renal physiology lecture: renal sodium and potassium regulation: lecture 4
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
ways to study for renal physiology
ways to study for renal physiology

c. secretion
because we are adding it to the fluid to become urine
movement of a solute from the interstitial fluid across the basolateral plasma membrane of the cell, through the cytoplasm, and across the luminal (apical) plasma membrane of the cell is an example of which renal process?
a. filtration
b. reabsorption
c. secretion
d. excretion
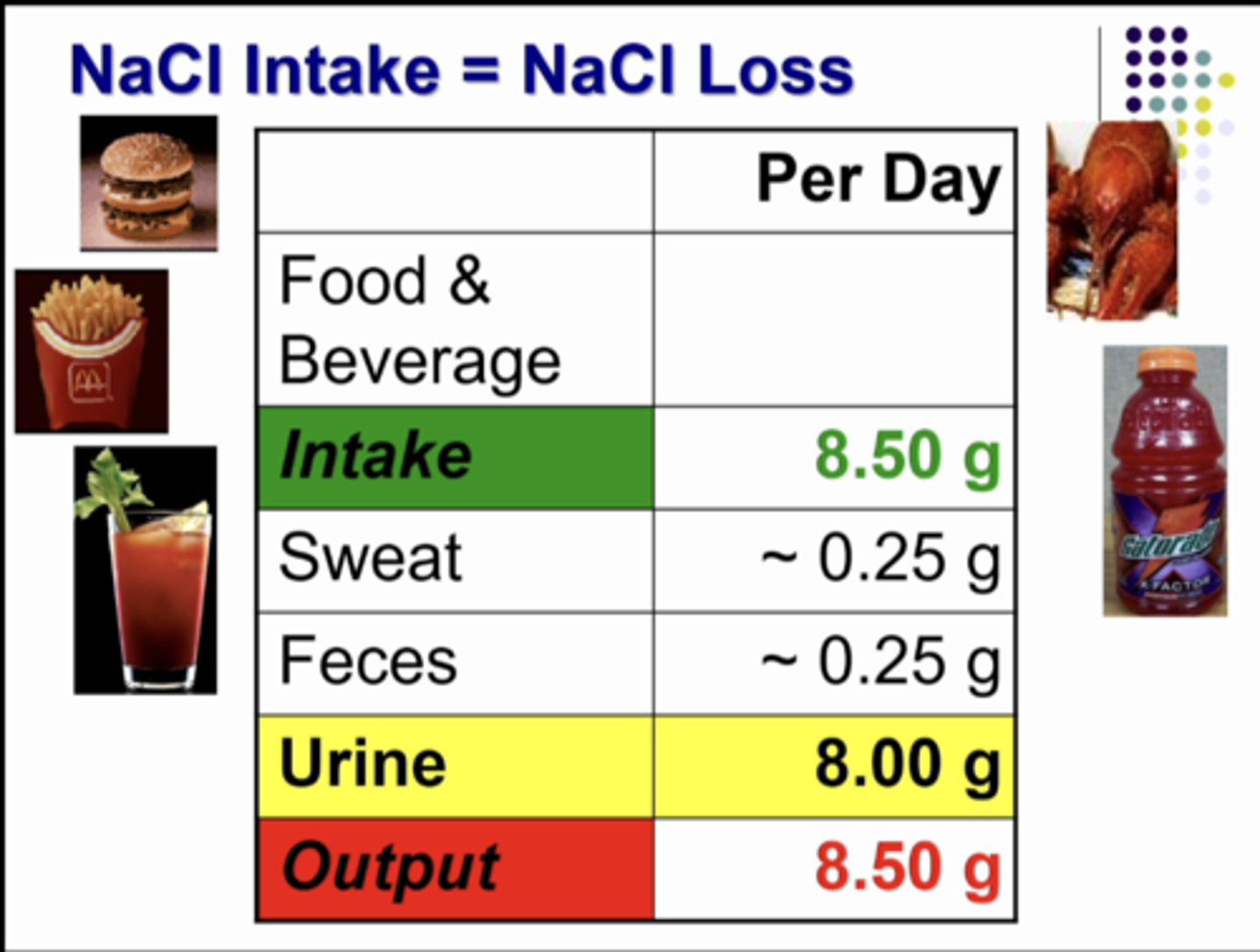
the amount of salt we take into our bodies each day by the food and beverages that we consume (8.50 g). so if the body consumes 8.50g then the body needs to excrete 8.50g as well. the kidneys match exactly what is left over after sweat and feces have excretes some of the fluid.
what is this table showing
kidneys
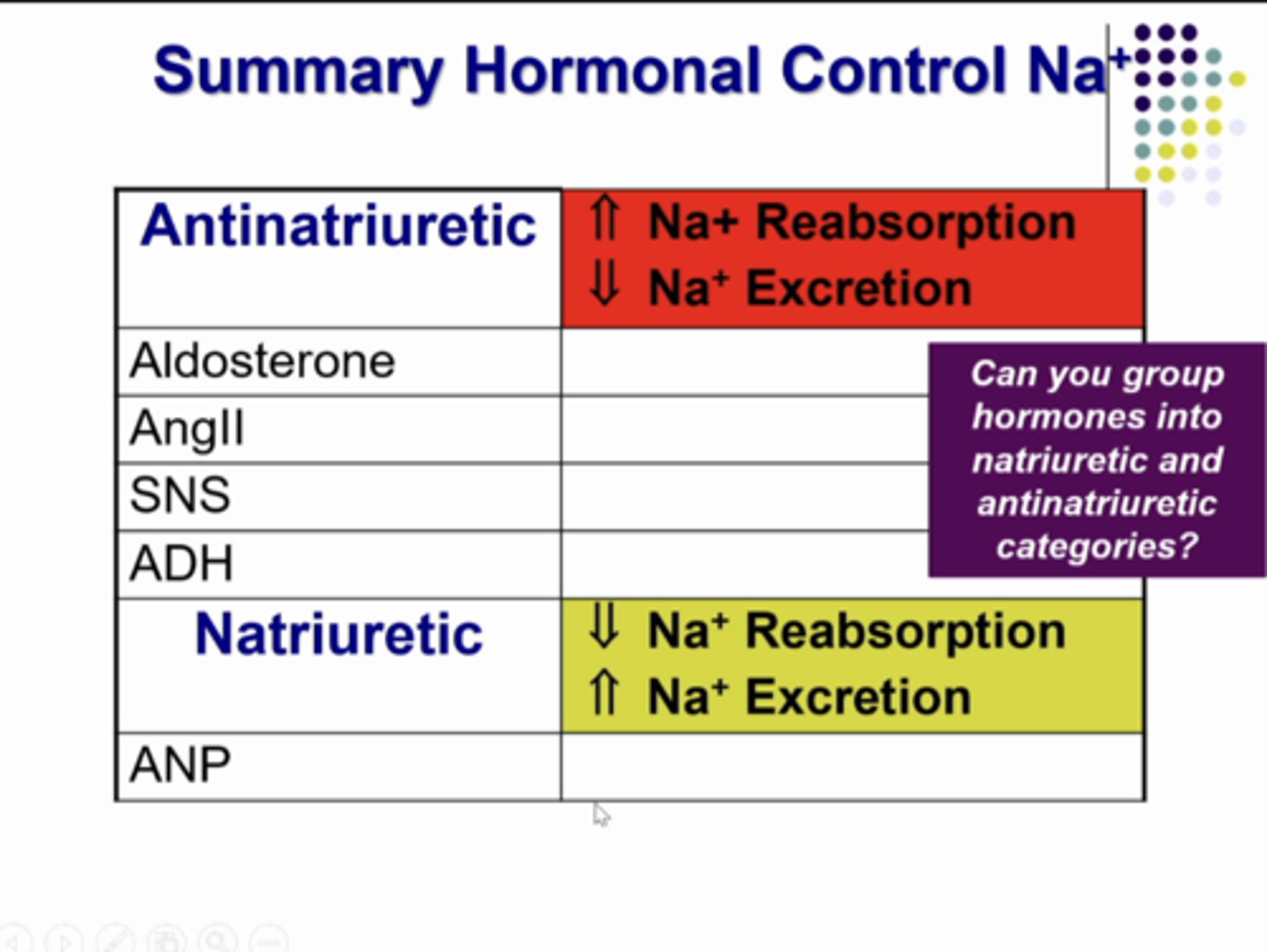
maintain extracellular fluid volume by regulating amount of Na+ in urine
Na+
freely filtered and reabsorbed.... IT IS NOT SECRETED
osmolality
Na+ is most important to ECF _____________
change the amount of fluid being filtered or the amount of Na+ being reabsorbed
the only way the kidneys can change the amount of sodium in the urine is to....
natriuresis
rate of urinary Na+ excretion by kidneys above usual levels
anti
opposed to; against
Antinatriuresis
low rate of Na+ excretion
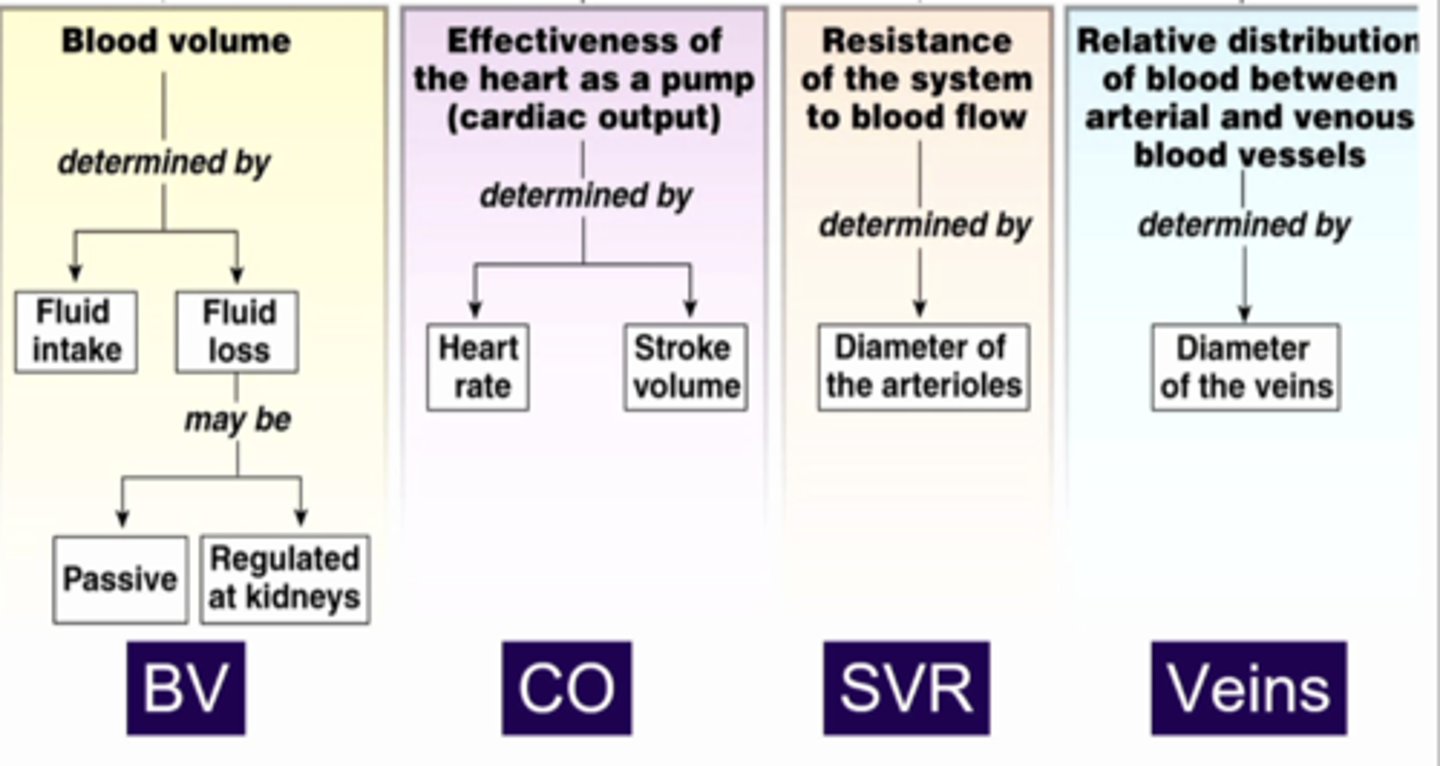
cardiac output, systemic vascular resistance, veins, blood volume
the kidneys are important in regulating MABP, what are the 4 components of determine that MABP
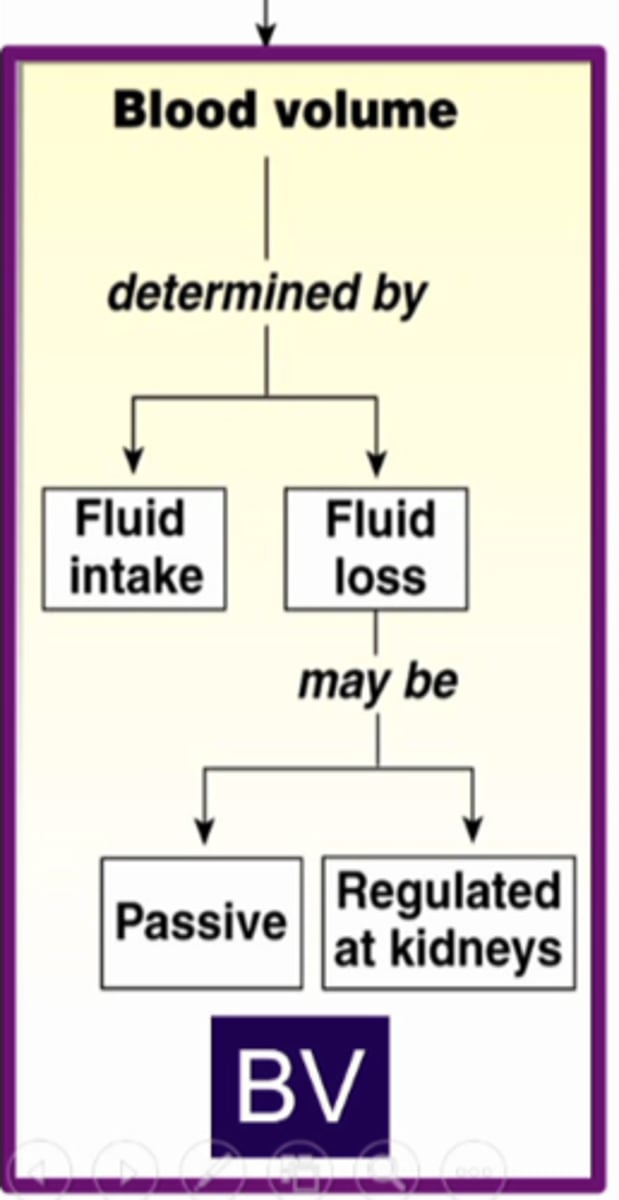
kidneys playing a big part in determining blood volume because the BV is determined by the fluid intake and loss from the body. the fluid loss can be passive since it is in the moisture that we expire as well as the moisture that evaporates from our body. the remainder of fluid that is lost is regulated by the kidneys.
