UNIT 6 APHG FINAL
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Nation
a group of people with unifying cultural characteristics and a perceived home. It consists of people with a common ethnic identity.
State
this is an area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government that has sovereignty over its internal and external affairs. (Ex: North and South Korea)
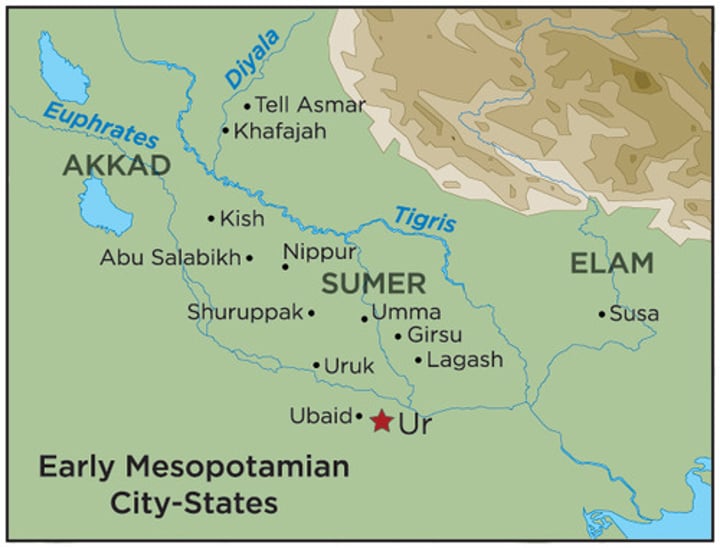
City-state
A state whose territory is confined to a city’s boundaries (Ex. The first states in Mesopotamia, which was at the eastern end of the Fertile Crescent, were known as city-states.)
Nation-state
is where political boundaries coincide with the territory occupied by a particular ethnicity that has been transformed into a nationality. (Ex. Denmark)
Multinational state
a state that contains two or more ethnic groups. Territorial conflict often occurs in multinational states. (Ex. The island of Cyprus contains two ethnic groups, Greek and Turkish.)
Self-determination
the right to become an independent state. (Ex.there are still ethnic groups within Russia like Chechnya fighting for self-determination.)

Sovereignty
a government or state with a supreme power or authority to govern itself or another state. (Ex. Morocco and Western Sahara.)

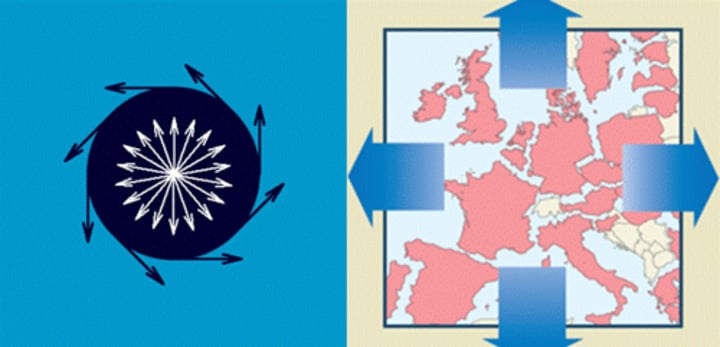
Centrifugal Forces
promotes division within a state—pulls countries apart.
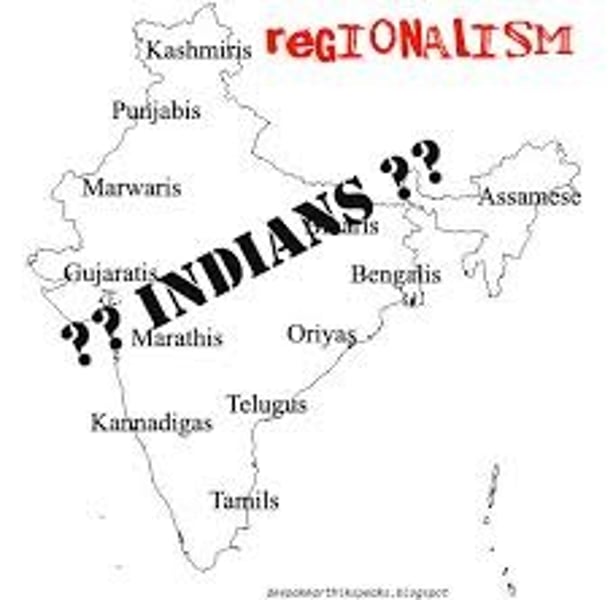
Regionalism
is the identification with a minority group and region rather than a state.
Centripetal Forces
promotes unification within a state—pulls countries together.

Nationalism
is the loyalty and identification with one nation or state and its goals, above all others.

Colonialism
a policy by which a nation maintains or extends its control over foreign dependencies.
Imperialism
refers to the control of territory by a foreign power
United Nations (UN)
a global organization that focuses on peace and security.
established in 1945
political/military alliance
headquarters in NYC
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
a regional economic alliance between the US, Mexico, and Canada
European Union (EU)
a regional economic union that also includes elements of political unity including a common currency
Established in 1958
Promote peace through economics and international trade
Economic alliance
Supranational Organizations
includes the membership of two or more states that relinquish some degree of sovereignty for the benefits of an alliance with other states. (Ex. European Union.)
North-Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
became the opposing military alliance of the Cold War. (International Alliance of 26 countries of Europe and North America.)
Established in 1949
Military alliance
Prevent soviet union from invading democracies of Europe
Terrorism
is the systematic use of violence by a group in order to intimidate a population or coerce a government into granting its demands.
Boundary
an invisible line that completely surrounds a state, marks the outer limits of its territorial control and gives it distinct shape. (Ex. Antarctica is divided up and claimed by countries.)
Physical Boundaries
follows an important geographic feature on the landscape. (Ex. Boundary between Spain and France is the crest of the Pyrenees Mountains.)
Cultural Boundaries
political boundary that separates different cultures. (Ex. former Yugoslavia.)
