Political Geography - AP Human Geography Unit 4
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
nation
An ethnic group; A culturally defined group of people that share the same beliefs, language, history, religion, and region.
state
A country that has a sovereign government, defined borders, and is recognized by other states.
nation-state
A state dominated by one ethnic group.
stateless nation
An ethnicity that is dispersed as a minority across more than one state.
microstate
a state or territory that is small in both population and area
colony
A territory that is legally tied to a sovereign state rather than completely independent.
sovereignty
State control; Independence; Authority in internal domestic affairs.
physical border
natural boundaries: rivers, lakes, oceans, mountains, or deserts

cultural border
boundaries between nations or ethnic groups - along religious, language lines.
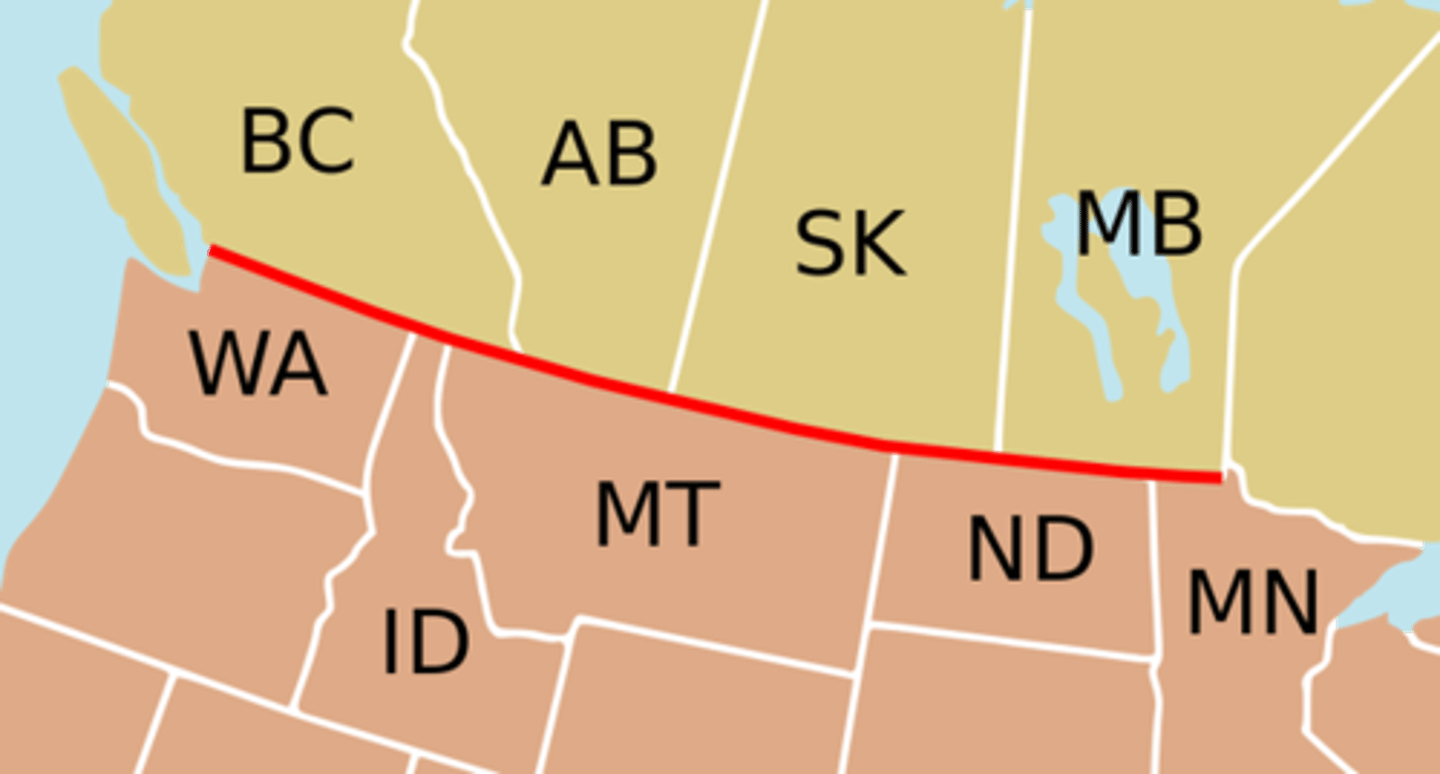
geometric border
boundaries of straight lines that do not conform to natural or ethnic boundaries; Usually along lines of latitude or longitude.
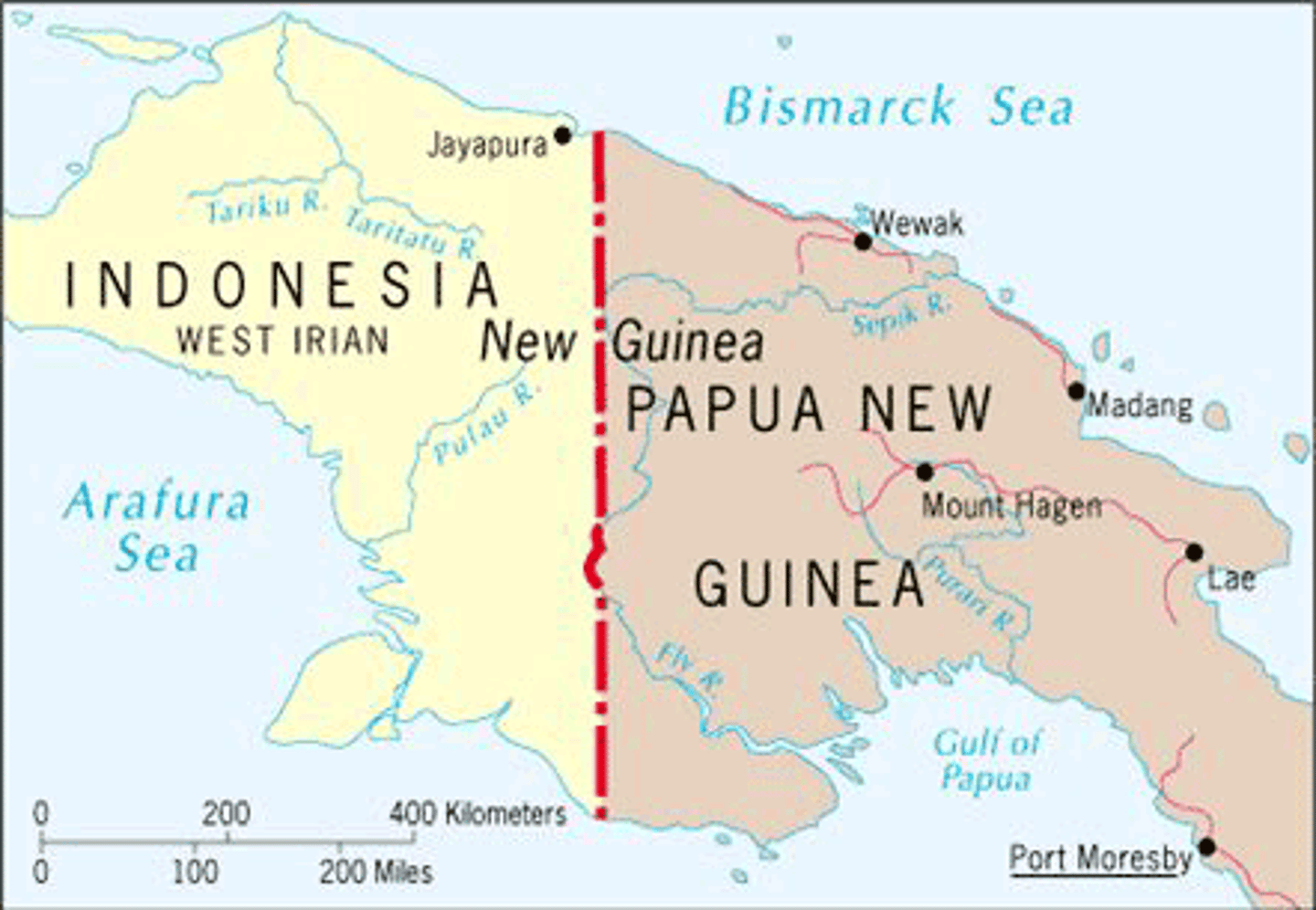
superimposed border
A border defined by an outside force that may not reflect the cultural landscape
relic border
No longer a boundary because of political changes; Still leaves an imprint on the physical or cultural landscape.

