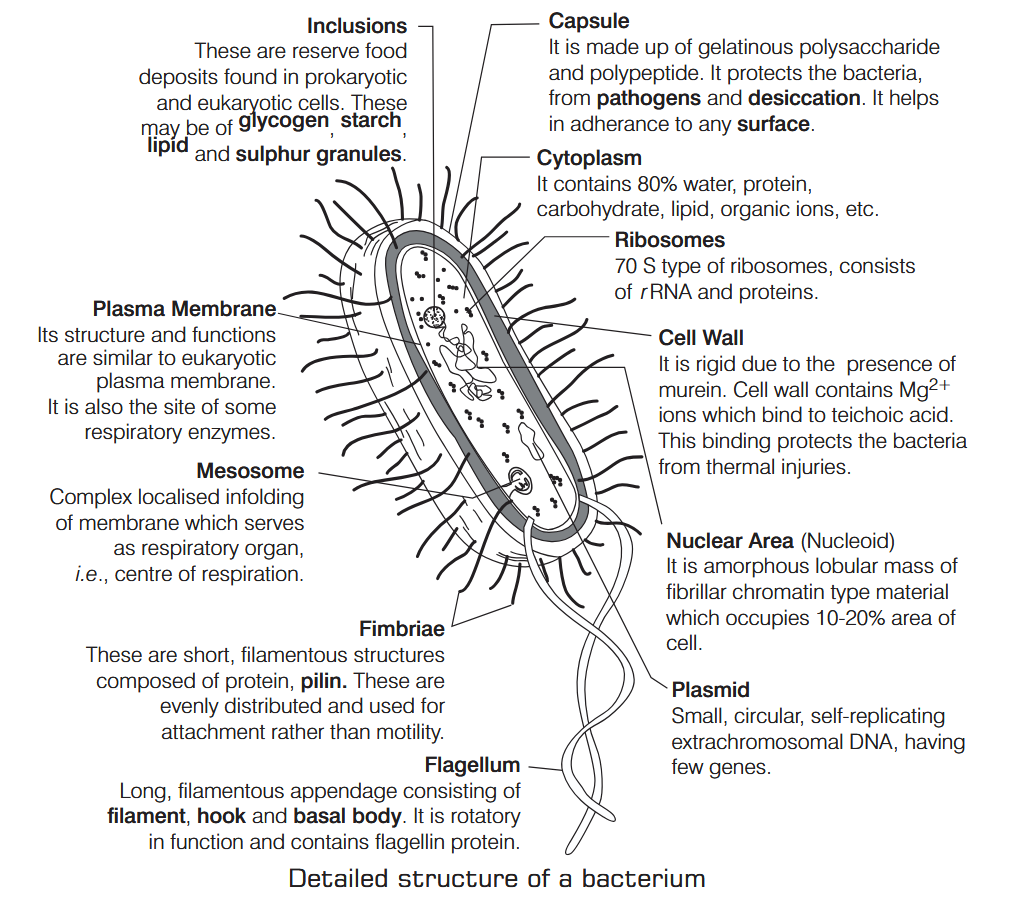
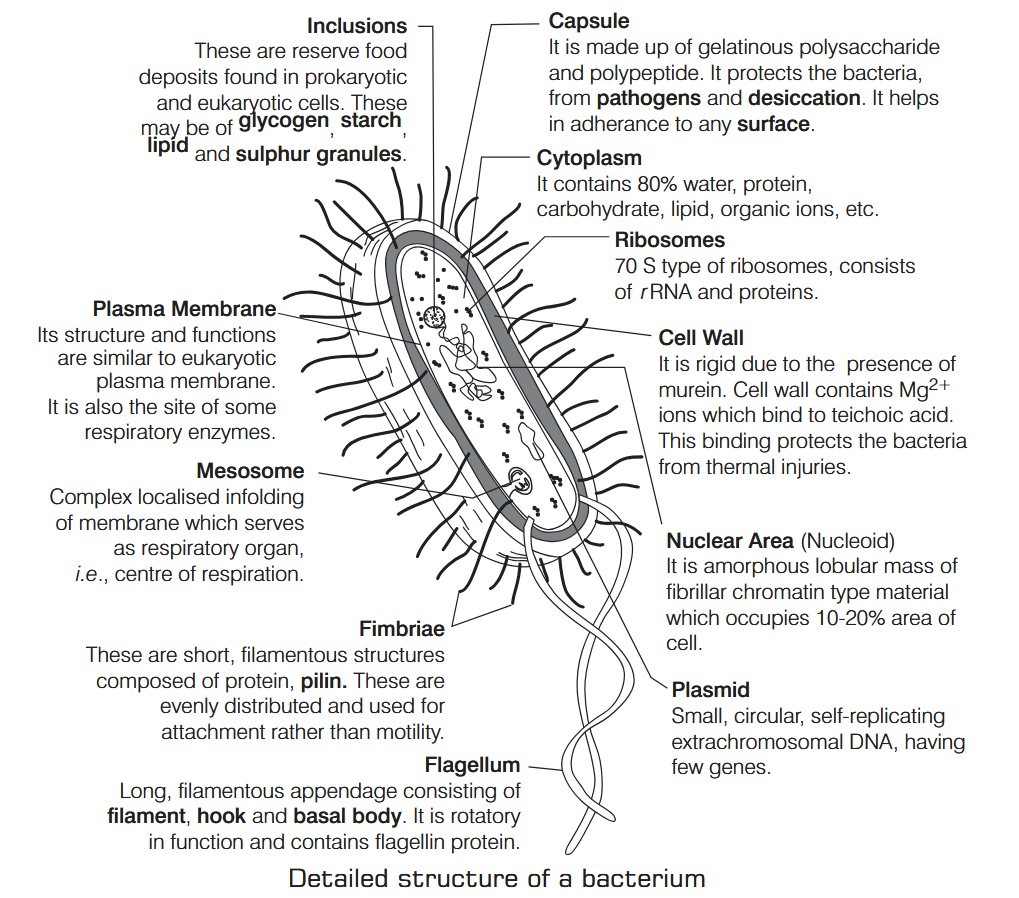
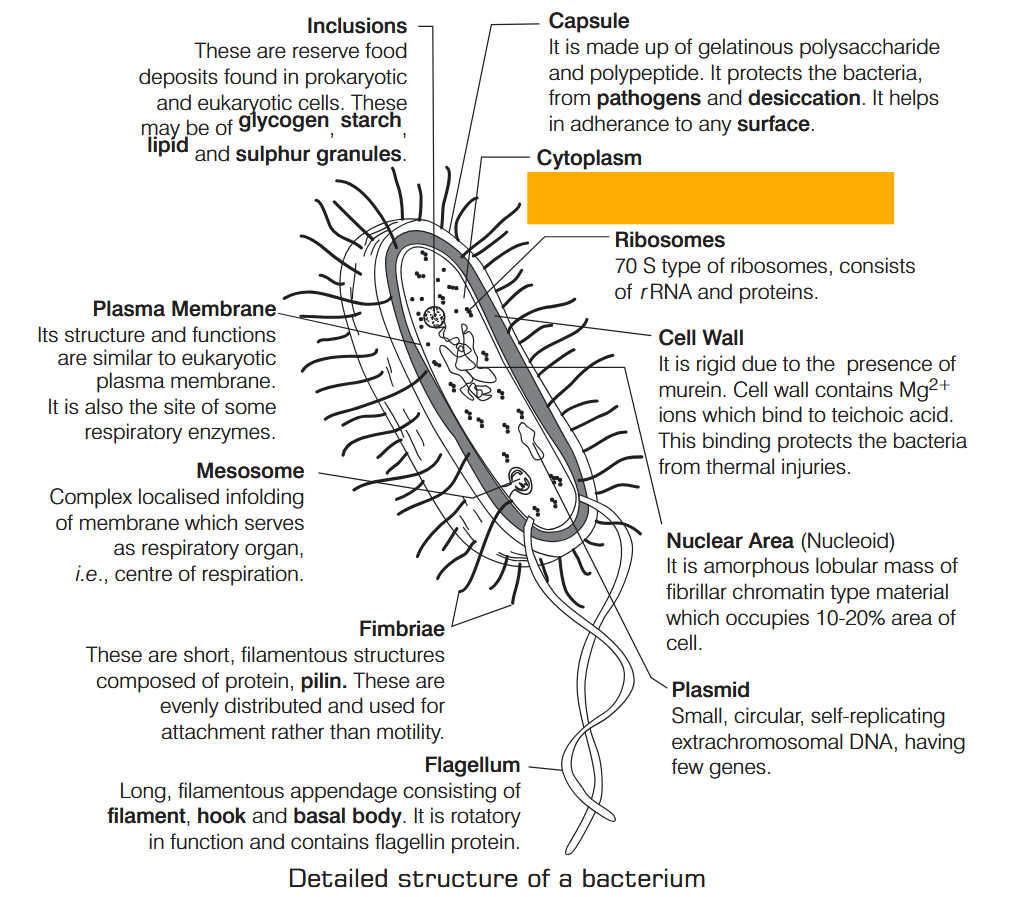
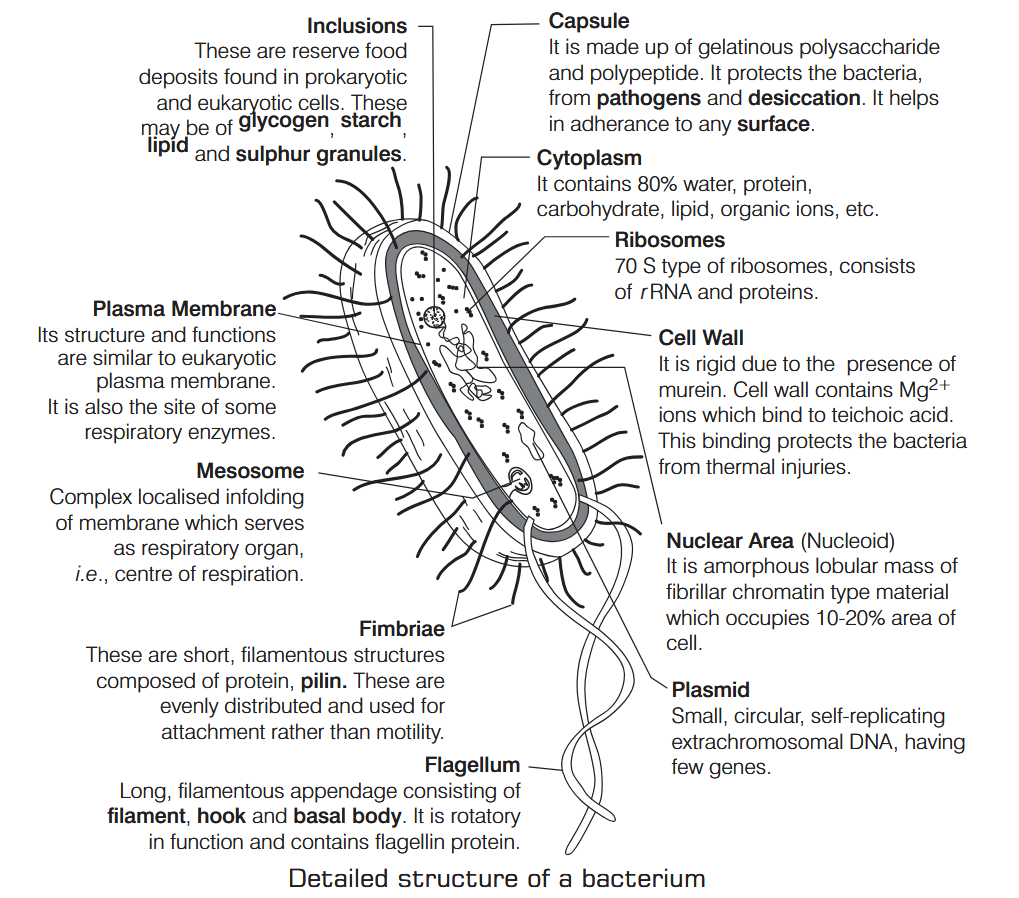
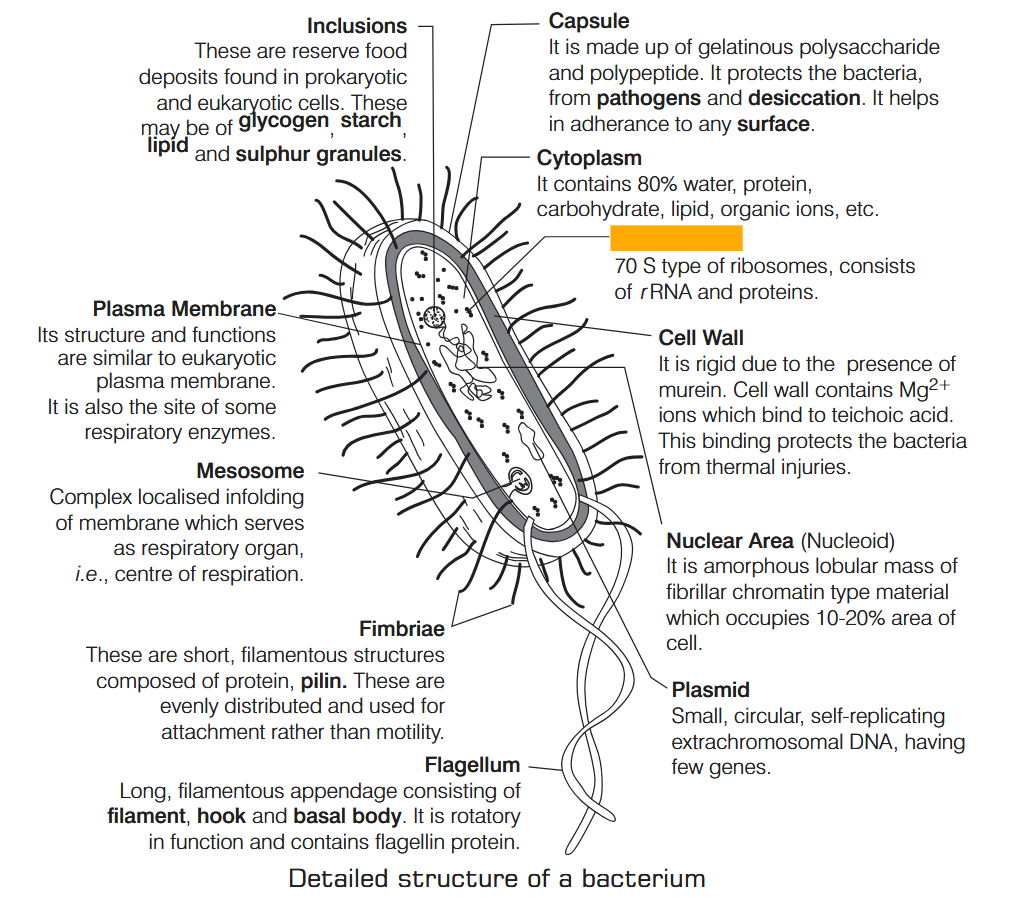
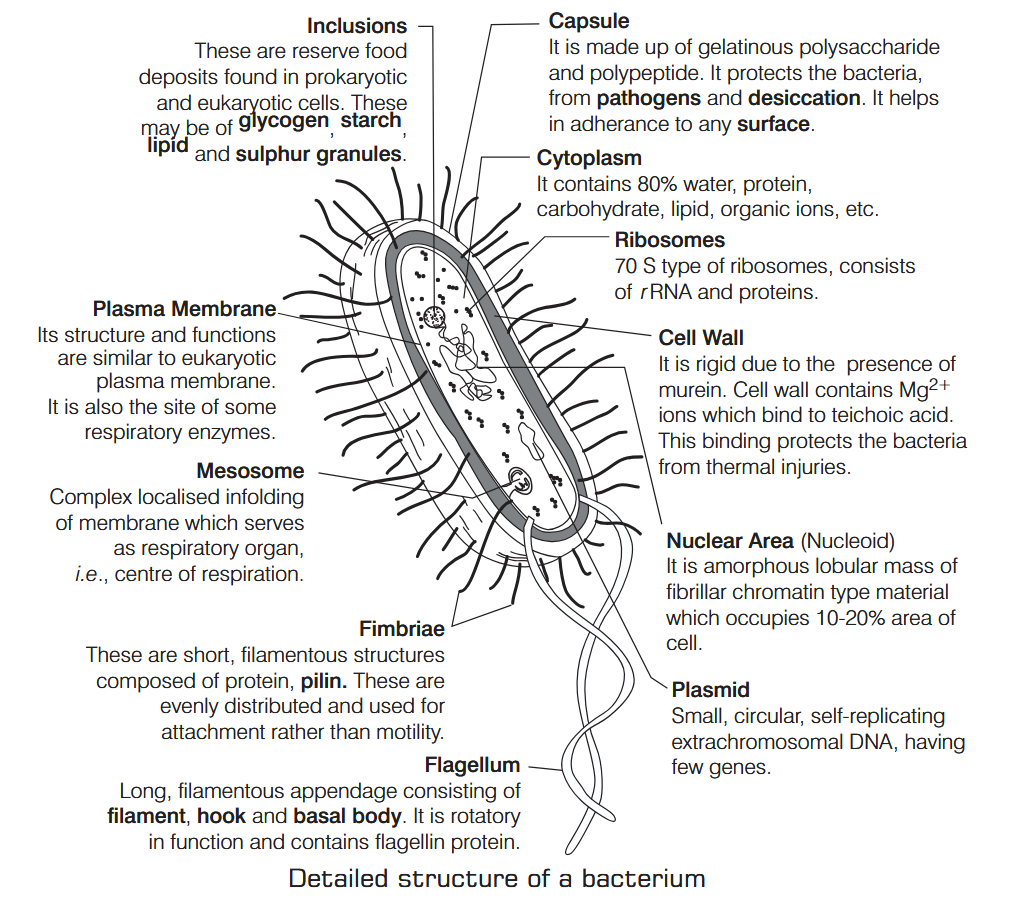
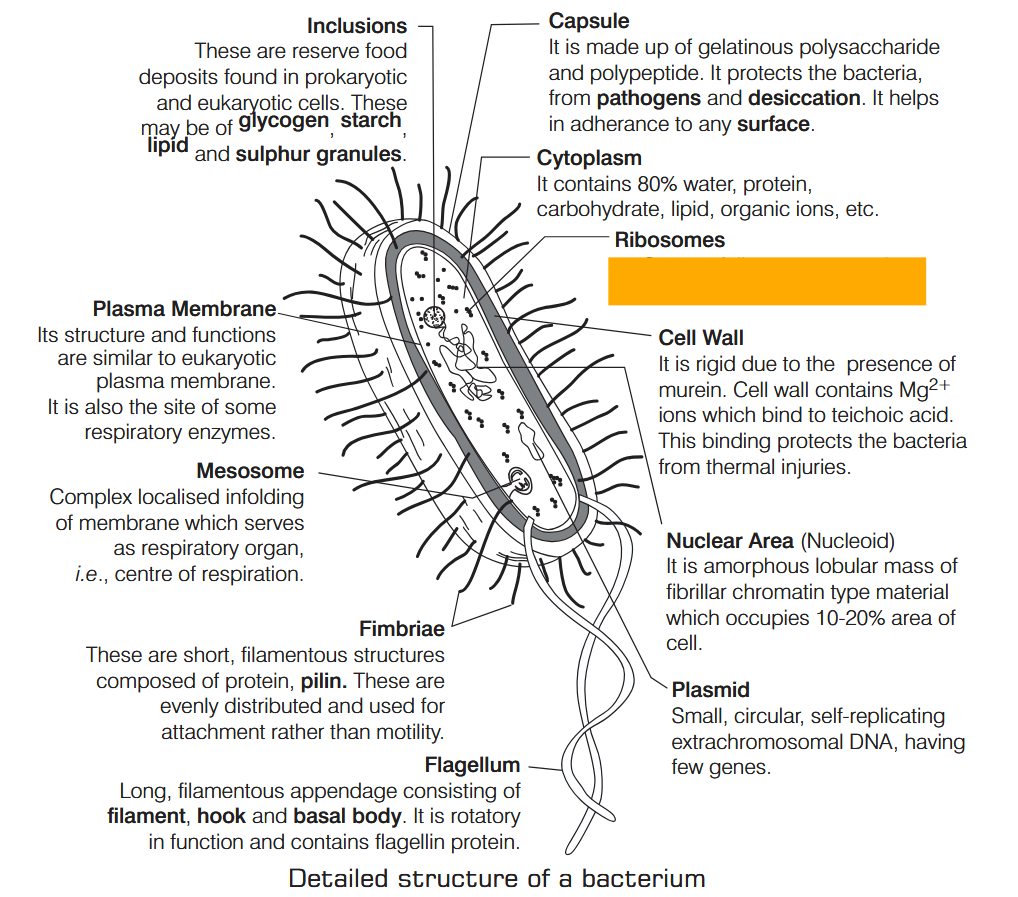