Religious Boundaries
boundary that separates different religions (Ex. Muslims are reorganized into Pakistan and Hindus into India.)
Language Boundaries
boundary that separates different language speakers (Ex. In Europe; France, Spain, Portugal etc. all based their boundary lines because of the language people spoke.)
Artificial (geometric) Boundaries
political boundaries defined and delimited as straight lines or arcs. (Ex. Mason-Dixon Line.)
Superimposed Boundary
forced onto a populated area by an outside power that is unconcerned with preexisting divisions. (Ex. African States)
Enclave
is a piece of territory that is surrounded by another political unit of which it is not part of.(Ex. Lesotho by South Africa.)
Exclave
states that have fragmented territory that lies completely within the boundary of another state.(Ex. West Berlin during the Cold War.)
Landlocked
states that lack access to the ocean or sea. (Ex.Lesotho)
Frontiers
is a zone or area between states where no state exercises complete control. (Ex. the Arabian Peninsula)
Political Geography
the spatial study of the organization and distribution of political phenomena. (Ex: boundaries, voting patterns, distribution of wealth etc.)
Geopolitics
the study of the influence of such factors as geography, economics and demography on politics.

State
this is an area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government that has sovereignty over its internal and external affairs. (Ex: North and South Korea)
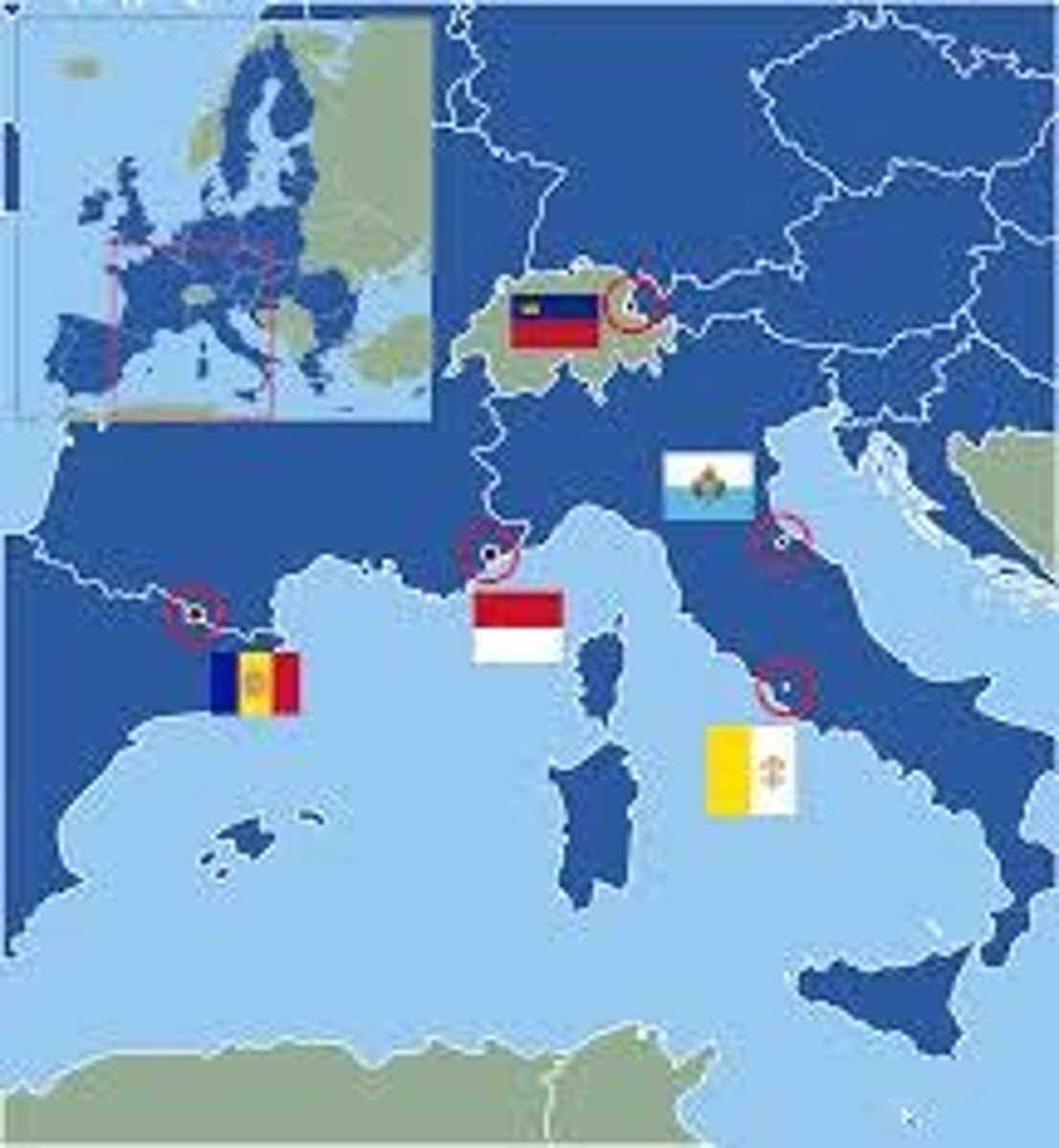
Micro-state
states with very small land areas. (Ex. The smallest micro-state in the United Nations is Monaco.)
