Small Ruminant Health and Husbandry
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to small ruminant health and husbandry, aiding in exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Lambing
The act of birthing in sheep.
Kidding
The act of birthing in goats.
Biosecurity
Steps taken to prevent the introduction or spread of disease on a farm.
Grazing Height of Pasture
Ideally, 80% of larvae are found in the first 2 inches of pasture, indicating optimal grazing height.
Body Condition Score (BCS)
A score based on muscle and fat cover, used to evaluate the health of sheep and goats.
Parasite Control Strategies
Methods to manage parasite infestations, including rotational grazing, deworming based on fecal egg counts, and maintaining hygiene.
Anthelmintic Resistance
The ability of parasites to survive after treatment with anthelmintic drugs, making control more difficult.
Nematodes
Worms that can infect small ruminants, causing damage in the gastrointestinal system.
Caseous Lymphadenitis
A bacterial infection that leads to abscess formation, often resulting in herd health issues.
Pink Eye
An infectious disease characterized by redness, swelling, and discharge in the eyes of sheep and goats.
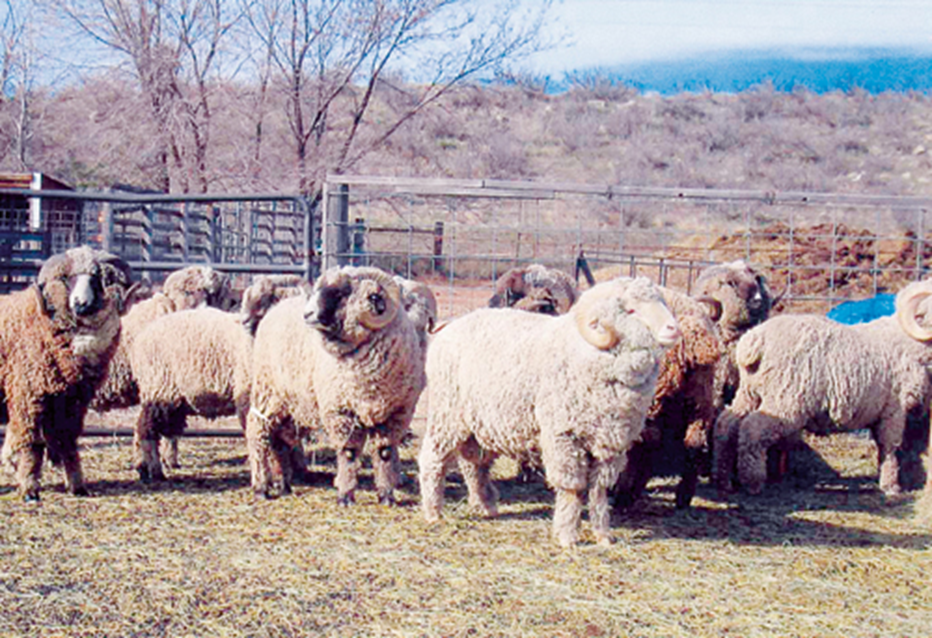

what breed and type of wool
Merino - fine wool
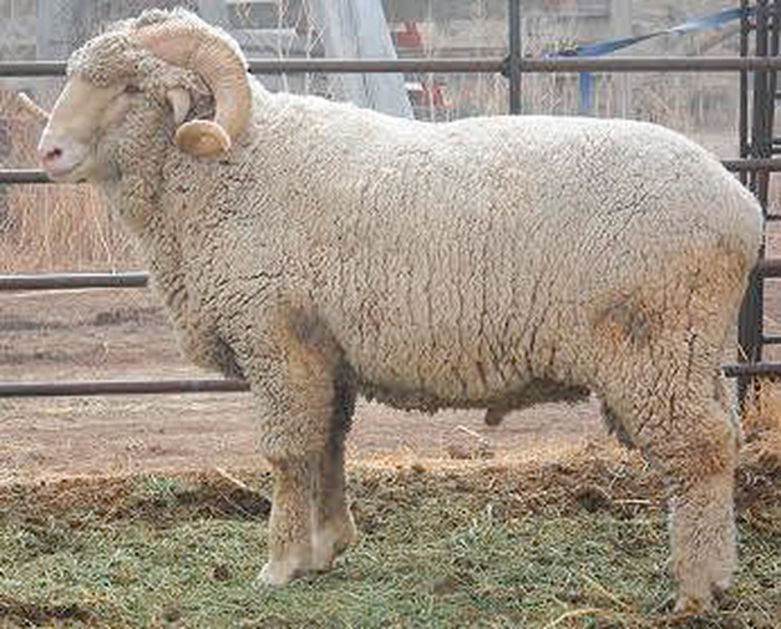