supranational organization
An organization that operates across multiple states for political, economic, or military cooperation; States transfer some sovereignty to the union by joining.
UN
United Nations, a supranational organization.

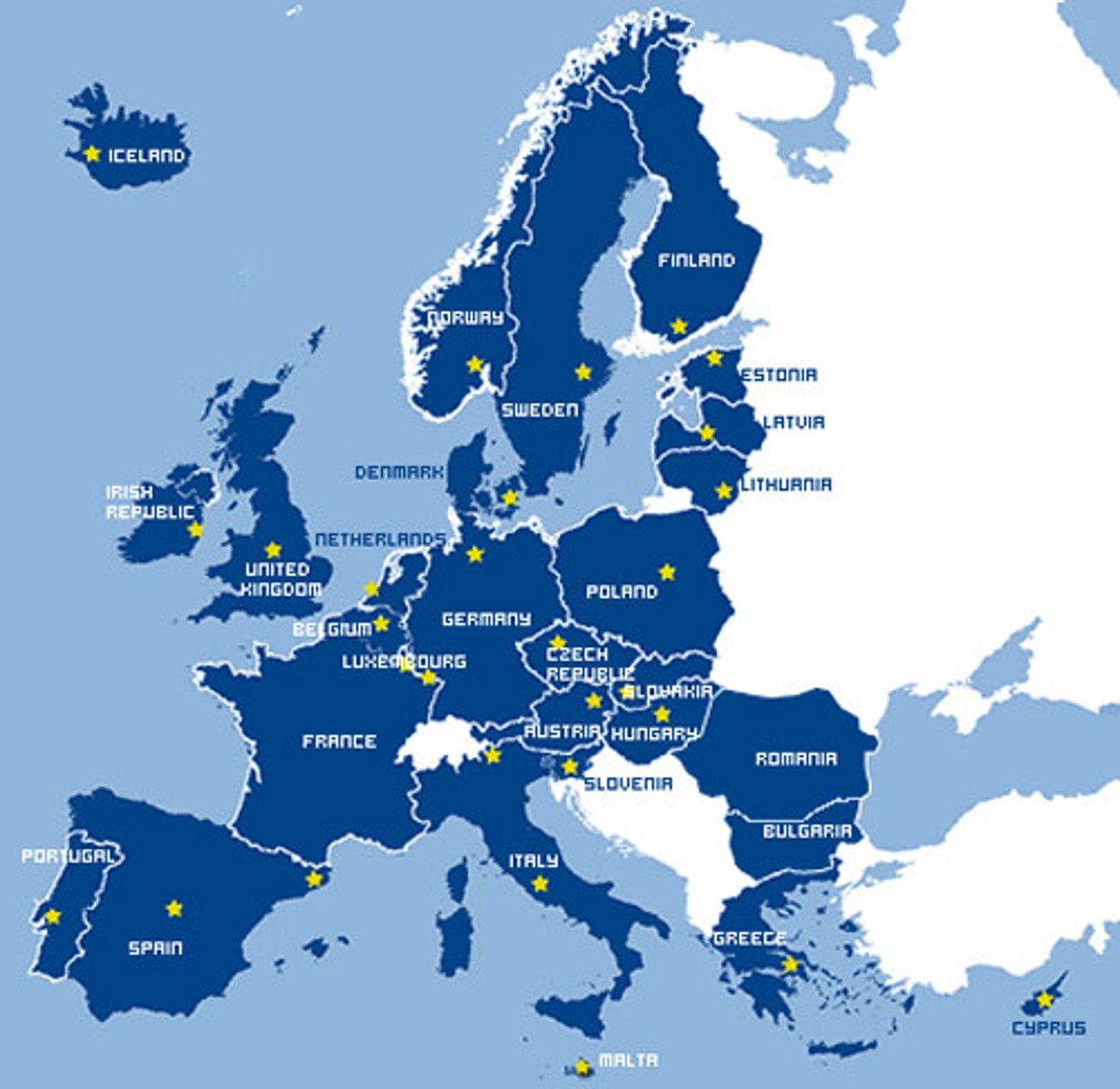
EU
European Union, an economic/political supranational organization.
