Economics and Personal Finance H Final Exam
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 1-3.8, 6.1, 6.3, 8.3, 9.1, 9.3, 9.4 (economics book) and Finance vocab
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
need
something essential for survival
want
something we desire that is not essential for survival
goods
physical objects that someone produces
services
actions or activities that one person performs for another
scarcity
the fact that there are limited goods and services to fulfill unlimited wants
economics
the study of how people seek to satisfy their wants and needs by making choices
shortage
when consumers want more of a good or service than producers are willing to make available at a particular price (demand is more than supply)
entrepreneurs
people who decide how to combine resources to create new goods and services
factors of production
resources used to make all goods and services (land, labor, capital)
land
a factor of production that consists of all natural resources used to produce goods and services
labor
a factor of production that consists of the effort people devote to tasks for which they are paid
capital
a factor of production that consists of any human-made resource that is used to produce other goods and services
physical capital
human made objects used to create other goods and services
human capital
the knowledge and skills a worker gains through education and experience
trade-off
the act of giving up one benefit in order to gain another, greater benefit
“guns and butter”
a term used to describe the common choice governments face: spending money on military or domestic needs
opportunity cost
the most desirable alternative somebody gives up as the result of a decision
thinking at the margin
the process of deciding whether to do or use one additional unit of some resource
cost/benefit analysis
a decision making process in which you compare what you will sacrifice and gain by a specific action
marginal cost
the extra cost of adding one unit
marginal benefit
the extra benefit of adding one unit
production possibilities curve
a graph that shows alternative ways to use an economy’s productive resources