what breed and type of wool
Rambouillet - fine wool

what breed and type of wool
suffolk - medium wool
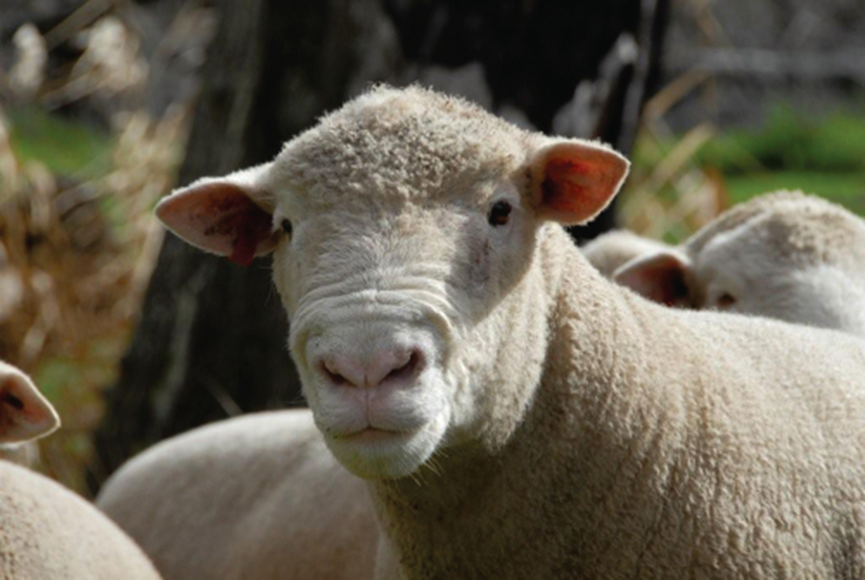

what breed and type of wool
dorset - medium wool
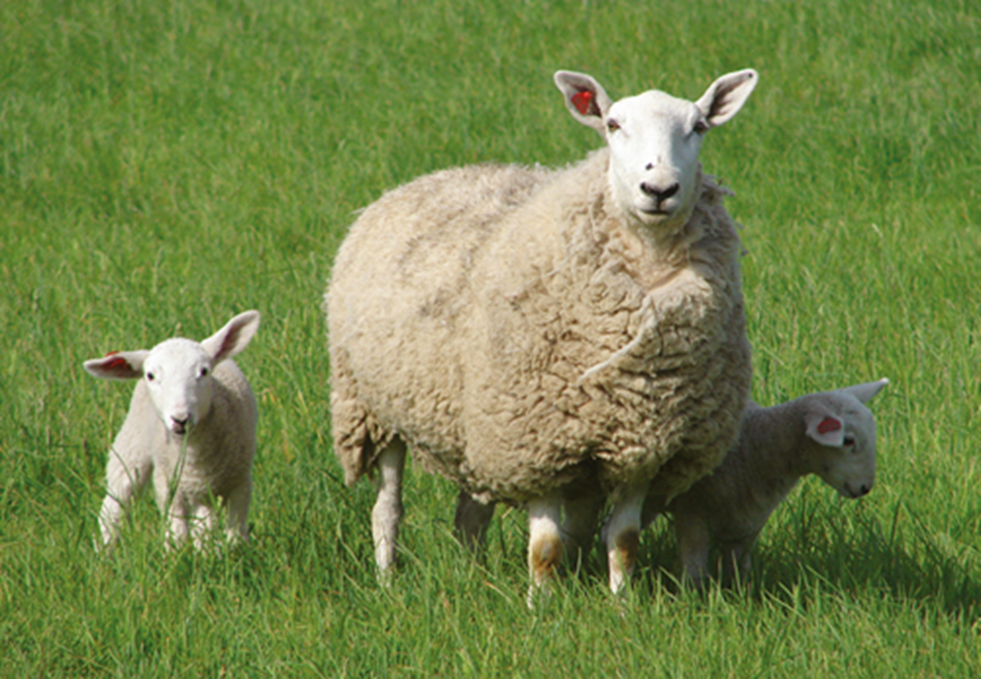

what breed and type of wool
cheviot - medium
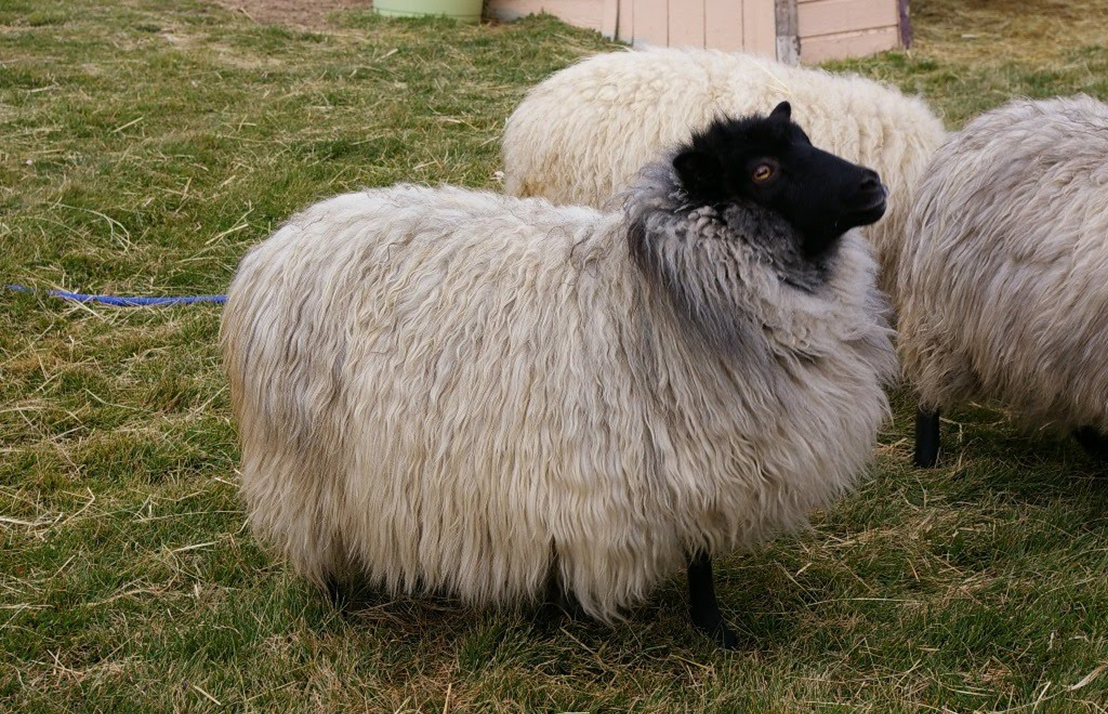