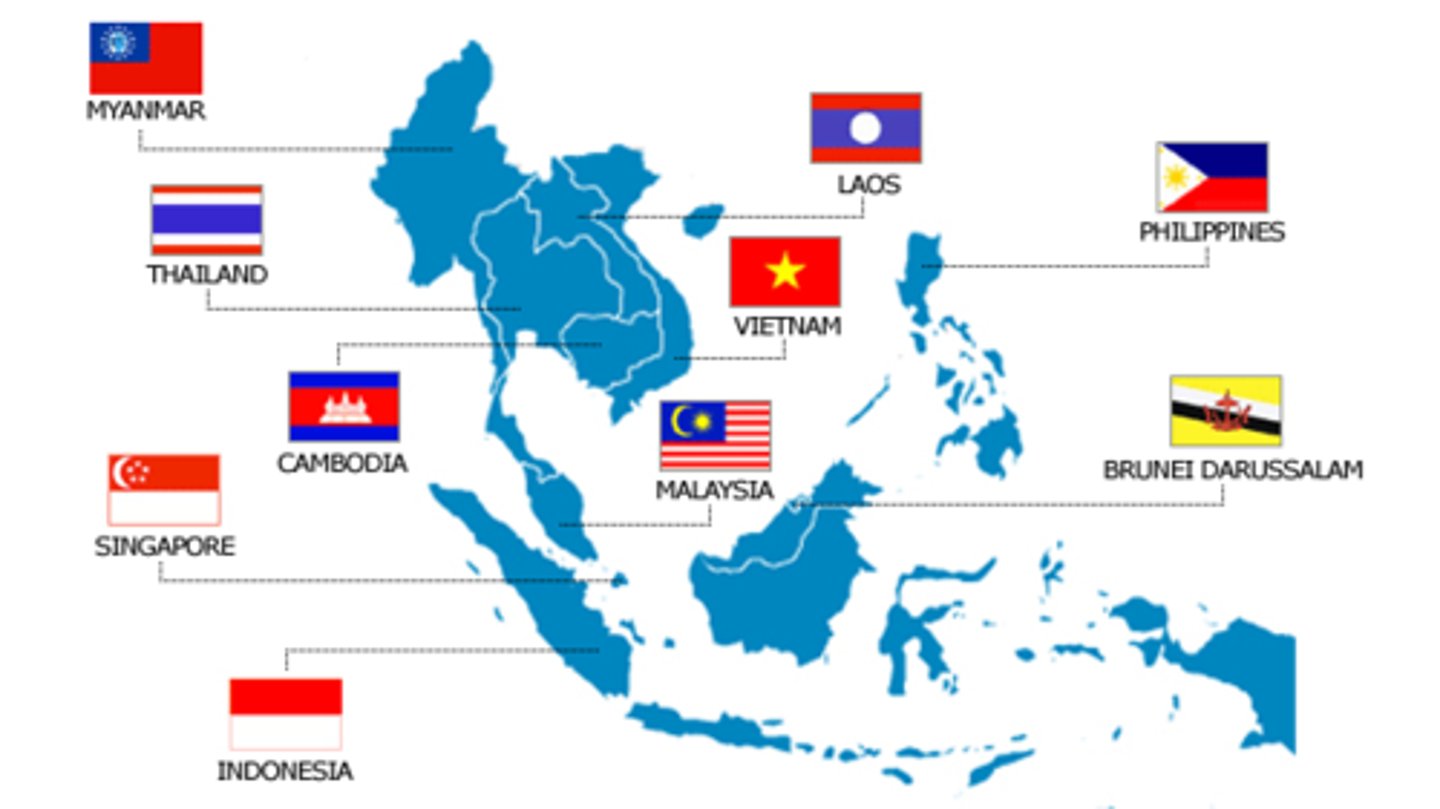
ASEAN
Association of Southeast Asian Nations, a supranational organization.
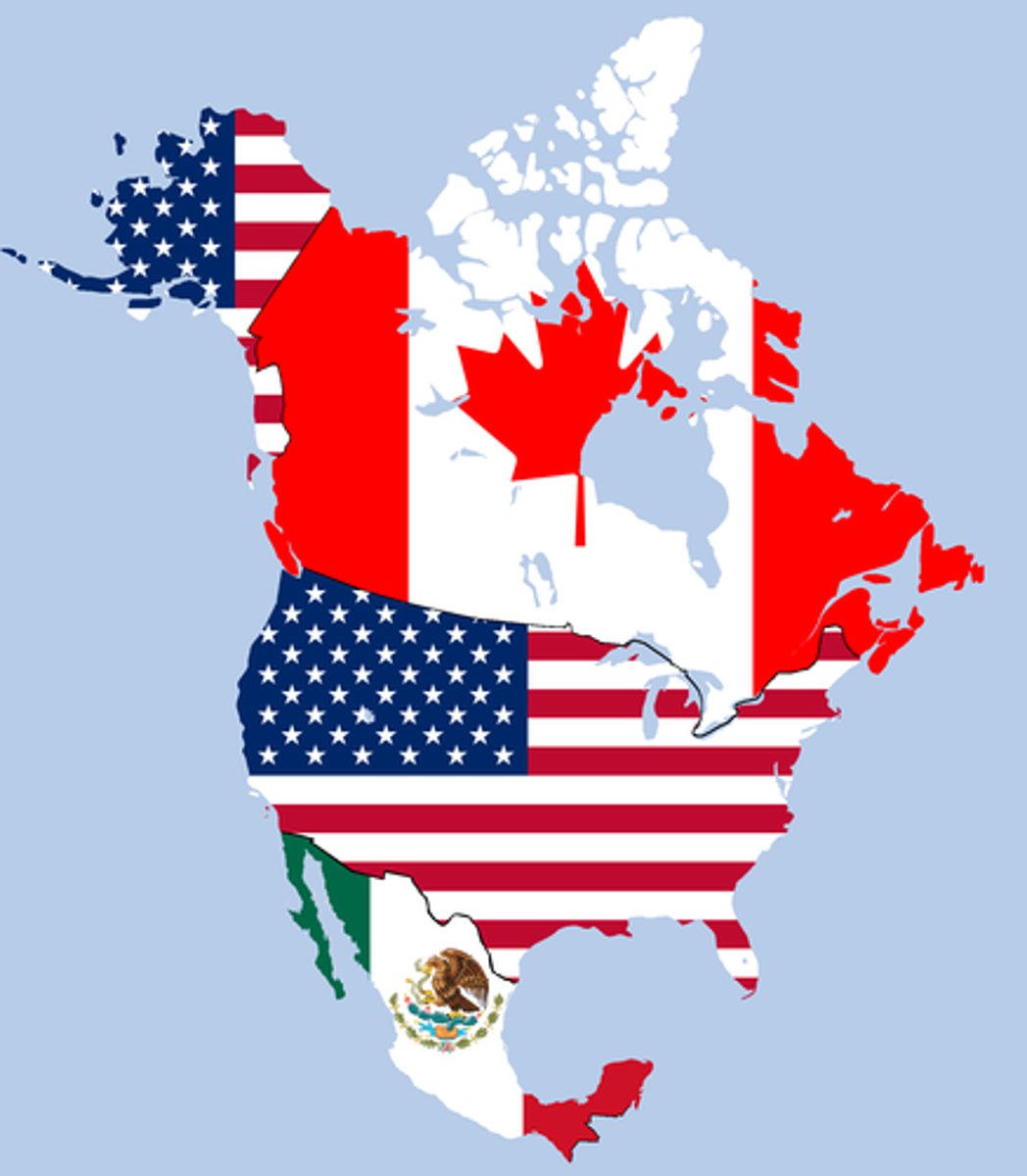
NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement, an economic supranational organization.