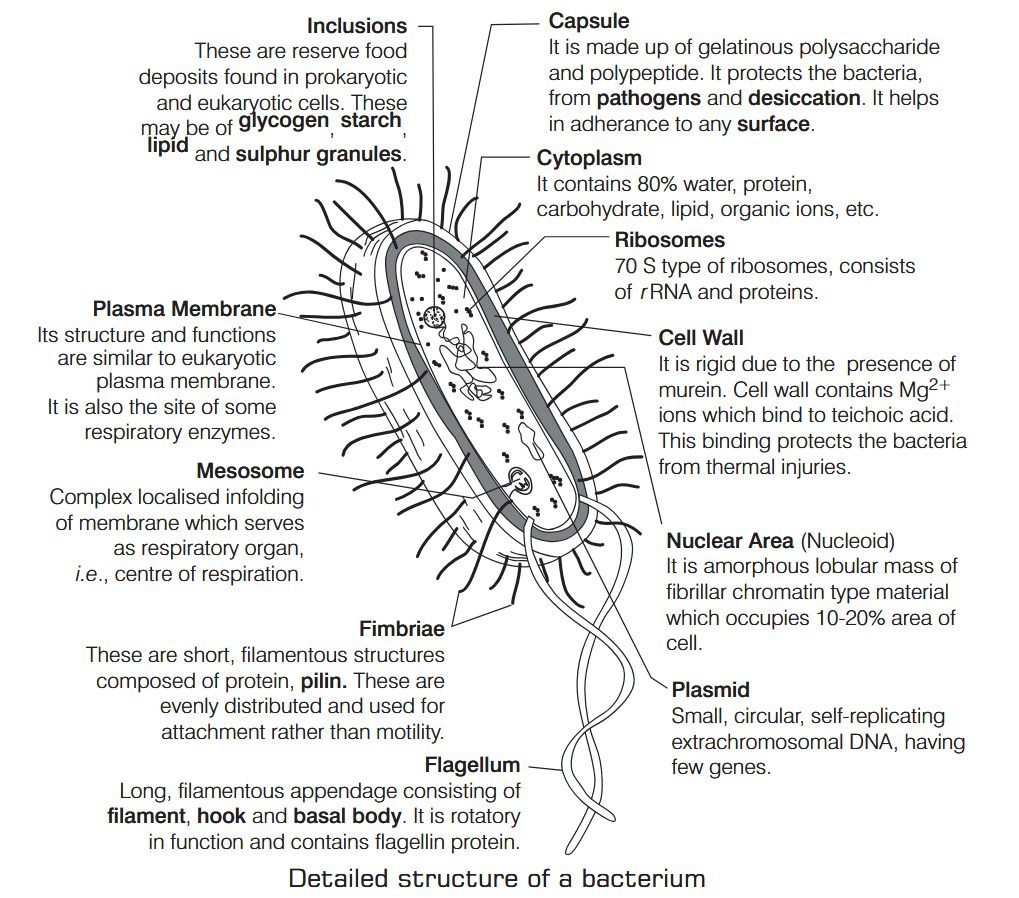
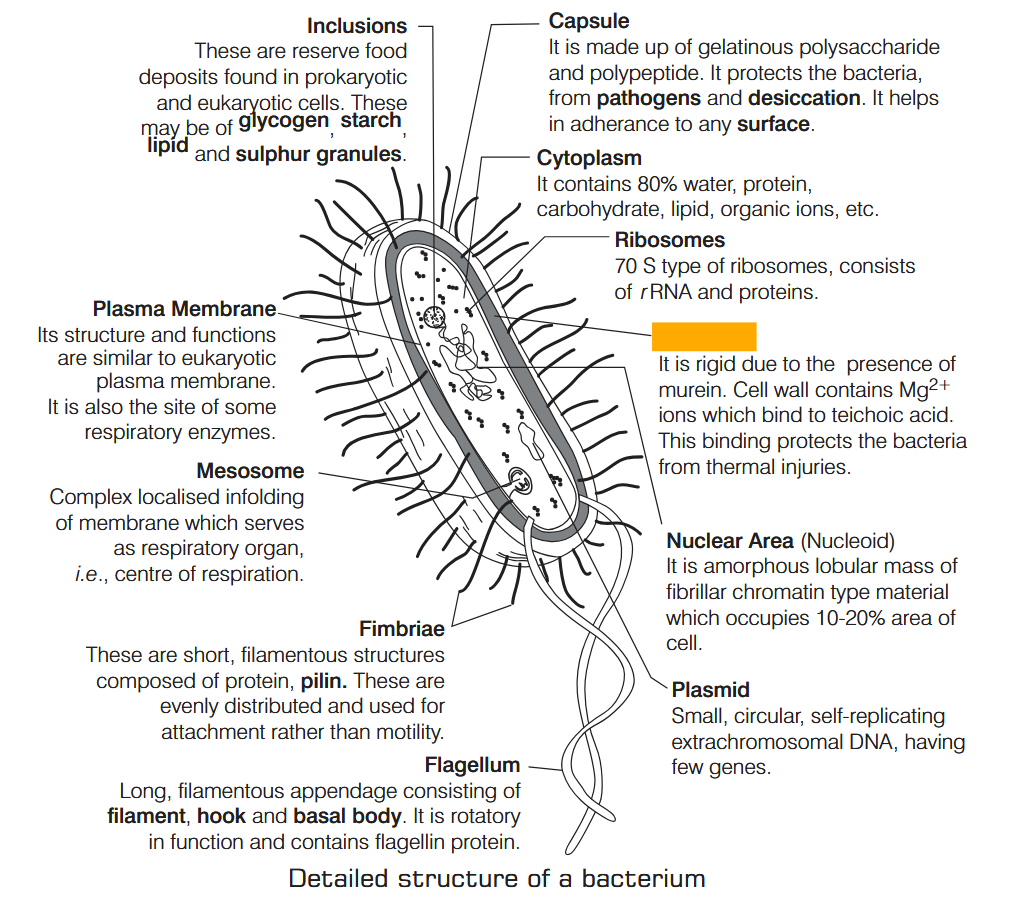
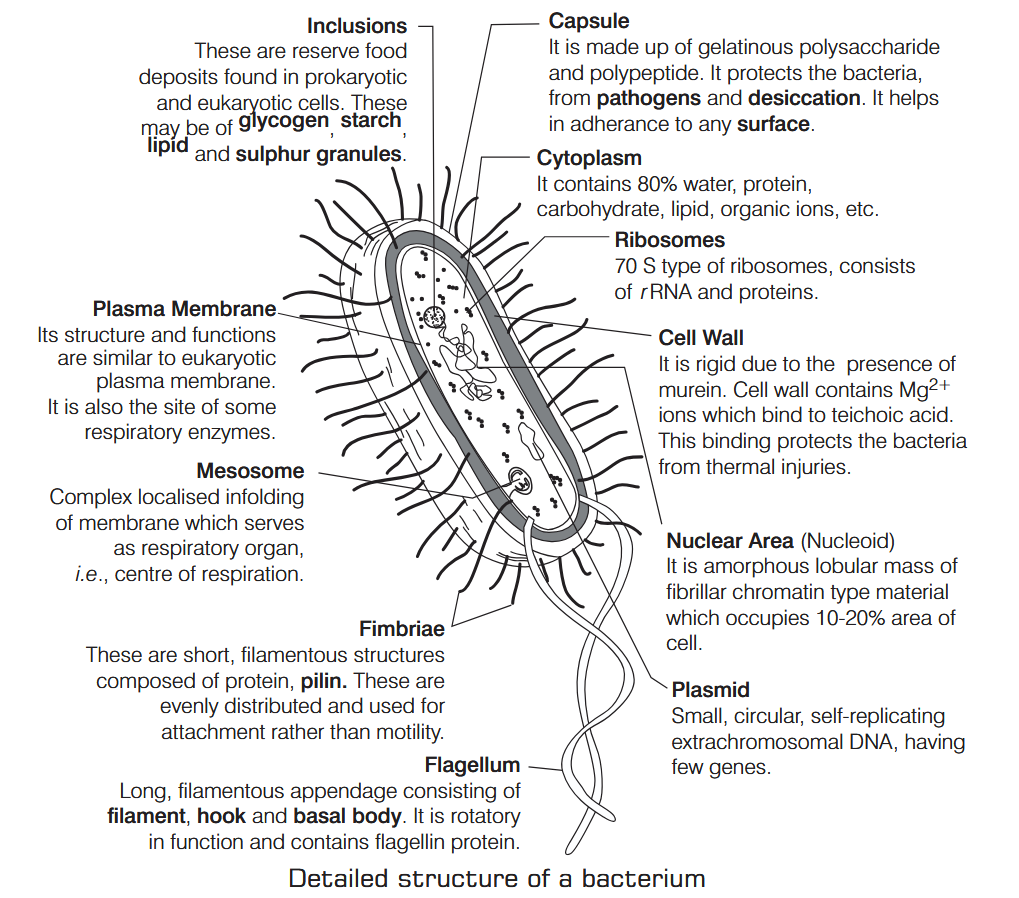
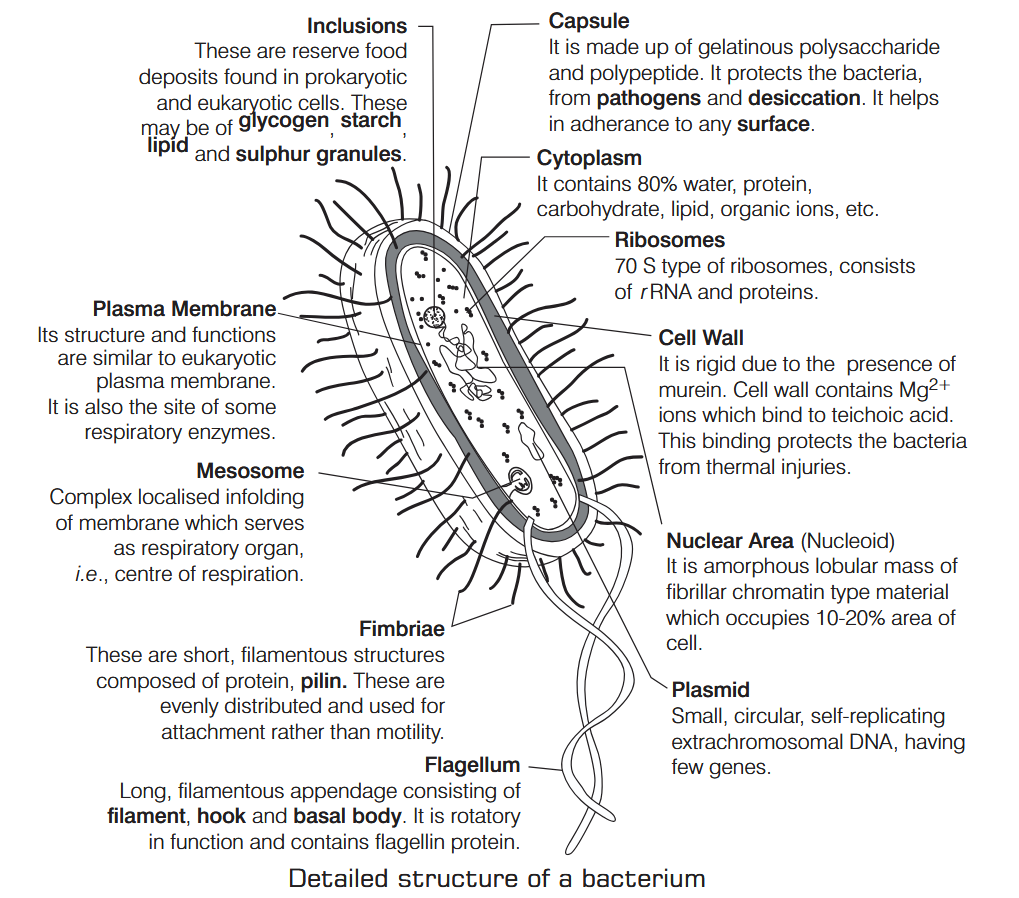
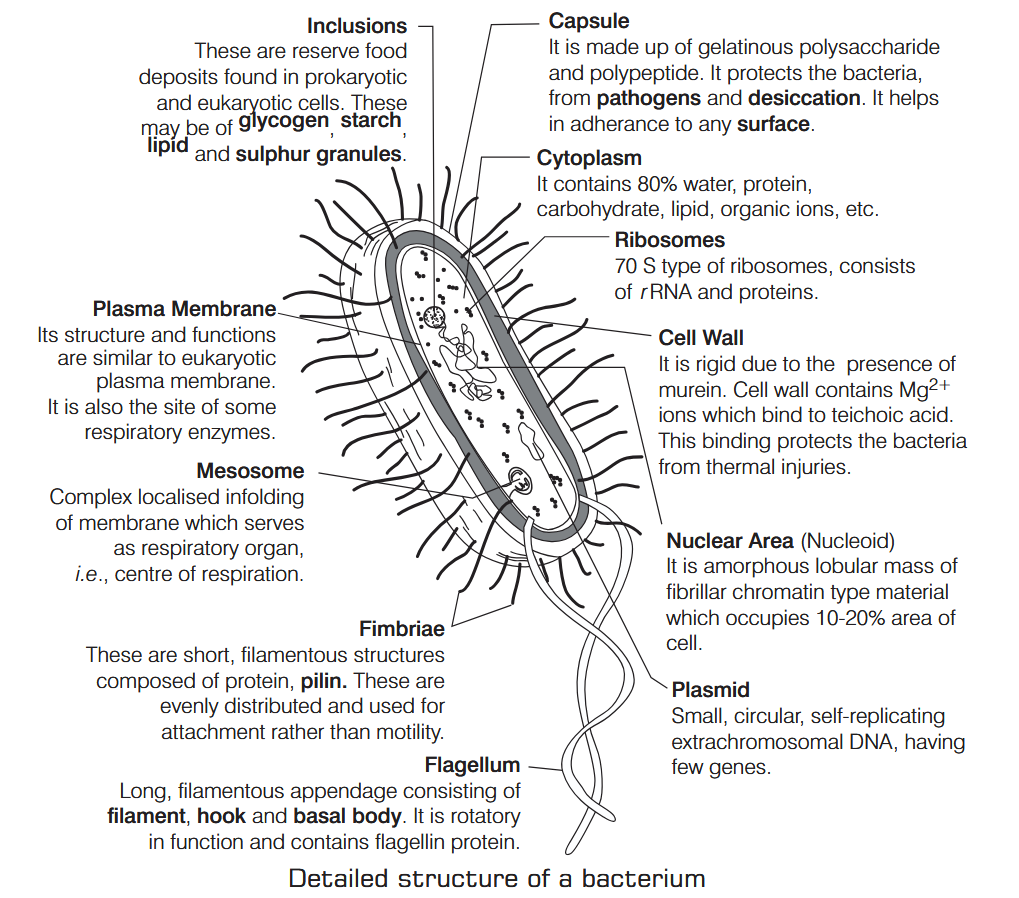
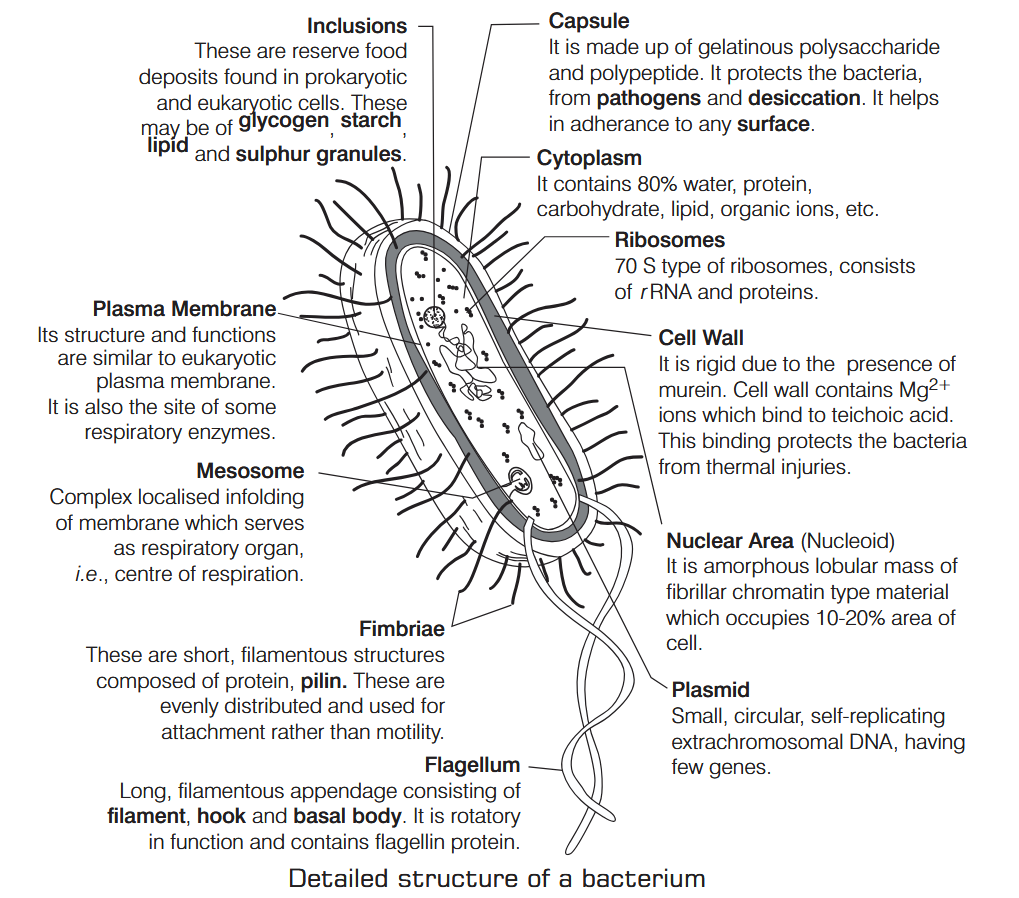
