oral pathology LO 9
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
A relatively common disease of unknown cause that affects periapical bone. Occurs most commonly in the anterior mandible of patients older than 30. More common in women than men- hormonal link. Early lesions are well circumscribed and radiolucent; with time, they becomes increasingly calcified. Teeth in the affected area are vital.
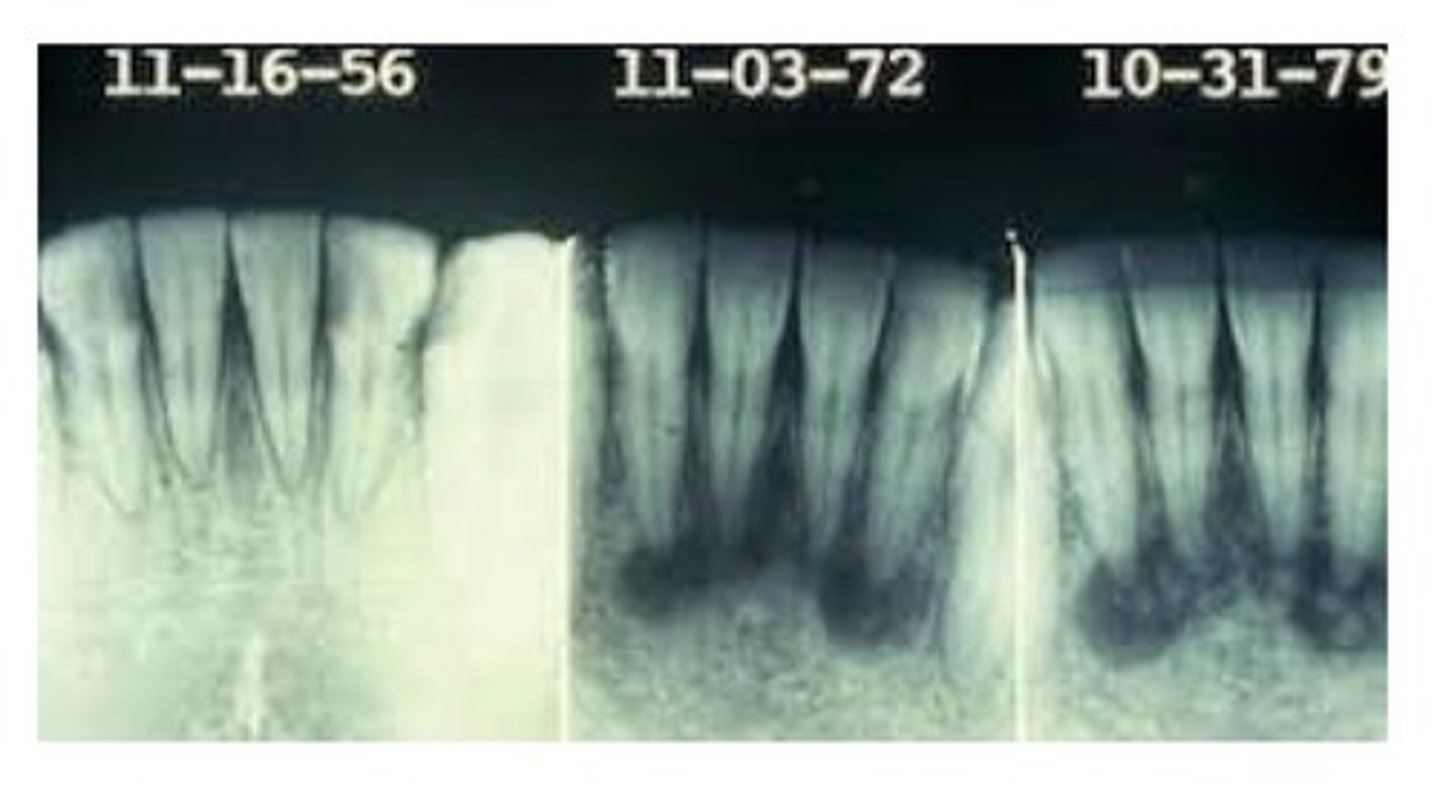
Florid cemento-osseous dysplasia
A condition of disordered cementum and bone development. Best diagnosed on the basis of its characteristic patient history, clinical presentation, and Radiographic appearance. If asymptomatic, doesn't require treatment. Masses of irregular opacification are noted that are composed of dense sclerotic bone, cementum, or both.
