NMSK 5 - Introduction to the distal limb
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Outline the features of the distal limb.
- Distal to the carpus/tarsus joint.
- Fore and hind are near identical
- Elongated in animals adapted for speed and reduced in mass
What are ray patterns?
The metacarpal/metatarsal bones, and the proximal, middle, and distal phalanges.
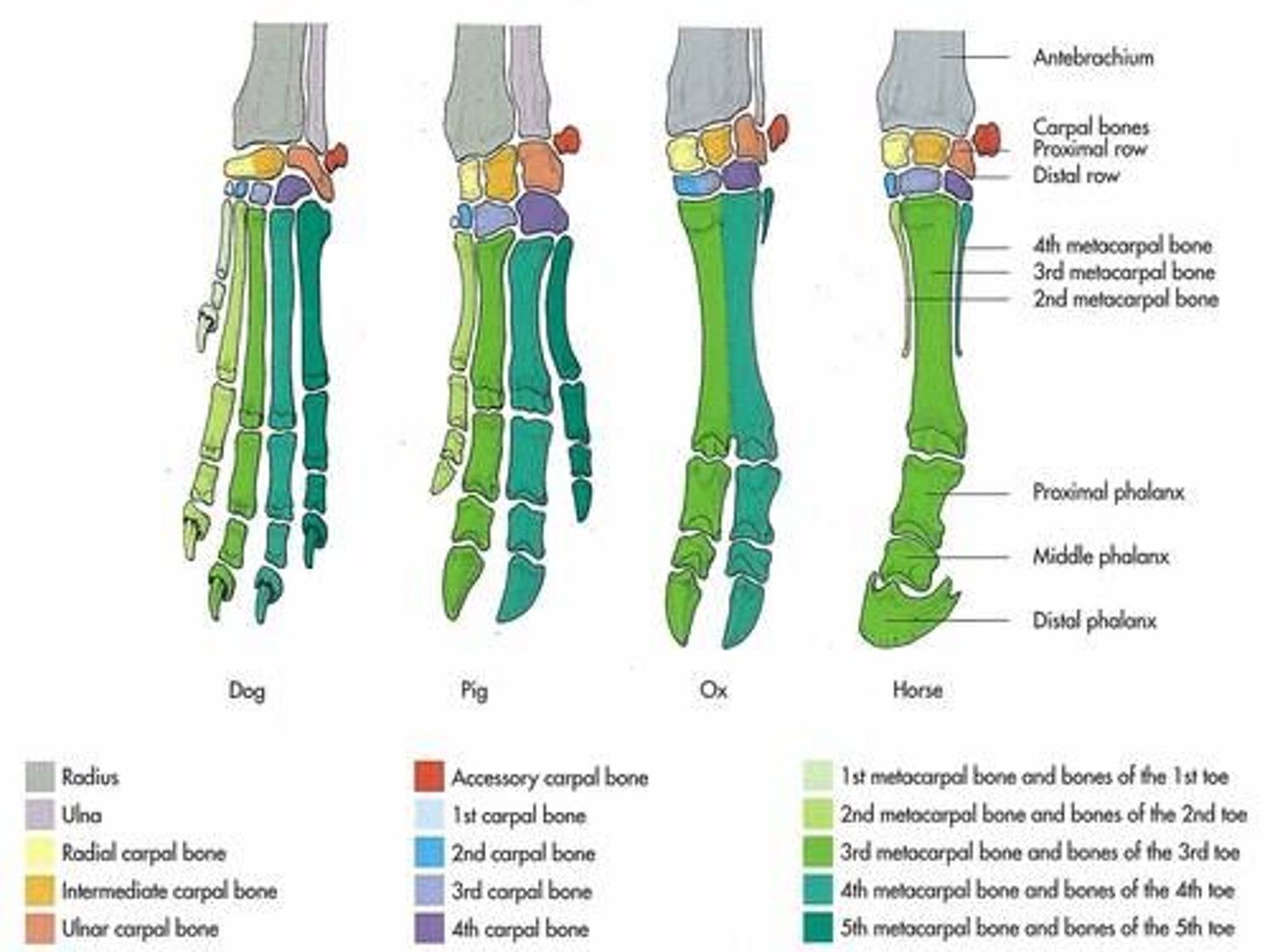
List the joints of the distal limb.
