GEO 101 EXAM 1 BSU
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What are the main processes and characteristics of science?
1) A way of knowing
2) Based on logic and evidence
3) Helps us understand reality
What is a hypothesis?
A reasonable explanation for the observation
what does falsifiability mean?
Hypotheses and the predictions they make must be capable of being tested against evidence that could prove them wrong
What does theory mean?
An explanation that has been tested over and over and has yet to be disproven
What is a consensus?
The collective judgement of the community of scientists in a feild of study
What energy sources drive plate tectonics?
- Gravity
- Internal heat
- Solar radiation
- Extraterrestrial impacts
How is heat/energy transferred by radiation?
Heat transfers by electromagnetic waves
How is heat/energy transferred by convection?
Heat transfers within a substance without internal movement
How old is the Earth?
~4.5 billion years
How does Earth’s tilt cause the seasons?
By changing the amount of direct sunlight a hemisphere receiver and altering the length of daylight hours - based off this image, when is it summer and when is it winter?

What event caused Earth's tilt?
The same massive impact that formed the moon
Why was early Earth able to separate into layers?
It was incredibly hot, allowing differentiation into layers based on density
What are Earth’s compositional layers?
Crust - outer layer (low density rock)
Mantle - high density rock
Core - (inner most layer) bery high density
What are Earth’s mechanical layers?
Lithosphere (crust and uppermost mantle)
Aesthenosphere (semi-fluid area below the lithophere)
What is the lithosphere made of and why do lithopheric plates move?
Crust and uppermost mantle and they moves partly because they are influenced by the flow of the mantle
What causes Earth's magnetic field?
The flow of the outer core around the inner core
What is the geosphere?
Crust ; mantle ; and core
What is the hydrosphere?
ice ; liquid water, water vapor
What is the biosphere?
Life ; organic remains
What is the atmosphere?
gases surrounding the earth
What was the evidence for continetial drifting?
- Continents fit like puzzle pieces
- Matching rock types and mountain ranges
- fossil distribution
- ancient glacial deposits and glacial station distrubution
How is plate tectonics different from continental drift?
Continental drift - argued that continents moved, but it proposed way of doing so didnt make sense and was dismissed
Plate Techtonics - offered a modern understanding of HOW continents moved
Who was Marie Tharp, and what did she discover?