what is this image showing
blood volume
long term control BP:
due to regulation of ....
blood volume
long term control BP:
major determinant of MABP
CV
-renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
-sodium and water retention, thirst drive
long term control BP:
controlled by ____ and kidney by regulation of blood volume
integration
long term control BP:
complex _____________ of multiple organ systems all working together to maintain homeostasis
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, arginine vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone), sympathetic nerves
*anti natriuretic because they produce reduced sodium excretion by kidneys
-increased salt and water reabsorption to increase ECFV
-decreased salt and water excretion to increase ECFV
-systemic and renal arteriole constriction to increase MABP
atrial natriuretic peptide
-decrease salt and water reabsorption to decrease ECFV
-increase salt and water excretion to decrease ECFV
-systemic and renal arteriole dilation to decrease MABP
the major sodium transport proteins:
primary active transport: Na K ATPase on basolateral membrane
ion channels: sodium channel in collecting duct
secondary active transport: Na amino acid co transporter and na h counter transporter in the luminal membrane of proximal tubule
what does this image show
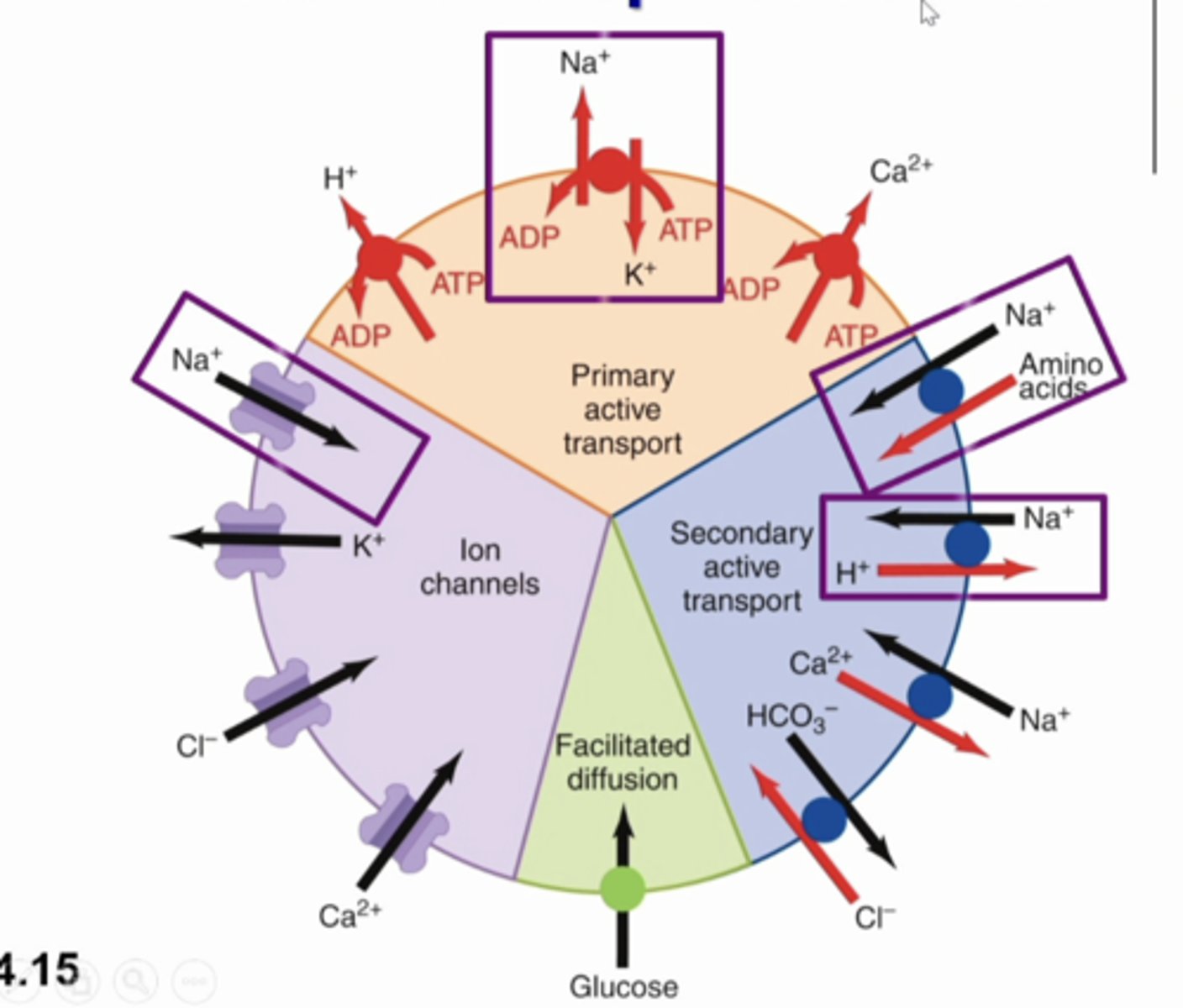
Na+
major extracellular solute, with associated anions, about 90% solute in ECF
△ECFV
Na+ is the major extracellular solute, with associated anions, about 90% solute in ECF, THEREFORE, △Na+ results in ......
kidney Na+ handling
mechanisms regulate ______________ _____ ___________ related to changes in ECFV
changes in plasma volume means changes in BP
ECF compartment includes plasma volume... so ...
there is low plasma volume meaning low BP which decreases baroreceptors, increases reflexes to decreased GFR and increased Na+ reabsorption
**negative feedback mechanisms
**physiological reflex
if there is low plasma Na+ what happens
higher blood pressure, excrete more fluid and water
if you have extra fluid in the vessels what happens to BP and how can the kidneys fix it?
Na+
most abundant cation in filtrate
active
Na+ reabsorption is almost always _________ transport
NEVER
Na+ is __________ secreted by nephron
Na+/K+ ATPase pump
active pumping of Na+ via....
Na+/K+ ATPase pump
-generates electrochemical gradient
-couples to passive entrance of other substances (glucose, amino acids) via co-transporters
---secondary active transport ^^

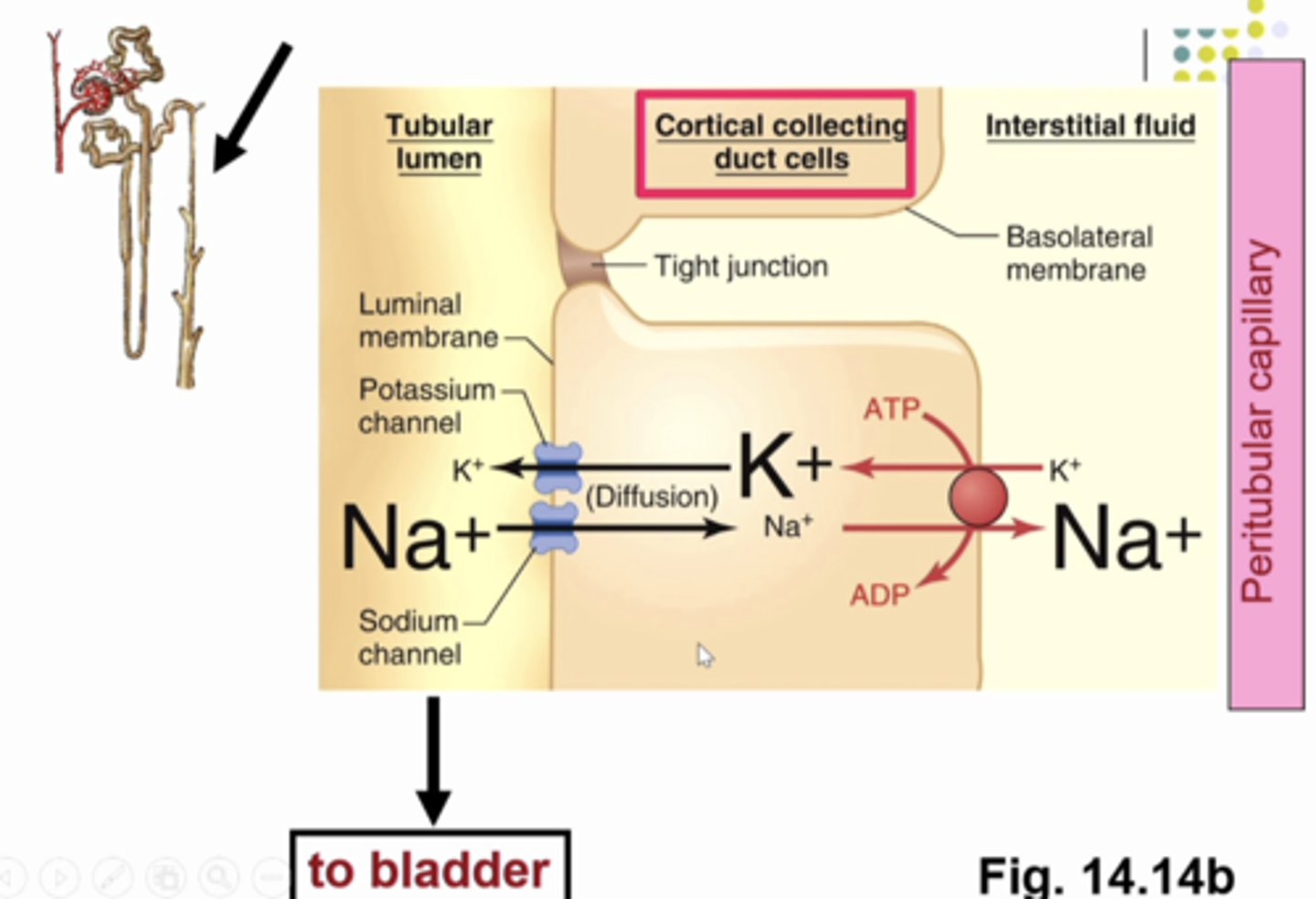
the process of sodium reabsorption in the cortical collecting duct cells. apical transports for na and k are different ion channels (these channels are in the luminal membrane). they only allow na or k to pass through. very selective. so the na/k atpase is driving na and k against gradient so ARP is needed. notice small font size... na lower concentration inside the cell and higher in the tubular fluid/interstitial fluid/capillary plasma therefore the na that is filtered from the glom cap into bowman's space that is traveling in the tubular fluid on its way to become urine can undergo tubular reabsorption in the collecting duct by passively passing through the sodium channel down its gradient to then be pumped into interstitial fluid and then it will be picked up in the peritubular capillaries so we are reabsorbing and keeping sodium in the body and water will follow.
