adrenergic antagonists
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
what are the 3 major cardiovascular disorder/vascular related diseases for adrenergic antagonists?
HTN
arrythmias
angina
T/F: generally, any non-hydroxy substitution will be an antagonist
true
what is the general backbone for non-selective adrenergic antagonists? (mixed alpha + beta)
phenethylamine backbone
phenyl ring, ethyl group, nitrogen
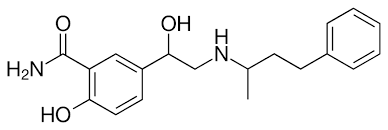
what type of drug is this?
non-selective adrenergic antagonist (labetalol/Normodyne)
only blocks alpha 1, beta 1, beta 2
phenethylamine backbone
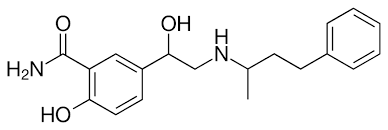
what is the use for labetalol?
nonselective alpha1 and beta1, beta 2 blocker
HTN
what is a contraindication for labetalol (Normodyne)?
asthma
blocks beta 2 receptors → bronchoconstriction
what is the brand name of Labetalol?
Normodyne
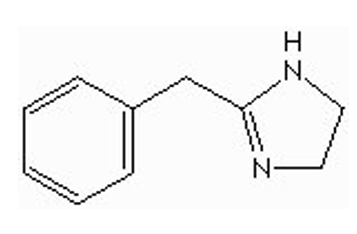
what type of drug is this?
non-selective alp[ha antagonist (tolazoline / Prsicoline)
imidazoline ring w/carbons/benzene
what structure is common with non-selective alpha antagonists?
imidazoline ring
T/F: phenethylamine backbones have a high affinity for alpha receptors
false
imidazoline ring = high affinity for alpha receptors
CH2 - imidazoline + heavily substituted benzene ring =
a) alpha 1 agonist
b) alpha 2 agonist
c) nonselective adrenergic antagonist
d) nonselective alpha antagonist
a) alpha 1 agonist
NH2 - imidazoline + heavily substituted benzene ring =
a) alpha 1 agonist
b) alpha 2 agonist
c) nonselective adrenergic antagonist
d) nonselective alpha antagonist
b) alpha 2 agonist
which of the following structures is an antagonist that is LESS lipophilic than the agonist?
a) phentolamine
b) quinazoline
c) tolazoline
d) labetalol
c) tolazoline
what is the indication for tolazoline?
pulmonary HTN (newborns with increased BP in lungs
administered IV
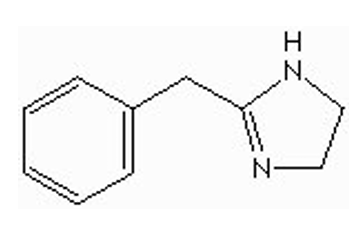
if this drug is given IV for injection, what type of salt will it be/used?
a) hydrochloride
b) sodium
a) hydrochloride
basic drug (imidazoline) = HCl
what nucleus loves alpha receptors?
a) imidazole
b) imidazoline
c) imidazolidine
d) all of the above
b) imidazoline
is there a use for selective alpha 2 antagonists?
no
no required therapeutic uses
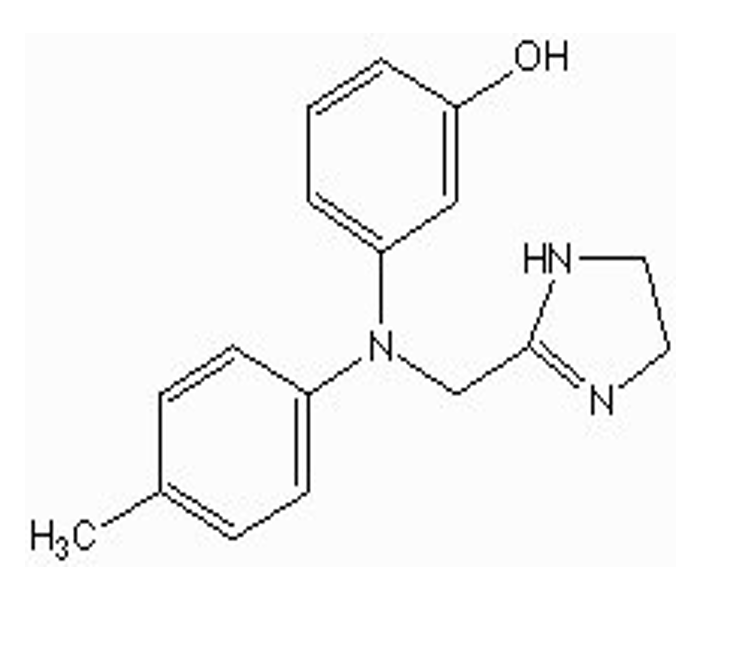
what type of drug is this?
non-selective alpha antagonist (phentolamine / Oraverse)
imidazoline
what is the use for phentolamine / Oraverse?