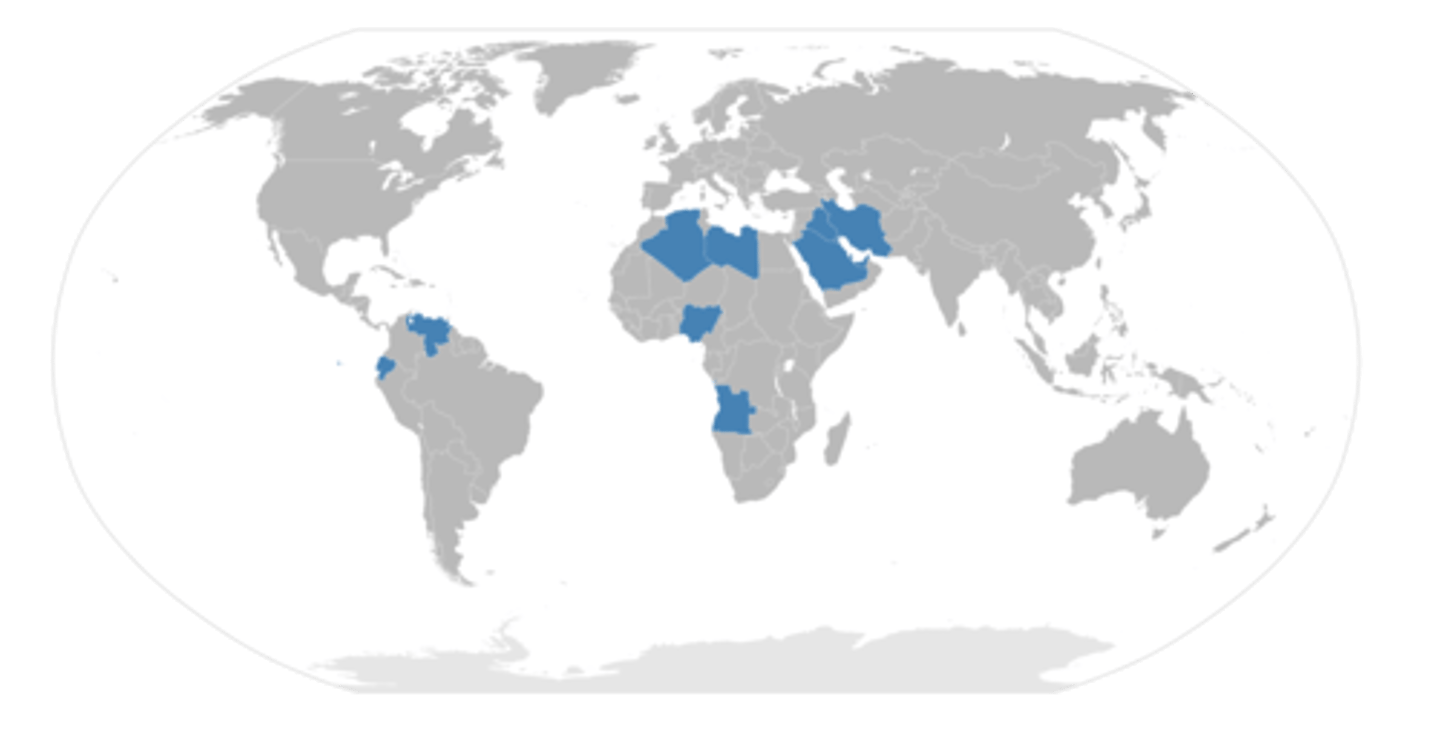
OPEC
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, a supranational organization.
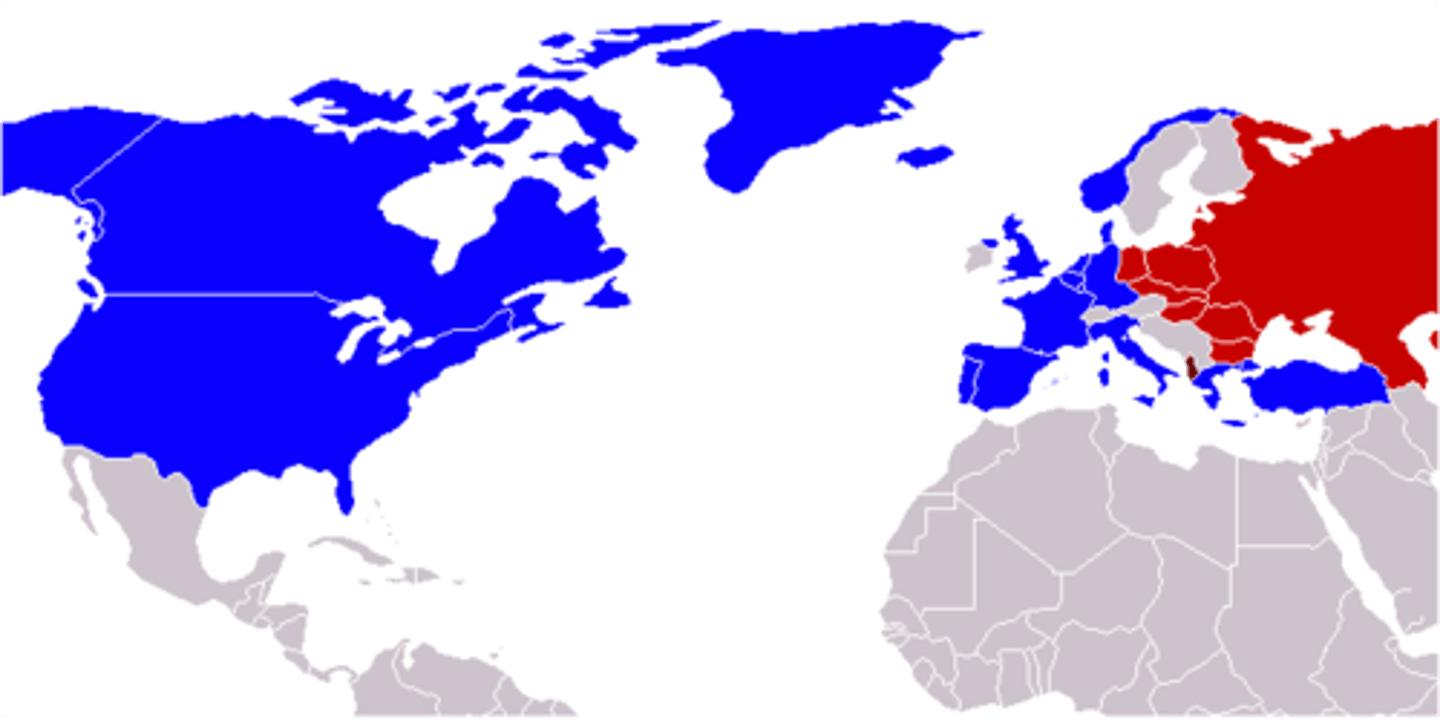
NATO
North Atlantic Treaty Organization, a supranational organization based on mutual security.