what is this image showing
we are now in the proximal tubule. we have transporters for na and other substances. by co transport in the same direction moving into the cell. ..we have a na/h counter transporter for na to move into the cell for na reabsorption while h moves out of the cell for h secretion
what is this image showing
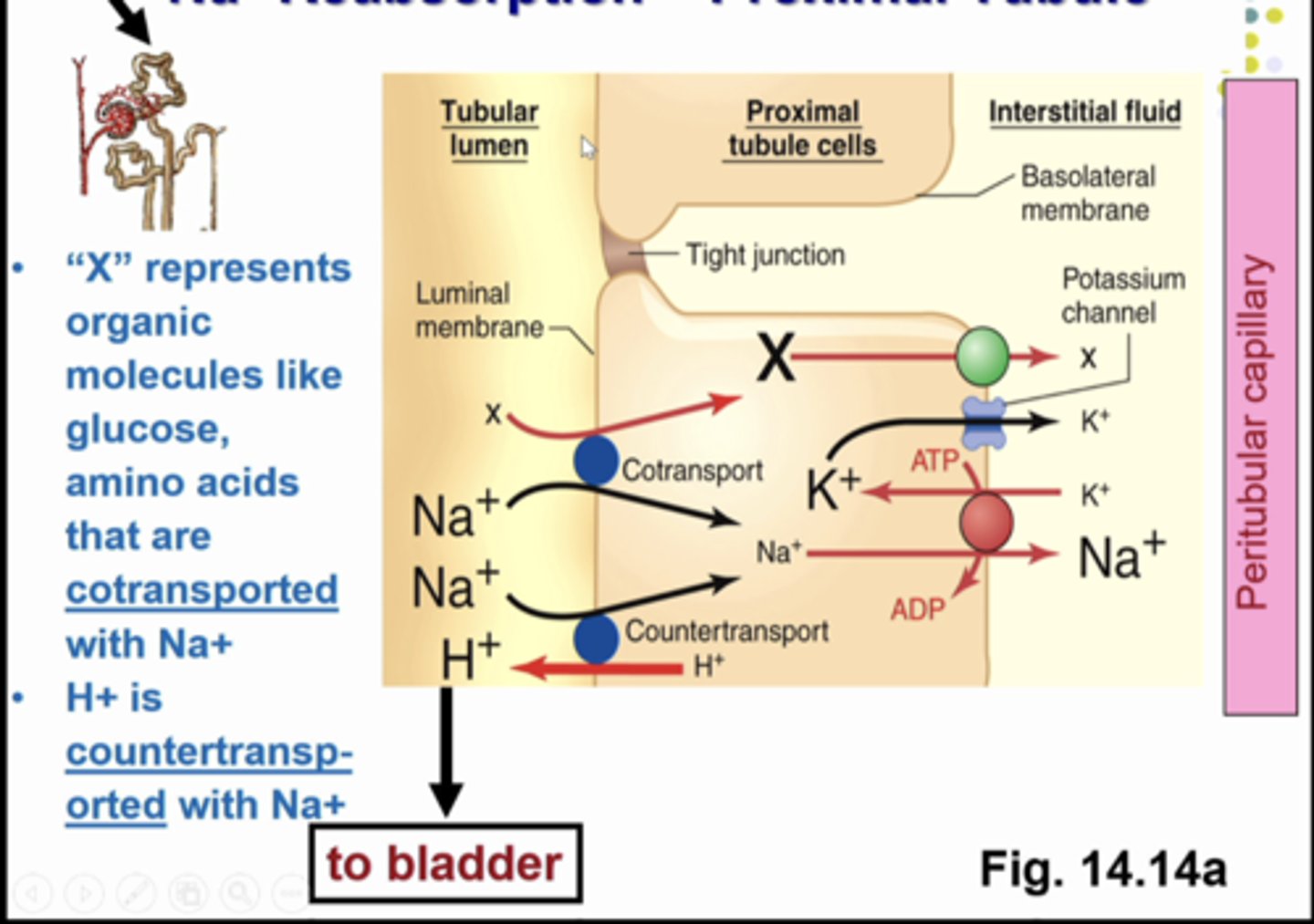
Na+ reabsorption
active process occurring in all tubular segments except descending limp of loop of henle (because .... there are no transport proteins in the loop of henle and you need those to move Na+)
water reabsorption
by diffusion, dependent upon Na+ absorption
aquaporin
water moves through ___________ channels
-presence of ___________ channels varies throughout tubule segments
-highly expressed in proximal tubule
-absent in collecting ducts unless antidiuretic hormone, ADH present

aquaporin 1
in proximal tubule
aquaporin 2, 3, 4
in collecting duct
2 full containers of mortons salt
-1500g/d
the amount of salt filtered into bowmans space is equivalent to ...

2 little tubes
-140g
the total amount of salt that is in the extracellular fluid compartment is equivalent to ...

two tiny tubes
-6 g/d
the amount of salt that is excreted in the urine is ...