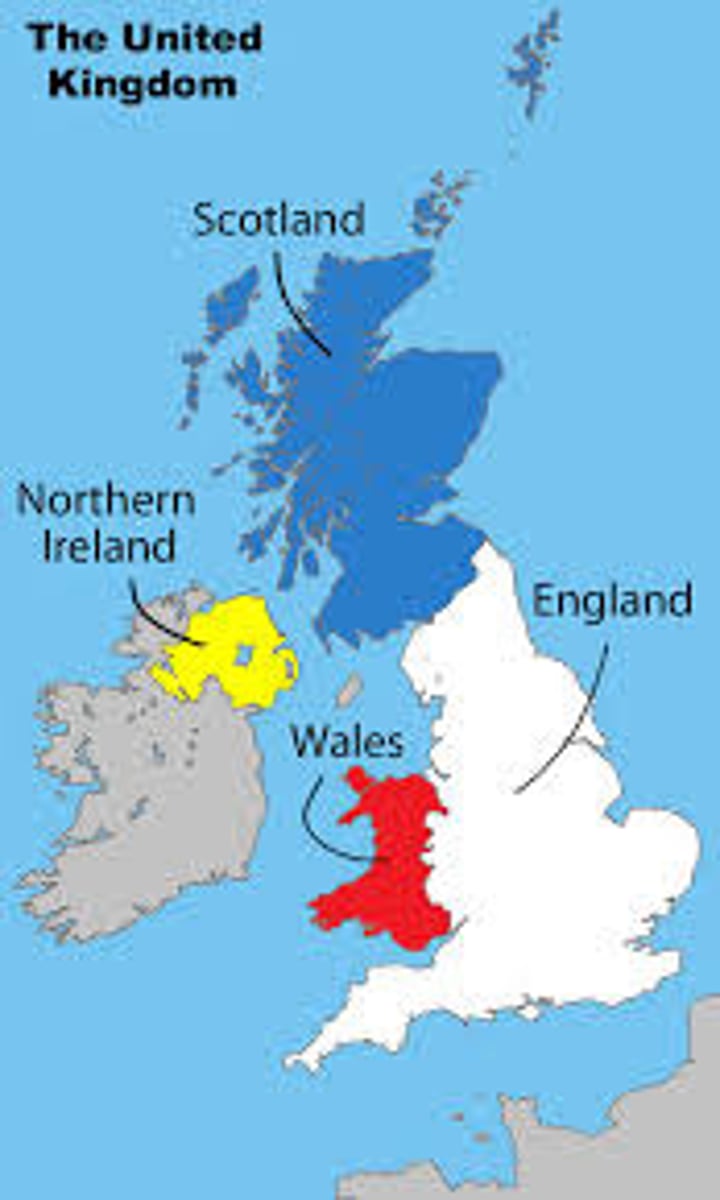
Multinational state
a state that contains two or more ethnic groups. Territorial conflict often occurs in multinational states. (Ex. The island of Cyprus contains two ethnic groups, Greek and Turkish.)
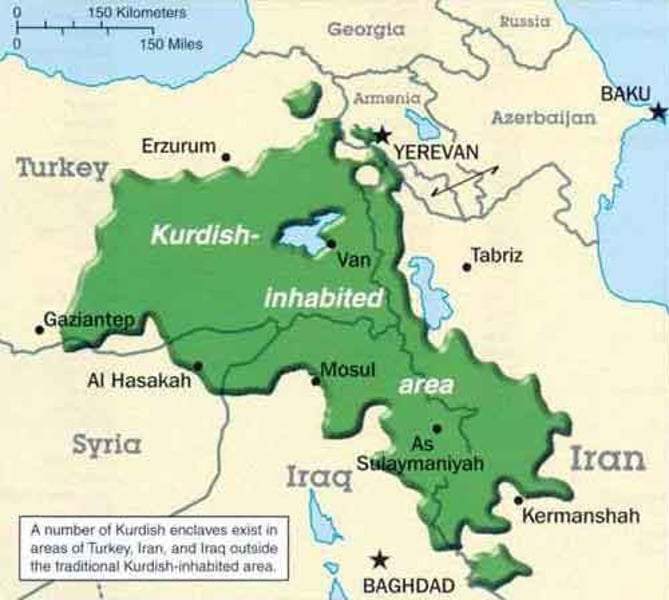
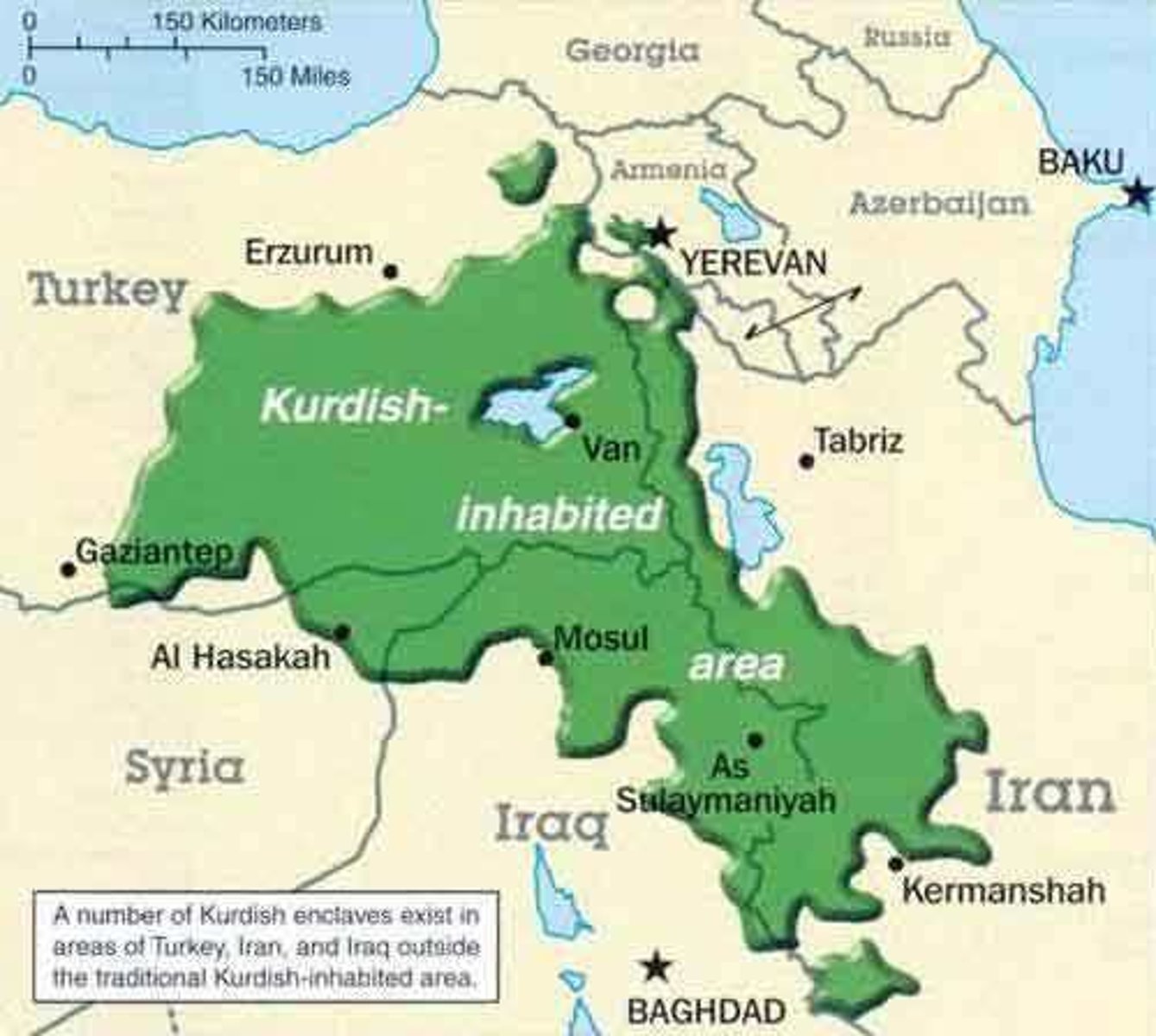