pheochromocytoma diagnosis and treatment
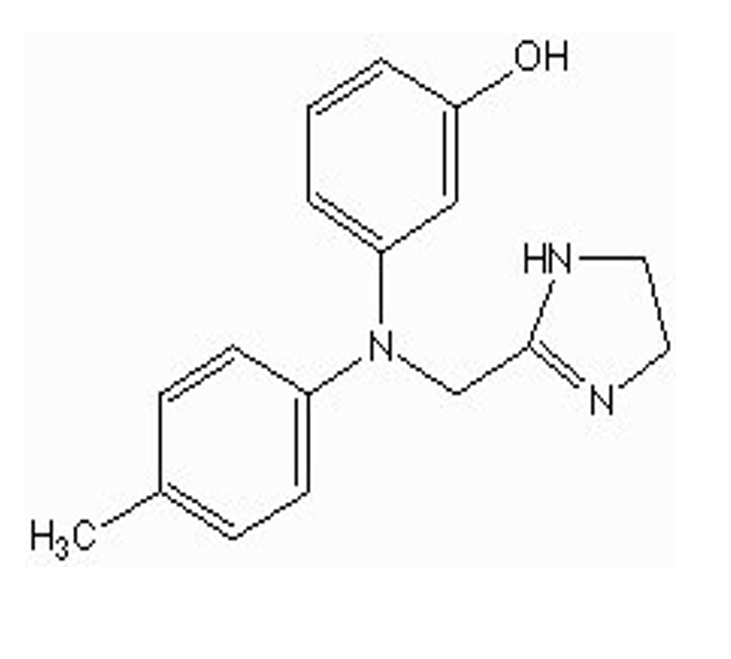
are there any electron withdrawing or donating substituents on the benzene?
no
what is the major use / only use for alpha 1 selective antagonists?
a) arrhythmias
b) cardiac block
c) angina
d) HTN
d) HTN
dilates blood vessels
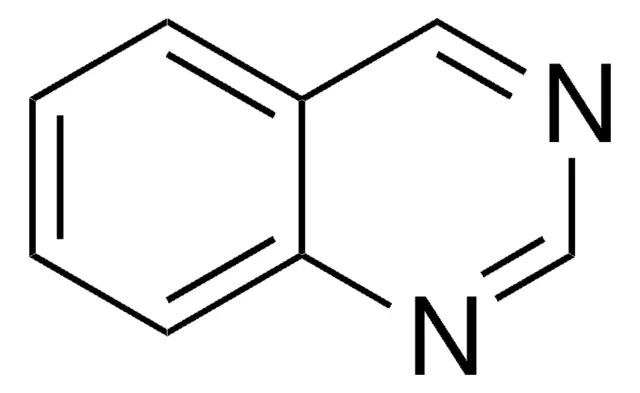
what is the name of this functional group?
quinazoline
add an extra nitrogen to quinolone
what are the common structures found in alpha-1 antagonists?
quinazoline nucleus
piperazine
carbonyl
amino group
6,7 dimethoxy
T/F: alpha-1 selective antagonists have a phenylethylamine backbone
false
have a QUINAZOLINE nucleus
what metabolizes quinazoline?
CYP in liver
what is the indication for prazosin (Minipress)
HTN
alpha-1 antagonist
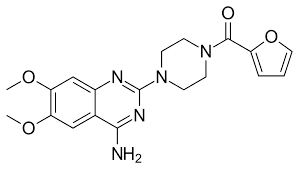
what type of drug is this?
alpha-1 selective antagonist (prazosin / Minipress)
quinazoline nucleus
piperazine
furan
in alpha-1 selective antagonists, the piperazine is always found at what position?
a) position 1
b) position 2
c) position 6
d) position 7
b) position 2
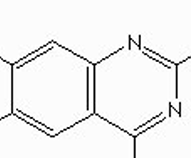
how do you number this quinazoline found in alpha-1 antagonists?
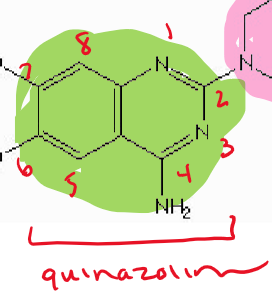
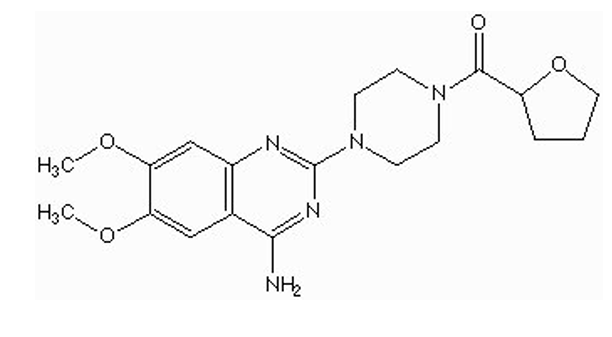
what type of drug is this?
alpha-1 antagonist ( Terazosin / Hytrin)
quinazoline nucleus
piperazine
what is the indication for Terazosin ?
HTN
alpha-1 antagonist
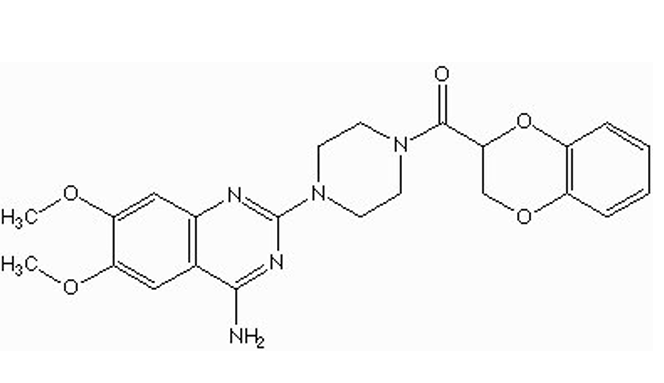
what type of drug is this?
alpha-1 antagonist (doxazosin / Cardura)
quinazoline nucleus
piperazine
what is the indication for doxazosin?