what breed and wool type
shetland - medium wool
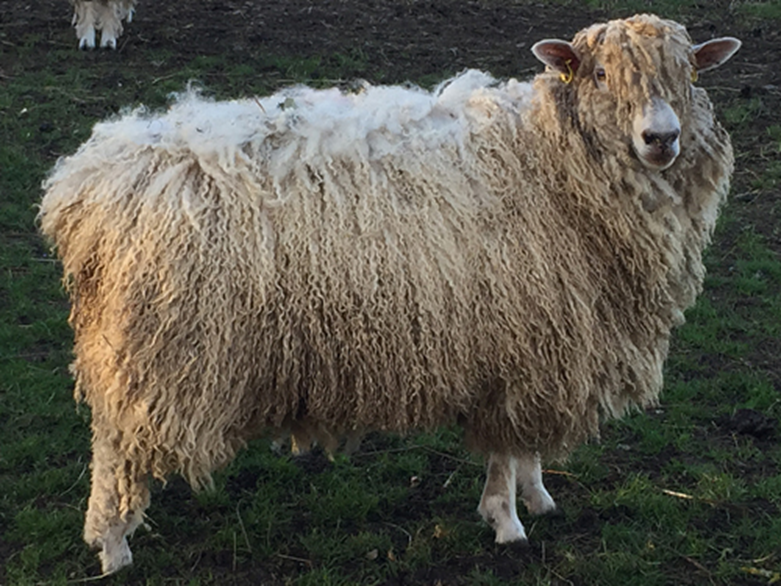

what breed and wool type
cotswold - long wool
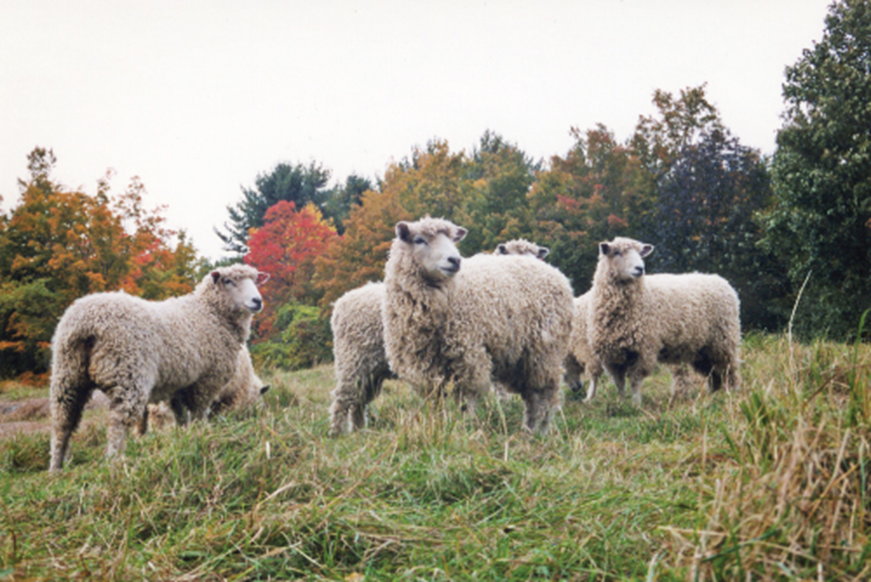

what breed and wool type
lincoln - long wool
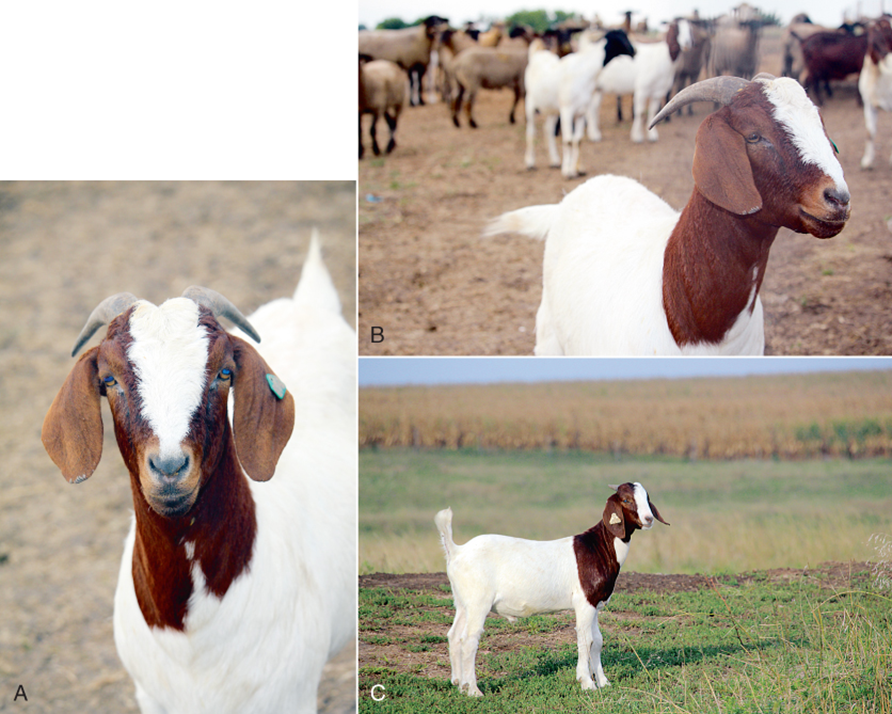