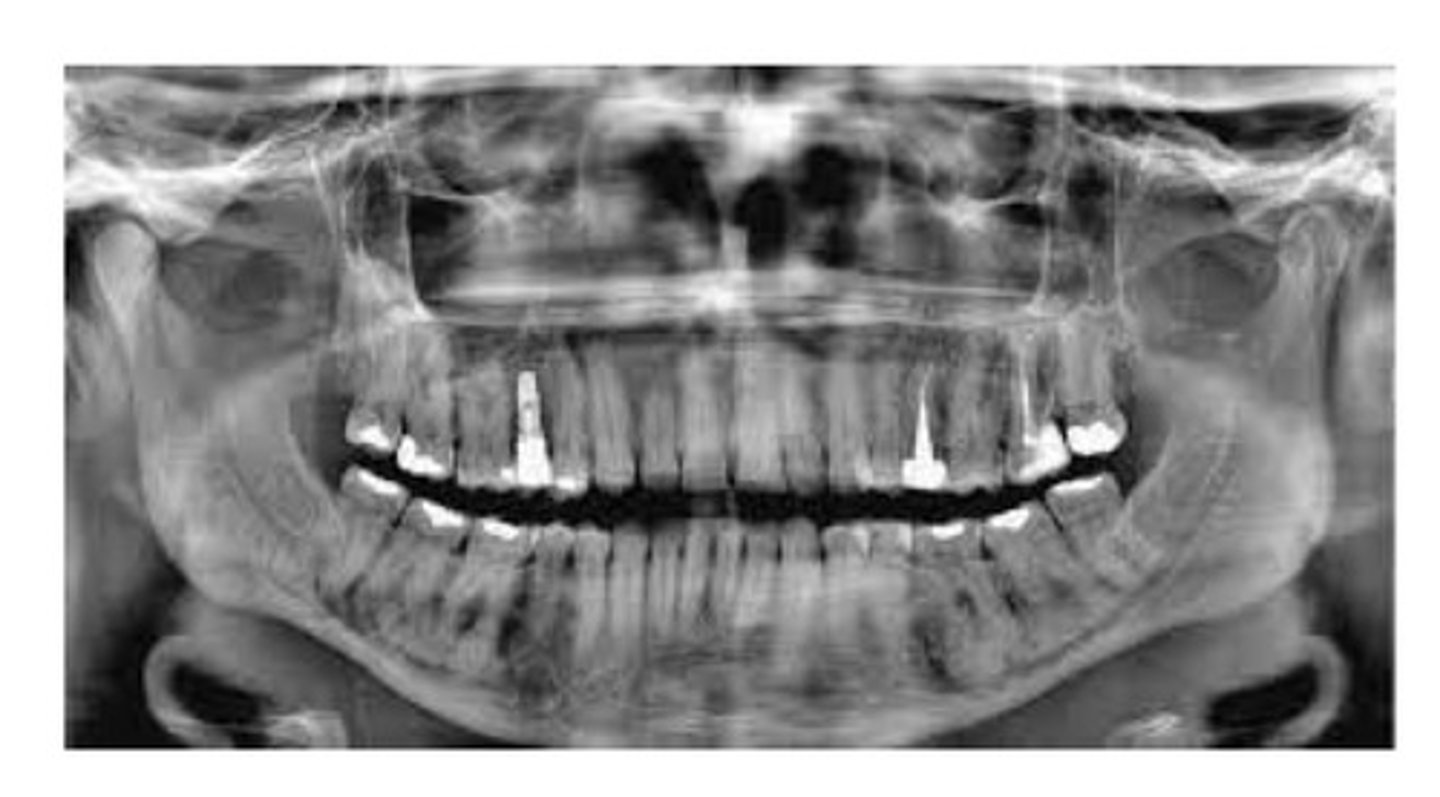
Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia.
An asymptomatic fibro-osseous lesion. Occurs in women between 30 and 50. Isolated, well-delineated radiolucent-to-radiopaque lesion. Less than 1.5cm in size.
Fibrous dysplasia.
Characterized by replacement of bone with abnormal fibrous connective tissue interspersed with a varying amounts of calcification. Histologically, it is a benign fibro-osseous lesion, with vascularized, cellular fibrous connective tissue interspersed with irregular trabeculae of bone.