Metacarpophalangeal
- Fetlock in horse and cow
- Hinge joint
Proximal interphalangeal
- Pastern
- Saddle joint
Distal interphalangeal
- Coffin
- Saddle joint
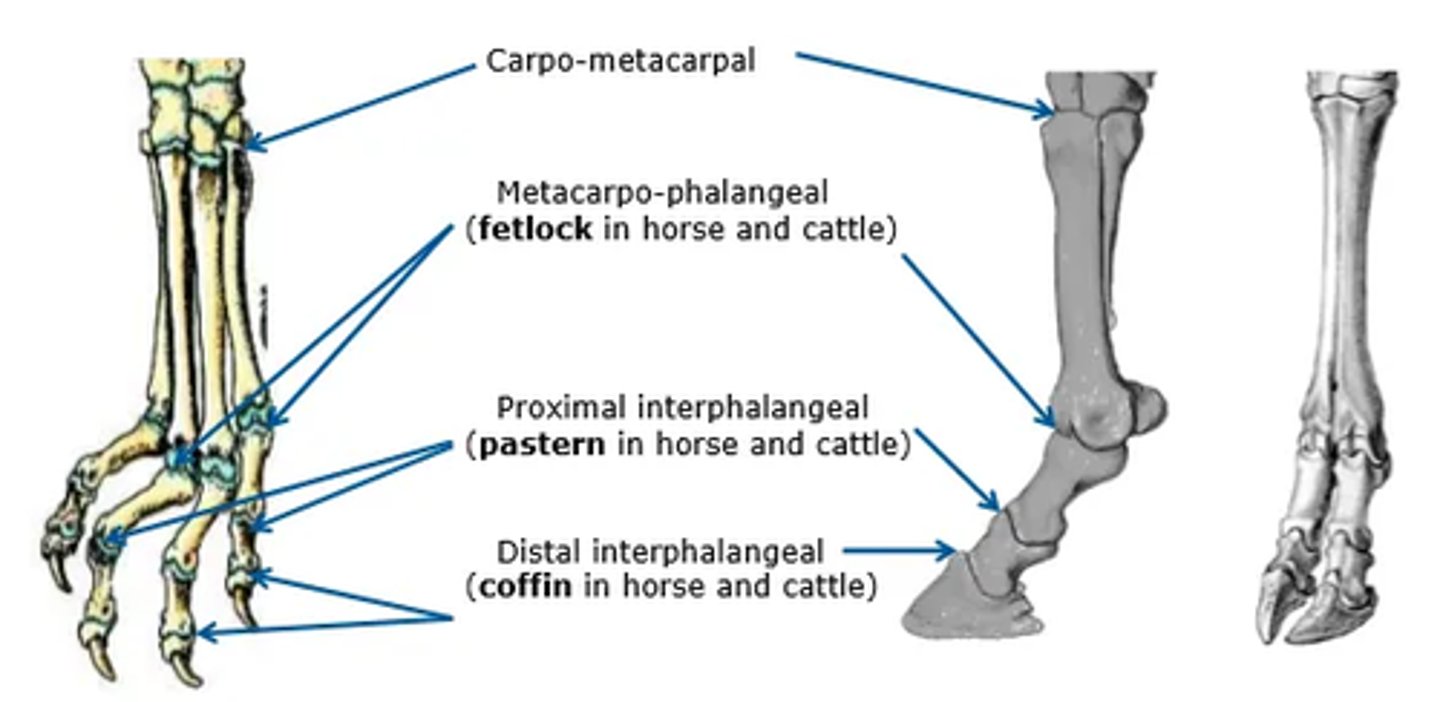
Describe the bones of the distal limb in horses.
Cannon bone: 3rd metacarpal/tarsal bone and condyle of cannon
Medial splint bone: 2nd metacarpal
Lateral splint bone: 4th metacarpal and 'button' of splint
Proximal sesamoids
Proximal phalanx: long pastern bone
Middle phalanx: short pastern bone