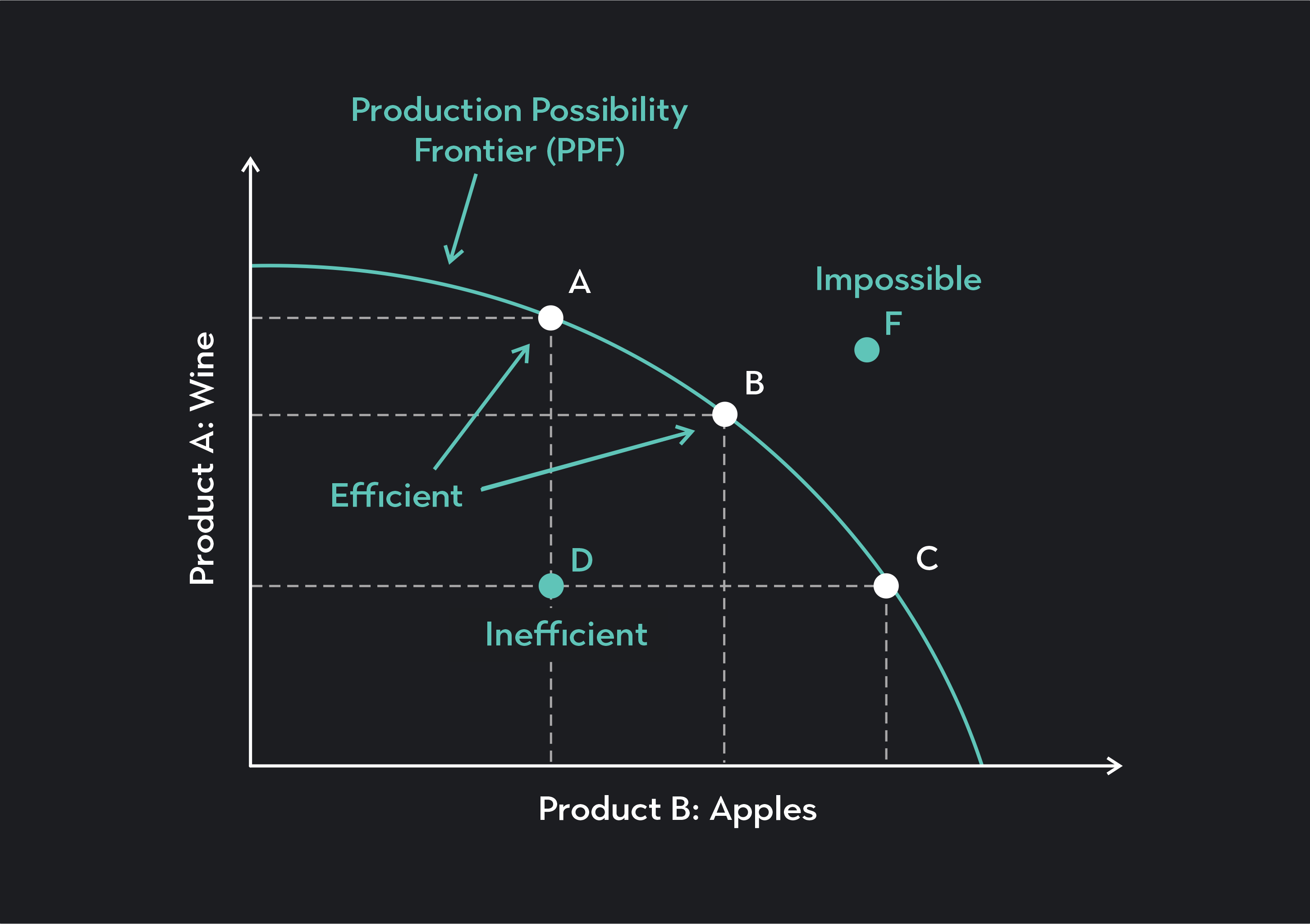
production possibilities frontier
a line on a production possibilities curve that shows the maximum possible output an economy can produce
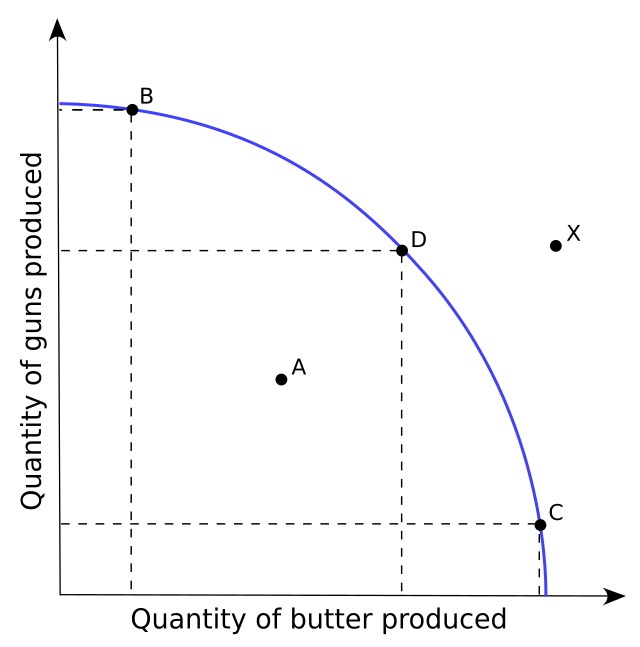
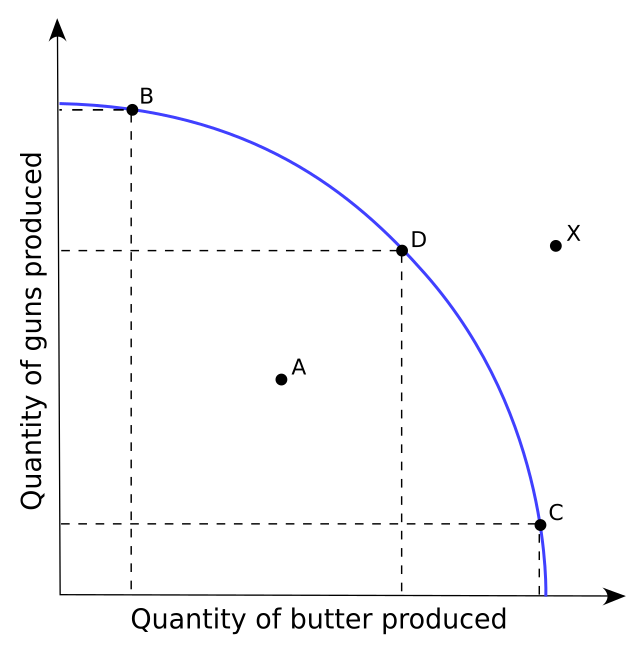
efficiency
the use of resources in such a way as to maximize the output of goods and services (B, D,C)
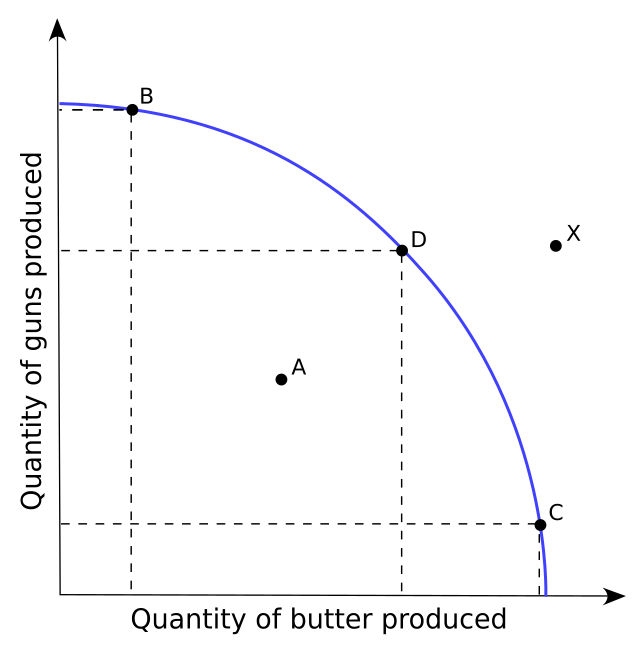
underutilization
the use of fewer resources than the economy is capable of using (A)
law of increasing costs
an economic principle which states that as production shifts from making one good or service to another, more resources are needed to increase production of the second good or service
economic system
the structure of methods and principles a society uses to produce and distribute goods and services
factor payments
the income people receive in return for supplying factors of production
profit
the amount of money a businessreceives in excess to its expenses
safety net
a set of programs to protect people who face unfavorable economic conditions such as layoffs, injuries, or natural disasters
What are the economic goals of a society?
efficiency, freedom, security, equity, growth
standard of living
level of economic prosperityinnovation
innovation
the process of bringing new methods, products, or ideas into use
traditional economy
relies on habit, custom or ritual to answer the three basic economic questions
What are the three basic economic questions?
What goods and services should be produced? How should these goods and services be produced? Who consumes these goods and services?
market
any arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things
specialization
the concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and businesses on a limited number of activities
free market economy
an economic system in which decisions on the three key economic questions are based on voluntary exchange in markets
households
a person or group of people living in a single residence
firms or businesses
an organization that uses resources to produce a product or service which it then sells