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
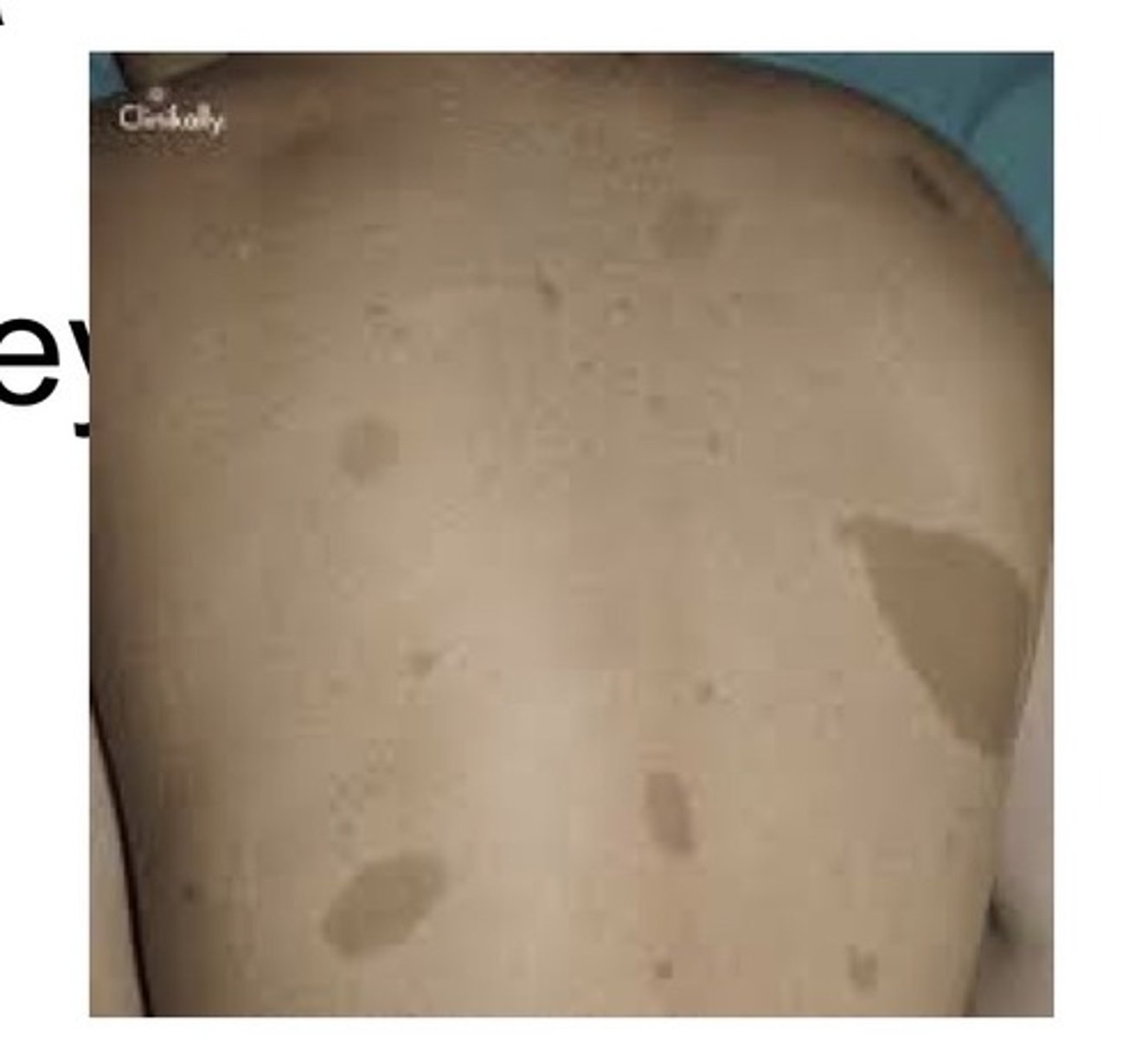
Characterized by involvement of more than one bone. Typically occurs in children with a female predilection. When long bones are involved, they may exhibit bowing and an associate dull aching pain. Patients may have skin lesions appearing as light brown macules called cafe au lait spots.
Craniofacial fibrous dysplasia
This is a type of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Involves the maxilla with extension into the sinuses and adjacent zygomatic, sphenoid, and occipital bones.