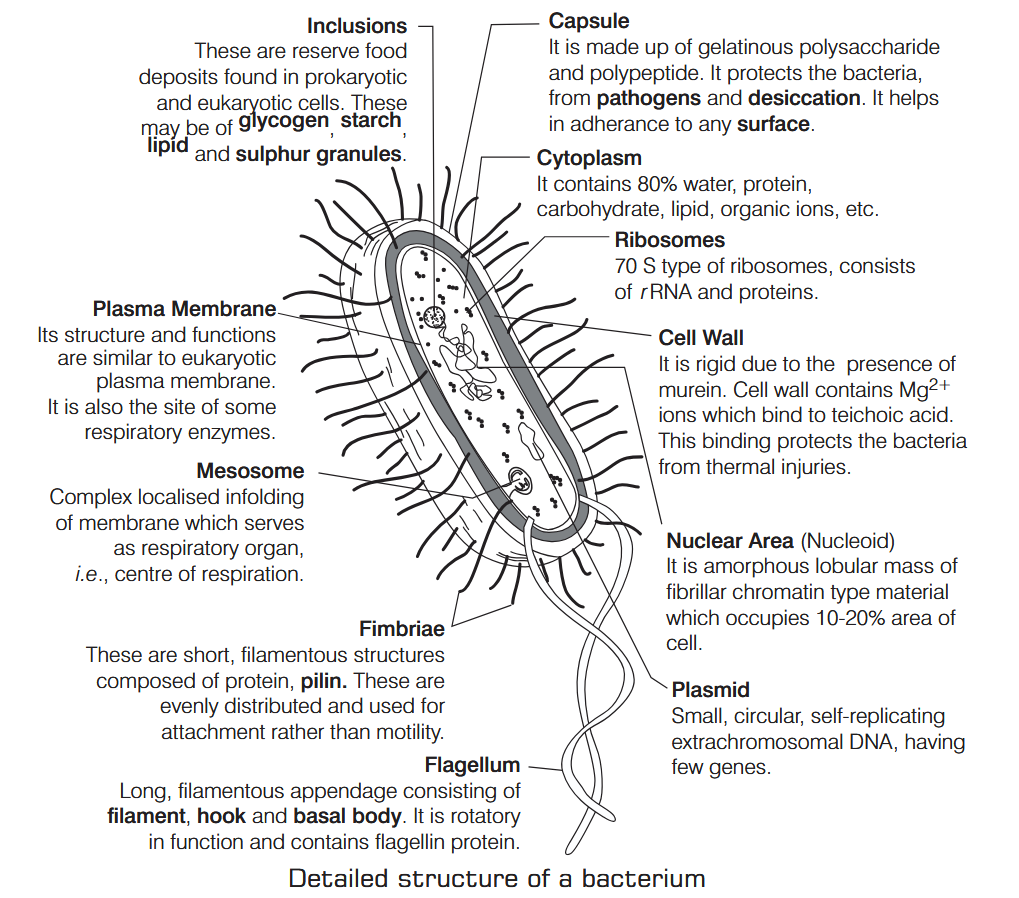
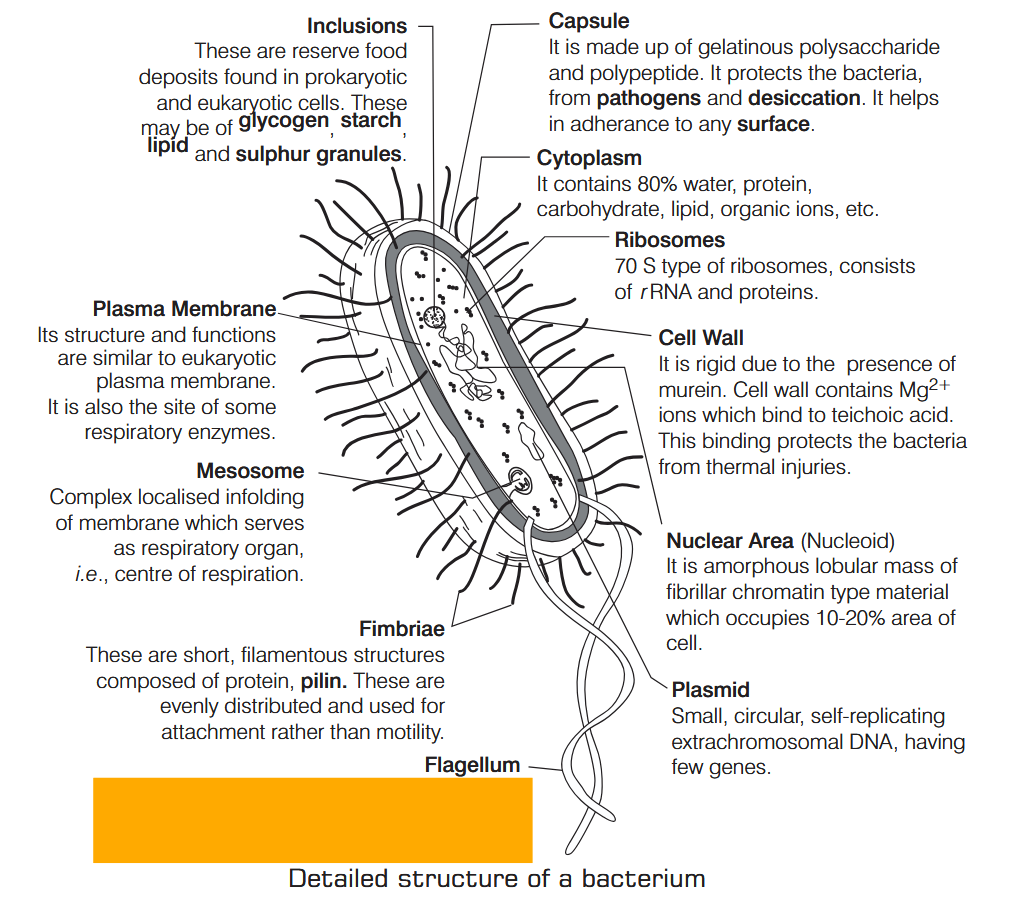
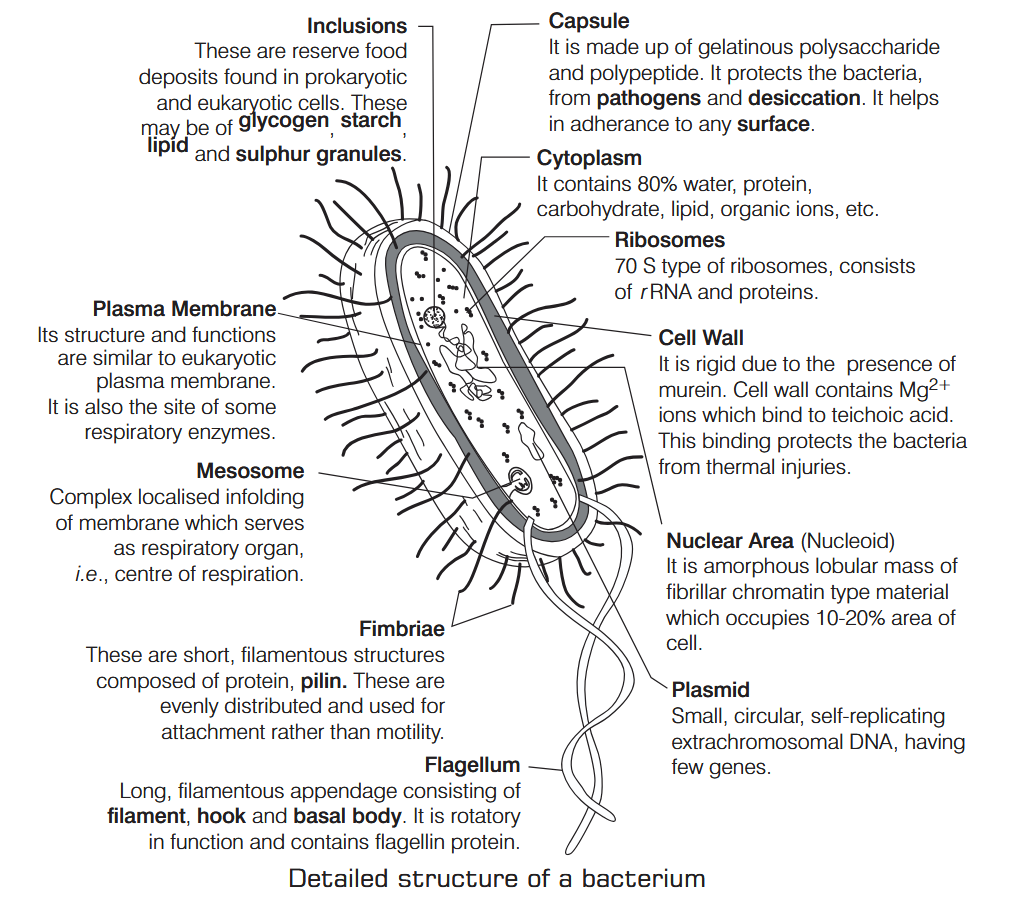
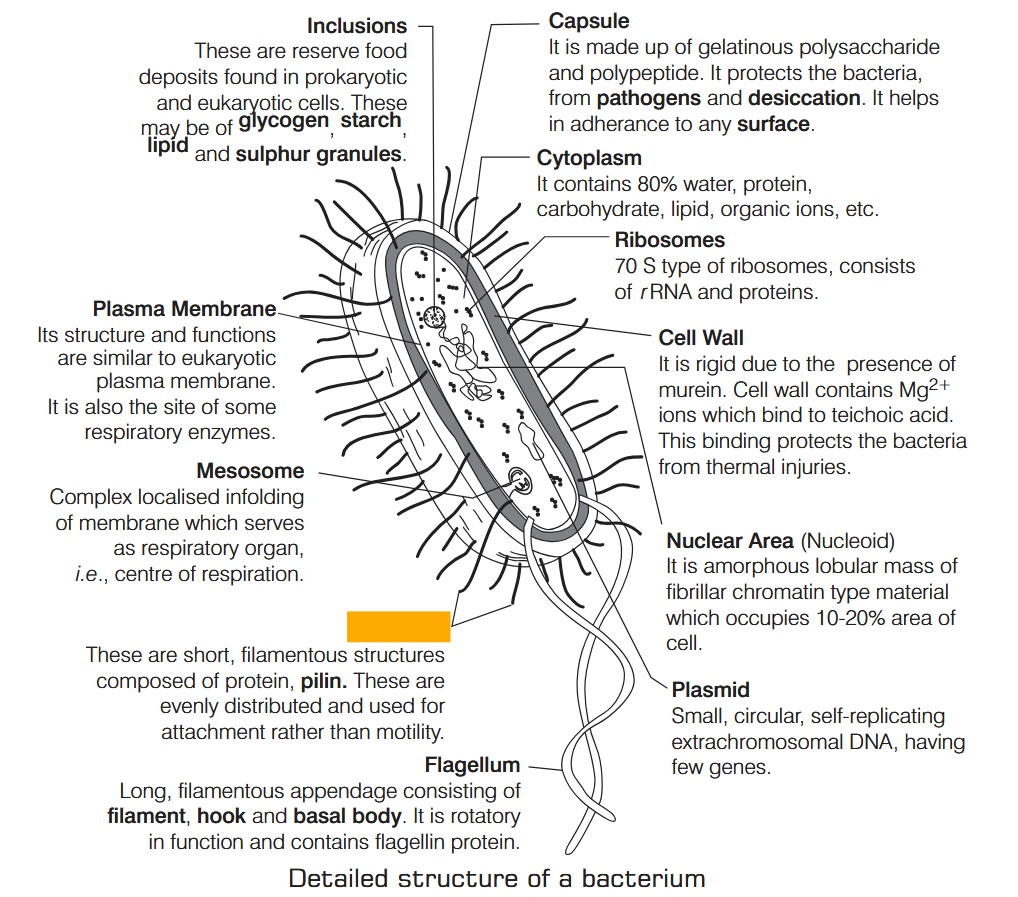
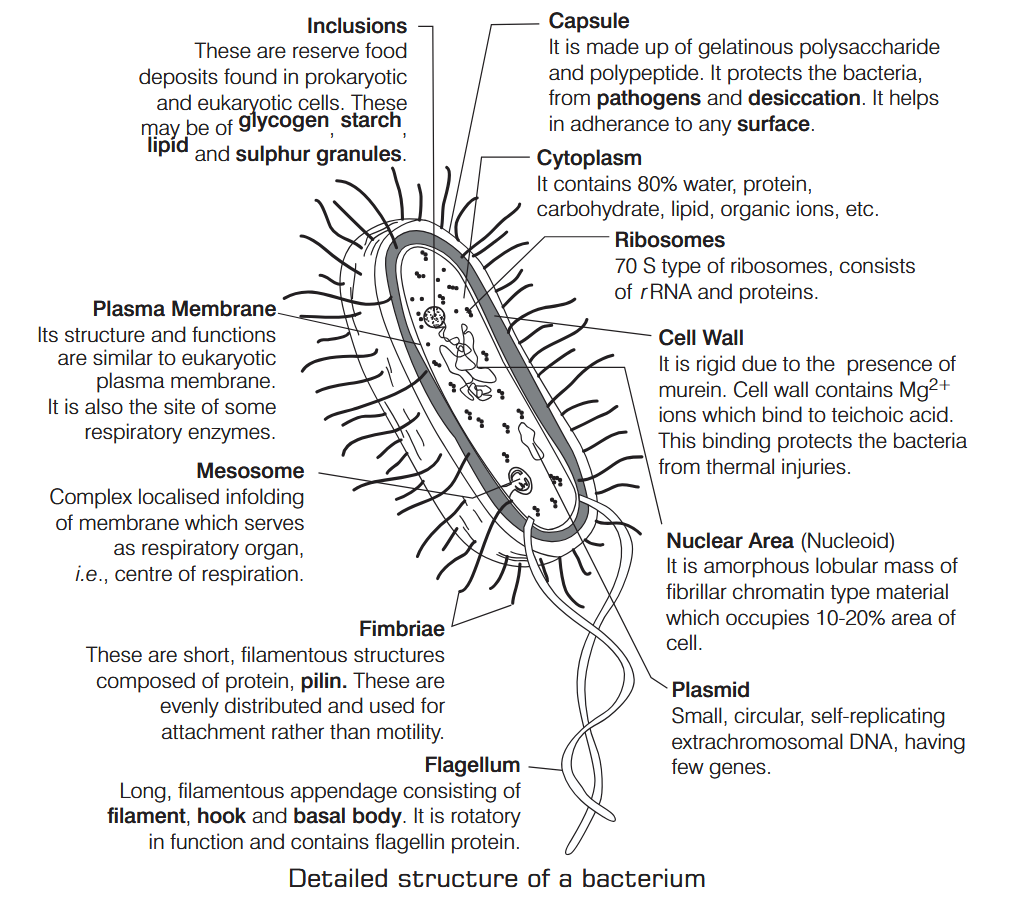
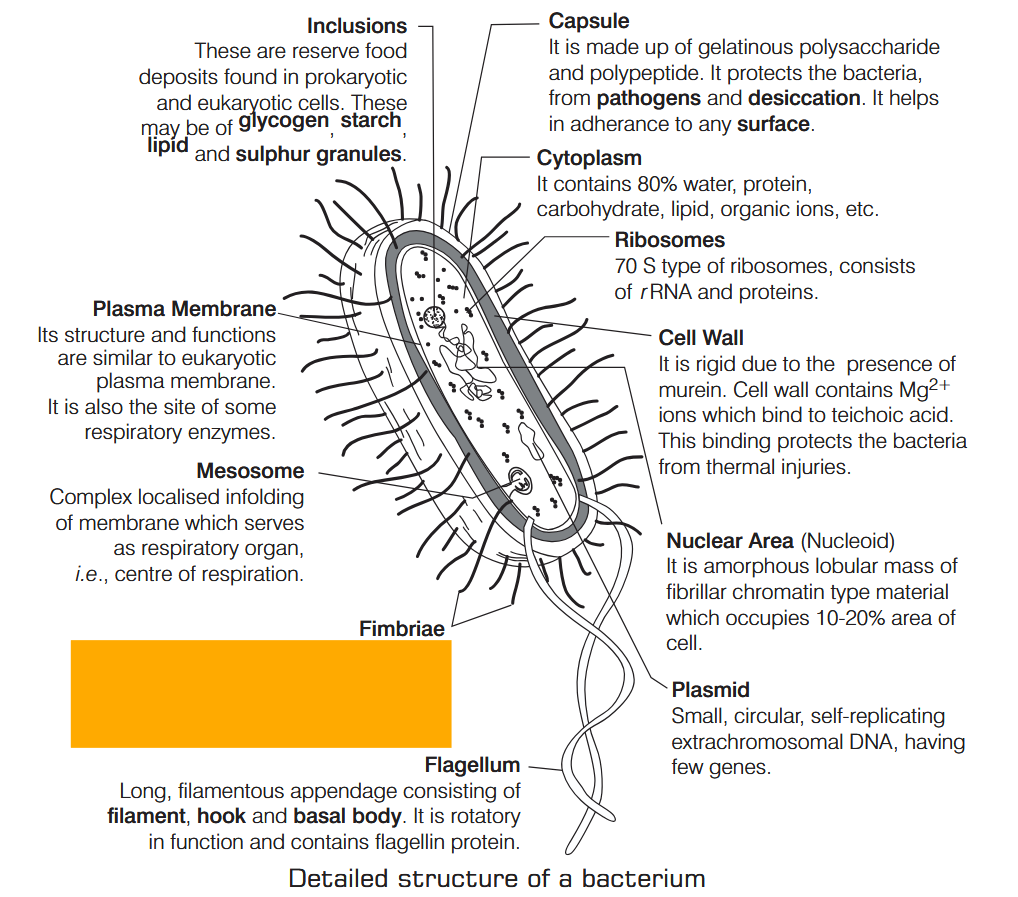
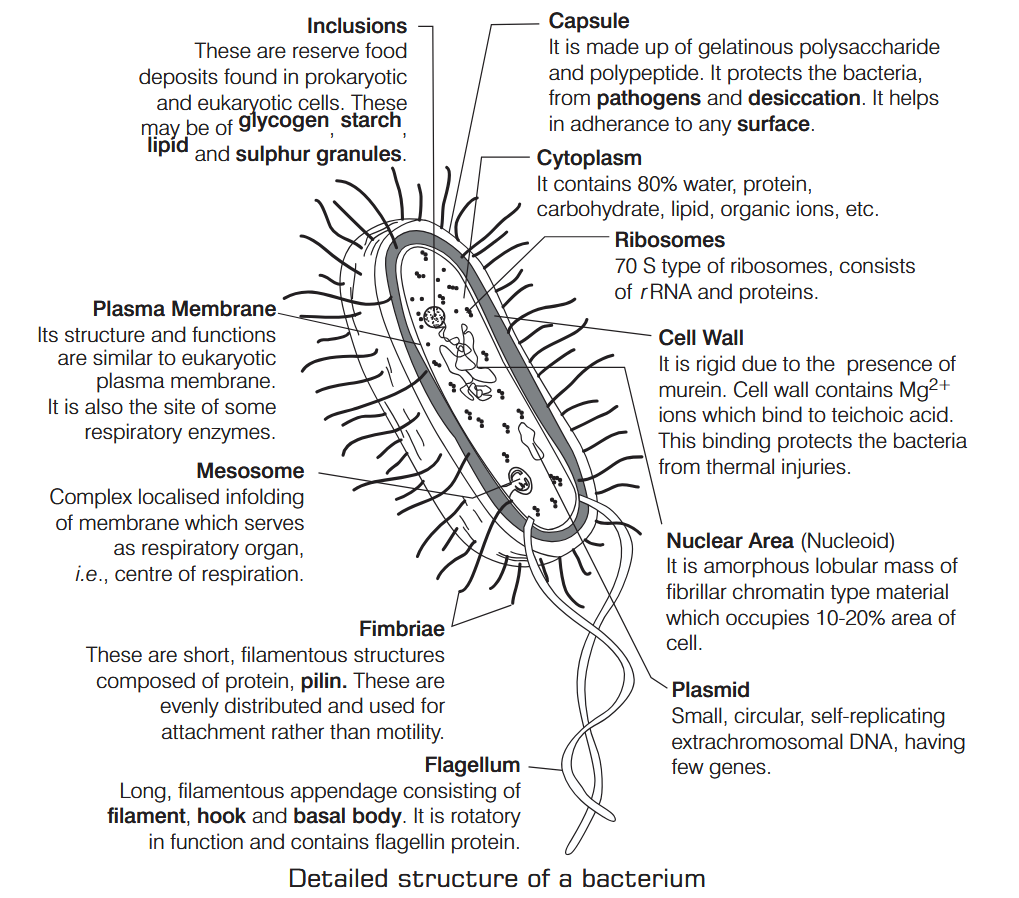
