CHEM 2100 Addition Reaction Mechanisms
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Hydrohalogenation
Addition of HX with H on less substituted side (Markovnikov)
If reacted with HBR what reaction would occur?
Hydrohalogenation with H on less substituted carbon
If reacted with HBR/ ROORwhat reaction would occur?
Hydrohalogenation but anti markovnikov (H on more substituted position)
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Addition of H in the presence of a metal catalyst, watch out for meso compounds
If reacted with H2/Pt what reaction would occur?
Catalytic hydrogenation
Dihydroxylation
Adding OH across an alkene
If reacted with 1)ROC3H/ 2)H3O+ what reaction would occur?
Anti dihydroxylation
If reacted with mcPBA or peroxyacteic acid (CH3O3H)/H/H20 what reaction would occur?
Anti dihydroxylation
If reacted with Na2SO3/ H2O reaction would occur?
Syn dihydroxylation
If reacted with NaHSO3/H2O what reaction would occur?
Syn dihydroxylation
If reacted with 1)OsO4/ 2) NAHSO3,H2O what reaction would occur?
Syn dihydroxylation
If reacted with KMnO4, NaOH/ cold what reaction would occur?
Syn dihydroxylation
Acid Catalyzed Hydration
Addition of OH on the more substituted carbon (Markovnikov)
If reacted with H3O+ what reaction would occur?
Acid catalyzed hydration
If reacted with H2SO4 what reaction would occur?
Acid catalyzed hydration
Hydroboration Oxidaiton
Installs OH at the less substituted carbon (anti- Markovnikov)
If reacted with 1)BH2, THR/ 2) H2O2, NaOH what reaction would occur?
Hydroboration Oxidation
Halogenation
Addition of either CL2 or Br2 across an alkene, with anti addition
If reacted with Br2 what reaction would occur?
Halogenation
Halohydrin formation
OH added at more substituted position
If reacted with Br2/H2O what reaction would occur?
Halohydrin formation
Ozonolysis
Cleaving of the double bond into separate molecules
If reacted with 1) O3/ 2)DMS what reaction would occur?
Ozonolysis
If reacted with 1)O3/ 2)Zn/H2O what reaction would occur?
Ozonolysis
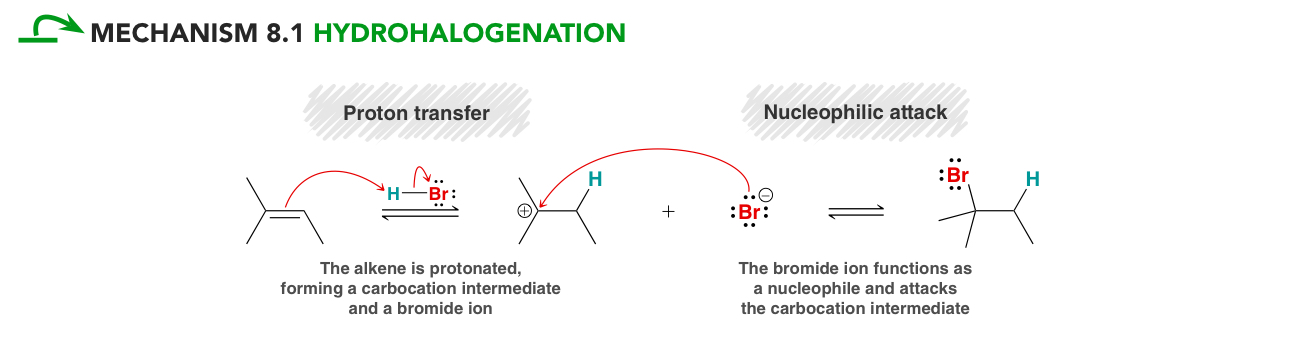
Hydrohalogenation mechanism
Alkene acts as a base and accepts a proton
Carbocation formation (with possible rearrangements)
Nucleophilic attack
lookout for enantiomers!