Jaffe type
This is a type of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Involves multiple bones along with cafe au lait macules on the skin.
Albright syndrome
This is a type of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Characterized by endocrine abnormalities, precocious puberty in females, stunting for deformity of skeletal growth in both sexed as a result of premature closing of the epiphyseal plates, cafe au lait spots.
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia.
Typically a painless, progressive, unilateral enlargement of the mandible or maxilla. The classic Radiographic appearance is a diffuse radiopacity looking like "ground glass". Characterized by cellular fibrous CT interspersed with irregularly shaped bony trabeculae.
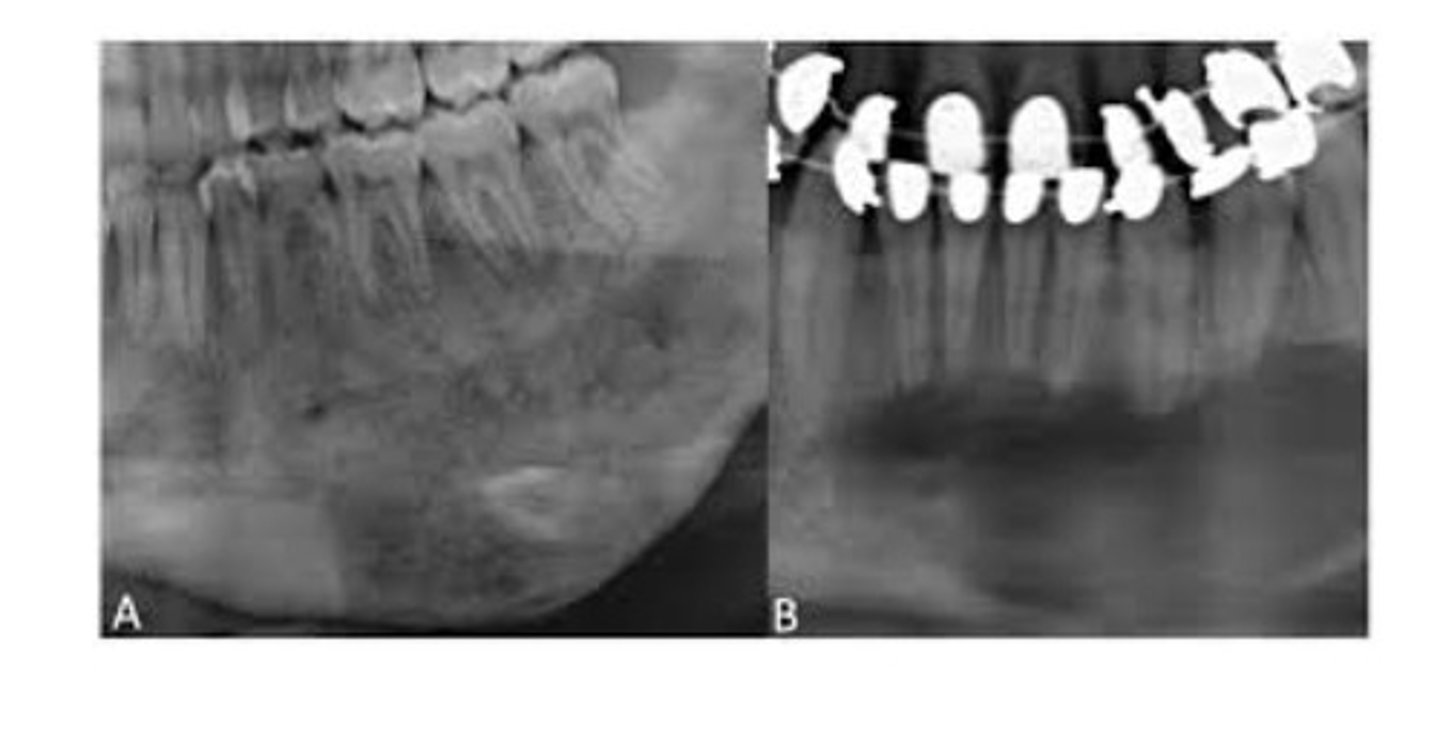
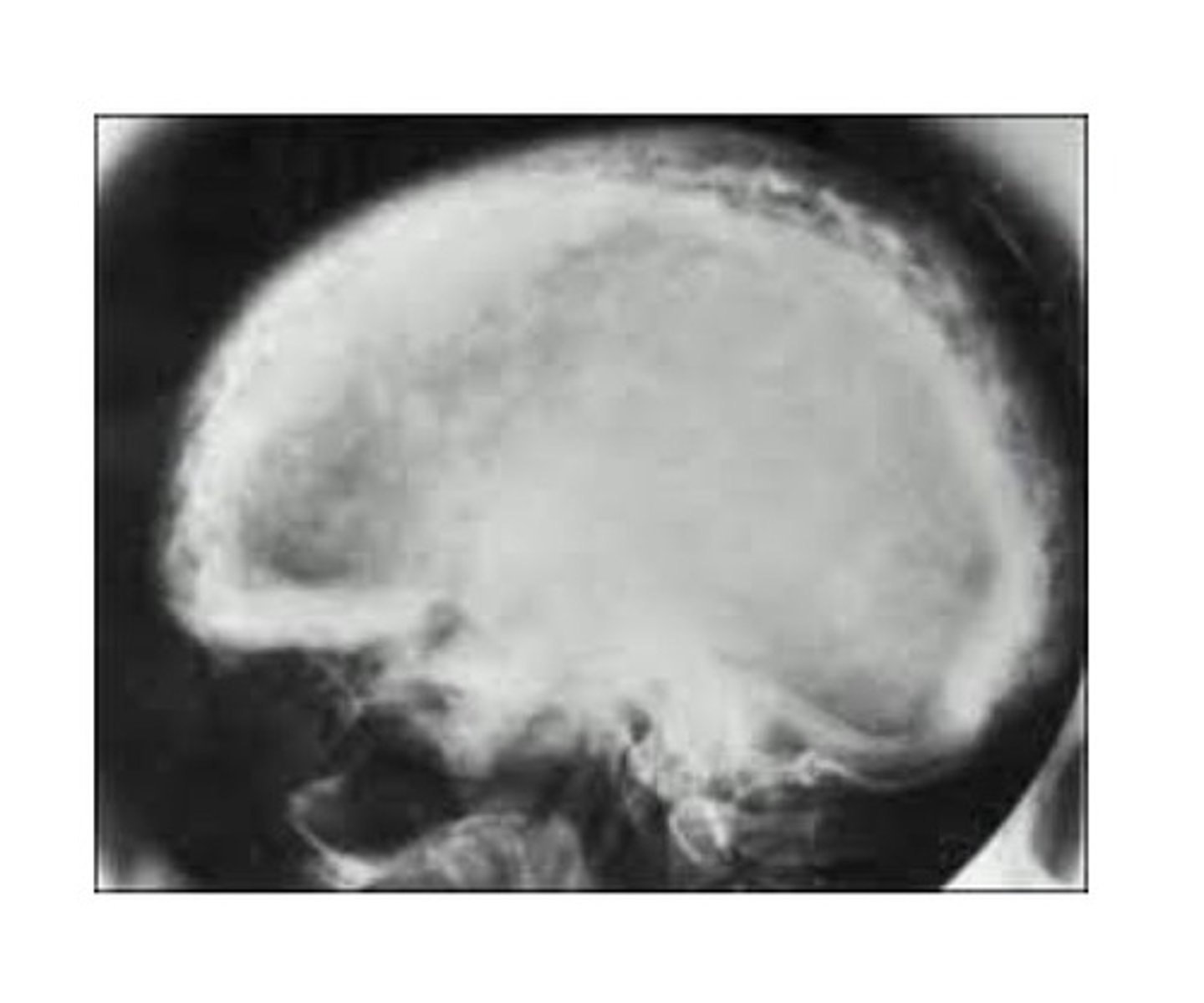
Paget disease of bone
A chronic metabolic bone disease. Characterized by resorption, osteoblastic repair, and remineralization of involved bone. Unknown cause, may be due to a virus. Most commonly occurs in men over age 50 yrs. Maxilla more commonly effected than mand. Enlargement of affected bone, pt often complains of pain, spaces may increase between teeth as jaw bone enlarges. Radiographic: a patchy and radiopacity, "cotton wool". Hypercementosis, loss of lamina dura, and obliteration of PDL may occur.