Europe
Birthplace of the modern nation-state; i.e. England and France.
colonialism
Policy by which a nation administers a foreign territory and develops its resources for the benefit of the colonial power.
imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.

nationalism
Identifying with, becoming attached to, and pledging loyalty to one's nation.
centripetal force
Phenomena that bring a nation together to support the state.
centrifugal force
Phenomena that divide the state.
unitary state
Power concentrated in the hands of central government officials.
federal state
Shared power between a central government and local governments. Two levels of government
devolution
The transfer of power from the central government to regional governments within the state.
voting districts
generic term adopted by the Bureau of the Census to include the wide variety of small polling areas, such as election districts, precincts, or wards, that State and local governments create for the purpose of administering elections
gerrymandering
Redistricting for the benefit of one political party or group.

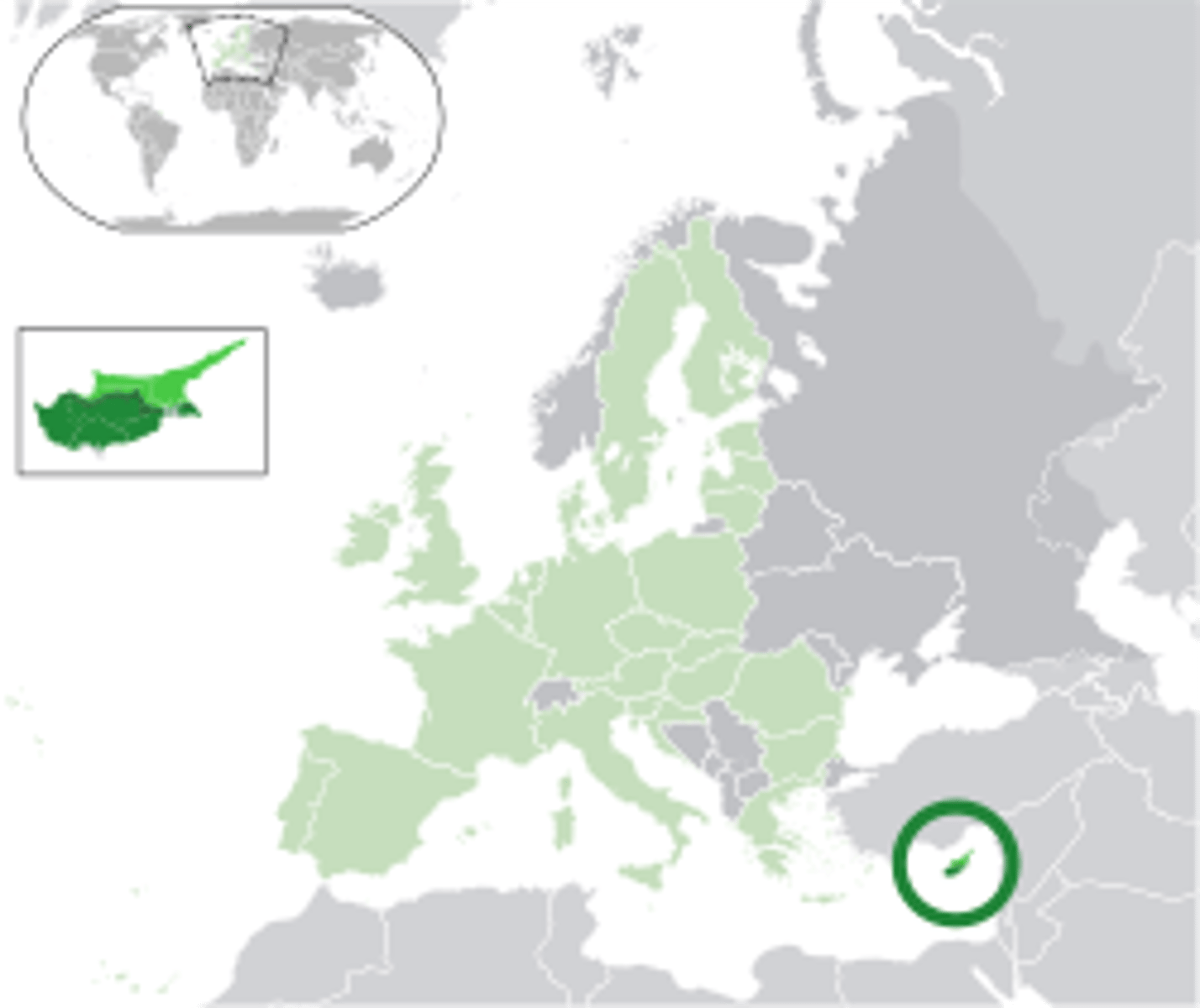
Cyprus
An island state in the eastern Mediterranean Sea that is split between Greek and Turkish nations.
