Cells, DNA, Protein Synthesis, Mutations
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Are plant and animals cells the same?
No they are similar but also different.
Cell Membrane
Thin covering that separates the inside of the cell from its external environment
Cell wall
rigid structure and provides support and structure
Is the cell wall in plant and animal cells?
No only plant cells
Cytoplasm
watery jelly like fluid in which internal organs float
What are organelles?
Special parts in the cell that carry out specific functions to ensure the cells survival
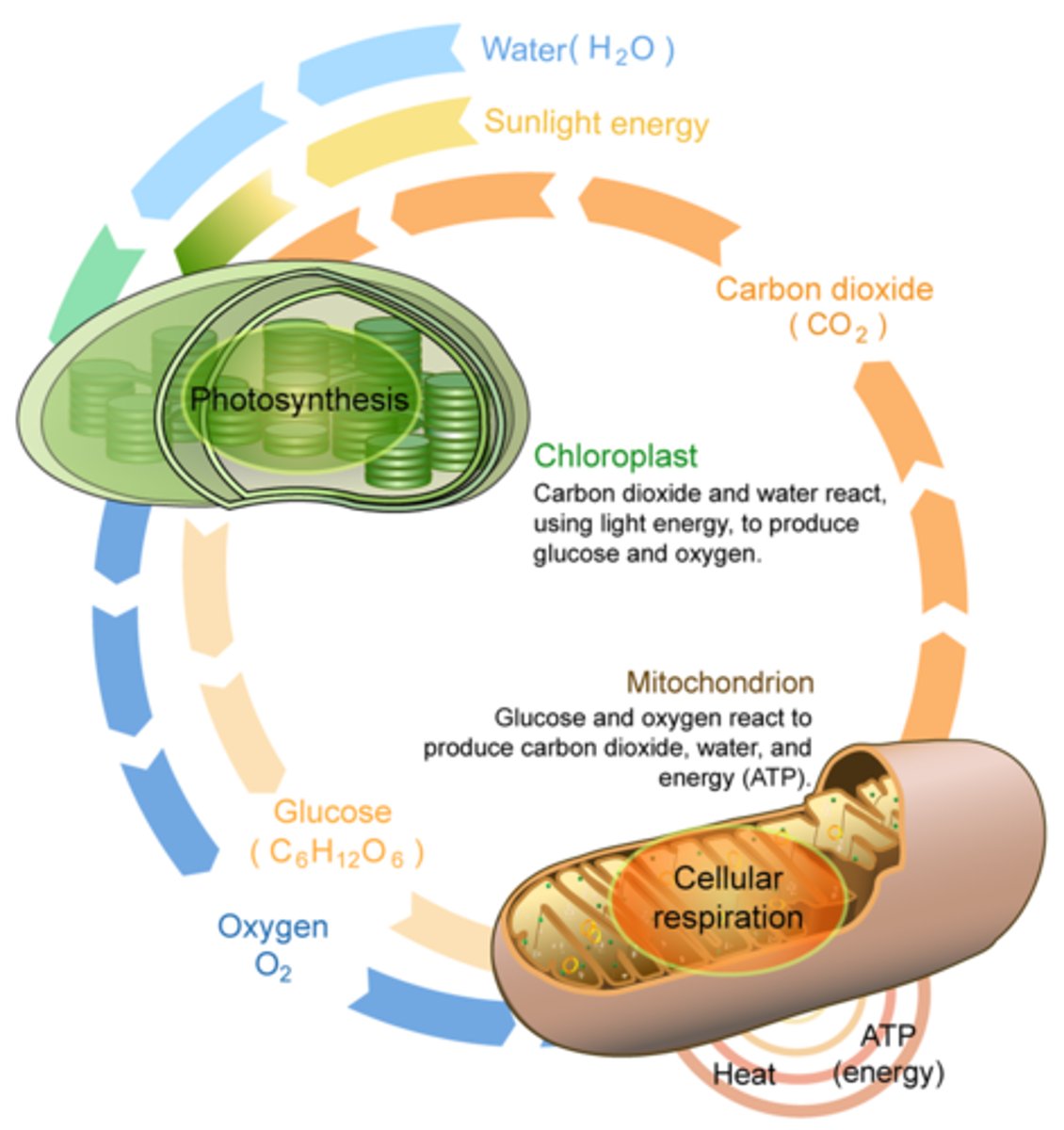
Mitochondria
power house of the cell, bean shaped, makes energy through cellular respiration, converts sugar into usable energy
Chloroplast
use light energy from the sun, carbon dioxide and water to make sugar through a process called photosynthesis
True or False
Chloroplasts are in animal cells
False
What is another name for sugar?