BPH
CHF (congestive heart failure)
HTN
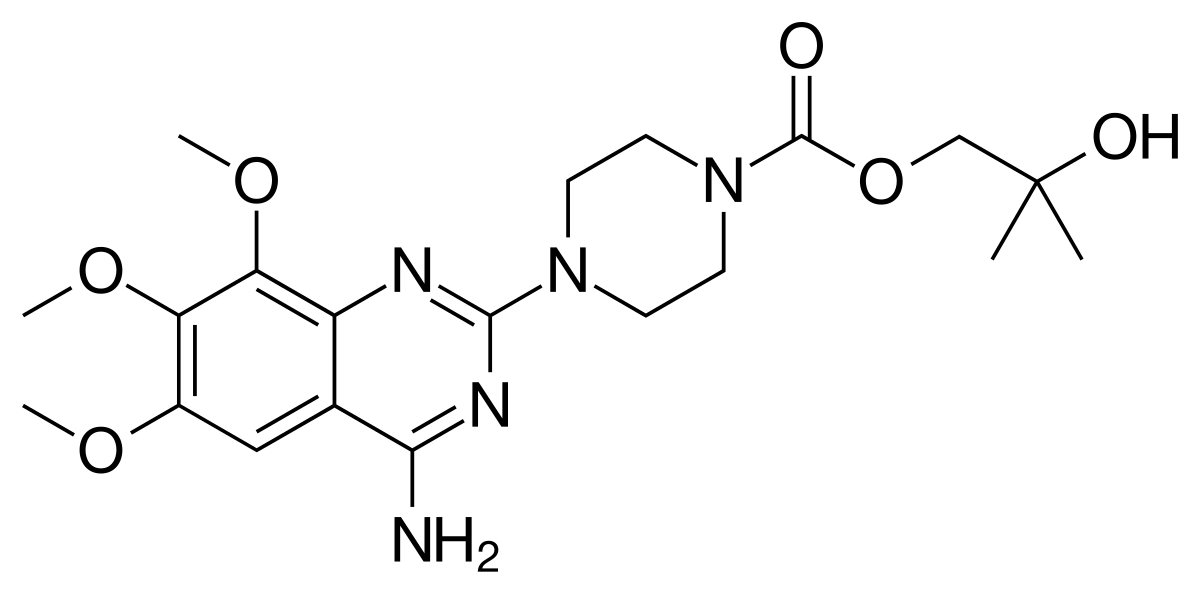
what type of drug is this?
alpha-1 antagonist ( Trimazosin)
quinazoline nucleus
piperazine
what is the indications for Trimazosin?
HTN
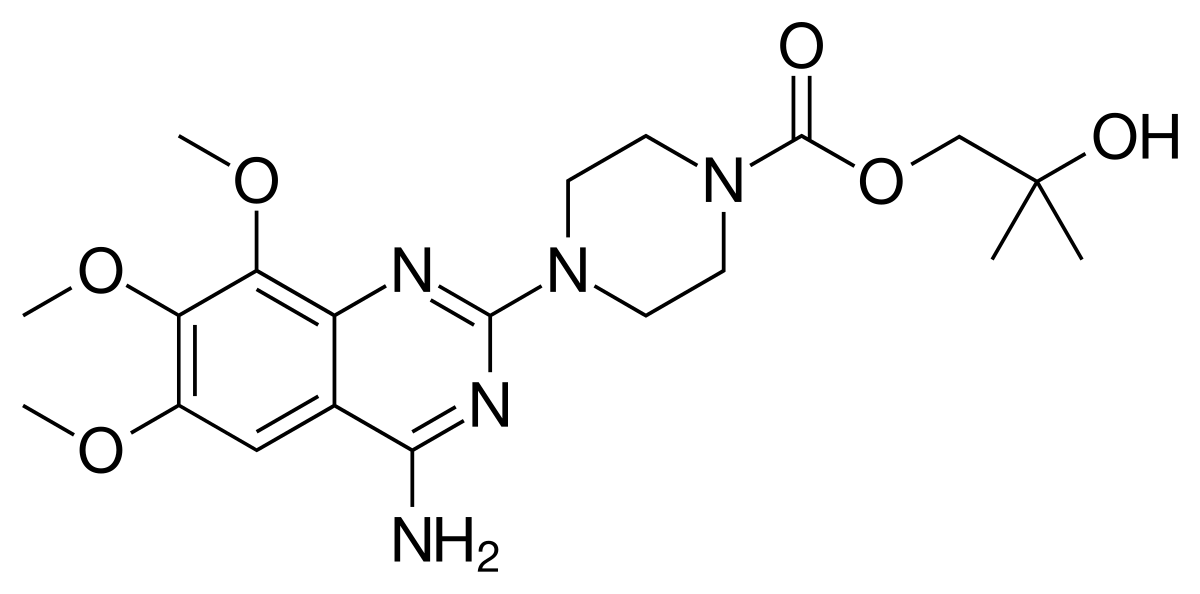
what is the purpose of the -OH group in Trimazosin?
makes it short acting
metabolized directly into phase 2-conjugation
most alpha-1 antagonists are metabolized how and where?
metabolized by O-demethylation
by CYP in the liver (microsomes)
alpha-1 antagonists are all given as …
injection for HTN
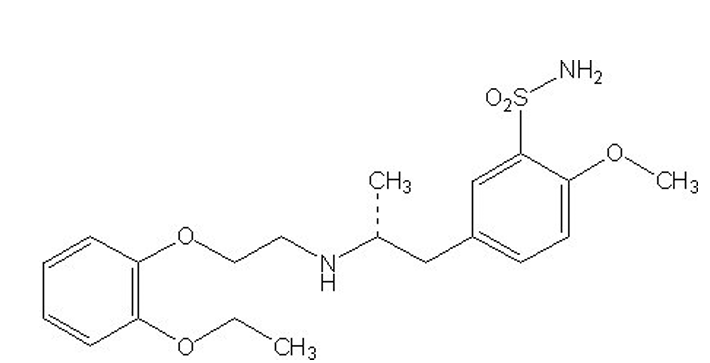
what type of drug is this?