Distal sesamoid: navicular bone
Distal phalanx: coffin bone
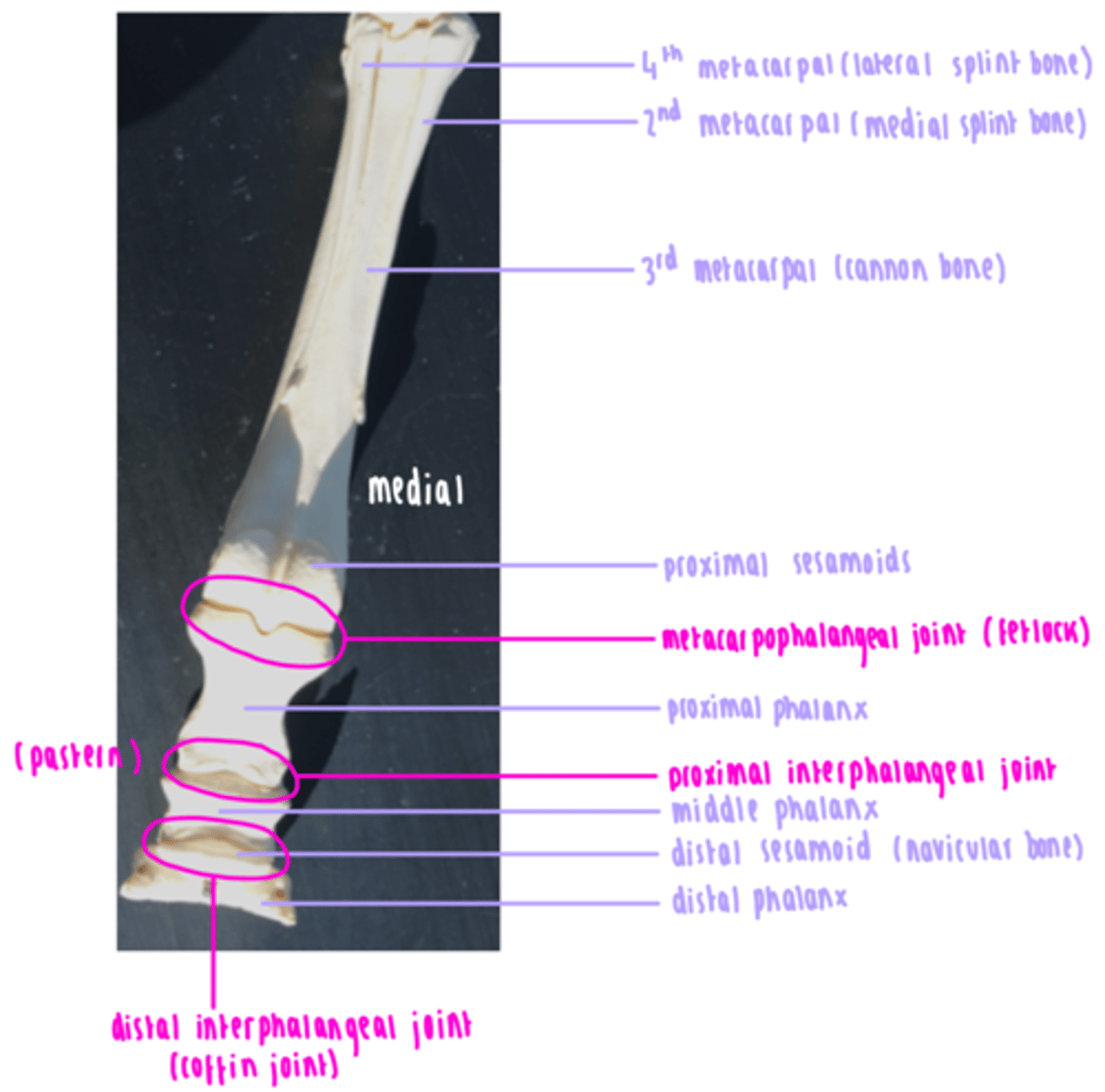
Describe the bones of the distal limb in bovines.
Fused metacarpals III and IV
Metacarpophalangeal joint
Proximal sesamoids
Proximal phalanx
Proximal interphalangeal joint
Middle phalanx
Distal interphalangeal joint
Distal sesamoid
Distal phalanx
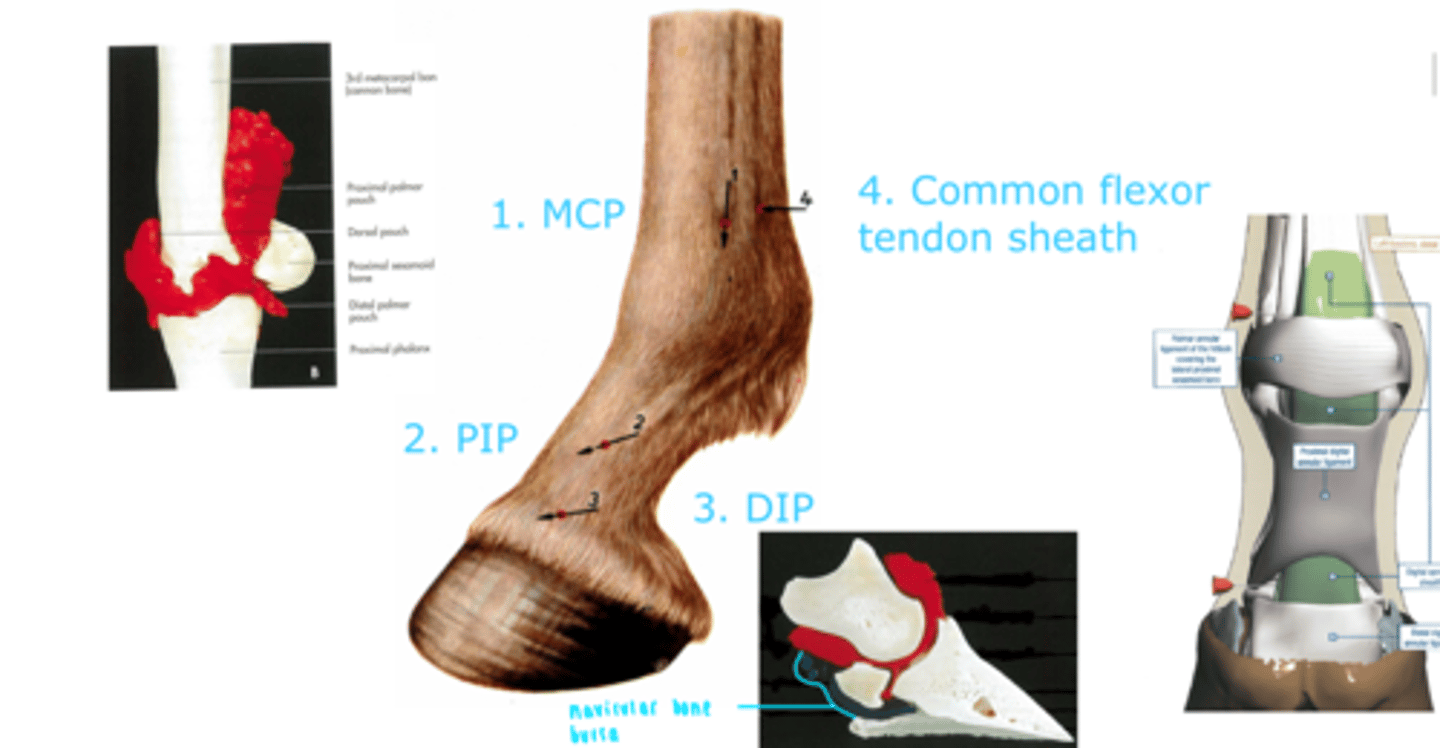
List the sites for intra-articular injection in the horse (synovial structures).
