Recognition and Escalation of Deteriorating Physical and Mental Health (ADN501)
1/822
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
823 Terms
non opiods

NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
Opiods

What are NSAIDs
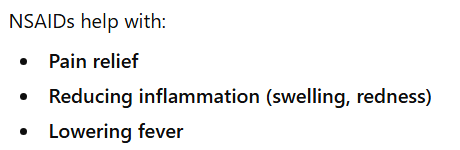
Antiarrhythmics

Antiarrhythmics drugs

Antibiotics

Antibiotic drugs
Amoxicillin.
Flucloxacillin.
Meropenem.
Vancomycin.
Gentamycin.
Clarithromycin.
Co-amoxiclav.
Cefuroxime.
Doxycycline
Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants, commonly referred to as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time.
Anticoagulant drugs
Warfarin.
Rivaroxaban.
Apixaban.
Enoxaparin.
Heparin.
Anticonvulsants
are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of both epileptic and non-epileptic seizures.
Anticonvulsants drugs
Diazapam.
Lorazepam.
Levetiracetam (Keppra).
Gabapentin.
Antidepressants are
drugs used for the treatment of depressive disorders and usually fall into one of the following categories; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), noradrenaline and specific serotonergic antidepressants (NASSAs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
Antidepressant drugs
Fluoxetine.
Amitriptyline.
Sertraline
Antiemetics are
drugs used to treat vomiting and nausea and are typically used to treat motion sickness and the side effects of opioid analgesics, general anaesthetics and chemotherapy directed against cancer.
Antiemetic drugs
Cyclizine.
Ondansetron.
Metoclopramide.
Antihypertensives are
used to treat hypertension and usually fall into one of several categories; angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, calcium channel blockers (CCBs), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and beta-blockers
Antihypertensive drugs
Atenolol.
Bisoprolol.
Amlodipine
Ramipril.
Losartan.
Antihyperglycemics
are used in the treatments of raised blood sugars, typically in diabetic patients.
Antihyperglycemics drugs
Metformin.
Insulin.
Gliclazide.
Bronchodilators
Bronchodilators are used to help make breathing easier by relaxing the muscles in the lungs and widening of the bronchi.
Bronchodilator eg
Salbutamol.
Tiotropium.
Diuretics
are drugs that increased the production of urine these usually fall into one of several categories; loop diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics and thiazides.
Diuretics drugs
Furosemide.
Bumetanide.
Spironolactone.
Intravenous Fluids
are infusion fluids and usually fall into one of two categories; colloid and crystalloid and can include supplements such as potassium and magnesium.
Intravenous Fluids eg
Hartmans
Sedatives
are a group of medications that are using for a calming effect. They can be used to promote sleep, ease withdrawal symptoms or reduce agitation and irritability.
Sedatives eg
Midazolam.
Diazepam.
Lorazepam.
Statins
Statins or lipid-lowering medications are a group of medications that have been found to lower the level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the blood. Usually, they are prescribed to help reduce the risk of; stroke, coronary heart disease, heart attacks and angina.
Statins eg
Simvastatin.
Atorvastatin.
Pravastatin.
Supplements are
medications that generally include hormones, vitamins, minerals, fibre, fatty acids or amino acids and other substances.
Supplements eg
Levothyroxine
Adcal / Calcichew.
Ferrous Fumarate.
Ferrous Sulphate
Sando k
Folate
Laxatives
are used to treat either acute or chronic constipation and usually fall into one of the following categories; bulk-forming, osmotic, stimulant or stool softening.
Laxatives eg
Lactulose.
Senna.
Movicol.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
are a group of drugs whose main action is the reduction in gastric acid production.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) eg
Omeprazole.
Lansoprazole.
Esomeprazole.
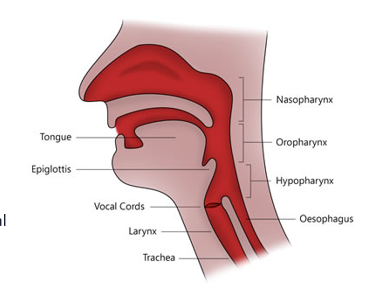
Air obstruction is an