Stateless nation
an ethnic group is divided among more than one state. (Ex. In the Caucasus region the Kurds.)
Rimland Theory
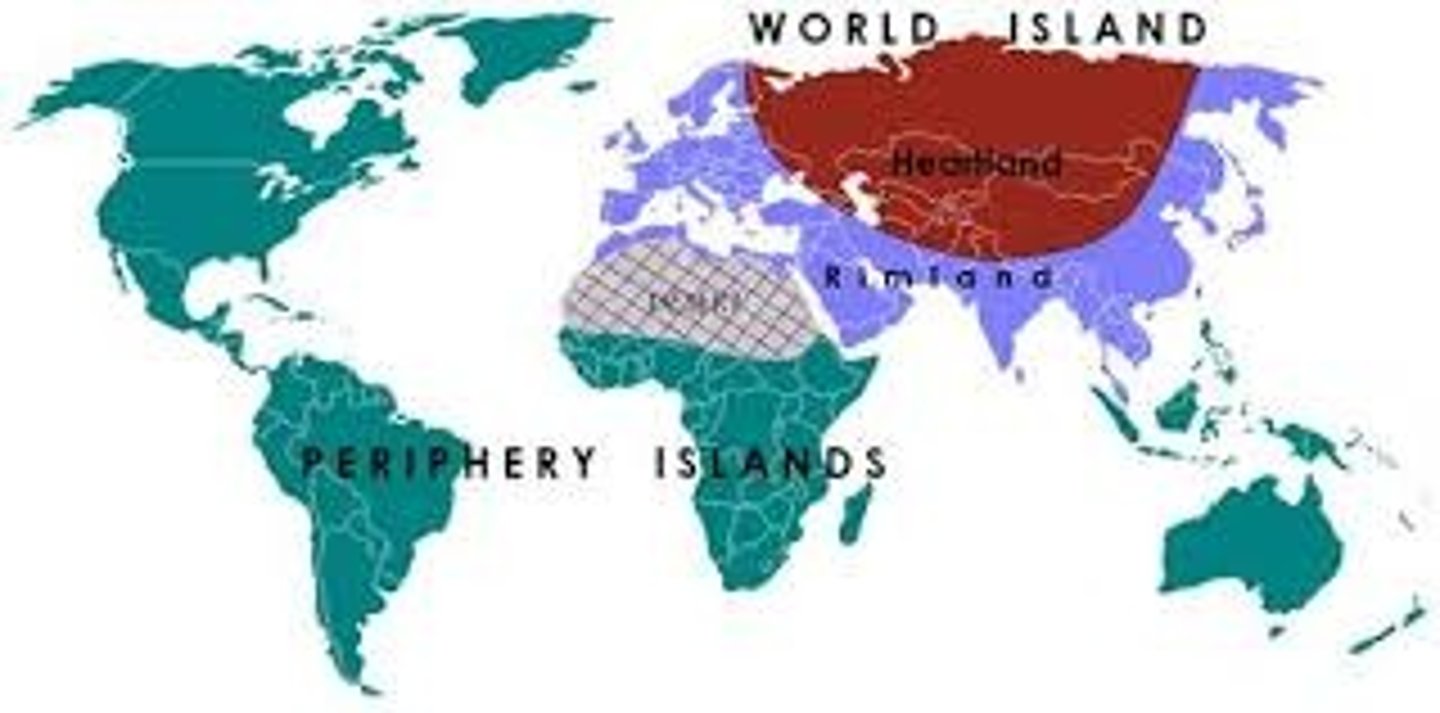
Nicholas Spykman developed this theory arguing that the rimland area surrounding the heartland (including the world's oceans) was the key to world political power.