renin-angiotensin system
renin-angiotensin system
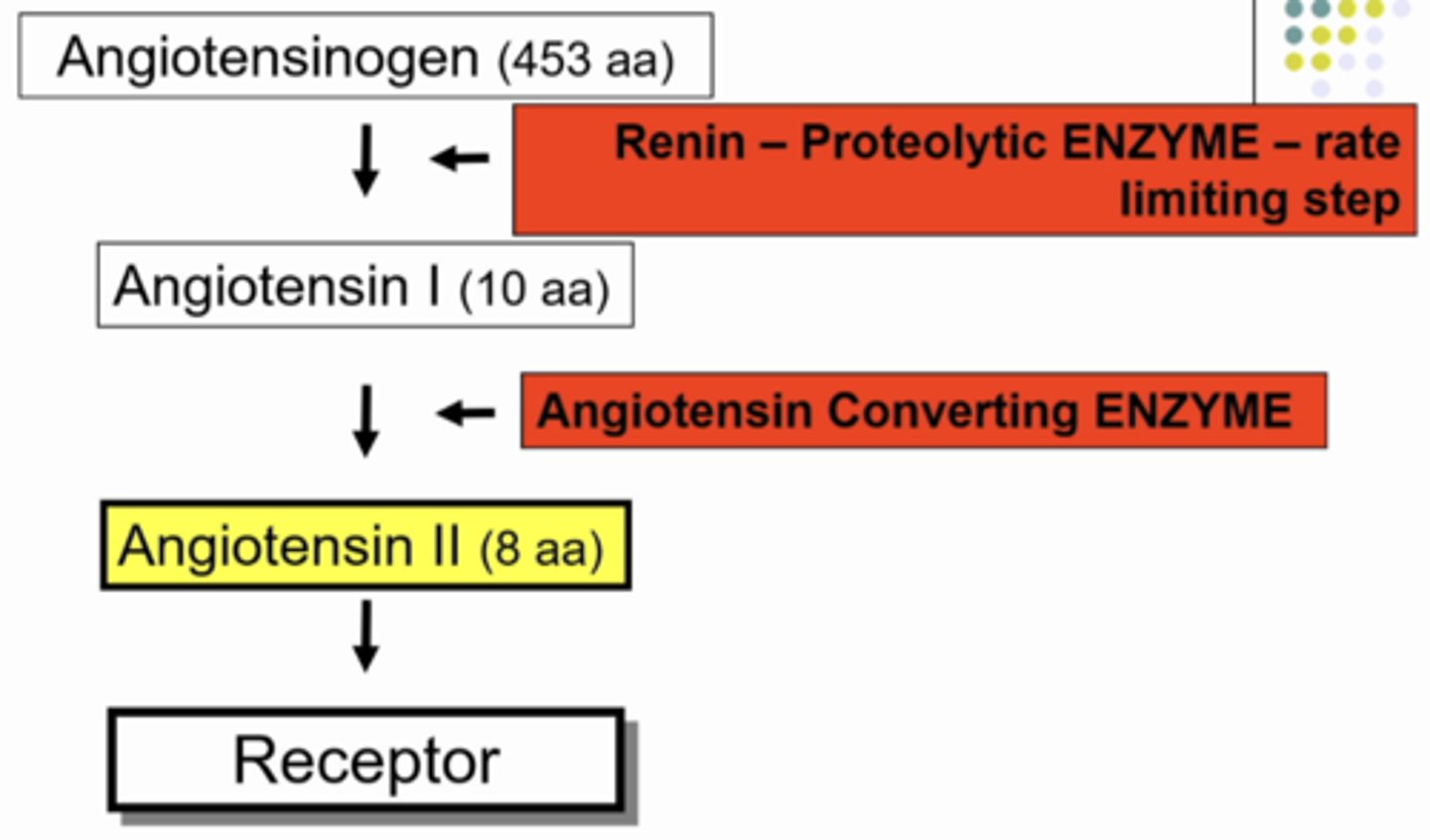
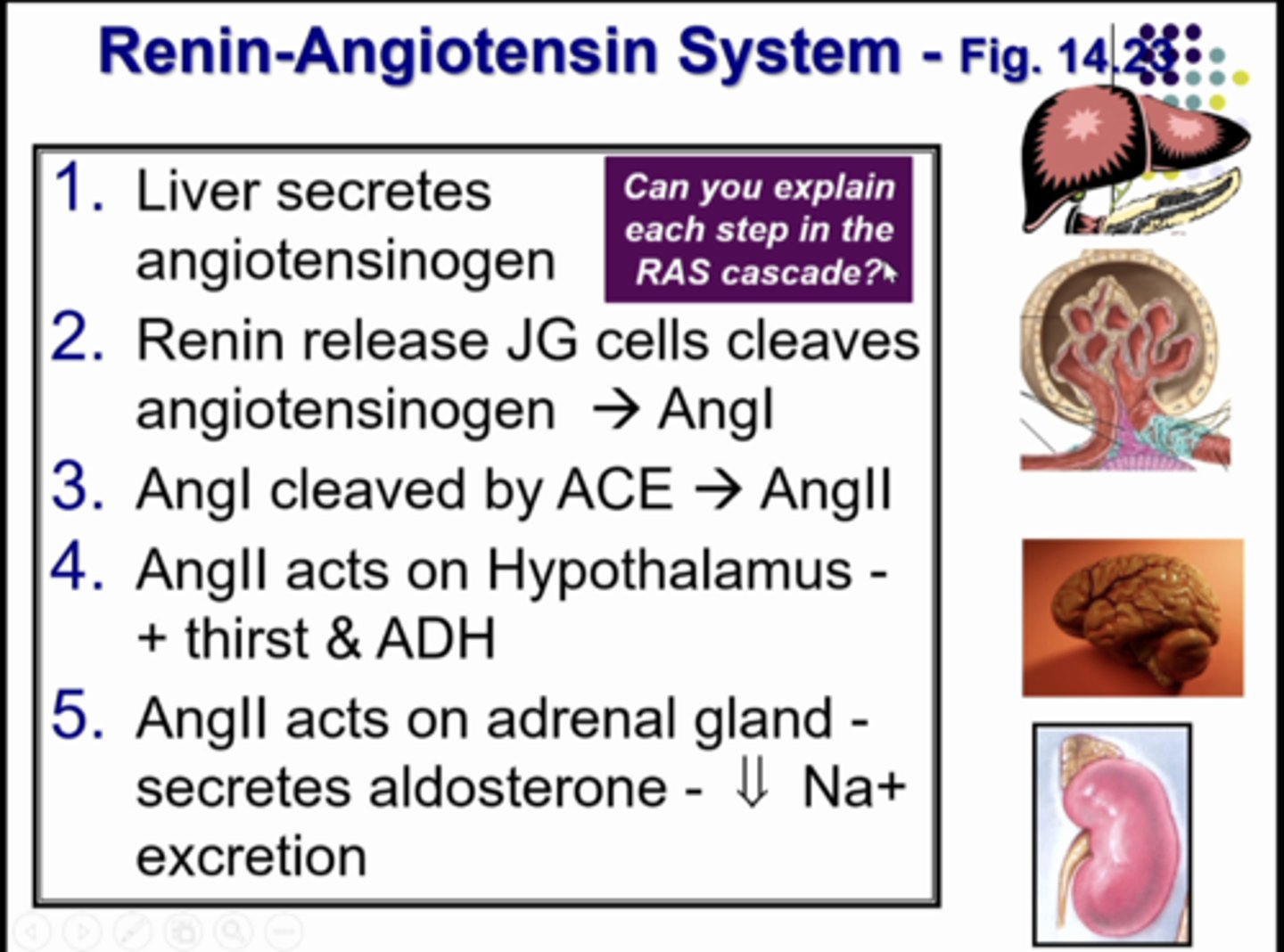
starting point: protein angiotensinogen (453 aa) that does nothing, it is just floating around.... UNTIL it comes into contact with RENIN - PROTEOLYTIC ENZYME (rate limiting step). so when angiotensinogen comes into contact with renin, renin cuts a small piece of a peptide off of angiotensinogen (10 amino acids), and the 443 aa protein keeps circulating in the body doing nothing. the 10 aa peptide that renin cut off of angiontensinogen is called angiotensin I and it does nothing.... UNTIL it comes into contact with another enzyme called ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME. when this contact happens it cuts off 2 aa from ANGIOTENSIN I so now it is just 8aa peptide called ANGIOTENSIN II. anddd angiontensin II DOES A LOT OF THINGS. but...... it NEEDS A RECEPTOR (a g coupled protein receptor) when it binds.. it can cause the secretion of aldosterone from adrenal cortex, VSMC to constrict, & Na reabsorption
explain the steps of the renin-angiotensin system
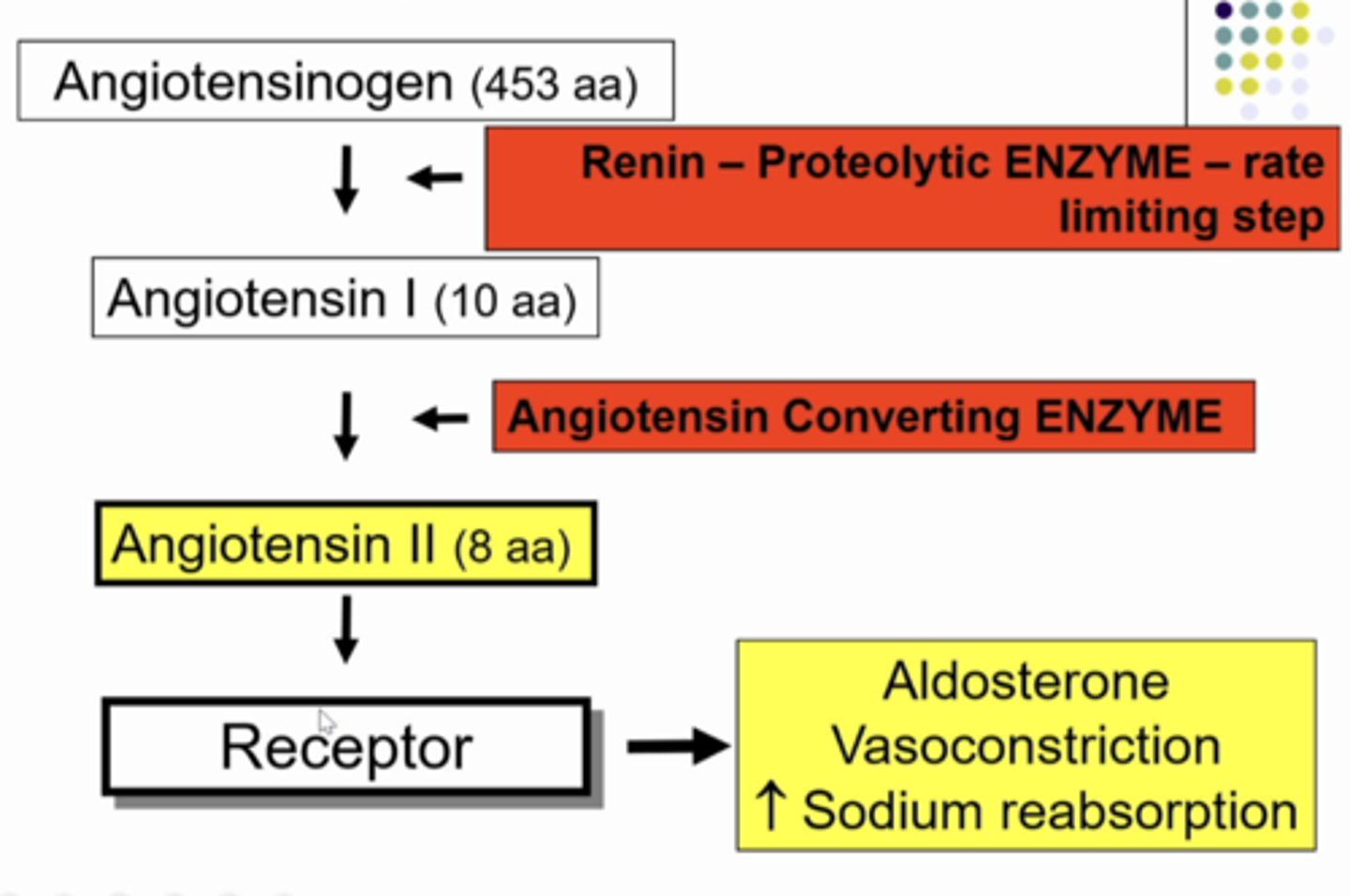
BP increases
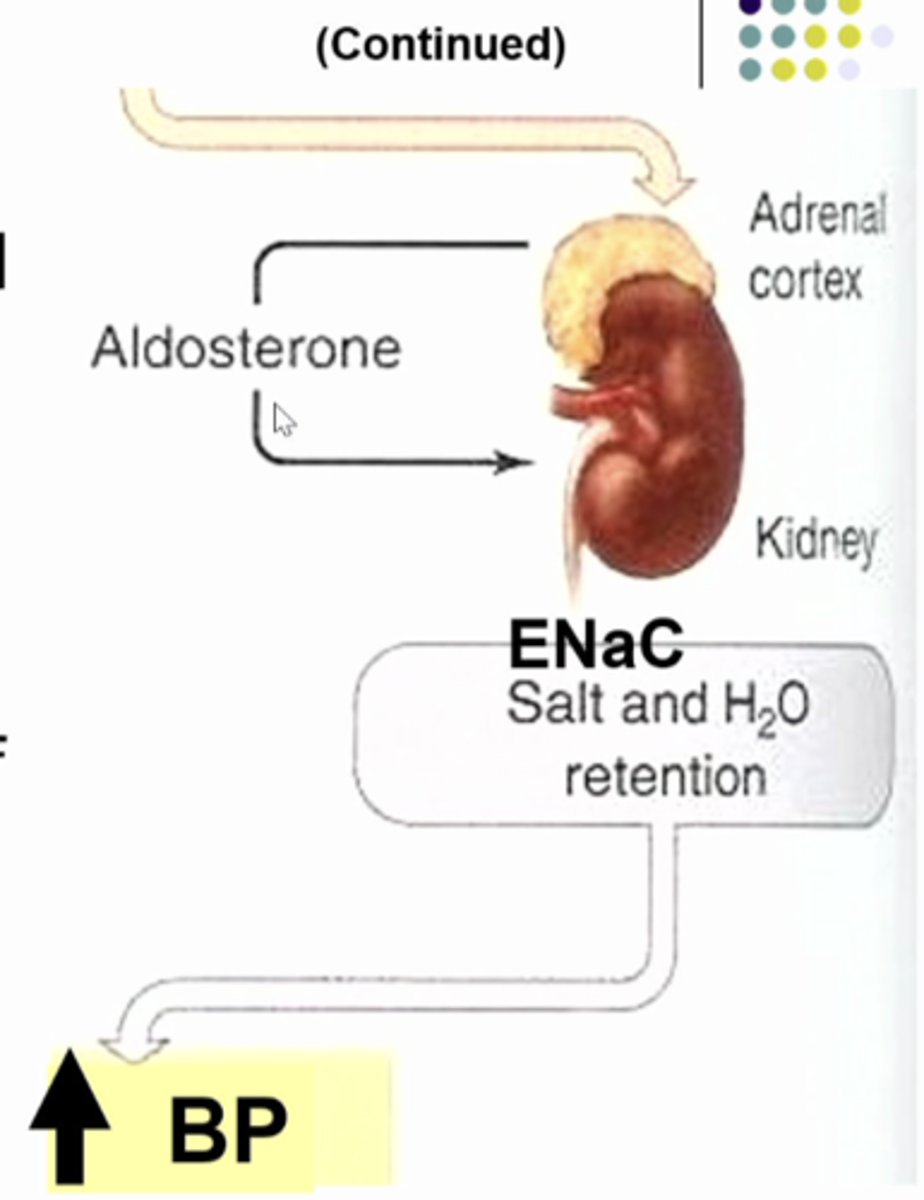
if you keep more sodium and water in the body....