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Mechanism
Proton transfer (alkene is protonated) resulting in a carbocation forming
Nucleophilic attack: Water acts as a nucleophile attacking the carbocation intermediate
Proton transfer: water functions as a base deprotonating the oxonium ion
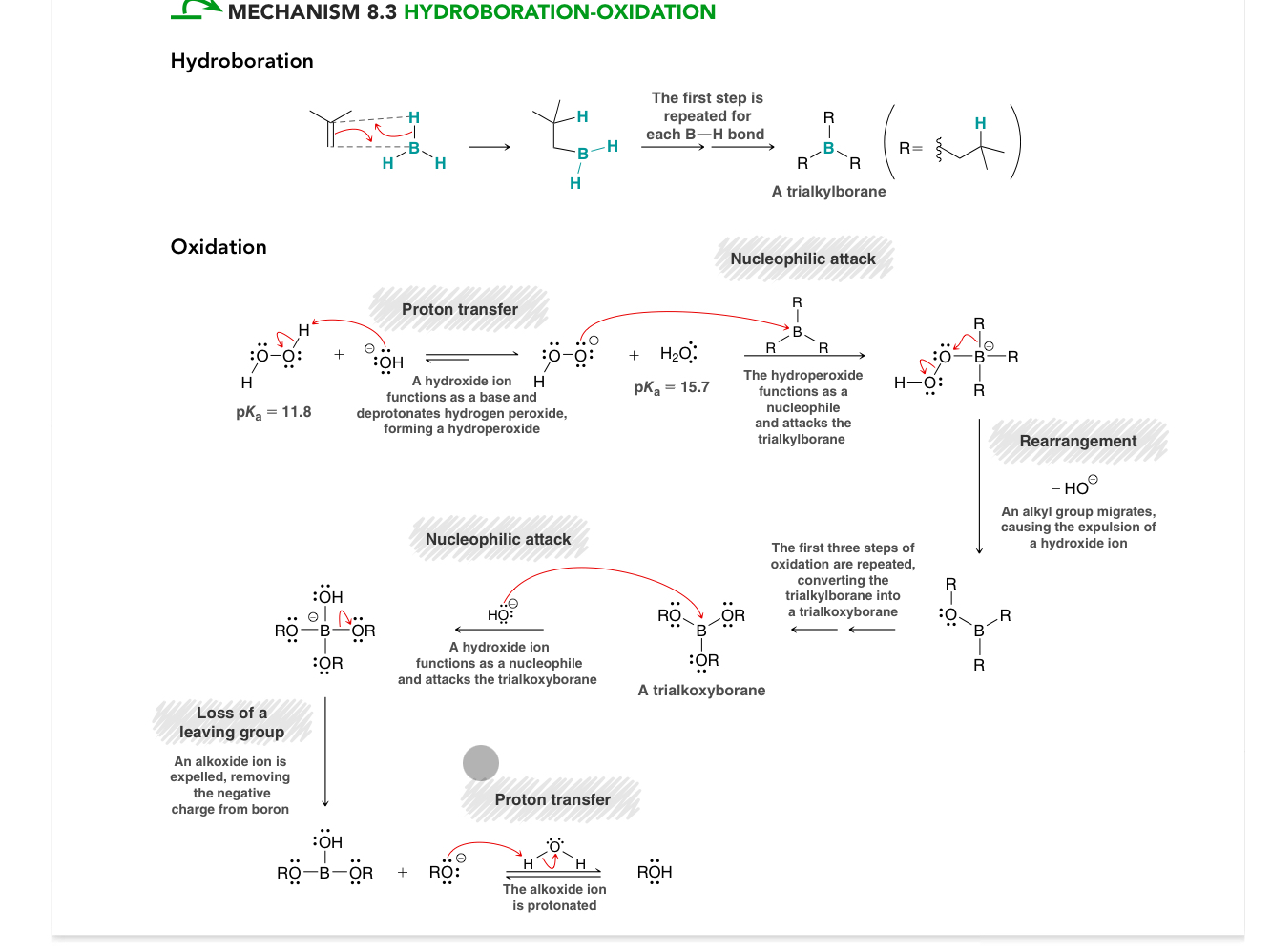
Hydroboration oxidation mechanism
Hydroboration, the alkene attacks the B simultaneously as the H attacks the C, first step re[easts for each B-H bond forming a trialkylborane
Oxidation:
1. Proton transfer: OH- ions functions as a base and deprotonates hydrogen periodic forming a hydroperoxide
Nucleophilic attack: hydroperpxide acts as a nucleophile attacking the trialkylborane
Rearrangement (alkyl group migrates explaining a hydroxide ion *happens again until trialylborane turns into trialkoxyborane
Nucleophilic attack: hydroxide ion attacks trialkoxyborane
Loss of a leading group, all oxide is expelled removing negative change form boron
Proton transfer
Halogenation Mechanism