special alpha-1 antagonists ( Tamsulosin / Flomax)
alpha 1A antagonist
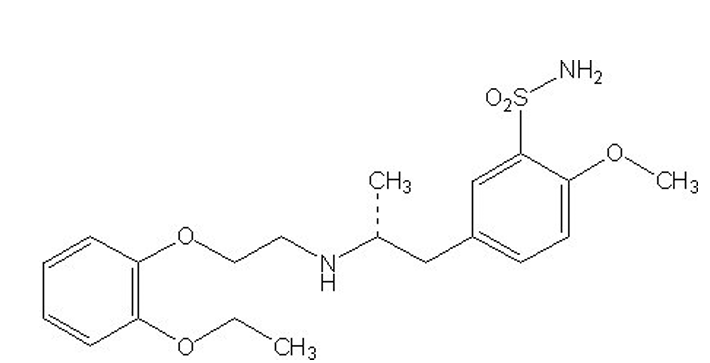
what is the difference between Tamsulosin from other alpha-1 antagonists?
phenethylamine nucleus instead of quinazoline nucleus
no affinity to blood vessels
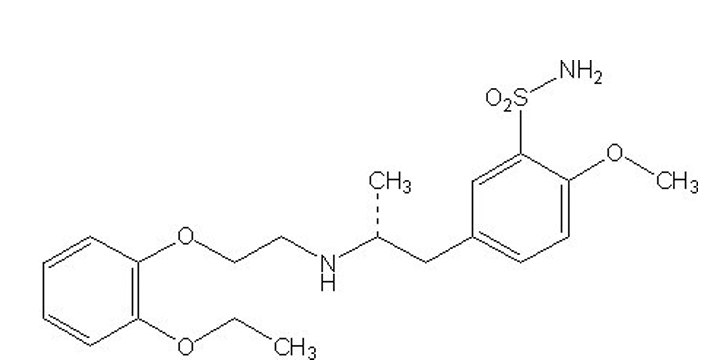
what is the purpose of the sulfur/sulfonnamine group in tamsulosin?
liver HATES sulfonamine
drug goes directly to kidneys
what is the indication for Tamsulosin?
BPH
alpha 1A antagonist
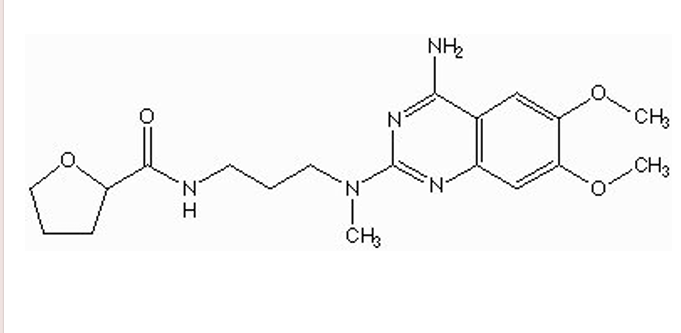
what type of drug is this?
alpha 1A antagonist (Alfuzosin/ Uroxatral)
quinazoline nucleus
NO piperazine
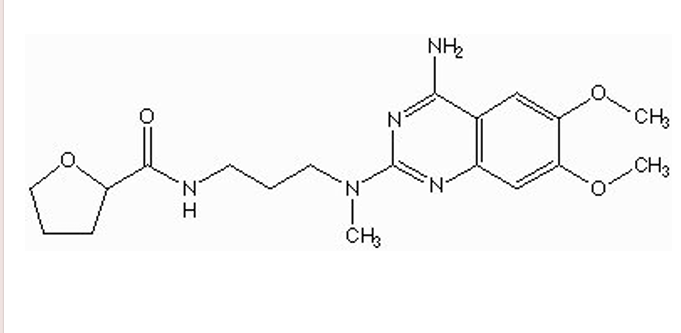
what is different about Alfuzosin compared to other alpha-1 antagonists?
NO piperazine ring system → less affinity to circulatory = selective to Alpha 1 A
alpha 1A antagonist
what is the indication for alfuzosin?
BPH
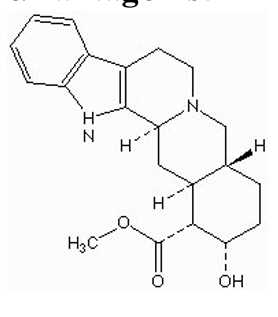
what type of drug is this?
alpha-2 antagonist (Yohimbine HCl)
what is the indication for Yohimbine?
sexual dysfunction ( impetus)
what is contraindicated with nonselective beta antagonists?
asthma + diabetes
what are the uses for B1 antagonists/ nonselective beta antagonists?
HTN
arrythmia (treat/correct)
angina
how is the structure of beta antagonists similar to NE?
take OH away from NE structure = antagonist
non-hydroxyl substitution
what are the common structures found in non-selective beta antagonists?
O-CH2 between ethylamine and phenyl ring
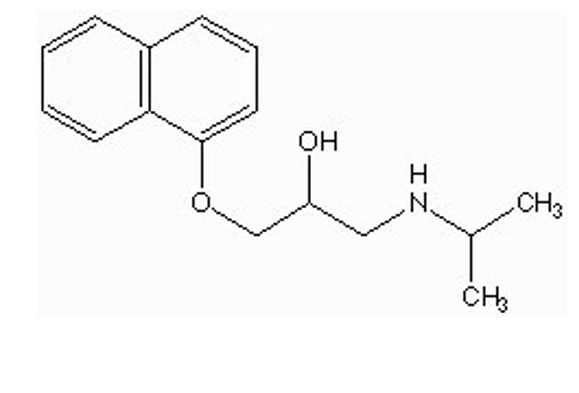
what type of drug is this?