what breed and used for
boer - meat goat
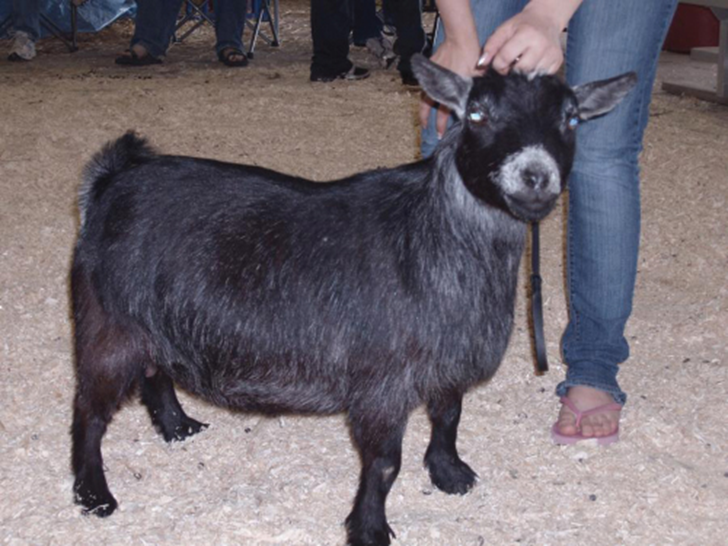

what breed and used for
pygmy - meat goat
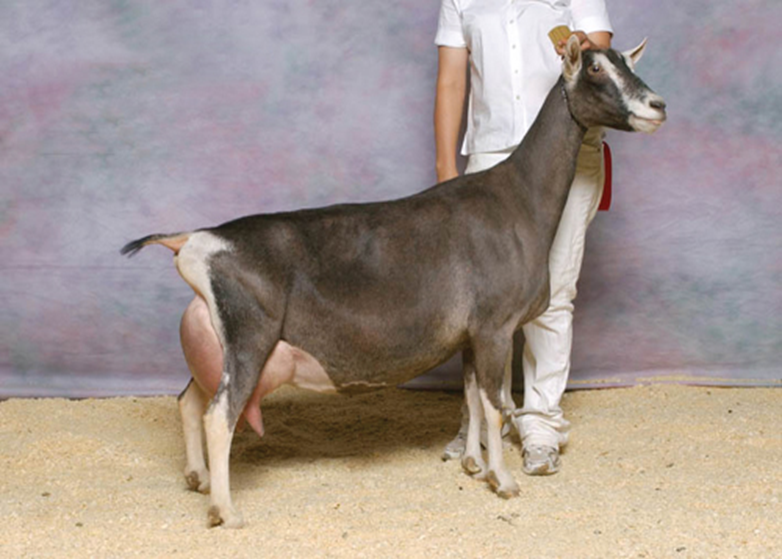

what breed and used for
french alpine - dairy goat

what breed and used for
nubian - dairy goat
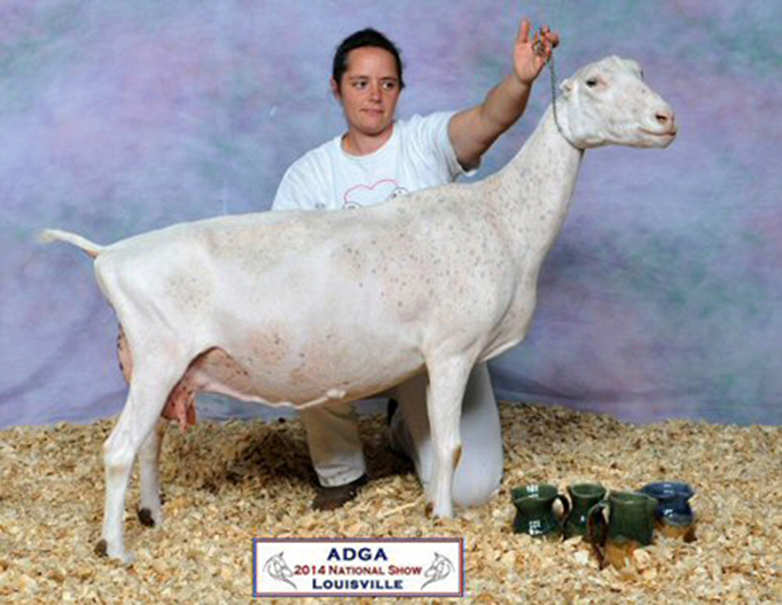

