Reaction Mechanisms
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is a curly arrow used to show in reaction mechanisms
Movement of an electron pair during a reaction
What can a curly arrow represent
Heterolytic fission or formation of a covalent bond
What is fission
Breaking of a covalent bond
Define homolytic fission
Each atom receives one electron from the bonded pair
Products of homolytic fission
Two radicals
Arrow type for homolytic fission
Single-headed curly arrow
Define heterolytic fission
One atom receives both electrons from the bonded pair
Products of heterolytic fission
Positive ion and negative ion
Arrow type for heterolytic fission
Double-headed curly arrow
Which fission occurs in most mechanisms
Heterolytic fission
What is a radical
Species with an unpaired electron
How are radicals represented
By a dot
Define addition reaction
Reactants combine to form a single product
Define substitution reaction
One functional group replaced by another
Define oxidation
Loss of at least one electron
Define reduction
Gain of at least one electron
Define polymerisation
Many monomers join to form a long repeating polymer
Define elimination
A small molecule is removed from a larger molecule
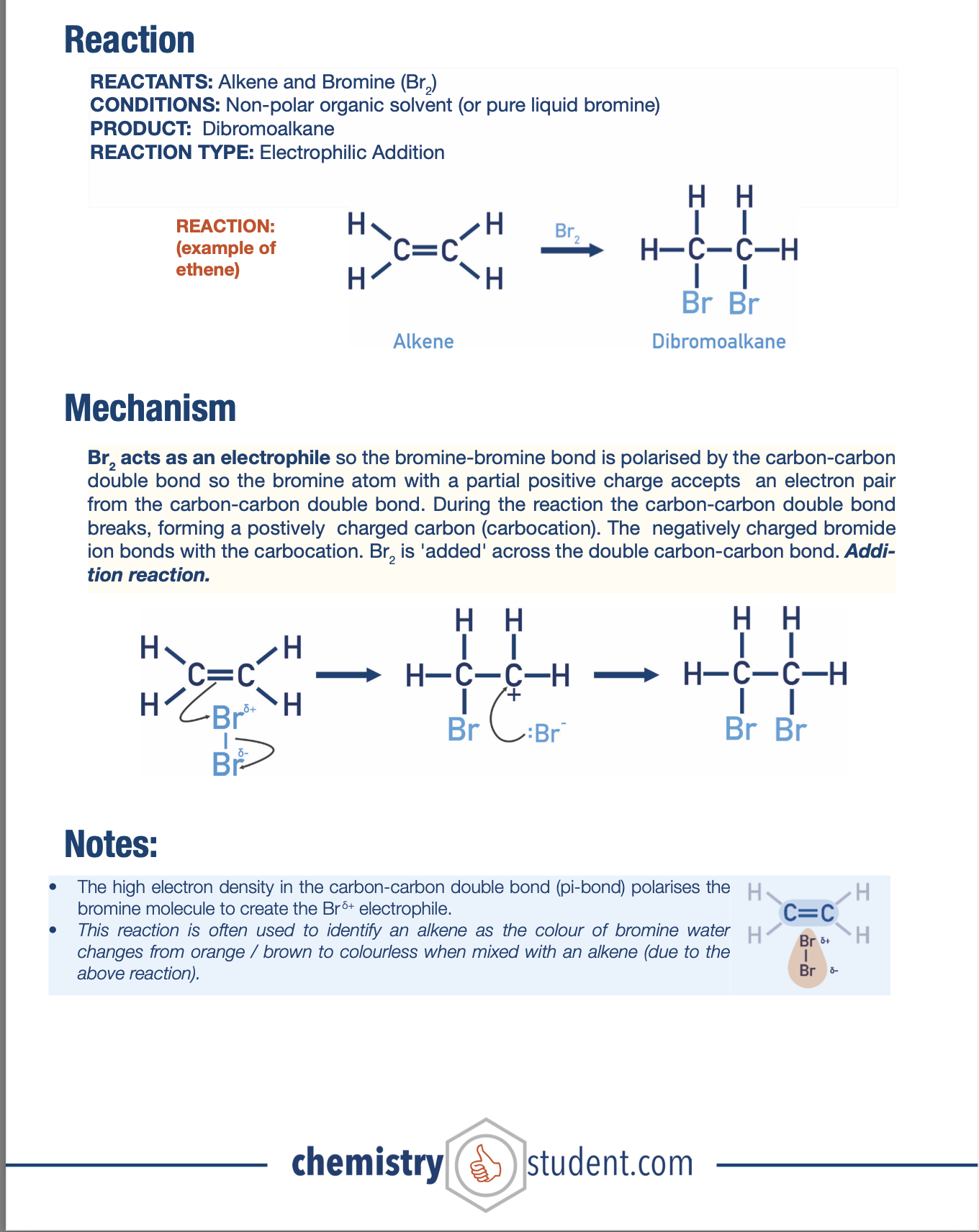
Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with Br2 Mechanism
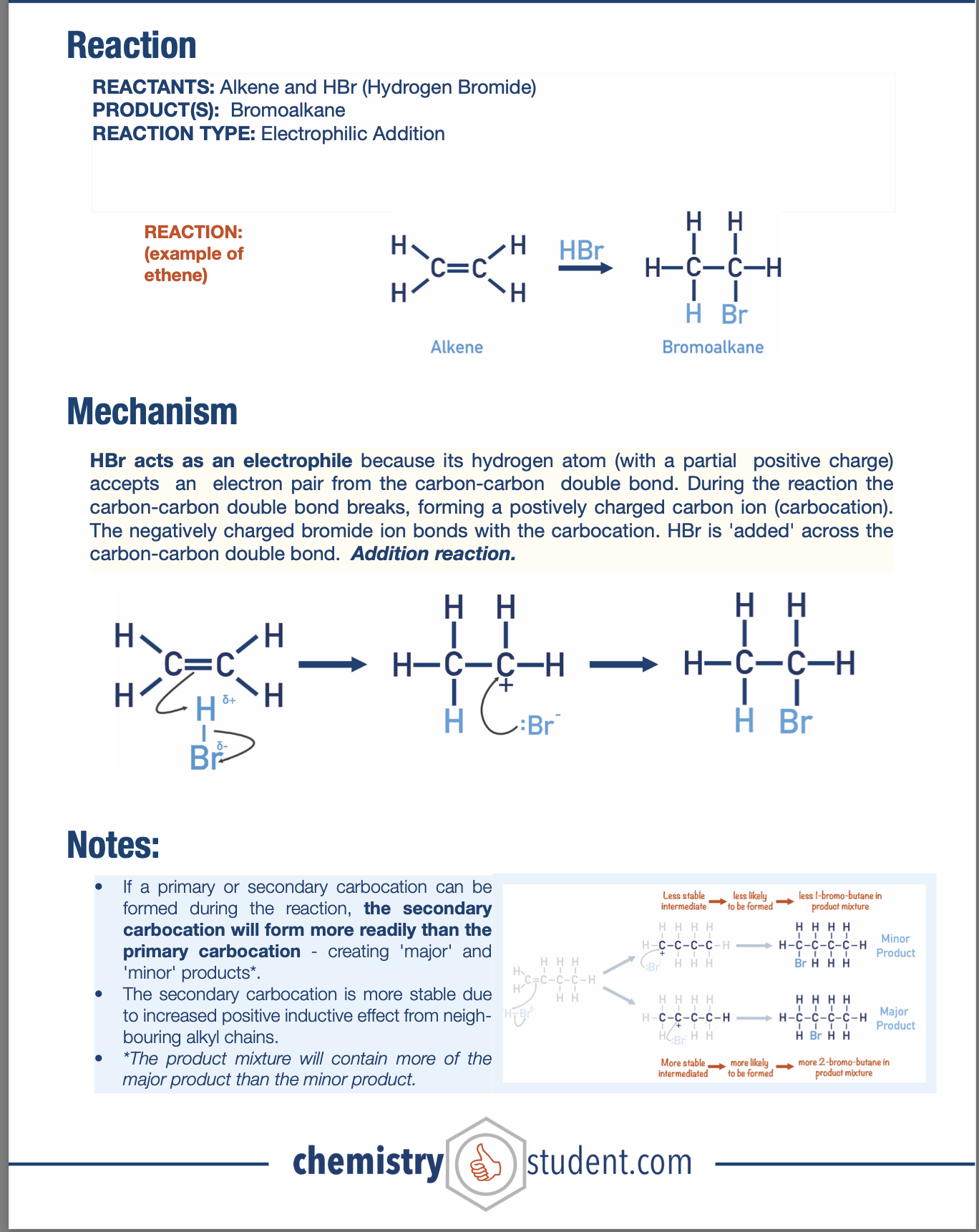
Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with HBr Mechanism
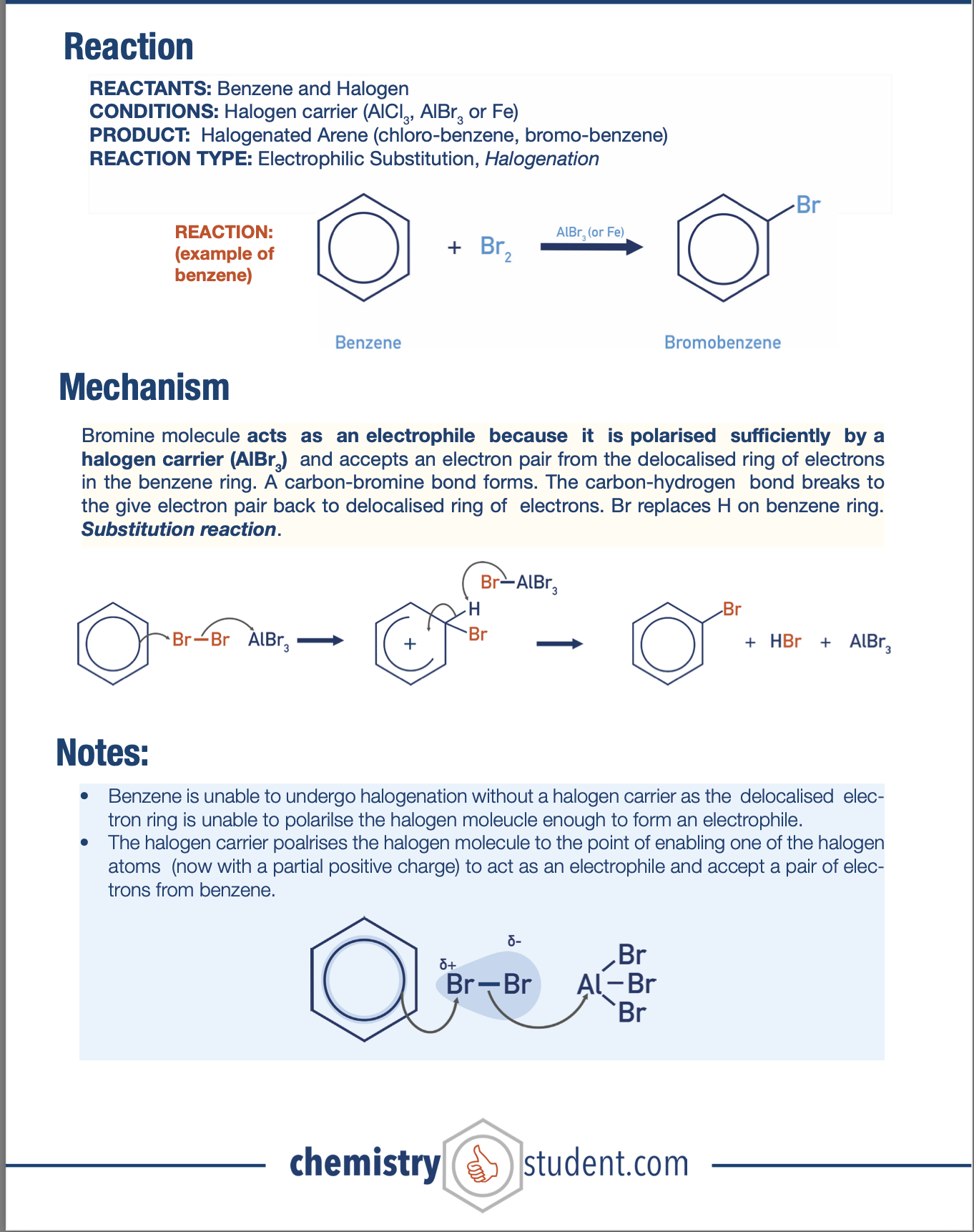
Halogenation with Benzene Mechanism
Nitration of Benzene Mechanism
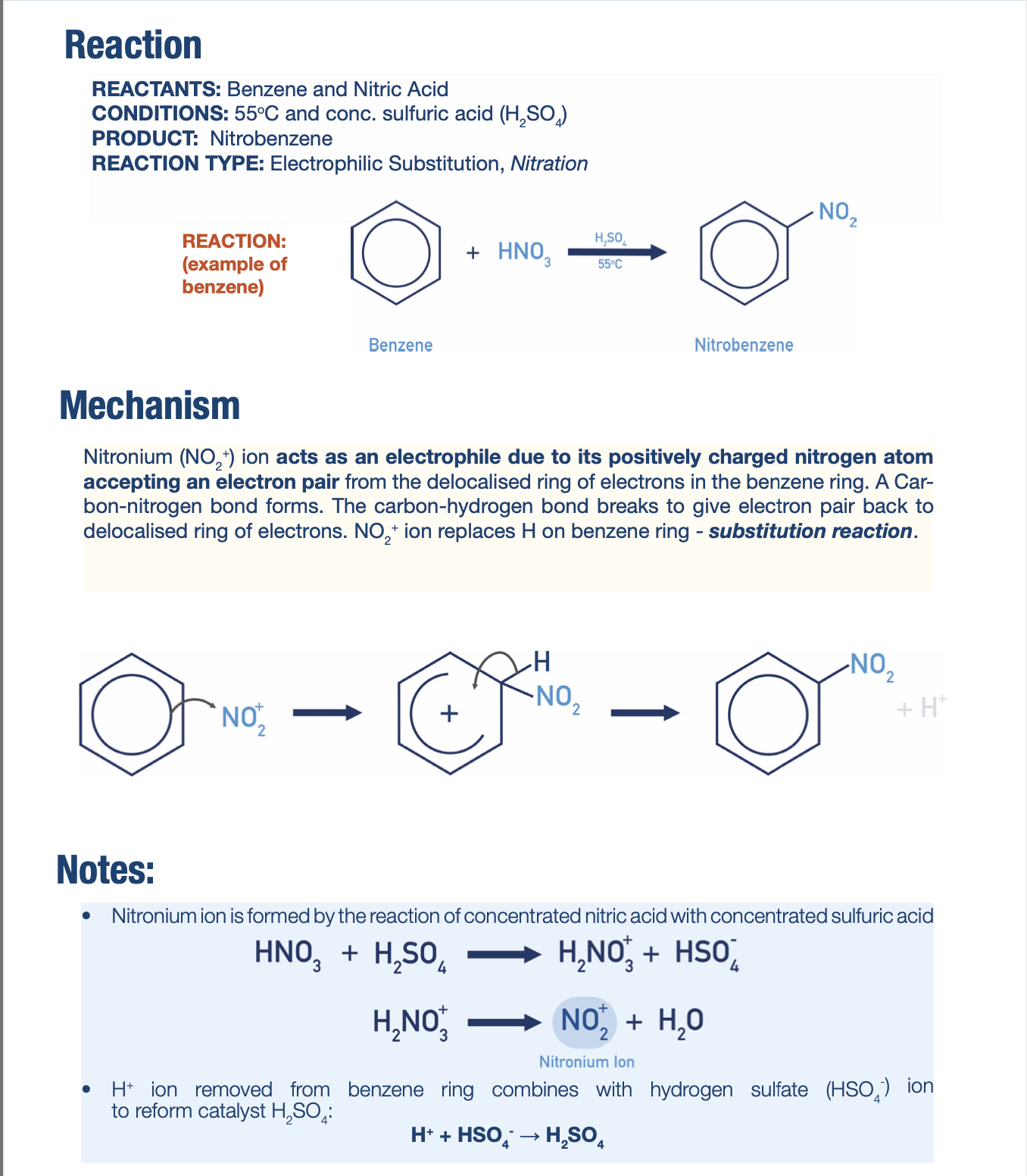
Nucleophilic Addition to a Carbonyl with Cyanide Mechanism