aldosterone
-steroid homrone, produced by adrenal cortex
-increases Na+ reabsorption in DT (distal tubule), CD (collecting ducts)
-induces synthesis of K and Na (ENaC) channels, Na/K ATP pump in CD
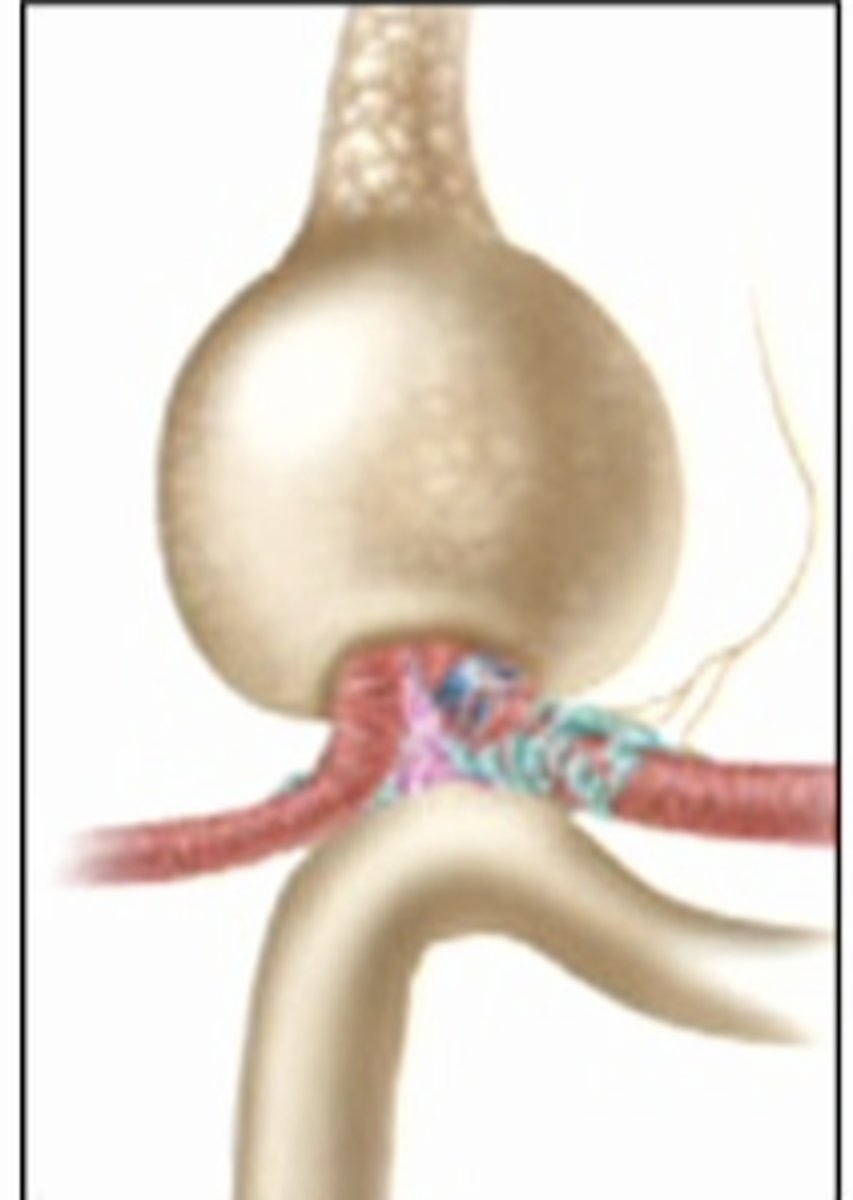
juxtaglomerular cells in the AA in blood vessels that secrete renin into the interstitial fluid. the juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of juxtaglomerular cells in the vasculature together with the epithelial cells in the distal tubule or macula densa cells
what is this image showing
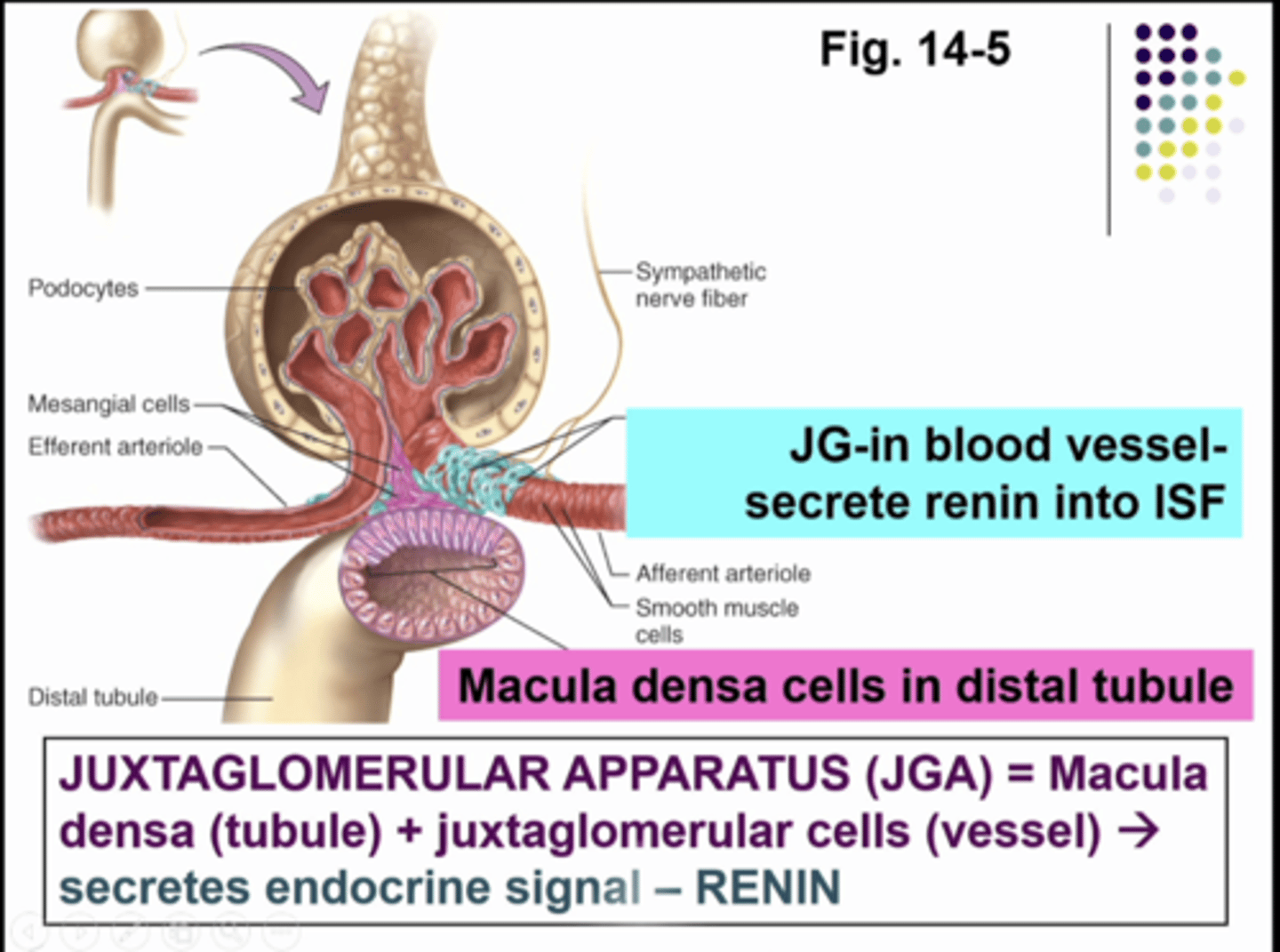
granular cells
juxtaglomerular or JG cells in vessels are part of vasculature
-mechanoreceptors
mechanoreceptors
stretch receptors sense stretch in afferent arteriole, innervated by SNS
-enlarged smooth muscle cells with secretory granules, contain hormone RENIN
-part of renin-angiotensin system, raises BP
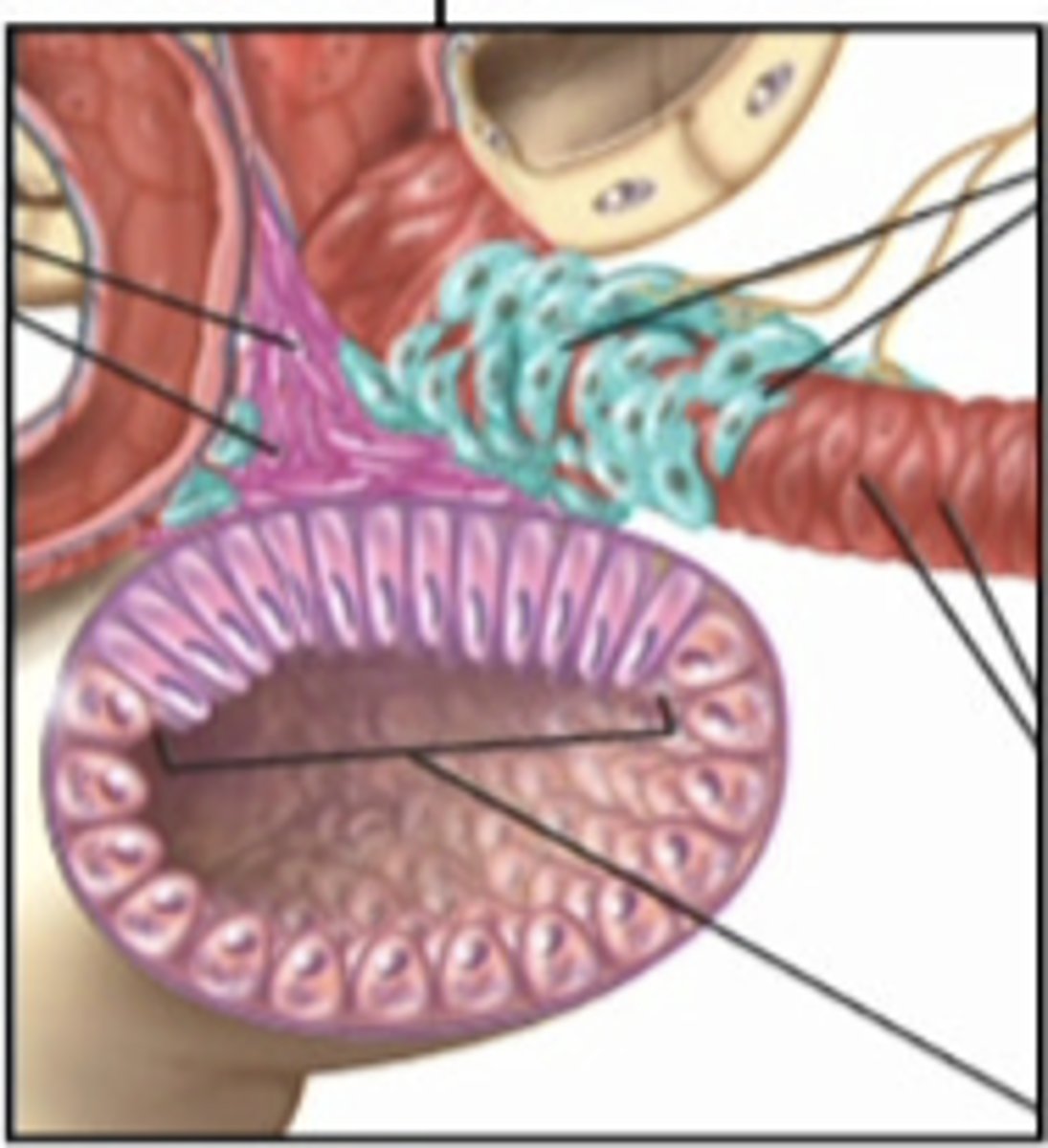
mucla densa cells
part of tubule
-chemoreceptors - respond to changes in NaCL (chemicals) content of filtrate
-group of tall, closely packed tubular epithelial cells adjacent to granular JG cells
-cells work in tandem and critical regulators of BP
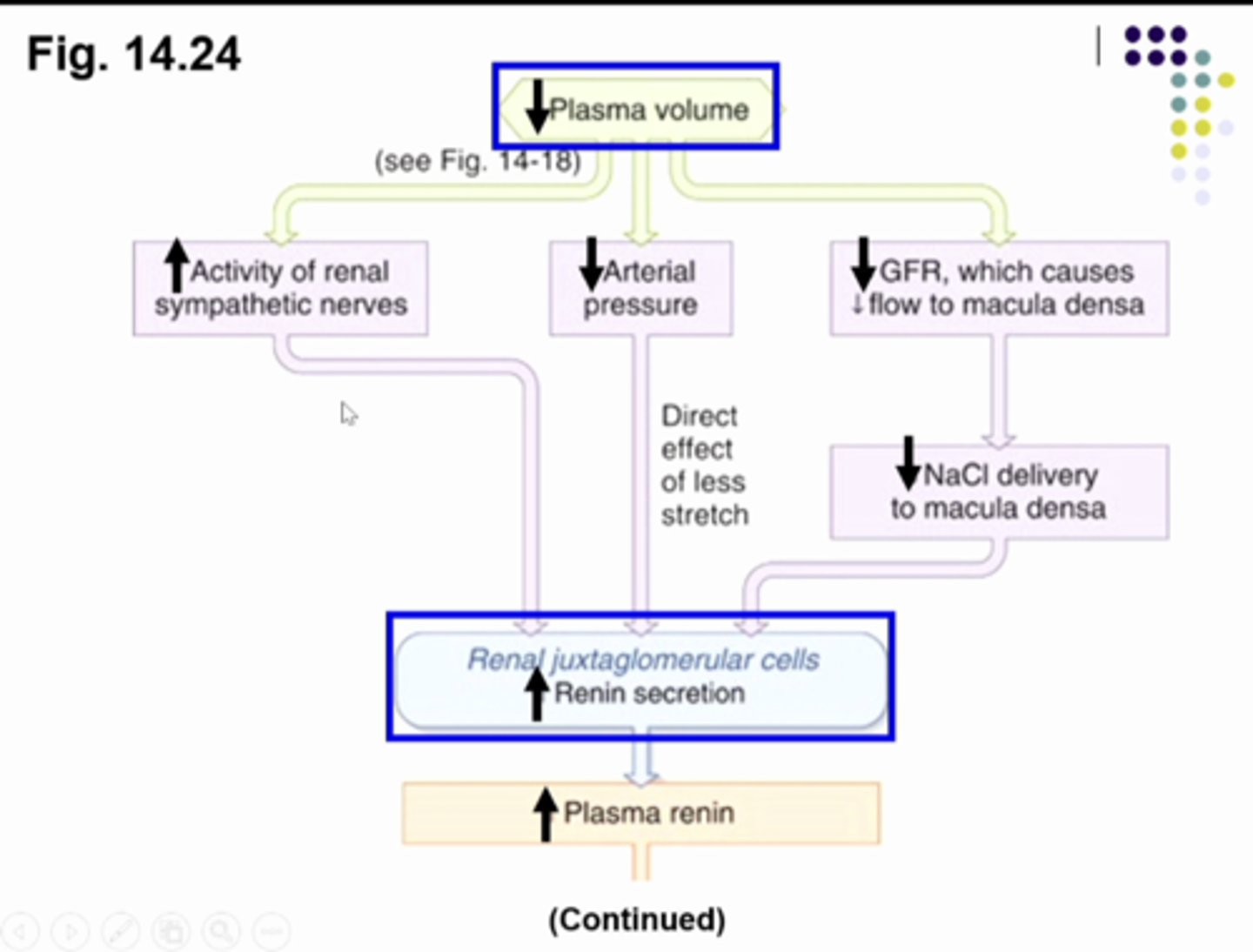
increase
pathways that _________ RENIN secretion --> ____________ ANGIOTENSIN II levels
1. increase SNS
2. decrease BP
3. decrease GFR
when plasma volume is decreased....
