cell bio unit 1
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chs 1, 2, 3, 13, 14, 4, 16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
building blocks of all living tissues
cells
how are cells generated?
from pre-existing cells
where do cells get their characteristics?
inherit from their predecessor cell
central dogma
DNA → RNA → protein
are viruses living?
no because they require a host to replicate; “molecular parasites”
what kind of genetic material do viruses have?
varies, can have:
DNA
RNA
double-stranded
single-stranded
“our _____ hold the code, but its their _____ that determines function”
genes
expression
what unit are cells measures in?
micrometers (μm)
light microscope characteristics (4)
use light
contain optics
living cells glow under this
units of measurement: ~50 μm
confocal microscope characteristics (4)
uses a laser
only used 1 wavelength of light
florissant dye used to highlight specific proteins
units of measurement: ~10 μm
electron microscope characteristics (2)
units of measurement: nm (smaller than μm)
allow u to see organelles of the cell
prokaryote characteristics (5)
small + simple + single celled
most diverse of all cells
can adapt to extreme environments
domains: bacteria, archea
many different sources of “food” (O2, H, S, photosynthesis)
eukaryote characteristics
bigger + elaborate organisms
can be single or multi cellular
have membrane-bound organelles
have nucleus
why are some organelles membrane-bound?
allows for division of areas
nickname: plasma membrane
fence
nickname: nucleus
government
nickname: ribosomes
factories
nickname: mitochondria
power plant
nickname: chloroplasts
solar power plant
nickname: endoplasmic reticulum
highway
nickname: golgi body
post office
nickname: lysosome
waste disposal system
nickname: peroxisomes
chemical plant
nickname: cytoskeleton
cell scaffolding
function: plasma membrane
to separate / act as a barrier
function: nucleus
holds DNA
manages cellular activities
function: nuclear membrane
keeps DNA safe inside the nucleus
function: ribosomes
translate RNA to proteins
function: mitochondria
oxidate food mlcls to generate ATP
_____ contain their own DNA and reproduce themselves (like bacteria)
mitochondria
how did mitochondria evolve?
from bacteria
was ingested by a eukaryote and became a part of the eukaryotic cell since
what did eukaryotes likely evolve as?
predators
what is the most abundant organelle?
mitochondria
function: endoplasmic reticulum
moves proteins around
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
ribosome-coated ER with makes proteins to be secreted
smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
involved in lipid synthesis
function: golgi body
sorts proteins for final delivery destiny
function: lysosomes
intracellular degradation:
break down food + release back to cell
break down waste for recycling or excretions
function: peroxisomes
chemical break down
H2O2 (peroxide) generated + degraded inside
function: cytoskeleton
physical strength
scaffolding
allow for cellular movement
import by endocytosis; export by exosytosis
function: chloroplasts
photosynthesis
_____ have both mitochondria + chloroplasts
plants
rules of the cell
continually exchanging environment
not a closed system
central dogma: DNA → RNA → protein
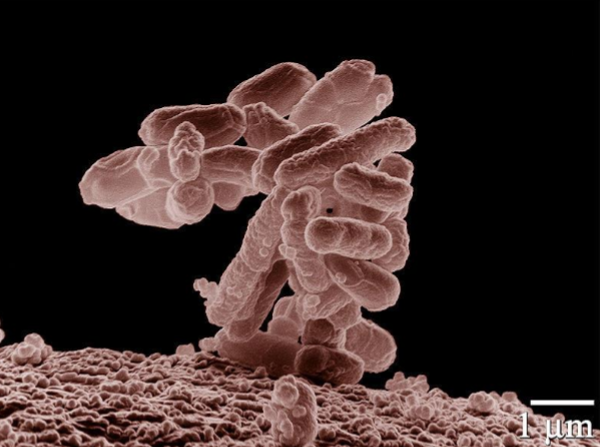
Escherichia coli
E. coli
most thoroughly understood organism
prokaryote
genome is fully mapped
single, circular double strand of DNA; ~4.6 million nucleotide pairs long
produces 4300 diff kinds of proteins
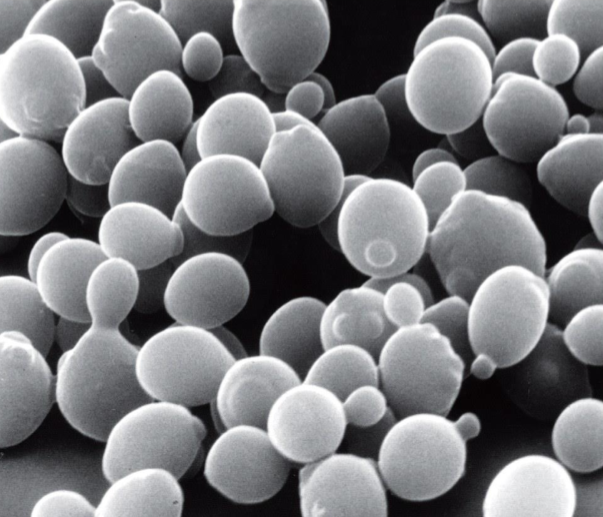
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
yeast
minimal model eukaryote
single celled
Arabidopsis thaliana
common wall crest
go through generations quickly: prods thousands of offspring in 8 - 10 weeks
easy to grow indoors
complete DNA sequence is known