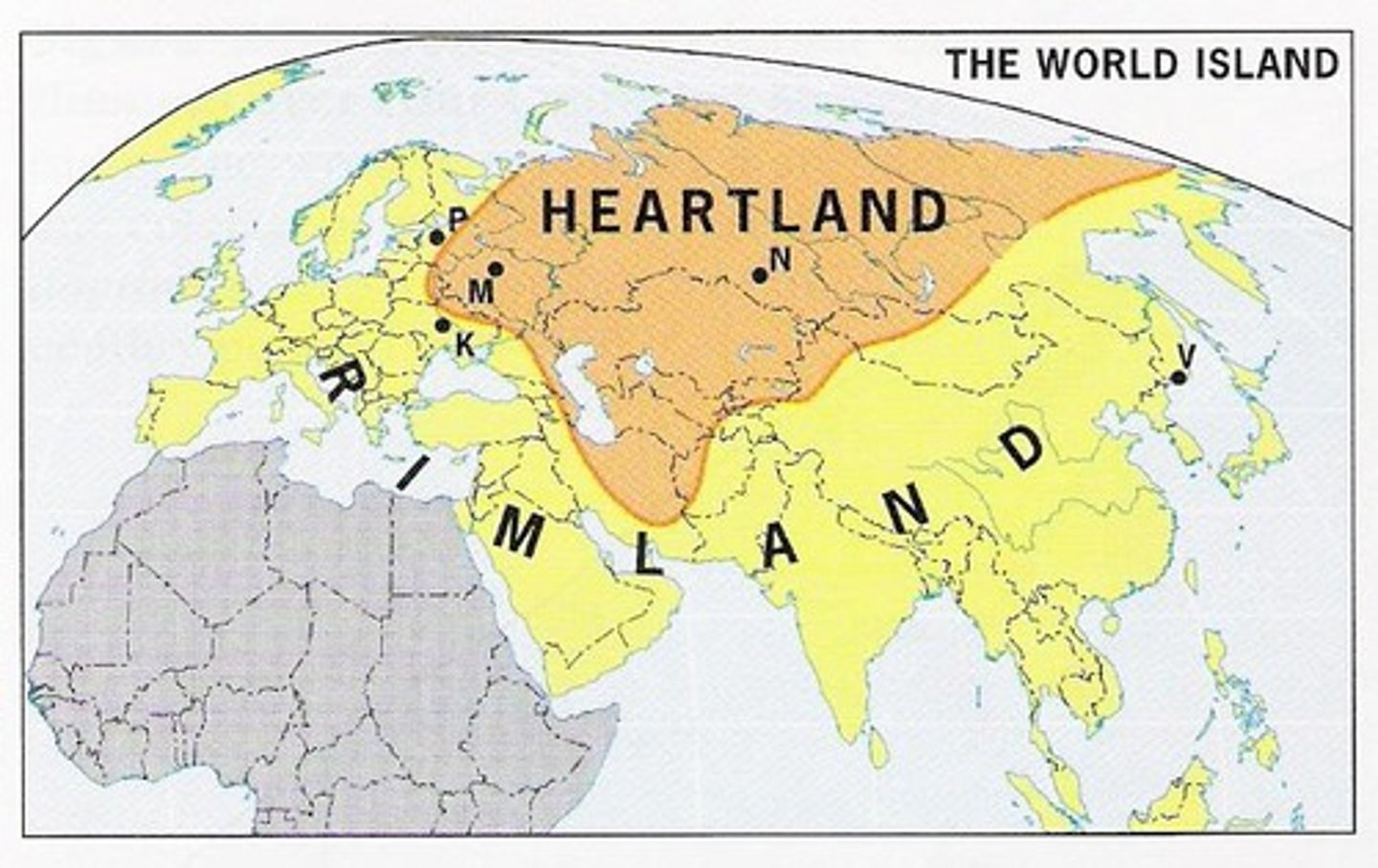
Heartland Theory
Sir Halford Mackinder developed this theory in the beginning of the 20th century that stated that the Eurasian landmass was the world's heartland and thus the key to world domination.
Sovereignty
a government or state with a supreme power or authority to govern itself or another state. (Ex. Morocco and Western Sahara.)

Regionalism
is the identification with a minority group and region rather than a state.

Colonialism
a policy by which a nation maintains or extends its control over foreign dependencies.
Colonies
a group of people who settle in a distant land but remain under the political jurisdiction of their native land. Colonialism refers to the control of territory previously inhabited. (Ex. Europeans in Latin America, Asia and Africa)
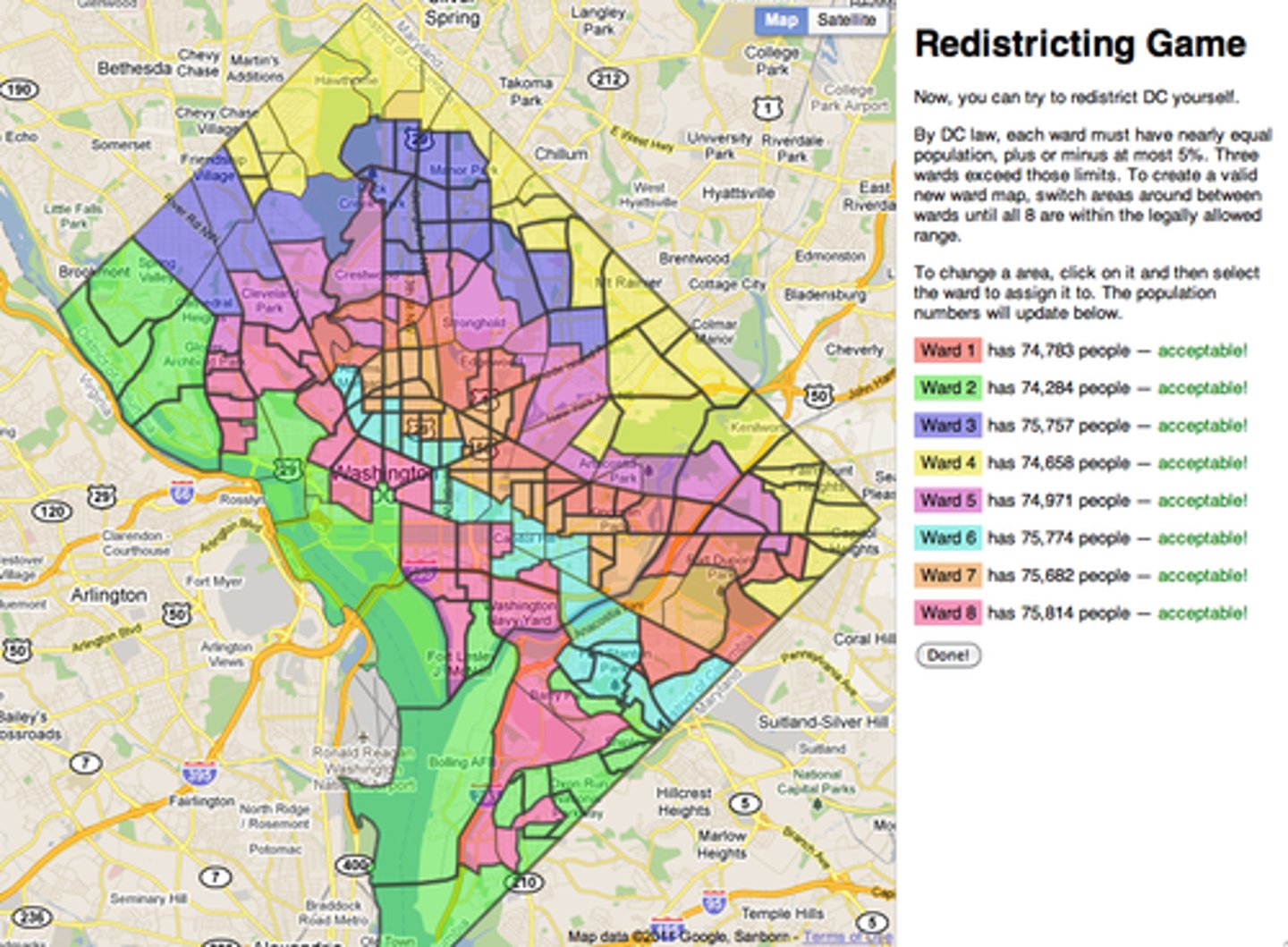
Gerrymandering
is the redrawing of legislative boundaries to benefit a specific political party in power.
Unitary State
country with a centralized government and cultural homogeneity. (Ex. Unitary states include Western Europe such as Britain or France.)
Advantageous for an ethnically homogenous state
Japan, Saudi Arabia, France, Spain
Most governmental powers reside at the national level
Typically smaller states
Federal States
allocate significant power to the units of local government and work well in multinational states where there is potential ethnic conflict. (Ex. The United States)
Governmental powers split between national and local levels
Germany, Brazil, India, US
Large states where communication is difficult
Local governments empower ethnicities
Supranational Organizations
includes the membership of two or more states that relinquish some degree of sovereignty for the benefits of an alliance with other states. (Ex. European Union.)
Warsaw Pact
a treaty of mutual defense and military aid signed at Warsaw on May 14, 1955( after WW11), by communist states of Europe under Soviets influence.
Balance of Power
when a large number of states were of roughly equal strength, no single state could dominate.
Terrorism
is the systematic use of violence by a group in order to intimidate a population or coerce a government into granting its demands.