what breed and used for
lamancha - dairy goat
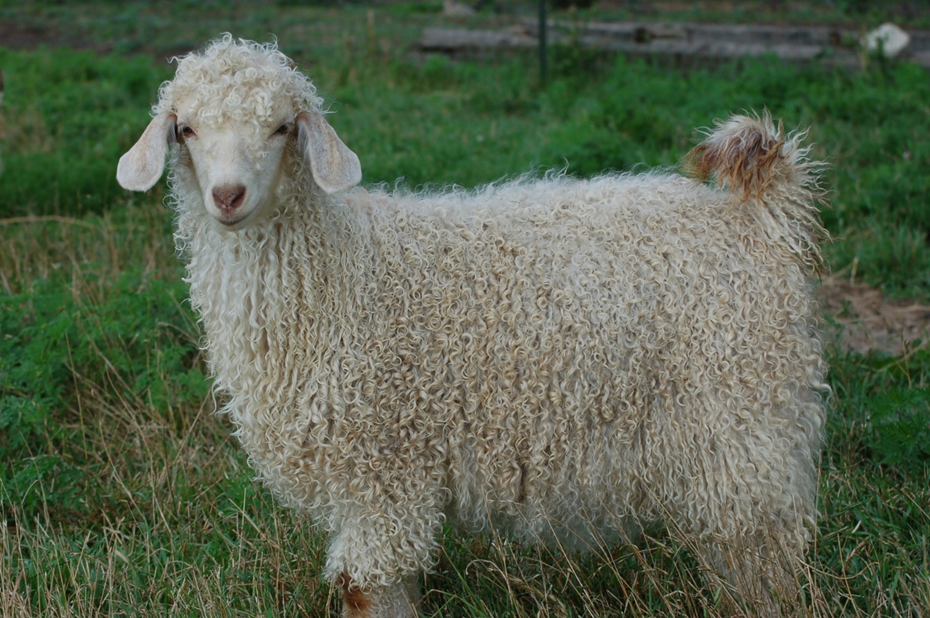

what breed and used for
angora - fiber goat
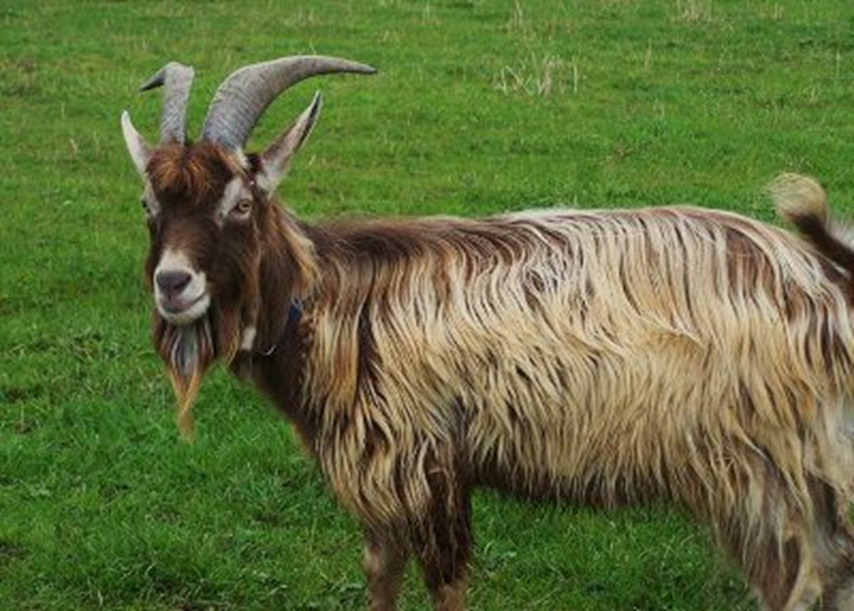