Drosophila melanogaster
fruit fly
helped us understand genetics more than any other organism
showed us how to trace case + effect from DNA instruction to structure of adult multicellular organism

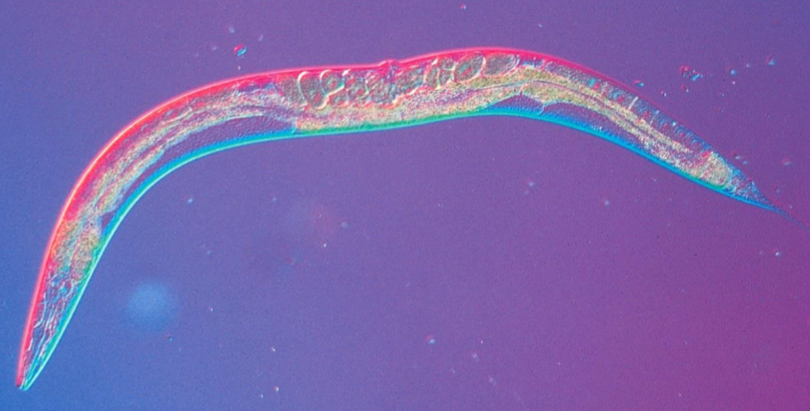
Caenorhabditis elegans
C elegans
brain is completely mapped
used in VCU alcohol studies
all body cells are known (959)
led to understanding of programmed cell death
discoveries made involving fetal alcohol syndrome: showed alc at any does is unsafe; neurons don’t always die but they do misbehave
Danio rerio
zebra fish
transparent for 1st 2 weeks of life
excellent for developmental studies

Mus musculus
mouse
helped us learn about Kit gene mutations (white stripe on forehead)
social networks are comparable to humans
many similarities to homosapiens while still being a lower mammal

Homo sapiens
last step model organism for drug trial FDA clearance
we are a model organism
primary cell culture
isolated directly from live organism
limited lifespan
hayflick limit: the number of times a normal somatic, differentiated human cell population will divide before cell division stops
normally functioning cells
immortalized cell line
“transformed” cells
can grow indefinitely like cancer
unlimited uses: study cell behavior, response to drugs, and environment, industrial products
covalent bonds
molecular marriage
strongest bond
electrons are shared
determine shape of mlcls
ionic bonds
valence electrons do bonding
e- are giver or taken
non-covalent → molecular dating
close to the weakest bond
cation: (+)
anion: (-)
hydrogen bonding
i.e. water
weak bond
non-covalent → covalent dating
atom
smallest particle of an element that retain distinctive chemical properties
atom parts
nucleus: dense positively charged; contains protons + neutrons
electrons
atomic / molecular weight
number of protons + neutrons
_____ determine how atoms interact
electrons
electrostatic attraction
attractive force occurring between oppositely charged atoms
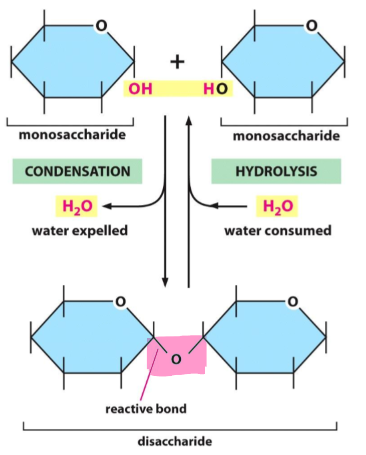
polymerization
joining monomers into a polymer

polysaccharides
monomer: monosaccharides
joined by the covalent glycosidic bond
100s - 1000s of monomers
i.e. glycogen
glycosidic bond
created by the condensation reaction (mlcl of water is expelled as bond forms)
broken by hydrolysis (mlcl of water is consumed)
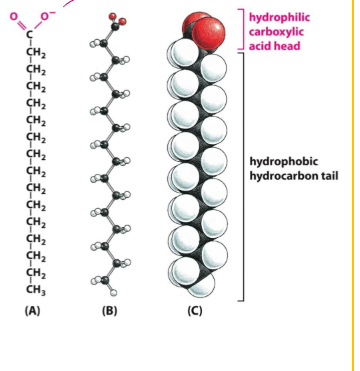
lipids
monomer: fatty acids
parts
carboxyl group
chemically reactive
behaves as an acid
hydrophilic head
long hydrocarbon chain
not chemically reactive
hydrophobic tails
lipids: saturated
no DB
only single bonds
makes mlcl flexible
means solid @ room temp
pack together in solid mass
think clogged artery
bad for health
found in meats, dairies, and coconut oil