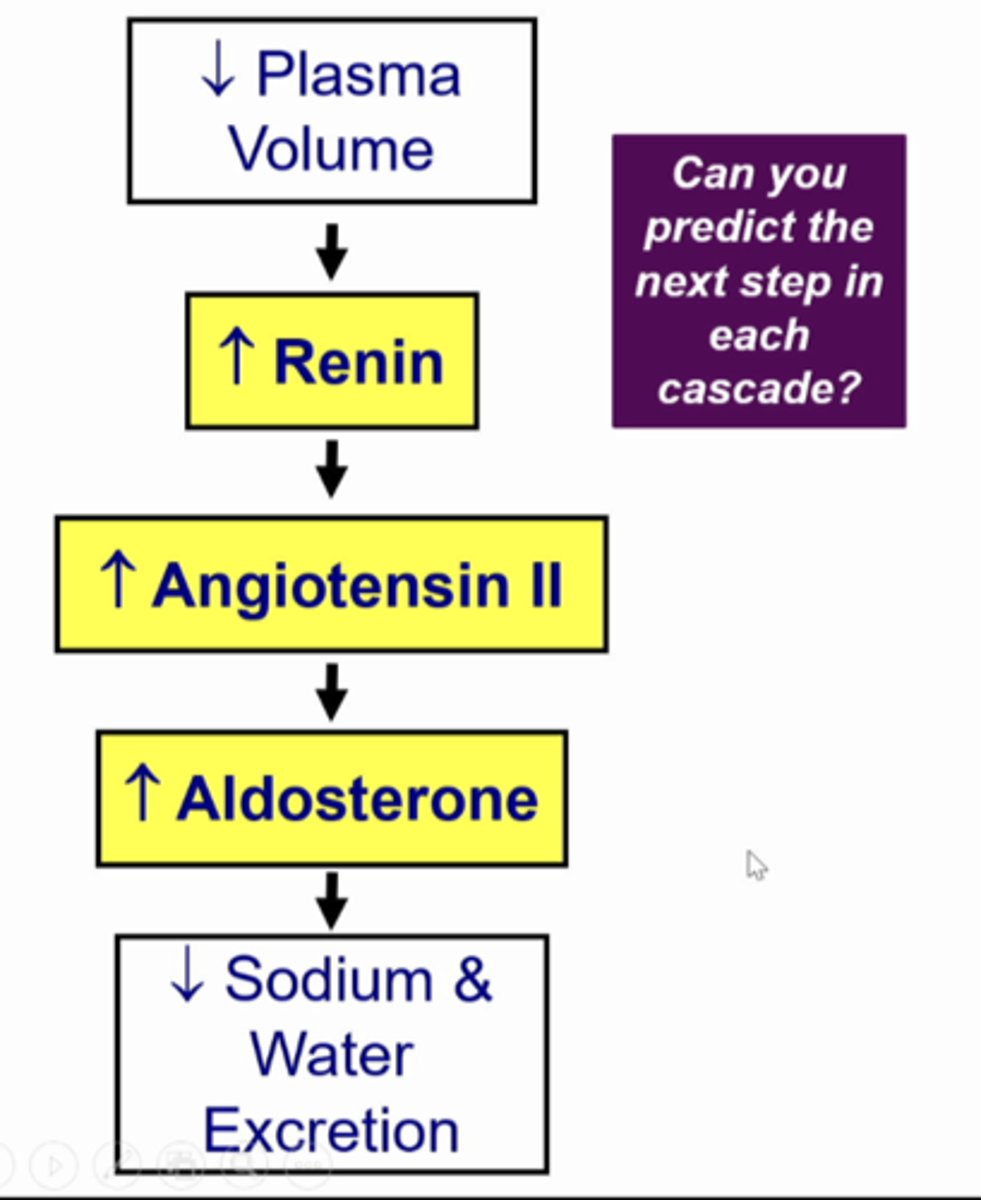
the initial stimulus is a decrease plasma volume, so the kidney will make a urine with less sodium and less water. we get this by increasing reabsorption of sodium. this will increase sympathetic nerves to the whole body including the kidney which is going to increase renin secretion from juxtaglomerular cells. the decrease plasma volume will cause the arterial blood pressure to decrease and the mechanoreceptors will increase renin secretion. when the plasma volume decrease... it decreases GFR and when you less fluid entering bowmans space you wil have less fluid passing the macula densa cells so they send a signal to juxtaglomerular cells to secrete renin
SO..... DECREASE PLASMA VOLUME = INCREASE RENIN... go to next card for continued explanation
what is this image showing... go to next card for continued explanation
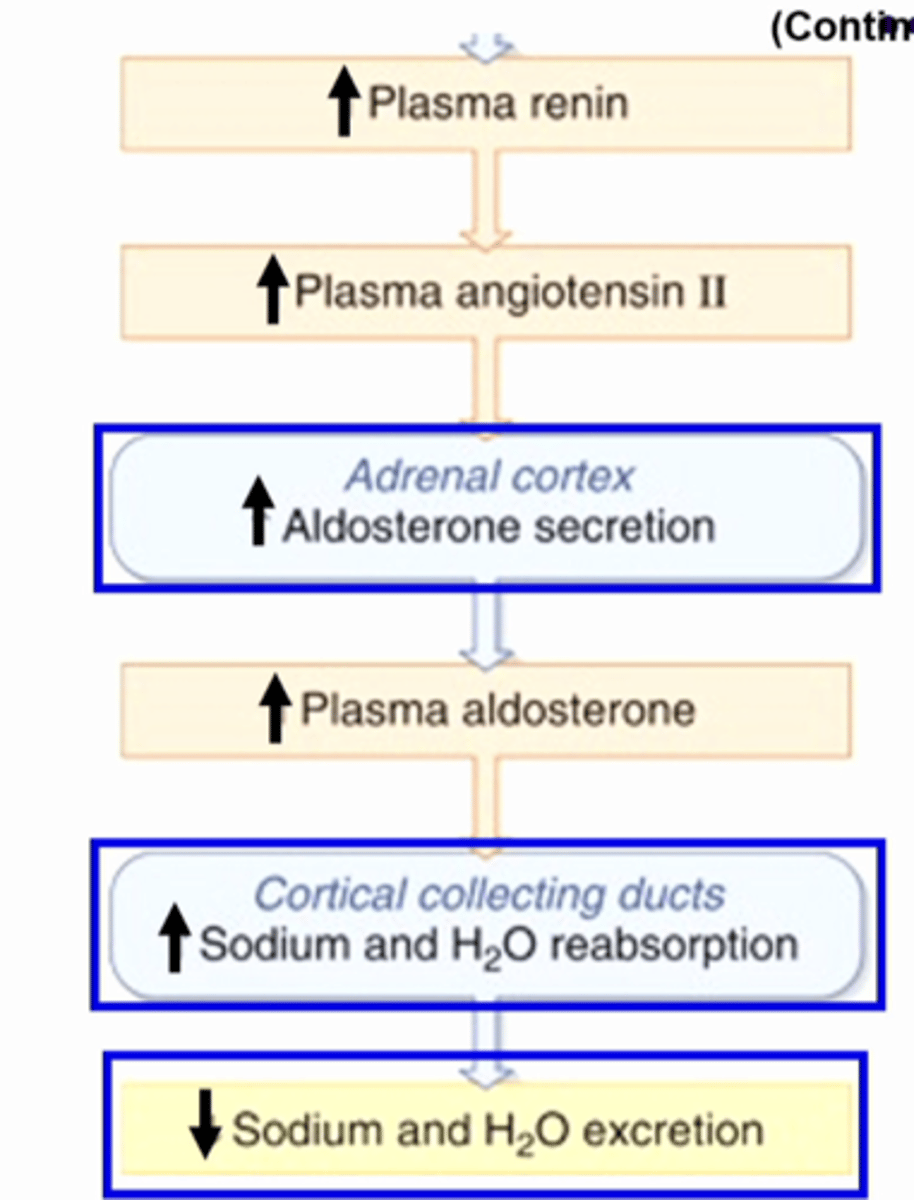
the increase plasma renin will contribute to an increased formation of angiotensin II, it will stimulate aldosterone secretion so circulating levels of aldosterone will increase. then the collecting duct cells that express the receptor for aldosterone will cause the cell to increase sodium reabsorption and water reabsorption and decrease sodium and water excretion soooo decrease sodium and water in the toilet....
SO:
1. decrease plasma volume
2. increase renin
3. increase angiotensin II
4. increase aldosterone
5. decrease sodium and water excretion
CONTINUED PLASMA VOLUME/RENIN CHAIN OF EVENTS EXPLANATION.....
