E/Z isomers
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
What are stereoisomers?
Stereoisomers have the same structural formula but their atoms are arranged differently in space. E/Z isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism.
What is important about C=C bonds?
Atoms can’t rotate around them like they can around single bonds
In fact, double bonds are fairly rigid and don’t bend much
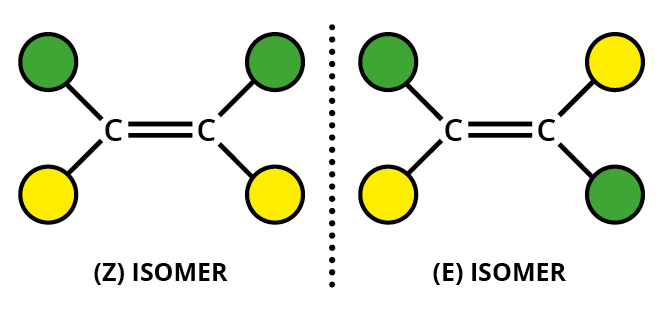
What is E/Z isomerism in alkenes?
If both double-bond carbons have 2 different atoms of groups attached to them you get an E-isomer and a Z-isomer
The E-isomer is the one that has the matching groups across the double bond from each other
The Z-isomer is the one with the matching groups both above or both below the double bond
What are the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Priority rules?
Start by assigning a priority to the two atoms attached to each side of the double bond. To do this, you look at the atoms that are directly bonded to each of the C=C carbon
The atom with higher atomic number on each carbon is given the higher priority
If the atoms directly bonded to each carbon are the same, then you look at the next atom in the group to work out which has the higher priority
To work out which isomer you have, just look at how the two highest priority groups are arranged. If they are positioned across the double bond from each other, you have the E isomer. If they’re both above or below the double bond, you have the Z-isomer