what breed and used for
toggenburg - fiber goat
What are the normal TPRs+rumination for sheep?
T: 101-104
P: 55-115
R: 10-30
Ruminations: 2 per minute
What are the normal TPRs+Ruminations for goats?
T: 101-104.5
P: 70-120
R: 33-36
respiration: 1-2 per minute
where are venipunctures normally done on goats and sheep
jugular vein, cephalic, femoral
IM injection sites for goats and sheep
Gluteals, lateral cervical muscles, longissimus
SQ best injection sites
behind the elbow, neck in front of shoulder, over ribs
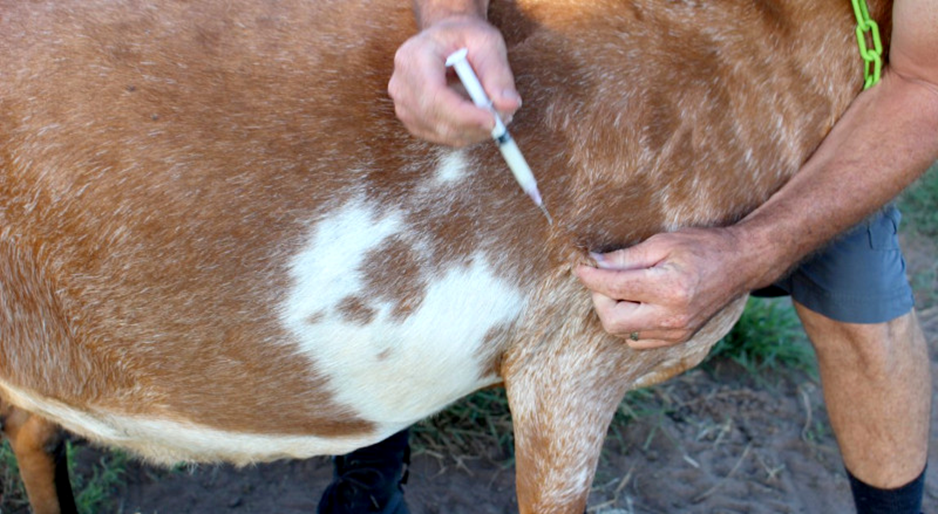
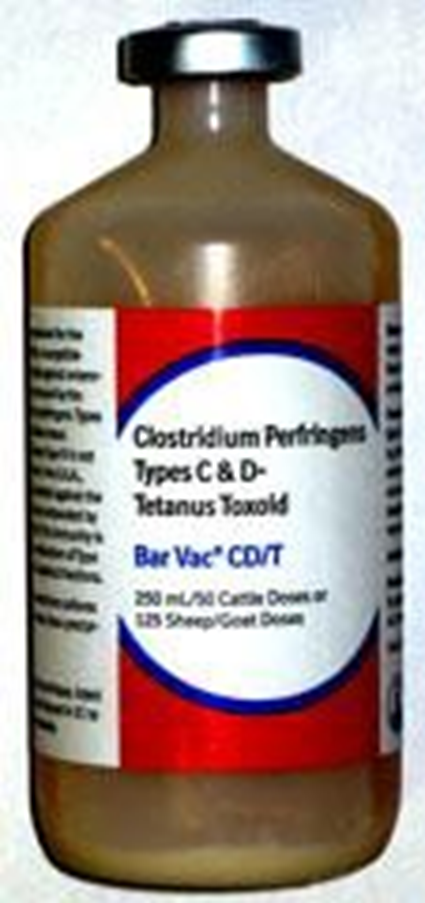
vaccinations for goats and sheep
ALL small ruminants should be protected against the common clostridial diseases and tetanus. The CDT vaccine
what is coccidia
One celled organism- protozoa
▶ Biggest problem in weaned kids and younger animals
▶ Virtually all goats are carriers and shed some coccidia
▶ Good sanitation most important step in control
clinical signs in coccidia
Mild infection - No symptoms
▶ Clinical signs worse if there is stress or overcrowding
▶ Poor health, lowered immune statue
▶ Dirty environment, lots of oocysts ingested
▶ Diarrhea, may be bloody, look like pure blood if very severe
▶ Temp. 104o or less
▶ Anemia, dehydration, decreased appetite
▶ Prolonged recovery with low weight gains and poor feed intakes
treatment for coccidia
▶ Isolate affected animals
▶ Sulfa drugs
▶ Amprolium
▶ Ponazuril $$$
▶ Supportive care if diarrhea or blood loss too severe
what are the three nematodes
▶ H = Haemonchus “barber pole worm”
▶ O = Ostertagia
▶ T = Trichostrongylus
▶ Three nematodes (worms) that cause the most damage
in small ruminants.
barber pole worm (haemonchus contorus)
blood-sucking round worm
▶ The primary symptom is anemia (paleness of the mucous membranes) and “bottle jaw”, accumulation of edema under the jaw
▶ Effect of parasite can be hyperacute (sudden death), acute (clinical and treatable), or chronic (sub-clinical)
▶ Diarrhea IS NOT a common symptom
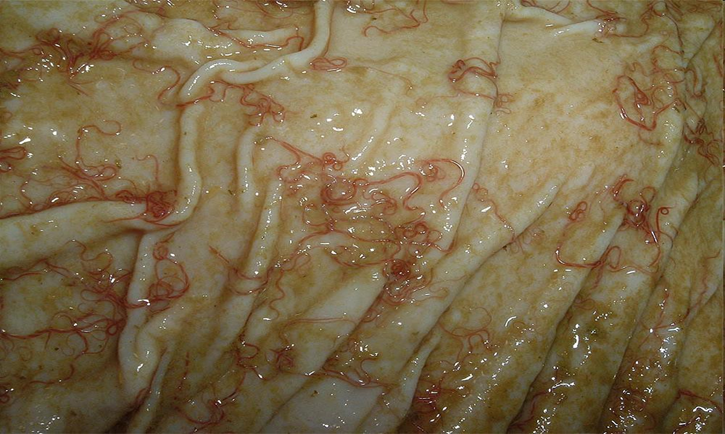
identify this worm
barber pole worm (haemonchus contorus)
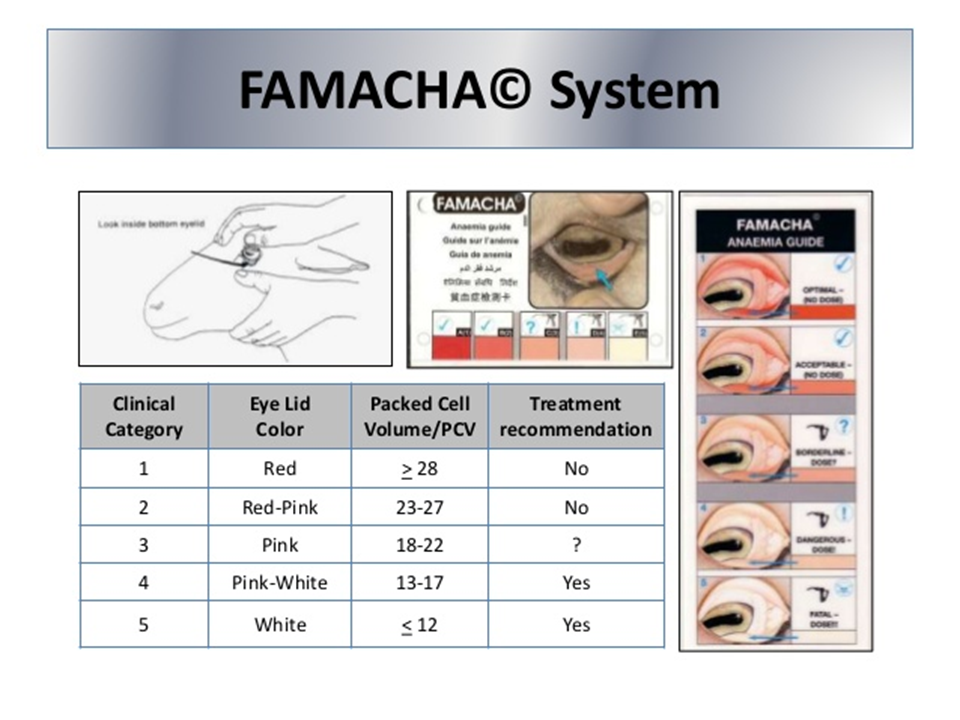
what is FAMACHA
a test to determine the degree of anemia
how should sheep and goats be dewormed?
Sheep and goats should always be dewormed with oral formulations of wormers, NOT pour on
▶ Oral dewormers should be given by mouth and deposited over the tongue
▶ Dosing should be based on accurate weight
▶ Goats need 1.5 – 2 X as much as sheep dose
explain the steps on how to trim a hoof
▶ Use tin snips or hoof nippers
▶ Trim tip off toe
▶ Snip off sides that have overgrown
▶ Rasp irregular growth
what is listeriosis?
A bacterial infection caused by Listeria monocytogenes, often affecting sheep and goats, leading to neurological symptoms or abortion. It can be found in soil, feedstuffs, and feces from healthy animals. commonly associated with the feeding of moldy or spoiled hay, but can occur sporadically because it naturally lives in the environment.