nonselective beta antagonist (propranolol / Inderal)
O-CH2 between ethylamine + phenyl ring
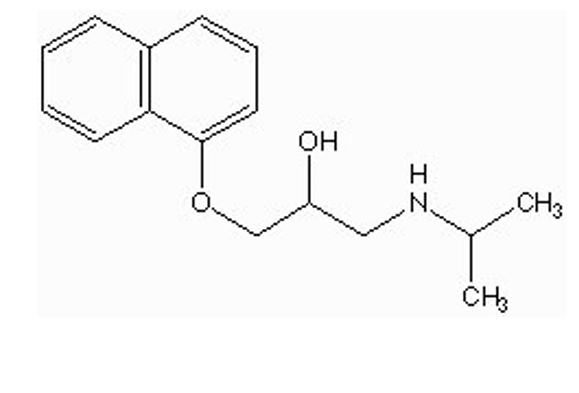
how is propranolol metabolized? `
aromatic hydroxylation by CYP in liver
some goes directly → phase II conjugation
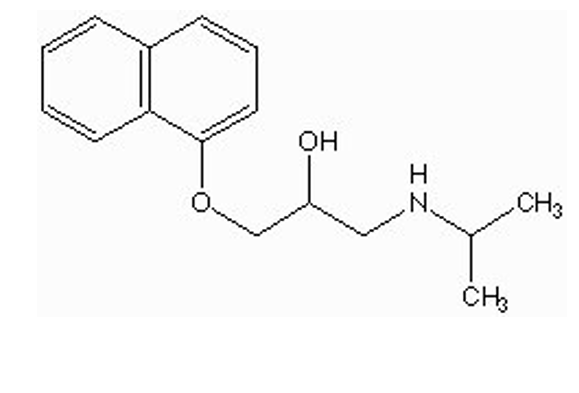
why should propranolol not be given to a patient with liver (cirrhosis)?
propranolol is metabolized by liver (aromatic hydroxylation)
can lead to toxicity
what structure is essential for beta antagonists?
O separating benzene + ethyl group
what is the indication for propranolol
angina
HTN
arrhythmia
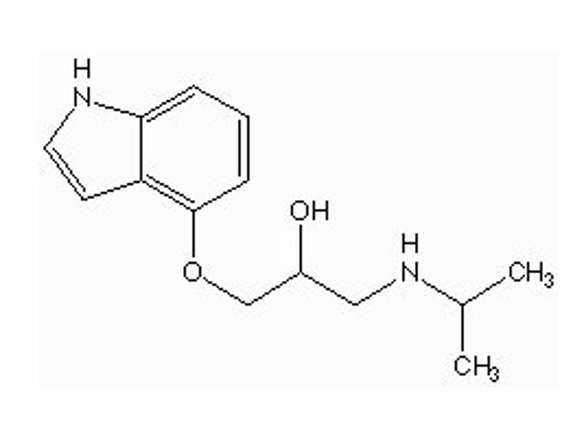
what type of drug is this?
non-selective beta antagonists ( Pindolol / Visken)
O-CH2 separates ethylamine and phenyl ring
what is the indication for pindolol?
angina
HTN
arrhythmia
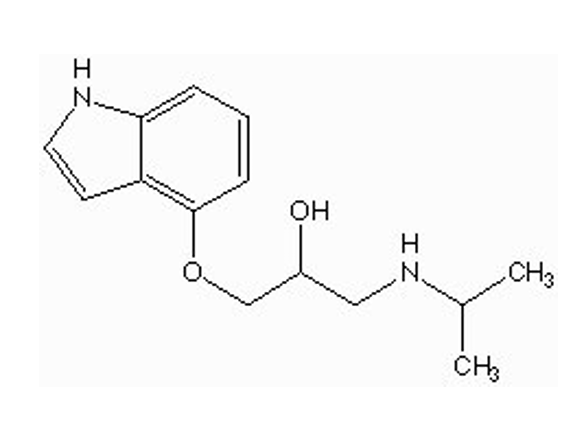
what is the nucleus for pindolol?
indole
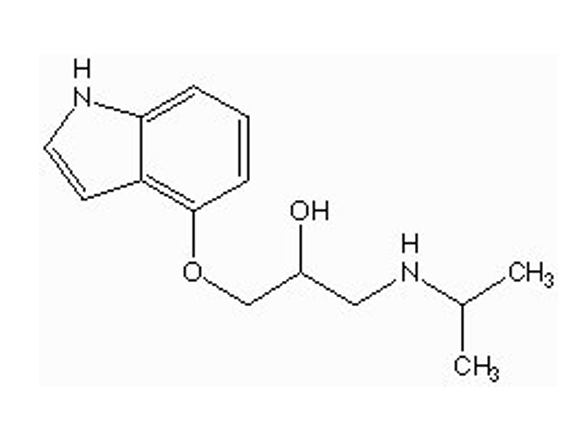
why should pindolol not be given to patients with liver failure (cirrhosis)
drug is metabolized by liver
can cause toxicity
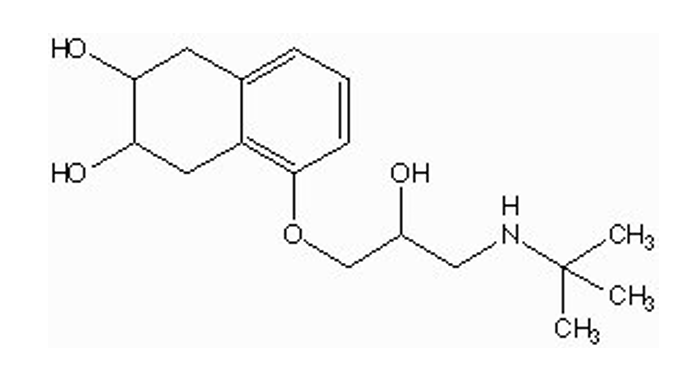
what type of drug is this?
