Isomerism and Carbonyls
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What can aldehydes be reduced to?
Primary alcohols
How can we represent a reducing agent?
[H]
What reducing agent can be used to reduce aldehydes?
Aqueous Sodium tetrahydridoborate/NaBH4
What is the name of the mechanism for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones?
Nucleophilic addition
What is required for nucleophilic addition?
A slightly positive carbon and slightly negative oxygen joined by a double bond
What happens during nucleophilic addition
A hydride (H- ion) or another nucleophile with a lone pair of electrons attacks the delta positive carbon
The pi bond in the C=O bond breaks and the electrons move from the bond to the oxygen so that carbon will only be bonded to 4 atoms
This forms an intermediate with a negative O with a lone pair of electrons and a hydrogen from the hydride ion or nucleophile attached to the carbon
A H+ ion from the NaBH4 solution then forms a bond from the lone pair of electrons on the negative oxygen
This forms an alcohol
When do optical isomers occur?
They occur when a carbon is attached to four different groups
We call this a chiral carbon
How do we represent a chiral carbon?
With an asterisk next to the chiral carbon in the compound
What is another name for optical isomers?
Enantiomers
What is the definition of an optical isomer?
Optical isomers have the same physical properties, but they rote the plane of polarised light in equal and opposite directions by the same amount
They are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
How can we describe enantiomers in terms of their image?
They are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
This means that they are mirror images that cannot be perfectly stacked on top of one another
What is plane polarised light?
Light only travelling in one plane
This is produced with the use of a polarising filter which has slits to only let one plane of light through
When plane polarised light passes through separate solutions of a pair of enantiomers, they rotate the light in equal and opposite directions
Under standard lab conditions, what percentage of each optical isomer will be formed in a reaction? How will this affect a plane of polarised light?
50%
If we have a solution like this the effects of each enantiomer will be cancelled out
We refer to them as optically inactive
A mixture of two enantiomers in a solution is called a racemic mixture
What are hydroxynitriles?
Compounds that contain O-H and C≡N
What is the priority of nitriles in terms of functional groups?
Second only to carboxylic acids
How can hydroxynitriles be formed?
By the reaction of an aldehyde with KCN followed by the addition of H2SO4
This is a nucleophilic addition reaction where the cyanide ion acts as a nucelophile
What should you remember about the charge on the cyanide ion?
The negative charge should be on the carbon
Why do we form hydroxynitriles from KCN and H2SO4 and not HCN?
HCN is incredibly lethal
Smells like almonds so yk its cooked
Why can we form racemic mixtures with KCN/H2SO4 or NaBH4
The nucleophile is equally likely to attack above or below the carbon in the aldehyde group to form a chiral carbon
This means we can form two compounds that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other- they are enantiomers
Standard answer for why we form racemic mixtures with KCN/H2SO4 or NaBH4? What are some exceptions to this?
The planar carbonyl group is equally likely to be attacked above or below its place
This leads to equal quantities of both isomers being formed- a racemic mixture is produced
One isomers will rotate plane polarised right clockwise, the other anticlockwise so the effects on plane polarised light cancel out
Exceptions to this are:
Methanol
Symmetrical ketones
What reactions can carboxylic acids have?
Acid + base → salt + water
Acid + metal carbonate+ Salt + carbon dioxide + water
Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
How do we draw metal ions attached to a carboxylic acid?
You need to draw a negative charge on the oxygen that has lost the hydrogen and a positive charge on the metal ion to show ionic bonding
If the charge of the ion is not +1, draw how many carboxylic acid molecules you would need to cancel the charge out in brackets next to the ion
How can we form esters?
By condensation reactions between carboxylic acids and alcohols
The OH must come from the carboxylic acid, the H must come from the alcohol
What is the general word equation for the reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohol?
Carboxylic acid + alcohol → Ester + water
What does an ester functional group look like?