explain respiratory disease in sheep and goats
Respiratory disease in sheep and goats refers to various infections and conditions affecting their respiratory system, often caused by pathogens such as bacteria or viruses, resulting in symptoms like coughing, nasal discharge, and difficulty breathing. treat with antibiotics - penicillin, or tetracycline, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
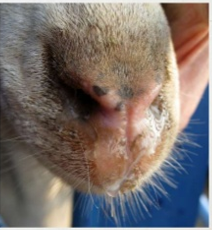
what is sore mouth
▶ Contagious ecthyma, orf
▶ Pox virus – causes proliferative sores in mouth and other areas
▶ Rarely fatal – weight loss because of reluctance to eat
▶ Can be vaccinated against if in herd
▶ Zoonotic
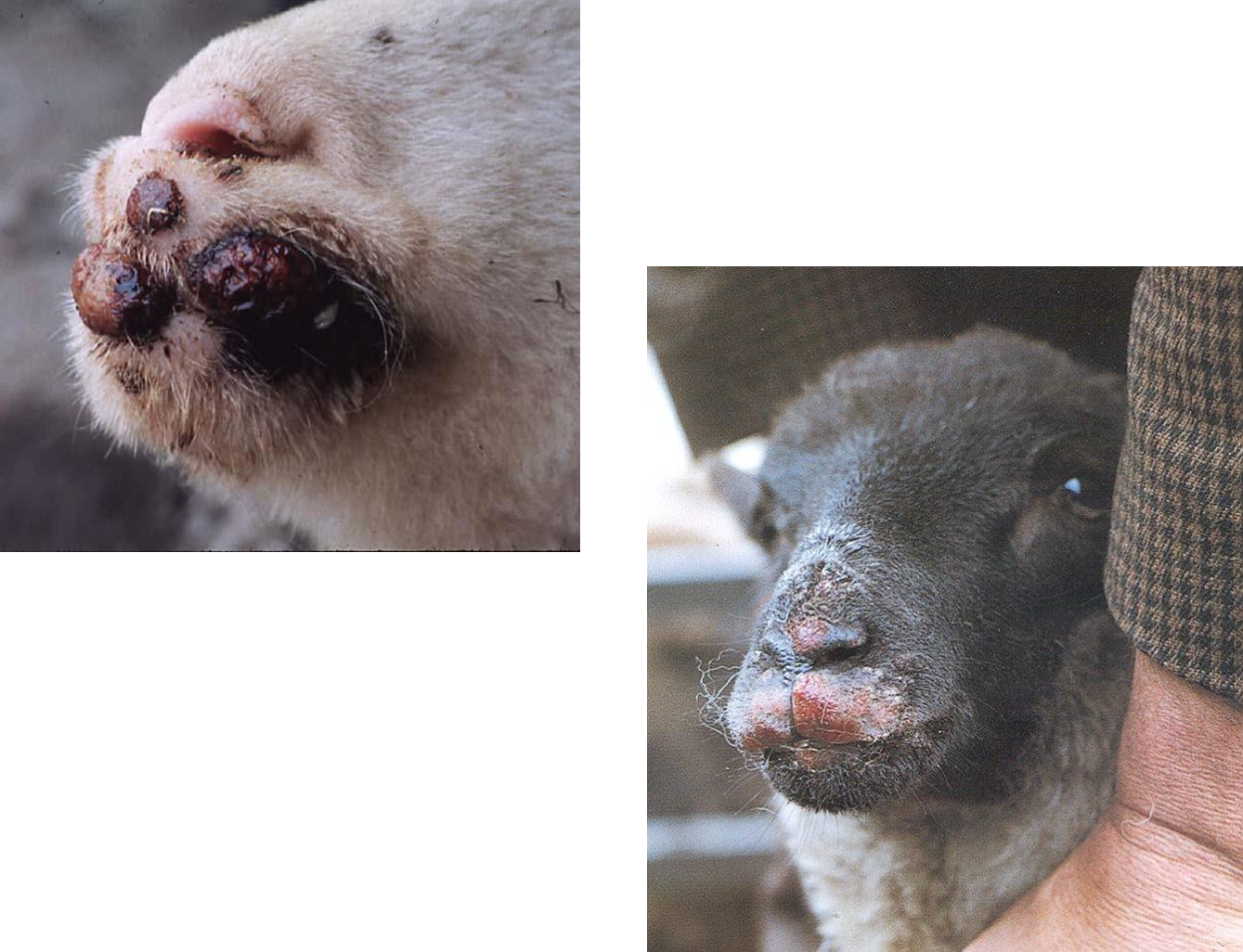