nonselective beta antagonists (nadolol / Corgard)
O-CH2 separates ethylamine + phenyl ring
what is the indication for nadolol?
angina
HTN
arrhythmia
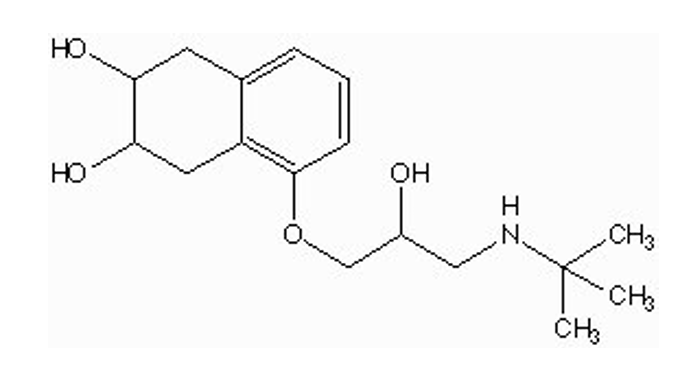
why should nadolol not be given to a patient with liver failure?
conjugated in phase II reactions in liver and kidney
polar group (secondary nitrogen, secondary alcohol) w/ glucuronic acid
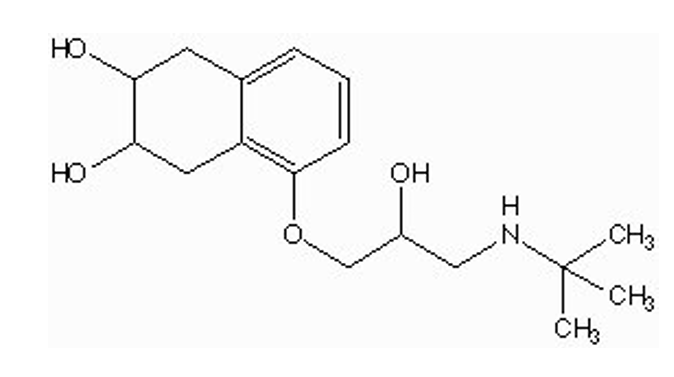
does nadolol have a catechol group?
NO
3,5 hydroxyl group but it is not on a benzene ring
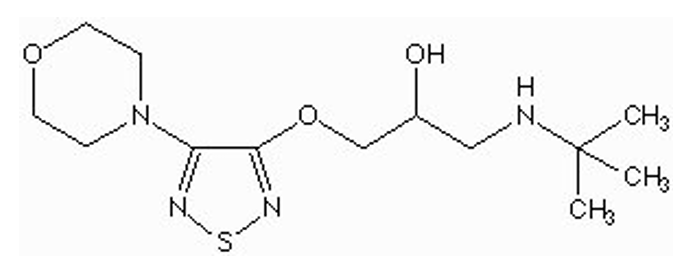
what type of drug is this?
nonselective beta antagonist ( Timolol Maleate)
O-CH2 separates thiadiazole and ethylamine
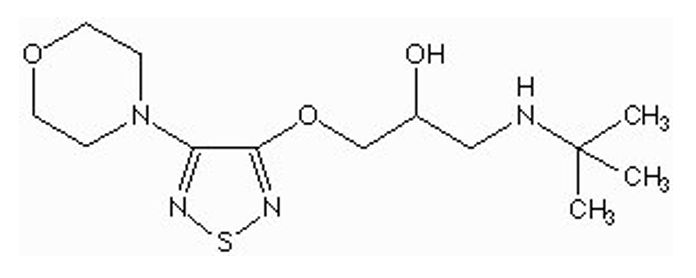
what is the indication for Timolol
glaucoma eye drops (more polar with hydrophilic side chain (hetero atoms)
opens canal of Schlemm
T/F: the N-substitutions in nonselective beta antagonists are always bigger than methyl and ethyls
true (isopropyl or butyl)
what are the common structures found in selective beta1 antagonists?
isopropyl N-substiution
O-CH2 spacer between ethyl and benzene
single benzene ring with 1 substitution at position 4 (para)
if a drug structure has a single benzene ring with 1 substitution at positon 4/ para, it is most indicative of a
a) nonselective alpha antagonist
b) selective alpha-1 antagonist
c) nonselective beta antagonist
d) selective beta 1 antagonist
d) selective beta 1 antagonist
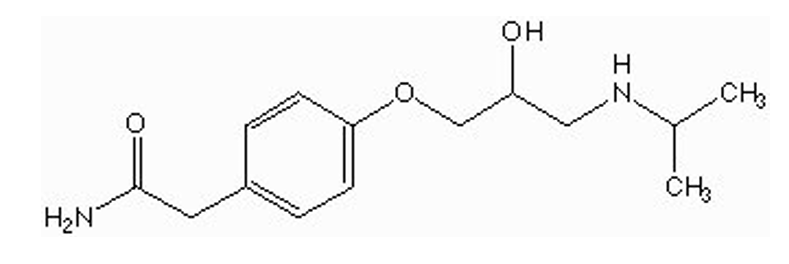
what type of drug is this?
selective beta-1 antagonists (atenolol / Tenormin)
only 1 benzene ring w/ substituent at position 4
OCH2 spacer
what is the indication for Atenolol ?