- The woman who mapped the mid-ocean ridges (underwater mountain ranges)
- Discovered deep-sea trenches (deep areas in the ocean) that showed evidence of continents being ripped apart
Who was Harry Hess, and what was his idea of seafloor spreading?
- The man who published a groundbreaking paper describing the process of seafloor spreading (first time accurate mechanism for plate motion was found)
- Seafloor spreading - the formation of new areas of oceanic crust, which occurs through the upwelling of magma at midocean ridges and its subsequent outward movement on either side.
How did the hypothesis of seafloor spreading explain the observation that seafloor mud layers are thinner near mid-ocean ridges and thicker further away?
- "drill core" suggests that the seafloor near the mid-ocean ridge is young
- Thin mud layers (sediments) near the mid-ocean ridges are much thinner, meaning they have had less time to accumulate
What is it called when the magnetic field has "flipped"
Magnetic polarity reversals ( the pattern of these is also perfectly consistent with the seafloor spreading hypothesis
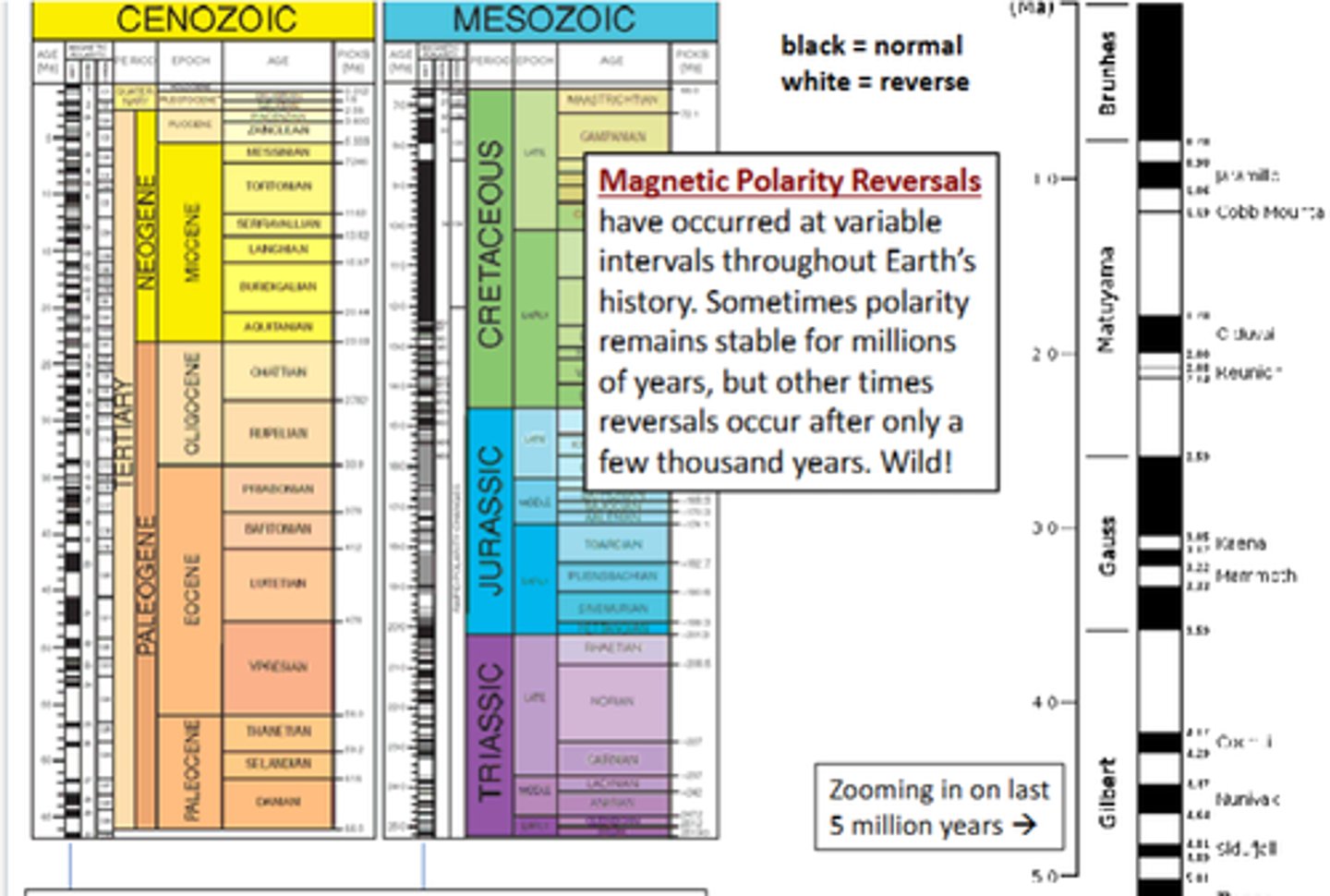
When did plate tectonics become a scientific consensus?
1970's
In an ocean basin, where are seafloor rocks youngest? Where are they oldest?
Youngest - closest to mid-ocean ridges
Oldest - Furthest away from mid-ocean ridges

How fast do tectonic plates move on average?
~3cm per year
What is an active margin?
When two plates are actively splitting apart at the mid-ocean ridge (also known as a plate boundary)
What is a passive margin?
Where continental rock transitions to oceanic rock within a single plate
What happens at a convergent boundary?
Plates move towards eachother
What happens at a divergent boundary?
Plates pull apart
What happens at a transform boundary?
Plates slide past one another
What are mid-ocean ridges?
Long underwater mountain chains
What are continental rifts?
Regions where a continent is being pulled apart, causing the crust to thin and eventually form valleys or new ocean basins.
How are continental rifts related to seafloor spreading?
They are the starting stage of seafloor spreading
Explain the processes of seafloor spreading
Plates pull apart during seafloor spreading, molten lava rises to the surface to push the plates apart - melts down to form new crust
What is a subduction zone?
a boundary where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another into the mantle, often creating earthquakes, volcanoes, and deep ocean trenches.
What features are always found at subduction zones?
- Deep-sea trenches
- Volcanic arcs
Why does the oceanic plate subduct instead of the continental plate?