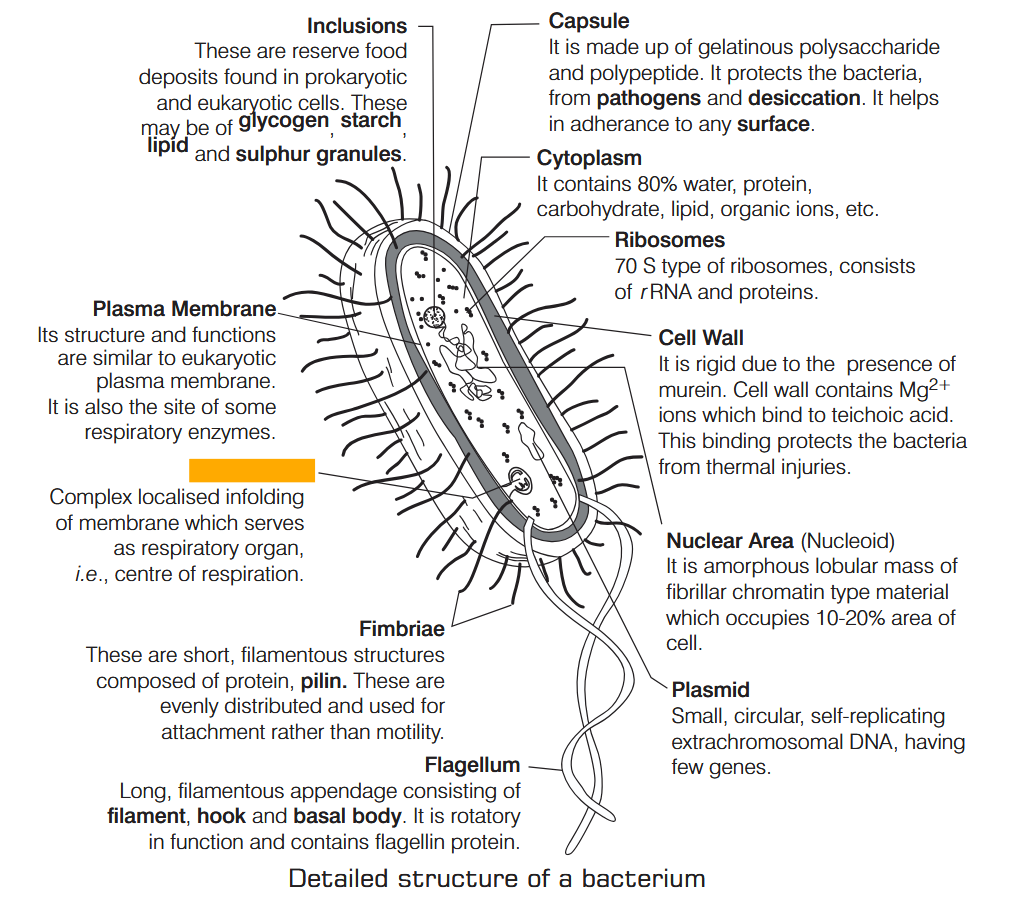
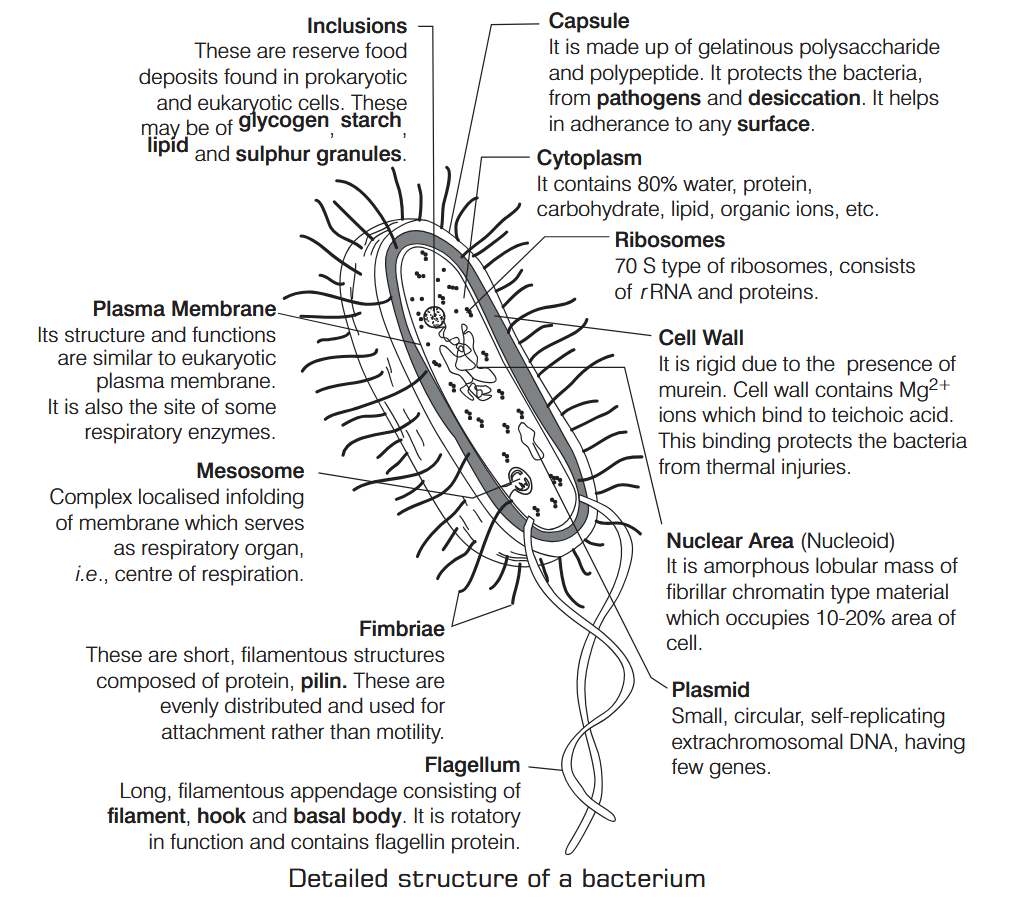
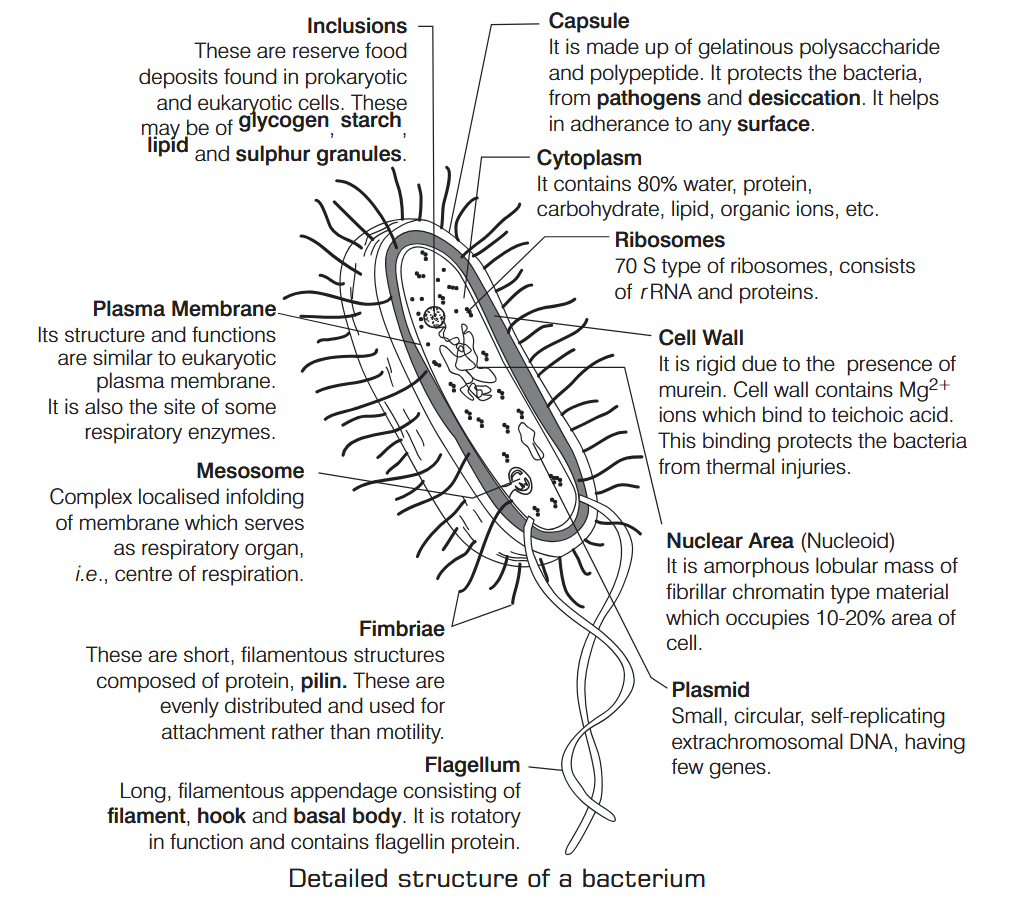
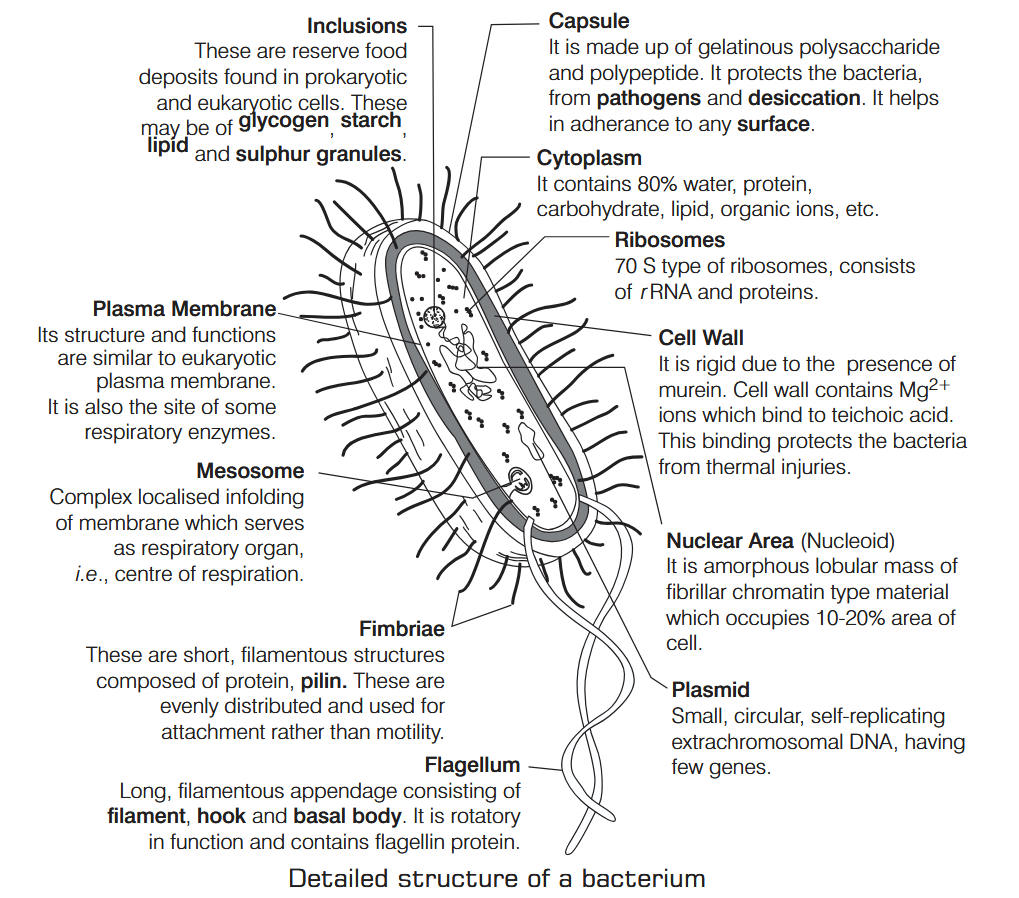
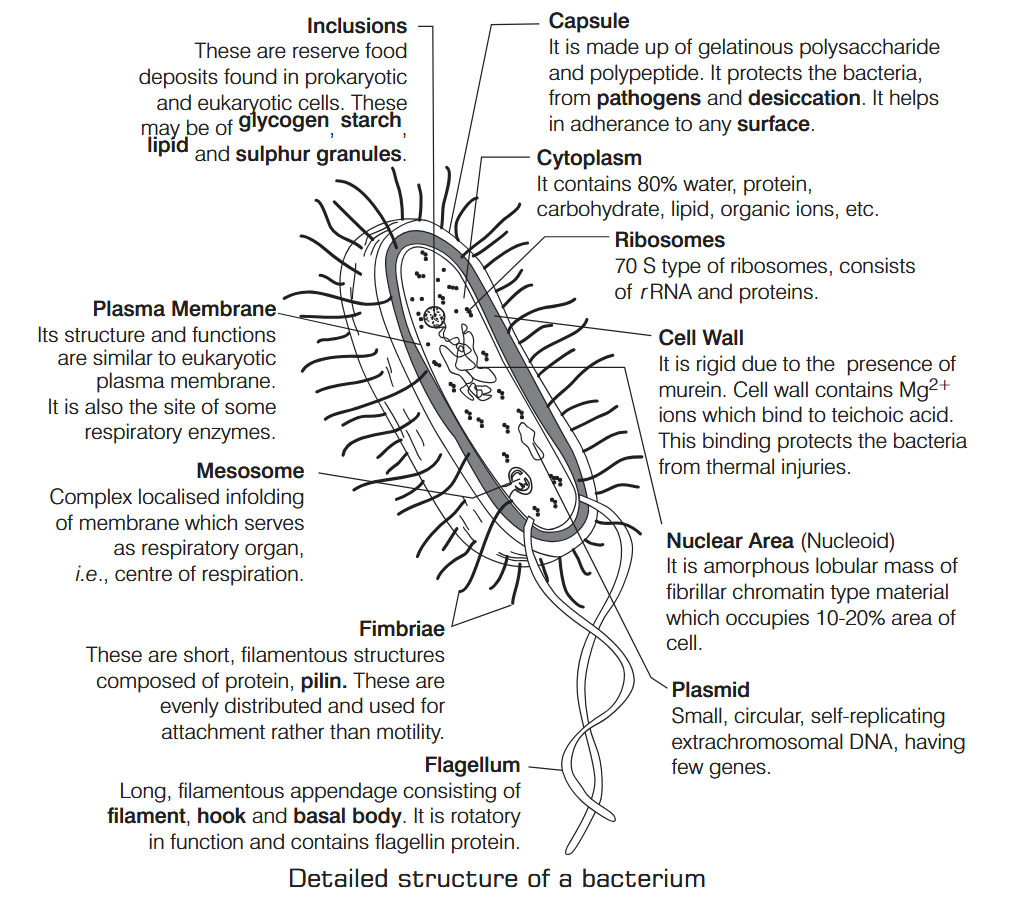
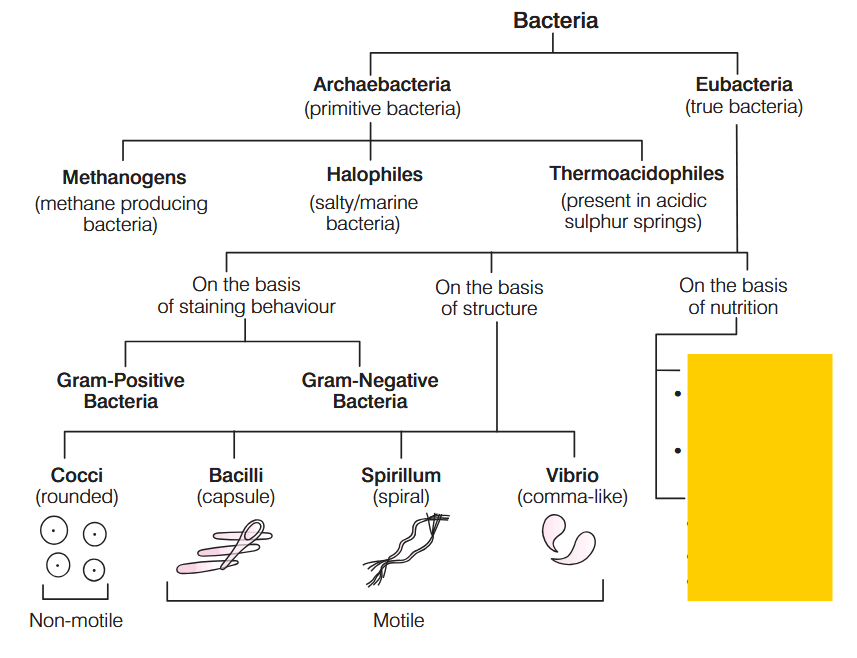
What is Nutrition?
The process of acquiring energy and nutrients, is called nutrition.
On the basis of mode of nutrition, bacteria are of two types– ____________ and ____________.
Autotrophic and Heterotrophic.
What percentage of bacteria show autotrophic mode of nutrition?
1%
What percentage of bacteria show heterotrophic mode of nutrition?
99%
How do Chemosynthetic bacteria acquire energy?
Chemosynthetic bacteria oxidise various inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites and ammonia and use the released energy for their ATP production.

Where does respiration occur in bacteria?
Respiration occurs in the plasma membrane of bacteria
How does aerobic respiration occur in bacteria?
Glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water using oxygen in aerobic cellular respiration.
How does anaerobic respiration occur in bacteria?
Other molecules such as nitrate are broken down in anaerobic respiration.
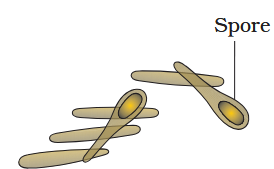
What are the three methods of asexual reproduction in bacteria?
Fisson
Budding
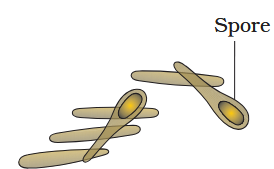
Spore formation