1. Metacarpophalangeal joint (fetlock)
2. Proximal interphalangeal joint (pastern joint)
3. Distal interphalangeal joint (coffin)
4. Common flexor tendon sheath
List the extensor tendon(s) of the forelimb digits in horses and bovines.
Common digital extensor
- Dorso-lateral aspect
- Muscles are innervated by the radial nerve
*Lateral digital extensor not functional in horses as no lateral digits*
List the extensor tendon(s) of the hindlimb digits in horses and bovines.
Long digital extensor
- Dorso-lateral aspect
- Muscles are innervated by the fibula nerve
List the flexor tendon(s) of the forelimb and hindlimb digits.
*Both located on the palmer aspect*
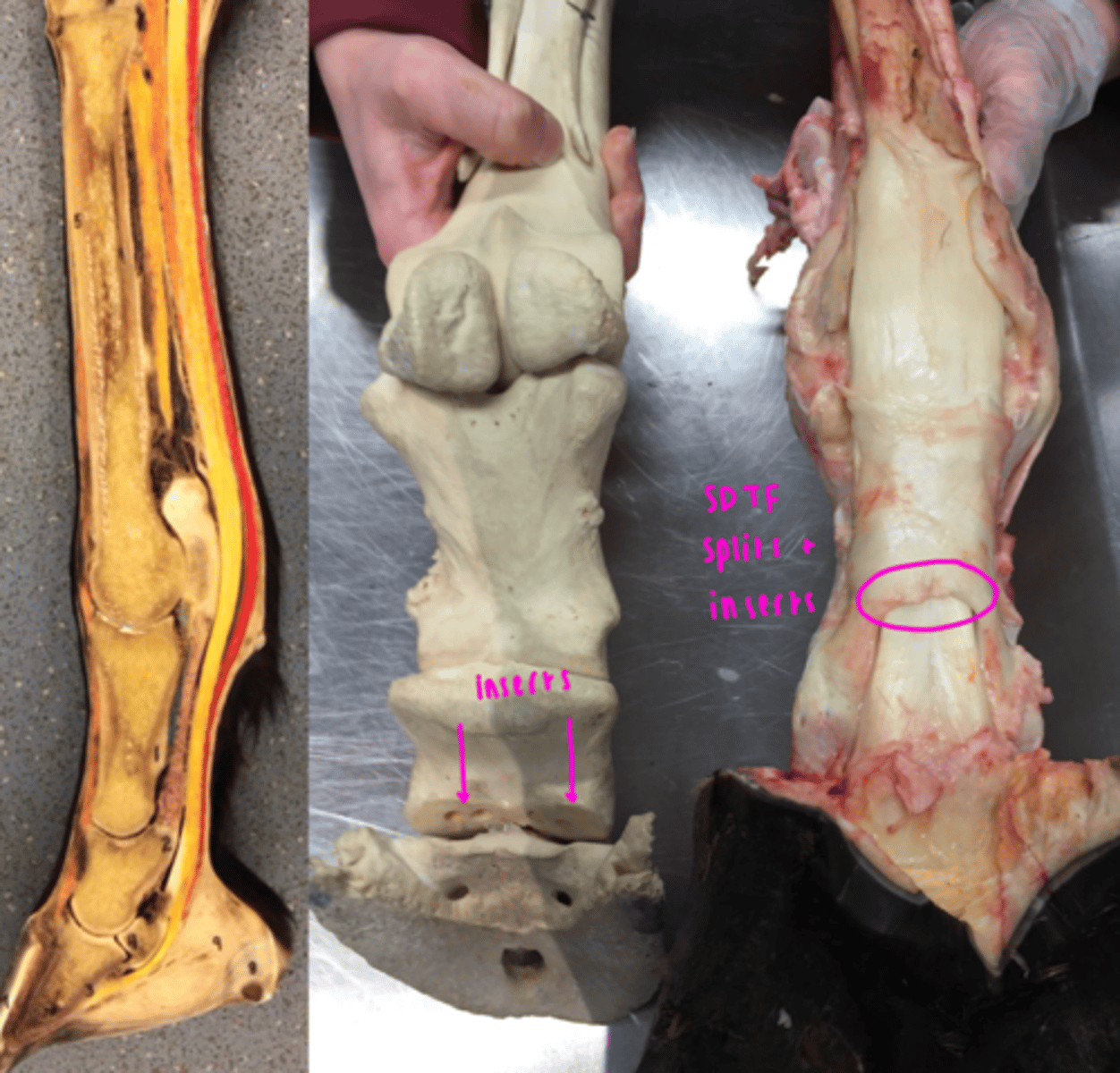
Superficial digital flexor tendon
- Subcutaneous and palpable
- At distal end of P1 and inserts on P2
- Forms a sleeve around DDTF at proximal sesamoids (manica flexoria)
- Flexes the whole digit and stabilises the fetlock
Deep digital flexor tendon
- Runs deep to SDFT
- Passes through manica flexoria
