BSCI170: Passive Transport
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
notes from 10/20 + 10/15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
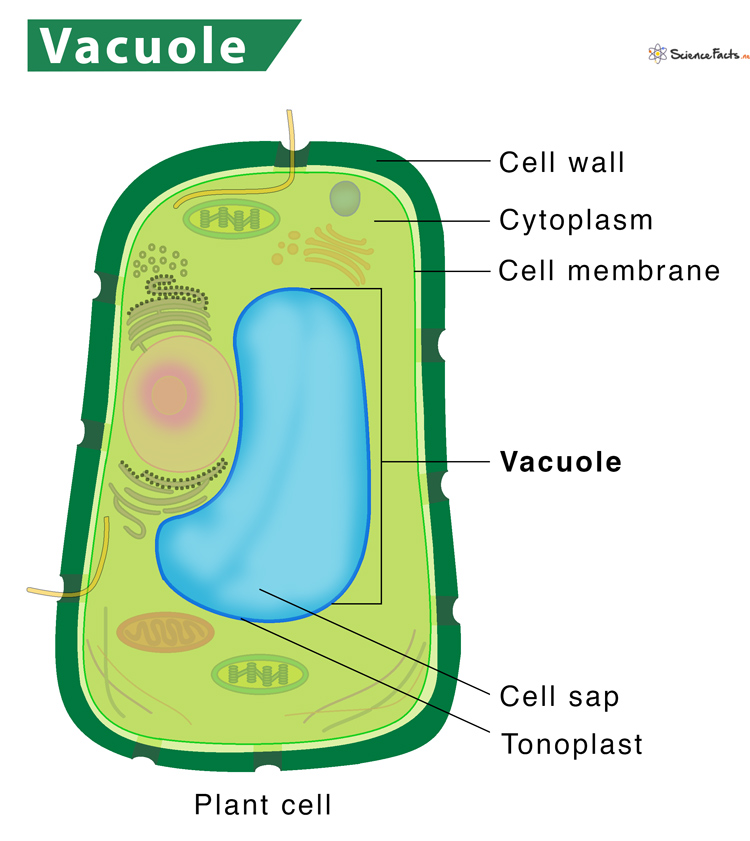
What are the functions of the central vacuole in plant cells?
regulates transport of water
maintains cell wall rigidity bc when it inflates with water, it puts pressure on the walls
Passive Transport: characteristics
naturally occurring
no energy needed
most direct forms of transport are passive
used for small, nonpolar molecules
Passive Transport: Types of Passive Transport
Diffusion
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