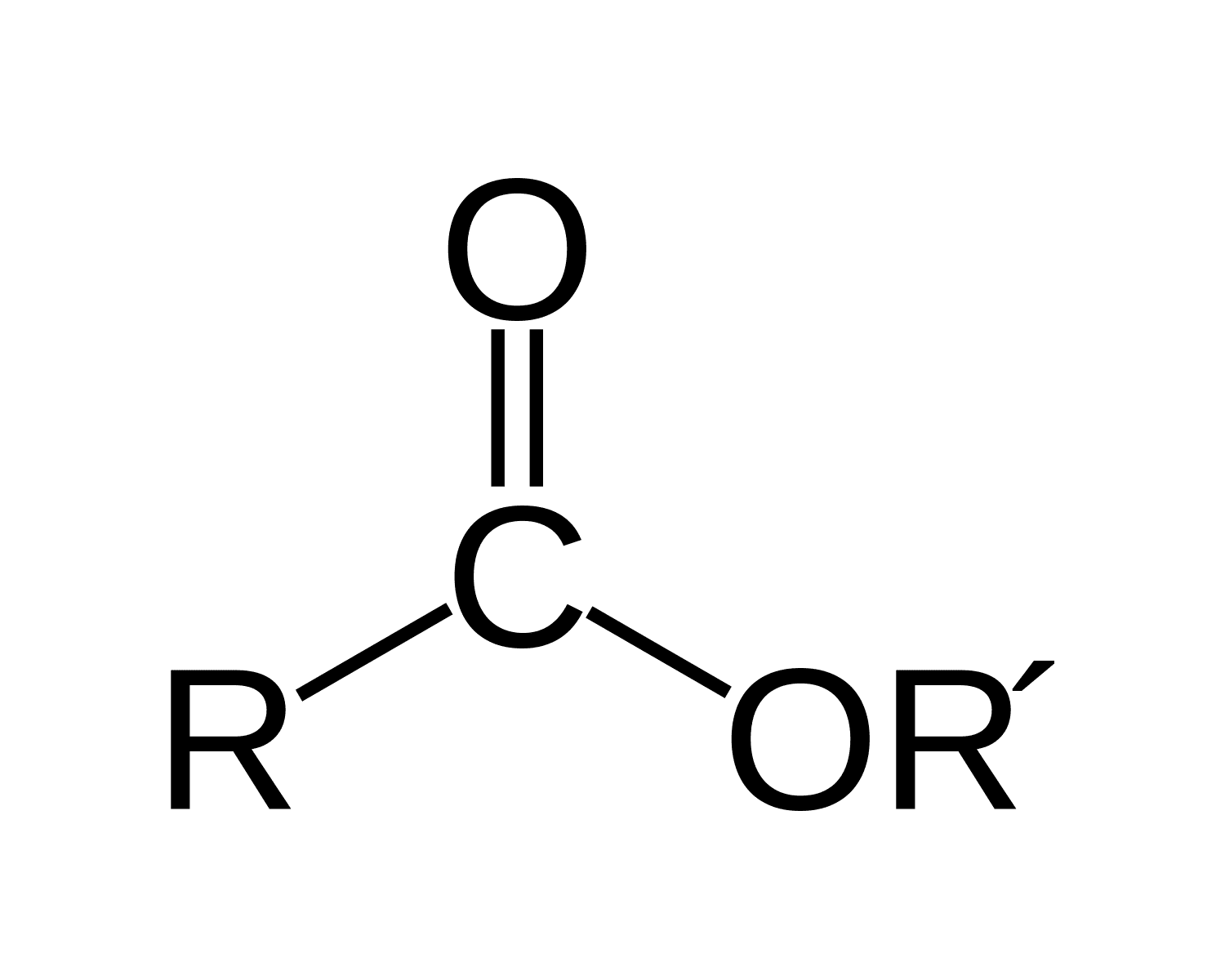
How do we name esters?
The first component of the name is derived from the alcohol (methanol = methyl)
The second component is derived from the carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid = ethanoate)
The name in this example would be methyl ethanoate
How do we name esters made from secondary alcohols?