- Inserts on flexor tuberosity of distal phalanx of each functional digit
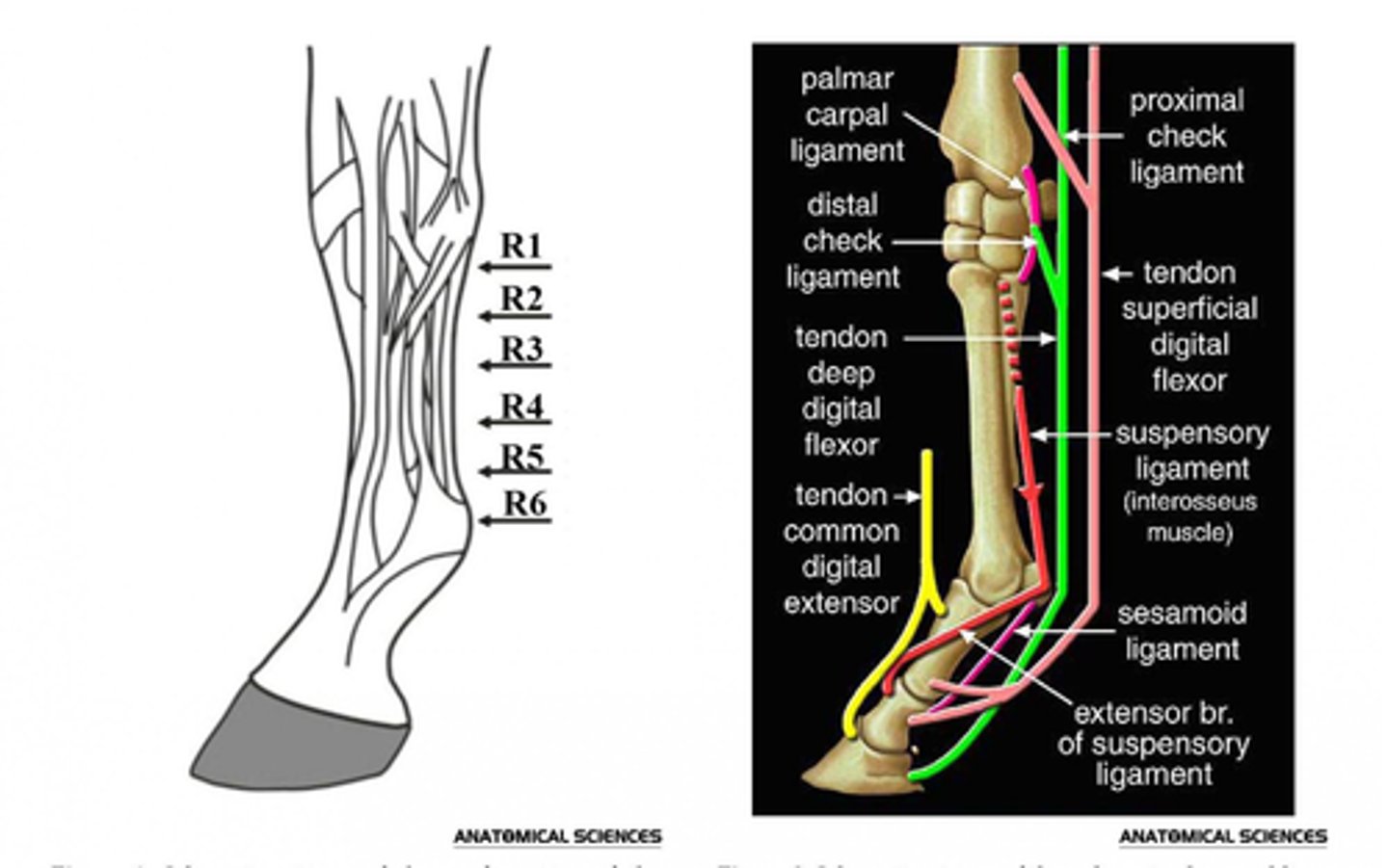
Outline the soft tissue structures that provide support to the distal limb.
Interosseous (aka TIOM or suspensory ligament)
- Supports the fetlock, preventing excessive extension.
- Mostly tendinous in horse, muscular in dog and cat
- Part of the suspensory apparatus
- Arises from proximal metacarpal between splint bones, deep to SDFT and DDFT
- Divides above the fetlock into extensor branches, before inserting on abaxial surface of proximal sesamoids
- Extensor branches run to extensor tendon
- Continues as sesamoidean ligament to phalanges beyond sesamoid bones
Accessory (check) ligaments: absent in the hindlimb
Proximal check
- Accessory of the SDFT
- From distal radius to middle phalanx
Distal check
- Accessory of DDFT
- From carpus and attaches on third metacarpal
- Limits movement of the tendon to prevent over-stressing and to support the fetlock joint through anchoring flexor tendons
Describe the structures that protect the distal limb.