factor market
the area of exchange in which firms purchase the factors of production from households
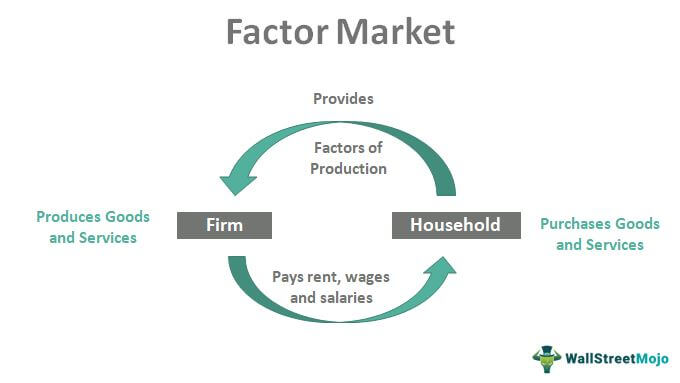
product market
the arena of exchange in which households purchase goods and services from firms
Adam Smith
competition and self-interest fuel a marketplace and help to keep it functioning
self interest
a persons own personal gain
incentive
the hope of reward or fear of penalty that encourages a person to behave in a certain way
competition
the struggles among producers for the dollars of consumers
price competition
producers compete to offer the lowest price for a good that is identical to goods made by other producers
non-price competition
producers compete by offering higher quality goods or goods with different features
consumer sovereignty
consumers have the power to decide what gets produced
socialism
a range of economic and political systems based on the belief that wealth should be distributed evenly throughout a society
communism
central government owns and controls all resources and means of production and makes all economic decisions
authoritarian
limits individual freedoms and requires strict obedience from their citizens
laissez-faire
the doctrine that government generally should not intervene in the marketplace
centrally planned economy
also called command economy, an economic system in which the government makes all decisions on the three key economic questions
private property
property owned by individuals or companies and not by the government
intellectual property
creations, such as books, songs, or symbols, that consist of ideas rather than physical objects
mixed economy
an economic system that has some market-based elements and some government involvement
economic transition
a period in which a nation moves from one economic system to another
privitazation
selling enterprises operated by the government to individuals
profit motive
the incentives that drives individuals and business owners to improve their material well-being
open opportunity
anyone can compete in the marketplace
legal equality
the principle that everyone has the same legal rights