airway consists of

Airway role

airway labelled
when assessing remember
look,listen and feel
Airway look

airway listen

airway feel

Airway assessment

Airway management

airway obstruction signs

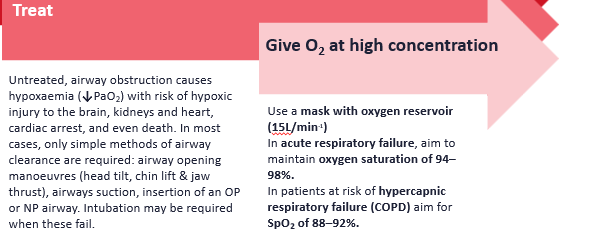
airway obstruction treatment
breathing

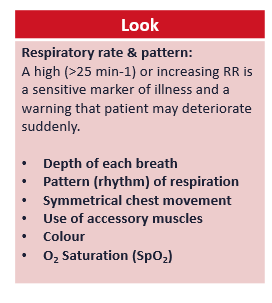
signs of respiratory distress

breathing assessment

breathing management

breathing look

look 2
Breathing listen

listen 2

Breathing feel

feel 2

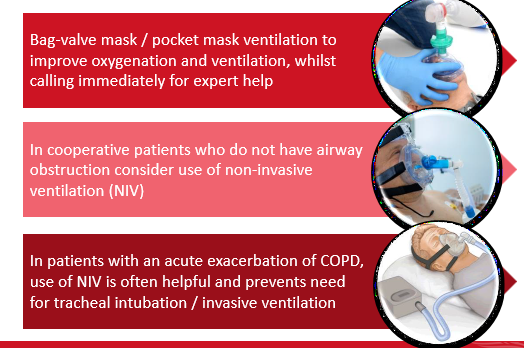
if breathing is inadequate
circulation

Circulation assessment

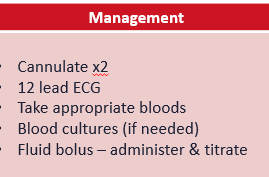
circulation management
circulation look

look 2
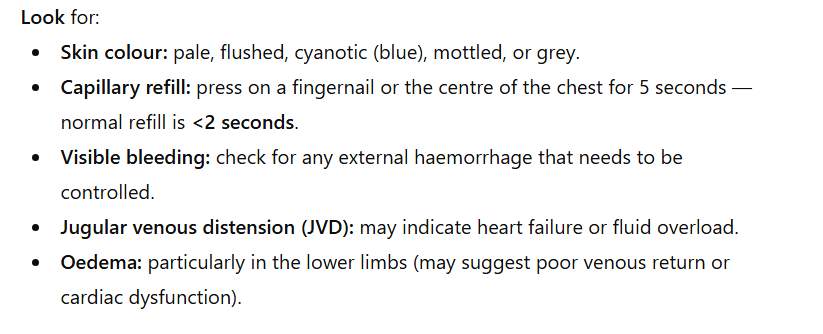
circulation listen

listen 2

circulation feel
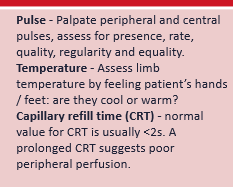
circulation feel 2

disability acvpu
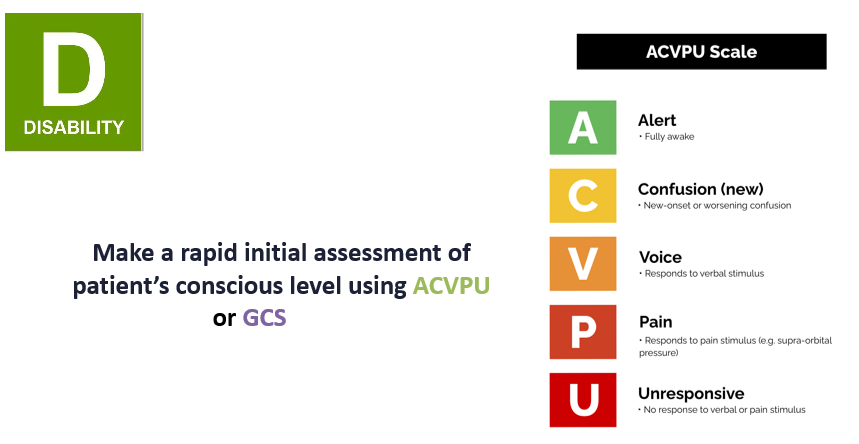
Disability assessment

Disability management

GCS
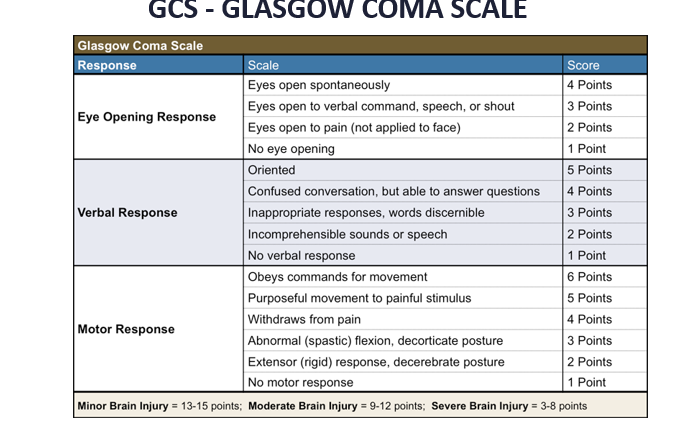
exposure assess