Bursae
- Cushion tendons in areas at risk of damage, distributes pressure
- Navicular bursitis can be inflammatory or infectious
Digital flexor tendon sheaths (DFTS)
- Surrounds flexor tendons of the fore and hindlimbs
- Extends from above the fetlock joint to middle of P2
Annular ligaments
- Local thickening of fascia
- Stabilise tendons
- Located in different places: palmar/plantar, proximal digital, distal digital, and interdigital in cattle
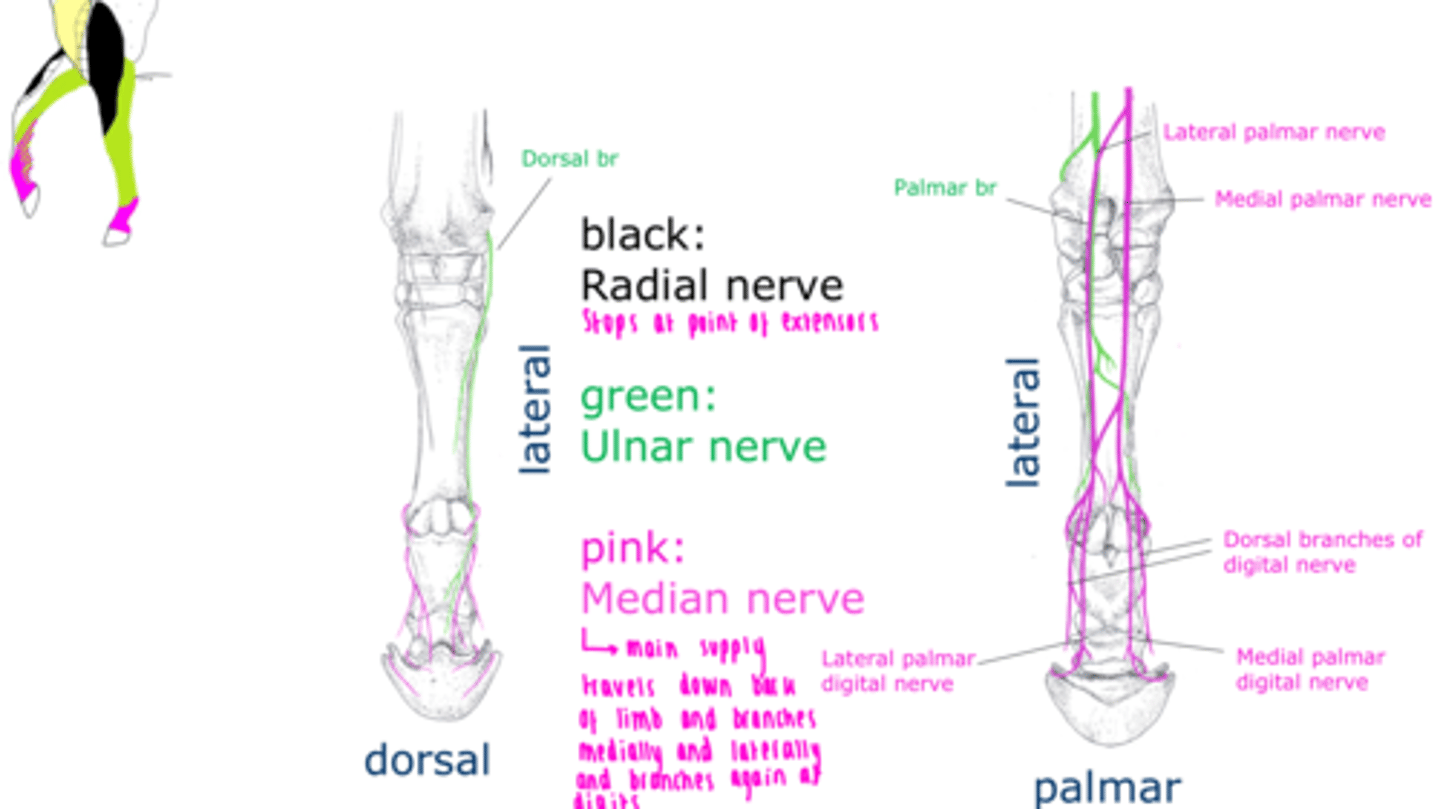
List the main nerves of equine distal forelimb and their cutaneous supply.
Radial nerve
- Extensors of the elbow, carpus, and digits
- Craniolateral surface of forearm
Median nerve
- Flexors of the carpus and digits
- Palmer surface of manus and dorsal digit in horse
Ulnar nerve
- Flexors of the carpus and digits
- Caudal surface of of forearm and dorsal digit in horse
List the main nerves of equine distal hindlimb and their cutaneous supply.