We name it as we normally would
Then we can give the number 1 to the alkyl group attached- this is the only time this happens
How can we form cyclic esters?
If a molecule has both an alcohol and carboxylic acid group, a condensation reaction can occur between these two groups to form a cyclic ester
How can we from di-esters?
Di-esters are formed when a di-carboxylic acid reacts with 2 moles of alcohol
Also occurs when a di-alcohol reacts with 2 moles of carboxylic acid
How can tri-esters be formed?
Reaction a tri-alcohol with 3 carboxylic acids
Essentially making a lipid
What are some uses for esters?
Fragrances, essential oils, artificial flavours
Used as an organic solvent
Natural esters found in pheromones
Naturally occurring fats and oils are fatty acid esters of glycerol
Nitrate esters known for explosive properties
Polyesters used to make plastics
Esters used to make surfactants like soap
What does the hydrolysis of esters produce?
Alcohol
Carboxylic acid
What are the conditions of the hydrolysis of esters?
Acid or alkali in solution
Reflux
Why is the % yield of the hydrolysis of esters never 100%
It is a reversible reaction
What is base catalysed hydrolysis of esters?
Done with sodium hydroxide under reflux
In practice alkaline conditions are normally used as equilibrium lies to the right hand side and the reaction is also quicker
In this reaction, the sodium salt of the carboxylic acid and an alcohol is formed
How can base hydrolysis be used in saponification?
This is the production of soap
Triglycerides can be hydrolysed using 3 moles of sodium hydroxide under reflux to form glycerol and the sodium salts of long chain carboxylic acids
Sodium salts of long chain carboxylic acids are used to make soap
What can base hydrolysis be used for the the manufacture of biodiesel?
Referred to as transesterification
Triglycerides HAVE to react with methanol
This is heated under reflux with concentrated potassium hydroxide which forms glycerol and long chain methyl esters
What is the functional group for acyl chlorides?
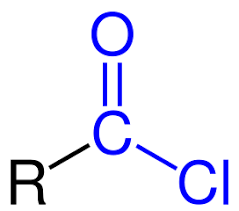
What is the mechanism for the reactions of acyl chlorides with nucleophiles?
Nucleophilic addition elimination
Why can acyl chlorides undergo nucleophilic addition elimination?
Because of the oxygen and the chlorine which both withdraw electron density from the carbon
What are potential nucleophiles which can react with acyl chlorides and what conditions are needed?
H2O
ROH alcohol
NH3
RNH2 (primary amine)
The last 3 need anhydrous conditions
What happens during nucleophilic addition elimination? (For acyl chlorides)
The nucleophile (Nu) with a hydrogen attached attacks the delta positive carbon
The pi bond in the C=O bond breaks
This forms an intermediate with a positively charged central nucleophile atom and a negative oxygen with a lone pair of electrons
The lone pair of electrons move to the C-O bond to reform the C=O bond
To compensate, the weakest bond of the carbon is broken as the electrons move to the to them atom that is separated from the compound
The one of the Nu-H bonds breaks with the electrons moving to the positively charged nucleophile in order to discharge it
This will form HCl as well as our other product
What are the four word equations for the reaction of acyl chlorides with it’s nucleophiles (water, alcohols, ammonia and primary amines)
Acyl chlorides + water → carboxylic acid + HCl
Acyl chlorides + alcohol → ester + HCl
Acyl chlorides + ammonia → amide+ HCl
Acyl chlorides + primary amine → N-substituted amide + HCl
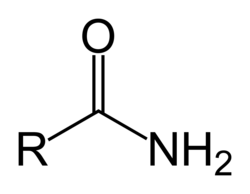
What is the difference between an amide and an N substituted amide?
An N substituted amide has had one or both of the hydrogens swapped for an alkyl group
An amide has only hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen
How do we name N-substituted amides?
Put an N in front of the name
The first part of the name comes from the alkyl group attached to the nitrogen atom
The second part of the name comes from the length of the carbon chain from the C=O bond onwards
e.g. N-methyl ethnamide
Amide group
Acid anhydride functional group
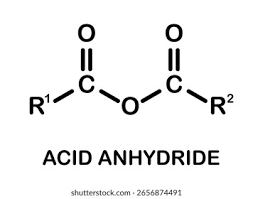
How are acid anhydrides formed?