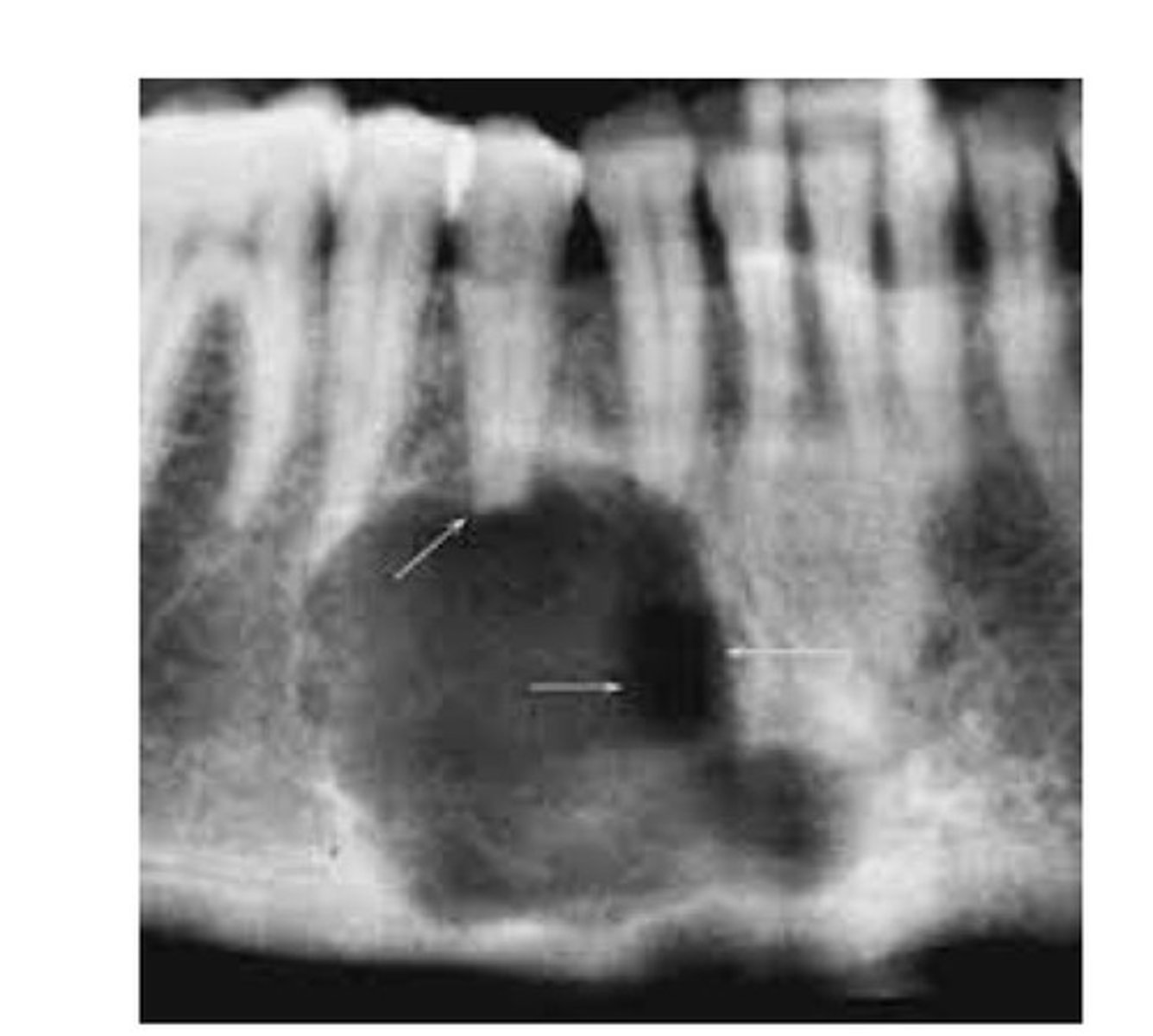
Central giant cell granuloma (central giant cell lesion)
Composed of well-vascularized connective tissue containing many multinucleated giant cells. Occurs in both peripheral (tissue) and central (bone) locations. Often related to chronic infection. Pt may experience pain; not common, slow growing lesion, destructive, unilocular or multilocular radiolucency, ill-defined boarders, divergence of roots.
Aneurismal bone cyst
Pseudocyst. Consists of blood filled spaces surrounded by multinucleated giant cells and fibrous CT. Radiographic: "honeycomb" or "soap bubbles". Often related to a trauma.