Because it is thinner and denser than the continental plate
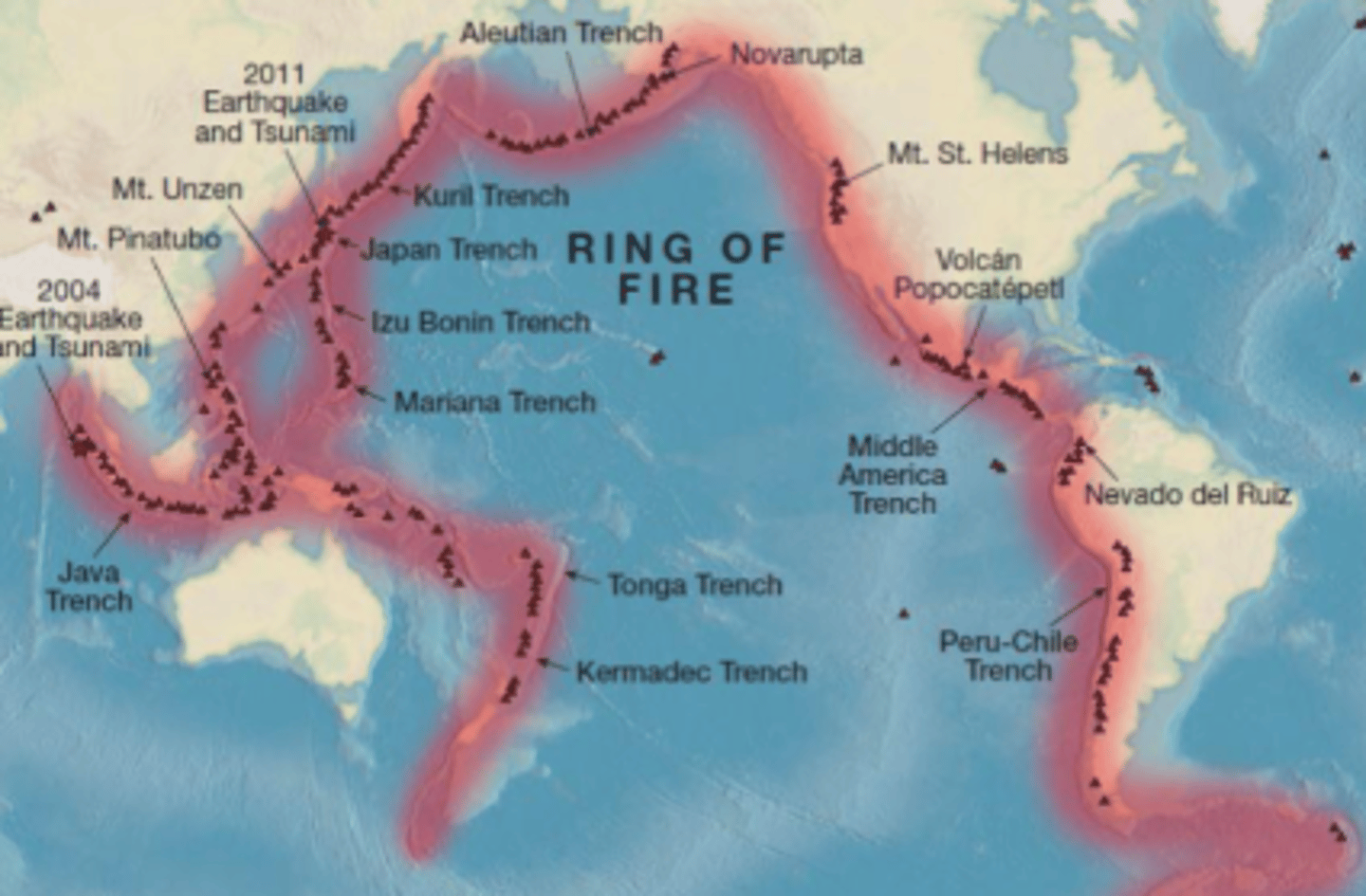
Where is the ring of fire, and how does it relate to subduction?
-around the edges of the Pacific Ocean
- All the deep-sea trenches, volcanic arcs, and earthquakes happen due to subduction
What happens during a continental collision?
Two continents collide and crumble into huge mountain ranges

Why don't continents subduct?
Becuase they are too thick and boyuant to subduct
What transform boundary divides the US into two different plates, and where?
San Andreas Fault, CA
True or False: Do all plate boundaries have earthquakes?
True
Which plate boundaries also have volcanoes?
Divergent and Convergent

What types of mountains form at divergent plate boundaries?
Mid-ocean ridges
What types of mountains form at transform plate boundaries?
Relatively small mountians
What types of mountains form at convergent plate boundaries?
- HUGE non-volcanic mountains at continental collisions
- volcanic arcs at subduction zones
How does plate tectonics represent a cycle of creation and destruction?
New crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges through seafloor spreading, while old crust is destroyed at subduction zones where it sinks back into the mantle.
What is convection, and how does it move plates?
Hot rock moves inside Earth and slowly pushes plates.
What does ridge-push mean, and how does it pull plates apart?
New crust at mid-ocean ridges slides downhill and pushes plates apart
What does slab-pull mean, and how does it pull plates apart?
A sinking plate at a trench pulls the rest of the plate with it
What is a hot spot?
When hot plumes rise from the deep mantle and melt massive amounts of lithosphere/crust, they do NOT migrate within Earth's mantle, but can be tracked by volcanic activity, and they also do NOT necessarily occur at plate boundaries
How do hot spot volcanic patterns differ from subduction zone or mid-ocean ridge patterns?
Hot spot tracks: Older volcanoes move away from a fixed hot spot as the plate shifts.
Mid-ocean ridges: New crust forms at the ridge, and rocks get older farther from it.
What are the two requirements for something to be a mineral?