angina
arrhythmia
HTN
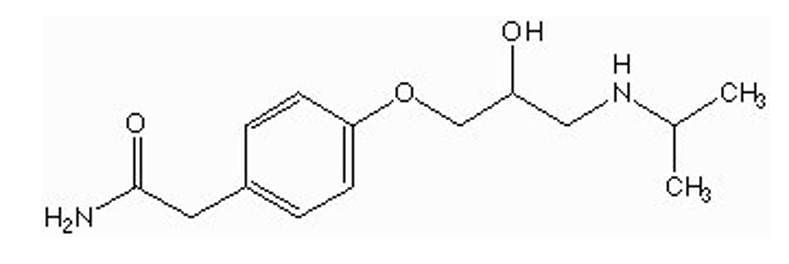
how is atenolol metabolized?
metabolized by amidases in liver
produces ammonia + carboxylic group
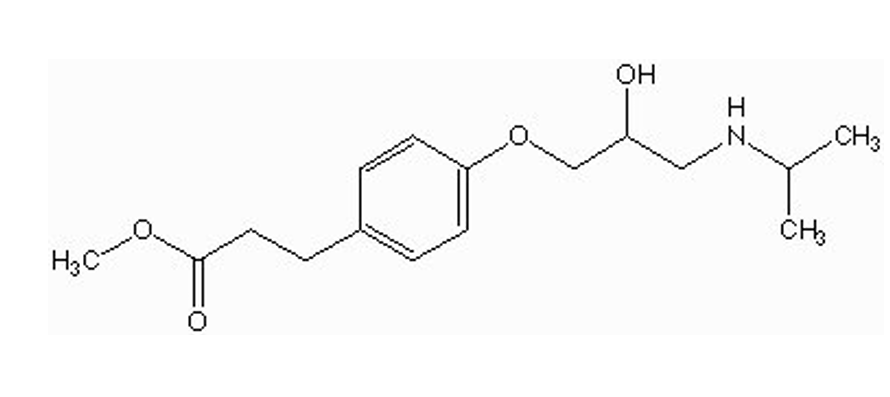
what type of drug is this?
selective beta1 antagonist (esmolol / Brevibloe)
1 benzene ring w/ substituent at position 4
OCH2 spacer
what is the indication for esmolol
INJECTION for acute MI, HTN, arrhythmia
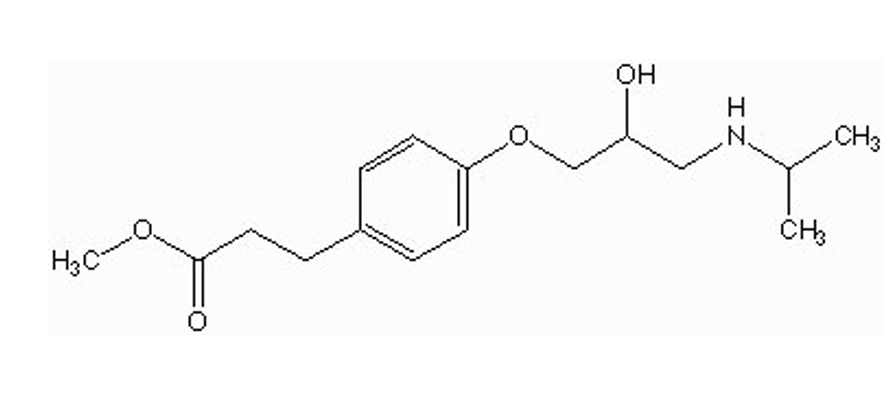
how is esmolol metabolized? where?
ester substituent → esterases in GIT
fast metabolism
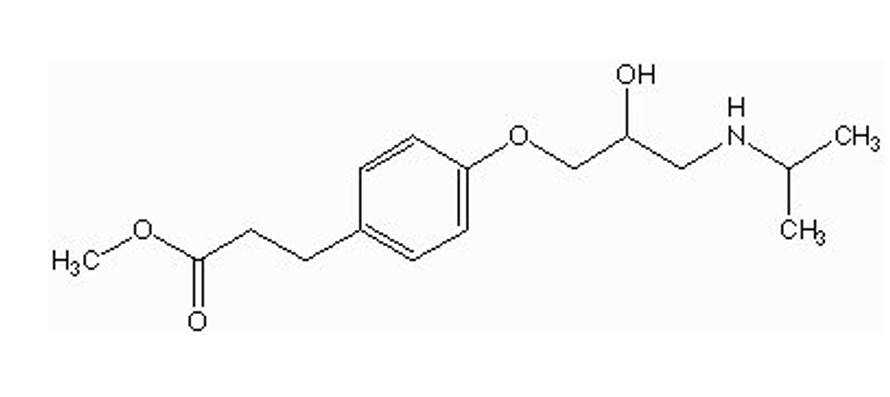
what type of salt is esmolol given for injection?
a) Hydrochloride
b) sodium
a) Hydrochloride
basic secondary Nitrogen
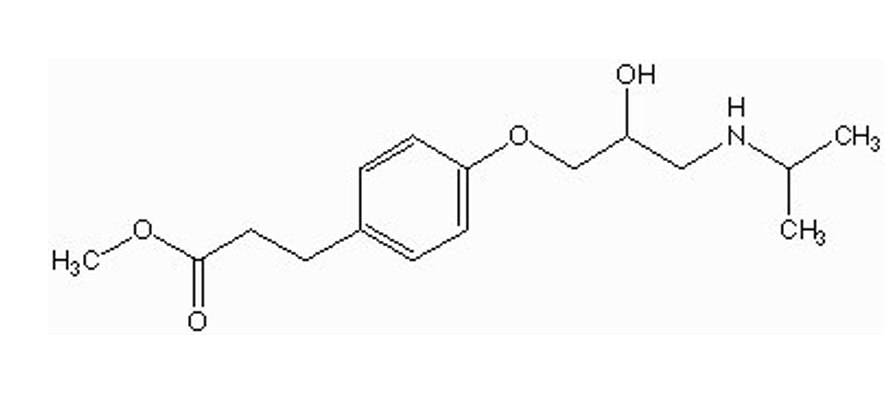
can you give esmolol orally?