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
-synthesized, secreted - cardiac atria
-stimulus:
1. increase atrial distention
2. increase plasma volume
-response:
1. increase GFR
2. decrease renal Na+ reabsorption
-so
1. increase Na+ and water excretion
OPPOSITE
the atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is __________ to the renin-angiotensin system
response to change in plasma volume
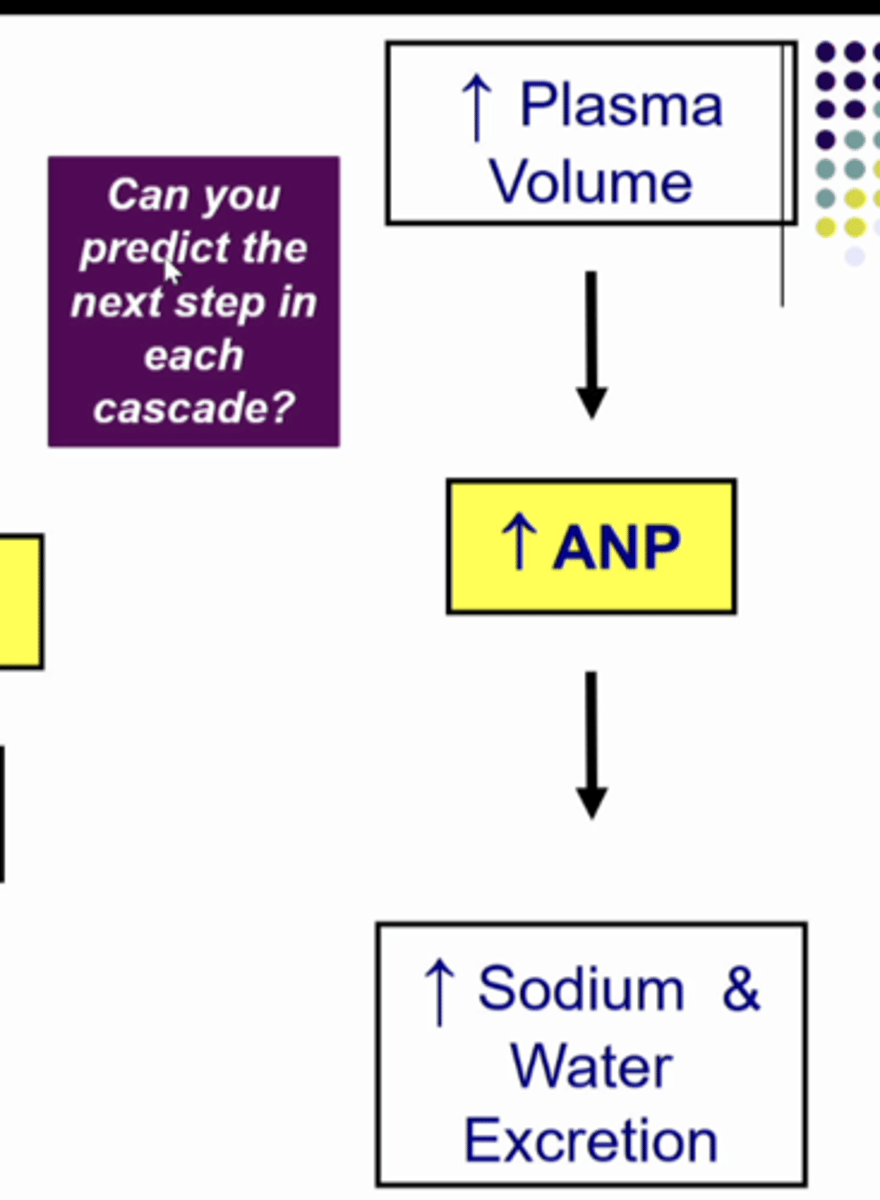
increase plasma volume ( too much salt and water), distend the atrial myocytes, increase atrial natriuretic peptide secretion and increase plasma ANP
SO:
1. increase plasma volume
2. increase atrial natriuretic peptide
what is this image showing... go to next card for continued explanation
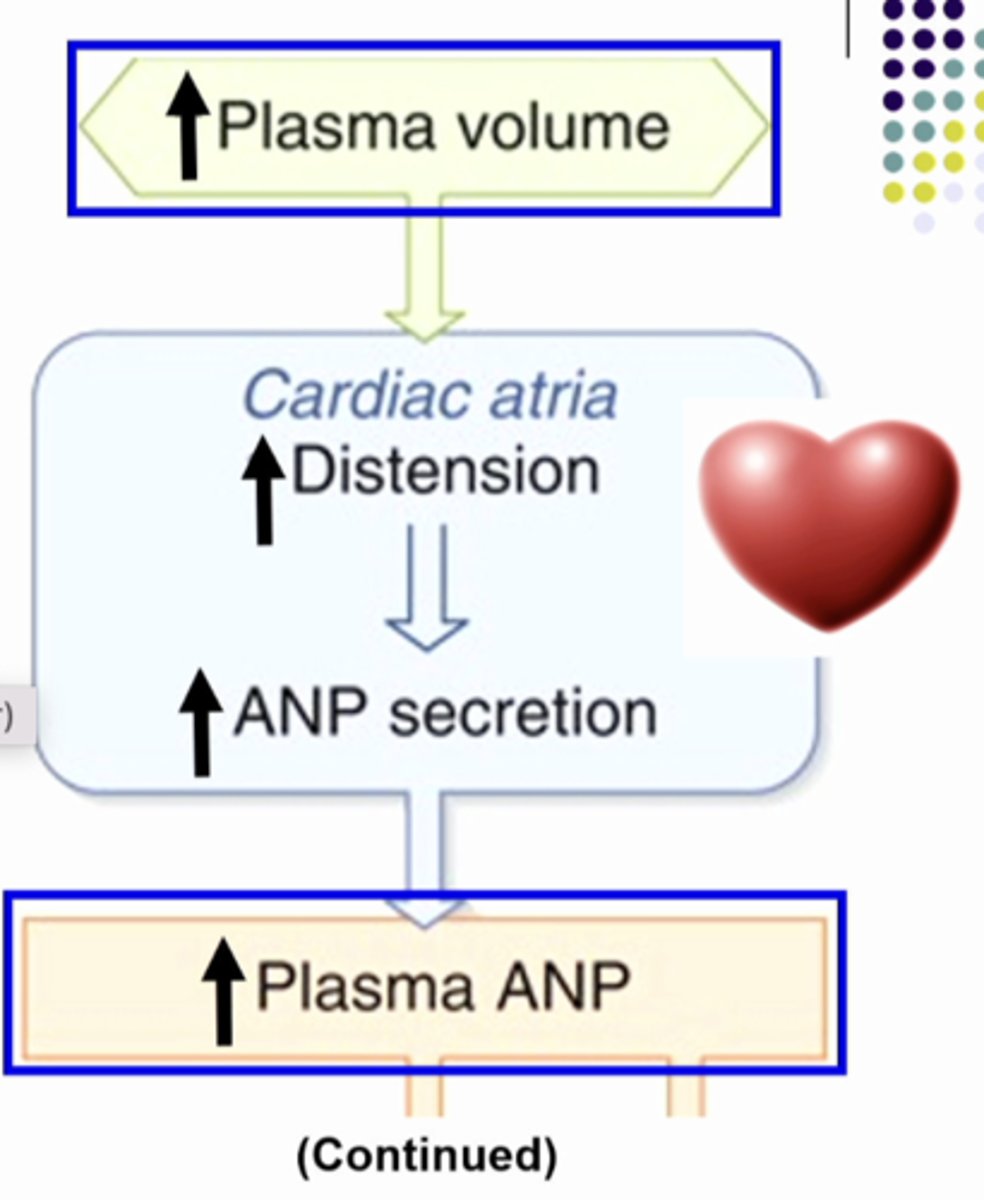
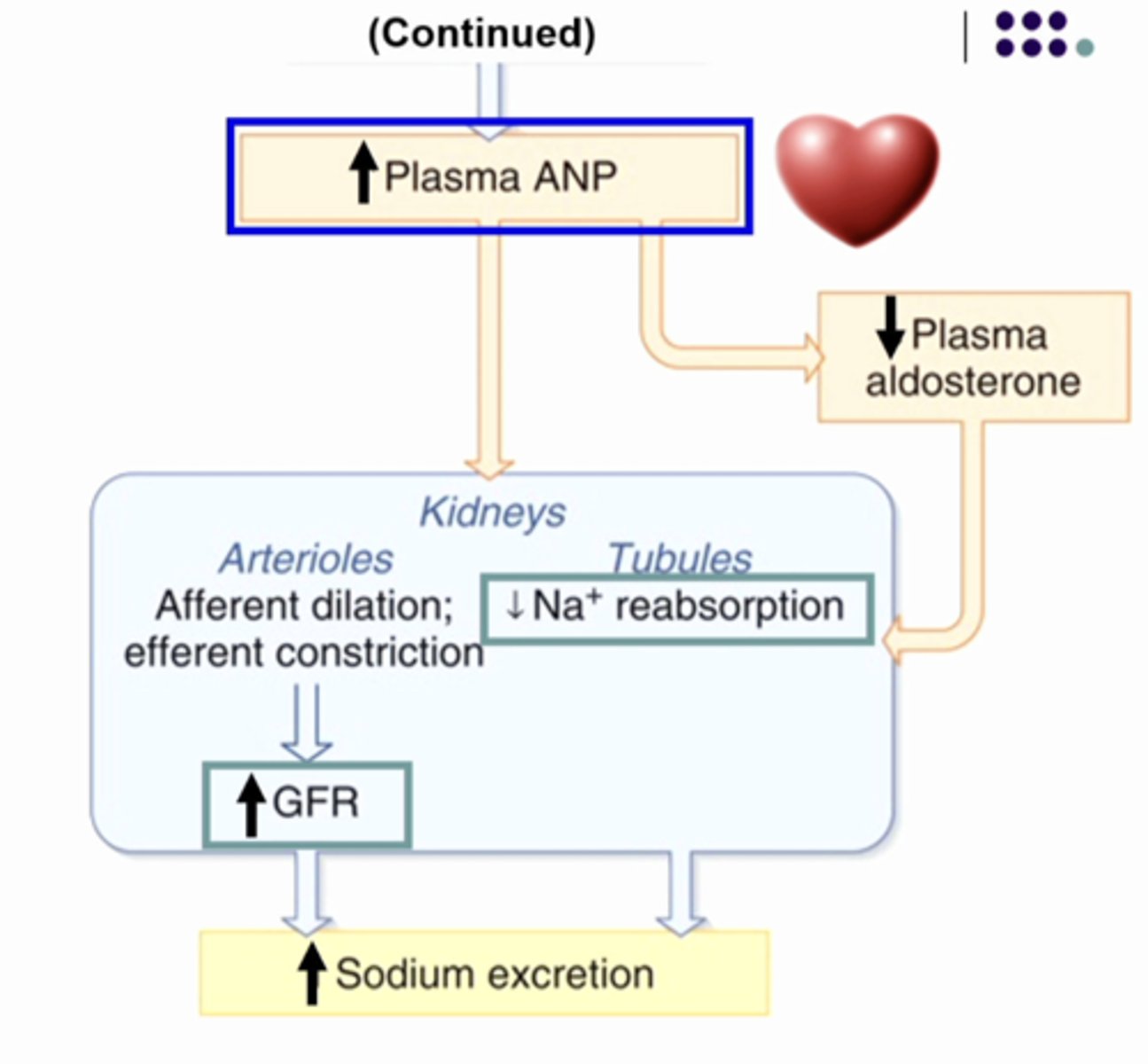
ANP inhibits aldosterone so it makes plasma aldosterone go lower than normal. so it will decrease sodium reabsorption. and ANP causes the GFR to increase so you have more salt and water entering the nephron so you have more salt and water entering the lumen and you are reabsorbing less so there is more in the toilet so sodium excretion increases
SO:
1. increase plasma volume
2. increase ANP
3. decrease aldosterone
4. increase sodium excretion
NEXT CARD CONTINUED EXPLANATION OF ANP and PLASMA VOLUME
potassium critical for cell function
-excitable tissues - nerve and muscle
--resting membrane potential
--cell growth
-sensitive △[K+]e
--increase P[K+] of 4mEq/L
---EKG problem
---heart attack
---skeletal muscle contraction abnormalities
