4.3 MEIOSIS
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
T/F? MEMBERS OF THE SAME SPECIES HAVE THE SAME GENES.
True.
WHAT DOES IT MEAN TO BE A GENETICALLY DIVERSE POPULATION?
When a population has many different alleles for a particular gene.
WHAT IS THE GENE POOL?
Total information from all of the genes and alleles of the breeding individuals of a population at a particular time.
WHAT DOES GENETIC DIVERSITY CREATE?
WHAT IS IT A RESULT OF?
It creates variation WITHIN a species.
It therefore allows natural selection.
RESULT OF:
Mutations.
Meiosis.
Random fusion of gametes.
WHAT TYPE OF CELL DOES MEIOSIS PRODUCE (HINT HAPLOID OR DIPLOID)?
In the formation of gametes:
Ovum, sperm, ovule, pollen grain.
HOW DOES MEIOSIS RESULT IN HAPLOID CELLS?
1. DNA replication forms chromatids;
2. Two (nuclear) divisions;
3. Separation of homologous chromosomes and cells become haploid.
4. Separation of sister chromatids by centromere breaking.
WHAT IS CHROMOSOME DISJUNCTION?
Sometimes homologous chromosomes don’t separate and both chromosomes of a pair go into the same cell.
As a consequence, after fetilisation, zygotes can end up with an extra copy of a particular gene.
HOW DOES MEIOSIS LEAD TO INTRASPECIFIC VARIATION?
Meiosis provides opportunities of new combinations of alleles to occur in the gametes.
WHY ARE CELLS FROM MEIOSIS GENETICALLY DIFFERENT?
Independent segregation.
Crossing Over.
Different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
WHAT IS INDEPENDANT SEGRAGTION?
First division, the pairs of homologous chromosomes pair up at the start.
When they line up along the equator, their orientation is completely random.
Subsequent separation of these pairs result in random shuffling of maternal and paternal chromosomes ::: different combinations of in the gametes formed.
2n.
CROSSING OVER AND HOW DOES IT INCREASE GENETIC DIVERSITY?
Homologous pairs of chromosomes associate.
Chiasma(ta) form.
(Equal) lengths of (non-sister) chromatids / alleles are exchanged.
Producing new combinations of alleles.
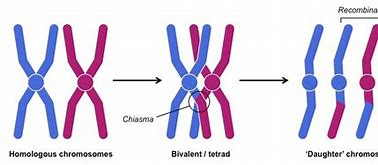
HOW CAN GENETIC VARIATION BE FURTHER INCREASED?
Further increased in sexual reproduction due to random recombination of maternal and paternal gametes during fertilisation,
IF THERE ARE X CHROMOSOMES, HOW MANY CHROMATIDS WILL THERE BE IN THE ZYGOTE?
4X
WHY WILL ALL THE CELLS OF THE BODY HAVE THE MUTATION?
Mutation in gamete.
All cells derived from single zygote during mitosis.