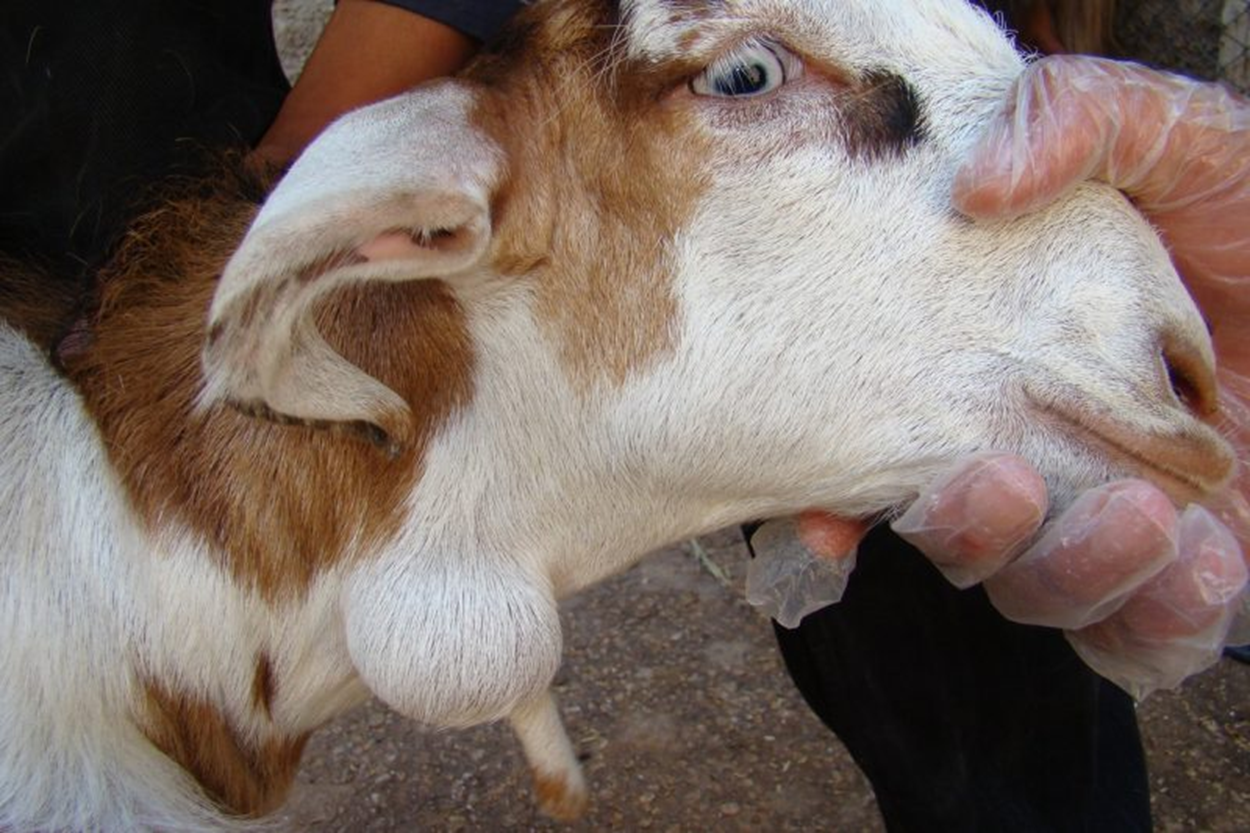
what is caseous lymphadenitis
▶ Corynebacteria pseudotuberculosis
▶ Bacteria entry into the body via from cuts, tooth eruption
▶ Forms abscesses – usually around head and neck
▶ Soil infected from pus from open abscesses – infects other goats. Tends to become herd problem
▶Fatal if abscess develops internally