Boundary
an invisible line that completely surrounds a state, marks the outer limits of its territorial control and gives it distinct shape. (Ex. Antarctica is divided up and claimed by countries.)
Compact state
states that are roughly circular in shape and the distance from the edges to the center are minimal. (Ex. Poland, Zimbabwe, and Uruguay.)
Fragmented state
a state that is divided into several discontinuous pieces of territories.(Ex. Philippines and Indonesia.)
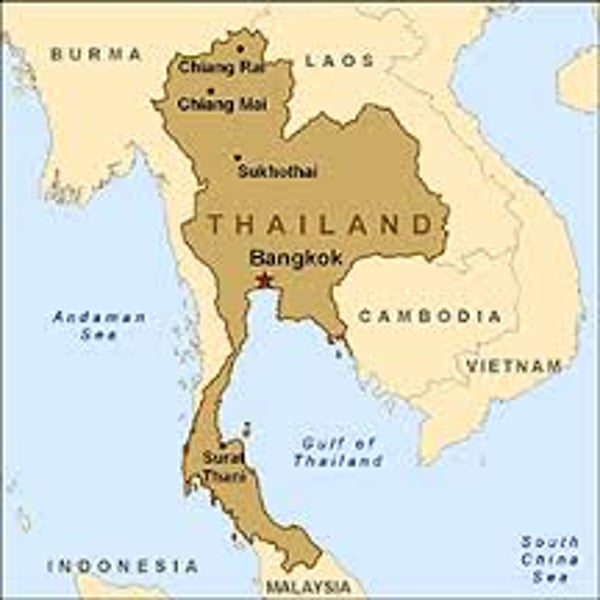
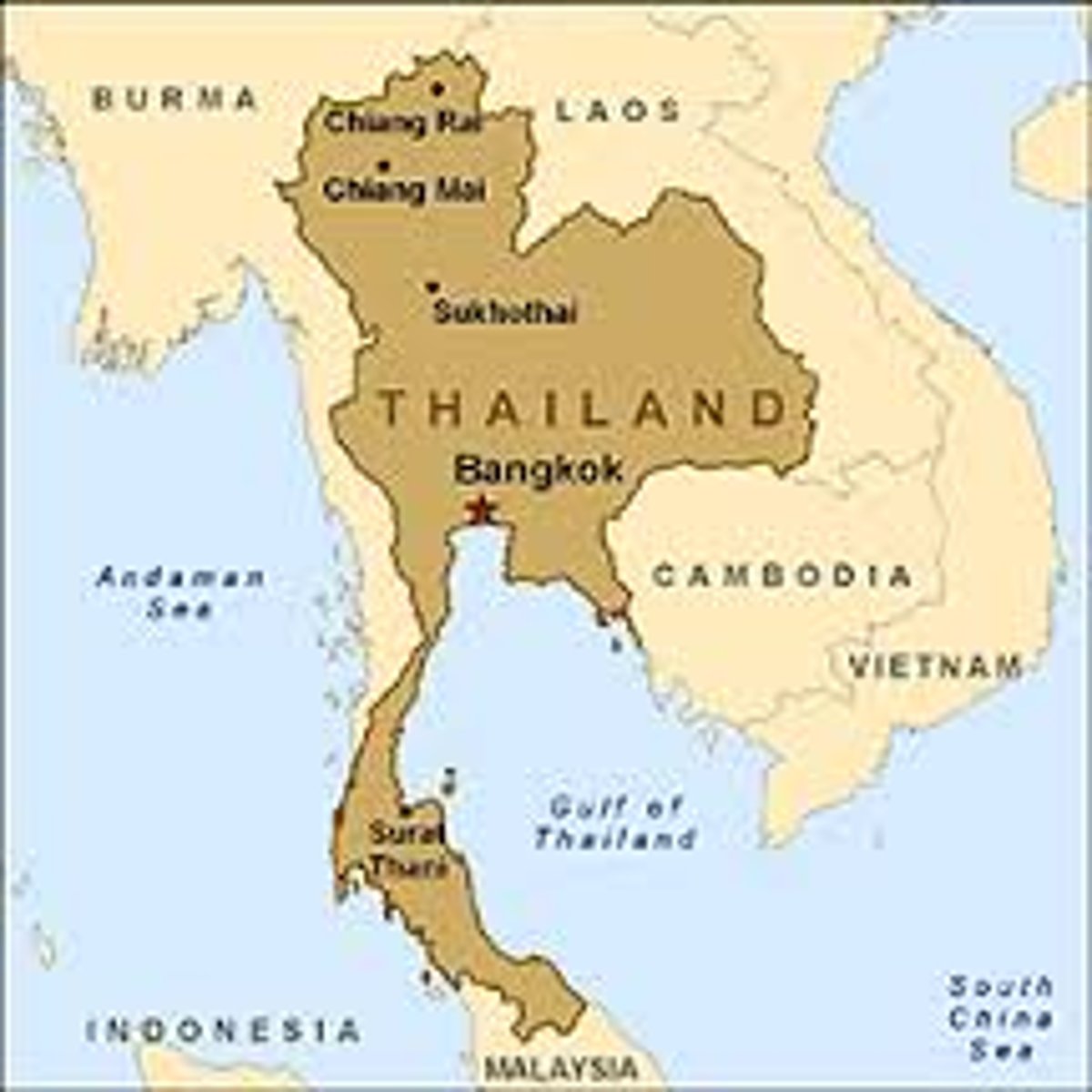
Prorupted state
compact states with a large projecting extension.(Ex. Thailand.)
Perforated state
states completely surrounded by other states.(Ex. Italy, South Africa.)
Elongated state
states that suffer from poor internal communications because they are so long and thin.(Ex. Chile and The Gambia.)
Landlocked
states that lack access to the ocean or sea. (Ex.Lesotho)
Territoriality
In political geography, a country's or more local community's sense of property and attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it inviolable and strongly defended.
Types of physical boundaries
Desert, Mountain, Water (be sure to know the problems and benefits of using these as boundaries)
territorial waters
up to 12 nautical miles from shore, a state may set laws regulating passage by ships registered in other states
Contiguous Zone
Between 12 and 24 nautical miles from shore, a state may enforce laws concerning pollution, taxation, customs, and immigration
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
between 24 and 200 nautical miles, a state has the sole right to the fish and other marine life
international waters
the areas of the sea that are not under the jurisdiction of any state's control
wasted vote gerrymandering
opposition supporters are spread across many districts but in the minority
excess vote gerrymandering
opposition supporters are concentrated into a few districts
stacked vote gerrymandering
distant areas of like-minded voters are linked through oddly shaped boundaries
The Warsaw pact