lipids: unsaturated
contain at least one DB
means very rigid structure
rigid structure causes kinks
means liquid @ room temperature (DB / kinks prevent tight packing)
types
monounsaturated (1 DB)
polyunsaturated (multiple DBs)
proteins
monomer: amino acids
parts
carboxylic acid group → C terminus
amino group → N terminus
side chain → R group
hydrogen
a-carbon: links tg all parts
peptide bond
covalent linkage bn adjacent AAs in protein chain
formed through condensation reaction (water mlcl expelled)
nucleotides
monomer: nucleic acids
connected by phosphodiester bond
5’ → 3’
RNA
ribonucleic acid
bases: A + U, G + C
usually (but not always) single stranded
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
bases: A + T, G + C
only 1 hydroxyl group (think deoxy so 1 oxy is gone)
double stranded
how are macromlcls linked?
covalent bonds
catabolism
breaking down mlcls
big → small
useful form of energy
small mlcls needed as building blocks
anabolism
building up mlcls
small → big
uses energy generated by catabolism for the synthesis of mlcls that form the cell
2nd law of thermodynamics
the degree of disorder (entropy) can only increase in the universe
1st law of thermodynamics
energy can be converted to other forms but CANNOT be created nor destroyed
photosynthesis
converts electromagnetic energy (sunlight) into chemical bond energy in cells
light + CO2 + H2O → sugar + O2 + heat energy
coupled rxns
when two reactions work in tandem
when u use the energy from a favorable rxn to carry out an unfavorable rxn
require an energy carrier
phosphoanhydride bonds
bonds in ATP / ADP
high energy
tough
covalent
stepwise breakdown to create energy
step 1: glycolysis
step 1.5: pyruvate oxidized to acetyl coa
step 2: citric acid cycle
step 3: oxidative phosphorylation
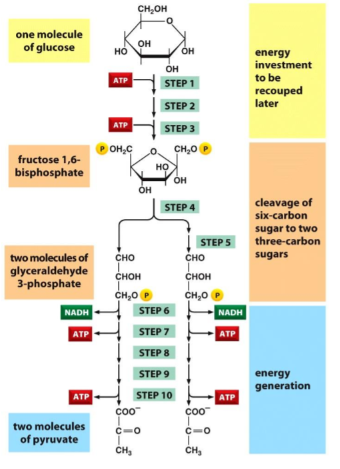
glycolysis
glucose → 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
2 ATP generated
O2 not needed but can be used
happens in cytoplasm
when, where, and how is pyruvate oxidized to acetyl coa?
when: after glycolysis (step 1.5)
where: mitochondrial matrix
how: via pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (large multi-enzyme complex)
what, other than pyruvate, can be converted to acetyl coa?
lipids
benefits of converting lipids to acetyl coa (as opposed to pyruvate with sugars)
generate 6x as much energy as sugars per weight → so generate a lot of acetyl coa
calorie dense
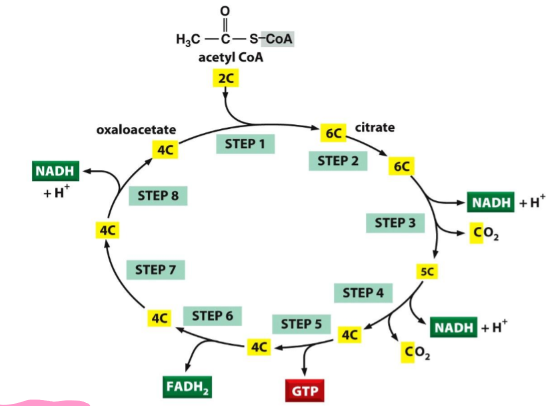
citric acid cycle
acetyl coa → 1 GTP, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2, 3 NADH
1 GTP generated
does NOT req O2
happens in mitochondrial matrix
oxidative phosphorylation
O2 → H2O
30 ATP generated
O2 needed !
occurs in the inner mitochondrial matrix membrane
gluconeogenesis
reverse rxn of glycolysis
steps 1, 3, 10 are irreversible
takes a LOT of energy → makes you feel horrible
what type of cells would gluconeogenesis highly benefit?
brain cells → depend almost completely on glucose
glycogen
multi-branched polysaccharide comprised of glucose
acts as the primary, rapid-access energy reserve in animals
balance of glycogen is regulated by hormones: insulin, glucagon, and adrenaline
glycogen phosphorylase
enzyme that breaks glycogen
condition used in: when no energy / food / sugar in system → want to break glycogen to release glucose into our systems
glycogen synthase
enzyme that makes glycogen
condition used in: when we have a lot of sugar in system → want to store excess energy
how is fat stored?
as droplets of water-insoluble triacylglycerols in specialized adipose tissue
what happens to excess sugar that’s intaken?
converted into fatty acids + stored
animals : glycogen → plants : _____
starch
how do plant cells store energy?
starch: branched polymer of glucose (like glycogen)
fat: like animals but unsaturated fatty acids predominate
how do mitochondria divide?
fission
what is it call when mitochondria join together?
fusion
what are mitochondria comparable to and why?
bacteria
divide like bacteria → fission
no nucleus nor organelles
have circular copies of DNA
where in the cell might you find mitochondria?
where energy is needed
i.e. cardiac tissue, neurons, sperm tails