Nucleophilic attack & loss of a leaving group (simultaneously)
Alkene functions as nucleophile and attack Bromine, expelling bromide as a LG which forms a bridged intermediate (bromonium ion)
Bromide acts as a nucleophile in an SN2 process (backside attack) attacked the Br ion (why the product is anti addition)

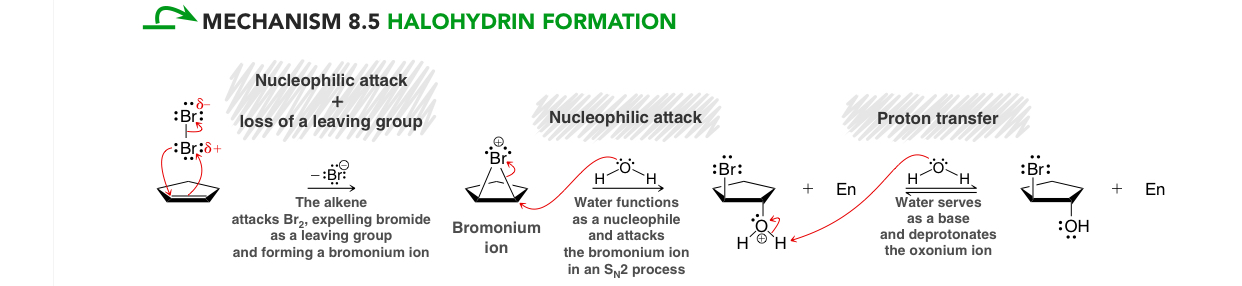
Halohydrin formation mechanism
Nucleophilic attack & loss of LG (simultaneously), expels Br
can be drawn as a transition state
Nucleophilic attack: water functions as nucleophile attacking the Br ion in an SN2 process
Proton transfer: water serves as a base and deprotonates the oxonium ion resulting in anti addition
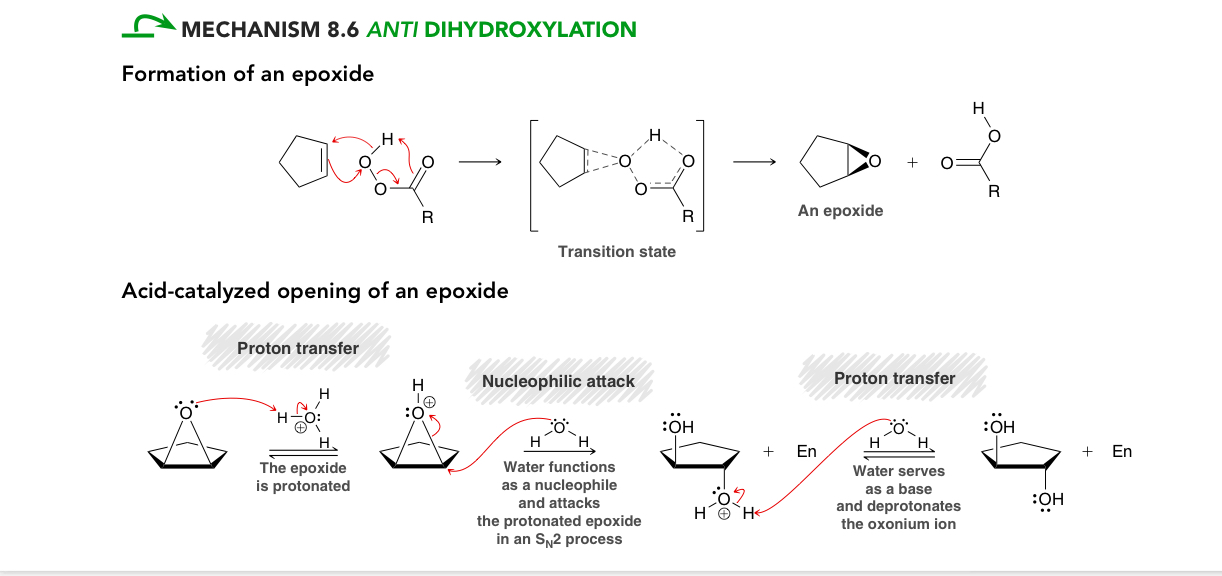
Dihydroxylation mechanism
Formation of an epoxide (transition state)
Acid catalyzed opening of an epoxide
proton transfer (epoxide gets protonated)
Nucleophilic attack water acts as a nucleophile and in an SN2 process attacks. The protonated epoxide
Proton transfer : water acts ad a base deprotonation the oxonium ion