- Crystalline structure
- Chemical Composition
Why is volcanic glass NOT a mineral?
Because it lacks crystaline structure
Why are diamond and graphite different minerals even though both are carbon?
They have the same chemical composistion but DIFFERENT crystal structures
What is crystal habit?
The ordered internal arrangement of atoms that leads to unique shames of minerals on a larger scale
What is cleavage?
The tendency of a mineral to break along smooth places parrallel to weak bonding
What is fracture?
Tendancy of minerals to break along irregular surfaces
Is a mineral always the same color?
No, sometimes minerals show a large variation in colors, usually due to elemental ranges or impurities
What are the three main ways minerals form?
1) when lava cools down
2) evaporation (precipitation)
3) metemorphism - high presures and temperatures
What are the two most common elements in Earth's crust?
Oxyen and Silicon
What is a silica ion?
- one silicon surrounded by four oxygens
- Minerals containing silica ions are, by far, are the mostcommon minerals in Earth's crust
What are isolated silicates?
Minerals in whcih silica ions are not linked
- They have the lowest silica concentration
- example : Olivine
What are framework silicates?
Minerals in which silica ions are thoroughly interlinked
- They have this highest concentration of silica
- example : quartz
What is olivine?
An Isolated Silicate Mineral
What is quartz?
A Framework silicate
What is the difference between felsic and mafic minerals?
Felsic - HIGH concentrations of silica and LOW concentrations of iron / magnesium
Mafic - LOW convectrations of silica and HIGH concentrations of iron / magnesium
How do felsic and mafic minerals differ in density and color?
Felsic - lighter colored and low density
Mafic - darker colored and denser
What are rocks made of?
aggregates (combos) of minerals
What are native metals?
Metals that can be found in their pure forms in nature
What are ore minerals?
Minerals that contain metals and other elements that can be extracted.
What are oxides?
Common ore minerals that for, when cation (usally metallic) reacts with oxygen.
What are sulfides?
Common ore minerals that form when a cation (usally metallic) reacts with sulfur
What is smelting?
The thermal/chemical process used to separate desired metals from their ores
How can cooling magma bodies create ore deposits?
Ore minerals form and often settle out of magma as it cools
How can hydrothermal activity create ore deposits?
Water ineracts with undergorund magma bodies and surrounding rocks - Hot water dissolves metals, allowing them to combine with other elements
How can placer deposits form ore deposits?
Streams erode rocks containing ores and or native metals - lighter sediments are carried away, but heavier ores and native metals arent easily transportand and become concentrated
What are Banded Iron Formations (BIFs) and what do they prove?
- Formations formed when dissolved iron in the ocean starting reactive with oxygen to form HUGE rust (iron oxide) deposits.
- They provide evidence for the inital accumulation of 02 on our planet
What is the relationship between ore grade and economic value?
- High value metals can be mined at lower grades
- Low value metals need high grades to be profitable
What is acid mine runoff and why is it harmful?
When mining exposes sulfide-bearing rocks which react with air/water to form sulfuric acid
What other aspects of ore proccessing causes pollution?
Trailing piles and smelting
Why does decompression cause melting at divergent boundaries?
Pressure is lowered as the over-riding plates are pulled apart, thinned, and split. Pressure is also lowered as new mantle rock rises to fill that space
Why does adding water cause melting at subduction zones?
The subducting slab gets so hot and pressurized that water contained within minerals is released, melting the surrounding rocks. The melt rises and eventual forms valcanoes at the surface
Why does increasing temperature cause melting at hot spots?
melting occures when the hot mantle plumes rise from great depth
How do igneous rocks form?
When magma/lava cools down and solidifies (=crystallization)
What are intrusive igneous rocks and why are they coarse-grained?
Rocks formed when magma cools undergorund
-Coarse grained becuase large minerals cool slowly underground
What are extrusive igneous rocks and why are they fine-grained?
Forms when lava cools and solidifies on the serface
- Fine-grained because small minerals cool quickly
What does a mix of fine- and coarse-grained minerals mean?
Slow cooling underground followed by rapic cooling on the surface
What is ash?
Lava spray that rapidly solidifies into tiny shards of glass
What does felsic mean in terms of silica content, iron/magnesium content, mineral/rock color, and mineral /rock density
More silica, less iron and magnesium, lighter colored, less dense
What does felsic mean in terms of silica content, iron/magnesium content, mineral/rock color, and mineral /rock density
less silica, more iron and magnesium, darker, denser
What is the composition of continental crust?
relatively felsic
What is the composition of oceanic crust?
Mafic
What is the composition of the mantle?
Extremely mafic
What are the texture and composition of granite?
coarse grained, intrusive, felsic
What are the texture and composition of andesite?
fine-grained, extrusive, intermediate