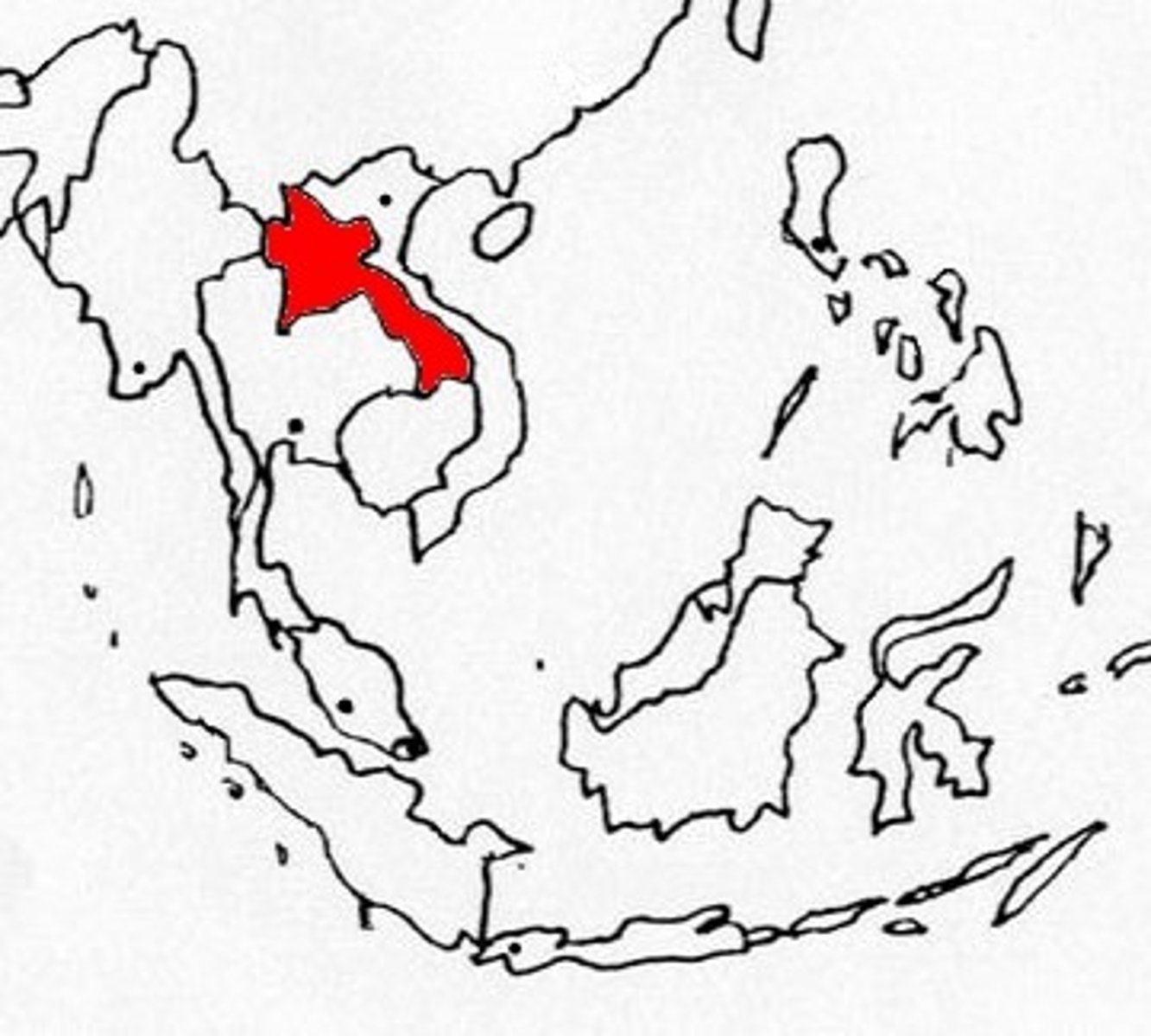
Laos
Landlocked state in Southeast Asia
landlocked state
A state without access to ocean resources.
compact
State shape that is most efficient. About equidistant from center to boarders

elongated
State shape that can be challenging for communication because of its long form.
prorupted
State shape that has a protrusion in order to give the state access to resources.
perforated
State shape that completely surrounds another state.
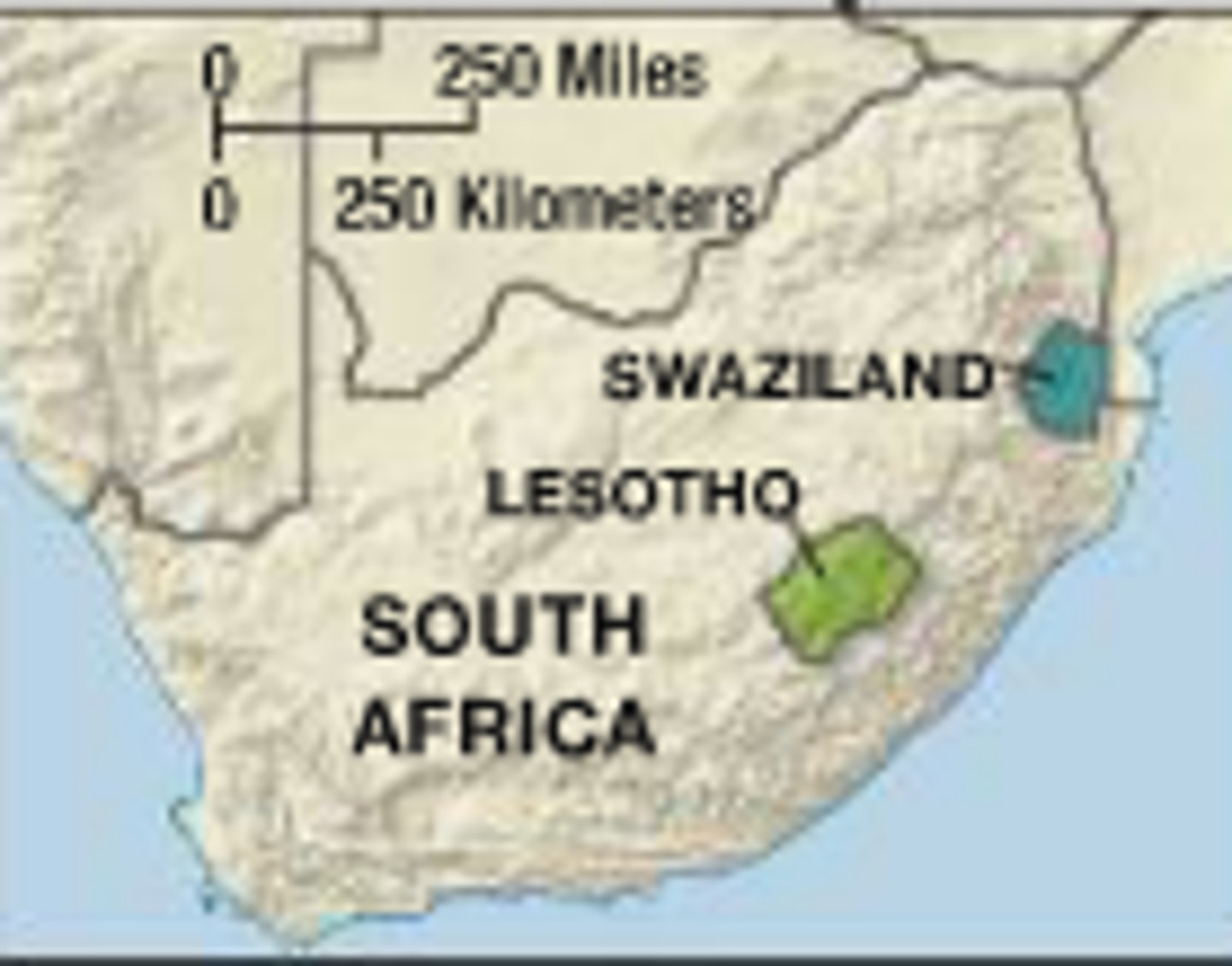
fragmented
State shape that has separations either by ocean (islands) or an intervening state.