Tibial
- Muscular supply to extensors of the hock and flexors of the digits
- Plantar surface
Fibular
- Muscular supply to flexors of the hock/extensors of the digits
- Dorsal surface
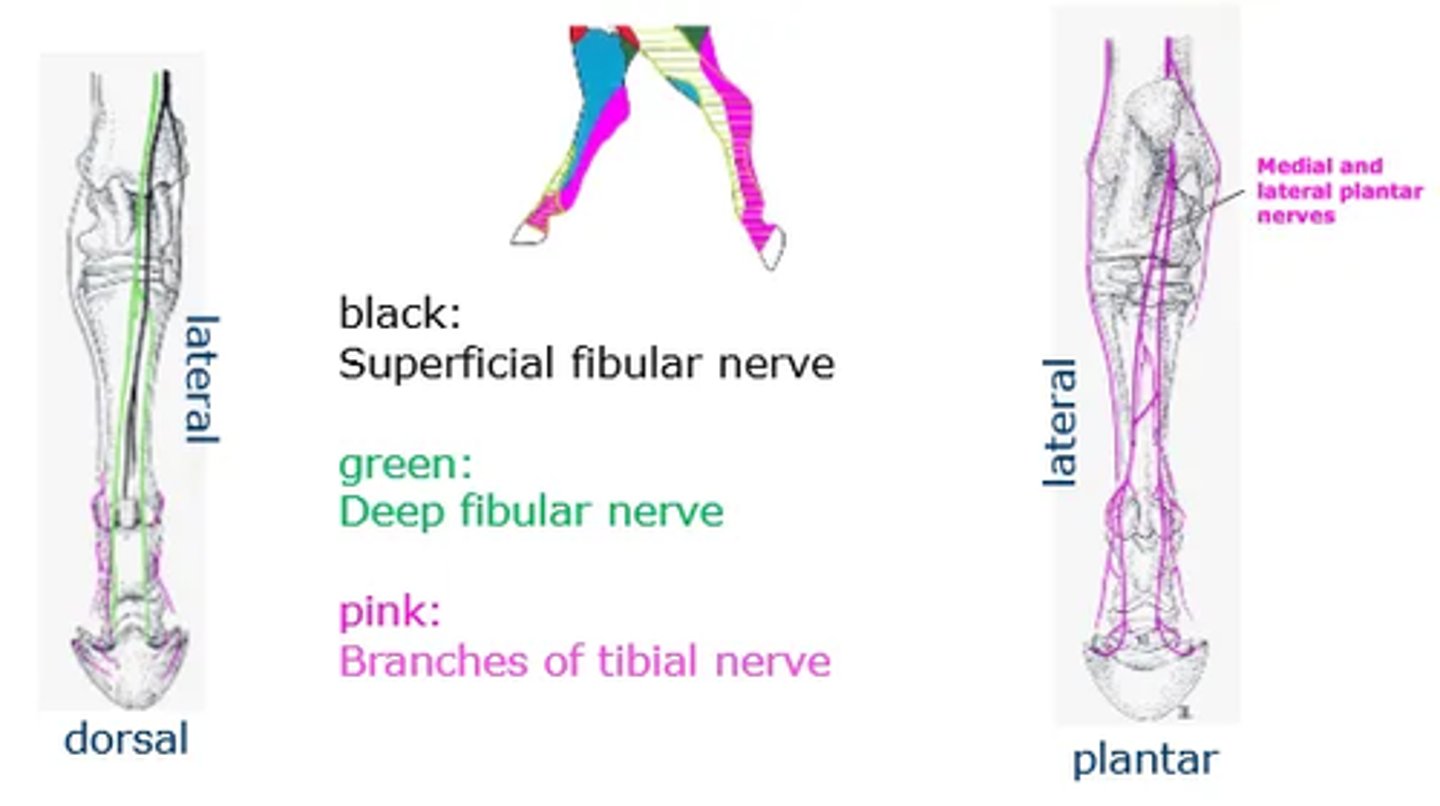
Outline the regions for nerve blocks in the equine distal limb.
Most distal structures are blocked first to determine where lameness is.
Palmar digital nerve block
- Palmar digital nerves in pastern region
- Neurovascular bundles can be palpated abaxial to flexor tendons
- VAN = nerve most palmar
- Desensitises hoof structures other than dorsal coronary band
- Done medially and laterally
Abaxial sesamoid nerve block
- Palmar digital nerves on abaxial surface of proximal sesamoid bones
- Neurovascular bundles can be palpated over sesamoids