What is diffusion?
Movement of area from high concentration to area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached
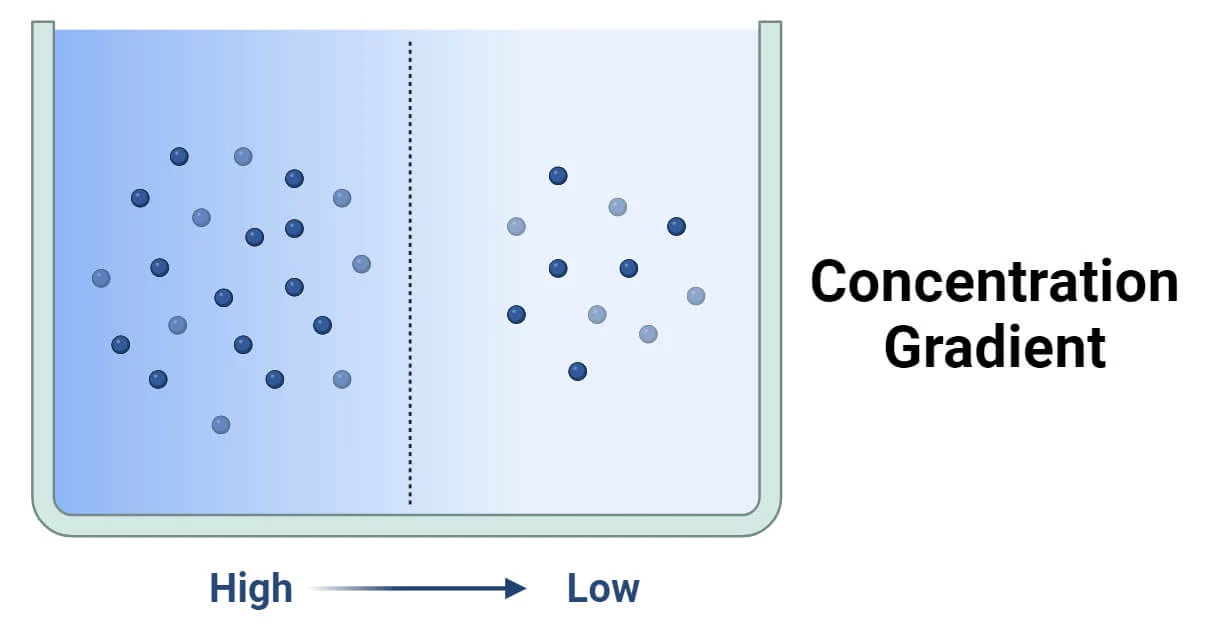
What is a concentration gradient?
difference in concentration of a solute across a region
things move down a concentration gradient
What is simple diffusion
diffusion that transports small, nonpolar molecules through the cell membrane
What is facilitated diffusion
diffusion that transports polar, charged molecules w/ the help of transport proteins
faster than simple diffusion
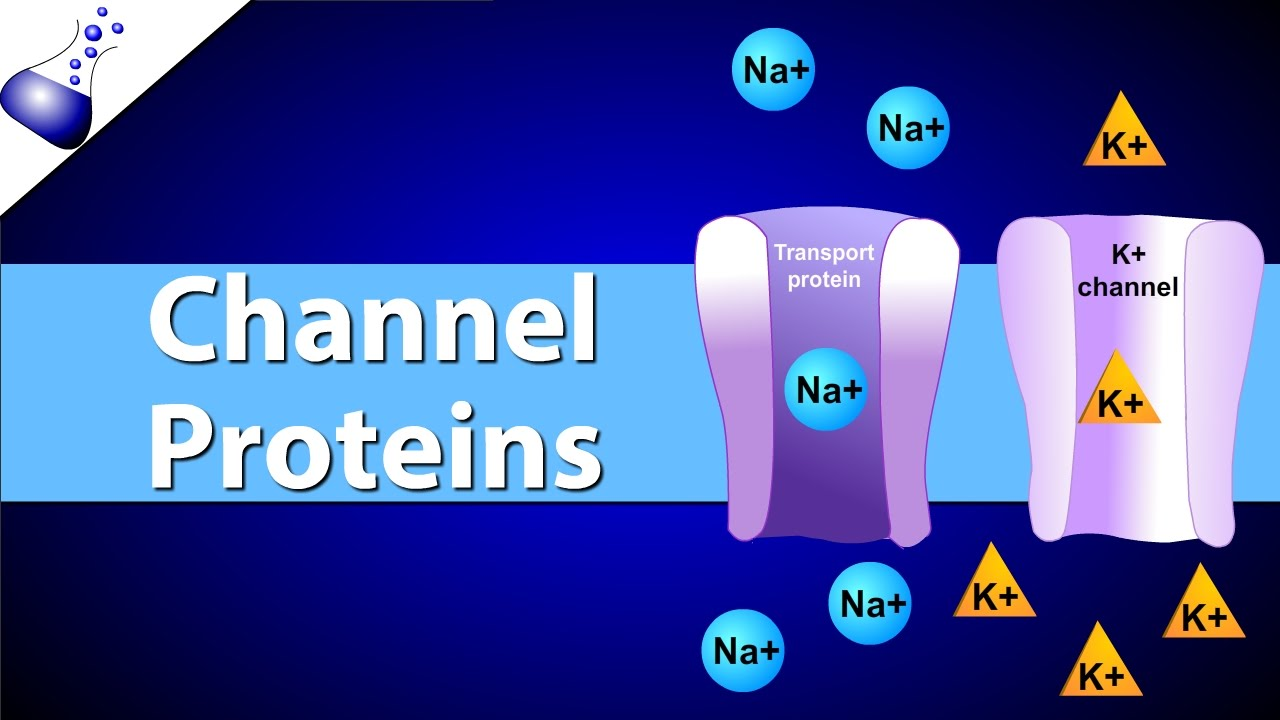
Types of transport proteins?