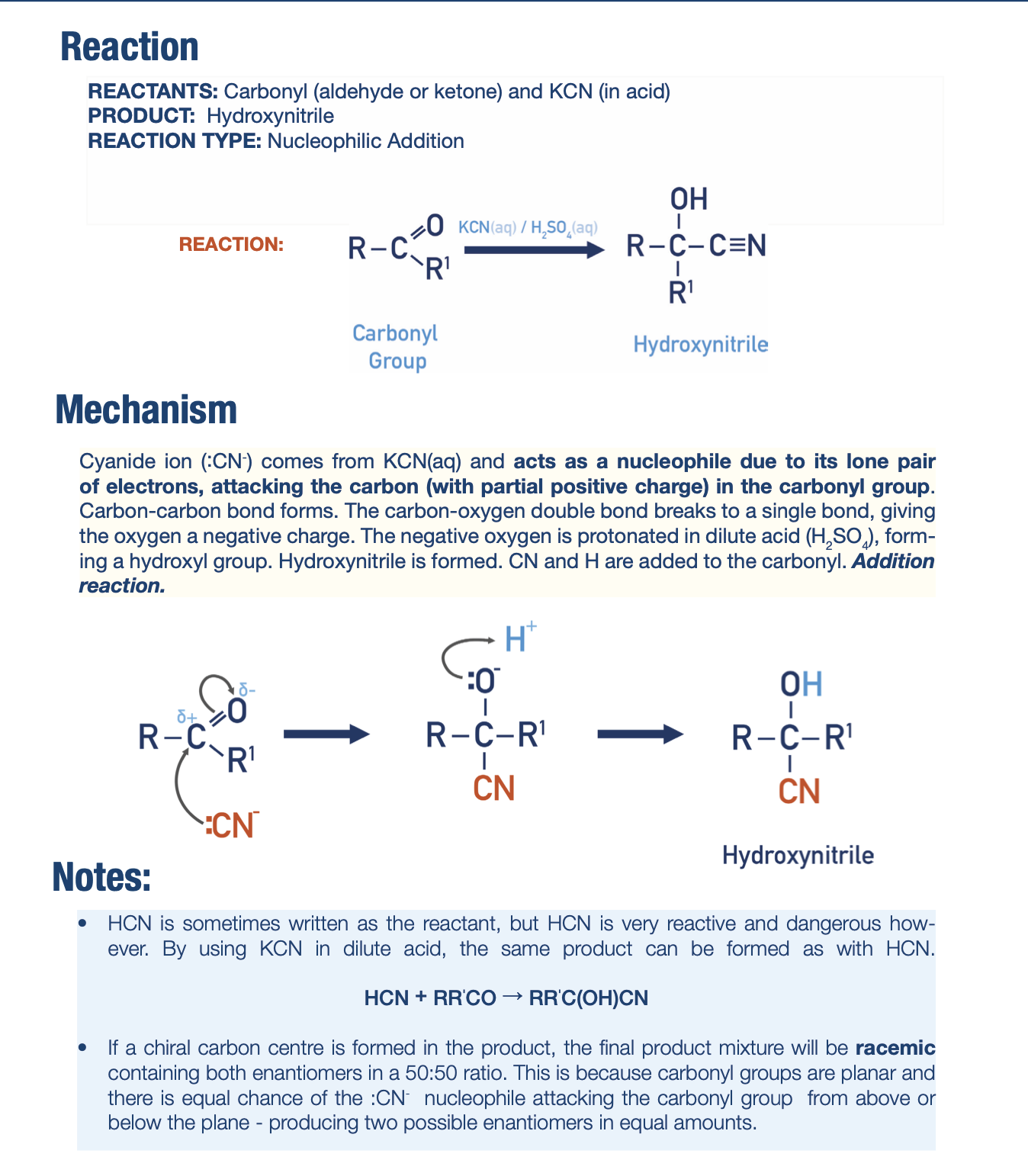
Reduction of Carbonyls Mechanism
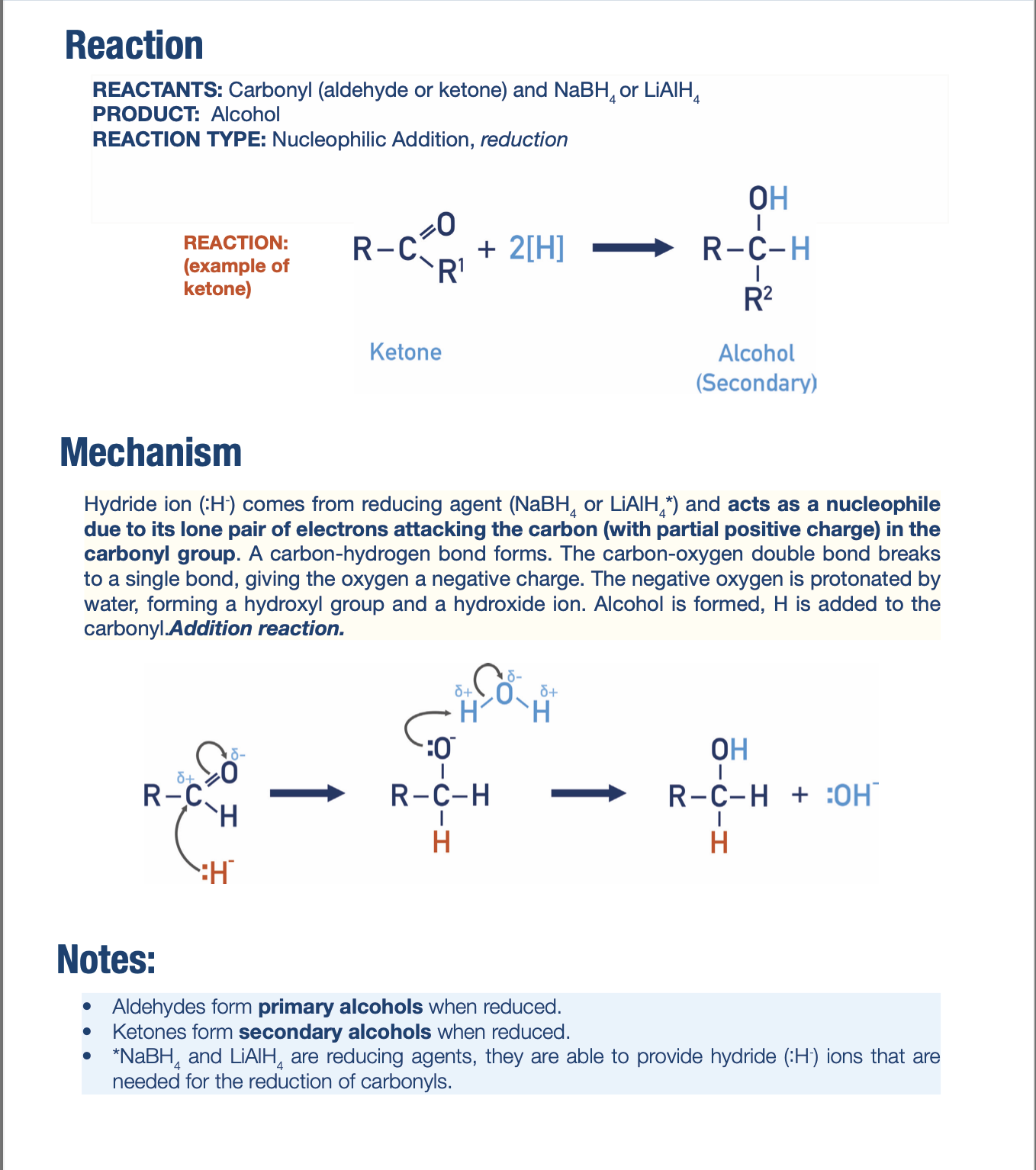
Nucleophilic Substitution of Haloalkanes Mechanism
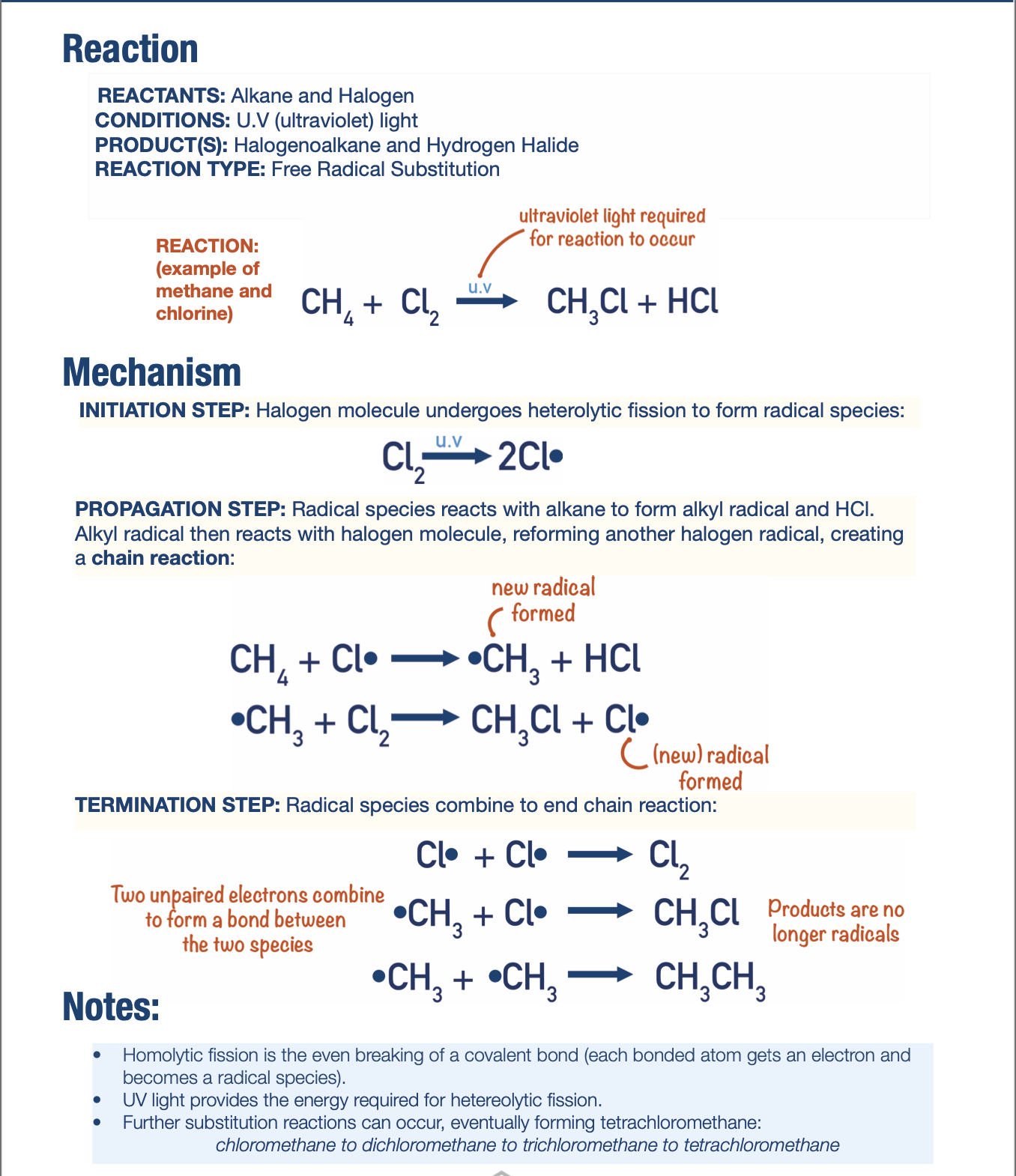
Free Radical Substitution Mechanism