glucose
respiration and photosynthesis
Respiration= energy stored-energy released
Photosynthesis=sunlight-energy stored
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
Where are the ribosomes found?
float in cytoplasm or attached to ER
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
membrane covered channels, transport materials through the cytoplasm
Rough ER
Ribosomes are attached
Smooth ER
Ribosomes are not atached
Where are fats made?
Smooth ER
Vesicles
membrane-covered sacs, form at the end of the ER, transport new protein to the Golgi body
Golgi apparatus (Golgi body)
sorts and packages proteins to be transported out of the cell, packaged into vesicles and carried to the cell membrane
Vacuole
membrane covered organelle, stores water, nutrients, waste
Small vacuoles for starch and large ones for water
Plant Cells
Small Vacuoles
Animal Cells
Nucleus
controls all cell activities
The nucleus contains _______ for the cell
instructions
The nucleus determines the _______,______, and _____ of a cell
growth, division, death
nucleur membrane
Surrounds and protects the nucleus
nucleur pores
openings in nuclear membrane that control what materials leave/enter nucleus
Nucleolus
membrane free organelle, found in the nucleus, makes ribosomes
Prokaryotic organelles
are not surrounded by a membrane (one celled organisms)
Examples of a prokaryotic organelle
bacteria
Eukaryotic organelles
surrounded by a membrane
examples of a eukaryotic organelle
plant and animal cells
Cells and organisms have the same ______ but not all cells in a organism have the same _______
contents, function
There are different types of ______ and each type has a specific _________
cells, function
DNA has instructions for what?
making, running, and repairing a cell
DNA stores?
DNA stores genetic information of a organism
what does DNA stand for?
deoxyribonucleic acid
Where is DNA located/
in the nucleus
What is a double helix?
a double stranded molecule
DNA exist as _____________
2 long strands
What does a double helix look like?
shaped like a twisted ladder.
what are the sides of the ladder made of?
The sides of the ladder are made of sugar and phosphate
What are the steps of the ladder made of?
4 nitrogen bases
what are all of the nitrogen bases?
(A) Adenine
(G) Guanine
(C) Cytosine
(T) Thymine
Nitrogen base pairs
Nitrogen bases are in pairs to make the steps of the ladder
what does A pair up with
A-T
what does G pair up with?
G-C
True or False
Are pairs always the same?
True
DNA message
how DNA is arranged
The arrangement of the pairs of nitrogen bases in DNA
directs all cell activity
Chromatin
in each strand of chromatin there is one molecule of DNA
Where are chromatins?
inside the nucleus where DNA is stored
Chromosome
condensed structure that is passed on from the parents to the offspring during reproduction
How are chromosomes and chromatin related?
Chromatin coils into a compact structure called a chromosome
True or False
Every organism has the same number of chromosomes
False
every organism has a certain number of chromosomes
Where are chromosomes located?
Chromosomes are in pairs in the nucleus
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
How many chromosomes do fruit flies have?
8 (4 pairs)
Genes
small segments of DNA located at specific places on a chromosome. Has instructions to make a specific protein.
How long is a gene?