Channel protein
Carrier protein
What is a channel protein? Examples?
channel for small nonpolar molecules to go through
specific for one type of ion/molecule
ex. aquaporins for water, ion channels (either open 24/7 or gated) for ions
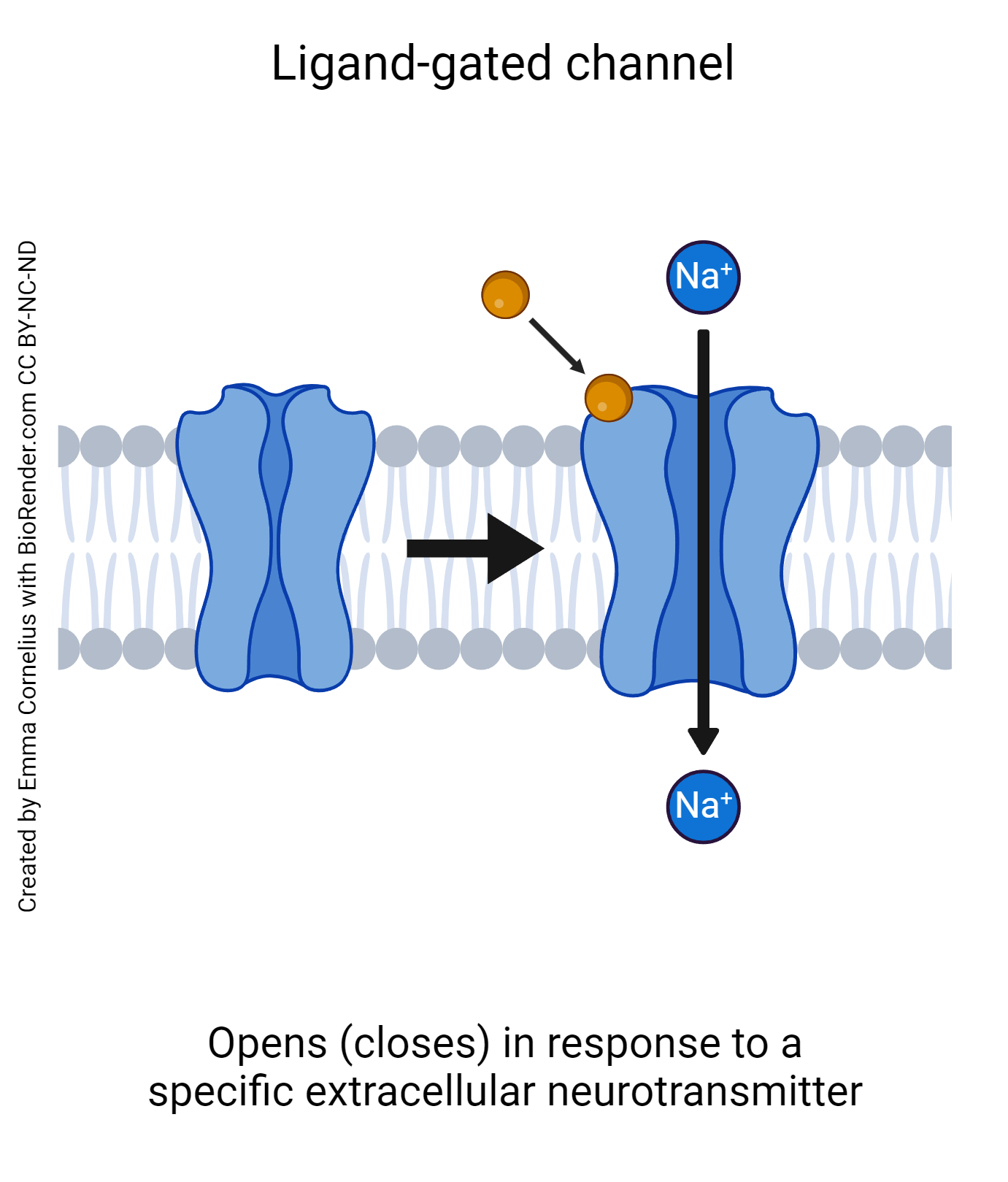
What are the types of gated channels?