An alliance between the Soviet Union and other Communist Eastern European states. Disbanded in 1991
European Union (EU)
the world's largest common market, composed of 28 European nations. The main task is to promote development within member states through economic and political cooperation currently the United Kingdom is in the process of leaving the EU, known as "Brexit"
Balkanization
Refers to the breakup of a region or state into smaller, often hostile units along ethnic, religious, or cultural lines
The Balkans in the southeastern Europe serve as a historical example, where the term originated due to the complex ethnic and religious diversity leading to conflicts and the eventual breakup of Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia was a multi-ethnic state in southeastern Europe that disintegrated in the 1990s due to ethnic tensions, leading to a series of violent conflicts and the emergence of several independent nations such as Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, etc.
Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
Rooted in competing claims to the land of historic Palestine, this conflict involves Israelis (mostly Jews) and Palestinian (mostly Arabs)
Key issues include borders, settlements, the state of Jerusalem, Palestinian statehood, and the rights of refugees
Various wars and uprisings, such as the Arab-Israeli Wars, Intifadas, and conflicts in Gaza, have marked this protracted conflict
Treaty of Versailles and Creation of Israel
The Treaty of Versailles, which ended World War 1, redrew the map of Europe and the Middle East, leading to the breakup of empires and the creation of new states based on ethnic and national identities
The creation of Israel in 1948 resulted from Zionist aspirations for a Jewish homeland and led to ongoing conflicts with Palestinian Arabs over territory and national rights
Rwandan Genocide
In 1994, ethnic Hutu extremists targeted ethnic Tutsis and moderate Hutus in Rwanda, resulting in the mass slaughter of approximately 800,000 people.
Historical tensions, exacerbated by colonial legacies and political manipulation, culminated in one of the most devastating genocides in modern history.