no
fast metabolism by esterases in GIT = will inactive drug before absorption
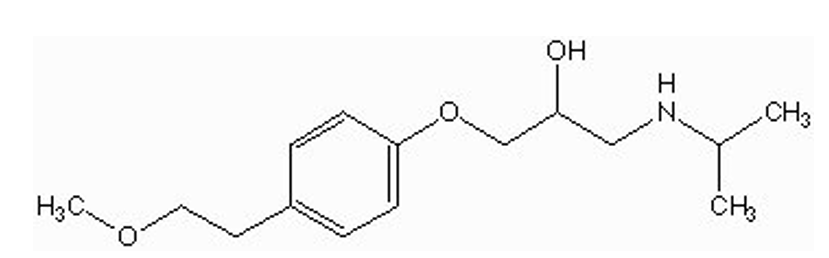
what type of drug is?
beta-1 antagonist (metoprolol succinate / Toprol XL) (metoprolol tartrate/ Lopressor)
1 benzene ring w/ substituent at position 4
OCH2 spacer
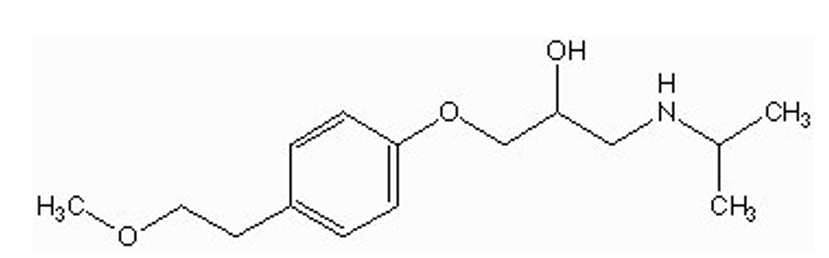
how is metoprolol metabolized?
O-demethylation by CYP in liver
what is the indication for metoprolol?
angina
arrhythmia
HTN
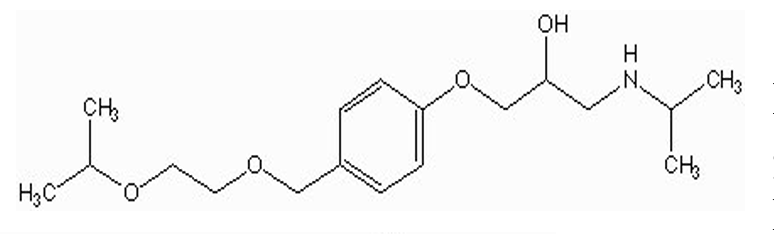
what type of drug is this?
beta-1 antagonist (bisoprolol fumarate / Zebeta)
1 benzene ring w/ substituent at position 4
OCH2 spacer
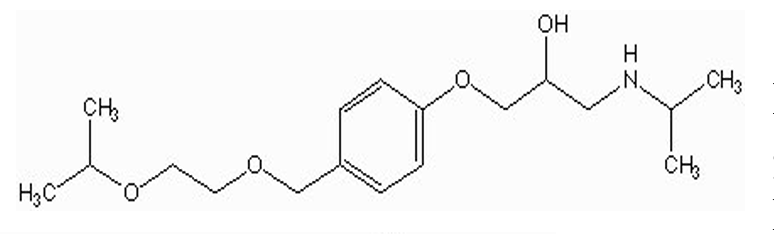
is metoptolol or bisoprolol more long-acting?
bisoprolol
Isopropyl in ether = less likely to undergo O-demethylation by CYP in liver
what is the indication for bisoprolol fumarate?
HTN
CHF (congestive heart failure)
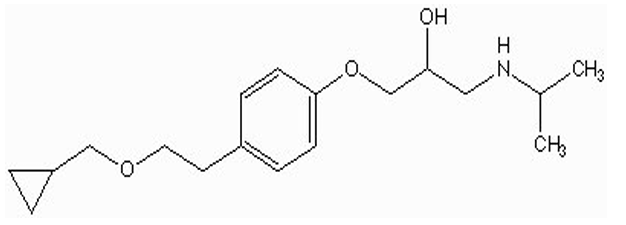
what type of drug is this?
b1 antagonist (betaxolol / Beptic S; Kerlone)
single benzene w/ substituent at postion 4
OCH2 spacer
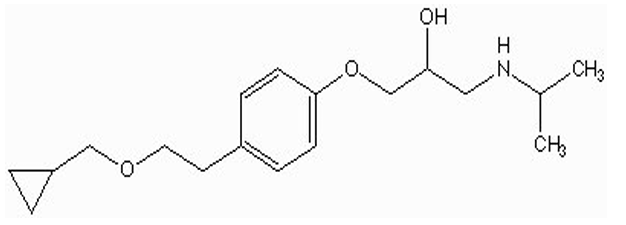
does betaxolol or metoprolol have longer action of duration?
betaxolol
less likely undergo O-demethylation by CYP in liver = longer duration of action than metoprolol
what is the indication for betaxolol ?
glaucoma
HTN
angina
SATA: which of the following drugs have a longer action of duration than metoprolol?
a) esmolol
b) bisoprolol
c) betaxolol
d) atenolol
b) bisoprolol
c) betaxolol
which of the following is metabolized by esterase?
a) atenolol
b) esmolol
c) metoprolol
d) bisoprolol
b) esmolol
which of the following is metabolized by amidases?
a) atenolol
b) esmolol
c) metoprolol
d) bisoprolol
a) atenolol
which of the following is most likely to be metabolized by CYP for o-demthylation?
a) atenolol
b) betaxolol
c) metoprolol
d) bisoprolol
c) metoprolol