Ligand
Voltage
What is a ligand channel?
type of gated channel protein that opens and closes in response to binding a specific ligand/chemical signal
What is a voltage channel?
type of gated channel protein that opens and closes in response to a change in voltage
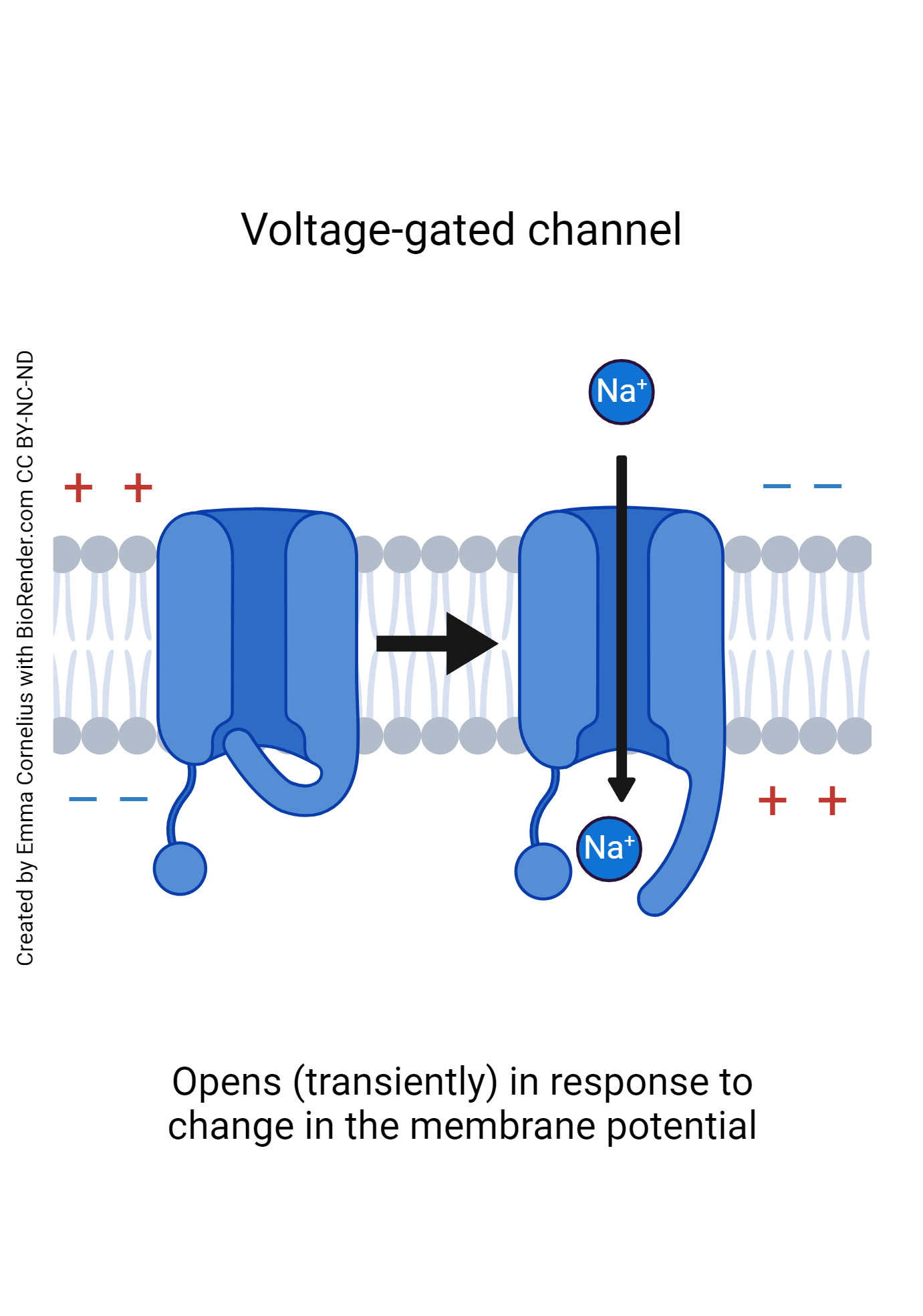
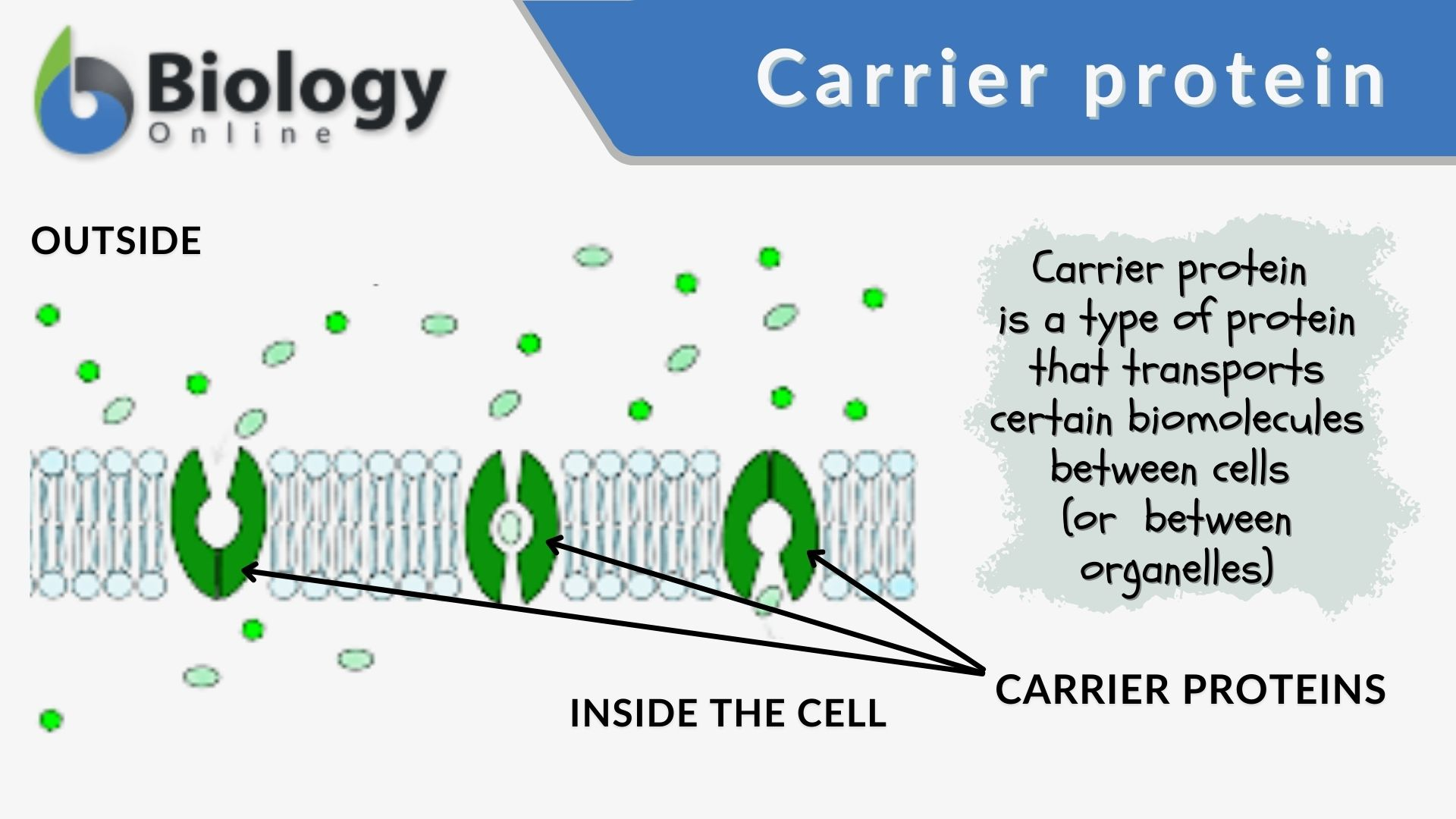
What are carrier proteins?