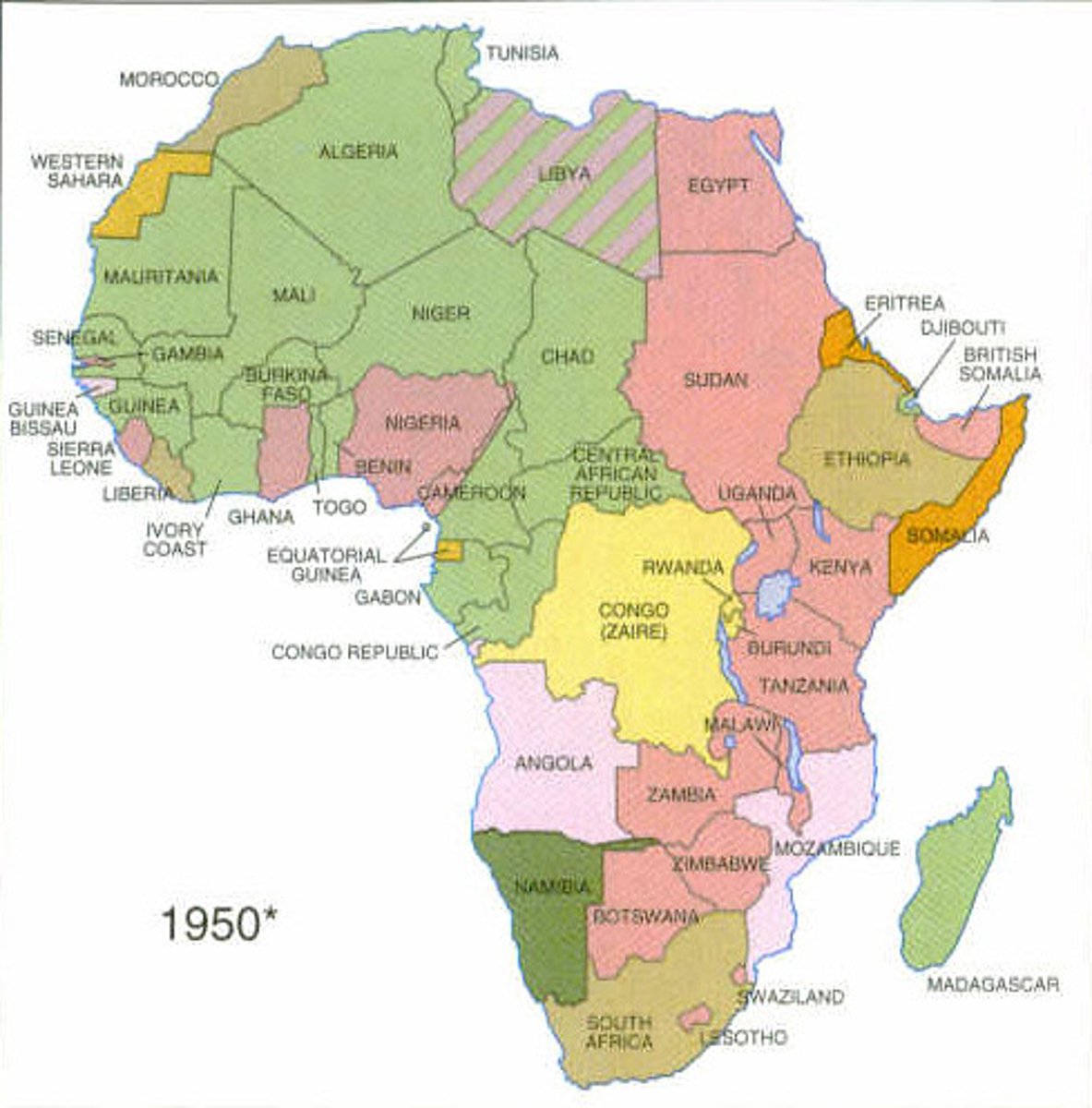
Berlin Conference
The Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 was a meeting among European powers to partition Africa and establish colonial boundaries
This conference ignored ethnic and cultural realities, leading to arbitrary borders that divided indigenous ethnic groups and contributed to conflicts and instability in post-colonial Africa
Cracking
Spreading minority votes over many districts as possible
Advantageous for the majority
Packing
Concentrating majority votes few districts as possible
Advantageous for the minority
Constitutional Government
Organization, responsibilities, and powers of a government are codified in a document
Colony
Territory legally tied to a sovereign state and not completely independent
Historic reasons for acquiring colonies
To increase relative power European powers
To extract useful resources and to serve as captive markets
To promote Christianity
What defines a state?
Defined boundaries
A permanent resident population
An organized economy and circulation system
Political sovereignty
Ancient States
City states
Concept of citizenship
Medieval States
Centralized government
States grow very large in size, mostly through conquest
Modern States
Constitutional government
Nation-states
Armenia
A genocide occurred at the hands of the Turks during WW1 in this country
Azerbaijan
The region of Nakhichevan is exclave to this country
Moldova
Ethnic Romanians make up the majority of the population in this country
Ukraine
The Crimea was formerly part of this country
Georgia
Abkhazia and Ossetia are disputed regions of this country
1824
Most of the Americas had gained their independence
1884
European powers conquered Asia and Africa
1936
Colonial Japan controlled Korea, Manchuria, Indonesia
1968
Most colonies in Africa and Asia had gained independence
How many states are there in the world today?
200
Census
The process that counts where people (both citizens and non citizens) live in the U.S.
Reapportionment
The process of determining how many Congressional Districts each state should have.
Controlled by US Federal/National congress
Redistricting
The process of determining the boundaries of each Congressional District.
controlled by individual us state legislatures
Supernationalism
The process of states organizing politically and economically into one organization
Relic boundary
A nonfunctional boundary that still exists
Suspect state
A state that is secretly developing a nuclear weapon
Aspect of Cold War
A war fought with words, ideas, and threats
A bi-polar world of conflict between communists and democratic states
Mutually assured destruction used as a deterrent
What percentage of Hispanics make up US?
18%