- VAN = nerve most palmer
- Desensitises the digit and caudal fetlock joint
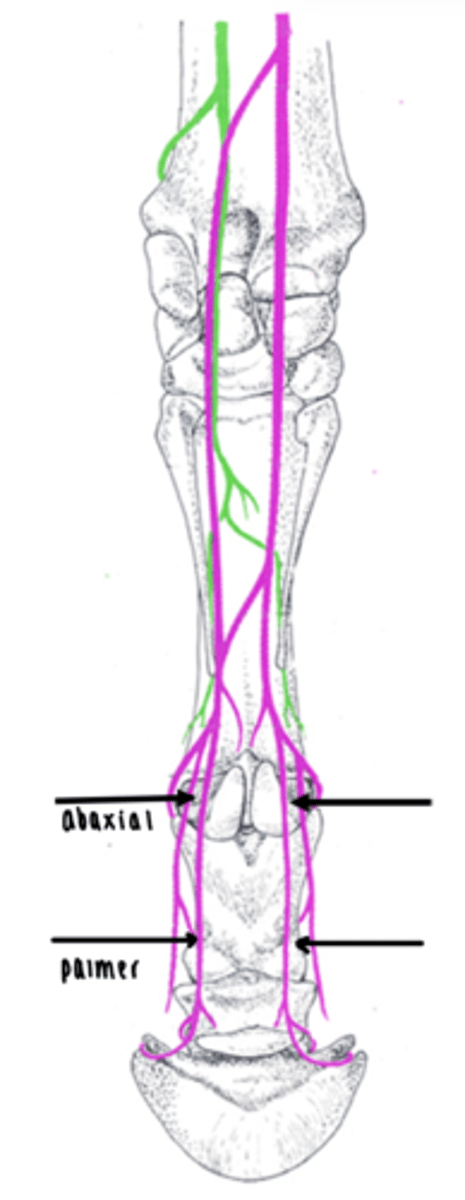
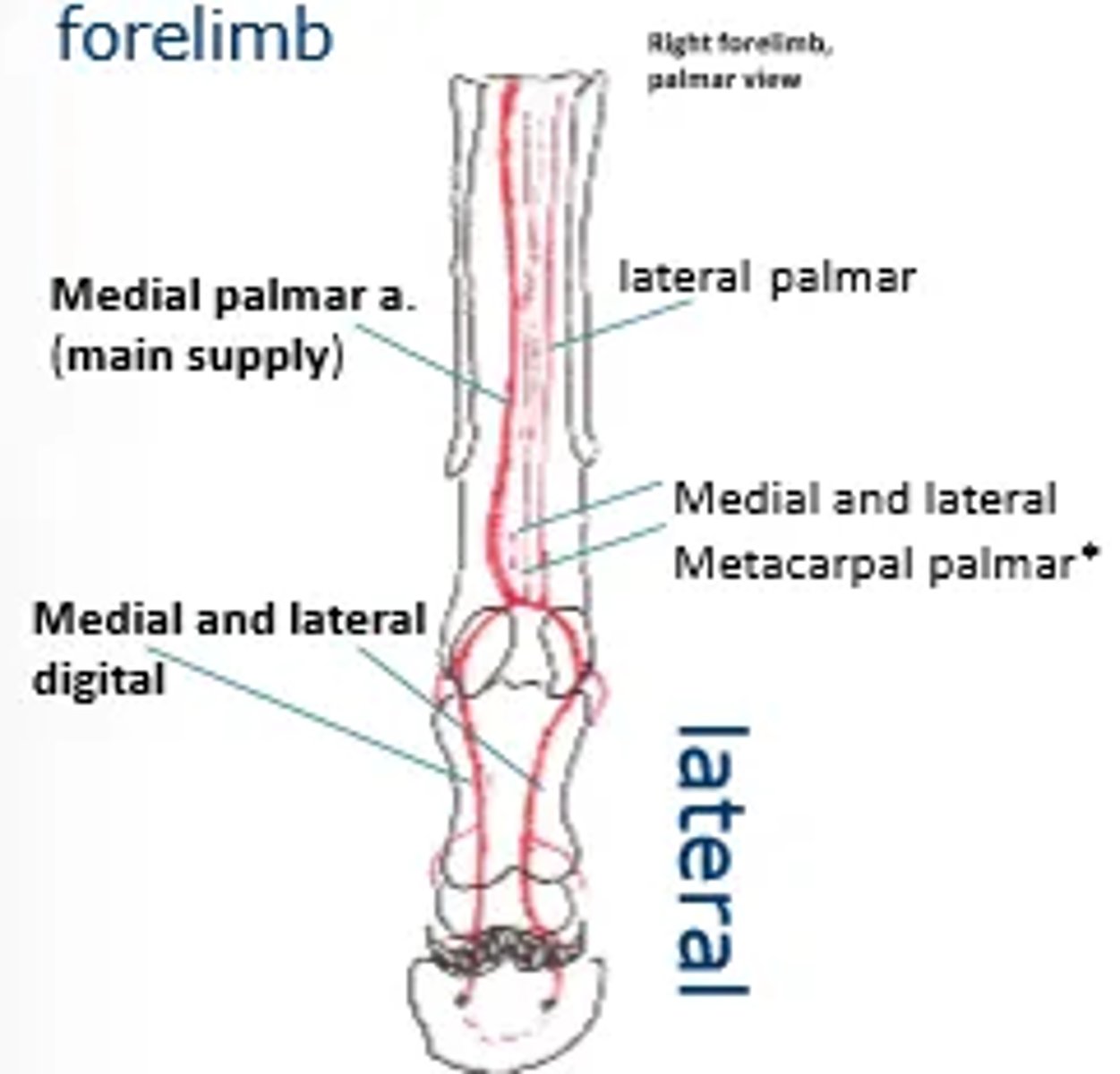
List the main vasculature supply to the forelimb of a horse.
Axillary artery
Brachial artery
Median palmar artery
Medial and lateral palmer digital
There is not dorsal supply in horses
How does bovine distal limb vasculature differ?
Dorsal common digital artery in the forelimb and dorsal metatarsal arteries in the hindlimb.
What is the clinical importance of ruminant distal limb vasculature?
- The stump of the axial palmer artery bleeds most profusely upon digit amputation and must be ligated.
- The dorsal common digital vein is used for intravenous anaesthesia