From the condensation reaction between two carboxylic acids
Why are carbons in acid anhydrides susceptible to attack?
The oxygens attached to the withdraw electron density, making the carbons slightly positive
The lone pair of electrons on a nucleophile are attracted to this carbon, so a bond is formed
By what mechanism do acid anhydrides react with nucleophiles?
Nucleophilic addition elimination
What are the four word equations for the reaction of acid anhydrides with it’s nucleophiles (water, alcohols, ammonia and primary amines)
acid anhydrides + water → 2 x carboxylic acid
acid anhydrides + alcohol → carboxylic acid + ester
acid anhydrides + ammonia → amide + carboxylic acid
acid anhydrides + primary amine → N-substituted amide + carboxylic acid
Reduced pressure filtration apparatus
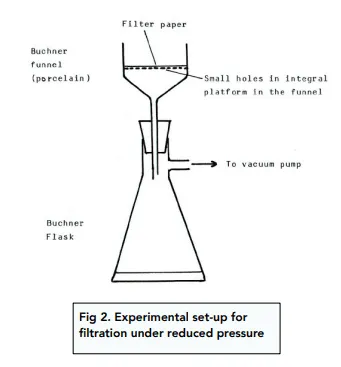
RP10: Steps for preparation of an organic solid
Dissolve the impure solid in a minimum volume of hot solvent
Hot to increase solubility
Minimum to form a saturated solution so that sold will recrystalise upon cooling
Filter to remove insoluble impurities
Cool the solution down as slowly as possible
This allows larger and purer crystals to be formed
Scratch the inside of the conical flask and place in ice bath to help formation of crystals
Scratching creates grooves which increases the surface area for the formation of crystals
Filter sample under reduced pressure and wash with a cold solvent
Cold ensures that the crystals don’t dissolve back in solution
Leave to dry in a warm place or in an oven for 24 hours
Drying means that we won’t calculate % yield that could be over 100% which isn’t possible
RP10: Melting point determination
Also, what affect do impurities have on melting point?
Compare sample to mpt of pure substance
Impurities will decrease the mpt as they get in the way of IMF
The larger the mpt range, the more impure our sample is
Method
Place sample of organic solvent into a capillary tube sealed at the end
Place capillary tube into melting point apparatus
Heat rapidly at first then slowly when approaching mpt
Record temperature when solid starts and finishes melting
What is the old method of melting point determination, what problems are there and how can we fix it?
A test tube filled with water with a thermometer and capillary tube attached above the bulb
The sample needs to be in line with the bulb due to the temperature gradient of the water
The water will evaporate if our sample has a melting point of of over 100 degrees celsius
We can use oil instead
RP10: Purification of an organic solvent- solvent extraction
This works as organic solvents are immiscible in water (doesn’t mix)
Method
Place organic liquid in separating funnel and add water, then remove the lower aqueous layer to remove any water soluble impurities
Add sodium carbonate/sodium hydrogen carbonate solution to remove excess acid used as a catalyst and shake with the organic liquid- if fizzing is seen, release the gas from the funnel to prevent an explosion by a build up of gas- remove the lower aqueous layer
Place organic layer into a conical flask and add a drying agent such as anhydrous calcium chloride or magnesium sulfate- filter off the solid
Could do a further distillation
Write out a general equation for the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a reducing agent
Aldehyde/Ketone + 2[H] → Primary/secondary alcohol
What are some disadvantages to using acyl chloride for the manufacture of aspirin?
Acyl chlorides are difficult to handle as they react very readily with water- anhydrous conditions needed
React to produce corrosive HCl
Why are are acid anhydrides favoured over acyl chlorides for the manufacture of aspirin?
Cheaper to produce
Not as moisture sensitive
Less corrosive
Carboxylic acids produced are safer than HCl