exposure management

NEWS
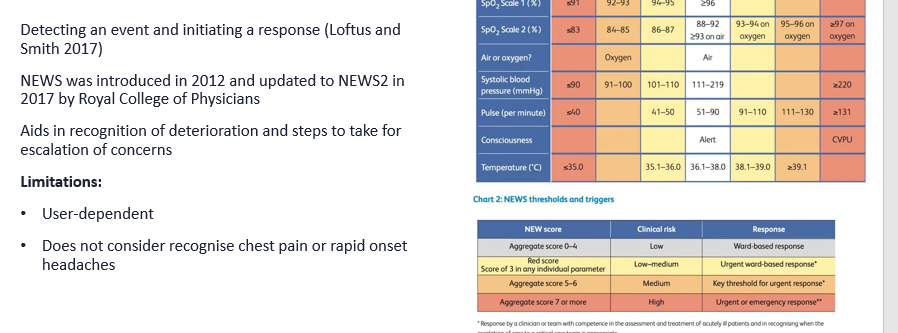
Situation

Background

Assessment

reccomendation

human factors nursing

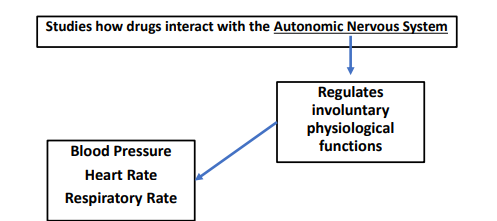
Autonomic pharmacology


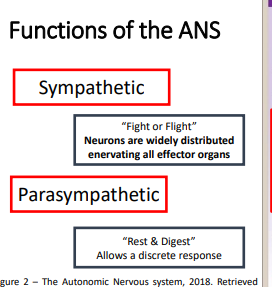
Functions of the ANS
Baroreceptors

Chemoreceptors

Stretch receptors

Vagus nerves

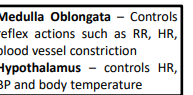
medulla oblangata and hypothalamus
Synaptic transmission

Afferent neurons

Efferent neurons
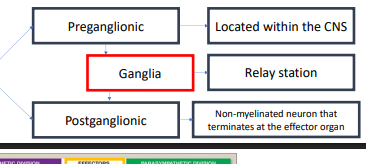
pre ,post ,ganglia

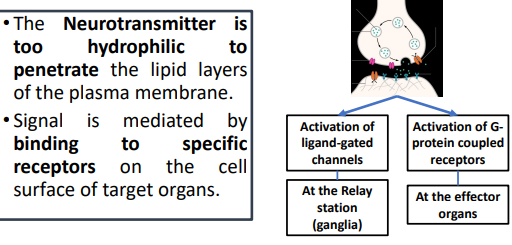
Signal transmission ANS
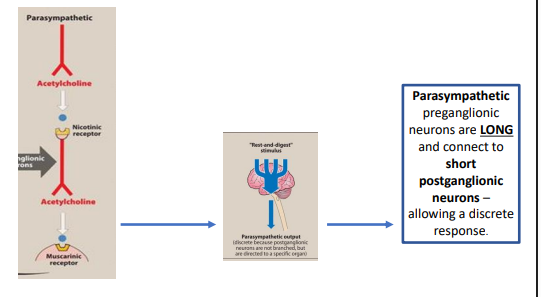
Para,post neurons
Sympathetic
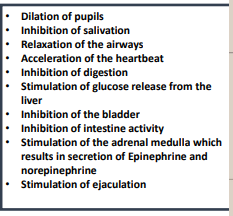
Parasympathetic

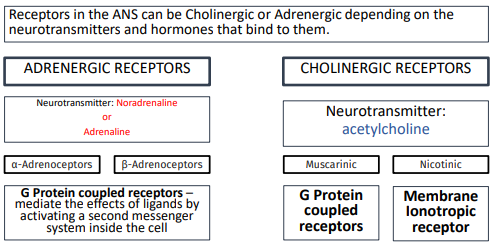
receptors in the ANS
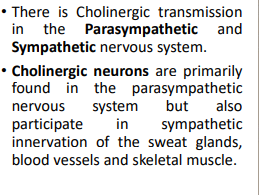
Cholinergic transmission
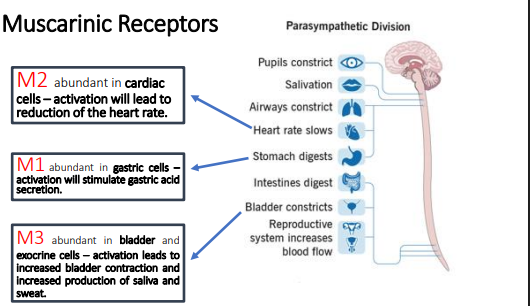
Muscarinic receptors,nicotinic
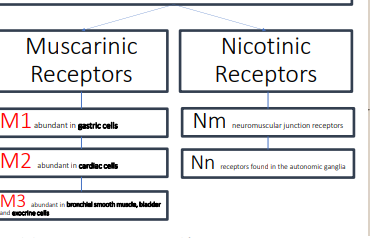
Muscarinic receptors