binds w/ molecules and changes shape to push polar molecules through
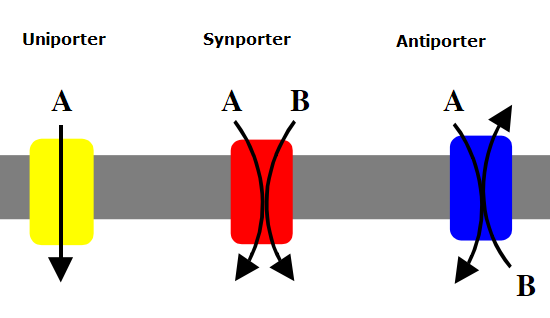
Types of carrier proteins and their function
Uniporter: carries 1 specific molecule
Symporters: carries 2 different molecules in the same direction
antiporters: carries 2 different molecules in different directions
What affects diffusion rate?
extent of concentration gradient: the difference in concentration
mass of molecules: heavier molecules move slower
temperature: high temp leadsto faster movement
solvent density: more dense = slower
solubility: nonpolar molecules diffuse faster than polar ones
surface area: more surface area = faster
distance: greater distance = slower
What is osmosis?
diffusion of water from an area of low solute concentration more water to an area of high solute concentration *less water*
water is inversely proportional to concentration of solute; more solute = less water, less water = more solute
What is osmolarity?
total solute concentration
What is tonicity, and what are the types of tonicity?
how a solute and osmosis affects a cell volume by describing the concentration in/out of a cell
hypotonic
hypertonic
isotonic
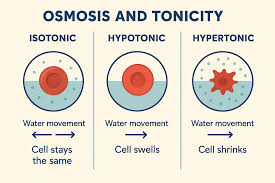
Isotonic
solute concentration is the same in and out of the cell. no net movement of water
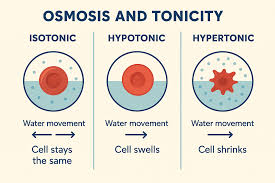
Hypotonic
solute concentration is less on the outside. net water movement into the cell
cell can burst
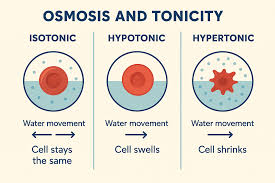
Hypertonic
solute concentration is more on the inside, net water movement out of the cell
cell shrinks and dies
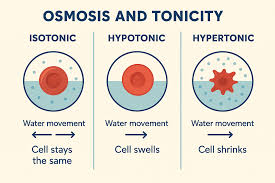
What is active transport
molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration
goes against the concentration gradient, which is why it needs energy
Types of Active Transport and their Characteristics
Primary active transport: uses ATP hydrolysis (breaks ATP to gain energy)
Secondary active transport: doesn’t directly use ATP; uses the energy of one molecule moving down to move another molecule down