![<p>-excitable tissues - nerve and muscle</p><p>--resting membrane potential</p><p>--cell growth</p><p>-sensitive △[K+]e</p><p>--increase P[K+] of 4mEq/L</p><p>---EKG problem</p><p>---heart attack</p><p>---skeletal muscle contraction abnormalities</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0acef03b-c81b-479a-84b8-278921b34050.jpg)
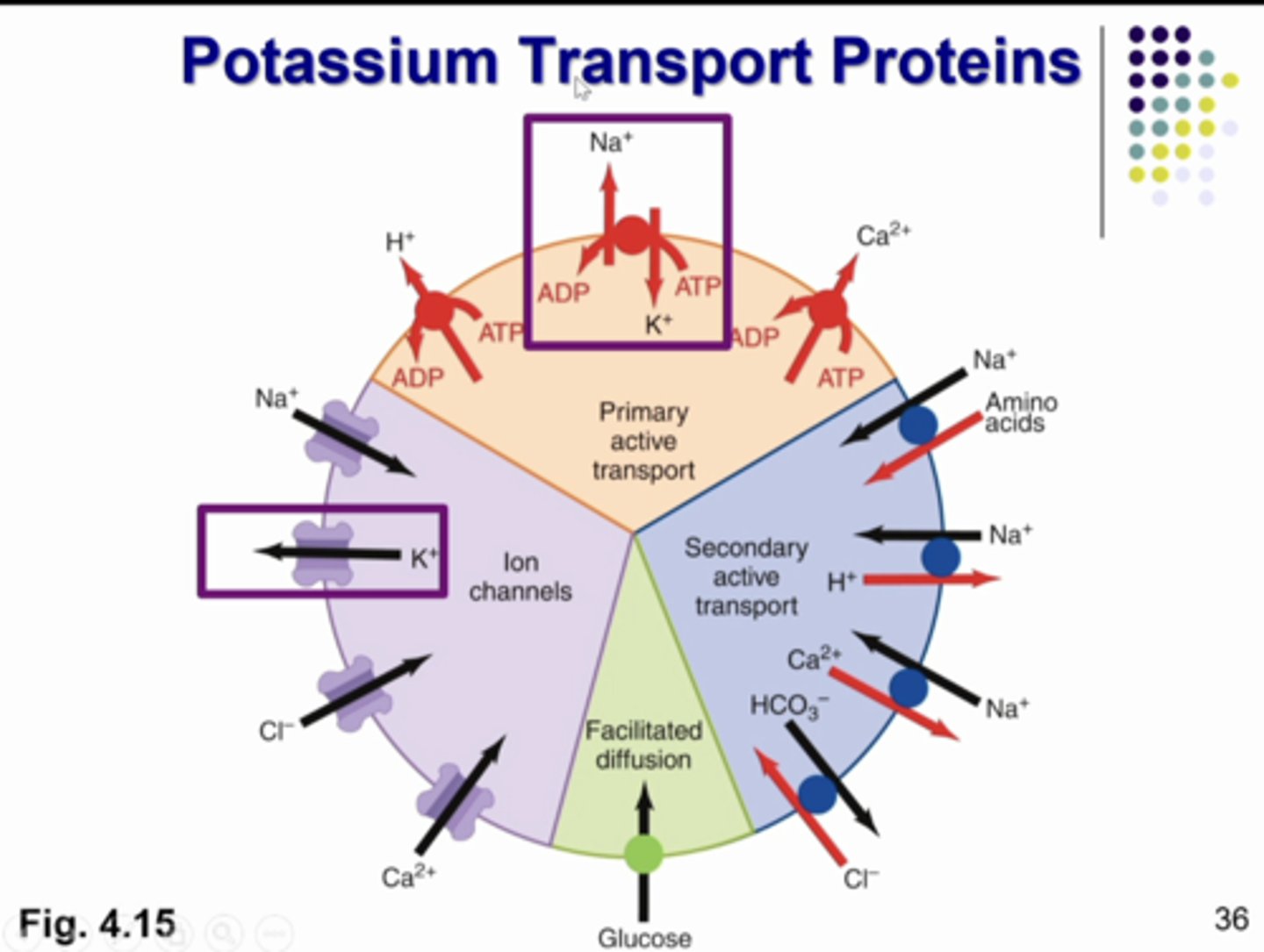
potassium transport proteins
potassium transport proteins
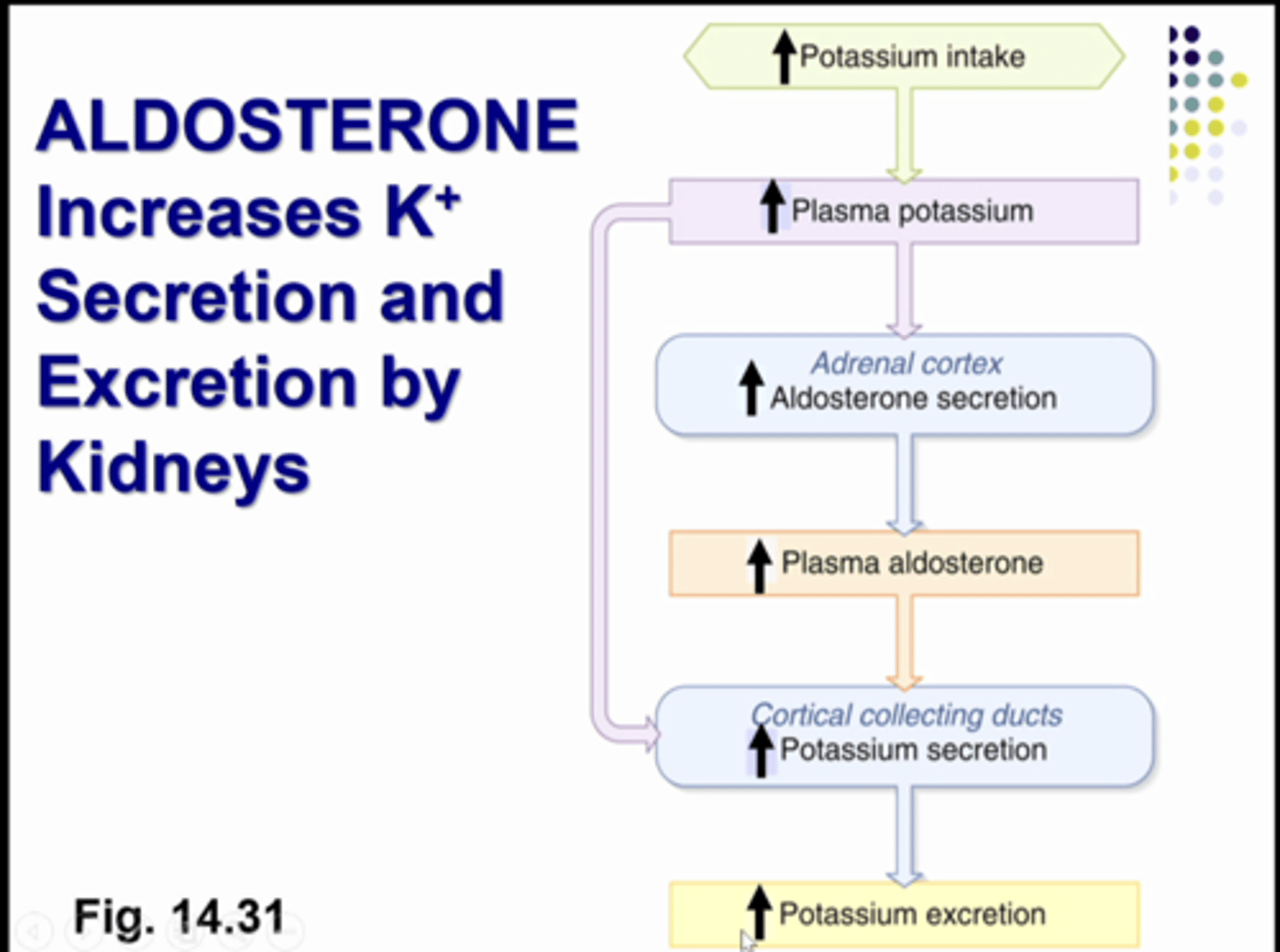
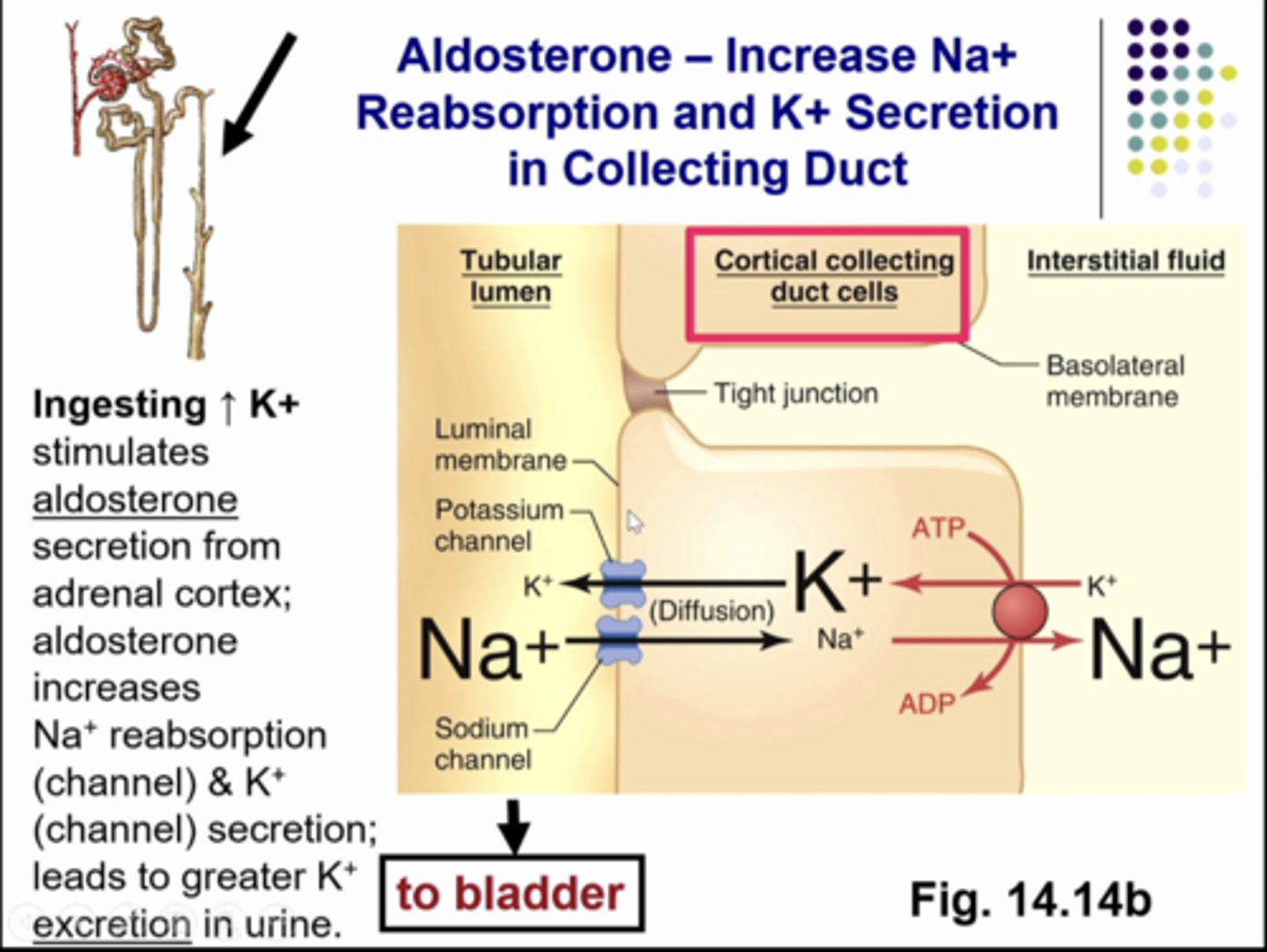
if you eat a lot of potassium, then plasma potassium concentration will increase. so this will cause adrenal gland to release aldosterone. so plasma aldosterone concentration will increase. the kdiney will produce a urine with a lot of potassium to fix the problem. in order to get more potassium in the toilet you need to secrete more. you do this by having aldosterone cause the collecting duct epithelial cells to increase potassium secretion so you have more potassium moving from blood into tubular fluid so excretion will increase
what does aldosterone do to potassium secretion?
when you increase potassium intake, you get increased aldosterone and aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption and it increases potassium secretion by increasing the number of proteins that synthesis the potassium channel and puts more protein in the channels so it stays open longer for more secretion
what is this image showing
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying

slides to aid in studying
slides to aid in studying