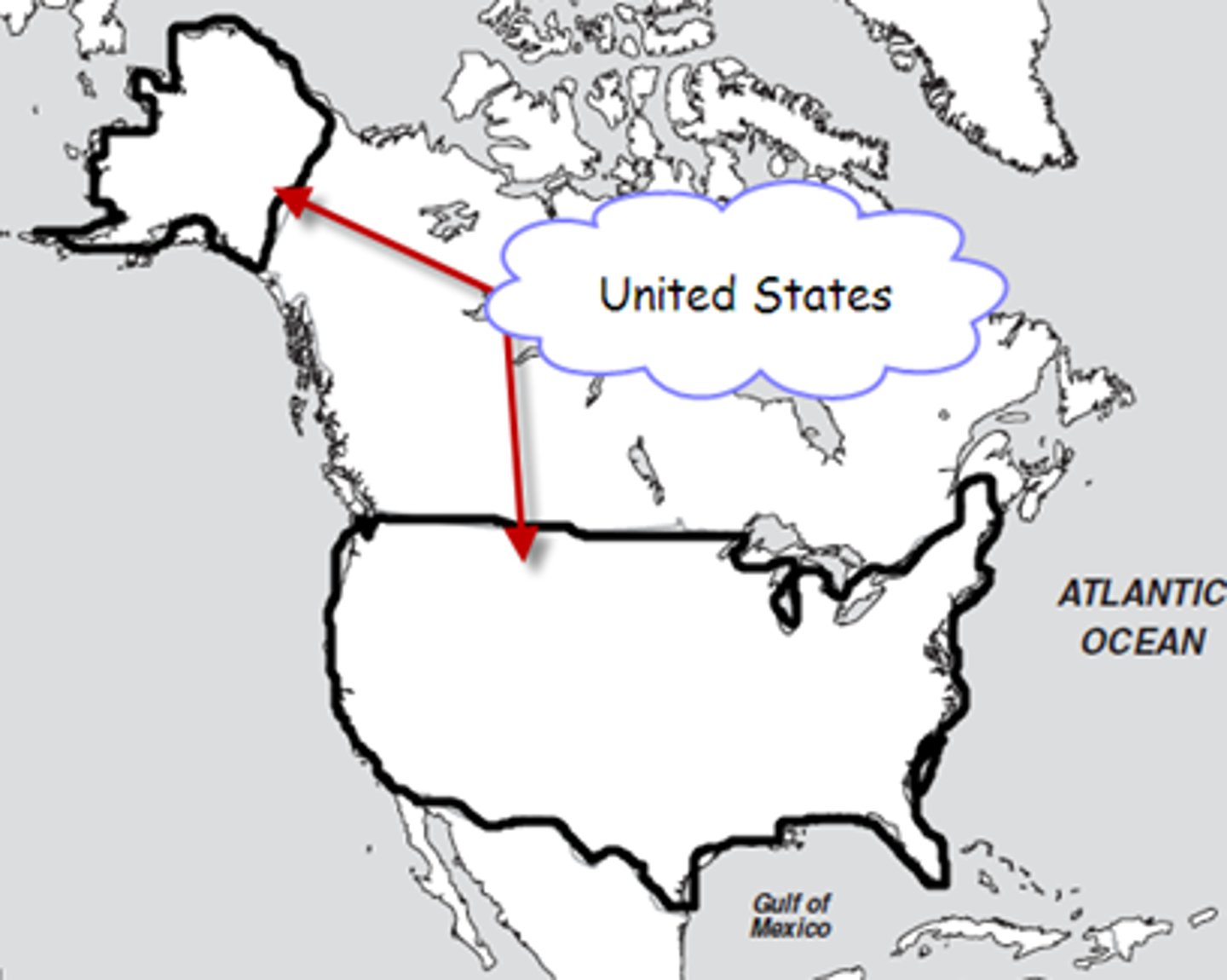
enclave
A state that is surrounded by another state or states.
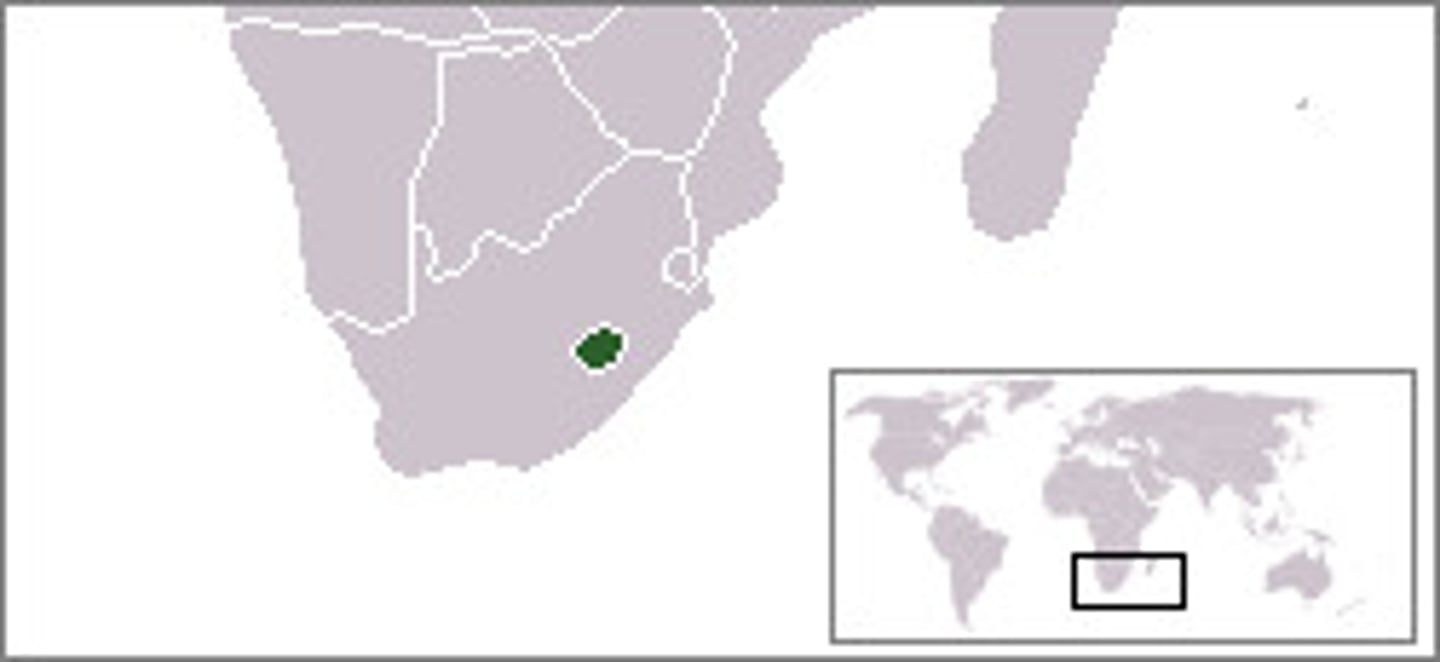
autocracy
A state that is run according to the interests of the ruler rather than the people; Where stability is the primary function of the state.
democracy
A state in which citizens vote and run for election in government.