Very in length hundred-thousand bases
How many genes are in each chromosome?
Each chromosome has thousands of genes.
How many genes do humans have?
25000 genes
How many proteins do humans have?
90000 proteins.
Proteins
Proteins determine the functions of cells.
Each cell in your body contains the same _________ ____________ but not all cells have the same __________
genetic, information, function
Why do cells have different functions?
Cells have different functions because only specific genes are "read" in each type of cell, meaning each type of cell makes specific proteins
How do cells ensure that the right proteins are made for specific functions, such as muscle movement?
proteins needed to make muscles work are made only in muscle cells
Enzymes
specialized proteins that speed up chemical reaction
Hormones
proteins that act as chemical messengers
what is a example of a hormone?
growth hormone
make sure cells have enough nutrients for division
How are proteins produced? 9 Steps
1. The nucleus receives a chemical signal to make a specific protein
2. DNA message is copied into RNA
3. RNA leaves through a nuclear pore
4. RNA message is delivered to the ribosomes
Ribosomes make the protein
5. The manufactured protein enter the ER
6. A vesicle forms of the end of the ER carries the proteins to the Golgi body
7. The Golgi body packages proteins for transport out of the cell
8. A vesicle forms off the end of the Golgi body to carry the protein to the cell membrane
9. the vesicle attaches to the cell membrane and its protein contents are released out of the cell
Gene mutations
a change in the specific order of the nitrogen bases that make a specific gene
types of genetic mutations. 3
Deletion
Addition
Substitution
Deletion
one base is missing
Addition
one base is added
Substitution
one base is substituted for another
Proteins produced by DNA mutations can be _____________, __________, ___________
positive
negative
neutral
positive mutation
benefits the organism
negative mutation
harm the organism
neutral mutation
have no effect on the organism
Positive mutation examples
some people have a mutation that makes them resistant to HIV and AIDS
Positive mutation example
some plants are resistant to bacteria and fungal infections
Negative mutation examples
sickle cell anemia which makes abnormally shaped red blood cells that cannot carry oxygen efficiently
Negative mutation examples
cystic fibrosis the body does not correctly make proteins that transport chloride ions into and out of the cell so mucus builds up
Neutral mutation example
the gene mutaion that causes the white coat of spirit bears has non significant effec on its survival
Mutagens
factors that can cause mutations in DNA
Mutagen examples
cigarette smoke, UV rays, Household chemicals, radiation, pollutants
what does damaged DNA result in?
Damaged DNA results in incorrect production of proteins
gene therapy
reasearchers replace a mutated gene with a healthy copy of the gene
Why is gene therapy un common?
it is risky and is only tested on diseases without a known cause
What is asexual reproduction?
A type of reproduction that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
Key characteristics of asexual reproduction
Involves a single parent organism.
Offspring are genetically identical to the parent (clones).
Does not involve the fusion of gametes (sex cells).
Occurs rapidly and produces a large number of offspring.
What are the common types of asexual reproduction?
Binary Fission
Budding
Fragmentation
Vegetative Reproduction (in plants)
Spore Formation
Binary Fission
A form of asexual reproduction where a single celled organism divides into two equal halves, each becoming a new organism.
Example: Bacteria, Amoeba
Budding
Asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site.
Example: Yeast, Hydra
Fragmentation
Asexual reproduction where a parent organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment develops into a new, complete individual.
Example: Starfish, flatworms, some algae
Vegetative Reproduction
Asexual reproduction in plants where new plants grow from vegetative parts like stems, roots, or leaves, without seeds or spores.
Examples:
Runners/Stolons: Strawberries
Tubers: Potatoes
Rhizomes: Ginger
Bulbs: Onions
Cuttings: Roses, Pothos
Spore Formation
Asexual reproduction where an organism produces specialized reproductive cells called spores, which can develop into new individuals under favorable conditions.
Example: Fungi (e.g., bread mold), ferns, mosses