Balkanization
Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities
Boundary
invisible line that marks the extent of a state's territory
Genocide
systematic killing of a racial or cultural group
ethnic cleansing
Process in which more powerful ethnic group forcibly removes a less powerful one in order to create an ethnically homogeneous region
Reapportionment
the process of reassigning representation based on population, after every census
Redistricting
The redrawing of congressional and other legislative district lines following the census, to accommodate population shifts and keep districts as equal as possible in population.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
a code of maritime law approved by the United Nations in 1982 that authorizes, among other provisions, territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles from shore and 200-nautical-mile-wide exclusive economic zones
Territorial Zone of the Law of the Sea
12 nautical miles - all laws apply
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
the seazone extending 200 nautical miles from the coast over which a state has special rights as to the exploration and use of marine resources
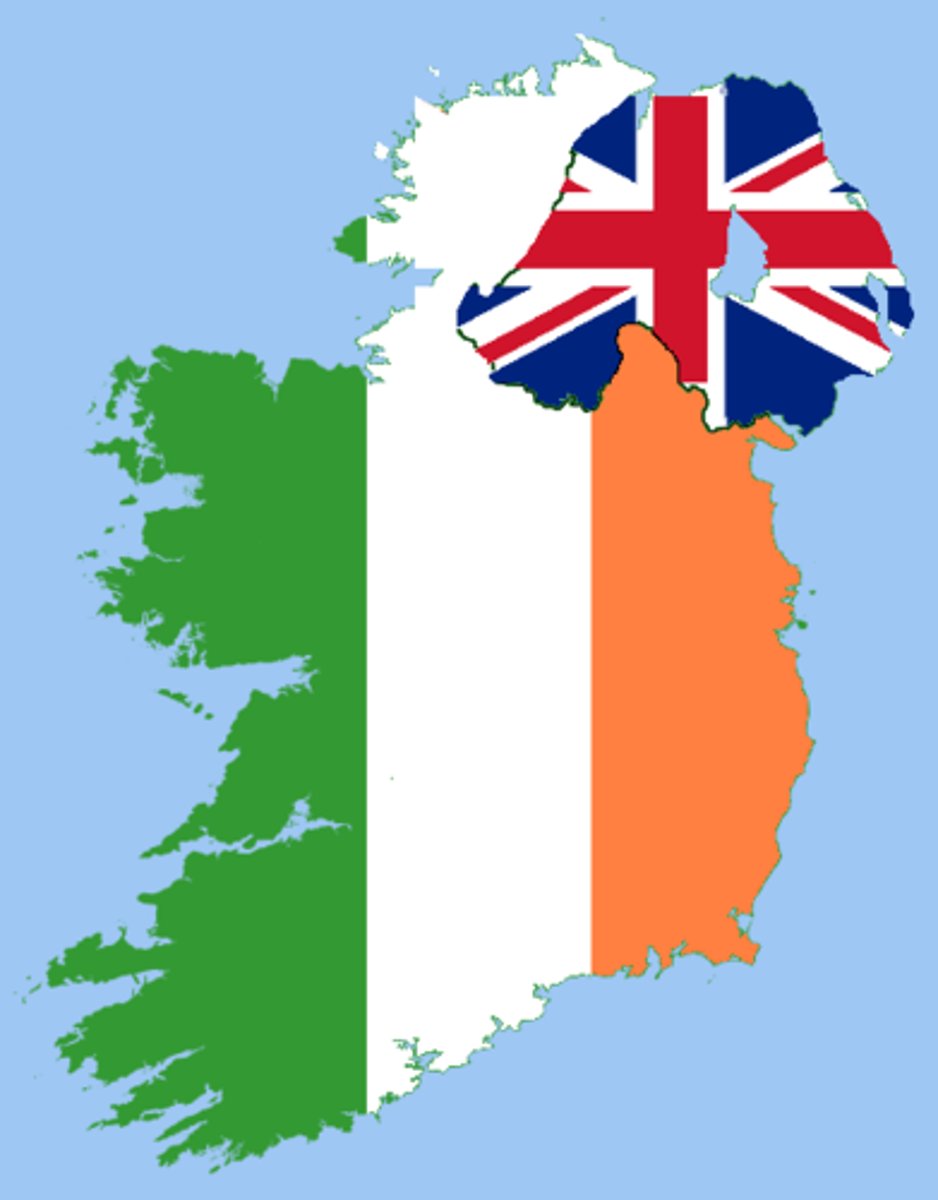
Subsequent Boundary Origin
a boundary that was created before today's cultural landscape.
Ex. Ireland and Northern Ireland
Antecedent Boundary Origin
a boundary that existed before the cultural landscape emerged and stayed in place while people moved in to occupy the surrounding area...
Self-determination
Concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves
Nunavut Territory
territory was created by the Canadian government as a homeland for the Inuit people
Locational Boundary Dispute
Conflict over the location or place of a boundary
functional boundary dispute
a disagreement between neighboring states over policies to be applied to their common border; often induced by differing customs regulations, movement of nomadic groups, or illegal immigration or emigration.
Heartland Theory
Hypothesis proposed by Halford MacKinder that held that any political power based in the heart of Eurasia could gain enough strength to eventually dominate the world.
Rimland Theory
Nicholas Spykman's theory that the domination of the coastal fringes of Eurasia would provided the base for world conquest.
Organic Theory
The theory that a state needs expansive land in order to prosper
Cold War
A conflict that was between the US and the Soviet Union. The nations never directly confronted each other on the battlefield but deadly threats went on for years.
Domino Theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control.
wasted vote
spreads opposition supporters across many districts but in the minority also called cracking
excess vote
concentrates opposition supporters into a few districts also called packing